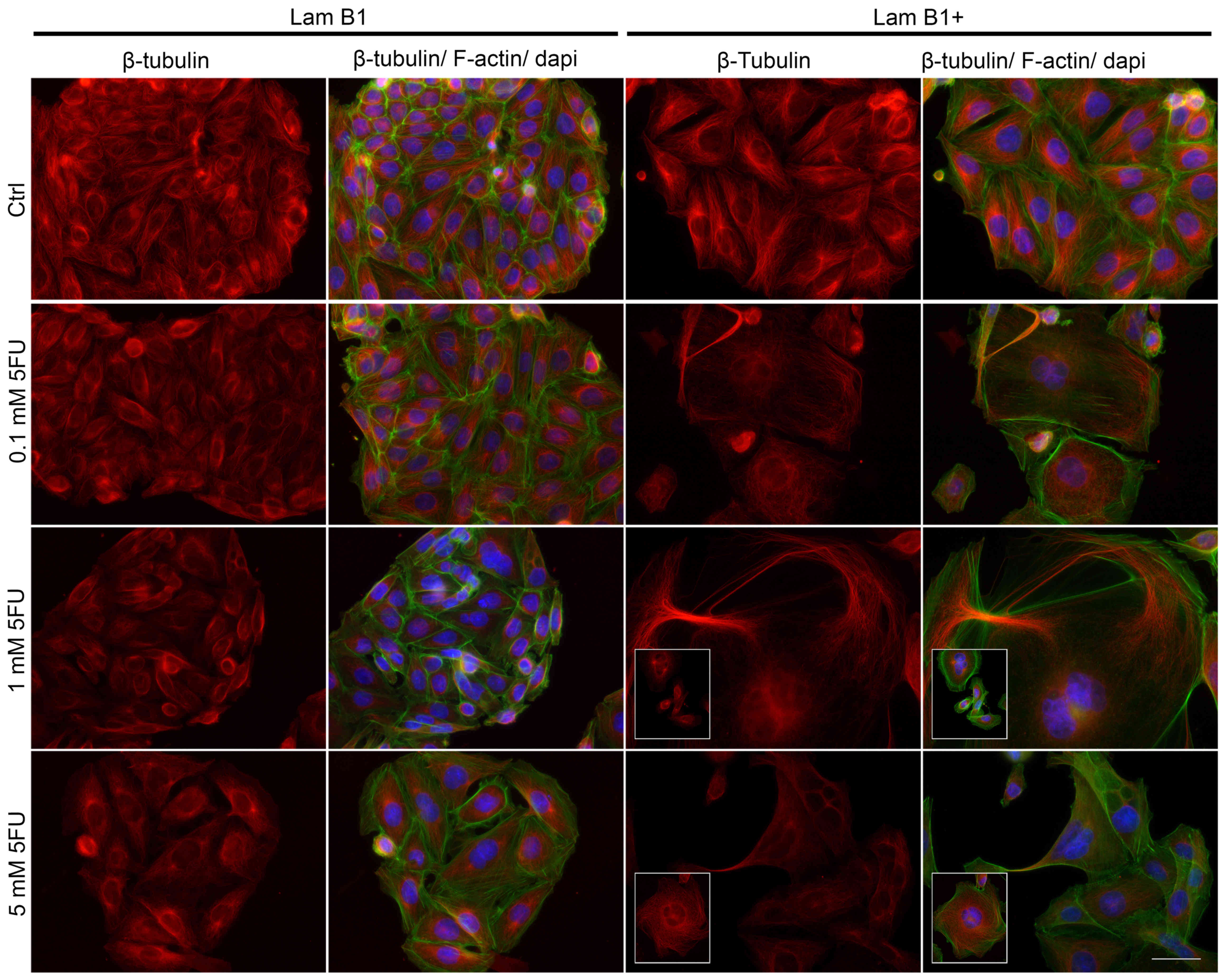
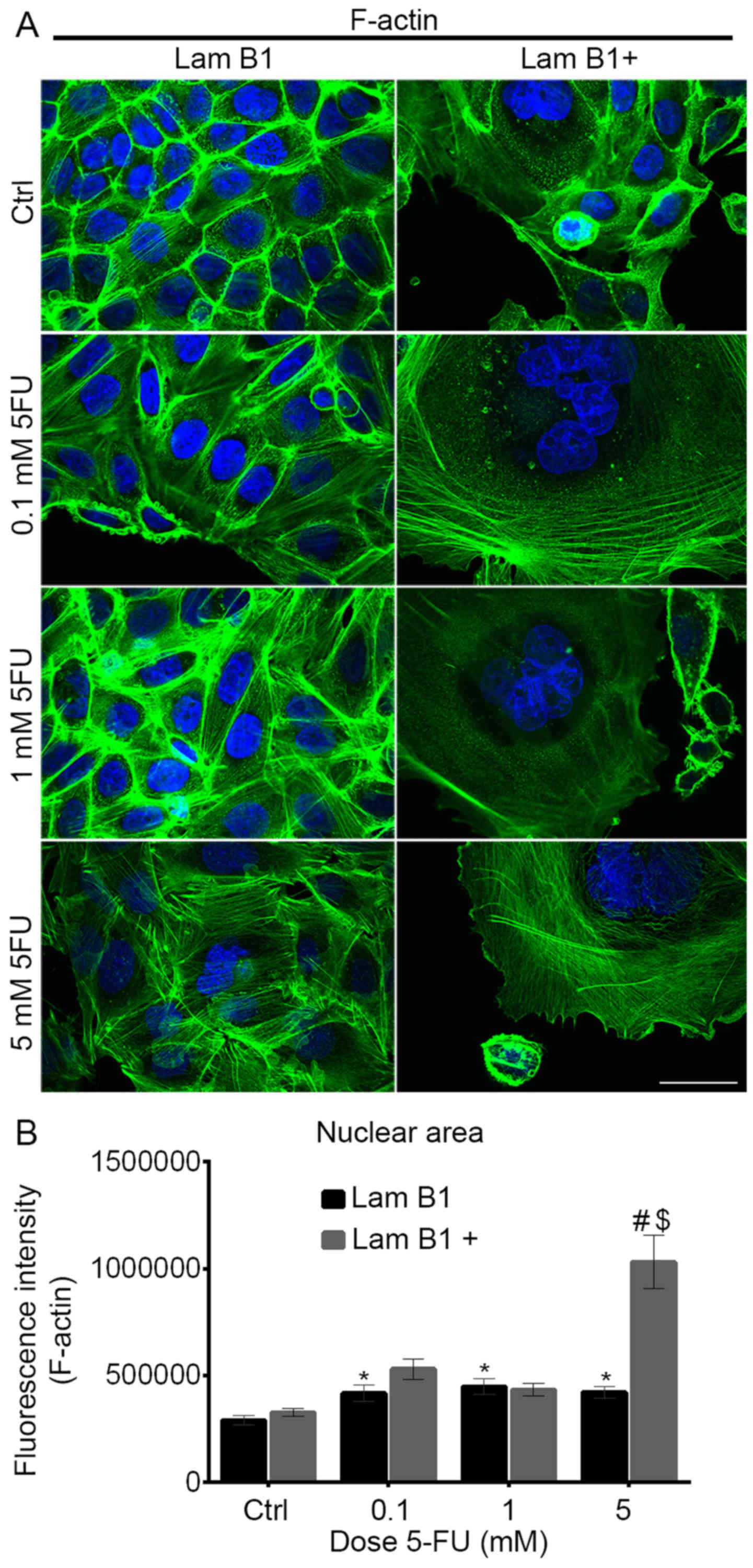
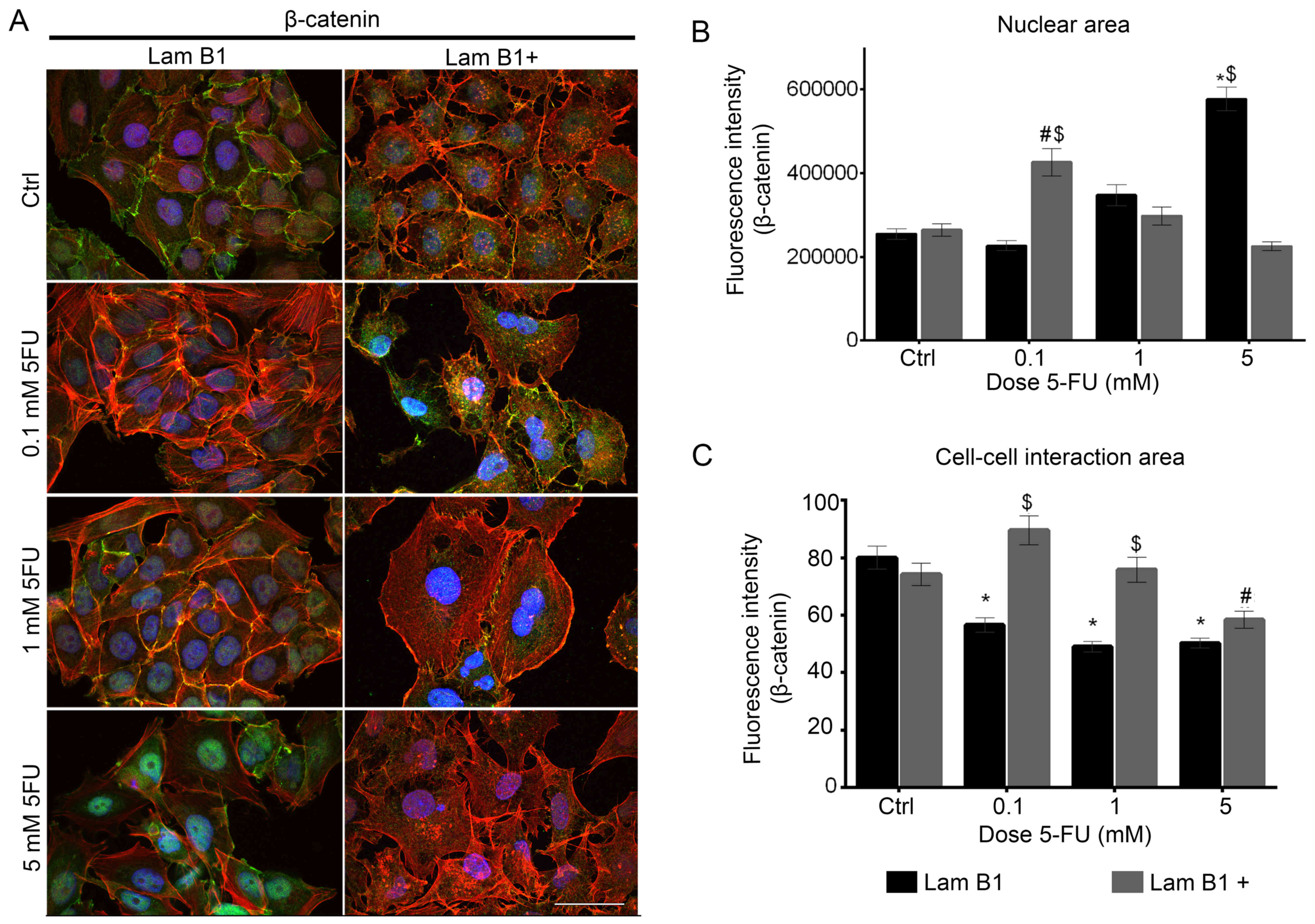
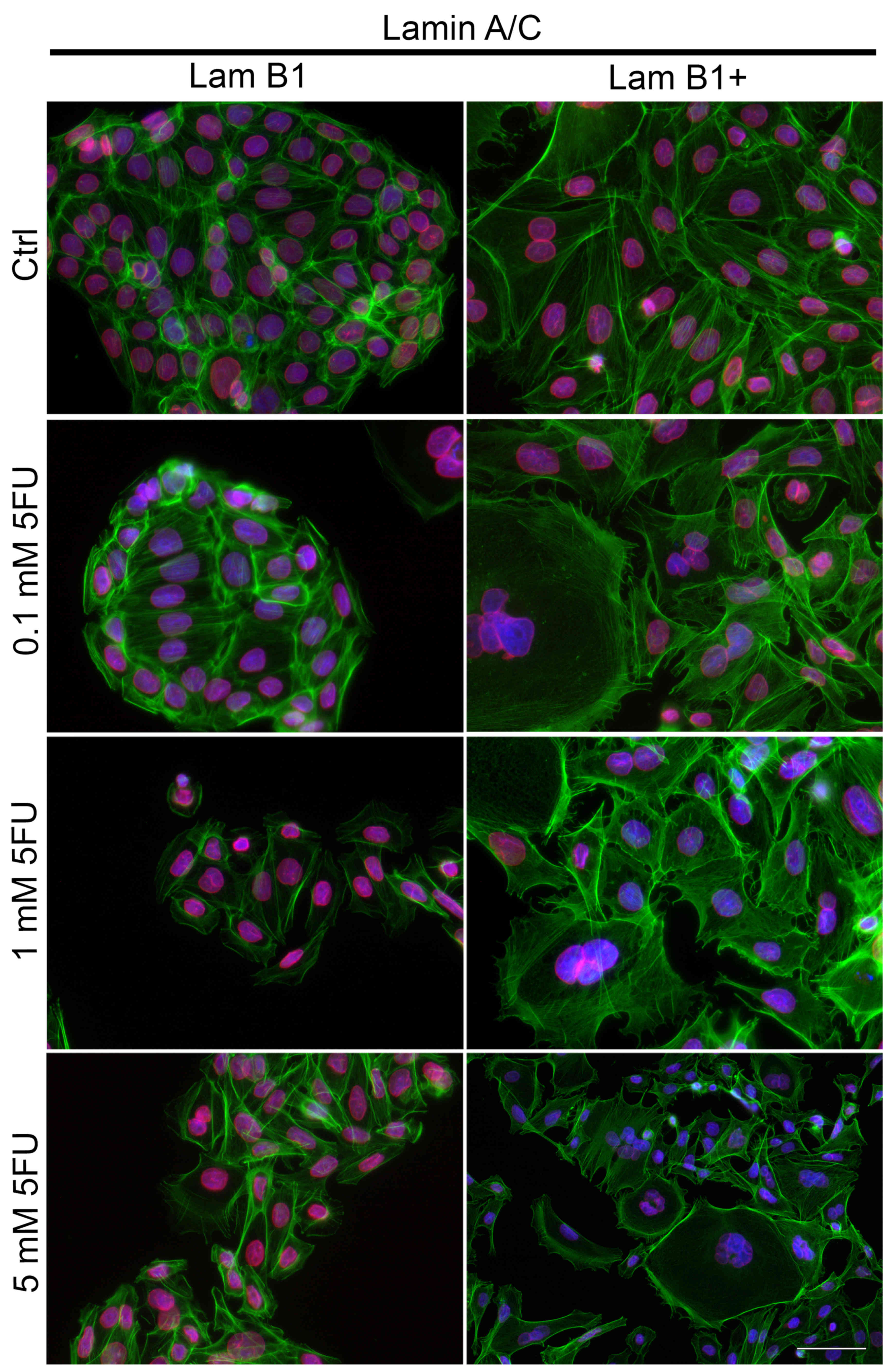
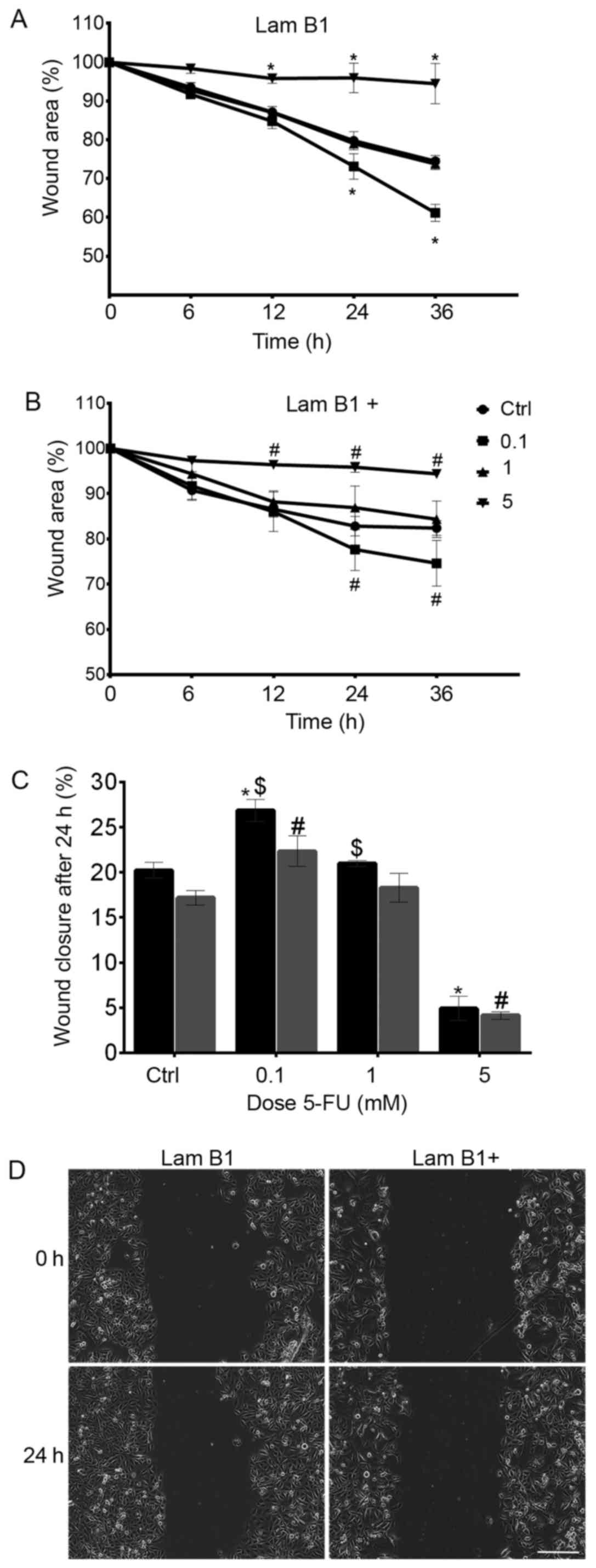
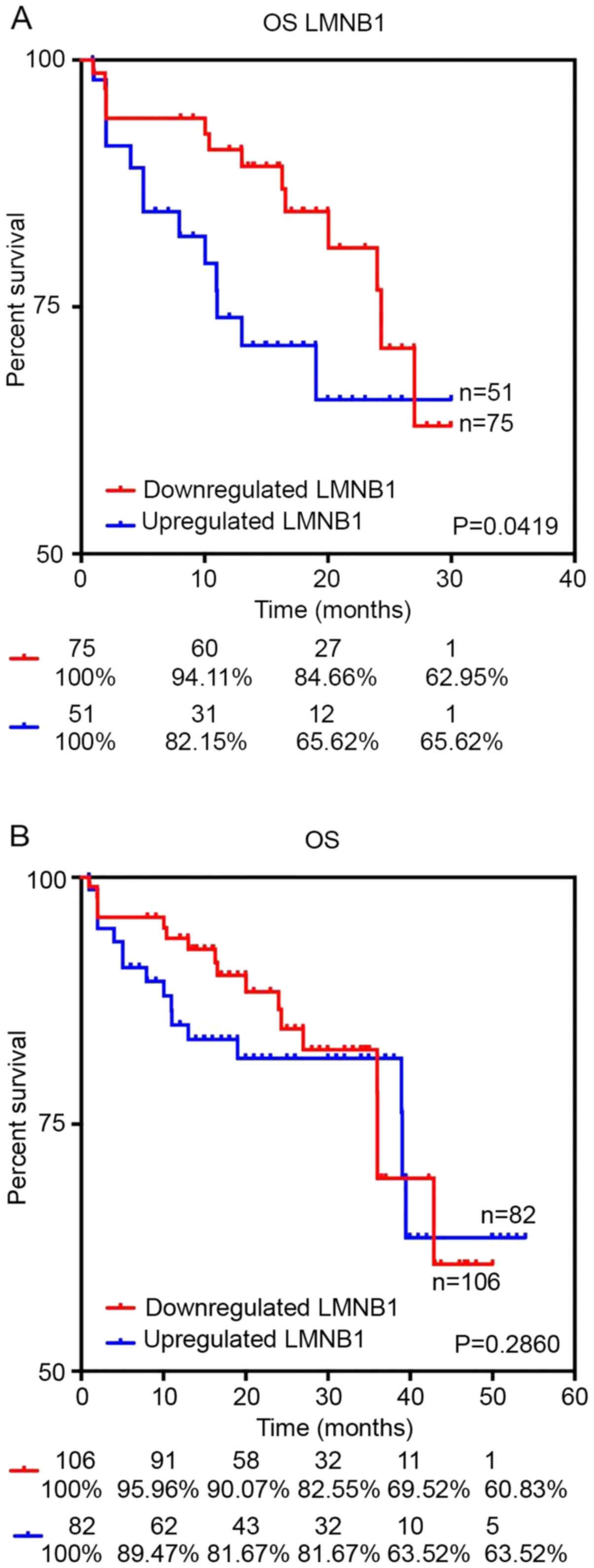
|
1
|
Dittmer TA and Misteli T: The lamin
protein family. Genome Biol. 12:2222011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Butin-Israeli V, Adam SA, Goldman AE and
Goldman RD: Nuclear lamin functions and disease. Trends Genet.
28:464–471. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sakthivel KM and Sehgal P: A Novel role of
lamins from genetic disease to cancer biomarkers. Oncol Rev.
10:3092016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li L, Du Y, Kong X, Li Z, Jia Z, Cui J,
Gao J, Wang G and Xie K: Lamin B1 is a novel therapeutic target of
betulinic acid in pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 19:4651–4661.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Irianto J, Pfeifer CR, Ivanovska IL, Swift
J and Discher DE: Nuclear lamins in cancer. Cell Mol Bioeng.
9:258–267. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jensen NF, Stenvang J, Beck MK, Hanáková
B, Belling KC, Do KN, Viuff B, Nygård SB, Gupta R, Rasmussen MH, et
al: Establishment and characterization of models of chemotherapy
resistance in colorectal cancer: Towards a predictive signature of
chemoresistance. Mol Oncol. 9:1169–1185. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hofmann WA: Cell and molecular biology of
nuclear actin. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 273:219–263. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Falahzadeh K, Banaei-Esfahani A and
Shahhoseini M: The potential roles of actin in the nucleus. Cell J.
17:7–14. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Houben F, Ramaekers FC, Snoeckx LH and
Broers JL: Role of nuclear lamina-cytoskeleton interactions in the
maintenance of cellular strength. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1773:675–686. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Han J, Gao B, Jin X, Xu Z, Li Z, Sun Y and
Song B: Small interfering RNA-mediated downregulation of
beta-catenin inhibits invasion and migration of colon cancer cells
in vitro. Med Sci Monit. 18:BR273–BR280. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jamieson C, Sharma M and Henderson BR: Wnt
signaling from membrane to nucleus: B-catenin caught in a loop. Int
J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:847–850. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Serebryannyy LA, Yemelyanov A, Gottardi CJ
and de Lanerolle P: Nuclear α-catenin mediates the DNA damage
response via β-catenin and nuclear actin. J Cell Sci.
130:1717–1729. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE,
Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, et
al: The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring
multi-dimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2:401–404.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Simon DN, Zastrow MS and Wilson KL: Direct
actin binding to A- and B-type lamin tails and actin filament
bundling by the lamin A tail. Nucleus. 1:264–272. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tariq Z, Zhang H, Chia-Liu A, Shen Y, Gete
Y, Xiong ZM, Tocheny C, Campanello L, Wu D, Losert W, et al: Lamin
A and microtubules collaborate to maintain nuclear morphology.
Nucleus. 8:433–446. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brembeck FH, Rosário M and Birchmeier W:
Balancing cell adhesion and Wnt signaling, the key role of
beta-catenin. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 16:51–59. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Houben F, Willems CH, Declercq IL,
Hochstenbach K, Kamps MA, Snoeckx LH, Ramaekers FC and Broers JL:
Disturbed nuclear orientation and cellular migration in A-type
lamin deficient cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1793:312–324. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Moss SF, Krivosheyev V, de Souza A, Chin
K, Gaetz HP, Chaudhary N, Worman HJ and Holt PR: Decreased and
aberrant nuclear lamin expression in gastrointestinal tract
neoplasms. Gut. 45:723–729. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang N, Yin Y, Xu SJ and Chen WS:
5-Fluorouracil: Mechanisms of resistance and reversal strategies.
Molecules. 13:1551–1569. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang L, Song R, Gu D, Zhang X, Yu B, Liu
B and Xie J: The role of GLI1 for 5-Fu resistance in colorectal
cancer. Cell Biosci. 7:172017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Das D, Preet R, Mohapatra P, Satapathy SR,
Siddharth S, Tamir T, Jain V, Bharatam PV, Wyatt MD and Kundu CN:
5-Fluorouracil mediated anti-cancer activity in colon cancer cells
is through the induction of Adenomatous Polyposis Coli: Implication
of the long-patch base excision repair pathway. DNA Repair (Amst).
24:15–25. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wang Z, Jiang B, Chen L, Di J, Cui M, Liu
M, Ma Y, Yang H, Xing J, Zhang C, et al: GOLPH3 predicts survival
of colorectal cancer patients treated with 5-fluorouracil-based
adjuvant chemotherapy. J Transl Med. 12:152014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang Y, Yuan S, Li L, Yang D, Xu C, Wang S
and Zhang D: Novel proapoptotic agent SM-1 enhances the inhibitory
effect of 5-fluorouracil on colorectal cancer cells in vitro and in
vivo. Oncol Lett. 13:4762–4768. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mhaidat NM, Bouklihacene M and Thorne RF:
5-Fluorouracil-induced apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells is
caspase-9-dependent and mediated by activation of protein kinase
C-δ. Oncol Lett. 8:699–704. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nita Me, Nagawa H, Tominaga O, Tsuno N,
Fujii S, Sasaki S, Fu CG, Takenoue T, Tsuruo T and Muto T:
5-Fluorouracil induces apoptosis in human colon cancer cell lines
with modulation of Bcl-2 family proteins. Br J Cancer. 78:986–992.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Milczarek M, Psurski M, Kutner A and
Wietrzyk J: Vitamin d analogs enhance the anticancer activity of
5-fluorouracil in an in vivo mouse colon cancer model. BMC Cancer.
13:2942013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen J, Ding Z, Peng Y, Pan F, Li J, Zou
L, Zhang Y and Liang H: HIF-1α inhibition reverses multidrug
resistance in colon cancer cells via downregulation of
MDR1/P-glycoprotein. PLoS One. 9:e988822014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li Z, Wang N, Huang C, Bao Y, Jiang Y and
Zhu G: Down-regulation of caveolin-1 increases the sensitivity of
drug-resistant colorectal cancer HCT116 cells to 5-fluorouracil.
Oncol Lett. 13:483–487. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hamam R, Ali D, Vishnubalaji R, Alsaaran
ZF, Chalisserry EP, Alfayez M, Aldahmash A and Alajez NM and Alajez
NM: Enhanced efficacy of 5-fluorouracil in combination with a dual
histone deacetylase and phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase inhibitor
(CUDC-907) in colorectal cancer cells. Saudi J Gastroenterol.
23:34–38. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yao CM, Kang KA, Piao MJ, Ryu YS, Fernando
PMDJ, Oh MC, Park JE, Shilnikova K, Na SY, Jeong SU, et al: Reduced
autophagy in 5-fluorouracil resistant colon cancer cells. Biomol
Ther (Seoul). 25:315–320. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Tang JC, Feng YL, Liang X and Cai XJ:
Autophagy in 5-fluorouracil therapy in gastrointestinal gancer:
Trends and challenges. Chin Med J (Engl). 129:456–463. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Shimizu S, Kanaseki T, Mizushima N, Mizuta
T, Arakawa-Kobayashi S, Thompson CB and Tsujimoto Y: Role of Bcl-2
family proteins in a non-apoptotic programmed cell death dependent
on autophagy genes. Nat Cell Biol. 6:1221–1228. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, Garuti R,
Liang XH, Mizushima N, Packer M, Schneider MD and Levine B: Bcl-2
antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell.
122:927–939. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
de la Cruz Morcillo MA, Valero ML,
Callejas Valera JL, Arias González L, Melgar Rojas P, Galán Moya
EM, García-Gil E, García-Cano J and Sánchez-Prieto R: P38MAPK is a
major determinant of the balance between apoptosis and autophagy
triggered by 5-fluorouracil: implication in resistance. Oncogene.
31:1073–1085. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Oliver Metzig M, Fuchs D, Tagscherer KE,
Gröne HJ, Schirmacher P and Roth W: Inhibition of caspases primes
colon cancer cells for 5-fluorouracil-induced TNF-α-dependent
necroptosis driven by RIP1 kinase and NF-κB. Oncogene.
35:3399–3409. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Liu L, Wang J, Shi L, Zhang W, Du X, Wang
Z and Zhang Y: β-Asarone induces senescence in colorectal cancer
cells by inducing lamin B1 expression. Phytomedicine. 20:512–520.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yoshikawa R, Kusunoki M, Yanagi H, Noda M,
Furuyama JI, Yamamura T and Hashimoto-Tamaoki T: Dual antitumor
effects of 5-fluorouracil on the cell cycle in colorectal carcinoma
cells: A novel target mechanism concept for pharmacokinetic
modulating chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 61:1029–1037. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Grzanka D, Marszałek A, Gagat M, Izdebska
M, Gackowska L and Grzanka A: Doxorubicin-induced F-actin
reorganization in cofilin-1 (nonmuscle) down-regulated CHO AA8
cells. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 48:377–386. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen XX, Lai MD, Zhang YL and Huang Q:
Less cytotoxicity to combination therapy of 5-fluorouracil and
cisplatin than 5-fluorouracil alone in human colon cancer cell
lines. World J Gastroenterol. 8:841–846. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Guo X, Goessl E, Jin G, Collie-Duguid ES,
Cassidy J, Wang W and O'Brien V: Cell cycle perturbation and
acquired 5-fluorouracil chemoresistance. Anticancer Res. 28(1A):
9–14. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nie F, Zhao SY, Song FX and Li PW: Changes
of cytoskeleton and cell cycle in Lovo cells via deletion of Rac1.
Cancer Biomark. 14:335–342. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Huang X, Halicka HD, Traganos F, Tanaka T,
Kurose A and Darzynkiewicz Z: Cytometric assessment of DNA damage
in relation to cell cycle phase and apoptosis. Cell Prolif.
38:223–243. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Darzynkiewicz Z, Juan G, Li X, Gorczyca W,
Murakami T and Traganos F: Cytometry in cell necrobiology: Analysis
of apoptosis and accidental cell death (necrosis). Cytometry.
27:1–20. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Oberhammer F, Wilson JW, Dive C, Morris
ID, Hickman JA, Wakeling AE, Walker PR and Sikorska M: Apoptotic
death in epithelial cells: Cleavage of DNA to 300 and/or 50 kb
fragments prior to or in the absence of internucleosomal
fragmentation. EMBO J. 12:3679–3684. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tao D, Wu J, Feng Y, Qin J, Hu J and Gong
J: New method for the analysis of cell cycle-specific apoptosis.
Cytometry A. 57:70–74. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Camps J, Erdos MR and Ried T: The role of
lamin B1 for the maintenance of nuclear structure and function.
Nucleus. 6:8–14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Horbay R and Stoika R: Giant cell
formation: The way to cell death or cell survival? Cent Eur J Biol.
6:675–684. 2011.
|
|
48
|
Erenpreisa J and Cragg MS: Mitotic death:
A mechanism of survival? A review. Cancer Cell Int. 1:12001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Butin-Israeli V, Adam SA, Jain N, Otte GL,
Neems D, Wiesmüller L, Berger SL and Goldman RD: Role of lamin b1
in chromatin instability. Mol Cell Biol. 35:884–898. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
Liu NA, Sun J, Kono K, Horikoshi Y, Ikura
T, Tong X, Haraguchi T and Tashiro S: Regulation of homologous
recombi-national repair by lamin B1 in radiation-induced DNA
damage. FASEB J. 29:2514–2525. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hall A: The cytoskeleton and cancer.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 28:5–14. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Pollard TD: The cytoskeleton, cellular
motility and the reductionist agenda. Nature. 422:741–745. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hałas M, Izdebska M,
Klimaszewska-Wiśniewska A, Gagat M, Radciniewska D, Glińska A,
Gizler K, Bielińska E and Grzanka A: Caffeine induces cytoskeletal
changes and cell death in H1299 cells. Cent Eur J Biol. 9:727–738.
2014.
|
|
54
|
Pawlik A, Szczepański MA, Klimaszewska A,
Gackowska L, Zuryn A and Grzanka A: Phenethyl
isothiocyanate-induced cytoskeletal changes and cell death in lung
cancer cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:3577–3594. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Grzanka D, Marszałek A, Izdebska M,
Gackowska L, Andrzej Szczepanski M and Grzanka A: Actin
cytoskeleton reorganization correlates with cofilin nuclear
expression and ultrastructural changes in cho aa8 cell line after
apoptosis and mitotic catastrophe induction by doxorubicin.
Ultrastruct Pathol. 35:130–138. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Izdebska M, Gagat M, Grzanka D, Halas M
and Grzanka A: The role of exportin 6 in cytoskeletal-mediated cell
death and cell adhesion in human non-small-cell lung carcinoma
cells following doxorubicin treatment. Folia Histochem Cytobiol.
52:195–205. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Desouza M, Gunning PW and Stehn JR: The
actin cytoskeleton as a sensor and mediator of apoptosis.
Bioarchitecture. 2:75–87. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Grzanka A and Grzanka D: Distribution of
actin in etoposide-induced human leukemia cell line K-562 using
fluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy technique. Pol J Pathol.
53:43–50. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Grzanka A, Grzanka D and Orlikowska M:
Cytoskeletal reorganization during process of apoptosis induced by
cytostatic drugs in K-562 and HL-60 leukemia cell lines. Biochem
Pharmacol. 66:1611–1617. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Grzanka A, Grzanka D, Zuryń A, Grzanka AA
and Safiejko-Mroczka B: Reorganization of actin in K-562 and HL-60
cells treated with taxol. Neoplasma. 53:56–61. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Levee MG, Dabrowska MI, Lelli JL Jr and
Hinshaw DB: Actin polymerization and depolymerization during
apoptosis in HL-60 cells. Am J Physiol. 271:C1981–C1992. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Grzanka D, Grzanka A, Izdebska M,
Gackowska L, Stepien A and Marszalek A: Actin reorganization in CHO
AA8 cells under-going mitotic catastrophe and apoptosis induced by
doxorubicin. Oncol Rep. 23:655–663. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Erenpreisa J, Ivanov A, Wheatley SP,
Kosmacek EA, Ianzini F, Anisimov AP, Mackey M, Davis PJ, Plakhins G
and Illidge TM: Endopolyploidy in irradiated p53-deficient tumour
cell lines: Persistence of cell division activity in giant cells
expressing Aurora-B kinase. Cell Biol Int. 32:1044–1056. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Grzanka D, Gagat M and Izdebska M:
Involvement of the SATB1/F-actin complex in chromatin
reorganization during active cell death. Int J Mol Med.
33:1441–1450. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Grzanka D, Izdebska M,
Klimaszewska-Wisniewska A and Gagat M: The alterations in sATB1 and
nuclear F-actin expression affect apoptotic response of the MCF-7
cells to geldanamycin. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 53:79–87. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Grzanka D, Kowalczyk AE, Izdebska M,
Klimaszewska-Wisniewska A and Gagat M: The interactions between
sATB1 and F-actin are important for mechanisms of active cell
death. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 53:152–161. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Hoelzle MK and Svitkina T: The
cytoskeletal mechanisms of cell-cell junction formation in
endothelial cells. Mol Biol Cell. 23:310–323. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
68
|
Braga VM: Cell-cell adhesion and
signalling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 14:546–556. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Matter K and Balda MS: Signalling to and
from tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 4:225–236. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Astudillo P and Larraín J: Wnt signaling
and cell-matrix adhesion. Curr Mol Med. 14:209–220. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Macdonald BT, Tamai K and He X:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases.
Dev Cell. 17:9–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Itoh M, Nagafuchi A, Moroi S and Tsukita
S: Involvement of ZO-1 in cadherin-based cell adhesion through its
direct binding to alpha catenin and actin filaments. J Cell Biol.
138:181–192. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Gagat M, Grzanka D, Izdebska M and Grzanka
A: Effect of L-homocysteine on endothelial cell-cell junctions
following F-actin stabilization through tropomyosin-1
overexpression. Int J Mol Med. 32:115–129. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Gooding JM, Yap KL and Ikura M: The
cadherin-catenin complex as a focal point of cell adhesion and
signalling: New insights from three-dimensional structures.
BioEssays. 26:497–511. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Cavallaro U and Christofori G: Cell
adhesion and signalling by cadherins and Ig-CAMs in cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 4:118–132. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Willis ND, Cox TR, Rahman-Casañs SF, Smits
K, Przyborski SA, van den Brandt P, van Engeland M, Weijenberg M,
Wilson RG, de Bruïne A, et al: Lamin A/C is a risk biomarker in
colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 3:e29882008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|