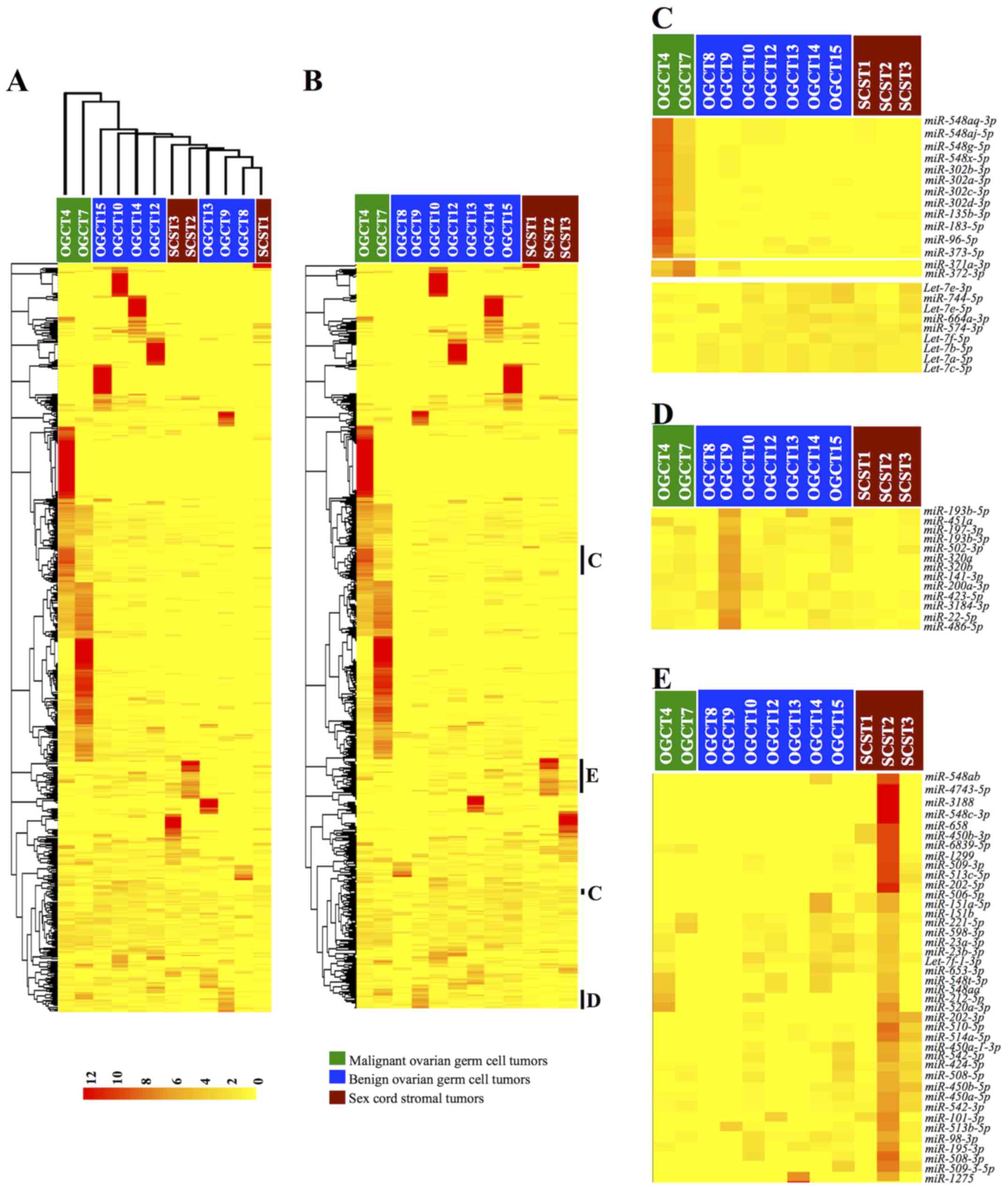
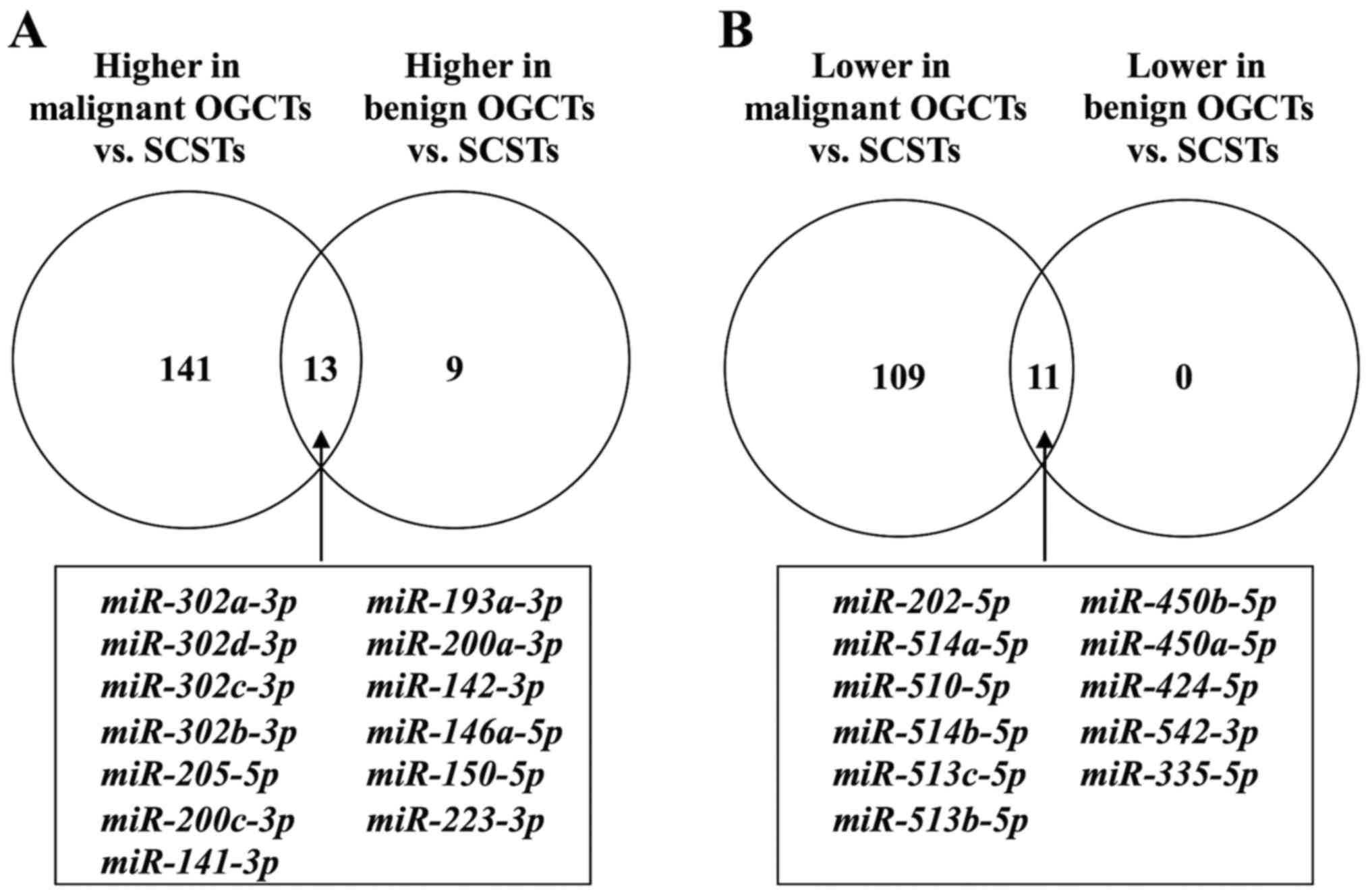
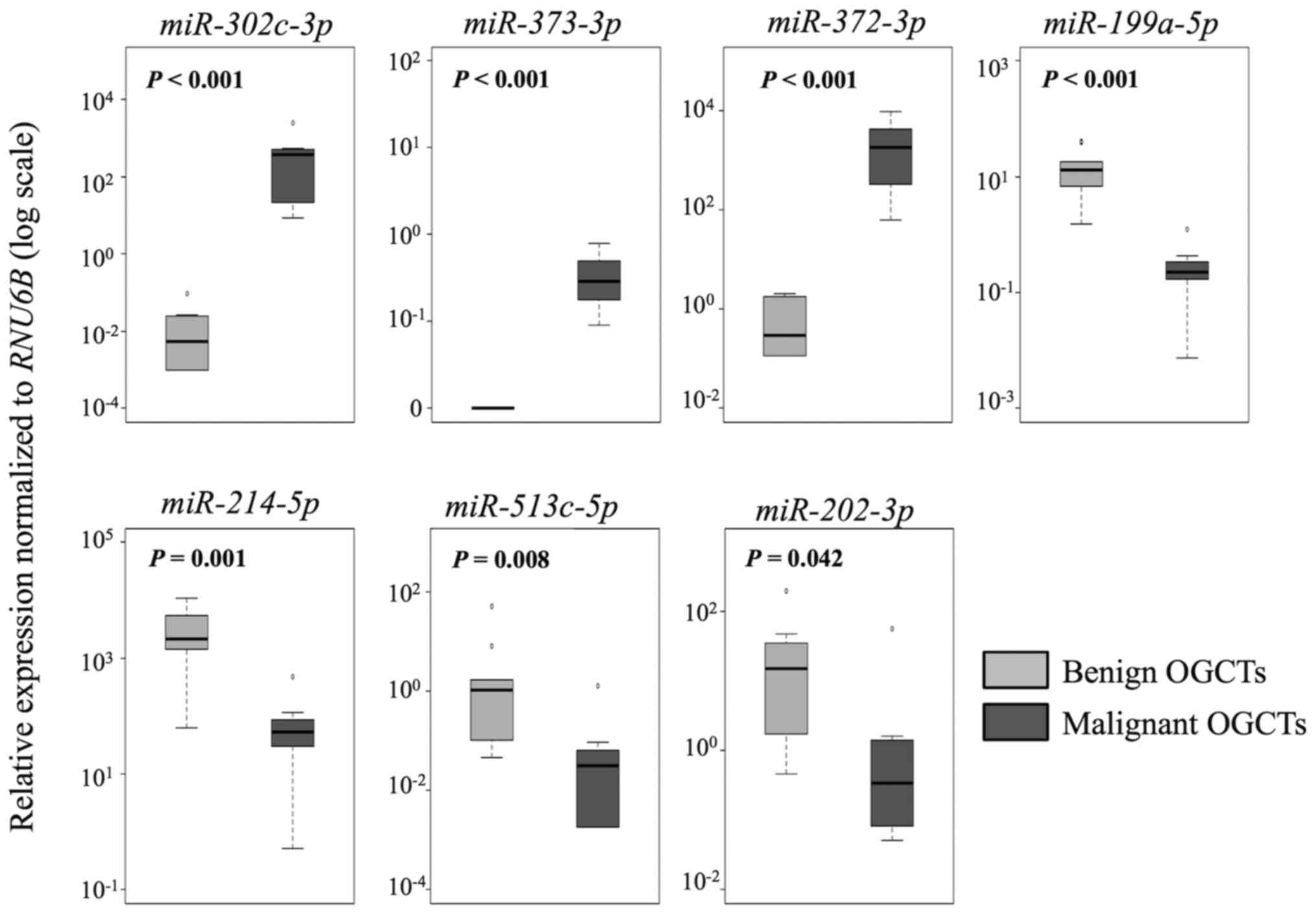
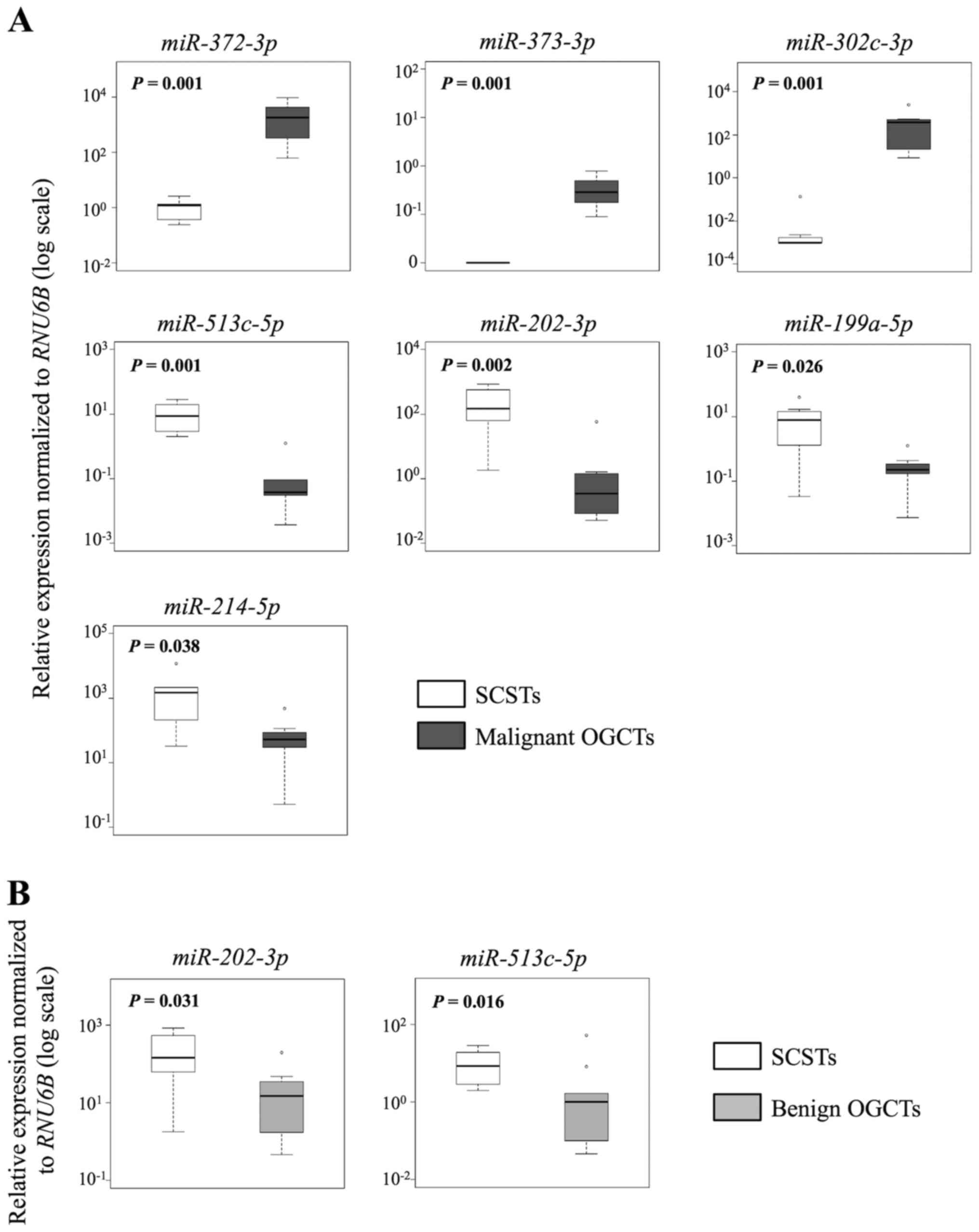
|
1
|
Curado MP, Edwards B, Shin HR, Storm H,
Ferlay J, Heanue M and Boyle P: Cancer incidence in five continents
Volume IX. IARC Sci Publ. 160:1–837. 2008.
|
|
2
|
Colombo N and Peiretti M: Non-epithelial
ovarian cancer: ESMO clinical recommendations for diagnosis,
treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 20(Suppl 4): 24–26. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kraggerud SM, Hoei-Hansen CE, Alagaratnam
S, Skotheim RI, Abeler VM, Rajpert-De Meyts E and Lothe RA:
Molecular characteristics of malignant ovarian germ cell tumors and
comparison with testicular counterparts: Implications for
pathogenesis. Endocr Rev. 34:339–376. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chi JG, Lee YS, Park YS and Chang KY:
Fetus-in-fetu: Report of a case. Am J Clin Pathol. 82:115–119.
1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sergi C, Ehemann V, Beedgen B, Linderkamp
O and Otto HF: Huge fetal sacrococcygeal teratoma with a completely
formed eye and intratumoral DNA ploidy heterogeneity. Pediatr Dev
Pathol. 2:50–57. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kuno N, Kadomatsu K, Nakamura M,
Miwa-Fukuchi T, Hirabayashi N and Ishizuka T: Mature ovarian cystic
teratoma with a highly differentiated homunculus: A case report.
Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 70:40–46. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Arlikar JD, Mane SB, Dhende NP, Sanghavi
Y, Valand AG and Butale PR: Fetus in fetu: Two case reports and
review of literature. Pediatr Surg Int. 25:289–292. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Scully RE: Classification of human ovarian
tumors. Environ Health Perspect. 73:15–25. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schultz KA, Harris AK, Schneider DT, Young
RH, Brown J, Gershenson DM, Dehner LP, Hill DA, Messinger YH and
Frazier AL: Ovarian sex cord-stromal tumors. J Oncol Pract.
12:940–946. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hoei-Hansen CE, Kraggerud SM, Abeler VM,
Kaern J, Rajpert-De Meyts E and Lothe RA: Ovarian dysgerminomas are
characterised by frequent KIT mutations and abundant expression of
pluripotency markers. Mol Cancer. 6:122007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Murray MJ, Saini HK, Siegler CA, Hanning
JE, Barker EM, van Dongen S, Ward DM, Raby KL, Groves IJ, Scarpini
CG, et al CCLG: LIN28 expression in malignant germ cell tumors
downregulates let-7 and increases oncogene levels. Cancer Res.
73:4872–4884. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shah SP, Köbel M, Senz J, Morin RD, Clarke
BA, Wiegand KC, Leung G, Zayed A, Mehl E, Kalloger SE, et al:
Mutation of FOXL2 in granulosa-cell tumors of the ovary. N Engl J
Med. 360:2719–2729. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim JH, Yoon S, Park M, Park HO, Ko JJ,
Lee K and Bae J: Differential apoptotic activities of wild-type
FOXL2 and the adult-type granulosa cell tumor-associated mutant
FOXL2 (C134W). Oncogene. 30:1653–1663. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kim JH, Kim YH, Kim HM, Park HO, Ha NC,
Kim TH, Park M, Lee K and Bae J: FOXL2 posttranslational
modifications mediated by GSK3β determine the growth of granulosa
cell tumours. Nat Commun. 5:29362014.
|
|
15
|
Heravi-Moussavi A, Anglesio MS, Cheng SW,
Senz J, Yang W, Prentice L, Fejes AP, Chow C, Tone A, Kalloger SE,
et al: Recurrent somatic DICER1 mutations in nonepithelial ovarian
cancers. N Engl J Med. 366:234–242. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Bushati N and Cohen SM: microRNA
functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 23:175–205. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Croce CM: Causes and consequences of
microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 10:704–714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gillis AJ, Stoop HJ, Hersmus R, Oosterhuis
JW, Sun Y, Chen C, Guenther S, Sherlock J, Veltman I, Baeten J, et
al: High-throughput microRNAome analysis in human germ cell
tumours. J Pathol. 213:319–328. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Palmer RD, Murray MJ, Saini HK, van Dongen
S, Abreu-Goodger C, Muralidhar B, Pett MR, Thornton CM, Nicholson
JC, Enright AJ, et al: Children's Cancer and Leukaemia Group:
Malignant germ cell tumors display common microRNA profiles
resulting in global changes in expression of messenger RNA targets.
Cancer Res. 70:2911–2923. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Murray MJ, Saini HK, van Dongen S, Palmer
RD, Muralidhar B, Pett MR, Piipari M, Thornton CM, Nicholson JC,
Enright AJ, et al: The two most common histological subtypes of
malignant germ cell tumour are distinguished by global microRNA
profiles, associated with differential transcription factor
expression. Mol Cancer. 9:2902010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fustino N, Rakheja D, Ateek CS, Neumann JC
and Amatruda JF: Bone morphogenetic protein signalling activity
distinguishes histological subsets of paediatric germ cell tumours.
Int J Androl. 34:e218–e233. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Witten D, Tibshirani R, Gu SG, Fire A and
Lui WO: Ultra-high throughput sequencing-based small RNA discovery
and discrete statistical biomarker analysis in a collection of
cervical tumours and matched controls. BMC Biol. 8:582010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M and Salzberg
SL: Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences
to the human genome. Genome Biol. 10:R252009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T,
Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G and Durbin R; 1000 Project
Genome Data Processing Subgroup: The Sequence Alignment/Map format
and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 25:2078–2079. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Anders S, Pyl PT and Huber W: HTSeq - a
Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data.
Bioinformatics. 31:166–169. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Robinson MD and Oshlack A: A scaling
normalization method for differential expression analysis of
RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 11:R252010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:5502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Voorhoeve PM, le Sage C, Schrier M, Gillis
AJ, Stoop H, Nagel R, Liu YP, van Duijse J, Drost J, Griekspoor A,
et al: A genetic screen implicates miRNA-372 and miRNA-373 as
oncogenes in testicular germ cell tumors. Cell. 124:1169–1181.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gillis AJ, Rijlaarsdam MA, Eini R,
Dorssers LC, Biermann K, Murray MJ, Nicholson JC, Coleman N,
Dieckmann KP, Belge G, et al: Targeted serum miRNA (TSmiR) test for
diagnosis and follow-up of (testicular) germ cell cancer patients:
A proof of principle. Mol Oncol. 7:1083–1092. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Murray MJ, Halsall DJ, Hook CE, Williams
DM, Nicholson JC and Coleman N: Identification of microRNAs From
the miR-371~373 and miR-302 clusters as potential serum biomarkers
of malignant germ cell tumors. Am J Clin Pathol. 135:119–125. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Özata DM, Li X, Lee L, Liu J, Warsito D,
Hajeri P, Hultman I, Fotouhi O, Marklund S, Ährlund-Richter L, et
al: Loss of miR-514a-3p regulation of PEG3-activates the NF-kappa B
pathway in human testicular germ cell tumors. Cell Death Dis.
8:e27592017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chen BF, Suen YK, Gu S, Li L and Chan WY:
A miR-199a/miR-214 self-regulatory network via PSMD10, TP53 and
DNMT1 in testicular germ cell tumor. Sci Rep. 4:64132014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhong X, Li N, Liang S, Huang Q, Coukos G
and Zhang L: Identification of microRNAs regulating reprogramming
factor LIN28 in embryonic stem cells and cancer cells. J Biol Chem.
285:41961–41971. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nakano H, Yamada Y, Miyazawa T and Yoshida
T: Gain-of-function microRNA screens identify miR-193a regulating
proliferation and apoptosis in epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Int
J Oncol. 42:1875–1882. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao Y, Li C, Wang M, Su L, Qu Y, Li J, Yu
B, Yan M, Yu Y, Liu B, et al: Decrease of miR-202-3p expression, a
novel tumor suppressor, in gastric cancer. PLoS One. 8:e697562013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yi H, Liang B, Jia J, Liang N, Xu H, Ju G,
Ma S and Liu X: Differential roles of miR-199a-5p in
radiation-induced autophagy in breast cancer cells. FEBS Lett.
587:436–443. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li Y, Jiang W, Hu Y, Da Z, Zeng C, Tu M,
Deng Z and Xiao W: MicroRNA-199a-5p inhibits cisplatin-induced drug
resistance via inhibition of autophagy in osteosarcoma cells. Oncol
Lett. 12:4203–4208. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ames K, Da Cunha DS, Gonzalez B, Konta M,
Lin F, Shechter G, Starikov L, Wong S, Bülow HE and Meléndez A: A
non-cell-autonomous role of BEC-1/BECN1/Beclin1 in coordinating
cell-cycle progression and stem cell proliferation during germline
development. Curr Biol. 27:905–913. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gawriluk TR, Hale AN, Flaws JA, Dillon CP,
Green DR and Rucker EB III: Autophagy is a cell survival program
for female germ cells in the murine ovary. Reproduction.
141:759–765. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rounge TB, Furu K, Skotheim RI, Haugen TB,
Grotmol T and Enerly E: Profiling of the small RNA populations in
human testicular germ cell tumors shows global loss of piRNAs. Mol
Cancer. 14:1532015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dieckmann KP, Spiekermann M, Balks T, Flor
I, Löning T, Bullerdiek J and Belge G: MicroRNAs miR-371-3 in serum
as diagnostic tools in the management of testicular germ cell
tumours. Br J Cancer. 107:1754–1760. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Syring I, Bartels J, Holdenrieder S,
Kristiansen G, Müller SC and Ellinger J: Circulating serum miRNA
(miR-367-3p, miR-371a-3p, miR-372-3p and miR-373-3p) as biomarkers
in patients with testicular germ cell cancer. J Urol. 193:331–337.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Subramanyam D, Lamouille S, Judson RL, Liu
JY, Bucay N, Derynck R and Blelloch R: Multiple targets of miR-302
and miR-372 promote reprogramming of human fibroblasts to induced
pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 29:443–448. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fareh M, Turchi L, Virolle V, Debruyne D,
Almairac F, de-la-Forest Divonne S, Paquis P, Preynat-Seauve O,
Krause KH, Chneiweiss H, et al: The miR 302–367 cluster drastically
affects self-renewal and infiltration properties of
glioma-initiating cells through CXCR4 repression and consequent
disruption of the SHH-GLI-NANOG network. Cell Death Differ.
19:232–244. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Yang CM, Chiba T, Brill B, Delis N, von
Manstein V, Vafaizadeh V, Oellerich T and Groner B: Expression of
the miR-302/367 cluster in glioblastoma cells suppresses
tumorigenic gene expression patterns and abolishes transformation
related phenotypes. Int J Cancer. 137:2296–2309. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gu KL, Zhang Q, Yan Y, Li TT, Duan FF, Hao
J, Wang XW, Shi M, Wu DR, Guo WT, et al: Pluripotency-associated
miR-290/302 family of microRNAs promote the dismantling of naive
pluripotency. Cell Res. 26:350–366. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li HL, Wei JF, Fan LY, Wang SH, Zhu L, Li
TP, Lin G, Sun Y, Sun ZJ, Ding J, et al: miR-302 regulates
pluripotency, teratoma formation and differentiation in stem cells
via an AKT1/OCT4-dependent manner. Cell Death Dis. 7:e20782016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cheung HH, Davis AJ, Lee TL, Pang AL,
Nagrani S, Rennert OM and Chan WY: Methylation of an intronic
region regulates miR-199a in testicular tumor malignancy. Oncogene.
30:3404–3415. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lee YB, Bantounas I, Lee DY, Phylactou L,
Caldwell MA and Uney JB: Twist-1 regulates the miR-199a/214 cluster
during development. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:123–128. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
Cheung HH, Lee TL, Davis AJ, Taft DH,
Rennert OM and Chan WY: Genome-wide DNA methylation profiling
reveals novel epigenetically regulated genes and non-coding RNAs in
human testicular cancer. Br J Cancer. 102:419–427. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gu S, Cheung HH, Lee TL, Lu G, Poon WS and
Chan WY: Molecular mechanisms of regulation and action of
microRNA-199a in testicular germ cell tumor and glioblastomas. PLoS
One. 8:e839802013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Yang H, Kong W, He L, Zhao JJ, O'Donnell
JD, Wang J, Wenham RM, Coppola D, Kruk PA, Nicosia SV, et al:
MicroRNA expression profiling in human ovarian cancer: miR-214
induces cell survival and cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN.
Cancer Res. 68:425–433. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chen R, Alvero AB, Silasi DA, Kelly MG,
Fest S, Visintin I, Leiser A, Schwartz PE, Rutherford T and Mor G:
Regulation of IKKbeta by miR-199a affects NF-kappaB activity in
ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene. 27:4712–4723. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yin G, Chen R, Alvero AB, Fu HH, Holmberg
J, Glackin C, Rutherford T and Mor G: TWISTing stemness,
inflammation and proliferation of epithelial ovarian cancer cells
through MIR199A2/214. Oncogene. 29:3545–3553. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Sontakke SD, Mohammed BT, McNeilly AS and
Donadeu FX: Characterization of microRNAs differentially expressed
during bovine follicle development. Reproduction. 148:271–283.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wainwright EN, Jorgensen JS, Kim Y, Truong
V, Bagheri-Fam S, Davidson T, Svingen T, Fernandez-Valverde SL,
McClelland KS, Taft RJ, et al: SOX9 regulates microRNA
miR-202-5p/3p expression during mouse testis differentiation. Biol
Reprod. 89:342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Bannister SC, Smith CA, Roeszler KN, Doran
TJ, Sinclair AH and Tizard ML: Manipulation of estrogen synthesis
alters MIR202* expression in embryonic chicken gonads. Biol Reprod.
85:22–30. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Tao W, Sun L, Shi H, Cheng Y, Jiang D, Fu
B, Conte MA, Gammerdinger WJ, Kocher TD and Wang D: Integrated
analysis of miRNA and mRNA expression profiles in tilapia gonads at
an early stage of sex differentiation. BMC Genomics. 17:3282016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Bizuayehu TT, Babiak J, Norberg B,
Fernandes JM, Johansen SD and Babiak I: Sex-biased miRNA expression
in Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus) brain and gonads.
Sex Dev. 6:257–266. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Chen J, Cai T, Zheng C, Lin X, Wang G,
Liao S, Wang X, Gan H, Zhang D, Hu X, et al: MicroRNA-202 maintains
spermatogonial stem cells by inhibiting cell cycle regulators and
RNA binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:4142–4157. 2017.
|
|
61
|
Eggers S, Ohnesorg T and Sinclair A:
Genetic regulation of mammalian gonad development. Nat Rev
Endocrinol. 10:673–683. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Streicher KL, Zhu W, Lehmann KP,
Georgantas RW, Morehouse CA, Brohawn P, Carrasco RA, Xiao Z, Tice
DA, Higgs BW, et al: A novel oncogenic role for the miRNA-506-514
cluster in initiating melanocyte transformation and promoting
melanoma growth. Oncogene. 31:1558–1570. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Liu G, Sun Y, Ji P, Li X, Cogdell D, Yang
D, Parker Kerrigan BC, Shmulevich I, Chen K, Sood AK, et al:
MiR-506 suppresses proliferation and induces senescence by directly
targeting the CDK4/6-FOXM1 axis in ovarian cancer. J Pathol.
233:308–318. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Singhal R, Bard JE, Nowak NJ, Buck MJ and
Kandel ES: FOXO1 regulates expression of a microRNA cluster on X
chromosome. Aging (Albany NY). 5:347–356. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Gross DN, van den Heuvel AP and Birnbaum
MJ: The role of FoxO in the regulation of metabolism. Oncogene.
27:2320–2336. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Richards JS, Sharma SC, Falender AE and Lo
YH: Expression of FKHR, FKHRL1, and AFX genes in the rodent ovary:
Evidence for regulation by IGF-I, estrogen, and the gonadotropins.
Mol Endocrinol. 16:580–599. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Liu Z, Castrillon DH, Zhou W and Richards
JS: FOXO1/3 depletion in granulosa cells alters follicle growth,
death and regulation of pituitary FSH. Mol Endocrinol. 27:238–252.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Shen M, Liu Z, Li B, Teng Y, Zhang J, Tang
Y, Sun SC and Liu H: Involvement of FoxO1 in the effects of
follicle-stimulating hormone on inhibition of apoptosis in mouse
granulosa cells. Cell Death Dis. 5:e14752014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Liu Z, Ren YA, Pangas SA, Adams J, Zhou W,
Castrillon DH, Wilhelm D and Richards JS: FOXO1/3 and PTEN
depletion in granulosa cells promotes ovarian granulosa cell tumor
development. Mol Endocrinol. 29:1006–1024. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
You SY, Park YS, Jeon HJ, Cho DH, Jeon HB,
Kim SH, Chang JW, Kim JS and Oh JS: Beclin-1 knockdown shows
abscission failure but not autophagy defect during oocyte meiotic
maturation. Cell Cycle. 15:1611–1619. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Hale AN, Ledbetter DJ, Gawriluk TR and
Rucker EB III: Autophagy: Regulation and role in development.
Autophagy. 9:951–972. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Song ZH, Yu HY, Wang P, Mao GK, Liu WX, Li
MN, Wang HN, Shang YL, Liu C, Xu ZL, et al: Germ cell-specific Atg7
knockout results in primary ovarian insufficiency in female mice.
Cell Death Dis. 6:e15892015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Herpin A, Englberger E, Zehner M, Wacker
R, Gessler M and Schartl M: Defective autophagy through epg5
mutation results in failure to reduce germ plasm and mitochondria.
FASEB J. 29:4145–4161. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhang Y, Yan L, Zhou Z, Yang P, Tian E,
Zhang K, Zhao Y, Li Z, Song B, Han J, et al: SEPA-1 mediates the
specific recognition and degradation of P granule components by
autophagy in C elegans. Cell. 136:308–321. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Wang H, Lu Q, Cheng S, Wang X and Zhang H:
Autophagy activity contributes to programmed cell death in
Caenorhabditis elegans. Autophagy. 9:1975–1982. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Vera VS, Kenchappa CS, Landberg K,
Bressendorff S, Schwarzbach S, Martin T, Mundy J, Petersen M,
Thelander M and Sundberg E: Autophagy is required for gamete
differentiation in the moss Physcomitrella patens. Autophagy. Aug
24–2017.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Agnello M, Chiarelli R, Martino C, Bosco L
and Roccheri MC: Autophagy is required for sea urchin oogenesis and
early development. Zygote. 24:918–926. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Rossi M, Colecchia D, Ilardi G, Acunzo M,
Nigita G, Sasdelli F, Celetti A, Strambi A, Staibano S, Croce CM,
et al: MAPK15 upregulation promotes cell proliferation and prevents
DNA damage in male germ cell tumors. Oncotarget. 7:20981–20998.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Shen Y, Li DD, Wang LL, Deng R and Zhu XF:
Decreased expression of autophagy-related proteins in malignant
epithelial ovarian cancer. Autophagy. 4:1067–1068. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Kandala PK and Srivastava SK: Regulation
of macroautophagy in ovarian cancer cells in vitro and in vivo by
controlling glucose regulatory protein 78 and AMPK. Oncotarget.
3:435–449. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|