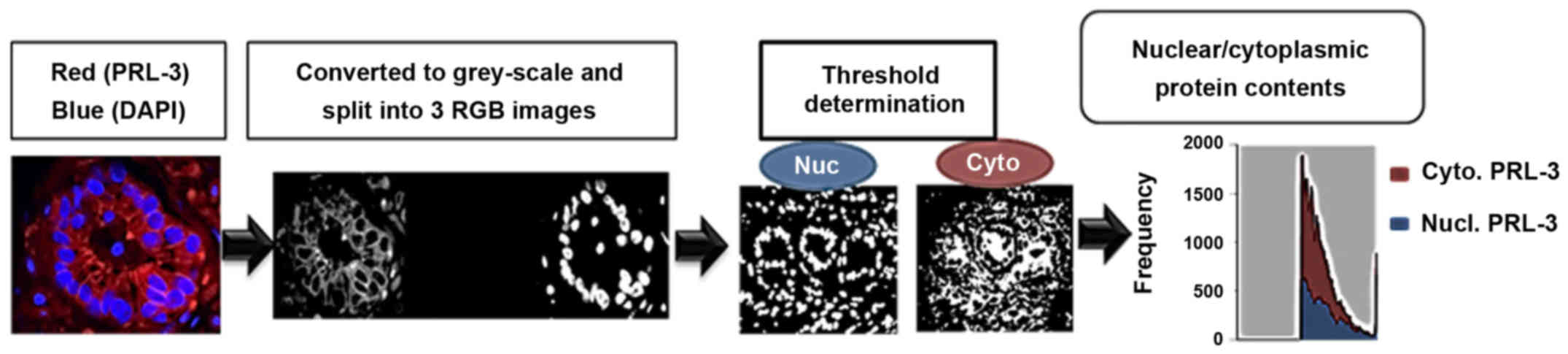
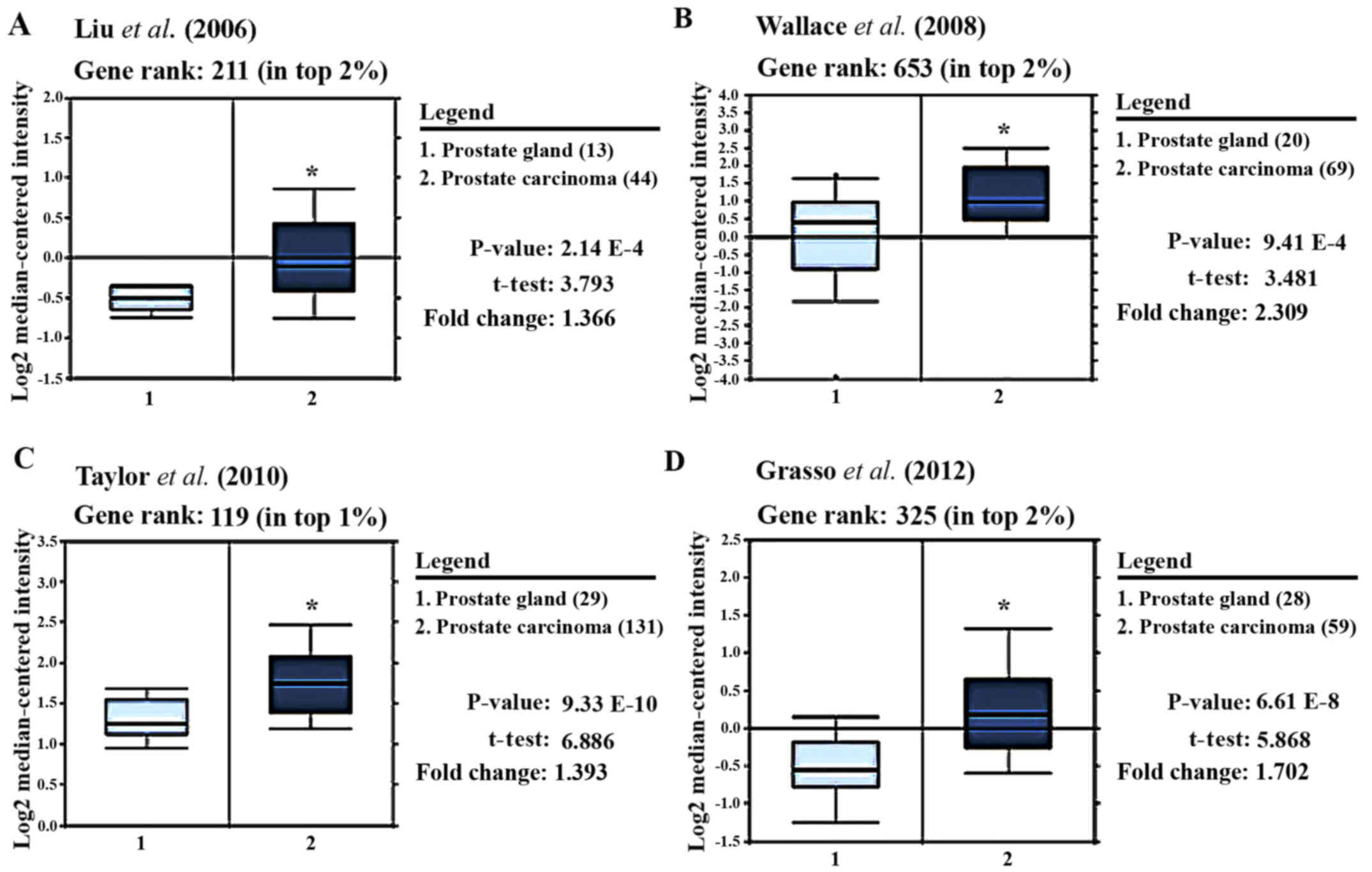
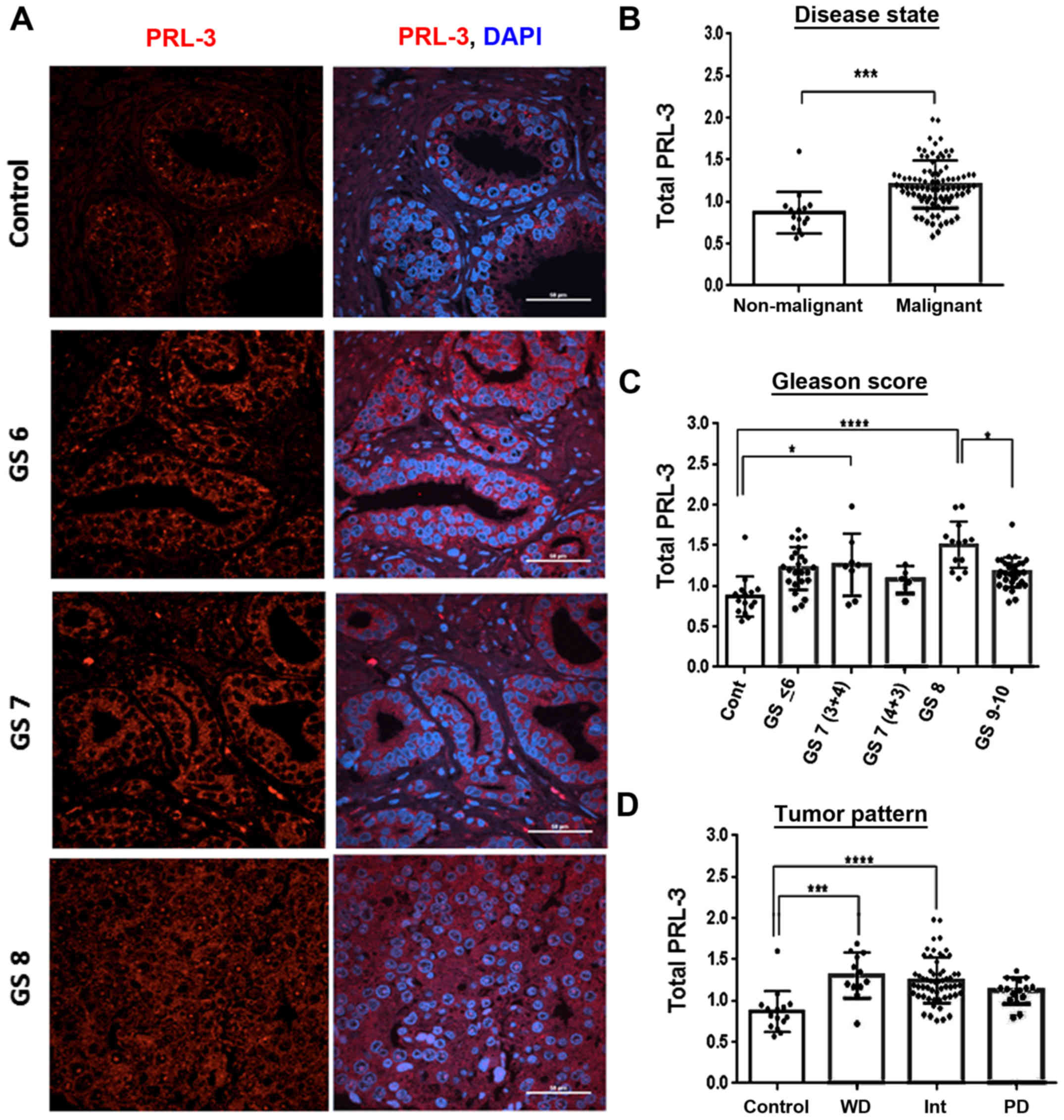
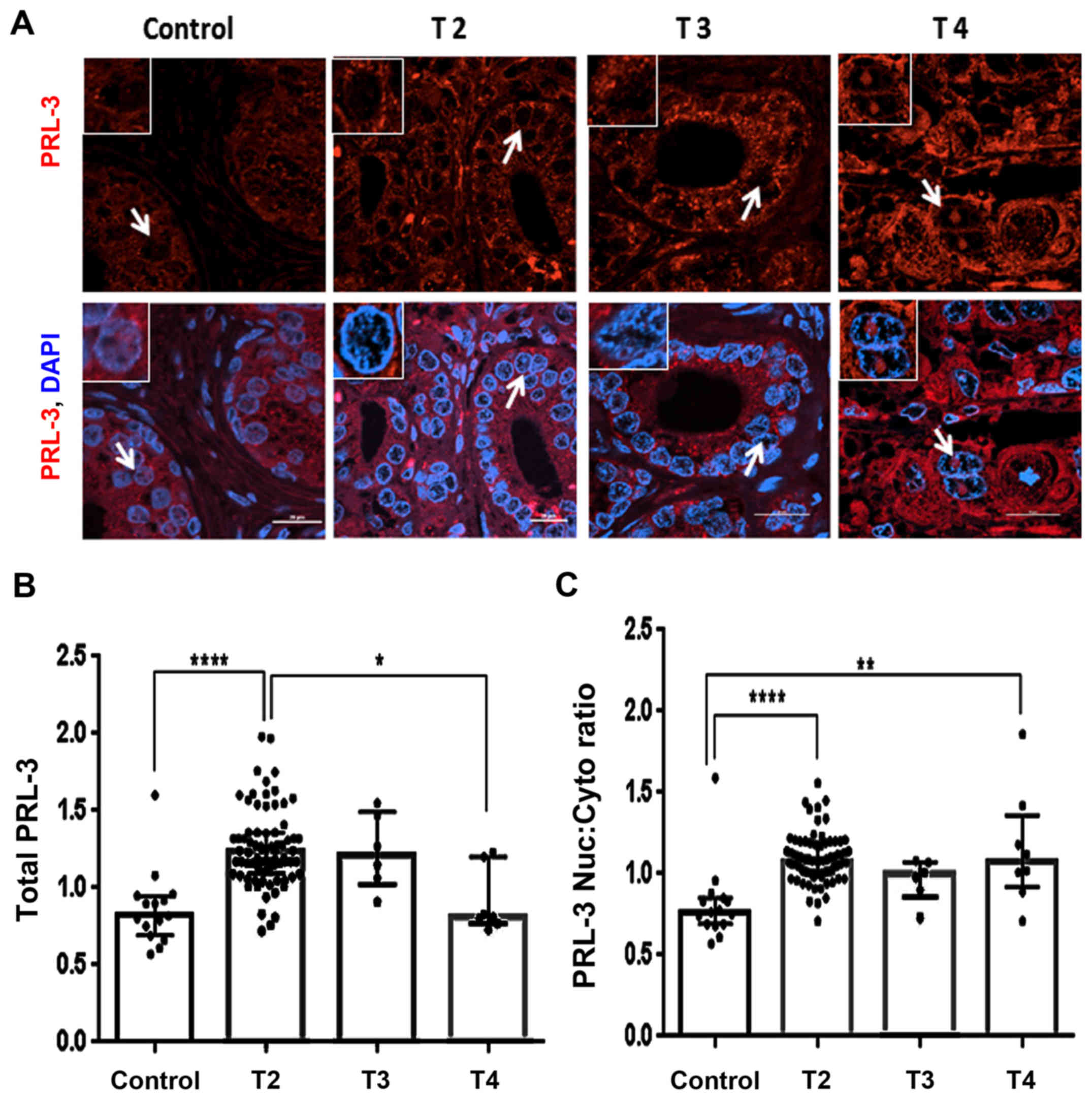
|
1
|
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Garshell
J, Miller D, Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Yu M, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z,
Mariotto A, Lewis DR, Chen HS, Feuer EJ and Cronin KA: SEER Cancer
Statistics Review 1975–2011. National Cancer Institute; Bethesda,
MD: https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2011/.
Accessed December 17, 2014.
|
|
2
|
Hayes JH and Barry MJ: Screening for
prostate cancer with the prostate-specific antigen test: A review
of current evidence. JAMA. 311:1143–1149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bussemakers MJ, van Bokhoven A, Verhaegh
GW, Smit FP, Karthaus HF, Schalken JA, Debruyne FM, Ru N and Isaacs
WB: DD3: A new prostate-specific gene, highly overexpressed in
prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 59:5975–5979. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tomlins SA, Laxman B, Varambally S, Cao X,
Yu J, Helgeson BE, Cao Q, Prensner JR, Rubin MA, Shah RB, et al:
Role of the TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusion in prostate cancer. Neoplasia.
10:177–188. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Font-Tello A, Juanpere N, de Muga S,
Lorenzo M, Lorente JA, Fumado L, Serrano L, Serrano S, Lloreta J
and Hernández S: Association of ERG and TMPRSS2-ERG with grade,
stage, and prognosis of prostate cancer is dependent on their
expression levels. Prostate. 75:1216–1226. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Penney KL, Pettersson A, Shui IM, Graff
RE, Kraft P, Lis RT, Sesso HD, Loda M and Mucci LA: Association of
prostate cancer risk variants with TMPRSS2:ERG status: Evidence for
distinct molecular subtypes. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
25:745–749. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Al-Aidaroos AQ and Zeng Q: PRL-3
phosphatase and cancer metastasis. J Cell Biochem. 111:1087–1098.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu Y, Zhou J, Chen J, Gao W, Le Y, Ding Y
and Li J: PRL-3 promotes epithelial mesenchymal transition by
regulating cadherin directly. Cancer Biol Ther. 8:1352–1359. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Basak S, Jacobs SB, Krieg AJ, Pathak N,
Zeng Q, Kaldis P, Giaccia AJ and Attardi LD: The
metastasis-associated gene Prl-3 is a p53 target involved in
cell-cycle regulation. Mol Cell. 30:303–314. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Min SH, Kim DM, Heo YS, Kim HM, Kim IC and
Yoo OJ: Downregulation of p53 by phosphatase of regenerating liver
3 is mediated by MDM2 and IRH2. Life Sci. 86:66–72. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang H, Quah SY, Dong JM, Manser E, Tang
JP and Zeng Q: PRL-3 down-regulates PTEN expression and signals
through PI3K to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer
Res. 67:2922–2926. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
den Hollander P, Rawls K, Tsimelzon A,
Shepherd J, Mazumdar A, Hill J, Fuqua SA, Chang JC, Osborne CK,
Hilsenbeck SG, et al: Phosphatase PTP4A3 promotes triple-negative
breast cancer growth and predicts poor patient survival. Cancer
Res. 76:1942–1953. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu H, Zeng Y, Liu L, Gao Q, Jin S, Lan Q,
Lai W, Luo X, Wu H, Huang Y, et al: PRL-3 improves colorectal
cancer cell proliferation and invasion through IL-8 mediated
glycolysis metabolism. Int J Oncol. 51:1271–1279. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiang Y, Liu XQ, Rajput A, Geng L, Ongchin
M, Zeng Q, Taylor GS and Wang J: Phosphatase PRL-3 is a direct
regulatory target of TGFbeta in colon cancer metastasis. Cancer
Res. 71:234–244. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Iwasa Y, Mizokami A, Miwa S, Koshida K and
Namiki M: Establishment and characterization of
androgen-independent human prostate cancer cell lines, LN-REC4 and
LNCaP-SF, from LNCaP. Int J Urol. 14:233–239. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
van Bokhoven A, Varella-Garcia M, Korch C,
Johannes WU, Smith EE, Miller HL, Nordeen SK, Miller GJ and Lucia
MS: Molecular characterization of human prostate carcinoma cell
lines. Prostate. 57:205–225. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Noursadeghi M, Tsang J, Haustein T, Miller
RF, Chain BM and Katz DR: Quantitative imaging assay for NF-kappaB
nuclear translocation in primary human macrophages. J Immunol
Methods. 329:194–200. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Rubin MA, Mucci NR, Figurski J, Fecko A,
Pienta KJ and Day ML: E-cadherin expression in prostate cancer: A
broad survey using high-density tissue microarray technology. Hum
Pathol. 32:690–697. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
McMenamin ME, Soung P, Perera S, Kaplan I,
Loda M and Sellers WR: Loss of PTEN expression in paraffin-embedded
primary prostate cancer correlates with high Gleason score and
advanced stage. Cancer Res. 59:4291–4296. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K, Deshpande N,
Varambally R, Ghosh D, Barrette T, Pandey A and Chinnaiyan AM:
ONCOMINE: A cancer microarray database and integrated data-mining
platform. Neoplasia. 6:1–6. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu P, Ramachandran S, Ali Seyed M,
Scharer CD, Laycock N, Dalton WB, Williams H, Karanam S, Datta MW,
Jaye DL, et al: Sex-determining region Y box 4 is a transforming
oncogene in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 66:4011–4019.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wallace TA, Prueitt RL, Yi M, Howe TM,
Gillespie JW, Yfantis HG, Stephens RM, Caporaso NE, Loffredo CA and
Ambs S: Tumor immunobiological differences in prostate cancer
between African-American and European-American men. Cancer Res.
68:927–936. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Taylor BS, Schultz N, Hieronymus H,
Gopalan A, Xiao Y, Carver BS, Arora VK, Kaushik P, Cerami E, Reva
B, et al: Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer.
Cancer Cell. 18:11–22. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Grasso CS, Wu YM, Robinson DR, Cao X,
Dhanasekaran SM, Khan AP, Quist MJ, Jing X, Lonigro RJ, Brenner JC,
et al: The mutational landscape of lethal castration-resistant
prostate cancer. Nature. 487:239–243. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chong PS, Zhou J, Cheong LL, Liu SC, Qian
J, Guo T, Sze SK, Zeng Q and Chng WJ: LEO1 is regulated by PRL-3
and mediates its oncogenic properties in acute myelogenous
leukemia. Cancer Res. 74:3043–3053. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu Y, Zheng P, Liu Y, Ji T, Liu X, Yao S,
Cheng X, Li Y, Chen L, Xiao Z, et al: An epigenetic role for PRL-3
as a regulator of H3K9 methylation in colorectal cancer. Gut.
62:571–581. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
van Oort IM, Witjes JA, Kok DE, Kiemeney
LA and Hulsbergen-Van De Kaa CA: The prognostic role of the
pathological T2 subclassification for prostate cancer in the 2002
Tumour-Nodes-Metastasis staging system. BJU Int. 102:438–441. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Caso JR, Tsivian M, Mouraviev V, Polascik
TJ and Moul JW: Pathological T2 sub-divisions as a prognostic
factor in the biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer. BJU Int.
106:1623–1627. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang L, Peng L, Dong B, Kong L, Meng L,
Yan L, Xie Y and Shou C: Overexpression of phosphatase of
regenerating liver-3 in breast cancer: Association with a poor
clinical outcome. Ann Oncol. 17:1517–1522. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ooki A, Yamashita K, Kikuchi S, Sakuramoto
S, Katada N, Waraya M, Kawamata H, Nishimiya H, Nakamura K and
Watanabe M: Therapeutic potential of PRL-3 targeting and clinical
significance of PRL-3 genomic amplification in gastric cancer. BMC
Cancer. 11:1222011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xing X, Lian S, Hu Y, Li Z, Zhang L, Wen
X, Du H, Jia Y, Zheng Z, Meng L, et al: Phosphatase of regenerating
liver-3 (PRL-3) is associated with metastasis and poor prognosis in
gastric carcinoma. J Transl Med. 11:3092013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Polato F, Codegoni A, Fruscio R, Perego P,
Mangioni C, Saha S, Bardelli A and Broggini M: PRL-3 phosphatase is
implicated in ovarian cancer growth. Clin Cancer Res. 11:6835–6839.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liang F, Liang J, Wang WQ, Sun JP, Udho E
and Zhang ZY: PRL3 promotes cell invasion and proliferation by
down-regulation of Csk leading to Src activation. J Biol Chem.
282:5413–5419. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ming J, Liu N, Gu Y, Qiu X and Wang EH:
PRL-3 facilitates angiogenesis and metastasis by increasing ERK
phosphorylation and up-regulating the levels and activities of
Rho-A/C in lung cancer. Pathology. 41:118–126. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Vandsemb EN, Bertilsson H, Abdollahi P,
Størkersen Ø, Våtsveen TK, Rye MB, Rø TB, Børset M and Slørdahl TS:
Phosphatase of regenerating liver 3 (PRL-3) is overexpressed in
human prostate cancer tissue and promotes growth and migration. J
Transl Med. 14:712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Burk U, Selter H, Zwergel T, Wullich B,
Montenarh M and Unteregger G: Different subnuclear localization of
wild-type and mutant p53 in human prostate-cancer cells. Int J
Oncol. 7:1355–1360. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vlatković N, Boyd MT and Rubbi CP:
Nucleolar control of p53: A cellular Achilles' heel and a target
for cancer therapy. Cell Mol Life Sci. 71:771–791. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Fagerli UM, Holt RU, Holien T, Vaatsveen
TK, Zhan F, Egeberg KW, Barlogie B, Waage A, Aarset H, Dai HY, et
al: Overexpression and involvement in migration by the
metastasis-associated phosphatase PRL-3 in human myeloma cells.
Blood. 111:806–815. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Hein N, Hannan KM, George AJ, Sanij E and
Hannan RD: The nucleolus: An emerging target for cancer therapy.
Trends Mol Med. 19:643–654. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Romero Otero J, Garcia Gomez B, Campos
Juanatey F and Touijer KA: Prostate cancer biomarkers: An update.
Urol Oncol. 32:252–260. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Donovan MJ and Cordon-Cardo C: Predicting
high-risk disease using tissue biomarkers. Curr Opin Urol.
23:245–251. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Stålhammar G, Fuentes Martinez N, Lippert
M, Tobin NP, Mølholm I, Kis L, Rosin G, Rantalainen M, Pedersen L,
Bergh J, et al: Digital image analysis outperforms manual biomarker
assessment in breast cancer. Mod Pathol. 29:318–329. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Khurana N, Talwar S, Chandra PK, Sharma P,
Abdel-Mageed AB, Mondal D and Sikka SC: Sulforaphane increases the
efficacy of anti-androgens by rapidly decreasing androgen receptor
levels in prostate cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 49:1609–1619. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Khurana N, Kim H, Chandra PK, Talwar S,
Sharma P, Abdel-Mageed AB, Sikka SC and Mondal D: Multimodal
actions of the phytochemical sulforaphane suppress both AR and
AR-V7 in 22Rv1 cells: Advocating a potent pharmaceutical
combination against castration-resistant prostate cancer. Oncol
Rep. 38:2774–2786. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|