Introduction
Breast cancer (BC) is the most common malignancy
affecting women worldwide and the leading cause of cancer-related
mortality in women. According to GLOBOCAN 2012, 1.7 million women
were diagnosed with BC and 521,000 succumbed to the disease in 2012
(1). Despite well-known mechanisms
and pathways contributing to disease progression, BC remains a
clinical challenge. Difficulties in determining an effective
treatment regimen arise from the fact that BC is a heterogeneous
disease. Breast tumours exhibit diverse histological patterns and
biological features resulting in different clinical behaviours. In
2011, The St. Gallen International Breast Cancer Conference
classified BC into four intrinsic subtypes i.e., luminal A, luminal
B, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive and
triple-negative (TN) (2). The
classification was established according to the immunohistochemical
(IHC) expression levels of oestrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone
receptor (PR), HER2 and Ki-67 antigen. From a clinical perspective,
each subtype has different clinical outcomes and different
responses to therapeutic options. Triple-negative breast cancer
(TNBC) comprises approximately 15% of all BC cases. The majority of
TNBCs fall into the basal-like subtype, which is the most
aggressive type of BC and is characterised by rapid tumour growth
and a poor outcome (3,4). The aggressive characteristics of TNBC
are presumably associated with an abundance of cancer stem cells
(CSCs). However the regulatory mechanisms of this interplay are not
yet fully understood (5).
Moreover, patients with TNBC cannot benefit from treatment with
trastuzumab and anti-oestrogens due to the lack of corresponding
receptors. As a result, the identification of novel molecules and
treatment targets for TNBC remains a great challenge in modern
oncology.
Nestin is an intermediate filament (IF) protein
participating in cytoskeletal organisation. It is expressed mostly
during embryogenesis in neuroepithelial stem cells (6). However, it is also detected in adults
in some types of immature and progenitor cells. Nestin expression
has also been observed in progenitor/stem cells isolated from
muscles (7,8), teeth (9), the pancreas (10), intestines (11), bone marrow (12), hair follicles (13) and other tissues. Nestin expression
is rather unique, since it occurs only in very specific cell types
and during specific processes, such as development and regeneration
(7,14). The expression of nestin is
downregulated and replaced by tissue-specific IFs during cell
differentiation. Of note, an enhanced nestin expression has been
noted in many human neoplasms, such as in central nervous system
tumours (15), melanoma (16), breast cancer (17), gastrointestinal stromal tumours
(18), prostate cancer (19) and pancreatic cancer (20). In tumours, nestin expression is not
limited only to cancer cells. It occurs primarily in newly-formed
tumour vessels (21) and cancer
stem cells (22,23). In the normal breast, nestin is
detected in the basal myoepithelial layer of the ducts and in
lobular acinar units (17).
Several studies have demonstrated that in BC, nestin expression is
almost exclusively limited to a basal-like molecular subtype of
TNBCs (17,24–26).
In our previous study, we demonstrated that nestin expression in
tumour vessels was associated with a more aggressive disease
course, a poorer prognosis and the TN phenotype of invasive ductal
carcinoma (IDC) (21).
The aim of the present study was to evaluate nestin
expression in tumour cells and to determine its prognostic value
among patients with BC. We also aimed to determine whether nestin
expression in tumour cells may influence the process of
angiogenesis. Accordingly, we compared nestin expression in cancer
cells to the area and number of vessels expressing vascular
antigens i.e., nestin, CD31, CD34 and SOX-18. Finally, we
investigated nestin expression in BC cell lines characterised by
various degrees of aggressiveness (MCF-7, SK-BR-3, MDA-MB-231 and
BO2 cells), which corresponds to different BC molecular
subtypes.
Materials and methods
Tissue samples and cell lines
The present study was conducted on 124 IDC tissue
specimens obtained from patients treated at the Lower Silesian
Oncology Centre in Wroclaw, Poland. All patients were treated by
mastectomy, quadrantectomy and/or axillary lymph node resection. In
total, 11 (8.9%) patients received neoadjuvant chemotherapy and 93
(75%) of patients received adjuvant chemotherapy. A total of 58
(46.8%) patients were treated with radiotherapy. The patients were
followed for 64 months (range, 1–80 months). The median follow-up
was 80 months. The clinical and pathological data were obtained
from the archives of the hospital. Tumour histological type and
malignancy grade (G) were determined according to the World Health
Organisation (WHO) criteria (27).
The patient and tumour characteristics are listed in Table I. The study was approved by the
Bioethics Committee of the Wroclaw Medical University and was
conducted according to GCP guidelines. Written informed consent was
obtained from all participants.
 | Table IClinicopathological characteristics
of investigated patients with IDC. |
Table I
Clinicopathological characteristics
of investigated patients with IDC.
| Parameters | n | % |
|---|
| Age | | |
| ≤50 | 36 | 29.0 |
| >50 | 88 | 71.0 |
| Menopausal
status | | |
| Pre- | 36 | 29.0 |
| Post- | 82 | 66.1 |
| No data | 6 | 4.8 |
| Tumour size | | |
| T1 | 63 | 50.8 |
| T2 | 43 | 34.7 |
| T3 | 11 | 8.9 |
| T4 | 4 | 3.2 |
| No data | 3 | 2.4 |
| Lymph nodes | | |
| Negative | 62 | 50.0 |
| Positive | 59 | 47.6 |
| No data | 3 | 2.4 |
| Grade | | |
| 1 | 11 | 8.9 |
| 2 | 63 | 50.8 |
| 3 | 50 | 40.3 |
| pTNM | | |
| I + II | 98 | 79.0 |
| III + IV | 23 | 18.5 |
| No data | 3 | 2.4 |
| ER | | |
| Negative | 34 | 27.4 |
| Positive | 90 | 72.6 |
| PR | | |
| Negative | 45 | 36.3 |
| Positive | 79 | 63.7 |
| HER2 | | |
| Negative | 69 | 55.6 |
| Positive | 55 | 44.4 |
| Ki-67 | | |
| 1 | 56 | 45.16 |
| 2 | 27 | 21.77 |
| 3 | 17 | 13.71 |
| 4 | 18 | 14.52 |
| No data | 6 | 4.84 |
|
Triple-negative | | |
| Yes | 19 | 15.3 |
| No | 105 | 84.7 |
| Overall
survival | | |
| Deaths | 34 | 27.4 |
| Alive | 88 | 71 |
| No data | 2 | 1.6 |
The human BC cell lines, MCF-7, MDA-MB-231 (both
from ATCC, Washington, DC, USA), SK-BR-3, (from the Cell Line
Collection of the Ludwik Hirszfeld Institute of Immunology and
Experimental Therapy of the Polish Academy of Sciences, Wroclaw,
Poland) and BO2 (derivative of the MDA-MB-231 cell line isolated
from bone metastasis; courtesy of Dr Philippe Clezardin, INSERM
U664, Lyon, France), were selected to determine the expression
levels of nestin. The BC cell lines were cultured in α-MEM
supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (FCS; Invitrogen, Carlsbad,
CA, USA), 2 mM L-glutamine and 1% penicillin-streptomycin solution
(Gibco, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The normal mammary epithelial cell
line, hTERT-HME1 (from ATCC), was cultured in MEGM Bullet kit
medium (Lonza, Basel, Switzerland).
IHC
The tissue samples were fixed in 4% buffered
formalin, dehydrated and embedded in paraffin. The IHC reactions
were examined on the 4-µm-thick paraffin sections in
Autostainer Link48 (Dako, Glostrup, Denmark). The sections were
boiled in EnVision FLEX Target Retrieval Solution (pH 9.0, 97°C, 20
min) using Pre-Treatment Link Platform (both from Dako). To
inactivate endogenous peroxidase, the sections were incubated for 5
min with EnVision FLEX Peroxidase-Blocking Reagent (Dako). As
primary antibodies, we used a panel of mouse-anti human monoclonal
antibodies against the following: nestin (1:100 dilution, OBT1610,
Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA), Ki-67 (ready-to-use, IR610, Dako),
CD31 (ready-to-use, IR610, Dako), CD34 (ready-to-use, IR632, Dako),
SOX-18 (1:25 dilution, sc-166025, Santa Cruz, CA, USA), ER clone
1D5 (ready-to-use, IR654; Dako) and PR clone 636 (ready-to-use,
IR068; Dako). The samples were incubated with the primary
antibodies for 20 min at room temperature and then incubated with
EnVision FLEX/HRP for 20 min (Dako). The sections were then
incubated for 10 min with 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB, Dako) as the
peroxidase substrate. All slides were counterstained with the
EnVision FLEX Hematoxylin (Dako) and closed with coverslips in Dako
Mounting Medium (Dako). The expression status of HER2 was
determined using the HercepTest and the HER2 FISH pharmDx kit (both
from Dako) following the procedure recommended by the
manufacturer.
Examination of IHC reactions
The IHC reactions were evaluated using a BX-41 light
microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). The reactions were evaluated
simultaneously by two observers in order to achieve a consensus
score. Nestin expression in tumour cells was evaluated using the
semi-quantitative immunoreactive score (IRS) of Remmele and Stegner
(28). The Chalkley count,
reflecting an area and number of vessels (29), was assessed on anti-nestin,
anti-CD31, anti-CD34 and anti-SOX18-stained slides. Firstly, the
slides were briefly examined under low magnification (×100) to
identify three areas with the highest vascular density (hot spots).
A 25-point Chalkley eyepiece graticule (Pyser Sgi., Edenbridge, UK)
was applied to each hot spot at a higher magnification (×200), and
oriented to permit the maximum number of points to hit on or within
the immunohistochemically stained microvessels (30). The final score for each slide was
presented as a mean value from the three hot-spots. The status of
ER and PR receptors was scored from 0 to 3 points, depending on the
percentage of positive cells (0 points, no reaction; 1 point,
1–10%; 2 points, 11–50%; 3 points, 51–100% stained cells) (31). HER2 expression was determined using
a scale considering the percentage of positive tumour cells and the
intensity of the membrane reaction (32). The nuclear expression of Ki-67
antigen was evaluated using a semi-quantitative 5-grade scale as
follows: 0 points (0% of cells stained), 1 point (1–10% of cells
stained), 2 points (11–25% of cells stained), 3 points (26–50% of
cells stained), or 4 points (51–100% of cells stained).
Immunocytochemistry (ICC) and
immunofluorescence (IF)
The investigated tumour cell lines were grown on
glass coverslips for 24 h at 37°C. The cells were then washed with
phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and then fixed in 4%
paraformaldehyde. After washing, the cells were permeabilised with
0.2% Triton-X. The ICC reactions in Dako Autostainer Link48 (Dako)
according to the procedure described above. The slides were
incubated with anti-nestin antibody for 20 min at room temperature,
and then incubated with EnVision FLEX (Dako) to visualize the
antigens. For IF reactions, the tumour cell lines were cultured and
fixed as stated above. All slides were incubated at 4°C overnight
with mouse monoclonal antibody against nestin (1:100, OBT1610,
Bio-Rad) solved in antibody diluent (Dako). Donkey anti-mouse
antibody conjugated with rhodamine (1:2,000, polyclonal;
715-025-151 Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories, Inc., West Grove,
PA, USA) was applied as a secondary antibody. The slides were
covered with ProLong® Gold Antifade Mountant mounting
medium (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, USA) with
4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) counterstaining. The reactions
were viewed using a BX51 fluorescence microscope (Olympus, with
DP72 camera and CellF software).
Total RNA isolation and real-time
PCR
Total RNA from was isolated from the hTERT-HME1,
MCF-7, SK-BR-3, MDA-MB-231 and BO2 cells using the RNeasy Mini kit
(Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer's
instructions. To eliminate genomic DNA, we applied on-column DNase
digestion. The quantity and the purity of the RNA were assessed by
measuring the absorbance at 260 and 280 nm using a NanoDrop-1000
spectrophotometer (NanoDrop Technologies, Wilmington, DE, USA).
First-strand cDNA was synthesised using High-Capacity cDNA Reverse
Transcription kits (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The
relative nestin gene (NES) expression level was determined
in relation to the expression of the normal mammary epithelial cell
line, hTERT-HME1, by quantitative (real-time) PCR with the 7500
Real-Time PCR System and the iTaq Universal Probes Supermix
(Bio-Rad), according to the manufacturer's instructions. For the
reactions, we applied the following human TaqMan probes: NES
Hs04187831_g1 for nestin and ACTB Hs99999903_m1 for β-actin
(both Applied Biosystems). β-actin was used as a reference gene for
determining relative NES expression in the analysed tumour
cell lines. The reactions were carried out in triplicate under the
following conditions: initial denaturation at 95°C for 10 min, 45
cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 15 sec, followed by annealing
and elongation at 60°C for 60 sec. The relative mRNA expression
level of the NES gene was calculated using the ΔΔCq method
(33).
Protein extraction and western blot
analysis
The cells from the cell culture were trypsinised,
washed in PBS and lysed with lysis buffer (50 mM Tris HCl, 150 mM
NaCl, 0.1% SDS, 1% Igepal CA-630, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate)
containing 1X protease inhibitor cocktails (Pierce, Rockford, IL,
USA) and 0.5 mM PMSF. Following 20 min of incubation on ice, the
contents were centrifuged at 12,000 × g at 4°C for 10 min. The
supernatants were collected and whole cell protein concentrations
were quantified using the BCA protein assay (Pierce). The protein
(30 µg) was processed for 6% SDS-PAGE, transferred onto
polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes (Immobilon; Millipore,
Bedford, MA, USA) and incubated with monoclonal mouse antibody
against nestin (1:1,000, OBT1610, Bio-Rad) overnight at 4°C. The
membranes were then incubated with a secondary anti-mouse antibody
conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (1:3,000, polyclonal;
715-035-150, Jackson Immunoresearch, Mill Valley, CA, USA) for 1 h
at room temperature, rinsed, and treated with the Immun-Star-HRP
Chemiluminescent Kit (Bio-Rad). β-tubulin, detected with
anti-β-tubulin antibody (rabbit anti-human, 1:1,000, poly-clonal;
ab6046, Abcam, Cambridge, UK), was used as an internal control to
normalize the amounts of nestin at the same membrane after
stripping. The protein bands were visualized and quantified with
densitometry using Image Lab 3.0 on a Molecular Imager ChemiDoc XRS
imaging system (Bio-Rad).
Flow cytometry (FC)
For flow cytometric immunophenotyping of
intercellular nestin, the cells were fixed and permeabilized with
BD Cytofix/Cytoperm™ (Becton-Dickinson, San Jose, CA, USA)
according to the manufacturer's instructions. Subsequently, the
cells were stained with mouse monoclonal antibody against human
nestin (1:100; OBT1610, Bio-Rad) for 30 min at room temperature and
then labelled with donkey anti-mouse antibody conjugated with
fluorescein (1:1,000, polyclonal; 715-096-151 Jackson
ImmunoResearch Laboratories). The cells were then analysed by flow
cytometry using BD FACSCanto™ II flow cytometer (Becton-Dickinson)
equipped with three lasers: blue (488 nm, air-cooled, 20 mW solid
state), red (633 nm, 17 mW HeNe) and violet (405 nm, 30 mW solid
state). Data were recorded for 20,000 events using BD FACSDiva™
software (Becton-Dickinson), analysed on the ungated population and
presented as histograms using WinMDI2.7 software (Scripps Research
Institute, La Jolla, CA, USA).
Statistical analysis
The data were analysed using Prism 5.0 (GraphPad, La
Jolla, CA, USA) software. Analysed results are presented as the
mean values ± standard deviation (SD). The associations between the
clinicopathological characteristics and the expression of nestin
were analysed by the non-parametric Mann-Whitney U test. The
differences between nestin expression levels in tumour cells were
analysed by one-way analysis of variance with a post hoc Tukey's
test. The correlations between the scores of the examined antigens
were tested using the Spearman rank correlation test. The
Kaplan-Meier method and the Mantel-Cox test were used to determine
the significance of patient overall survival (OS). In addition, for
the analysis of survival, the Cox's univariate and multivariate
proportional hazard model was used. Differences were considered
statistically significant with a value of P<0.05.
Results
Immunohistochemical expression of nestin
in primary BC tissues
A positive nestin expression was observed in 39
(31.5%) of investigated tumour cases. Nestin expression was
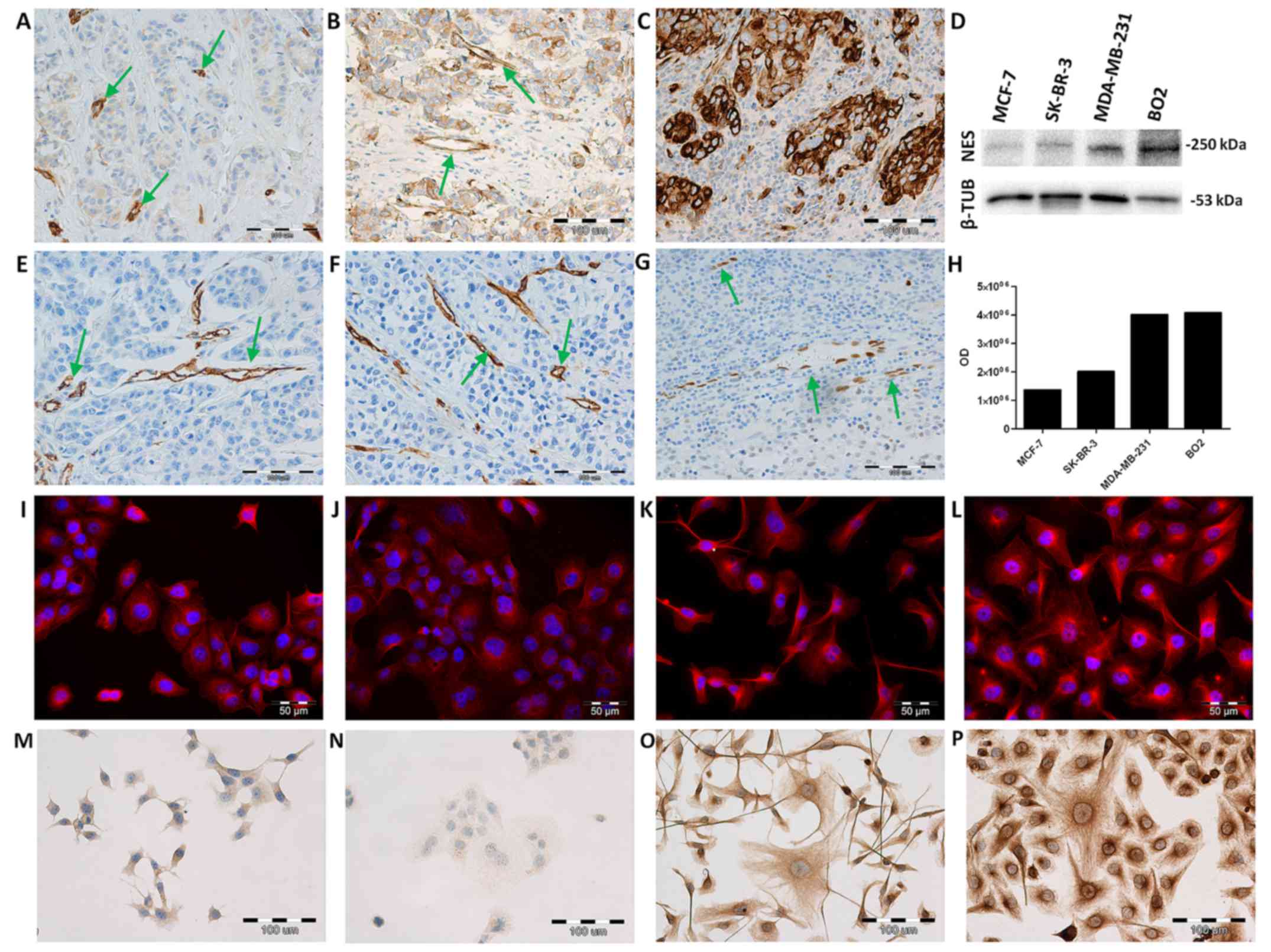
observed in the cytoplasm of tumour cells (Fig. 1A–C), tumour vessels (Fig. 1A and B) and in myoepithelial cells
of the breast ducts (data not shown). A significantly higher nestin
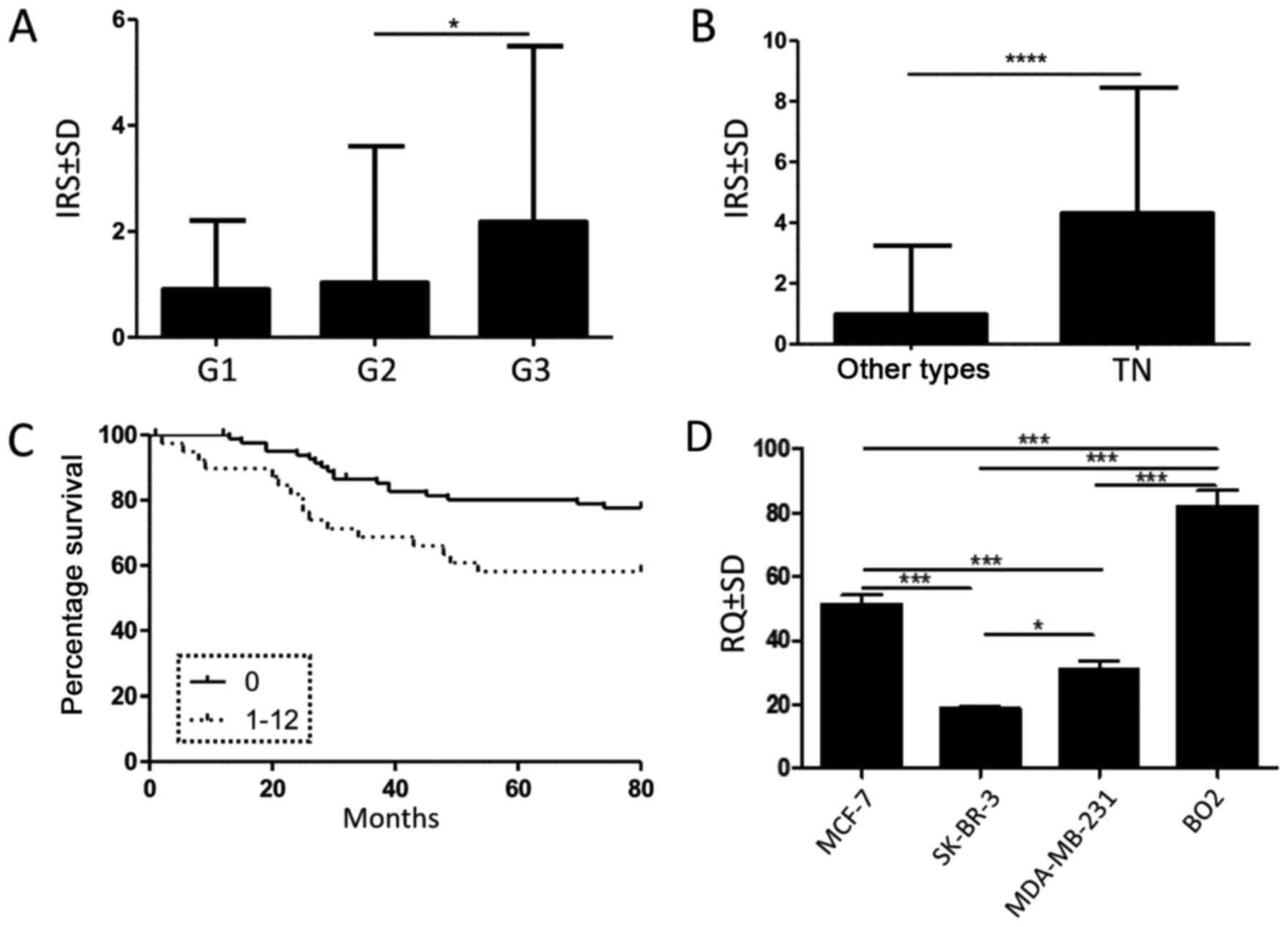
expression in tumour cells was noted in G3 compared to G2 cases
(Fig. 2A; P= 0.024; Mann-Whitney U
test). Moreover, our results revealed a significantly higher nestin
expression in TNBC (Fig. 2B;
P<0.0001; Mann-Whitney U test). Of note, nestin expression in
tumour cells negatively correlated (Spearman rank correlation test)
with ER (Fig. 3G; n=124, r=−0.39,
P<0.0001) and PR (Fig. 3H;
n=124, r=−0.23, P=0.012), but not with HER2 expression (Fig. 3I; n=124, r=−0.11, P=0.26). A
correlation was also noted between nestin expression in tumour
cells and Ki-67 expression in the cell nuclei of tumour cells
(Fig. 3F; n=112, r=0.25, P=0.0062;
Spearman rank test). Survival data analysis indicated that a
postive nestin expression (IRS ≥1) in tumour cells was associated
with a shorter patient overall survival (Fig. 2C; P=0.02; Mantel-Cox test).
However, multivariate analysis revealed that nestin was not an
independent prognostic factor (Table
III). We also found a correlation (Spearman rank correlation
test) between nestin expression in tumour cells and the area and
number of vessels immunolabelled with antibodies against CD31
(Fig. 3A; n=105, r=0.24, P=0.01),
CD34 (Fig. 3B; n=90, r=0.38,
P=0.0002), nestin (Fig. 3C; n=112,
r=0.19, P=0.04) and SOX-18 (Fig.
3D; n=101, r=0.27, P=0.005). A strong correlation was also
observed between the area and number of nestin+ vessels
and SOX-18+ vessels (Fig.
3E; n=101, r=0.34, P=0.0004; Spearman rank test).
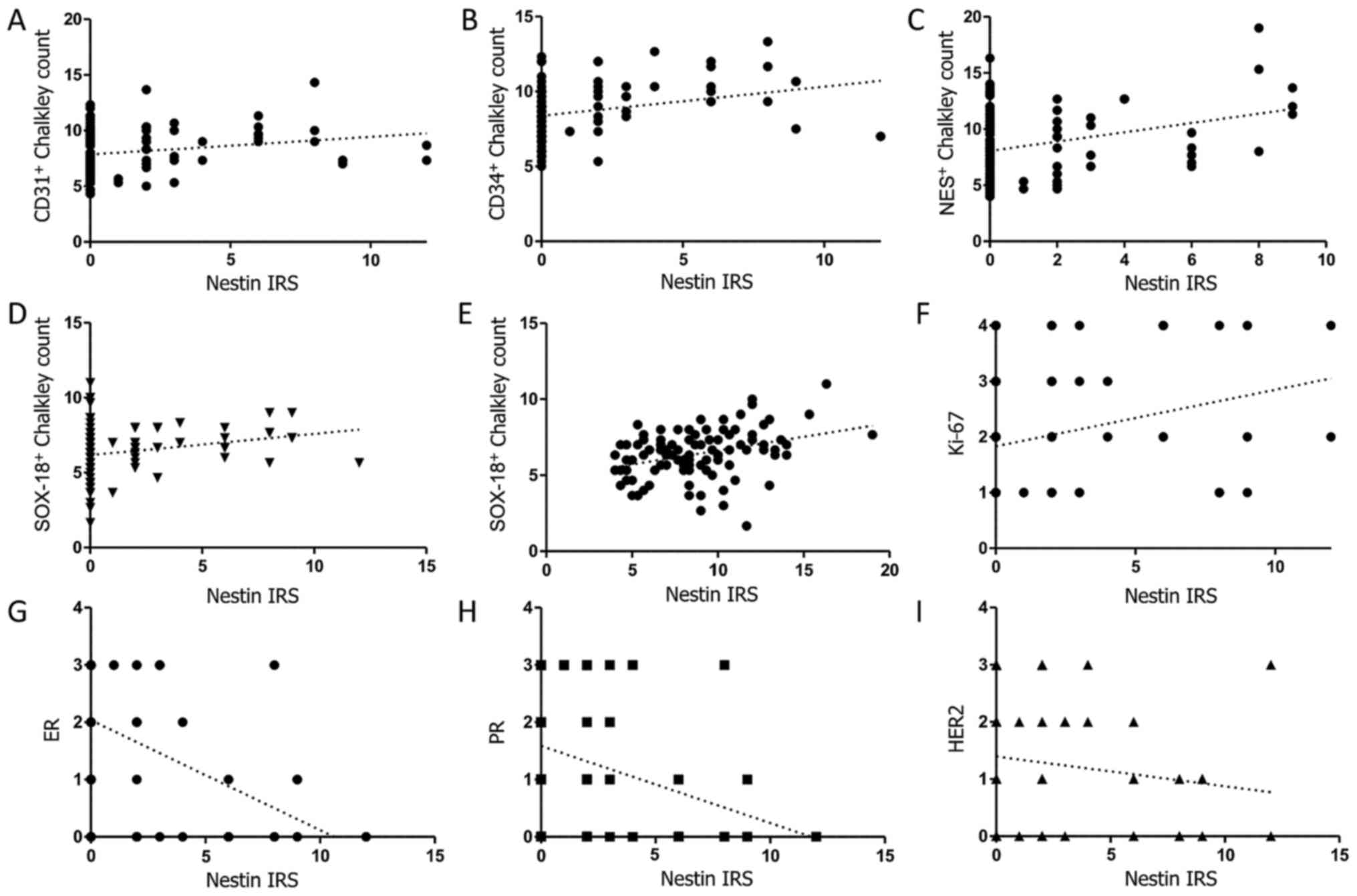 | Figure 3Correlations of nestin expression in
tumour cells with the area and number of vessels expressing CD31
[(A); n-105, r=0.24, P=0.01;], CD34 [(B); n=90, r=0.38, P=0.0002],
nestin [(C); n=112, r=0.19, P=0.04], SOX-18 [(D); n= 101, r=0.27,
P=0.005]; correlation of the area and number of nestin+
vessels and the area and number of SOX-18+ vessels [(E);
n=101, r=0.34, P=0.0004]; correlations of nestin expression in
tumour cells with the expression of Ki-67 antigen [(F); n=112,
r=0.25, P=0.0062] and oestrogen [(G); n=124, r=−0.39, P<0.0001],
progesterone [(H); n=124, r=−0.23, P=0.012] and HER2 [(I); n=124,
r=−0.11, P=0.26] receptors; (all Spearman rank correlation
test). |
 | Table IIIUni- and multivariate Cox analysis of
overall survival. |
Table III
Uni- and multivariate Cox analysis of
overall survival.
| Parameter | Univariate Cox
analysis
| Multivariate Cox
analysis
|
|---|
| P-value | HR | HR 95% lower | HR 95% upper | P-value | HR | HR 95% lower | HR 95% upper |
|---|
| Age | 0.16 | 1.98 | 0.77 | 5.1 | | | | |
| Menopausal
status | 0.29 | 0.65 | 0.29 | 1.44 | | | | |
| Grade |
<0.005 | 2.75 | 1.46 | 5.18 |
<0.005 | 2.69 | 1.37 | 5.26 |
| Stage |
<0.005 | 7.65 | 3.88 | 15.09 | 0.9 | 0.93 | 0.29 | 2.96 |
| pT |
<0.005 | 3.96 | 2.62 | 5.98 |
<0.005 | 3.57 | 2.045 | 6.24 |
| pN |
<0.005 | 2.77 | 1.95 | 3.94 |
<0.005 | 2.95 | 1.64 | 5.3 |
| ER | 0.3 | 1.01 | 0.99 | 1.03 | | | | |
| PR | 0.3 | 1.01 | 0.99 | 1.03 | | | | |
| HER2 | 0.25 | 1.01 | 0.99 | 1.03 | | | | |
| Nestin | 0.67 | 0.98 | 0.91 | 1.06 | | | | |
mRNA nestin level is the highest in the
metastatic BO2 cells
The NES mRNA expression level in BC cell
lines (MCF-7, SK-BR-3, MDA-MB-231, BO2) was determined by real-time
PCR. The relative NES expression was assessed in relation to the
expression of the normal mammary epithelial cell line, hTERT-HME1.
The highest NES expression was noted in the metastatic BO2
cell line when compared to the less aggressive MCF-7, SK-BR-3 cells
and MDA-MB-231 cells (Fig. 2D; all
P<0.001; ANOVA, Tukey's post hoc test). Of note, at the mRNA
level, NES expression was higher in the MCF-7 cells than in
the more aggressive SK-BR-3 and MDA-MB-231 cells (Fig. 2D; both P<0.001, ANOVA, Tukey's
post hoc test).
Nestin protein expression is related to
metastatic MDA-MB-231 and BO2 cells
The results of ICC and IF reactions revealed the
cytoplasmic expression of nestin in all investigated BC cell lines.
In both experiments, we observed more intense reactions in
metastatic MDA-MB-231 (Fig. 1G and
K) and BO2 (Fig. 1H and L)
cell lines than in the less aggressive MCF-7 (Fig. 1E and I) and SK-BR-3 cell lines
(Fig. 1F and J). The analysis of
nestin protein levels by western blot analysis in the BC cell lines
revealed an increased expression in the metastatic MDA-MB-231 and
BO2 cells (Fig. 1D). Weaker bands
were detected in the MCF-7 and SK-BR-3 cell lines (Fig. 1D). Flow cytometric analysis was
performed to determine the expression level of nestin in the
investigated BC cell lines. The mean fluorescence intensity (MFI)
for nestin was shown as MFI for samples incubated with primary and
secondary antibodies minus MFI for the isotype control (Table II). Measurements of the MFI
revealed a higher fluorescence intensity in the metastatic
MDA-MB-231 and BO2 cells (Table
II; MFI=20.43 and MFI=26.48) than in the less aggressive MCF-7
and SK-BR-3 cells (Table II;
MFI=17.2 and MFI=9.45).
 | Table IIMean values of fluorescence for
isotype control and nestin in MCF-7, SK-BR-3, MDA-MB-231 and BO2
cell lines. |
Table II
Mean values of fluorescence for
isotype control and nestin in MCF-7, SK-BR-3, MDA-MB-231 and BO2
cell lines.
| Cell line | Isotype
control | I+II antibody | Nestin |
|---|
| MCF-7 | 5.88 | 22.48 | 17.2 |
| SK-BR-3 | 8.82 | 18.27 | 9.45 |
| MDA-MB-231 | 8.33 | 28.75 | 20.43 |
| BO2 | 6.61 | 33.09 | 26.48 |
Discussion
Accumulating evidence indicates that nestin
expression in tumour cells and blood vessels is associated with
tumour progression. Nestin expression has been detected in tumour
cells of neuroectodermal, epithelial, mesenchymal and germ cell
tumours (34). Moreover, in some
tumours, nestin expression correlates with the histological grade
and is associated with an immature and invasive phenotype of
transformed cells (23). The
clinical implications of nestin have been well confirmed in BC,
where its expression is strongly associated with a poorly
differentiated basal-like BC subtype (17,25,26,35),
p53 overexpression and a poor prognosis (25). Recently, in a large
population-based study, Kruger et al confirmed that nestin
expression in tumour cells strongly correlated with the basal-like
molecular subtype of TNBC, with BRCA1-related BC and with a reduced
survival (26).
In this study, we evaluated nestin expression in
tumour cells and determined its prognostic value among patients
with IDC. Our results were consistent with those of previous
studies in which nestin expression in tumour cells was
preferentially related to the TN subtype of BC. Moreover, we
confirmed that nestin expression negatively correlated with the
expression of ER and PR, but not with HER2 expression, as
previously described by Gao et al (24). We determined that nestin expression
was related to poorly differentiated G3 tumours, a higher
proliferation index and a shorter overall survival, which is
consistent with the observations by Parry et al (36). In our study, we also aimed to
determine whether nestin expression in BC cells may be associated
with the formation of new tumour vessels. Therefore, we compared
nestin expression to the area and number of vessels expressing the
vascular antigens, nestin, CD31, CD34 and SOX-18. While CD31 and
CD34 are common endothelial markers, nestin and SOX-18 are proteins
involved in angiogenesis (21,37–39).
Our previous study indicated that in BC, nestin is a valuable
marker of newly-forming tumour vessels and reflects ongoing
angiogenesis (21). In the present
study, we demonstrated that nestin expression in tumour cells
correlated with the area and number of vessels expressing all
investigated antigens i.e., nestin, CD31, CD34 and SOX-18. A
positive correlation was noted with vessels expressing the
transcription factor, SOX-18, which is an important regulator of
vascular development (39). Of
note, we also found a positive correlation between the area and
number of nestin+ vessels and SOX-18+
vessels. Ikhapoh et al (40) demonstrated that SOX-18 contributed
to the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to
endothelial cells, whereas nestin is a well-known marker expressed
by MSCs (41). An interesting
interplay was previously noted between nestin and other
transcription factors from the SOX family. In lung adenocarcinoma,
SOX-2 promotes NES mRNA transcription (42), while in human melanoma cells SOX-9
and SOX-10 are required for the induction of nestin expression
(43). Recently, Feng et al
demonstrated that in TNBCs nestin expression was induced by SOX-10,
resulting in the regulation of stem-like features of TNBC cells
(4).
The association between nestin expression in tumour
cells and vascular density has been previously observed in
hepatocellular carcinoma (44),
ovarian carcinoma (45),
glioblastomas (46) and
ependymomas (47). To the best of
our knowledge, we are the first to demonstrate that nestin
expression in BC cells correlates with the area and number of
vessels expressing vascular antigens i.e., nestin, CD31, CD34 and
SOX-18. Previous studies on hepatocellular carcinoma, ovarian
carcinoma and ependymomas have indicated that nestin expression in
tumour cells is associated with higher vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF) levels and a higher CD34+ microvessel
density (44,45,47,48).
He et al (46) demonstrated
that in glioblastoma, the population of nestin+ and
CD133+ cells was concentrated around CD31+
vessels. Moreover, they showed that nestin expression in tumour
cells was strongly associated with nestin expression in endothelial
cells. Currently nestin is considered a reliable marker of CSCs
(23), which are defined as a
small subpopulation of undifferentiated cells in tumour tissues
that are able to self-renew and to differentiate into various types
of tumour cells (23). The
interactions between glioblastoma stem-like cells and the vascular
niche support the hypothesis that CSCs can transdifferentiate into
endothelial cells (49,50). Moreover, CSCs can contribute to
tumour angiogenesis by nonendothelial-lining vasculogenic mimicry
(51,52). In accordance with these hypotheses,
we demonstrated that nestin positivity in tumour cells correlated
with the area and number of nestin+ vessels. However, it
still needs to be determined whether a high vascular density may be
directly related to nestin expression in tumour cells or whether it
is only a hallmark of TNBC (21,53,54).
In this study, we also investigated nestin expression in human BC
cell lines (MCF-7, SK-BR-3, MDA-MB-231 and BO2 cells). Depending on
the phenotype and aggressiveness, BC cell lines can be classified
into three groups i.e., luminal epithelial (the MCF-7 cells),
weakly luminal epithelial-like (the SK-BR-3 cells) and
mesenchymal-like (MDA-MB-231 and BO2 cells) (55). MDA-MB-231 and BO2 cells exhibit
mesenchymal-like traits and they show no expression of ER, PR and
HER2 receptors (55,56). As expected, a considerable increase
in nestin protein expression was observed in the highly aggressive
MDA-MB-231 and BO2 cells. Less aggressive MCF-7 and SK-BR-3 cell
lines with a luminal phenotype expressed nestin protein at lower
levels. These results are consistent with the results obtained by
IHC where a higher level of nestin expression was related to the
TNBC phenotype and high histological grade. Surprisingly, a
differential NES gene expression pattern was observed in the
MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. The nestin mRNA level was higher in the
less aggressive MCF cells than in the more aggressive SK-BR-3 and
MDA-MB-231 cells. However, gene expression is controlled at many
different stages and in many different ways. The differences
between mRNA and protein level might be due to transcriptional and
posttranscriptional regulation, protein stability, protein
modification and proteolytic cleavage.
In conclusion, in this study, we confirmed that
nestin expression in BC cells is a poor prognostic factor. Based on
tissue samples and cell lines we also confirmed that nestin
expression was related to the TN phenotype of BC. Moreover, we
assume that in BC, nestin expression in tumour cells is associated
with enhanced angiogenesis. Although an association has been
established, the regulatory mechanisms behind this interplay
warrant further clarification.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Wroclaw Medical
University Grant Pbmn 192.
References
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gnant M, Harbeck N and Thomssen C: St
Gallen 2011: Summary of the Consensus Discussion. Breast Care
(Basel). 136–141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM,
Kahn HK, Sawka CA, Lickley LA, Rawlinson E, Sun P and Narod SA:
Triple-negative breast cancer: Clinical features and patterns of
recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4429–4434. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Feng W, Liu S, Zhu R, Li B, Zhu Z, Yang J
and Song C: SOX10 induced Nestin expression regulates cancer stem
cell properties of TNBC cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
485:522–528. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Idowu MO, Kmieciak M, Dumur C, Burton RS,
Grimes MM, Powers CN and Manjili MH: CD44(+)/CD24(−/low) cancer
stem/ progenitor cells are more abundant in triple-negative
invasive breast carcinoma phenotype and are associated with poor
outcome. Hum Pathol. 43:364–373. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lendahl U, Zimmerman LB and McKay RD: CNS
stem cells express a new class of intermediate filament protein.
Cell. 60:585–595. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sejersen T and Lendahl U: Transient
expression of the intermediate filament nestin during skeletal
muscle development. J Cell Sci. 106:1291–1300. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kachinsky AM, Dominov JA and Miller JB:
Intermediate filaments in cardiac myogenesis: Nestin in the
developing mouse heart. J Histochem Cytochem. 43:843–847. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
About I, Laurent-Maquin D, Lendahl U and
Mitsiadis TA: Nestin expression in embryonic and adult human teeth
under normal and pathological conditions. Am J Pathol. 157:287–295.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zulewski H, Abraham EJ, Gerlach MJ, Daniel
PB, Moritz W, Müller B, Vallejo M, Thomas MK and Habener JF:
Multipotential nestin-positive stem cells isolated from adult
pancreatic islets differentiate ex vivo into pancreatic endocrine,
exocrine, and hepatic phenotypes. Diabetes. 50:521–533. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vanderwinden JM, Gillard K, De Laet MH,
Messam CA and Schiffmann SN: Distribution of the intermediate
filament nestin in the muscularis propria of the human
gastrointestinal tract. Cell Tissue Res. 309:261–268. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vogel W, Grünebach F, Messam CA, Kanz L,
Brugger W and Bühring HJ: Heterogeneity among human bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and neural progenitor cells.
Haematologica. 88:126–133. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li L, Mignone J, Yang M, Matic M, Penman
S, Enikolopov G and Hoffman RM: Nestin expression in hair follicle
sheath progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:9958–9961.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Krum JM and Rosenstein JM: Transient
coexpression of nestin, GFAP, and vascular endothelial growth
factor in mature reactive astroglia following neural grafting or
brain wounds. Exp Neurol. 160:348–360. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Dahlstrand J, Collins VP and Lendahl U:
Expression of the class VI intermediate filament nestin in human
central nervous system tumors. Cancer Res. 52:5334–5341.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brychtova S, Fiuraskova M, Hlobilková A,
Brychta T and Hirnak J: Nestin expression in cutaneous melanomas
and melanocytic nevi. J Cutan Pathol. 34:370–375. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li H, Cherukuri P, Li N, Cowling V,
Spinella M, Cole M, Godwin AK, Wells W and DiRenzo J: Nestin is
expressed in the basal/myoepithelial layer of the mammary gland and
is a selective marker of basal epithelial breast tumors. Cancer
Res. 67:501–510. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tsujimura T, Makiishi-Shimobayashi C,
Lundkvist J, Lendahl U, Nakasho K, Sugihara A, Iwasaki T, Mano M,
Yamada N, Yamashita K, et al: Expression of the intermediate
filament nestin in gastrointestinal stromal tumors and interstitial
cells of Cajal. Am J Pathol. 158:817–823. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kleeberger W, Bova GS, Nielsen ME, Herawi
M, Chuang AY, Epstein JI and Berman DM: Roles for the stem cell
associated intermediate filament Nestin in prostate cancer
migration and metastasis. Cancer Res. 67:9199–9206. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Matsuda Y, Naito Z, Kawahara K, Nakazawa
N, Korc M and Ishiwata T: Nestin is a novel target for suppressing
pancreatic cancer cell migration, invasion and metastasis. Cancer
Biol Ther. 11:512–523. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nowak A, Grzegrzolka J, Paprocka M,
Piotrowska A, Rys J, Matkowski R and Dziegiel P: Nestin-positive
microvessel density is an independent prognostic factor in breast
cancer. Int J Oncol. 51:668–676. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao Z, Lu P, Zhang H, Xu H, Gao N, Li M
and Liu C: Nestin positively regulates the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
and the proliferation, survival and invasiveness of breast cancer
stem cells. Breast Cancer Res. 16:4082014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Neradil J and Veselska R: Nestin as a
marker of cancer stem cells. Cancer Sci. 106:803–811. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gao N, Xu H, Liu C, Xu H, Chen G, Wang X,
Li Y and Wang Y: Nestin: Predicting specific survival factors for
breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 35:1751–1755. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu C, Chen B, Zhu J, Zhang R, Yao F, Jin
F, Xu H and Lu P: Clinical implications for nestin protein
expression in breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 101:815–819. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Krüger K, Wik E, Knutsvik G, Nalwoga H,
Klingen TA, Arnes JB, Chen Y, Mannelqvist M, Dimitrakopoulou K,
Stefansson IM, et al: Expression of Nestin associates with BRCA1
mutations, a basal-like phenotype and aggressive breast cancer. Sci
Rep. 7:10892017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lakhani SR, Ellis IO, Schnitt SJ, Tan PH
and Vijver MJ: WHO Classification of Tumours of the Breast. IARC
Press; Lyon: 2012
|
|
28
|
Remmele W and Stegner HE: Recommendation
for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for
immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast
cancer tissue. Pathologe. 8:138–140. 1987.In German. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Offersen BV, Borre M and Overgaard J:
Quantification of angiogenesis as a prognostic marker in human
carcinomas: A critical evaluation of histopathological methods for
estimation of vascular density. Eur J Cancer. 39:881–890. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fox SB, Leek RD, Smith K, Hollyer J,
Greenall M and Harris AL: Tumor angiogenesis in node-negative
breast carcinomas–relationship with epidermal growth factor
receptor, estrogen receptor, and survival. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
29:109–116. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Goldhirsch A, Ingle JN, Gelber RD, Coates
AS, Thürlimann B and Senn HJ; Panel members: Thresholds for
therapies: Highlights of the St Gallen International Expert
Consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2009. Ann
Oncol. 20:1319–1329. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mueller-Holzner E, Fink V, Frede T and
Marth C: Immunohistochemical determination of HER2 expression in
breast cancer from core biopsy specimens: A reliable predictor of
HER2 status of the whole tumor. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 69:13–19.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Krupkova O Jr, Loja T, Zambo I and
Veselska R: Nestin expression in human tumors and tumor cell lines.
Neoplasma. 57:291–298. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Piras F, Ionta MT, Lai S, Perra MT, Atzori
F, Minerba L, Pusceddu V, Maxia C, Murtas D, Demurtas P, et al:
Nestin expression associates with poor prognosis and triple
negative phenotype in locally advanced (T4) breast cancer. Eur J
Histochem. 55:e392011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Parry S, Savage K, Marchiò C and
Reis-Filho JS: Nestin is expressed in basal-like and triple
negative breast cancers. J Clin Pathol. 61:1045–1050. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mokrý J, Cízková D, Filip S, Ehrmann J,
Osterreicher J, Kolár Z and English D: Nestin expression by newly
formed human blood vessels. Stem Cells Dev. 13:658–664. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Pula B, Olbromski M, Wojnar A,
Gomulkiewicz A, Witkiewicz W, Ugorski M, Dziegiel P and
Podhorska-Okolow M: Impact of SOX18 expression in cancer cells and
vessels on the outcome of invasive ductal breast carcinoma. Cell
Oncol (Dordr). 36:469–483. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Downes M and Koopman P: SOX18 and the
transcriptional regulation of blood vessel development. Trends
Cardiovasc Med. 11:318–324. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ikhapoh IA, Pelham CJ and Agrawal DK:
Sry-type HMG box 18 contributes to the differentiation of bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to endothelial cells.
Differentiation. 89:87–96. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xie L, Zeng X, Hu J and Chen Q:
Characterization of nestin, a selective marker for bone marrow
derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2015:7620982015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Narita K, Matsuda Y, Seike M, Naito Z,
Gemma A and Ishiwata T: Nestin regulates proliferation, migration,
invasion and stemness of lung adenocarcinoma. Int J Oncol.
44:1118–1130. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Flammiger A, Besch R, Cook AL, Maier T,
Sturm RA and Berking C: SOX9 and SOX10 but not BRN2 are required
for nestin expression in human melanoma cells. J Invest Dermatol.
129:945–953. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Yang XR, Xu Y, Yu B, Zhou J, Qiu SJ, Shi
GM, Zhang BH, Wu WZ, Shi YH, Wu B, et al: High expression levels of
putative hepatic stem/progenitor cell biomarkers related to tumour
angio-genesis and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut.
59:953–962. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Qin Q, Sun Y, Fei M, Zhang J, Jia Y, Gu M,
Xia R, Chen S and Deng A: Expression of putative stem marker nestin
and CD133 in advanced serous ovarian cancer. Neoplasma. 59:310–315.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
He H, Niu CS and Li MW: Correlation
between glioblastoma stem-like cells and tumor vascularization.
Oncol Rep. 27:45–50. 2012.
|
|
47
|
Nambirajan A, Sharma MC, Gupta RK, Suri V,
Singh M and Sarkar C: Study of stem cell marker nestin and its
correlation with vascular endothelial growth factor and
microvascular density in ependymomas. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol.
40:714–725. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Hlobilkova A, Ehrmann J, Knizetova P,
Krejci V, Kalita O and Kolar Z: Analysis of VEGF, Flt-1, Flk-1,
nestin and MMP-9 in relation to astrocytoma pathogenesis and
progression. Neoplasma. 56:284–290. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ricci-Vitiani L, Pallini R, Biffoni M,
Todaro M, Invernici G, Cenci T, Maira G, Parati EA, Stassi G,
Larocca LM, et al: Tumour vascularization via endothelial
differentiation of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Nature.
468:824–828. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang R, Chadalavada K, Wilshire J, Kowalik
U, Hovinga KE, Geber A, Fligelman B, Leversha M, Brennan C and
Tabar V: Glioblastoma stem-like cells give rise to tumour
endothelium. Nature. 468:829–833. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ping YF and Bian XW: Consice review:
Contribution of cancer stem cells to neovascularization. Stem
Cells. 29:888–894. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Liu TJ, Sun BC, Zhao XL, Zhao XM, Sun T,
Gu Q, Yao Z, Dong XY, Zhao N and Liu N: CD133+ cells
with cancer stem cell characteristics associates with vasculogenic
mimicry in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncogene. 32:544–553.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Mohammed RA, Ellis IO, Mahmmod AM, Hawkes
EC, Green AR, Rakha EA and Martin SG: Lymphatic and blood vessels
in basal and triple-negative breast cancers: Characteristics and
prognostic significance. Mod Pathol. 24:774–785. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Krüger K, Stefansson IM, Collett K, Arnes
JB, Aas T and Akslen LA: Microvessel proliferation by co-expression
of endothelial nestin and Ki-67 is associated with a basal-like
phenotype and aggressive features in breast cancer. Breast.
22:282–288. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Lacroix M and Leclercq G: Relevance of
breast cancer cell lines as models for breast tumours: An update.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 83:249–289. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Dzięgiel P, Owczarek T, Plazuk E,
Gomułkiewicz A, Majchrzak M, Podhorska-Okołów M, Driouch K,
Lidereau R and Ugorski M: Ceramide galactosyltransferase (UGT8) is
a molecular marker of breast cancer malignancy and lung metastases.
Br J Cancer. 103:524–531. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|