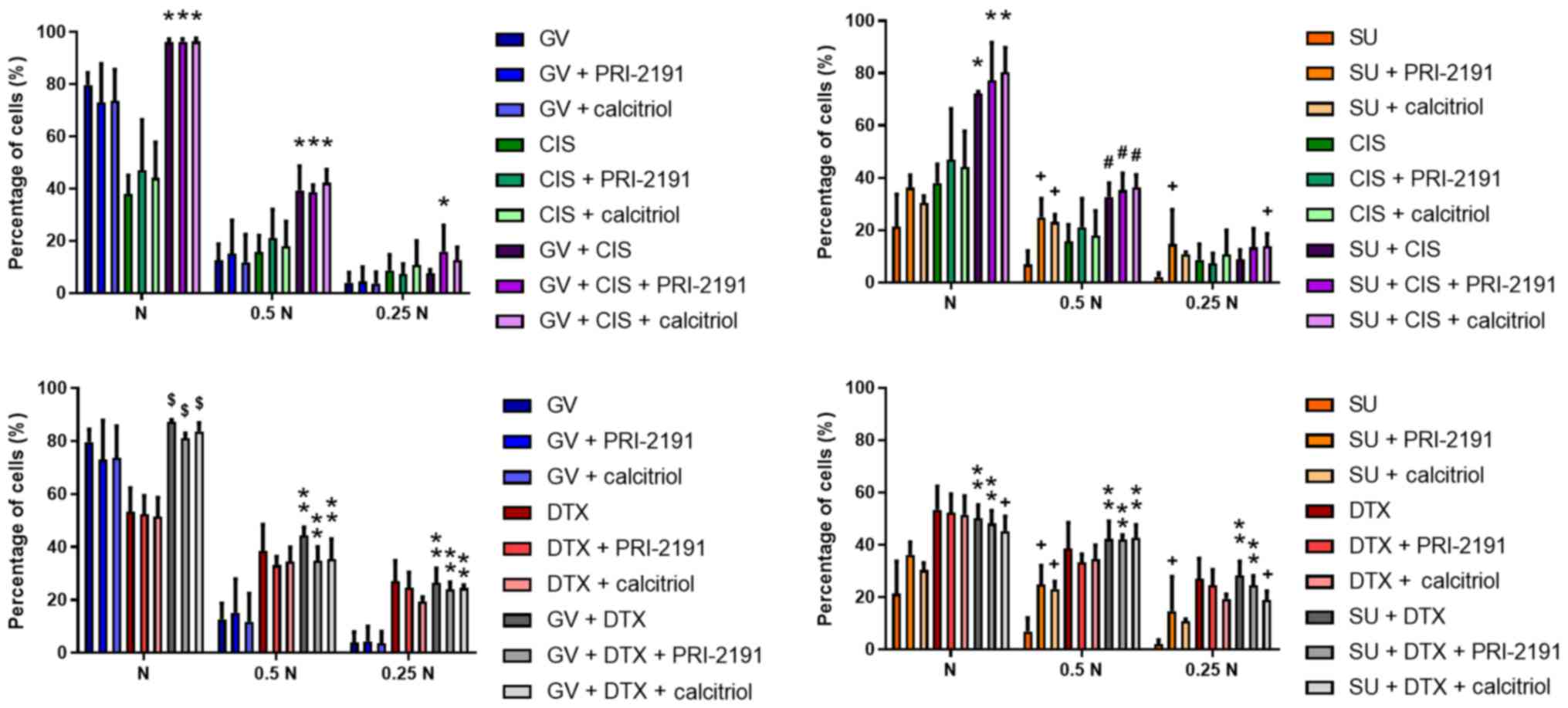
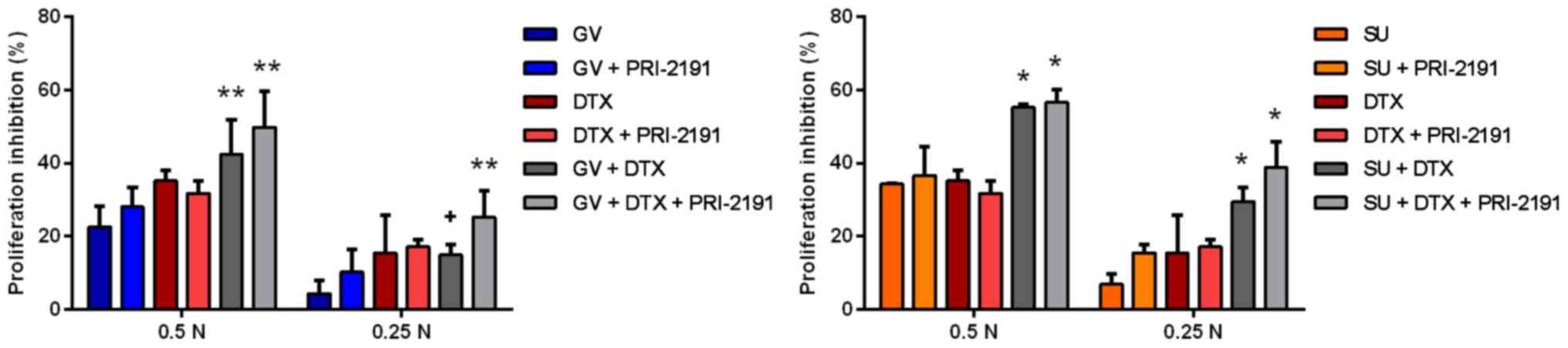
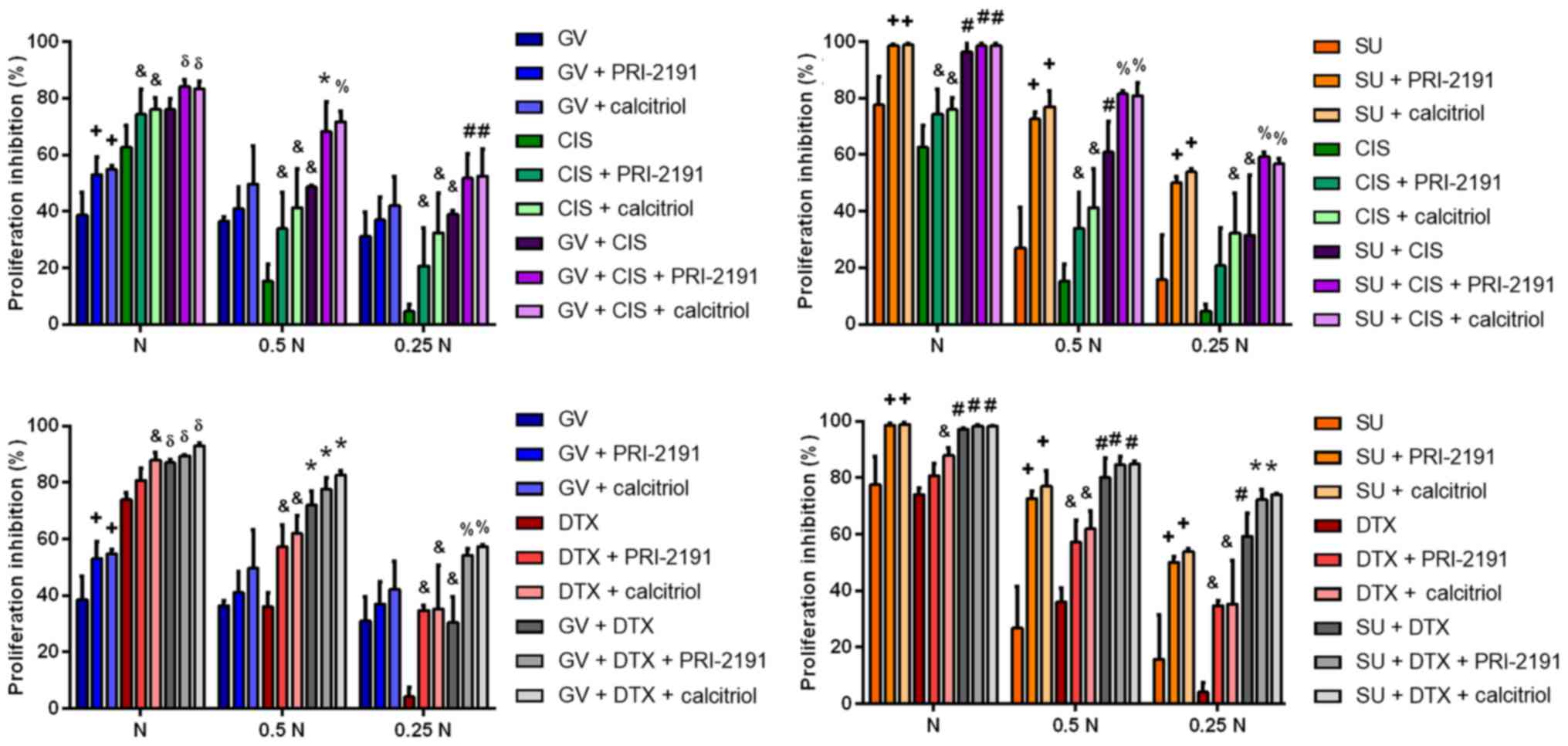
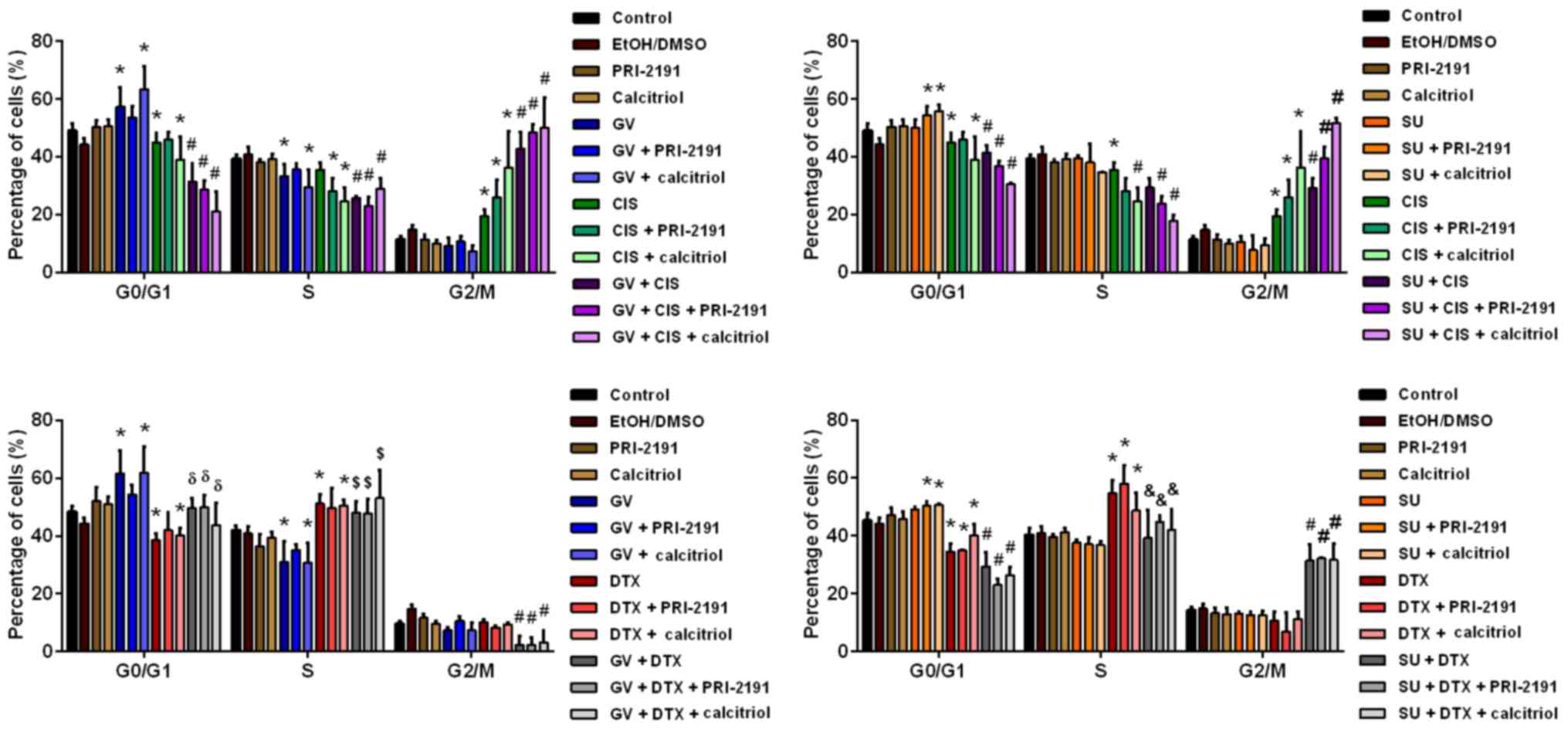
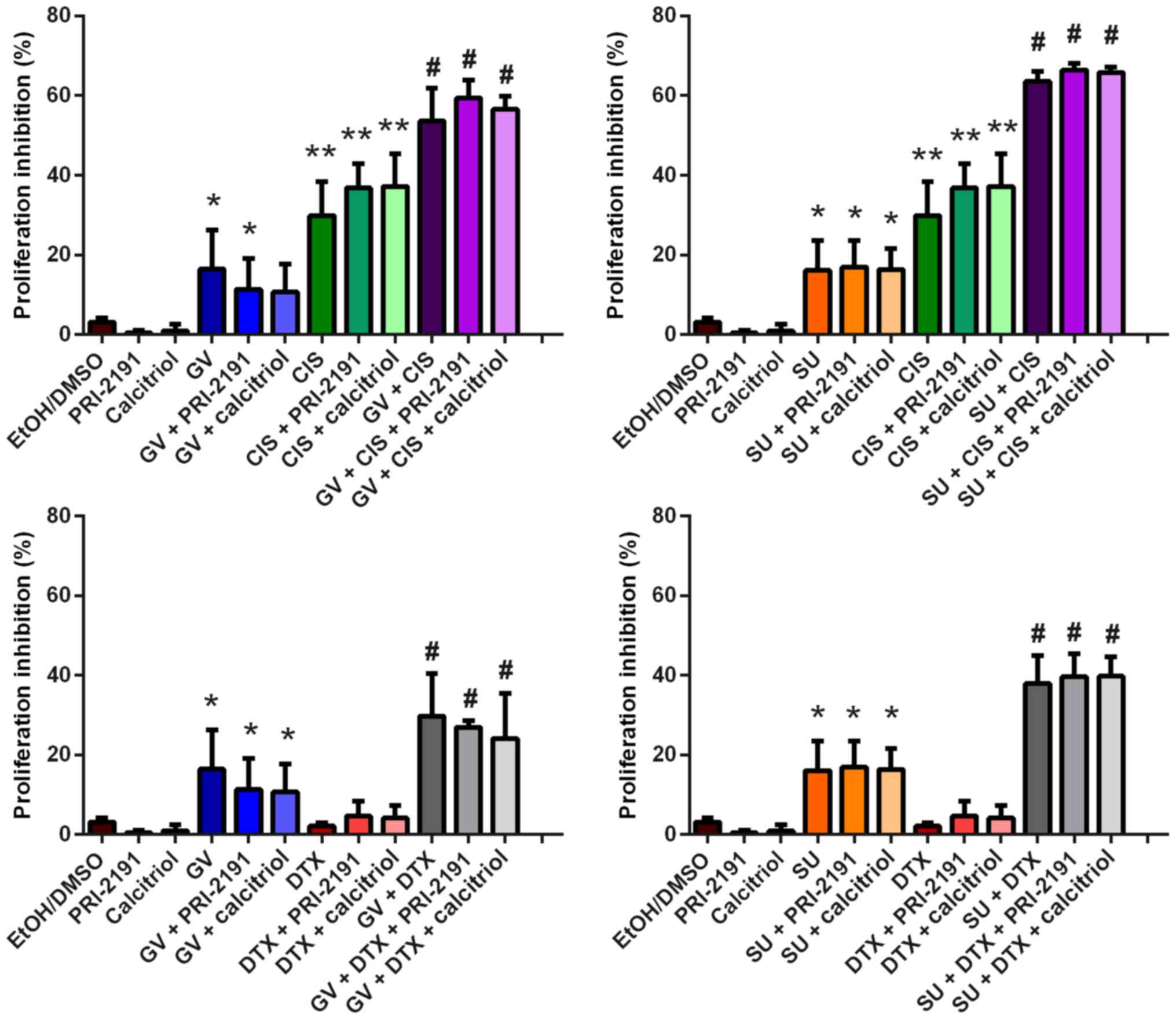
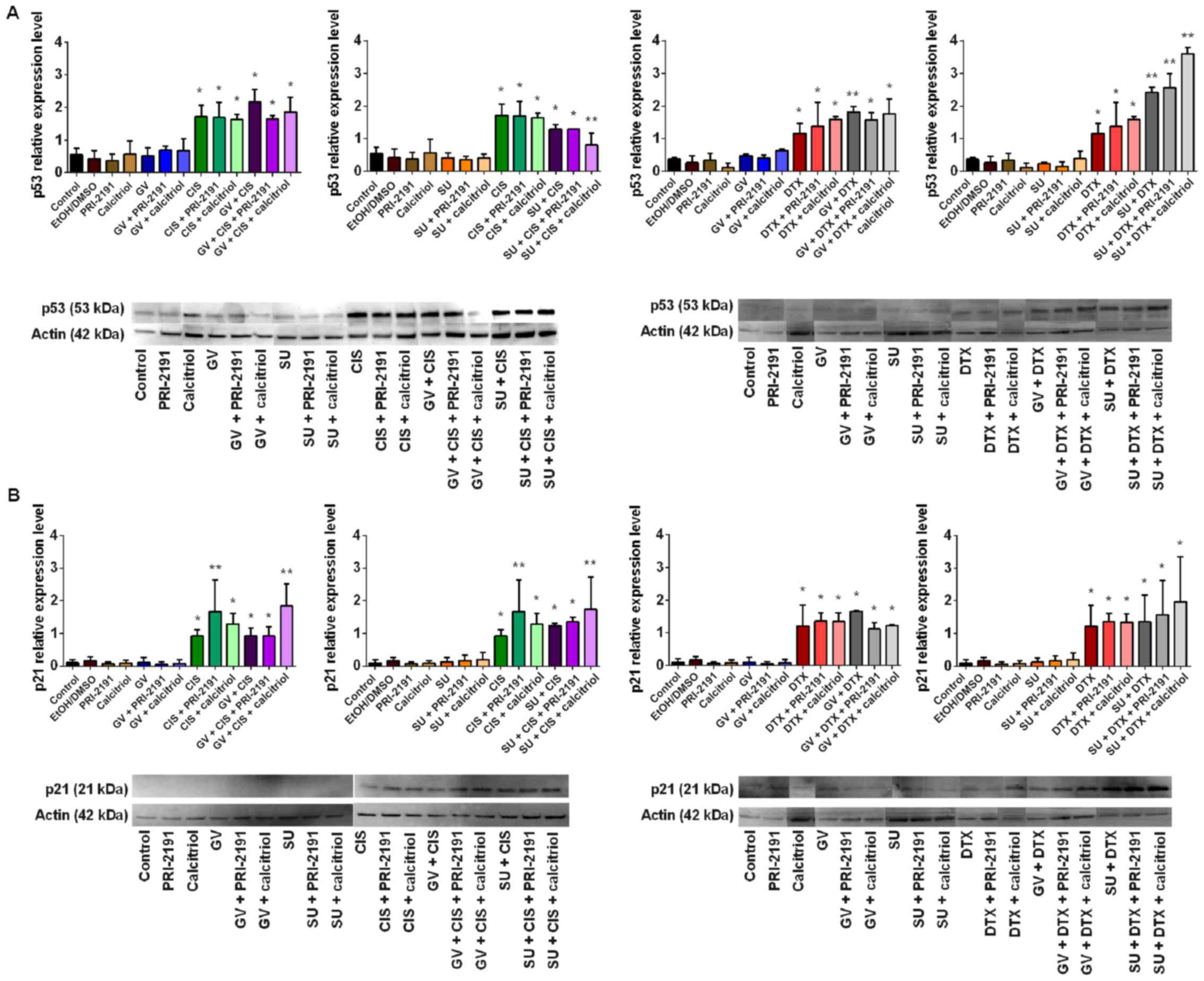
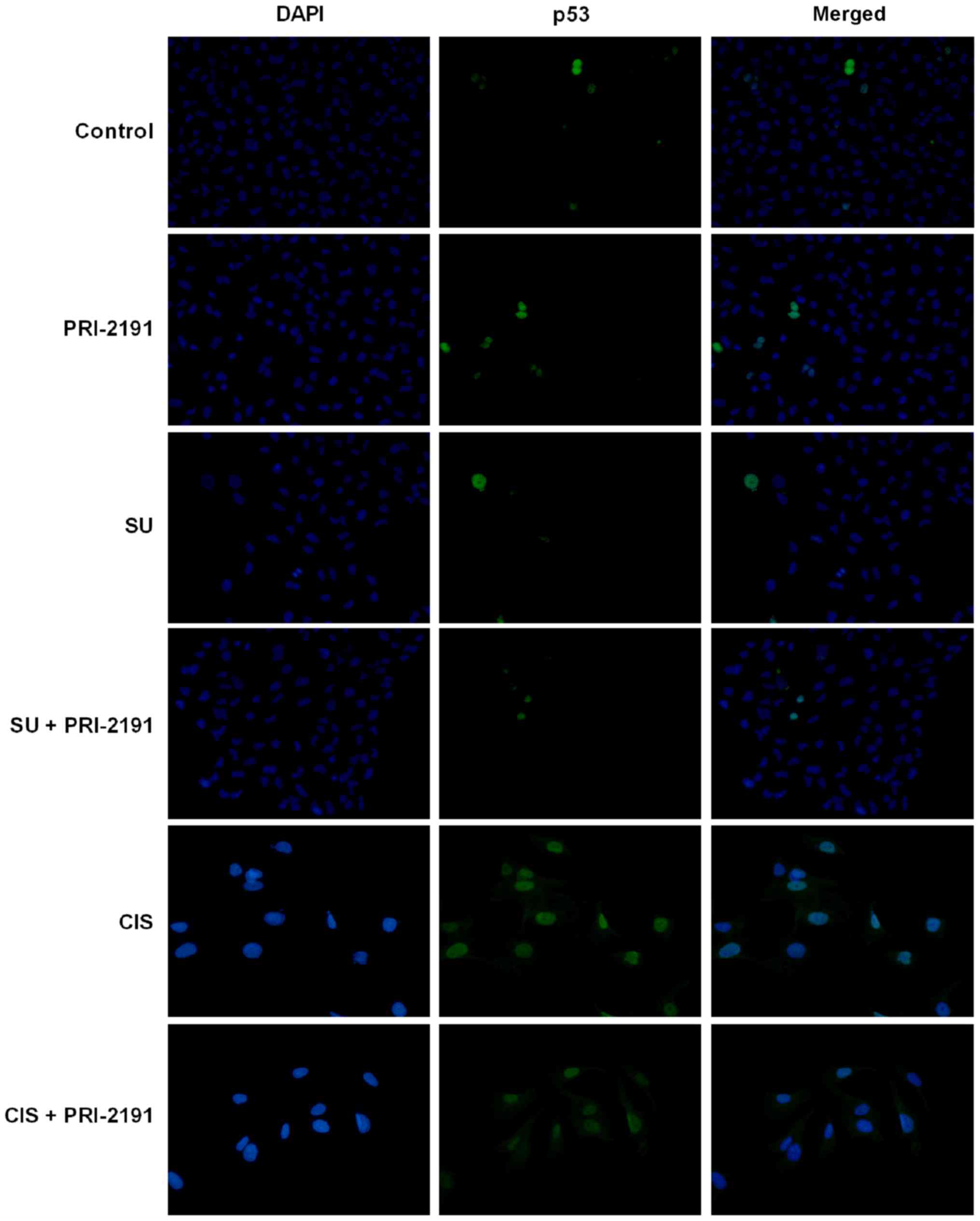
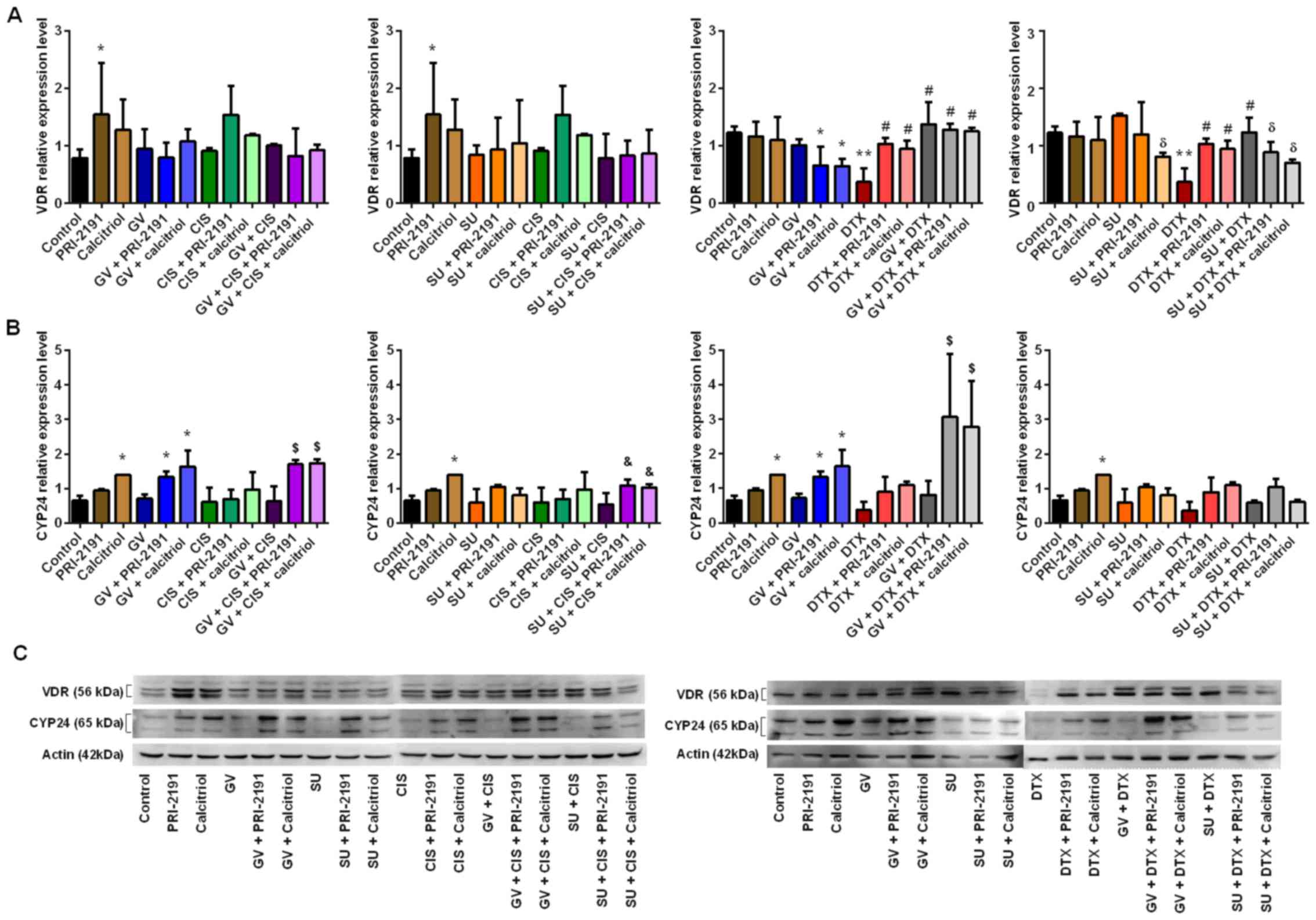
|
1
|
Adler I: Primary Malignant Growths of the
Lungs and Bronchi; A Pathological and Clinical Study. Longmans;
Green, New York, NY: 1912
|
|
2
|
Debakey M: Carcinoma of the lung and
tobacco smoking: A historical perspective. Ochsner J. 1:106–108.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Proctor RN: The history of the discovery
of the cigarette-lung cancer link: Evidentiary traditions,
corporate denial, global toll. Tob Control. 21:87–91. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dubey AK, Gupta U and Jain S: Epidemiology
of lung cancer and approaches for its prediction: A systematic
review and analysis. Chin J Cancer. 35:712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gadgeel SM, Ramalingam SS and Kalemkerian
GP: Treatment of lung cancer. Radiol Clin North Am. 50:961–974.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Feldman D, Krishnan AV, Swami S,
Giovannucci E and Feldman BJ: The role of vitamin D in reducing
cancer risk and progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:342–357. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Slominski AT, Brożyna AA, Zmijewski MA,
Jóźwicki W, Jetten AM, Mason RS, Tuckey RC and Elmets CA: Vitamin D
signaling and melanoma: Role of vitamin D and its receptors in
melanoma progression and management. Lab Invest. 97:706–724. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Higashimoto Y, Ohata M, Nishio K, Iwamoto
Y, Fujimoto H, Uetani K, Suruda T, Nakamura Y, Funasako M and Saijo
N: 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and all-trans-retinoic acid
inhibit the growth of a lung cancer cell line. Anticancer Res.
16(5A): 2653–2659. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Güzey M, Sattler C and DeLuca HF:
Combinational effects of vitamin D3 and retinoic acid (all trans
and 9 cis) on proliferation, differentiation, and programmed cell
death in two small cell lung carcinoma cell lines. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 249:735–744. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Young MRI, Ihm J, Lozano Y, Wright MA and
Prechel MM: Treating tumor-bearing mice with vitamin D3 diminishes
tumor-induced myelopoiesis and associated immunosuppression, and
reduces tumor metastasis and recurrence. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
41:37–45. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Young MRI, Lozano Y, Ihm J, Wright MA and
Prechel MM: Vitamin D3 treatment of tumor bearers can stimulate
immune competence and reduce tumor growth when treatment coincides
with a heightened presence of natural suppressor cells. Cancer
Lett. 104:153–161. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Norton R and O'Connell MA: Vitamin D:
Potential in the prevention and treatment of lung cancer.
Anticancer Res. 32:211–221. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mernitz H, Smith DE, Wood RJ, Russell RM
and Wang XD: Inhibition of lung carcinogenesis by
1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and 9-cis retinoic acid in the A/J
mouse model: Evidence of retinoid mitigation of vitamin D toxicity.
Int J Cancer. 120:1402–1409. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yudoh K, Matsuno H and Kimura T:
1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits in vitro invasiveness
through the extracellular matrix and in vivo pulmonary metastasis
of B16 mouse melanoma. J Lab Clin Med. 133:120–128. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ben-Shoshan M, Amir S, Dang DT, Dang LH,
Weisman Y and Mabjeesh NJ: 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3
(Calcitriol) inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1/vascular
endothelial growth factor pathway in human cancer cells. Mol Cancer
Ther. 6:1433–1439. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chung I, Han G, Seshadri M, Gillard BM, Yu
WD, Foster BA, Trump DL and Johnson CS: Role of vitamin D receptor
in the anti-proliferative effects of calcitriol in tumor-derived
endothelial cells and tumor angiogenesis in vivo. Cancer Res.
69:967–975. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bao BY, Yao J and Lee YF: 1alpha,
25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 suppresses interleukin-8-mediated prostate
cancer cell angiogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 27:1883–1893. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Crino L and Metro G: Therapeutic options
targeting angiogenesis in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Eur Respir
Rev. 23:79–91. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McMahon G: VEGF receptor signaling in
tumor angiogenesis. Oncologist. 5(Suppl 1): 3–10. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sandler A, Yi J, Dahlberg S, Kolb MM, Wang
L, Hambleton J, Schiller J and Johnson DH: Treatment outcomes by
tumor histology in Eastern Cooperative Group Study E4599 of
bevacizumab with paclitaxel/carboplatin for advanced non-small cell
lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 5:1416–1423. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, Brahmer J,
Schiller JH, Dowlati A, Lilenbaum R and Johnson DH:
Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 355:2542–2550. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Aggarwal C, Somaiah N and Simon G:
Antiangiogenic agents in the management of non-small cell lung
cancer: Where do we stand now and where are we headed? Cancer Biol
Ther. 13:247–263. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Calero R, Morchon E, Johnsen JI and
Serrano R: Sunitinib suppress neuroblastoma growth through
degradation of MYCN and inhibition of angiogenesis. PLoS One.
9:e956282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Teodoro JG, Evans SK and Green MR:
Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis by 53: A new role forthe guardian
of the genome. J Mol Med (Berl). 85:1175–1186. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wietrzyk J, Nevozhay D, Filip B, Milczarek
M and Kutner A: The antitumor effect of lowered doses of
cytostatics combined with new analogs of vitamin D in mice.
Anticancer Res. 27(5A): 3387–3398. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wietrzyk J, Nevozhay D, Milczarek M, Filip
B and Kutner A: Toxicity and antitumor activity of the vitamin D
analogs PRI-1906 and PRI-1907 in combined treatment with
cyclophosphamide in a mouse mammary cancer model. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 62:787–797. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Milczarek M, Rosinska S, Psurski M,
Maciejewska M, Kutner A and Wietrzyk J: Combined colonic cancer
treatment with vitamin D analogs and irinotecan or oxaliplatin.
Anticancer Res. 33:433–444. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Milczarek M, Psurski M, Kutner A and
Wietrzyk J: Vitamin D analogs enhance the anticancer activity of
5-fluorouracil in an in vivo mouse colon cancer model. BMC Cancer.
13:2942013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Milczarek M, Filip-Psurska B, Swiętnicki
W, Kutner A and Wietrzyk J: Vitamin D analogs combined with
5-fluorouracil in human HT-29 colon cancer treatment. Oncol Rep.
32:491–504. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Maj E, Filip-Psurska B, Świtalska M,
Kutner A and Wietrzyk J: Vitamin D analogs potentiate the antitumor
effect of imatinib mesylate in a human A549 lung tumor model. Int J
Mol Sci. 16:27191–27207. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Trynda J, Turlej E, Milczarek M,
Pietraszek A, Chodyński M, Kutner A and Wietrzyk J:
Antiproliferative activity and in vivo toxicity of double-point
modified analogs of 1,25-dihydroxyergocalciferol. Int J Mol Sci.
16:24873–24894. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kieda C, Paprocka M, Krawczenko A, Załecki
P, Dupuis P, Monsigny M, Radzikowski C and Duś D: New human
microvascular endothelial cell lines with specific adhesion
molecules phenotypes. Endothelium. 9:247–261. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Nevozhay D: Cheburator software for
automatically calculating drug inhibitory concentrations from in
vitro screening assays. PLoS One. 9:e1061862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
McDaid HM and Johnston PG: Synergistic
interaction between paclitaxel and 8-chloro-adenosine
3′,5′-monophosphate in human ovarian carcinoma cell lines. Clin
Cancer Res. 5:215–220. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chou TC: Drug combination studies and
their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer
Res. 70:440–446. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chou TC and Talalay P: Generalized
equations for the analysis of inhibitions of Michaelis-Menten and
higher-order kinetic systems with two or more mutually exclusive
and nonexclusive inhibitors. Eur J Biochem. 115:207–216. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chou TC and Talalay P: Quantitative
analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of
multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul. 22:27–55.
1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ekici OD, Li ZZ, Campbell AJ, James KE,
Asgian JL, Mikolajczyk J, Salvesen GS, Ganesan R, Jelakovic S,
Grütter MG, et al: Design, synthesis, and evaluation of aza-peptide
Michael acceptors as selective and potent inhibitors of caspases-2,
-3, -6, -7, -8, -9, and -10. J Med Chem. 49:5728–5749. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ramnath N, Kim S and Christensen PJ:
Vitamin D and lung cancer. Expert Rev Respir Med. 5:305–309. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Switalska M, Nasulewicz-Goldeman A,
Opolska A, Maciejewska M, Kutner A and Wietrzyk J: The in-vitro
antiproliferative effect of PRI-2191 and imatinib applied in
combined treatment with cisplatin, idarubicin, or docetaxel on
human leukemia cells. Anticancer Drugs. 23:70–80. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Pan F, Tian J, Zhang X, Zhang Y and Pan Y:
Synergistic interaction between sunitinib and docetaxel is sequence
dependent in human non-small lung cancer with EGFR TKIs-resistant
mutation. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 137:1397–1408. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhuravel E, Efanova O, Shestakova T,
Glushko N, Mezhuev O, Soldatkina M and Pogrebnoy P: Administration
of vitamin D3 improves antimetastatic efficacy of cancer vaccine
therapy of Lewis lung carcinoma. Exp Oncol. 32:33–39.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Socinski MA, Novello S, Brahmer JR, Rosell
R, Sanchez JM, Belani CP, Govindan R, Atkins JN, Gillenwater HH,
Pallares C, et al: Multicenter, phase II trial of sunitinib in
previously treated, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 26:650–656. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kerbel RS, Viloria-Petit A, Klement G and
Rak J: 'Accidental' anti-angiogenic drugs. Anti-oncogene directed
signal transduction inhibitors and conventional chemotherapeutic
agents as examples. Eur J Cancer. 36:1248–1257. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Klement G, Baruchel S, Rak J, Man S, Clark
K, Hicklin DJ, Bohlen P and Kerbel RS: Continuous low-dose therapy
with vinblastine and VEGF receptor-2 antibody induces sustained
tumor regression without overt toxicity. J Clin Invest.
105:R15–R24. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Man S, Bocci G, Francia G, Green SK, Jothy
S, Hanahan D, Bohlen P, Hicklin DJ, Bergers G and Kerbel RS:
Antitumor effects in mice of low-dose (metronomic) cyclophosphamide
administered continuously through the drinking water. Cancer Res.
62:2731–2735. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kollmannsberger C, Soulieres D, Wong R,
Scalera A, Gaspo R and Bjarnason G: Sunitinib therapy for
metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Recommendations for management of
side effects. Can Urol Assoc J. 1(Suppl): S41–S54. 2007.
|
|
49
|
Di Lorenzo G, Porta C, Bellmunt J,
Sternberg C, Kirkali Z, Staehler M, Joniau S, Montorsi F and
Buonerba C: Toxicities of targeted therapy and their management in
kidney cancer. Eur Urol. 59:526–540. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wietrzyk J, Pełczyńska M, Madej J, Dzimira
S, Kuśnierczyk H, Kutner A, Szelejewski W and Opolski A: Toxicity
and antineoplastic effect of (24R)-1,24-dihydroxyvitamin D3
(PRI-2191). Steroids. 69:629–635. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Díaz GD, Paraskeva C, Thomas MG, Binderup
L and Hague A: Apoptosis is induced by the active metabolite of
vitamin D3 and its analogue EB1089 in colorectal adenoma and
carcinoma cells: Possible implications for prevention and therapy.
Cancer Res. 60:2304–2312. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Pálmer HG, González-Sancho JM, Espada J,
Berciano MT, Puig I, Baulida J, Quintanilla M, Cano A, de Herreros
AG, Lafarga M, et al: Vitamin D(3) promotes the differentiation of
colon carcinoma cells by the induction of E-cadherin and the
inhibition of beta-catenin signaling. J Cell Biol. 154:369–387.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Teng CLJ, Yu CTR, Hwang WL, Tsai JR, Liu
HC, Hwang GY and Hsu SL: Effector mechanisms of sunitinib-induced
G1 cell cycle arrest, differentiation, and apoptosis in human acute
myeloid leukaemia HL60 and KG-1 cells. Ann Hematol. 92:301–313.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Nishikawa M, Miyake H and Fujisawa M:
Enhanced sensitivity to sunitinib by inhibition of Akt1 expression
in human castration-resistant prostate cancer C3 cells both in
vitro and in vivo. Urology. 85:1215.e1–1215.e7. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Uzu M, Sato H, Yamada R, Kashiba T,
Shibata Y, Yamaura K and Ueno K: Effect of enhanced expression of
connexin 43 on sunitinib-induced cytotoxicity in mesothelioma
cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 128:17–26. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Stepień A, Izdebska M and Grzanka A: The
types of cell death. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 61:420–428.
2007.In Polish.
|
|
57
|
Korwek Z and Alster O: The role of the DNA
damage response in apoptosis and cell senescence. Postepy Biochem.
60:248–262. 2014.In Polish.
|
|
58
|
Koren R, Wacksberg S, Weitsman GE and
Ravid A: Calcitriol sensitizes colon cancer cells to
H2O2-induced cytotoxicity while inhibiting
caspase activation. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 101:151–160. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Diker-Cohen T, Koren R, Liberman UA and
Ravid A: Vitamin D protects keratinocytes from apoptosis induced by
osmotic shock, oxidative stress, and tumor necrosis factor. Ann N Y
Acad Sci. 1010:350–353. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Lavallard VJ, Pradelli LA, Paul A,
Bénéteau M, Jacquel A, Auberger P and Ricci JE: Modulation of
caspase-independent cell death leads to resensitization of imatinib
mesylate-resistant cells. Cancer Res. 69:3013–3020. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Costa PM, Cardoso AL, Nóbrega C, Pereira
de Almeida LF, Bruce JN, Canoll P and Pedroso de Lima MC:
MicroRNA-21 silencing enhances the cytotoxic effect of the
antiangiogenic drug sunitinib in glioblastoma. Hum Mol Genet.
22:904–918. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
62
|
Liu ZL, Wang H, Liu J and Wang ZX:
MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) expression promotes growth, metastasis, and
chemo- or radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells by
targeting PTEN. Mol Cell Biochem. 372:35–45. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Xu L, Huang Y, Chen D, He J, Zhu W, Zhang
Y and Liu X: Downregulation of miR-21 increases cisplatin
sensitivity of non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Genet.
207:214–220. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhang YX, Yue Z, Wang PY, Li YJ, Xin JX,
Pang M, Zheng QY and Xie SY: Cisplatin upregulates MSH2 expression
by reducing miR-21 to inhibit A549 cell growth. Biomed
Pharmacother. 67:97–102. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Vakifahmetoglu H, Olsson M and Zhivotovsky
B: Death through a tragedy: Mitotic catastrophe. Cell Death Differ.
15:1153–1162. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kim SH, Chen G, King AN, Jeon CK,
Christensen PJ, Zhao L, Simpson RU, Thomas DG, Giordano TJ, Brenner
DE, et al: Characterization of vitamin D receptor (VDR) in lung
adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer. 77:265–271. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Naves M, Alvarez-Hernández D,
Fernández-Martín JL, Paz-Jiménez J, García-Prado P, Fernández-Coto
T, Santamaría I and Cannata-Andía J: Effect of VDR gene
polymorphisms on osteocalcin secretion in calcitriol-stimulated
human osteoblasts. Kidney Int Suppl. 63:S23–S27. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Alvarez-Hernandez D, Naves-Diaz M,
Gomez-Alonso C, Coto E and Cannata-Andia JB: Tissue-specific effect
of VDR gene polymorphisms on the response to calcitriol. J Nephrol.
21:843–849. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Dogan I, Onen HI, Yurdakul AS, Konac E,
Ozturk C, Varol A and Ekmekci A: Polymorphisms in the vitamin D
receptor gene and risk of lung cancer. Med Sci Monit.
15:BR232–BR242. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Fu Y, Li J and Zhang Y: Polymorphisms in
the vitamin D receptor gene and the lung cancer risk. Tumour Biol.
35:1323–1330. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Wu X, Cheng J and Yang K: Vitamin
D-related gene polymorphisms, plasma 25-hydroxy-vitamin D,
cigarette smoke and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) risk. Int J
Mol Sci. 17:202016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Vaughan-Shaw PG, O'Sullivan F, Farrington
SM, Theodoratou E, Campbell H, Dunlop MG and Zgaga L: The impact of
vitamin D pathway genetic variation and circulating
25-hydroxyvitamin D on cancer outcome: Systematic review and
meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. 116:1092–1110. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Slominski AT, Kim TK, Takeda Y, Janjetovic
Z, Brozyna AA, Skobowiat C, Wang J, Postlethwaite A, Li W, Tuckey
RC, et al: RORα and ROR γ are expressed in human skin and serve as
receptors for endogenously produced noncalcemic 20-hydroxy- and
20,23-dihydroxyvitamin D. FASEB J. 28:2775–2789. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Brożyna AA, Jóźwicki W, Skobowiat C,
Jetten A and Slominski AT: RORα and RORγ expression inversely
correlates with human melanoma progression. Oncotarget.
7:63261–63282. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Slominski AT, Kim TK, Hobrath JV, Oak ASW,
Tang EKY, Tieu EW, Li W, Tuckey RC and Jetten AM: Endogenously
produced nonclassical vitamin D hydroxy-metabolites act as 'biased'
agonists on VDR and inverse agonists on RORα and RORγ. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 173:42–56. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Du J and Xu R: RORα, a potential tumor
suppressor and therapeutic target of breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
13:15755–15766. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Slominski AT, Kim TK, Shehabi HZ, Semak I,
Tang EKY, Nguyen MN, Benson HAE, Korik E, Janjetovic Z, Chen J, et
al: In vivo evidence for a novel pathway of vitamin D-3 metabolism
initiated by P450scc and modified by CYP27B1. FASEB J.
26:3901–3915. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Slominski AT, Kim TK, Shehabi HZ, Tang
EKY, Benson HAE, Semak I, Lin Z, Yates CR, Wang J, Li W, et al: In
vivo production of novel vitamin D2 hydroxy-derivatives by human
placentas, epidermal keratinocytes, Caco-2 colon cells and the
adrenal gland. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 383:181–192. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Slominski AT, Kim TK, Li W, Postlethwaite
A, Tieu EW, Tang EKY and Tuckey RC: Detection of novel
CYP11A1-derived secosteroids in the human epidermis and serum and
pig adrenal gland. Sci Rep. 5:148752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Slominski AT, Kim TK, Li W and Tuckey RC:
Classical and non-classical metabolic transformation of vitamin D
in dermal fibroblasts. Exp Dermatol. 25:231–232. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
81
|
Zhang Q, Kanterewicz B, Shoemaker S, Hu Q,
Liu S, Atwood K and Hershberger P: Differential response to
1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1α,25(OH)2D3) in non-small cell lung
cancer cells with distinct oncogene mutations. J Steroid Biochem
Mol Biol. 136:264–270. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Mimori K, Tanaka Y, Yoshinaga K, Masuda T,
Yamashita K, Okamoto M, Inoue H and Mori M: Clinical significance
of the overexpression of the candidate oncogene CYP24 in esophageal
cancer. Ann Oncol. 15:236–241. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Horváth HC, Lakatos P, Kósa JP, Bácsi K,
Borka K, Bises G, Nittke T, Hershberger PA, Speer G and Kállay E:
The candidate oncogene CYP24A1: A potential biomarker for
colorectal tumorigenesis. J Histochem Cytochem. 58:277–285. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
84
|
Luo W, Hershberger PA, Trump DL and
Johnson CS: 24-Hydroxylase in cancer: Impact on vitamin D-based
anticancer therapeutics. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 136:252–257.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
85
|
Zhang Q, Kanterewicz B, Buch S, Petkovich
M, Parise R, Beumer J, Lin Y, Diergaarde B and Hershberger PA:
CYP24 inhibition preserves 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3)
anti-proliferative signaling in lung cancer cells. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 355:153–161. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Chung I, Yu WD, Karpf AR, Flynn G,
Bernardi RJ, Modzelewski RA, Johnson CS and Trump DL:
Anti-proliferative effects of calcitriol on endothelial cells
derived from two different microenvironments. J Steroid Biochem Mol
Biol. 103:768–770. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Spyridopoulos I, Brogi E, Kearney M,
Sullivan AB, Cetrulo C, Isner JM and Losordo DW: Vascular
endothelial growth factor inhibits endothelial cell apoptosis
induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha: Balance between growth and
death signals. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 29:1321–1330. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Aonuma M, Iwahana M, Nakayama Y, Hirotani
K, Hattori C, Murakami K, Shibuya M and Tanaka NG: Tumorigenicity
depends on angiogenic potential of tumor cells: Dominant role of
vascular endothelial growth factor and/or fibroblast growth factors
produced by tumor cells. Angiogenesis. 2:57–66. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Kieser A, Weich HA, Brandner G, Marmé D
and Kolch W: Mutant p53 potentiates protein kinase C induction of
vascular endothelial growth factor expression. Oncogene. 9:963–969.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Mukhopadhyay D, Tsiokas L and Sukhatme VP:
Wild-type p53 and v-Src exert opposing influences on human vascular
endothelial growth factor gene expression. Cancer Res.
55:6161–6165. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Niklińska W, Burzykowski T, Chyczewski L
and Nikliński J: Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor
(VEGF) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Association with p53
gene mutation and prognosis. Lung Cancer. 34(Suppl 2): S59–S64.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Fontanini G, Boldrini L, Vignati S, Chinè
S, Basolo F, Silvestri V, Lucchi M, Mussi A, Angeletti CA and
Bevilacqua G: Bcl2 and p53 regulate vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF)-mediated angiogenesis in non-small cell lung
carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 34:718–723. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Yuan A, Yu CJ, Luh KT, Kuo SH, Lee YC and
Yang PC: Aberrant p53 expression correlates with expression of
vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA and interleukin-8 mRNA and
neoangiogenesis in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol.
20:900–910. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Brown CJ, Lain S, Verma CS, Fersht AR and
Lane DP: Awakening guardian angels: Drugging the p53 pathway. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:862–873. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Sundaram P, Dang CV and Thomas-Tikhonenko
A: Myc and control of tumor neovascularization. Cancer Genome and
Tumor Microenvironment. Thomas-Tikhonenko A: Springer; New York,
NY: pp. 167–187. 2010, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Mahalingam D, Espitia CM, Medina EC,
Esquivel JA II, Kelly KR, Bearss D, Choy G, Taverna P, Carew JS,
Giles FJ, et al: Targeting PIM kinase enhances the activity of
sunitinib in renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 105:1563–1573.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Xie C, Pan Y, Hao F, Gao Y, Liu Z, Zhang
X, Xie L, Jiang G, Li Q and Wang E: C-Myc participates in
β-catenin-mediated drug resistance in A549/DDP lung adenocarcinoma
cells. APMIS. 122:1251–1258. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
O'Brate A and Giannakakou P: The
importance of p53 location: Nuclear or cytoplasmic zip code? Drug
Resist Updat. 6:313–322. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Levine AJ and Oren M: The first 30 years
of p53: Growing ever more complex. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:749–758. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Patel S and Player MR: Small-molecule
inhibitors of the p53-HDM2 interaction for the treatment of cancer.
Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 17:1865–1882. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Panka DJ, Liu Q, Geissler AK and Mier JW:
Effects of HDM2 antagonism on sunitinib resistance, p53 activation,
SDF-1 induction, and tumor infiltration by
CD11b+/Gr-1+ myeloid derived suppressor
cells. Mol Cancer. 12:172013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Gan L, Wang J, Xu H and Yang X: Resistance
to docetaxel-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells by
p38/p53/p21 signaling. Prostate. 71:1158–1166. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Kumagai T, O'Kelly J, Said JW and Koeffler
HP: Vitamin D2 analog 19-nor-1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D2: Antitumor
activity against leukemia, myeloma, and colon cancer cells. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 95:896–905. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Ma J, Sawai H, Ochi N, Matsuo Y, Xu D,
Yasuda A, Takahashi H, Wakasugi T and Takeyama H: PTEN regulates
angiogenesis through PI3K/Akt/VEGF signaling pathway in human
pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 331:161–171. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Clarke JM and Hurwitz HI: Understanding
and targeting resistance to anti-angiogenic therapies. J
Gastrointest Oncol. 4:253–263. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Giuliano S and Pagès G: Mechanisms of
resistance to anti-angiogenesis therapies. Biochimie. 95:1110–1119.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Joosten SC, Hamming L, Soetekouw PM, Aarts
MJ, Veeck J, van Engeland M and Tjan-Heijnen VC: Resistance to
sunitinib in renal cell carcinoma: From molecular mechanisms to
predictive markers and future perspectives. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1855:1–16. 2015.
|
|
108
|
Huang D, Ding Y, Zhou M, Rini BI, Petillo
D, Qian CN, Kahnoski R, Futreal PA, Furge KA and Teh BT:
Interleukin-8 mediates resistance to antiangiogenic agent sunitinib
in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 70:1063–1071. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Wysoczynski M, Shin DM, Kucia M and
Ratajczak MZ: Selective upregulation of interleukin-8 by human
rhabdomyosarcomas in response to hypoxia: Therapeutic implications.
Int J Cancer. 126:371–381. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Hoesel B and Schmid JA: The complexity of
NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer. 12:862013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Chen W, Li Z, Bai L and Lin Y: NF-kappaB
in lung cancer, a carcinogenesis mediator and a prevention and
therapy target. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 16:1172–1185. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Sanchez A, Tripathy D, Yin X, Luo J,
Martinez JM and Grammas P: Sunitinib enhances neuronal survival in
vitro via NF-κB-mediated signaling and expression of
cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase. J
Neuroinflammation. 10:932013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Barkett M and Gilmore TD: Control of
apoptosis by Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors. Oncogene.
18:6910–6924. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Aoki M, Nata T, Morishita R, Matsushita H,
Nakagami H, Yamamoto K, Yamazaki K, Nakabayashi M, Ogihara T and
Kaneda Y: Endothelial apoptosis induced by oxidative stress through
activation of NF-kappaB: Antiapoptotic effect of antioxidant agents
on endothelial cells. Hypertension. 38:48–55. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Royds JA, Dower SK, Qwarnstrom EE and
Lewis CE: Response of tumour cells to hypoxia: Role of p53 and
NFkB. Mol Pathol. 51:55–61. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Perkins ND and Gilmore TD: Good cop, bad
cop: The different faces of NF-kappaB. Cell Death Differ.
13:759–772. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Krishnan AV and Feldman D: Molecular
pathways mediating the anti-inflammatory effects of calcitriol:
Implications for prostate cancer chemoprevention and treatment.
Endocr Relat Cancer. 17:R19–R38. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|