|
1
|
Louis CU and Shohet JM: Neuroblastoma:
Molecular pathogenesis and therapy. Annu Rev Med. 66:49–63. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Smith MA, Seibel L, Altekruse SF, Ries LA,
Melbert DL, O'Leary M, Smith FO and Reaman GH: Outcomes for
children and adolescents with cancer: Challenges for the
twenty-first century. J Clin Oncol. 28:2625–2634. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Maris JM, Hogarty MD, Bagatell R and Cohn
SL: Neuroblastoma. Lancet. 369:2106–2120. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pinto NR, Applebaum MA, Volchenboum SL,
Matthay KK, London WB, Ambros PF, Nakagawara A, Berthold F,
Schleiermacher G, Park JR, et al: Advances in risk classification
and treatment strategies for neuroblastoma. J Clin Oncol.
33:3008–3017. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chevrier L, Meunier AC, Cochaud S, Muller
JM and Chadéneau C: Vasoactive intestinal peptide decreases MYCN
expression and synergizes with retinoic acid in a human
MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma cell line. Int J Oncol. 33:1081–1089.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Matthay KK, Villablanca JG, Seeger RC,
Stram DO, Harris RE, Ramsay NK, Swift P, Shimada H, Black CT,
Brodeur GM, et al: Children's Cancer Group: Treatment of high-risk
neuroblastoma with intensive chemotherapy, radiotherapy, autologous
bone marrow transplantation, and 13-cis-retinoic acid. N Engl J
Med. 341:1165–1173. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stafman LL and Beierle EA: Cell
proliferation in neuroblastoma. Cancers (Basel). 8:E132016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Nicolai S, Pieraccioli M, Peschiaroli A,
Melino G and Raschellà G: Neuroblastoma: Oncogenic mechanisms and
therapeutic exploitation of necroptosis. Cell Death Dis.
6:e20102015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Suita S, Tajiri T, Kaneko M, Hirai M,
Mugishima H, Sugimoto T and Tsuchida Y: Implications of MYCN
amplification in patients with stage 4 neuroblastoma who undergo
intensive chemotherapy. J Pediatr Surg. 42:489–493. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brodeur GM: Brodeur. Nat Rev Cancer.
3:203–216. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Goldsmith KC and Hogarty MD: Targeting
programmed cell death pathways with experimental therapeutics:
Opportunities in high-risk neuroblastoma. Cancer Lett. 228:133–141.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kang JH, Rychahou PG, Ishola TA, Qiao J,
Evers BM and Chung DH: MYCN silencing induces differentiation and
apoptosis in human neuroblastoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
351:192–197. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ong SE, Blagoev B, Kratchmarova I,
Kristensen DB, Steen H, Pandey A and Mann M: Stable isotope
labeling by amino acids in cell culture, SILAC, as a simple and
accurate approach to expression proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics.
1:376–386. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jensen ON, Wilm M, Shevchenko A and Mann
M: Sample preparation methods for mass spectrometric peptide
mapping directly from 2-DE gels. Methods Mol Biol. 112:513–530.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Formolo CA, Williams R, Gordish-Dressman
H, MacDonald TJ, Lee NH and Hathout Y: Secretome signature of
invasive glioblastoma multiforme. J Proteome Res. 10:3149–3159.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen EY, Tan CM, Kou Y, Duan Q, Wang Z,
Meirelles GV, Clark NR and Ma'ayan A: Enrichr: Interactive and
collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC
Bioinformatics. 14:1282013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kuleshov MV, Jones MR, Rouillard AD,
Fernandez NF, Duan Q, Wang Z, Koplev S, Jenkins SL, Jagodnik KM,
Lachmann A, et al: Enrichr: A comprehensive gene set enrichment
analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:W90–7. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Abouantoun TJ, Castellino RC and MacDonald
TJ: Sunitinib induces PTEN expression and inhibits PDGFR signaling
and migration of medulloblastoma cells. J Neurooncol. 101:215–226.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bayin NS, Frenster JD, Sen R, Si S, Modrek
AS, Galifianakis N, Dolgalev I, Ortenzi V, Illa-Bochaca I, Khahera
A, et al: Notch signaling regulates metabolic heterogeneity in
glioblastoma stem cells. Oncotarget. 8:64932–64953. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gonzalez-Villasana V, Fuentes-Mattei E,
Ivan C, Dalton HJ, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Fernandez-de Thomas RJ,
Aslan B, Del C, Monroig P, Velazquez-Torres G, Previs RA, et al:
Rac1/Pak1/38/MMP-2 axis regulates angiogenesis in ovarian cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 21:2127–2137. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fan Y, Gan Y, Shen Y, Cai X, Song Y, Zhao
F, Yao M, Gu J and Tu H: Leptin signaling enhances cell invasion
and promotes the metastasis of human pancreatic cancer via
increasing MMP-P13 production. Oncotarget. 6:16120–16134. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li Y, Zhang J, He J, Zhou W, Xiang G and
Xu R: MicroRNA-132 cause apoptosis of glioma cells through blockade
of the SREBP-1c metabolic pathway related to SIRT1. Biomed
Pharmacother. 78:177–184. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bao JM, He MY, Liu YW, Lu YJ, Hong YQ, Luo
HH, Ren ZL, Zhao SC and Jiang Y: AGE/RAGE/Akt pathway contributes
to prostate cancer cell proliferation by promoting Rb
phosphorylation and degradation. Am J Cancer Res. 5:1741–1750.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang J, Qi Q, Feng Z, Zhang X, Huang B,
Chen A, Prestegarden L, Li X and Wang J: Berberine induces
autophagy in glioblastoma by targeting the AMPK/mTOR/ULK1-pathway.
Oncotarget. 7:66944–66958. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
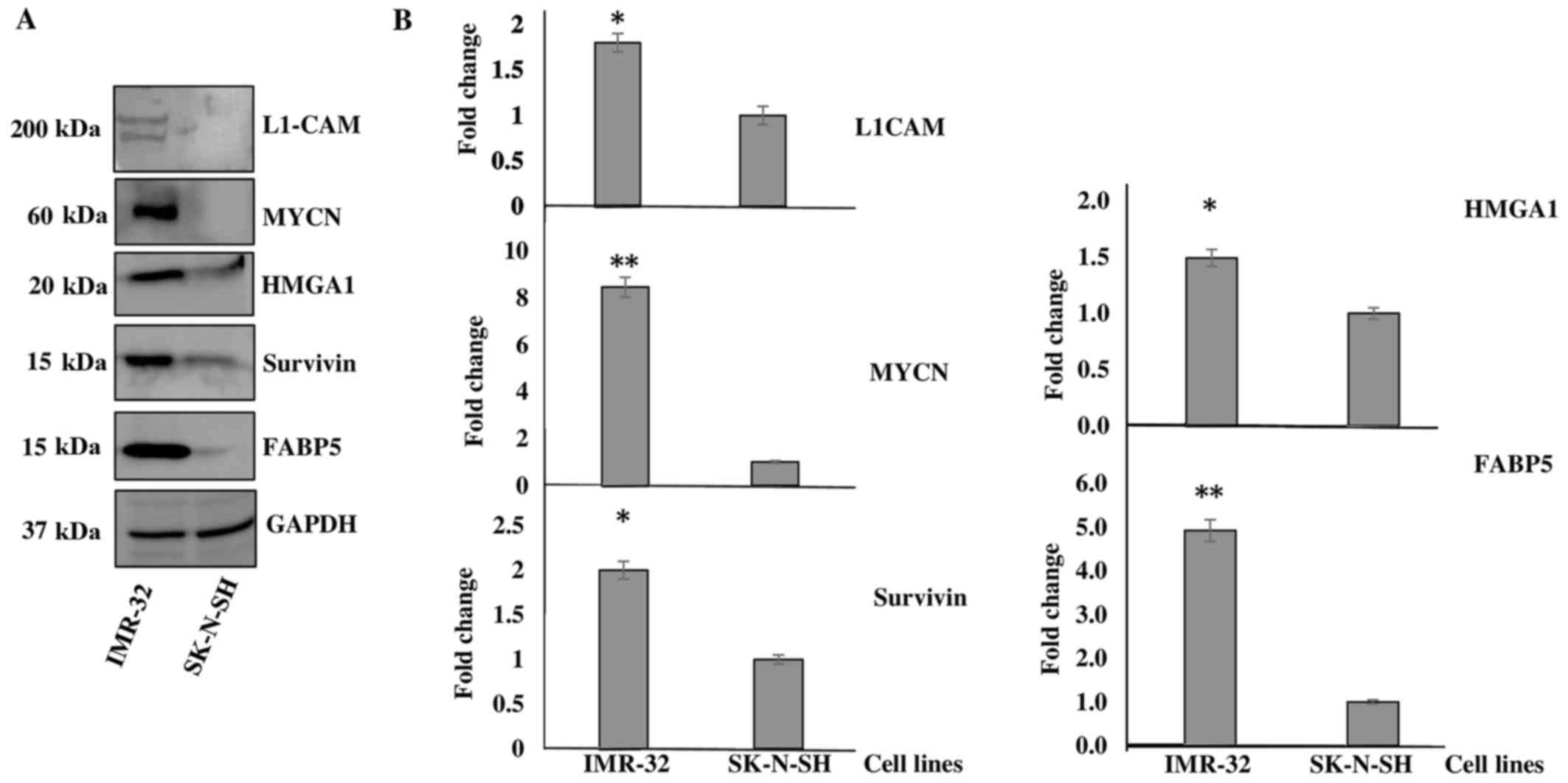
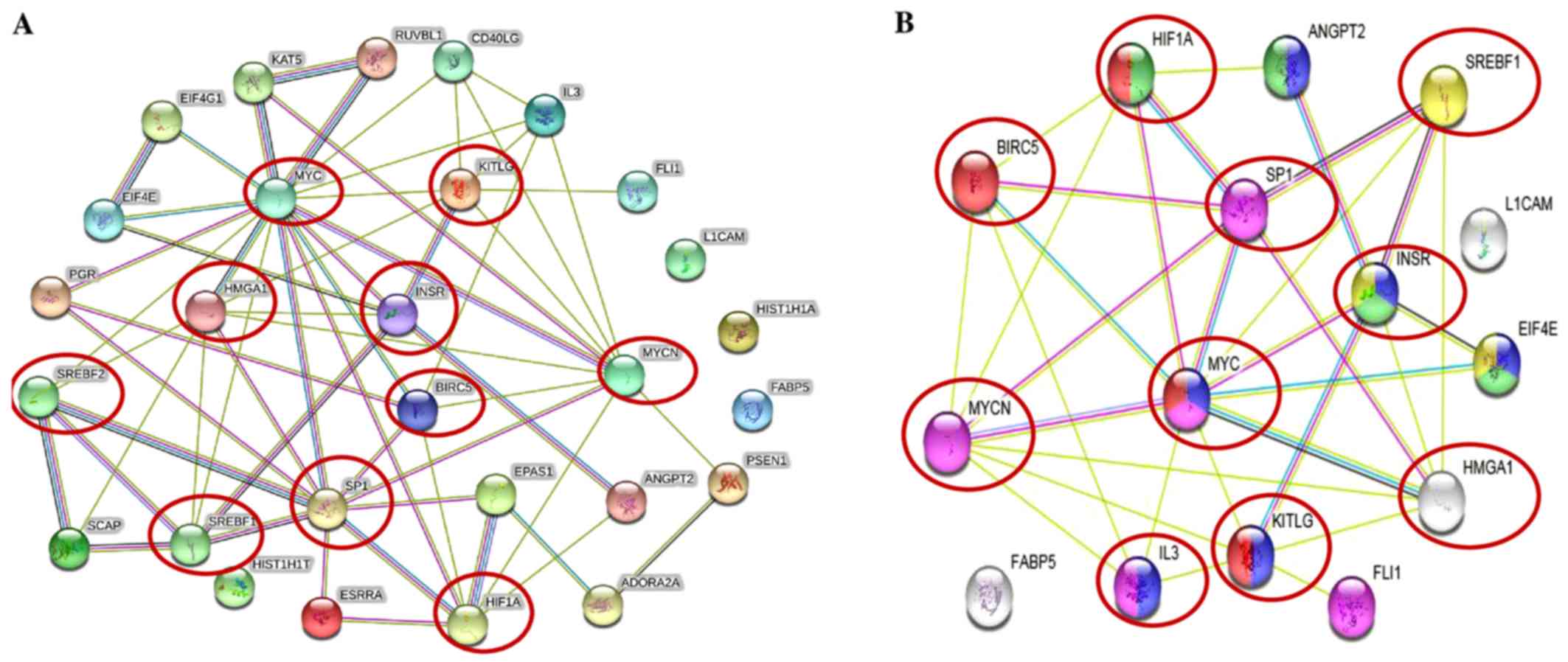
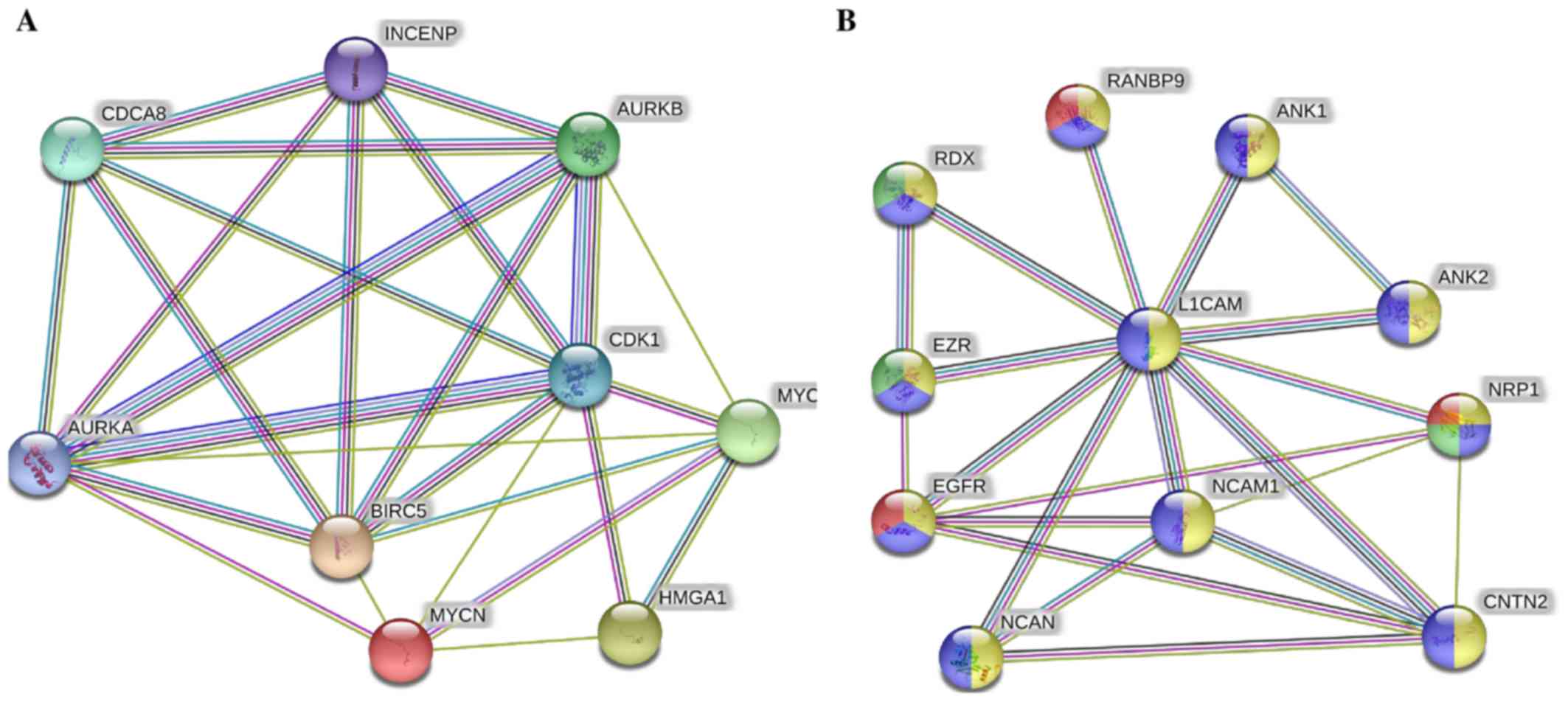
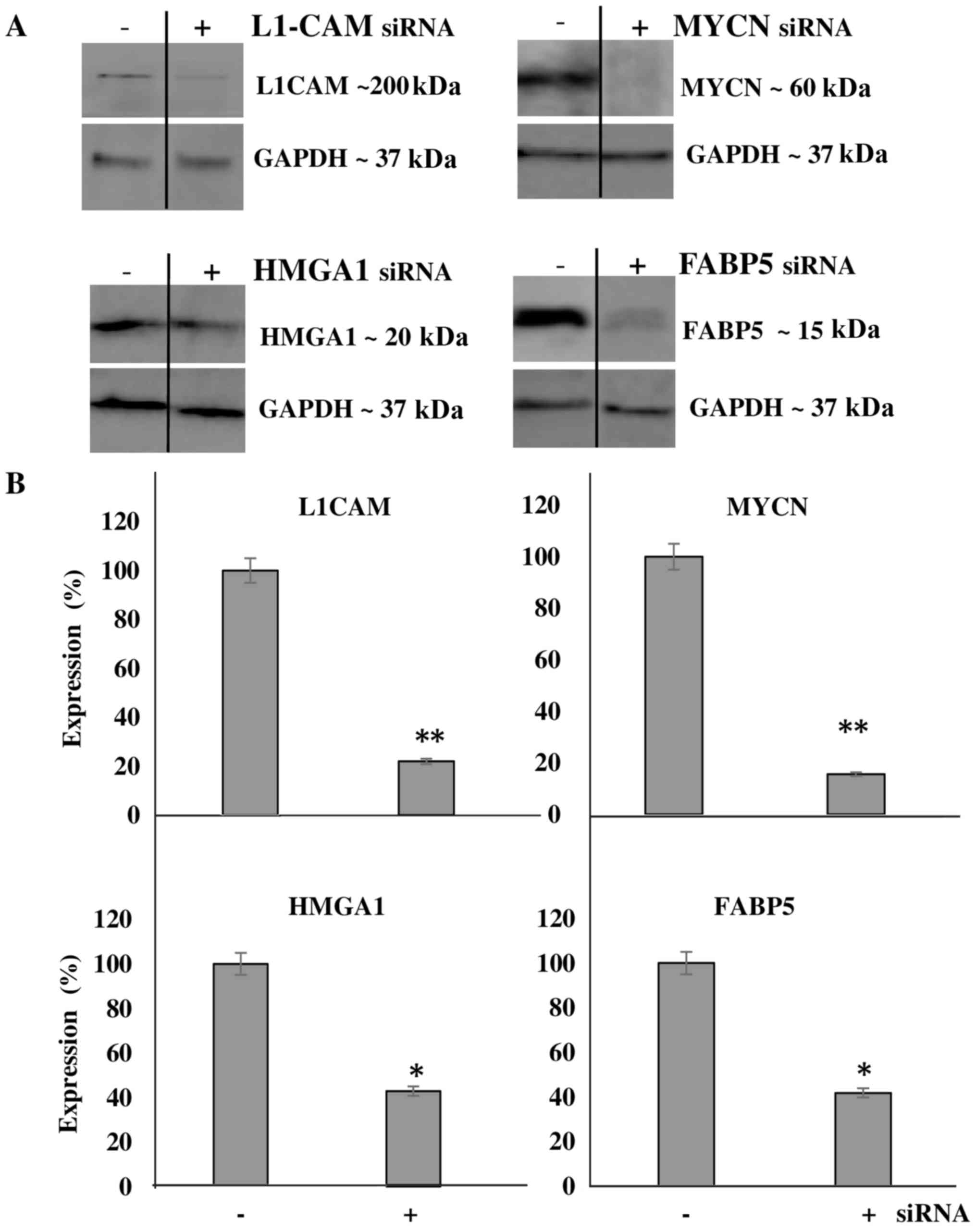
Rached J, Nasr Z, Abdallah J and
Abou-Antoun T: L1-CAM knock-down radiosensitizes neuroblastoma
IMR-32 cells by simultaneously decreasing MycN, but increasing PTEN
protein expression. Int J Oncol. 49:1722–1730. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fabian J, Opitz D, Althoff K, Lodrini M,
Hero B, Volland R, Beckers A, de Preter K, Decock A, Patil N, et
al: MYCN and HDAC5 transcriptionally repress CD9 to trigger
invasion and metastasis in neuroblastoma. Oncotarget.
7:66344–66359. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gangoda L, Keerthikumar S, Fonseka P,
Edgington LE, Ang CS, Ozcitti C, Bogyo M, Parker BS and Mathivanan
S: Inhibition of cathepsin proteases attenuates migration and
sensitizes aggressive N-Myc amplified human neuroblastoma cells to
doxorubicin. Oncotarget. 6:11175–11190. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Preis PN, Saya H, Nádasdi L, Hochhaus G,
Levin V and Sadée W: Neuronal cell differentiation of human
neuroblastoma cells by retinoic acid plus herbimycin A. Cancer Res.
48:6530–6534. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schwab M, Alitalo K, Klempnauer KH, Varmus
HE, Bishop JM, Gilbert F, Brodeur G, Goldstein M and Trent J:
Amplified DNA with limited homology to myc cellular oncogene is
shared by human neuroblastoma cell lines and a neuroblastoma tumor.
Nature. 305:245–248. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang T, Zhang Z, Wang K, Wang J, Jiang Y,
Xia J, Gou L, Liu M, Zhou L, He T, et al: Inhibitory effects of
BMP9 on breast cancer cells by regulating their interaction with
pre-adipocytes/adipocytes. Oncotarget. 8:35890–35901.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Segerström L, Baryawno N, Sveinbjörnsson
B, Wickström M, Elfman L, Kogner P and Johnsen JI: Effects of small
molecule inhibitors of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling on neuroblastoma
growth in vitro and in vivo. Int J Cancer. 129:2958–2965. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bäckman U and Christofferson R: The
selective class III/V receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor SU11657
inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis in experimental
neuroblastomas grown in mice. Pediatr Res. 57:690–695. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rawnaq T, Quaas A, Zander H, Gros SJ,
Reichelt U, Blessmann M, Wilzcak W, Schachner M, Sauter G, Izbicki
JR, et al: L1 is highly expressed in tumors of the nervous system:
A study of over 8000 human tissues. J Surg Res. 173:314–319. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Gavert N, Ben-Shmuel A, Raveh S and
Ben-Ze'ev A: L1-CAM in cancerous tissues. Expert Opin Biol Ther.
8:1749–1757. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Raveh S, Gavert N and Ben-Ze'ev A: L1 cell
adhesion molecule (L1CAM) in invasive tumors. Cancer Lett.
282:137–145. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ben-Arie A, Huszar M, Ben-Zvi N, Smirnov
A, Altevogt P and Fogel M: The role of L1-CAM immunohistochemial
staining in the diagnosis of abdominal-pelvic cancer of uncertain
primary site in women. Eur J Surg Oncol. 34:795–799. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bao S, Wu Q, Li Z, Sathornsumetee S, Wang
H, McLendon RE, Hjelmeland AB and Rich JN: Targeting cancer stem
cells through L1CAM suppresses glioma growth. Cancer Res.
68:6043–6048. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cheng L, Wu Q, Huang Z, Guryanova OA,
Huang Q, Shou W, Rich JN and Bao S: L1CAM regulates DNA damage
checkpoint response of glioblastoma stem cells through NBS1. EMBO
J. 30:800–813. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhao WJ and Schachner M: Neuregulin 1
enhances cell adhesion molecule L1 expression in human glioma cells
and promotes their migration as a function of malignancy. J
Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 72:244–255. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhao W: Zhao. Oncol Lett. 4:812–816. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ackermann MA, Petrosino JM, Manring HR,
Wright P, Shettigar V, Kilic A, Janssen PML, Ziolo MT and Accornero
F: TGF-β1 affects cell-cell adhesion in the heart in an
NCAM1-dependent mechanism. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 112:49–57. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Grosschedl R, Giese K and Pagel J: HMG
domain proteins: Architectural elements in the assembly of
nucleoprotein structures. Trends Genet. 10:94–100. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tallini G and Dal Cin P: HMGI(Y) and
HMGI-C dysregulation: A common occurrence in human tumors. Adv Anat
Pathol. 6:237–246. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chiappetta G, Tallini G, De Biasio MC,
Manfioletti G, Martinez-Tello FJ, Pentimalli F, de Nigris F, Mastro
A, Botti G, Fedele M, et al: Detection of high mobility group I
HMGI(Y) protein in the diagnosis of thyroid tumors: HMGI(Y)
expression represents a potential diagnostic indicator of
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 58:4193–4198. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Abe N, Watanabe T, Sugiyama M, Uchimura H,
Chiappetta G, Fusco A and Atomi Y: Determination of high mobility
group I(Y) expression level in colorectal neoplasias: A potential
diagnostic marker. Cancer Res. 59:1169–1174. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Giannini G, Cerignoli F, Mellone M,
Massimi I, Ambrosi C, Rinaldi C, Dominici C, Frati L, Screpanti I
and Gulino A: High mobility group A1 is a molecular target for MYCN
in human neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 65:8308–8316. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ru P, Hu P, Geng F, Mo X, Cheng C, Yoo JY,
Cheng X, Wu X, Guo JY, et al: Feedback loop regulation of
SCAP/SREBP-1 by miR-29 modulates EGFR signaling-driven glioblastoma
growth. Cell Reports. 16:1527–1535. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Guo D: SCAP links glucose to lipid
metabolism in cancer cells. Mol Cell Oncol. 3:e11321202016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Mohlin S, Hamidian A, von Stedingk K,
Bridges E, Wigerup C, Bexell D and Påhlman S: PI3K-mTORC2 but not
PI3K-mTORC1 regulates transcription of HIF2A/EPAS1 and
vascularization in neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 75:4617–4628. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hanes R, Grad I, Lorenz S, Stratford EW,
Munthe E, Reddy CC, Meza-Zepeda LA and Myklebost O: Preclinical
evaluation of potential therapeutic targets in dedifferentiated
liposarcoma. Oncotarget. 7:54583–54595. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Poynter JN, Hooten AJ, Frazier AL and Ross
JA: Associations between variants in KITLG, SPRY4, BAK1, and DMRT1
and pediatric germ cell tumors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer.
51:266–271. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Jiao DC, Lu ZD, Qiao JH, Yan M, Cui SD and
Liu ZZ: Expression of CDCA8 correlates closely with FOXM1 in breast
cancer: public microarray data analysis and immunohistochemical
study. Neoplasma. 62:464–469. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gohard FH, St-Cyr DJ, Tyers M and Earnshaw
WC: Targeting the INCENP IN-box-Aurora B interaction to inhibit CPC
activity in vivo. Open Biol. 4:1401632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chamcheu JC, Chaves-Rodriquez MI, Adhami
VM, Siddiqui IA, Wood GS, Longley BJ and Mukhtar H: Upregulation of
PI3K/AKT/mTOR, FABP5 and PPARβ/δ in human psoriasis and
imiquimod-induced murine psoriasiform dermatitis model. Acta Derm
Venereol. 96:854–856. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Connolly RM, Nguyen NK and Sukumar S:
Molecular pathways: Current role and future directions of the
retinoic acid pathway in cancer prevention and treatment. Clin
Cancer Res. 19:1651–1659. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Al-Jameel W, Gou X, Forootan SS, Al Fayi
MS, Rudland PS, Forootan FS, Zhang J, Cornford PA, Hussain SA and
Ke Y: Inhibitor SBFI26 suppresses the malignant progression of
castration-resistant PC3-M cells by competitively binding to
oncogenic FABP5. Oncotarget. 8:31041–31056. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Althoff K, Lindner S, Odersky A, Mestdagh
P, Beckers A, Karczewski S, Molenaar JJ, Bohrer A, Knauer S,
Speleman F, et al: miR-542 3p exerts tumor suppressive functions in
neuroblastoma by downregulating Survivin. Int J Cancer.
136:1308–1320. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Islam A, Kageyama H, Takada N, Kawamoto T,
Takayasu H, Isogai E, Ohira M, Hashizume K, Kobayashi H, Kaneko Y,
et al: High expression of Survivin, mapped to 17q25, is
significantly associated with poor prognostic factors and promotes
cell survival in human neuroblastoma. Oncogene. 19:617–623. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Azuhata T, Scott D, Griffith TS, Miller M
and Sandler AD: Survivin inhibits apoptosis induced by TRAIL, and
the ratio between survivin and TRAIL receptors is predictive of
recurrent disease in neuroblastoma. J Pediatr Surg. 41:1431–1440.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Mita AC, Mita MM, Nawrocki ST and Giles
FJ: Survivin: Key regulator of mitosis and apoptosis and novel
target for cancer therapeutics. Clin Cancer Res. 14:5000–5005.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Adida C, Berrebi D, Peuchmaur M,
Reyes-Mugica M and Altieri DC: Anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, and
prognosis of neuroblastoma. Lancet. 351:882–883. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Hossain MM, Banik L and Ray SK: Survivin
knockdown increased anti-cancer effects of
(-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate in human malignant neuroblastoma
SK-N-BE2 and SH-SY5Y cells. Exp Cell Res. 318:1597–1610. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Han L, Jorgensen JL, Brooks C, Shi C,
Zhang Q, Nogueras González GM, Cavazos A, Pan R, Mu H, Wang SA, et
al: Antileukemia efficacy and mechanisms of action of SL-101, a
novel anti-CD123 antibody conjugate, in acute myeloid leukemia.
Clin Cancer Res. 23:3385–3395. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Yin CP, Guan SH, Zhang B, Wang XX and Yue
SW: Upregulation of HIF-1α protects neuroblastoma cells from
hypoxia-induced apoptosis in a RhoA-dependent manner. Mol Med Rep.
12:7123–7131. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Yoon H, Min JK, Lee DG, Kim DG, Koh SS and
Hong HJ: L1 cell adhesion molecule and epidermal growth factor
receptor activation confer cisplatin resistance in intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 316:70–76. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Wang Y and Schachner M: The intracellular
domain of L1CAM binds to casein kinase 2α and is neuroprotective
via inhibition of the tumor suppressors PTEN and p53. J Neurochem.
133:828–843. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Puca F, Colamaio M, Federico A, Gemei M,
Tosti N, Bastos AU, Del Vecchio L, Pece S, Battista S and Fusco A:
HMGA1 silencing restores normal stem cell characteristics in colon
cancer stem cells by increasing p53 levels. Oncotarget.
5:3234–3245. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Mazar J, Rosado A, Shelley J, Marchica J
and Westmoreland TJ: The long non-coding RNA GAS5 differentially
regulates cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through activation of
BRCA1 and p53 in human neuroblastoma. Oncotarget. 8:6589–6607.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
69
|
Doberstein K, Pfeilschifter J and Gutwein
P: The transcription factor AX2 regulates ADAM10 expression in
renal cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 32:1713–1723. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Kawaguchi K, Kinameri A, Suzuki S, Senga
S, Ke Y and Fujii H: The cancer-promoting gene fatty acid-binding
protein 5 (FABP5) is epigenetically regulated during human prostate
carcinogenesis. Biochem J. 473:449–461. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Stoeck A, Gast D, Sanderson MP, Issa Y,
Gutwein P and Altevogt P: L1-CAM in a membrane-bound or soluble
form augments protection from apoptosis in ovarian carcinoma cells.
Gynecol Oncol. 104:461–469. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Künkele A, Taraseviciute A, Finn LS,
Johnson AJ, Berger C, Finney O, Chang CA, Rolczynski LS, Brown C,
Mgebroff S, et al: Preclinical assessment of CD171-directed CAR
T-cell adoptive therapy for childhood neuroblastoma: CE7 epitope
target safety and product manufacturing feasibility. Clin Cancer
Res. 23:466–477. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|