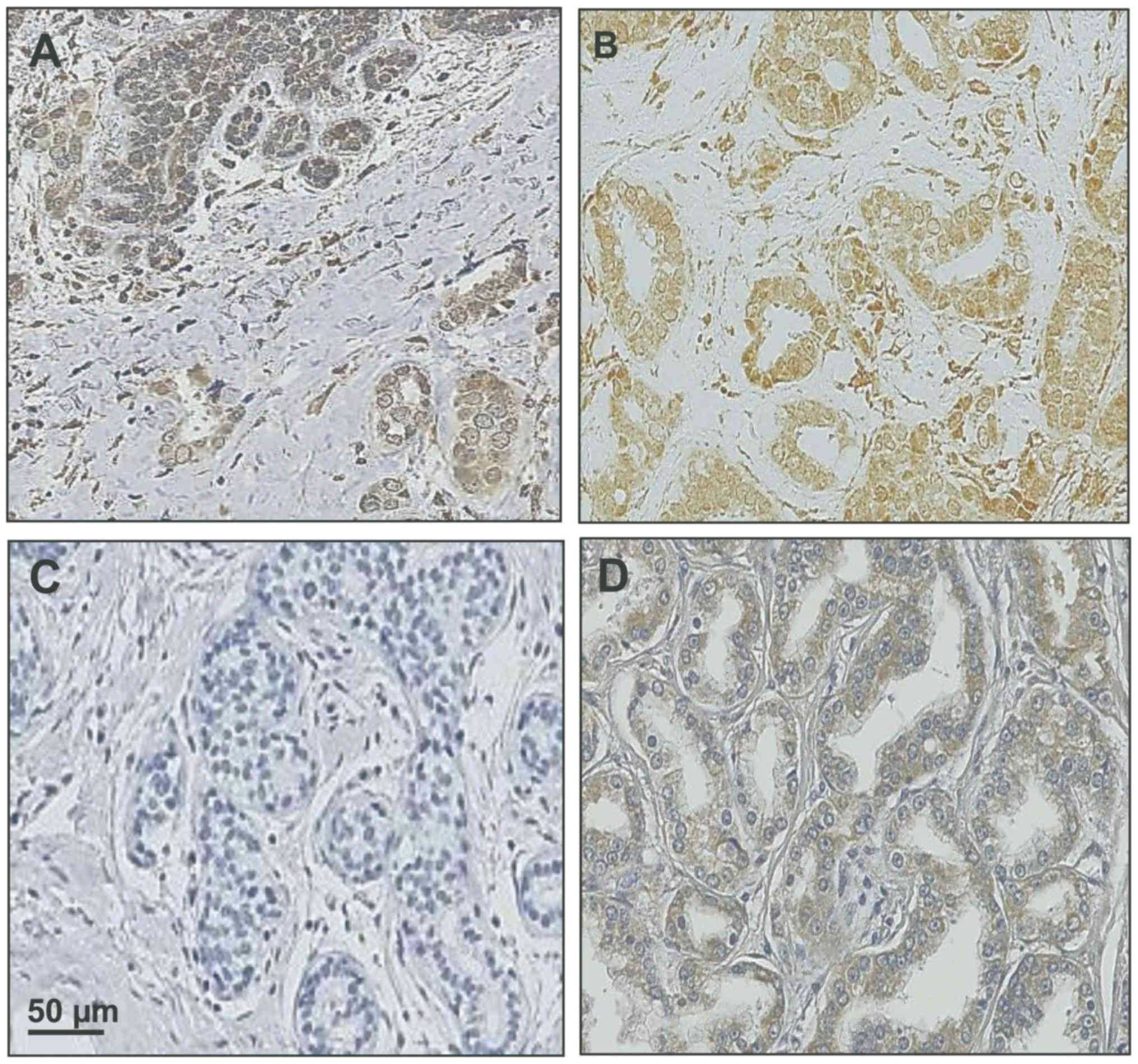
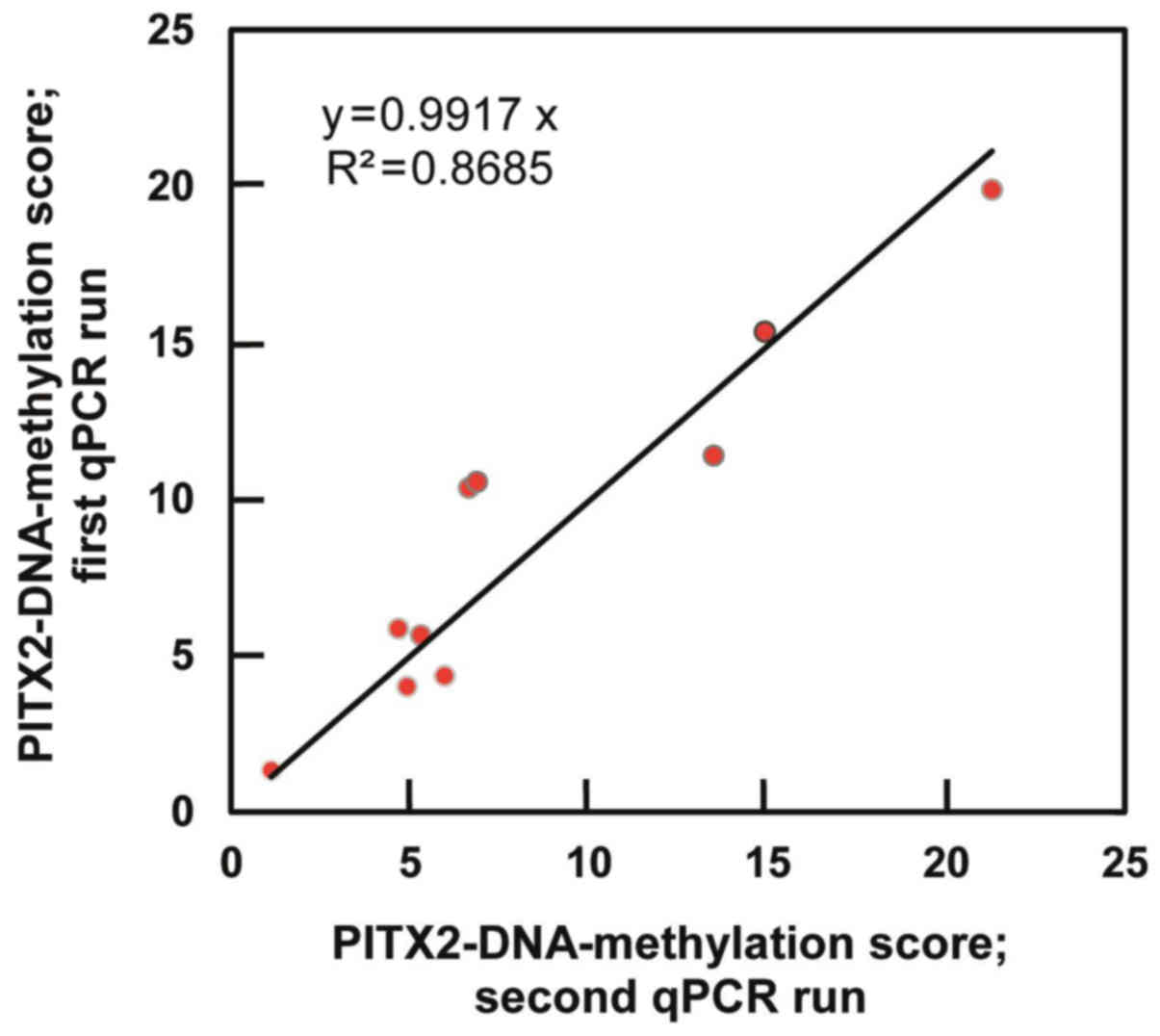
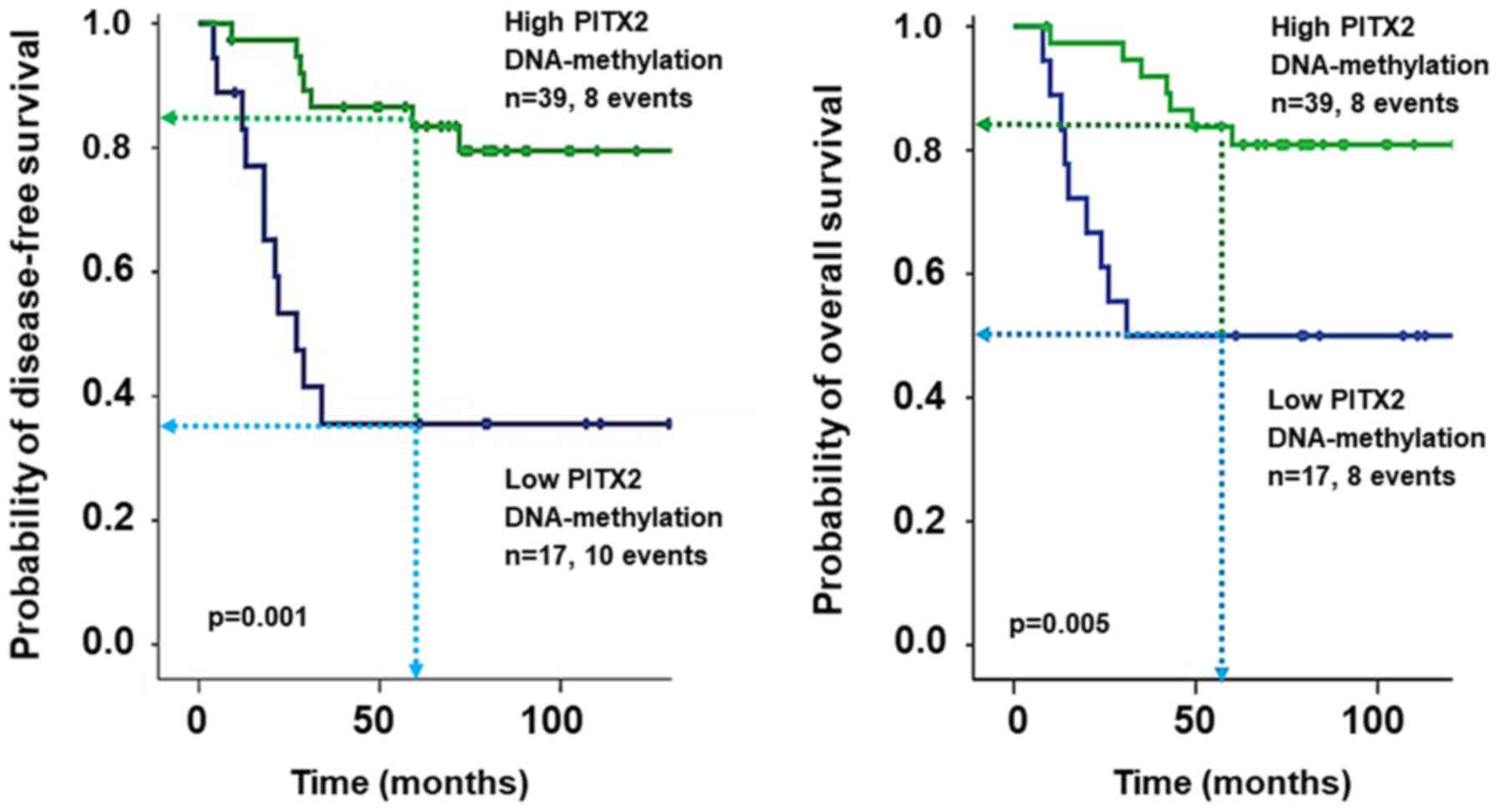
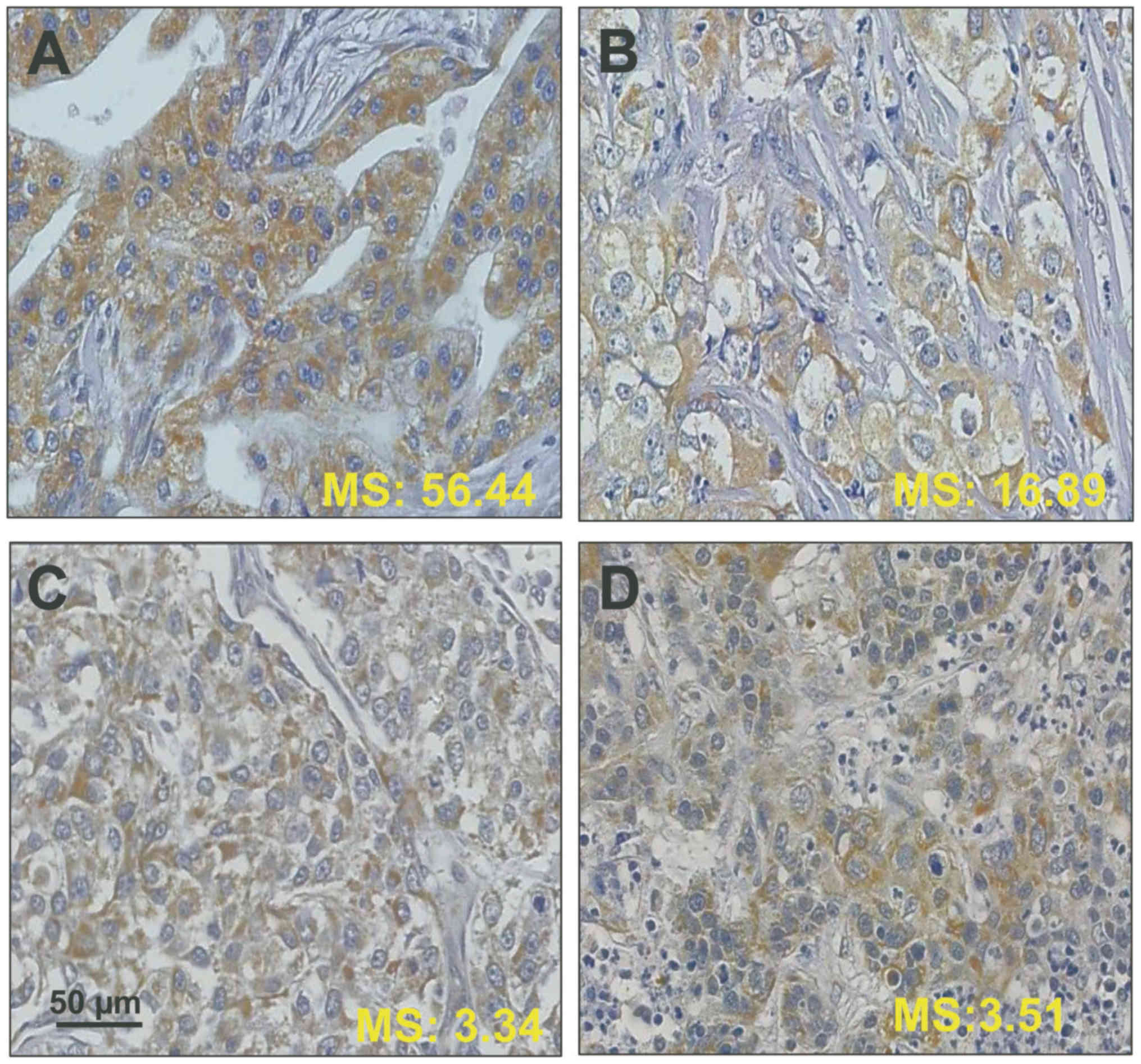
|
1
|
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Hicks DG, Dowsett M,
McShane LM, Allison KH, Allred DC, Bartlett JM, Bilous M,
Fitzgibbons P, et al American Society of Clinical Oncology; College
of American Pathologists: Recommendations for human epidermal
growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society
of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical
practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 31:3997–4013. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bauer KR, Brown M, Cress RD, Parise CA and
Caggiano V: Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor
(ER)-negative, progesterone receptor (PR)-negative, and
HER2-negative invasive breast cancer, the so-called triple-negative
phenotype: A population-based study from the California Cancer
Registry. Cancer. 109:1721–1728. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Harbeck N and Gnant M: Breast cancer.
Lancet. 389:1134–1150. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jiang T, Shi W, Wali VB, Pongor LS, Li C,
Lau R, Győrffy B, Lifton RP, Symmans WF, Pusztai L, et al:
Predictors of chemo-sensitivity in triple negative breast cancer:
An integrated genomic analysis. PLoS Med. 13:e10021932016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Liedtke C and Kiesel L: Breast cancer
molecular subtypes--modern therapeutic concepts for targeted
therapy of a heterogeneous entity. Maturitas. 73:288–294. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Irshad S, Ellis P and Tutt A: Molecular
heterogeneity of triple-negative breast cancer and its clinical
implications. Curr Opin Oncol. 23:566–577. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Karn T, Pusztai L, Holtrich U, Iwamoto T,
Shiang CY, Schmidt M, Müller V, Solbach C, Gaetje R, Hanker L, et
al: Homogeneous datasets of triple negative breast cancers enable
the identification of novel prognostic and predictive signatures.
PLoS One. 6:e284032011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM,
Kahn HK, Sawka CA, Lickley LA, Rawlinson E, Sun P and Narod SA:
Triple-negative breast cancer: Clinical features and patterns of
recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4429–4434. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T,
Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey
SS, et al: Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas
distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:10869–10874. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lord CJ and Ashworth A: BRCAness
revisited. Nat Rev Cancer. 16:110–120. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Spugnesi L, Gabriele M, Scarpitta R,
Tancredi M, Maresca L, Gambino G, Collavoli A, Aretini P, Bertolini
I, Salvadori B, et al: Germline mutations in DNA repair genes may
predict neoadjuvant therapy response in triple negative breast
patients. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 55:915–924. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mori H, Kubo M, Nishimura R, Osako T,
Arima N, Okumura Y, Okido M, Yamada M, Kai M, Kishimoto J, et al:
BRCAness as a biomarker for predicting prognosis and response to
anthracycline-based adjuvant chemotherapy for patients with
triple-negative breast cancer. PLoS One. 11:e01670162016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sharma P: Sharma. Oncologist.
21:1050–1062. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lips EH, Mulder L, Oonk A, van der Kolk
LE, Hogervorst FB, Imholz AL, Wesseling J, Rodenhuis S and Nederlof
PM: Triple-negative breast cancer: BRCAness and concordance of
clinical features with BRCA1-mutation carriers. Br J Cancer.
108:2172–2177. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cardoso F, Harbeck N, Barrios CH, Bergh J,
Cortés J, El Saghir N, Francis PA, Hudis CA, Ohno S, Partridge AH,
et al: Research needs in breast cancer. Ann Oncol Nov. 28:208–217.
2017.
|
|
16
|
Fleisher B, Clarke C and Ait-Oudhia S:
Current advances in biomarkers for targeted therapy in
triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press).
8:183–197. 2016.
|
|
17
|
Telli M: Optimizing chemotherapy in
triple-negative breast cancer: The role of platinum. Am Soc Clin
Oncol Educ Book. 33:e37–e42. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Guan X, Ma F, Fan Y, Zhu W, Hong R and Xu
B: Platinum-based chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled
trials. Anticancer Drugs. 26:894–901. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Anders CK, Abramson V, Tan T and Dent R:
The evolution of triple-negative breast cancer: From biology to
novel therapeutics. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 35:34–42. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gerratana L, Fanotto V, Pelizzari G,
Agostinetto E and Puglisi F: Do platinum salts fit all triple
negative breast cancers. Cancer Treat Rev. 48:34–41. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kern P, Kalisch A, Kolberg HC, Kimmig R,
Otterbach F, von Minckwitz G, Sikov WM, Pott D and Kurbacher C:
Neoadjuvant, anthracycline-free chemotherapy with carboplatin and
docetaxel in triple-negative, early-stage breast cancer: A
multicentric analysis of feasibility and rates of pathologic
complete response. Chemotherapy. 59:387–394. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zheng R, Han S, Duan C, Chen K, You Z, Jia
J, Lin S, Liang L, Liu A, Long H, et al: Role of taxane and
anthracycline combination regimens in the management of advanced
breast cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Medicine.
94:e8032015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Adium R and Liedtke C: Neoadjuvant therapy
for patients with triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). Rev Recent
Clin Trials. 12:73–80. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
von Minckwitz G, Schneeweiss A, Loibl S,
Salat C, Denkert C, Rezai M, Blohmer JU, Jackisch C, Paepke S,
Gerber B, et al: Neoadjuvant carboplatin in patients with
triple-negative and HER2-positive early breast cancer (GeparSixto;
GBG 66): A randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 15:747–756.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nabholtz JM, Abrial C, Mouret-Reynier MA,
Dauplat MM, Weber B, Gligorov J, Forest AM, Tredan O, Vanlemmens L,
Petit T, et al: Multicentric neoadjuvant phase II study of
panitumumab combined with an anthracycline/taxane-based
chemotherapy in operable triple-negative breast cancer:
Identification of biologically defined signatures predicting
treatment impact. Ann Oncol. 25:1570–1577. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
McClendon AK, Dean JL, Rivadeneira DB, Yu
JE, Reed CA, Gao E, Farber JL, Force T, Koch WJ and Knudsen ES:
CDK4/6 inhibition antagonizes the cytotoxic response to
anthracycline therapy. Cell Cycle. 11:2747–2755. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Reinisch M, von Minckwitz G, Harbeck N,
Janni W, Kümmel S, Kaufmann M, Elling D, Nekljudova V and Loibl S:
Side effects of standard adjuvant and neoadjuvant chemotherapy
regimens according to age groups in primary breast cancer. Breast
Care (Basel). 8:60–66. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Baylin SB and Jones PA: Epigenetic
determinants of cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 8:82016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wu Y, Sarkissyan M and Vadgama JV:
Epigenetics in breast and prostate cancer. Methods Mol Biol.
1238:425–466. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Atalay C: Atalay. Exp Oncol. 35:246–249.
2013.
|
|
31
|
Jovanovic J, Rønneberg JA, Tost J and
Kristensen V: The epigenetics of breast cancer. Mol Oncol.
4:242–254. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Basse C and Arock M: The increasing roles
of epigenetics in breast cancer: Implications for pathogenicity,
biomarkers, prevention and treatment. Int J Cancer. 137:2785–2794.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yang X, Lay F, Han H and Jones PA:
Targeting DNA methylation for epigenetic therapy. Trends Pharmacol
Sci. 31:536–546. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jones PA: Jones. J Clin Invest. 124:14–16.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shiratori H, Yashiro K, Shen MM and Hamada
H: Conserved regulation and role of Pitx2 in situs-specific
morphogenesis of visceral organs. Development. 133:3015–3025. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wilting J and Hagedorn M: Left-right
asymmetry in embryonic development and breast cancer: Common
molecular determinants. Curr Med Chem. 18:5519–5527. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Jezkova E, Kajo K, Zubor P, Grendar M,
Malicherova B, Mendelova A, Dokus K, Lasabova Z, Plank L and Danko
J: Methylation in promoter regions of PITX2 and RASSF1A genes in
association with clinicopathological features in breast cancer
patients. Tumour Biol. 37:15707–15718. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Martens JW, Margossian AL, Schmitt M,
Foekens J and Harbeck N: DNA methylation as a biomarker in breast
cancer. Future Oncol. 5:1245–1256. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Maier S, Nimmrich I, Koenig T,
Eppenberger-Castori S, Bohlmann I, Paradiso A, Spyratos F, Thomssen
C, Mueller V, Nährig J, et al European Organisation for Research
and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) PathoBiology group: DNA-methylation
of the homeodomain transcription factor PITX2 reliably predicts
risk of distant disease recurrence in tamoxifen-treated,
node-negative breast cancer patients--Technical and clinical
validation in a multi-centre setting in collaboration with the
European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC)
PathoBiology group. Eur J Cancer. 43:1679–1686. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Harbeck N, Nimmrich I, Hartmann A, Ross
JS, Cufer T, Grützmann R, Kristiansen G, Paradiso A, Hartmann O,
Margossian A, et al: Multicenter study using paraffin-embedded
tumor tissue testing PITX2 DNA methylation as a marker for outcome
prediction in tamoxifen-treated, node-negative breast cancer
patients. J Clin Oncol. 26:5036–5042. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hartmann O, Spyratos F, Harbeck N,
Dietrich D, Fassbender A, Schmitt M, Eppenberger-Castori S,
Vuaroqueaux V, Lerebours F, Welzel K, et al: DNA methylation
markers predict outcome in node-positive, estrogen
receptor-positive breast cancer with adjuvant anthracycline-based
chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 15:315–323. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nimmrich I, Sieuwerts AM, Meijer-van
Gelder ME, Schwope I, Bolt-de Vries J, Harbeck N, Koenig T,
Hartmann O, Kluth A, Dietrich D, et al: DNA hypermethylation of
PITX2 is a marker of poor prognosis in untreated lymph
node-negative hormone receptor-positive breast cancer patients.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 111:429–437. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kumar P and Aggarwal R: An overview of
triple-negative breast cancer. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 293:247–269.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Loibl S, Denkert C and von Minckwitz G:
Neoadjuvant treatment of breast cancer - Clinical and research
perspective. Breast. 24(Suppl 2): S73–S77. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Liedtke C and Rody A: New treatment
strategies for patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Curr
Opin Obstet Gynecol. 27:77–84. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Yfanti C, Mengele K, Gkazepis A, Weirich
G, Giersig C, Kuo WL, Tang WJ, Rosner M and Schmitt M: Expression
of metalloprotease insulin-degrading enzyme insulysin in normal and
malignant human tissues. Int J Mol Med. 22:421–431. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Schmitt M, Mengele K, Schueren E, Sweep
FC, Foekens JA, Brünner N, Laabs J, Malik A and Harbeck N; European
Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Pathobiology
Group: European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer
(EORTC) Pathobiology Group standard operating procedure for the
preparation of human tumour tissue extracts suited for the
quantitative analysis of tissue-associated biomarkers. Eur J
Cancer. 43:835–844. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube
SE, Gion M and Clark GM; Statistics Subcommittee of the NCI-EORTC
Working Group on Cancer Diagnostics: Reporting recommendations for
tumor marker prognostic studies (REMARK). J Natl Cancer Inst.
97:1180–1184. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Altman DG, McShane LM, Sauerbrei W and
Taube SE: Reporting recommendations for tumor marker prognostic
studies REMARK. Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med.
9:e10012162012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Hothorn T: Maxstat: maximally selected
rank statistics. R package version 0.7-14.
|
|
51
|
Team RD CR: A language and environment for
statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing
Vienna Austria: 2012
|
|
52
|
Blum M, Feistel K, Thumberger T and
Schweickert A: The evolution and conservation of left-right
patterning mechanisms. Development. 141:1603–1613. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Tabin CJ: Tabin. Cell. 127:27–32. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Levin M: Levin. Mech Dev. 122:3–25. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Paska AV and Hudler P: Aberrant
methylation patterns in cancer: A clinical view. Biochem Med
(Zagreb). 25:161–176. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Ahmed D, Danielsen SA, Aagesen TH,
Bretthauer M, Thiis-Evensen E, Hoff G, Rognum TO, Nesbakken A,
Lothe RA and Lind GE: A tissue-based comparative effectiveness
analysis of biomarkers for early detection of colorectal tumors.
Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 3:e272012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Berghoff AS, Hainfellner JA, Marosi C and
Preusser M: Assessing MGMT methylation status and its current
impact on treatment in glioblastoma. CNS Oncol. 4:47–52. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Darwiche K, Zarogoulidis P, Baehner K,
Welter S, Tetzner R, Wohlschlaeger J, Theegarten D, Nakajima T and
Freitag L: Assessment of SHOX2 methylation in EBUS-TBNA specimen
improves accuracy in lung cancer staging. Ann Oncol. 24:2866–2870.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Dietrich D, Jung M, Puetzer S, Leisse A,
Holmes EE, Meller S, Uhl B, Schatz P, Ivascu C and Kristiansen G:
Diagnostic and prognostic value of SHOX2 and SEPT9 DNA methylation
and cytology in benign, paramalignant and malignant pleural
effusions. PLoS One. 8:e842252013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Ilse P, Biesterfeld S, Pomjanski N, Wrobel
C and Schramm M: Analysis of SHOX2 methylation as an aid to
cytology in lung cancer diagnosis. Cancer Genomics Proteomics.
11:251–258. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Székely B, Silber AL and Pusztai L: New
therapeutic strategies for triple-negative breast cancer. Oncology
(Williston Park). 31:130–137. 2017.
|
|
62
|
Fung FK, Chan DW, Liu VW, Leung TH, Cheung
AN and Ngan HY: Increased expression of PITX2 transcription factor
contributes to ovarian cancer progression. PLoS One. 7:e370762012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kapoor S: Kapoor. APMIS. 121:10112013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Liu Y, Huang Y and Zhu GZ: Cyclin A1 is a
transcriptional target of PITX2 and overexpressed in papillary
thyroid carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 384:221–227. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Toyota M, Kopecky KJ, Toyota MO, Jair KW,
Willman CL and Issa JP: Methylation profiling in acute myeloid
leukemia. Blood. 97:2823–2829. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Uhl B, Gevensleben H, Tolkach Y, Sailer V,
Majores M, Jung M, Meller S, Stein J, Ellinger J, Dietrich D, et
al: PITX2 DNA Methylation as biomarker for individualized risk
assessment of prostate cancer in core biopsies. J Mol Diagn.
19:107–114. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Wang Q, Li J, Wu W, Shen R, Jiang H, Qian
Y, Tang Y, Bai T, Wu S, Wei L, et al: Smad4-dependent suppressor
pituitary homeobox 2 promotes PPP2R2A-mediated inhibition of Akt
pathway in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget. 7:11208–11222.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhang JX, Chen ZH, Xu Y, Chen JW, Weng HW,
Yun M, Zheng ZS, Chen C, Wu BL, Li EM, et al: Downregulation of
microRNA-644a promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
aggressiveness and stem cell-like phenotype via dysregulation of
PITX2. Clin Cancer Res. 23:298–310. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Zhang JX, Tong ZT, Yang L, Wang F, Chai
HP, Zhang F, Xie MR, Zhang AL, Wu LM, Hong H, et al: PITX2: A
promising predictive biomarker of patients' prognosis and
chemoradioresistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J
Cancer. 132:2567–2577. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Sailer V, Gevensleben H, Dietrich J, Goltz
D, Kristiansen G, Bootz F and Dietrich D: Clinical performance
validation of PITX2 DNA methylation as prognostic biomarker in
patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One.
12:e01794122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
López JI, Angulo JC, Martín A,
Sánchez-Chapado M, González-Corpas A, Colás B and Ropero S: A DNA
hypermethylation profile reveals new potential biomarkers for the
evaluation of prognosis in urothelial bladder cancer. APMIS.
125:787–796. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Harris LN, Ismaila N, McShane LM, Andre F,
Collyar DE, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Hammond EH, Kuderer NM, Liu MC,
Mennel RG, et al: American Society of Clinical Oncology: Use of
biomarkers to guide decisions on adjuvant systemic therapy for
women with early-stage invasive breast cancer: American Society of
Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Oncol.
34:1134–1150. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wan Abdul, Rahman WF, Fauzi MH and Jaafar
H: Expression of DNA methylation marker of paired-like homeodomain
transcription factor 2 and growth receptors in invasive ductal
carcinoma of the breast. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:8441–8445.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Bologna-Molina R, Mikami T, Pereira-Prado
V, Pires FR, Carlos-Bregni R and Mosqueda-Taylor A: Primordial
odonto-genic tumor: An immunohistochemical profile. Med Oral Patol
Oral Cir Bucal. 22:e314-e3232017.
|
|
75
|
Huang Y, Guigon CJ, Fan J, Cheng SY and
Zhu GZ: Pituitary homeobox 2 (PITX2) promotes thyroid
carcinogenesis by activation of cyclin D2. Cell Cycle. 9:1333–1341.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Denkert C, Liedtke C, Tutt A and von
Minckwitz G: Molecular alterations in triple-negative breast
cancer-the road to new treatment strategies. Lancet. 389:2430–2442.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Lehmann BD, Bauer JA, Chen X, Sanders ME,
Chakravarthy AB, Shyr Y and Pietenpol JA: Identification of human
triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for
selection of targeted therapies. J Clin Invest. 121:2750–2767.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Ring BZ, Hout DR, Morris SW, Lawrence K,
Schweitzer BL, Bailey DB, Lehmann BD, Pietenpol JA and Seitz RS:
Generation of an algorithm based on minimal gene sets to clinically
subtype triple negative breast cancer patients. BMC Cancer.
16:1432016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Bianchini G, Balko JM, Mayer IA, Sanders
ME and Gianni L: Triple-negative breast cancer: Challenges and
opportunities of a heterogeneous disease. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
13:674–690. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Yadav BS, Sharma SC, Chanana P and Jhamb
S: Systemic treatment strategies for triple-negative breast cancer.
World J Clin Oncol. 5:125–133. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Burstein HJ: Patients with triple negative
breast cancer: Is there an optimal adjuvant treatment? Breast.
22(Suppl 2): S147–S148. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Christenson ES, James T, Agrawal V and
Park BH: Use of biomarkers for the assessment of
chemotherapy-induced cardiac toxicity. Clin Biochem. 48:223–235.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
83
|
Basso SM, Santeufemia DA, Fadda GM,
Tozzoli R, D'Aurizio F and Lumachi F: Advances in the treatment of
triple-negative early breast cancer. Med Chem. 12:268–272. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Wahba HA and El-Hadaad HA: Current
approaches in treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer
Biol Med. 12:106–116. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Yao H, He G, Yan S, Chen C, Song L, Rosol
TJ and Deng X: Triple-negative breast cancer: Is there a treatment
on the horizon. Oncotarget. 8:1913–1924. 2017.
|
|
86
|
Locatelli MA, Curigliano G and Eniu A:
Extended adjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer.
Breast Care (Basel). 12:152–158. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Liedtke C, Thill M, Jackisch C, Thomssen
C, Müller V and Janni W: AGO Recommendations for the diagnosis and
treatment of patients with early breast cancer: Update. Breast Care
(Basel). 12. pp. 172–183. 2017, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Mori H, Kubo M, Nishimura R, Osako T,
Arima N, Okumura Y, Okido M, Yamada M, Kai M, Kishimoto J, et al:
BRCAness as a biomarker for predicting prognosis and response to
anthracycline-based adjuvant chemotherapy for patients with
triple-negative breast cancer. PLoS One. 11:e01670162016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Bouchalova K, Svoboda M, Kharaishvili G,
Vrbkova J, Bouchal J, Trojanec R, Koudelakova V, Radova L, Cwiertka
K, Hajduch M, et al: BCL2 is an independent predictor of outcome in
basal-like triple-negative breast cancers treated with adjuvant
anthracycline-based chemotherapy. Tumour Biol. 36:4243–4252. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Duffy MJ, Napieralski R, Martens JW, Span
PN, Spyratos F, Sweep FC, Brunner N, Foekens JA and Schmitt M;
EORTC PathoBiology Group: Methylated genes as new cancer
biomarkers. Eur J Cancer. 45:335–346. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Pillai SG, Dasgupta N, Siddappa CM, Watson
MA, Fleming T, Trinkaus K and Aft R: Paired-like Homeodomain
Transcription factor 2 expression by breast cancer bone marrow
disseminated tumor cells is associated with early recurrent disease
development. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 153:507–517. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Dietrich D, Hasinger O, Liebenberg V,
Field JK, Kristiansen G and Soltermann A: DNA methylation of the
homeobox genes PITX2 and SHOX2 predicts outcome in non-small-cell
lung cancer patients. Diagn Mol Pathol. 21:93–104. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|