|
1
|
Dandawate PR, Subramaniam D, Jensen RA and
Anant S: Targeting cancer stem cells and signaling pathways by
phytochemicals: Novel approach for breast cancer therapy. Semin
Cancer Biol. 40–41:192–208. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vessoni AT, Filippi-Chiela EC, Menck CF
and Lenz G: Autophagy and genomic integrity. Cell Death Differ.
20:1444–1454. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mowers EE, Sharifi MN and Macleod KF:
Autophagy in cancer metastasis. Oncogene. 36:1619–1630. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Ruocco N, Costantini S and Costantini M:
Blue-print autophagy: Potential for cancer treatment. Mar Drugs.
14:142016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang C, Hu Q and Shen HM: Pharmacological
inhibitors of autophagy as novel cancer therapeutic agents.
Pharmacol Res. 105:164–175. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee JS, Kim YJ, Kim CL and Lee GM:
Differential induction of autophagy in caspase-3/7 down-regulating
and Bcl-2 overexpressing recombinant CHO cells subjected to sodium
butyrate treatment. J Biotechnol. 161:34–41. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
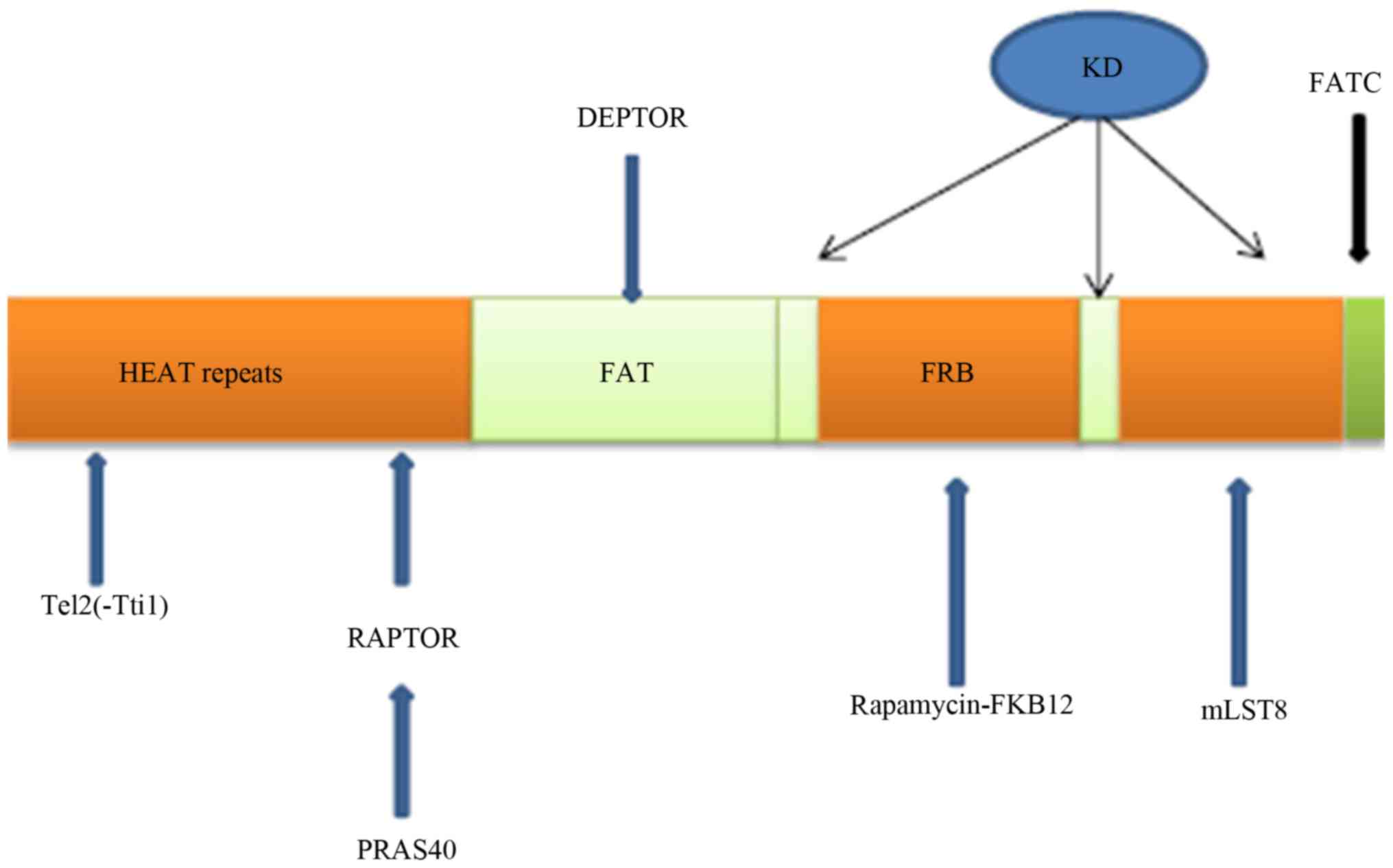
Knutson BA: Insights into the domain and
repeat architecture of target of rapamycin. J Struct Biol.
170:354–363. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sauer E, Imseng S, Maier T and Hall MN:
Conserved sequence motifs and the structure of the mTOR kinase
domain. Biochem Soc Trans. 41:889–895. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang H, Rudge DG, Koos JD, Vaidialingam B,
Yang HJ and Pavletich NP: mTOR kinase structure, mechanism and
regulation. Nature. 497:217–223. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim DH, Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Latek RR,
Guntur KV, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P and Sabatini DM: GbetaL, a
positive regulator of the rapamycin-sensitive pathway required for
the nutrient-sensitive interaction between raptor and mTOR. Mol
Cell. 11:895–904. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kaizuka T, Hara T, Oshiro N, Kikkawa U,
Yonezawa K, Takehana K, Iemura S, Natsume T and Mizushima N: Tti1
and Tel2 are critical factors in mammalian target of rapamycin
complex assembly. J Biol Chem. 285:20109–20116. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Takai H, Wang RC, Takai KK, Yang H and de
Lange T: Tel2 regulates the stability of PI3K-related protein
kinases. Cell. 131:1248–1259. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Peterson TR, Laplante M, Thoreen CC,
Sancak Y, Kang SA, Kuehl WM, Gray NS and Sabatini DM: DEPTOR is an
mTOR inhibitor frequently overexpressed in multiple myeloma cells
and required for their survival. Cell. 137:873–886. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wullschleger S, Loewith R and Hall MN: TOR
signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell. 124:471–484. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mammucari C, Milan G, Romanello V, Masiero
E, Rudolf R, Del Piccolo P, Burden SJ, Di Lisi R, Sandri C, Zhao J,
et al: FoxO3 controls autophagy in skeletal muscle in vivo. Cell
Metab. 6:458–471. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao J, Brault JJ, Schild A, Cao P, Sandri
M, Schiaffino S, Lecker SH and Goldberg AL: FoxO3 coordinately
activates protein degradation by the autophagic/lysosomal and
proteasomal pathways in atrophying muscle cells. Cell Metab.
6:472–483. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moscat J and Diaz-Meco MT: p62 at the
crossroads of autophagy, apoptosis, and cancer. Cell.
137:1001–1004. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sancak Y, Bar-Peled L, Zoncu R, Markhard
AL, Nada S and Sabatini DM: Ragulator-Rag complex targets mTORC1 to
the lysosomal surface and is necessary for its activation by amino
acids. Cell. 141:290–303. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sancak Y, Peterson TR, Shaul YD, Lindquist
RA, Thoreen CC, Bar-Peled L and Sabatini DM: The Rag GTPases bind
raptor and mediate amino acid signaling to mTORC1. Science.
320:1496–1501. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zoncu R, Bar-Peled L, Efeyan A, Wang S,
Sancak Y and Sabatini DM: mTORC1 senses lysosomal amino acids
through an inside-out mechanism that requires the vacuolar
H(+)-ATPase. Science. 334:678–683. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Settembre C, Zoncu R, Medina DL, Vetrini
F, Erdin S, Erdin S, Huynh T, Ferron M, Karsenty G, Vellard MC, et
al: A lysosome-to-nucleus signalling mechanism senses and regulates
the lysosome via mTOR and TFEB. EMBO J. 31:1095–1108. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Copetti T, Bertoli C, Dalla E, Demarchi F
and Schneider C: p65/RelA modulates BECN1 transcription and
autophagy. Mol Cell Biol. 29:2594–2608. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lu C, Wang W, Jia Y, Liu X, Tong Z and Li
B: Inhibition of AMPK/autophagy potentiates parthenolide-induced
apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. J Cell Biochem.
115:1458–1466. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,
Morrison SJ and Clarke MF: Prospective identification of
tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:3983–3988. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Abdal Dayem A, Choi HY, Yang GM, Kim K,
Saha SK and Cho SG: The anti-cancer effect of polyphenols against
breast cancer and cancer stem cells: Molecular mechanisms.
Nutrients. 8:581–618. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Ricardo S, Vieira AF, Gerhard R, Leitão D,
Pinto R, Cameselle-Teijeiro JF, Milanezi F, Schmitt F and Paredes
J: Breast cancer stem cell markers CD44, CD24 and ALDH1: Expression
distribution within intrinsic molecular subtype. J Clin Pathol.
64:937–946. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Idowu MO, Kmieciak M, Dumur C, Burton RS,
Grimes MM, Powers CN and Manjili MH: CD44(+)/CD24(−/low) cancer
stem/progenitor cells are more abundant in triple-negative invasive
breast carcinoma phenotype and are associated with poor outcome.
Hum Pathol. 43:364–373. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ahmed MA, Aleskandarany MA, Rakha EA,
Moustafa RZ, Benhasouna A, Nolan C, Green AR, Ilyas M and Ellis IO:
A CD44−/CD24+ phenotype is a poor prognostic
marker in early invasive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
133:979–995. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Fonseca NA, Cruz AF, Moura V, Simões S and
Moreira JN: The cancer stem cell phenotype as a determinant factor
of the heterotypic nature of breast tumors. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
113:111–121. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ingham PW and McMahon AP: Hedgehog
signaling in animal development: Paradigms and principles. Genes
Dev. 15:3059–3087. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
McMahon AP, Ingham PW and Tabin CJ:
Developmental roles and clinical significance of hedgehog
signaling. Curr Top Dev Biol. 53:1–114. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Murone M, Rosenthal A and de Sauvage FJ:
Sonic hedgehog signaling by the patched-smoothened receptor
complex. Curr Biol. 9:76–84. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bray SJ: Notch signalling: A simple
pathway becomes complex. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:678–689. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ishii H, Iwatsuki M, Ieta K, Ohta D,
Haraguchi N, Mimori K and Mori M: Cancer stem cells and
chemoradiation resistance. Cancer Sci. 99:1871–1877. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang M, Zhang J, Huang Y, Ji S, Shao G,
Feng S, Chen D, Zhao K, Wang Z and Wu A: Cancer-associated
fibroblasts autophagy enhances progression of triple-negative
breast cancer cells. Med Sci Monit. 23:3904–3912. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sun R, Shen S, Zhang YJ, Xu CF, Cao ZT,
Wen LP and Wang J: Nanoparticle-facilitated autophagy inhibition
promotes the efficacy of chemotherapeutics against breast cancer
stem cells. Biomaterials. 103:44–55. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liang DH, Choi DS, Ensor JE, Kaipparettu
BA, Bass BL and Chang JC: The autophagy inhibitor chloroquine
targets cancer stem cells in triple negative breast cancer by
inducing mitochondrial damage and impairing DNA break repair.
Cancer Lett. 376:249–258. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
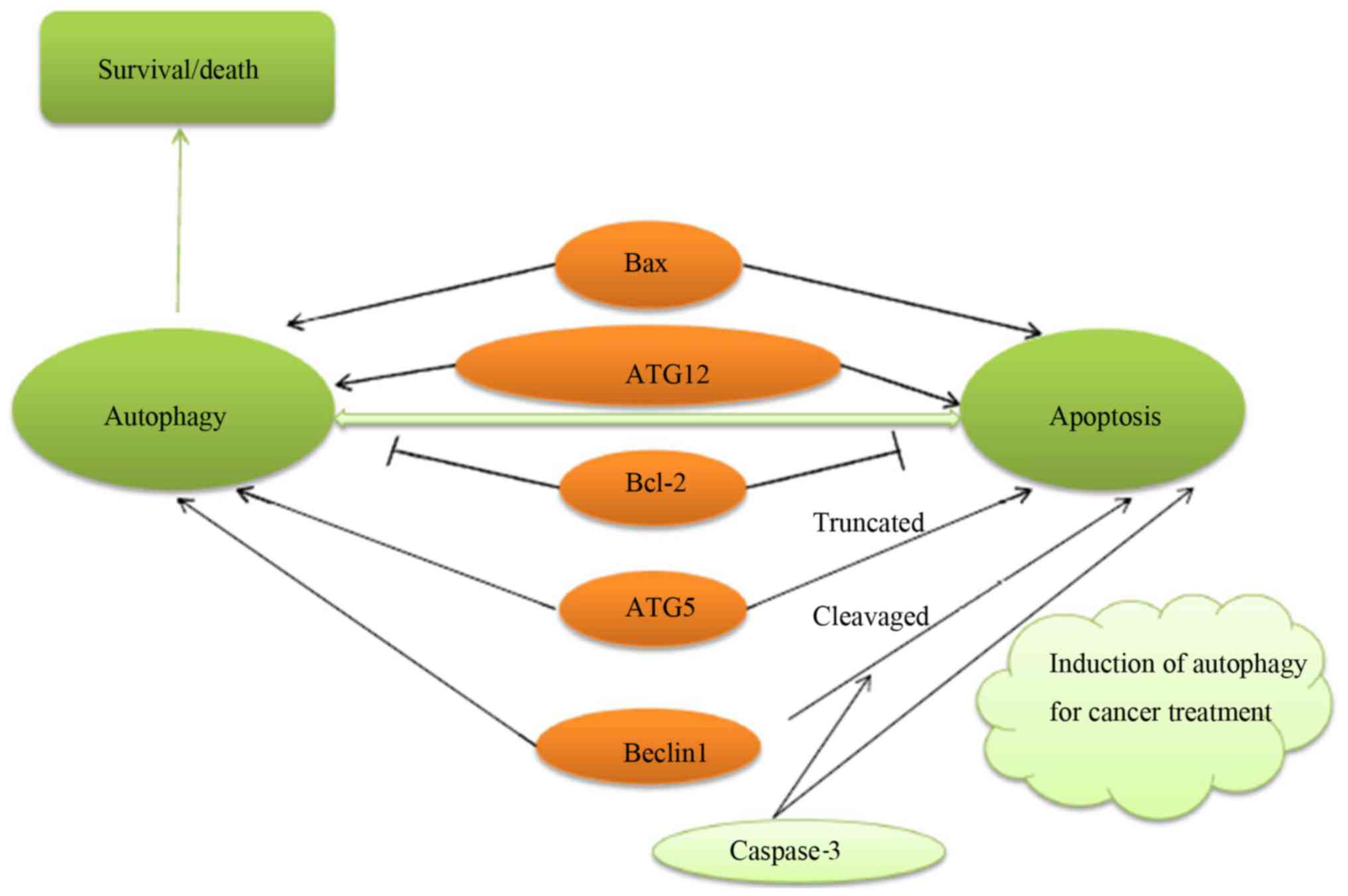
Bincoletto C, Bechara A, Pereira GJS,
Santos CP, Antunes F, Peixoto da-Silva J, Muler M, Gigli RD,
Monteforte PT, Hirata H, et al: Interplay between apoptosis and
autophagy, a challenging puzzle: New perspectives on antitumor
chemotherapies. Chem Biol Interact. 206:279–288. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yousefi S, Perozzo R, Schmid I, Ziemiecki
A, Schaffner T, Scapozza L, Brunner T and Simon HU:
Calpain-mediated cleavage of Atg5 switches autophagy to apoptosis.
Nat Cell Biol. 8:1124–1132. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
DeNardo DG, Barreto JB, Andreu P, Vasquez
L, Tawfik D, Kolhatkar N and Coussens LM: CD4(+) T cells regulate
pulmonary metastasis of mammary carcinomas by enhancing protumor
properties of macrophages. Cancer Cell. 16:91–102. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mukhopadhyay S, Panda PK, Sinha N, Das DN
and Bhutia SK: Autophagy and apoptosis: Where do they meet?
Apoptosis. 19:555–566. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yao D, Wang P, Zhang J, Fu L, Ouyang L and
Wang J: Deconvoluting the relationships between autophagy and
metastasis for potential cancer therapy. Apoptosis. 21:683–698.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Han Q, Deng Y, Chen S, Chen R, Yang M,
Zhang Z, Sun X, Wang W, He Y, Wang F, et al: Downregulation of
ATG5-dependent macroautophagy by chaperone-mediated autophagy
promotes breast cancer cell metastasis. Sci Rep. 7:47592017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kongara S, Kravchuk O, Teplova I, Lozy F,
Schulte J, Moore D, Barnard N, Neumann CA, White E and Karantza V:
Autophagy regulates keratin 8 homeostasis in mammary epithelial
cells and in breast tumors. Mol Cancer Res. 8:873–884. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kuraishy A, Karin M and Grivennikov SI:
Tumor promotion via injury- and death-induced inflammation.
Immunity. 35:467–477. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kung CP, Budina A, Balaburski G,
Bergenstock MK and Murphy M: Autophagy in tumor suppression and
cancer therapy. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 21:71–100. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
White E and DiPaola RS: The double-edged
sword of autophagy modulation in cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
15:5308–5316. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Choi KS: Autophagy and cancer. Exp Mol
Med. 44:109–120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Denton D, Nicolson S and Kumar S: Cell
death by autophagy: Facts and apparent artefacts. Cell Death
Differ. 19:87–95. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
51
|
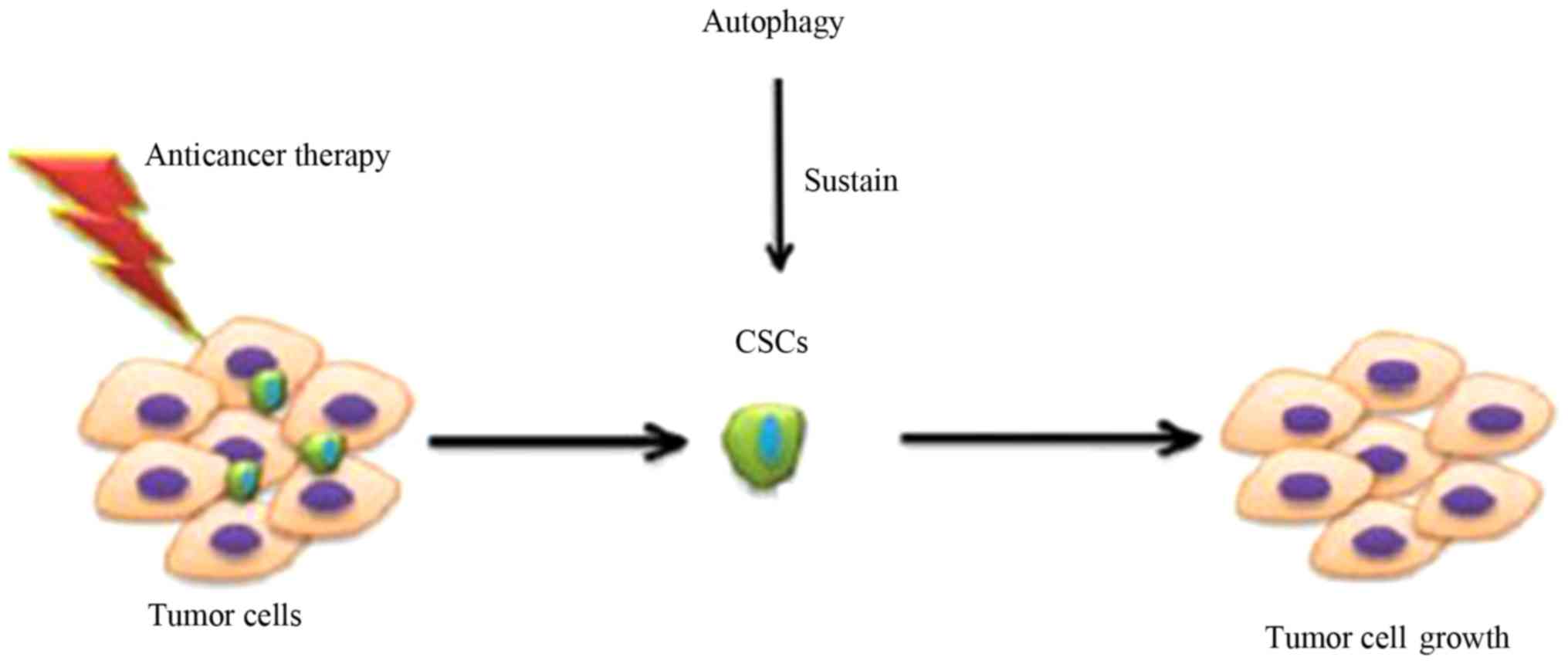
Maycotte P, Jones KL, Goodall ML, Thorburn
J and Thorburn A: Autophagy supports breast cancer stem cell
maintenance by regulating IL6 secretion. Mol Cancer Res.
13:651–658. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wolf J, Dewi DL, Fredebohm J,
Müller-Decker K, Flechtenmacher C, Hoheisel JD and Boettcher M: A
mammosphere formation RNAi screen reveals that ATG4A promotes a
breast cancer stem-like phenotype. Breast Cancer Res. 15:R1092013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gong C, Bauvy C, Tonelli G, Yue W,
Deloménie C, Nicolas V, Zhu Y, Domergue V, Marin-Esteban V,
Tharinger H, et al: Beclin 1 and autophagy are required for the
tumorigenicity of breast cancer stem-like/progenitor cells.
Oncogene. 32:2261–2272. 1–11. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
54
|
Zhao Y, Huang Q, Yang J, Lou M, Wang A,
Dong J, Qin Z and Zhang T: Autophagy impairment inhibits
differentiation of glioma stem/progenitor cells. Brain Res.
1313:250–258. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Singh BN, Kumar D, Shankar S and
Srivastava RK: Rottlerin induces autophagy which leads to apoptotic
cell death through inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in human
pancreatic cancer stem cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 84:1154–1163.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kumar D, Shankar S and Srivastava RK:
Rottlerin-induced autophagy leads to the apoptosis in breast cancer
stem cells: Molecular mechanisms. Mol Cancer. 12:1712013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wei MF, Chen MW, Chen KC, Lou PJ, Lin SY,
Hung SC, Hsiao M, Yao CJ and Shieh MJ: Autophagy promotes
resistance to photodynamic therapy-induced apoptosis selectively in
colorectal cancer stem-like cells. Autophagy. 10:1179–1192. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yue W, Hamaï A, Tonelli G, Bauvy C,
Nicolas V, Tharinger H, Codogno P and Mehrpour M: Inhibition of the
autophagic flux by salinomycin in breast cancer
stem-like/progenitor cells interferes with their maintenance.
Autophagy. 9:714–729. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chiang GG and Abraham RT: Targeting the
mTOR signaling network in cancer. Trends Mol Med. 13:433–442. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Xu K, Liu P and Wei W: mTOR signaling in
tumorigenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1846:638–654. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Mateo F, Arenas EJ, Aguilar H,
Serra-Musach J, de Garibay GR, Boni J, Maicas M, Du S, Iorio F,
Herranz-Ors C, et al: Stem cell-like transcriptional reprogramming
mediates metastatic resistance to mTOR inhibition. Oncogene.
36:2737–2749. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
62
|
Zhang L, Fu L, Zhang S, Zhang J, Zhao Y,
Zheng Y, He G, Yang S, Ouyang L and Liu B: Discovery of a small
molecule targeting ULK1-modulated cell death of triple negative
breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. Chem Sci (Camb). 8:2687–2701.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Jang JE, Eom JI, Jeung HK, Cheong JW, Lee
JY, Kim JS and Min YH: Targeting AMPK-ULK1-mediated autophagy for
combating BET inhibitor resistance in acute myeloid leukemia stem
cells. Autophagy. 13:761–762. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhou Y, Rucker EB III and Zhou BP:
Autophagy regulation in the development and treatment of breast
cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 48:60–74. 2016.
|
|
65
|
Yeo SK, Wen J, Chen S and Guan JL:
Autophagy differentially regulates distinct breast cancer stem-like
cells in murine models via EGFR/Stat3 and Tgfβ/Smad signaling.
Cancer Res. 76:3397–3410. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Nagy P, Kovács L, Sándor GO and Juhász G:
Stem-cell-specific endocytic degradation defects lead to intestinal
dysplasia in Drosophila. Dis Model Mech. 9:501–512. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Liu K, Zhao Q, Liu P, Cao J, Gong J, Wang
C, Wang W, Li X, Sun H, Zhang C, et al: ATG3-dependent autophagy
mediates mitochondrial homeostasis in pluripotency acquirement and
maintenance. Autophagy. 12:2000–2008. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhang L, Li J, Ouyang L, Liu B and Cheng
Y: Unraveling the roles of Atg4 proteases from autophagy modulation
to targeted cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 373:19–26. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Antonelli M, Strappazzon F, Arisi I,
Brandi R, D'Onofrio M, Sambucci M, Manic G, Vitale I, Barilà D and
Stagni V: ATM kinase sustains breast cancer stem-like cells by
promoting ATG4C expression and autophagy. Oncotarget.
8:21692–21709. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Liu H, He Z, von Rütte T, Yousefi S,
Hunger RE and Simon HU: Down-regulation of autophagy-related
protein 5 (ATG5) contributes to the pathogenesis of early-stage
cutaneous melanoma. Sci Transl Med. 5:202ra1232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Debnath J: The multifaceted roles of
autophagy in tumors-implications for breast cancer. J Mammary Gland
Biol Neoplasia. 16:173–187. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Chaterjee M and van Golen KL: Breast
cancer stem cells survive periods of farnesyl-transferase
inhibitor-induced dormancy by undergoing autophagy. Bone Marrow
Res. 2011:3629382011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Memni H, Macherki Y, Klayech Z,
Ben-Haj-Ayed A, Farhat K, Remadi Y, Gabbouj S, Mahfoudh W, Bouzid
N, Bouaouina N, et al: E-cadherin genetic variants predict survival
outcome in breast cancer patients. J Transl Med. 14:3202016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhuang W, Li B, Long L, Chen L, Huang Q
and Liang Z: Induction of autophagy promotes differentiation of
glioma-initiating cells and their radiosensitivity. Int J Cancer.
129:2720–2731. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Qin Z, Xue J, He Y, Ma H, Jin G, Chen J,
Hu Z, Liu X and Shen H: Potentially functional polymorphisms in
ATG10 are associated with risk of breast cancer in a Chinese
population. Gene. 527:491–495. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Sanchez CG, Penfornis P, Oskowitz AZ,
Boonjindasup AG, Cai DZ, Dhule SS, Rowan BG, Kelekar A, Krause DS
and Pochampally RR: Activation of autophagy in mesenchymal stem
cells provides tumor stromal support. Carcinogenesis. 32:964–972.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Cufí S, Vazquez-Martin A,
Oliveras-Ferraros C, Corominas-Faja B, Urruticoechea A,
Martin-Castillo B and Menendez JA: Autophagy-related gene 12
(ATG12) is a novel determinant of primary resistance to
HER2-targeted therapies: Utility of transcriptome analysis of the
autophagy interactome to guide breast cancer treatment. Oncotarget.
3:1600–1614. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Chang SJ, Ou-Yang F, Tu HP, Lin CH, Huang
SH, Kostoro J, Hou MF, Chai CY and Kwan AL: Decreased expression of
autophagy protein LC3 and stemness
(CD44+/CD24−/low) indicate poor prognosis in
triple-negative breast cancer. Hum Pathol. 48:48–55. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Carpenter RL, Sirkisoon S, Zhu D, Rimkus
T, Harrison A, Anderson A, Paw I, Qasem S, Xing F, Liu Y, et al:
Combined inhibition of AKT and HSF1 suppresses breast cancer stem
cells and tumor growth. Oncotarget. 8:73947–73963. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Petherick KJ, Williams AC, Lane JD,
Ordóñez-Morán P, Huelsken J, Collard TJ, Smartt HJ, Batson J, Malik
K, Paraskeva C, et al: Autolysosomal β-catenin degradation
regulates Wnt-autophagy-p62 crosstalk. EMBO J. 32:1903–1916. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Wang Y, Han C, Lu L, Magliato S and Wu T:
Hedgehog signaling pathway regulates autophagy in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology. 58:995–1010. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Espina V and Liotta LA: What is the
malignant nature of human ductal carcinoma in situ? Nat Rev Cancer.
11:68–75. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Yang H, Zheng Y, Zhang Y, Cao Z and Jiang
Y: Mesenchymal stem cells derived from multiple myeloma patients
protect against chemotherapy through autophagy-dependent activation
of NF-κB signaling. Leuk Res. 60:82–88. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Huang S, Wang D, Zhang S, Huang X, Wang D,
Ijaz M and Shi Y: Tunicamycin potentiates paclitaxel-induced
apoptosis through inhibition of PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways in
breast cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 80:685–696. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Sharma N, Thomas S, Golden EB, Hofman FM,
Chen TC, Petasis NA, Schönthal AH and Louie SG: Inhibition of
autophagy and induction of breast cancer cell death by mefloquine,
an antimalarial agent. Cancer Lett. 326:143–154. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Ma YW, Liu YZ and Pan JX: Verteporfin
induces apoptosis and eliminates cancer stem-like cells in uveal
melanoma in the absence of light activation. Am J Cancer Res.
6:2816–2830. 2016.
|
|
87
|
Shi TT, Yu XX, Yan LJ and Xiao HT:
Research progress of hydroxychloroquine and autophagy inhibitors on
cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 79:287–294. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Solomon VR, Almnayan D and Lee H: Design,
synthesis and characterization of novel quinacrine analogs that
preferentially kill cancer over non-cancer cells through the
down-regulation of Bcl-2 and up-regulation of Bax and Bad. Eur J
Med Chem. 137:156–166. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Siddharth S, Nayak D, Nayak A, Das S and
Kundu CN: ABT-888 and quinacrine induced apoptosis in metastatic
breast cancer stem cells by inhibiting base excision repair via
adenomatous polyposis coli. DNA Repair (Amst). 45:44–55. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Mishra P, Dauphinee AN, Ward C, Sarkar S,
Gunawardena AHLAN and Manjithaya R: Discovery of pan autophagy
inhibitors through a high-throughput screen highlights
macro-autophagy as an evolutionarily conserved process across 3
eukaryotic kingdoms. Autophagy. 13:1556–1572. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Liang S, Chen Z, Jiang G, Zhou Y, Liu Q,
Su Q, Wei W, Du J and Wang H: Activation of GPER suppresses
migration and angiogenesis of triple negative breast cancer via
inhibition of NF-κB/IL-6 signals. Cancer Lett. 386:12–23. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Torrente E, Parodi C, Ercolani L, De Mei
C, Ferrari A, Scarpelli R and Grimaldi B: Synthesis and in vitro
anticancer activity of the first cass of dual inhibitors of
REV-ERBβ and autophagy. J Med Chem. 58:5900–5915. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhou X, Yue GG, Chan AM, Tsui SK, Fung KP,
Sun H, Pu J and Lau CB: Eriocalyxin B, a novel autophagy inducer,
exerts anti-tumor activity through the suppression of
Akt/mTOR/p70S6K signaling pathway in breast cancer. Biochem
Pharmacol. 142:58–70. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Wong VKW, Zeng W, Chen J, Yao XJ, Leung
ELH, Wang QQ, Chiu P, Ko BCB and Law BYK: Tetrandrine, an activator
of autophagy, induces autophagic cell death via PKC-α inhibition
and mTOR-dependent mechanisms. Front Pharmacol. 8:3512017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Han H, Li J, Feng X, Zhou H, Guo S and
Zhou W: Autophagy-related genes are induced by histone deacetylase
inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid via the activation of
cathepsin B in human breast cancer cells. Oncotarget.
8:53352–53365. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Chen X, Yu X, Chen J, Yang Z, Shao Z,
Zhang Z, Guo X and Feng Y: Radiotherapy can improve the
disease-free survival rate in triple-negative breast cancer
patients with T1-T2 disease and one to three positive lymph nodes
after mastectomy. Oncologist. 18:141–147. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Chen X, Yu X, Chen J, Zhang Z, Tuan J,
Shao Z, Guo X and Feng Y: Analysis in early stage triple-negative
breast cancer treated with mastectomy without adjuvant
radiotherapy: Patterns of failure and prognostic factors. Cancer.
119:2366–2374. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Liu EY, Xu N, O'Prey J, Lao LY, Joshi S,
Long JS, O'Prey M, Croft DR, Beaumatin F, Baudot AD, et al: Loss of
autophagy causes a synthetic lethal deficiency in DNA repair. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:773–778. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Zhou ZR, Yang ZZ, Wang SJ, Zhang L, Luo
JR, Feng Y, Yu XL, Chen XX and Guo XM: The Chk1 inhibitor MK-8776
increases the radiosensitivity of human triple-negative breast
cancer by inhibiting autophagy. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 38:513–523.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Davison Z, de Blacquière GE, Westley BR
and May FEB: Insulin-like growth factor-dependent proliferation and
survival of triple-negative breast cancer cells: Implications for
therapy. Neoplasia. 13:504–515. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Wu W, Ma J, Shao N, Shi Y, Liu R, Li W,
Lin Y and Wang S: Co-targeting IGF-1R and autophagy enhances the
effects of cell growth suppression and apoptosis induced by the
IGF-1R inhibitor NVP-AEW541 in triple-negative breast cancer cells.
PLoS One. 12:e01692292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Maxfield KE, Macion J, Vankayalapati H and
Whitehurst AW: SIK2 restricts autophagic flux to support
triple-negative breast cancer survival. Mol Cell Biol.
36:3048–3057. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Gao J, Fan M, Peng S, Zhang M, Xiang G, Li
X, Guo W, Sun Y, Wu X, Wu X, et al: Small-molecule RL71-triggered
excessive autophagic cell death as a potential therapeutic strategy
in triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 8:e30492017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Zhang P, Liu X, Li H, Chen Z, Yao X, Jin J
and Ma X: TRPC5-induced autophagy promotes drug resistance in
breast carcinoma via CaMKKβ/AMPKα/mTOR pathway. Sci Rep.
7:31582017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Liu Z, Shi A, Song D, Han B, Zhang Z, Ma
L, Liu D and Fan Z: Resistin confers resistance to
doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cells through
autophagy induction. Am J Cancer Res. 7:574–583. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Poillet-Perez L, Jacquet M, Hervouet E,
Gauthier T, Fraichard A, Borg C, Pallandre JR, Gonzalez BJ, Ramdani
Y, Boyer-Guittaut M, et al: GABARAPL1 tumor suppressive function is
independent of its conjugation to autophagosomes in MCF-7 breast
cancer cells. Oncotarget. 8:55998–56020. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Rodríguez CE, Reidel SI, Bal de Kier Joffé
ED, Jasnis MA and Fiszman GL: Autophagy protects from
trastuzumab-induced cytotoxicity in HER2 overexpressing breast
tumor spheroids. PLoS One. 10:e01379202015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Zambrano J, Yeh ES and Zambrano J:
Autophagy and apoptotic crosstalk: Mechanism of therapeutic
resistance in HER2-positive breast cncer. Breast Cancer (Auckl).
10:13–23. 2016.
|
|
109
|
Cufí S, Vazquez-Martin A,
Oliveras-Ferraros C, Corominas-Faja B, Cuyàs E, López-Bonet E,
Martin-Castillo B, Joven J and Menendez JA: The anti-malarial
chloroquine overcomes primary resistance and restores sensitivity
to trastuzumab in HER2-positive breast cancer. Sci Rep. 3:24692013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Garbar C, Mascaux C, Giustiniani J,
Merrouche Y and Bensussan A: Chemotherapy treatment induces an
increase of autophagy in the luminal breast cancer cell MCF7, but
not in the triple-negative MDA-MB231. Sci Rep. 7:72012017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Maycotte P, Gearheart CM, Barnard R, Aryal
S, Mulcahy Levy JM, Fosmire SP, Hansen RJ, Morgan MJ, Porter CC,
Gustafson DL, et al: STAT3-mediated autophagy dependence identifies
subtypes of breast cancer where autophagy inhibition can be
efficacious. Cancer Res. 74:2579–2590. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Wang S, Wang K, Wang H, Han J and Sun H:
Autophagy is essential for flavopiridol-induced cytotoxicity
against MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 16:9715–9720. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Chang CT, Korivi M, Huang HC, Thiyagarajan
V, Lin KY, Huang PJ, Liu JY, Hseu YC and Yang HL: Inhibition of ROS
production, autophagy or apoptosis signaling reversed the
anticancer properties of Antrodia salmonea in triple-negative
breast cancer (MDA-MB-231) cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 103:1–17.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Zheng N, Liu L, Liu WW, Li F, Hayashi T,
Tashiro SI, Onodera S and Ikejima T: Crosstalk of ROS/RNS and
autophagy in silibinin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 human breast
cancer cells in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 38:277–289. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
115
|
Liu ZY, He KW, Song XG, Wang XZ, Zhuo PY,
Wang XW, Ma QH, Huo ZJ and Yu ZY: Effect of autophagy inhibitor
combined with EGFR inhibitor on triple-negative breast cancer
MDA-MB-468 and MDA-MB-231 cells. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi.
38:417–424. 2016.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Tran AT, Ramalinga M, Kedir H, Clarke R
and Kumar D: Autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine potentiates
apoptosis induced by dietary tocotrienols in breast cancer cells.
Eur J Nutr. 54:265–272. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Liu Z, He K, Ma Q, Yu Q, Liu C, Ndege I,
Wang X and Yu Z: Autophagy inhibitor facilitates gefitinib
sensitivity in vitro and in vivo by activating mitochondrial
apoptosis in triple negative breast cancer. PLoS One.
12:e01776942017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Wang H, Wang W, Xu Y, Yang Y, Chen X, Quan
H and Lou L: Aberrant intracellular metabolism of T-DM1 confers
T-DM1 resistance in human epidermal growth factor receptor
2-positive gastric cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 108:1458–1468. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Gong C, Hu C, Gu F, Xia Q, Yao C, Zhang L,
Qiang L, Gao S and Gao Y: Co-delivery of autophagy inhibitor ATG7
siRNA and docetaxel for breast cancer treatment. J Control Release.
266:272–286. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Shen P, Chen M, He M, Chen L, Song Y, Xiao
P, Wan X, Dai F, Pan T and Wang Q: Inhibition of ERα/ERK/P62
cascades induces 'autophagic switch' in the estrogen
receptor-positive breast cancer cells exposed to gemcitabine.
Oncotarget. 7:48501–48516. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Li HC, Xia ZH, Chen YF, Yang F, Feng W,
Cai H, Mei Y, Jiang YM, Xu K and Feng DX: Cantharidin inhibits the
growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells by suppressing
autophagy and inducing apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 43:1829–1840. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Gu Y, Chen T, Li G, Xu C, Xu Z, Zhang J,
He K, Zheng L, Guan Z, Su X, et al: Lower Beclin 1 downregulates
HER2 expression to enhance tamoxifen sensitivity and predicts a
favorable outcome for ER positive breast cancer. Oncotarget.
8:52156–52177. 2016.
|