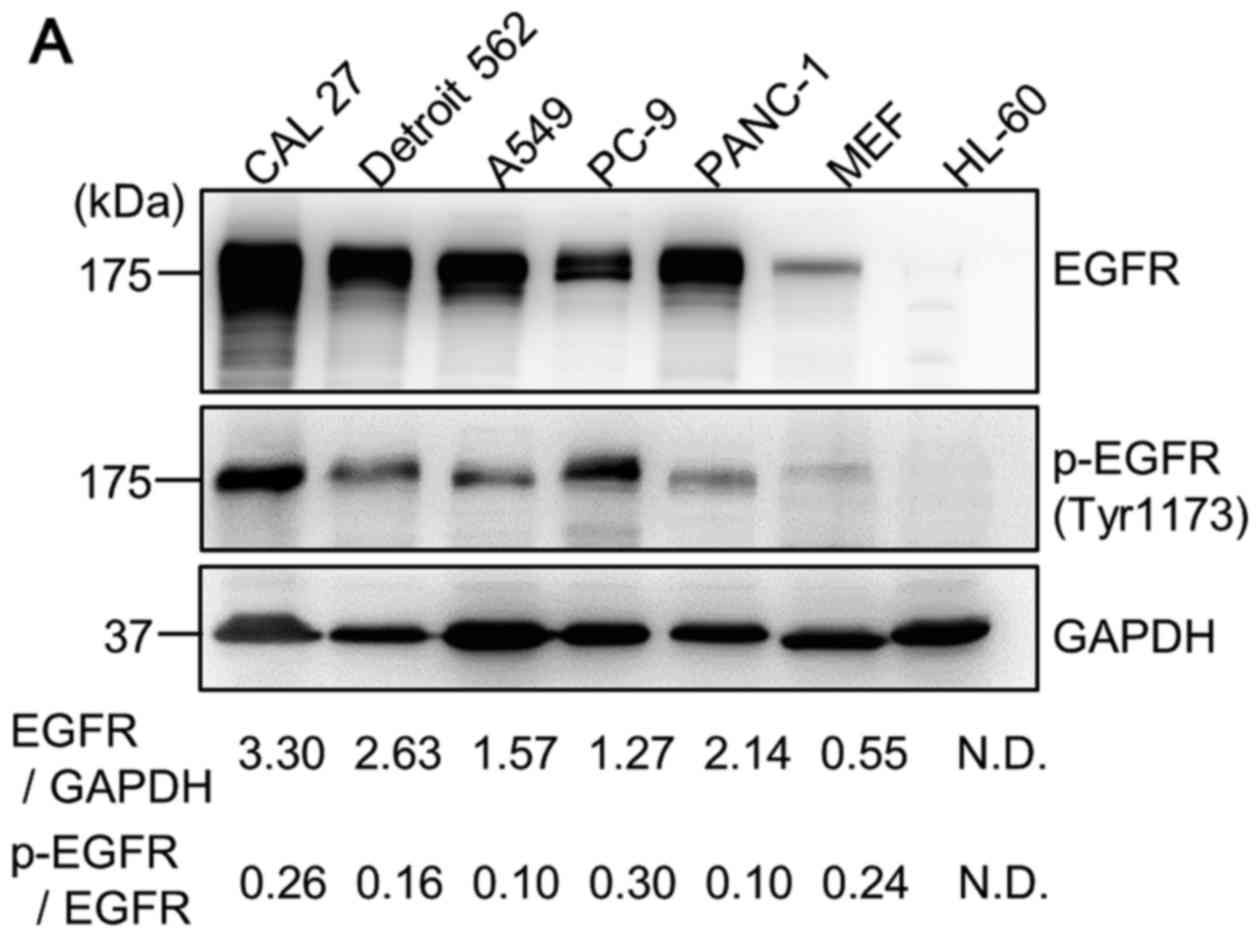
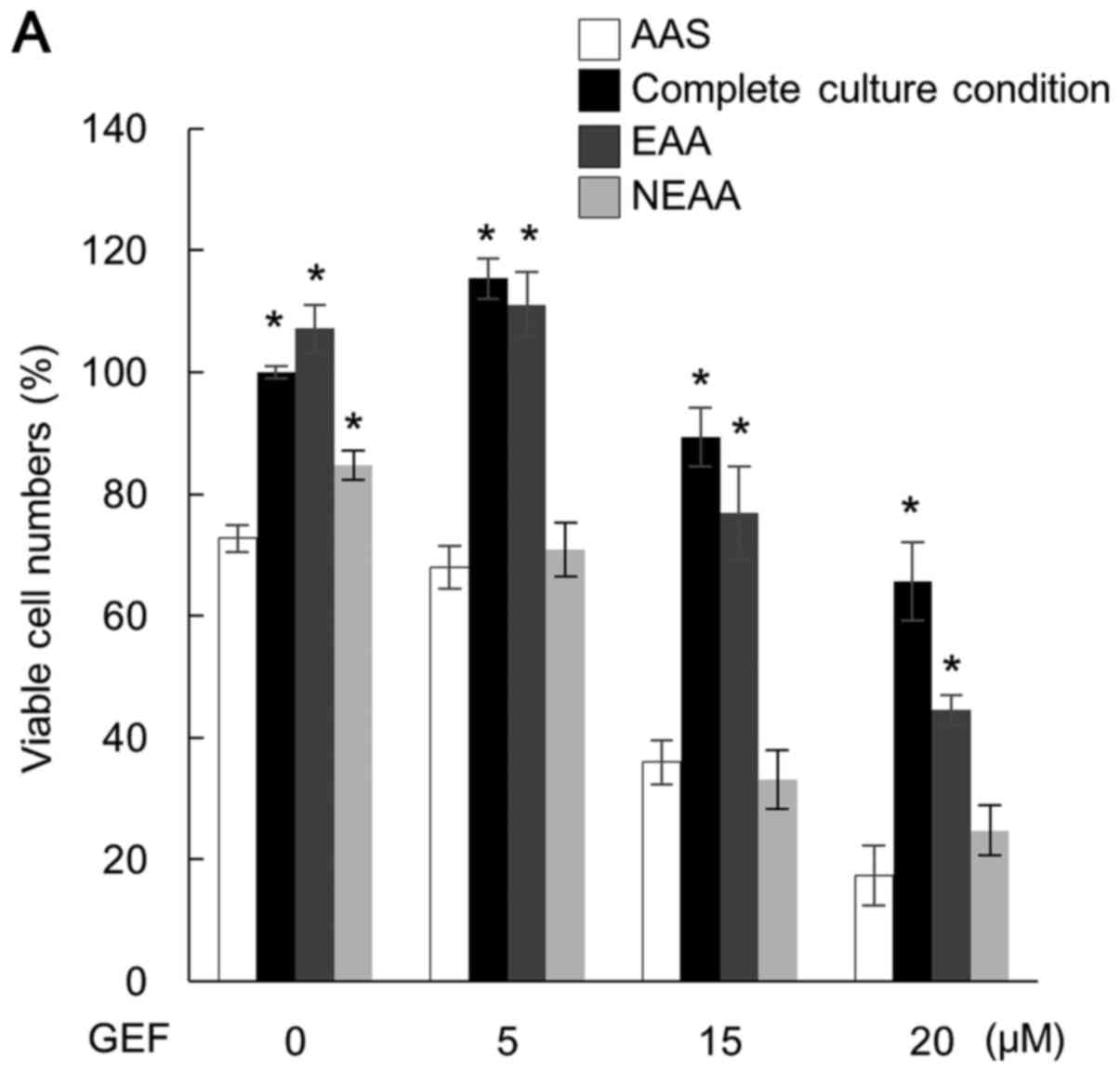
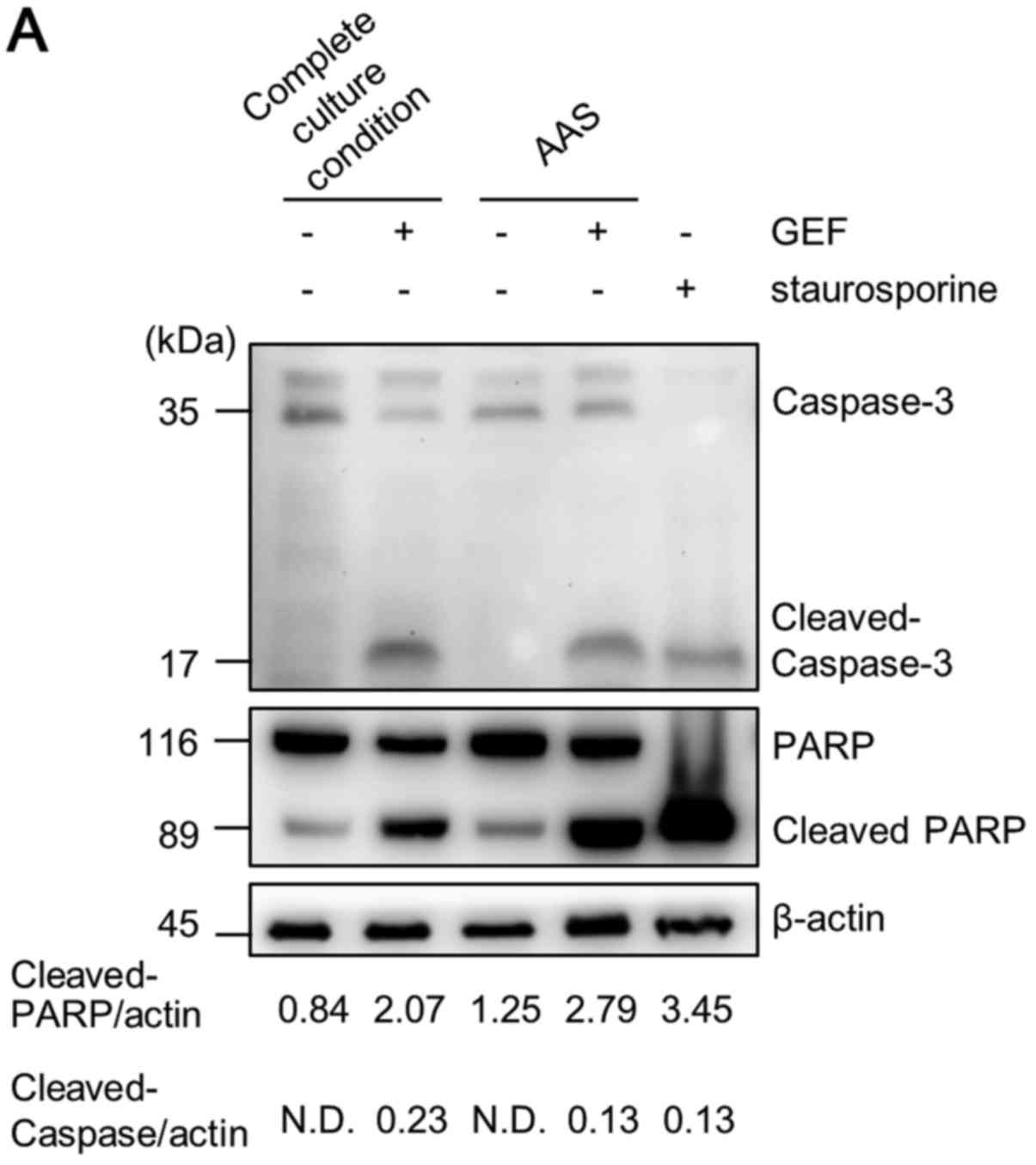
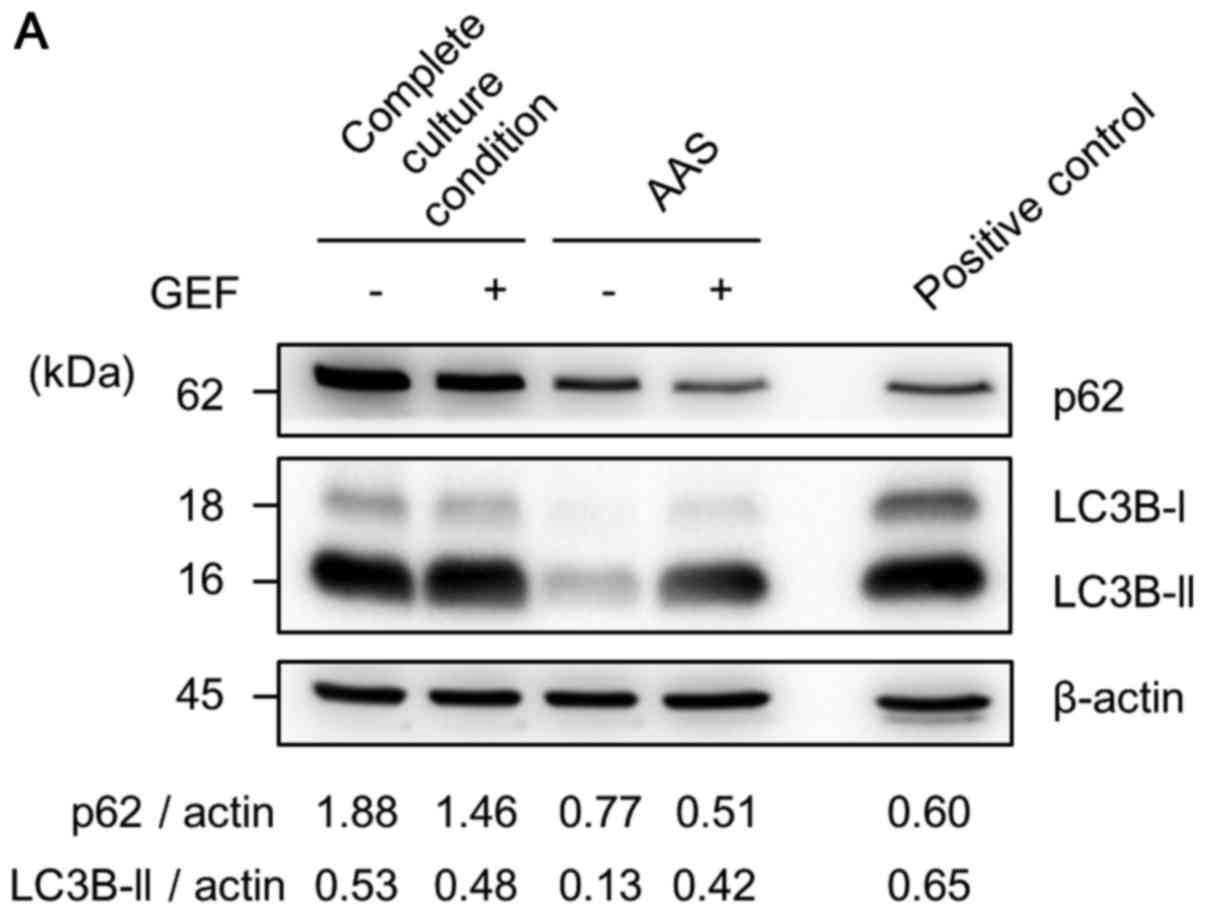
|
1
|
Kuma A and Mizushima N: Physiological role
of autophagy as an intracellular recycling system: With an emphasis
on nutrient metabolism. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 21:683–690. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Segawa H, Fukasawa Y, Miyamoto K, Takeda
E, Endou H and Kanai Y: Identification and functional
characterization of a Na+-independent neutral amino acid
transporter with broad substrate selectivity. J Biol Chem.
274:19745–19751. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yanagida O, Kanai Y, Chairoungdua A, Kim
DK, Segawa H, Nii T, Cha SH, Matsuo H, Fukushima J, Fukasawa Y, et
al: Human L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1): Characterization
of function and expression in tumor cell lines. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1514:291–302. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Oda K, Hosoda N, Endo H, Saito K,
Tsujihara K, Yamamura M, Sakata T, Anzai N, Wempe MF, Kanai Y, et
al: L-type amino acid transporter 1 inhibitors inhibit tumor cell
growth. Cancer Sci. 101:173–179. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sakata T, Ferdous G, Tsuruta T, Satoh T,
Baba S, Muto T, Ueno A, Kanai Y, Endou H and Okayasu I: L-type
amino-acid transporter 1 as a novel biomarker for high-grade
malignancy in prostate cancer. Pathol Int. 59:7–18. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Galluzzi L, Pietrocola F, Levine B and
Kroemer G: Metabolic control of autophagy. Cell. 159:1263–1276.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
White E: Deconvoluting the
context-dependent role for autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
12:401–410. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Han W, Pan H, Chen Y, Sun J, Wang Y, Li J,
Ge W, Feng L, Lin X, Wang X, et al: EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors
activate autophagy as a cytoprotective response in human lung
cancer cells. PLoS One. 6:e186912011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fung C, Chen X, Grandis JR and Duvvuri U:
EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibition induces autophagy in cancer cells.
Cancer Biol Ther. 13:1417–1424. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sugita S, Ito K, Yamashiro Y, Moriya S,
Che XF, Yokoyama T, Hiramoto M and Miyazawa K: EGFR-independent
autophagy induction with gefitinib and enhancement of its cytotoxic
effect by targeting autophagy with clarithromycin in non-small cell
lung cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 461:28–34. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mukai S, Moriya S, Hiramoto M, Kazama H,
Kokuba H, Che XF, Yokoyama T, Sakamoto S, Sugawara A, Sunazuka T,
et al: Macrolides sensitize EGFR-TKI-induced non-apoptotic cell
death via blocking autophagy flux in pancreatic cancer cell lines.
Int J Oncol. 48:45–54. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wei Y, Zou Z, Becker N, Anderson M,
Sumpter R, Xiao G, Kinch L, Koduru P, Christudass CS, Veltri RW, et
al: EGFR-mediated Beclin 1 phosphorylation in autophagy
suppression, tumor progression, and tumor chemoresistance. Cell.
154:1269–1284. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sordella R, Bell DW, Haber DA and
Settleman J: Gefitinib-sensitizing EGFR mutations in lung cancer
activate anti-apoptotic pathways. Science. 305:1163–1167. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ciardiello F and Tortora G: EGFR
antagonists in cancer treatment. N Engl J Med. 358:1160–1174. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tan X, Thapa N, Sun Y and Anderson RA: A
kinase-independent role for EGF receptor in autophagy initiation.
Cell. 160:145–160. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Moriya S, Che XF, Komatsu S, Abe A,
Kawaguchi T, Gotoh A, Inazu M, Tomoda A and Miyazawa K: Macrolide
antibiotics block autophagy flux and sensitize to bortezomib via
endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated CHOP induction in myeloma
cells. Int J Oncol. 42:1541–1550. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hirasawa K, Moriya S, Miyahara K, Kazama
H, Hirota A, Takemura J, Abe A, Inazu M, Hiramoto M, Tsukahara K,
et al: Macrolide antibiotics exhibit cytotoxic effect under amino
acid-depleted culture condition by blocking autophagy flux in head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. PLoS One.
11:e01645292016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim YC and Guan KL: mTOR: A pharmacologic
target for autophagy regulation. J Clin Invest. 125:25–32. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B and Guan KL:
AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of
Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. 13:132–141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dalle Pezze P, Ruf S, Sonntag AG,
Langelaar-Makkinje M, Hall P, Heberle AM, Razquin Navas P, van
Eunen K, Tölle RC, Schwarz JJ, et al: A systems study reveals
concurrent activation of AMPK and mTOR by amino acids. Nat Commun.
7:132542016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kondo Y, Kanzawa T, Sawaya R and Kondo S:
The role of autophagy in cancer development and response to
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:726–734. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shimizu S, Kanaseki T, Mizushima N, Mizuta
T, Arakawa-Kobayashi S, Thompson CB and Tsujimoto Y: Role of Bcl-2
family proteins in a non-apoptotic programmed cell death dependent
on autophagy genes. Nat Cell Biol. 6:1221–1228. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Teng X, Degterev A, Jagtap P, Xing X, Choi
S, Denu R, Yuan J and Cuny GD: Structure-activity relationship
study of novel necroptosis inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
15:5039–5044. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Degterev A, Huang Z, Boyce M, Li Y, Jagtap
P, Mizushima N, Cuny GD, Mitchison TJ, Moskowitz MA and Yuan J:
Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic
potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat Chem Biol. 1:112–119.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kawahara A, Yamamoto C, Nakashima K, Azuma
K, Hattori S, Kashihara M, Aizawa H, Basaki Y, Kuwano M, Kage M, et
al: Molecular diagnosis of activating EGFR mutations in non-small
cell lung cancer using mutation-specific antibodies for
immunohistochemical analysis. Clin Cancer Res. 16:3163–3170. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hosokawa N, Hara Y and Mizushima N:
Generation of cell lines with tetracycline-regulated autophagy and
a role for autophagy in controlling cell size. FEBS Lett.
581:2623–2629. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun XM, MacFarlane M, Zhuang J, Wolf BB,
Green DR and Cohen GM: Distinct caspase cascades are initiated in
receptor-mediated and chemical-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
274:5053–5060. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Miyahara K, Kazama H, Kokuba H, Komatsu S,
Hirota A, Takemura J, Hirasawa K, Moriya S, Abe A, Hiramoto M, et
al: Targeting bortezomib-induced aggresome formation using
vinorelbine enhances the cytotoxic effect along with ER stress
loading in breast cancer cell lines. Int J Oncol. 49:1848–1858.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hansen TE and Johansen T: Following
autophagy step by step. BMC Biol. 9:392011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Golden SH, Folsom AR, Coresh J, Sharrett
AR, Szklo M and Brancati F: Risk factor groupings related to
insulin resistance and their synergistic effects on subclinical
atherosclerosis: The atherosclerosis risk in communities study.
Diabetes. 51:3069–3076. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R,
Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat
SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, et al: Activating mutations in the
epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of
non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med.
350:2129–2139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang J, Chen X, Su L, Li P, Liu B and Zhu
Z: LAT-1 functions as a promotor in gastric cancer associated with
clinicopathologic features. Biomed Pharmacother. 67:693–699. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gong YN, Guy C, Olauson H, Becker JU, Yang
M, Fitzgerald P, Linkermann A and Green DR: ESCRT-III acts
downstream of MLKL to regulate necroptotic cell death and its
consequences. Cell. 169:286–300.e16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdelmohsen K, Abe A, Abedin
MJ, Abeliovich H, Acevedo Arozena A, Adachi H, Adams CM, Adams PD,
Adeli K, et al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays
for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy. 12:1–222. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen L, Meng Y, Guo X, Sheng X, Tai G,
Zhang F, Cheng H and Zhou Y: Gefitinib enhances human colon cancer
cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis of via autophagy- and JNK-mediated
death receptors upregulation. Apoptosis. 21:1291–1301. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Degterev A, Hitomi J, Germscheid M, Ch'en
IL, Korkina O, Teng X, Abbott D, Cuny GD, Yuan C, Wagner G, et al:
Identification of RIP1 kinase as a specific cellular target of
necrostatins. Nat Chem Biol. 4:313–321. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Weinlich R, Oberst A, Beere HM and Green
DR: Necroptosis in development, inflammation and disease. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 18:127–136. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Li J, McQuade T, Siemer AB, Napetschnig J,
Moriwaki K, Hsiao YS, Damko E, Moquin D, Walz T, McDermott A, et
al: The RIP1/RIP3 necrosome forms a functional amyloid signaling
complex required for programmed necrosis. Cell. 150:339–350. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang Y, Su SS, Zhao S, Yang Z, Zhong CQ,
Chen X, Cai Q, Yang ZH, Huang D, Wu R, et al: RIP1
autophosphorylation is promoted by mitochondrial ROS and is
essential for RIP3 recruitment into necrosome. Nat Commun.
8:143292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ros U, Peña-Blanco A, Hänggi K, Kunzendorf
U, Krautwald S, Wong WW and García-Sáez AJ: Necroptosis execution
is mediated by plasma membrane nanopores independent of calcium.
Cell Reports. 19:175–187. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sun L, Wang H, Wang Z, He S, Chen S, Liao
D, Wang L, Yan J, Liu W, Lei X, et al: Mixed lineage kinase
domain-like protein mediates necrosis signaling downstream of RIP3
kinase. Cell. 148:213–227. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Seto T, Kato T, Nishio M, Goto K, Atagi S,
Hosomi Y, Yamamoto N, Hida T, Maemondo M, Nakagawa K, et al:
Erlotinib alone or with bevacizumab as first-line therapy in
patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer
harbouring EGFR mutations (JO25567): An open-label, randomised,
multi-centre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 15:1236–1244. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ichihara E, Hotta K, Nogami N, Kuyama S,
Kishino D, Fujii M, Kozuki T, Tabata M, Harada D, Chikamori K, et
al: Phase II trial of gefitinib in combination with bevacizumab as
first-line therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer with
activating EGFR gene mutations: The Okayama Lung Cancer Study Group
Trial 1001. J Thorac Oncol. 10:486–491. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Huang D, Zheng X, Wang ZA, Chen X, He WT,
Zhang Y, Xu JG, Zhao H, Shi W, Wang X, et al: The MLKL channel in
necroptosis is an octamer formed by tetramers in a dyadic process.
Mol Cell Biol. 37:e00497-e162017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Goodall ML, Fitzwalter BE, Zahedi S, Wu M,
Rodriguez D, Mulcahy-Levy JM, Green DR, Morgan M, Cramer SD and
Thorburn A: The autophagy machinery controls cell death switching
between apoptosis and necroptosis. Dev Cell. 37:337–349. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bray K, Mathew R, Lau A, Kamphorst JJ, Fan
J, Chen J, Chen HY, Ghavami A, Stein M, DiPaola RS, et al:
Autophagy suppresses RIP kinase-dependent necrosis enabling
survival to mTOR inhibition. PLoS One. 7:e418312012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gump JM, Staskiewicz L, Morgan MJ, Bamberg
A, Riches DW and Thorburn A: Autophagy variation within a cell
population determines cell fate through selective degradation of
Fap-1. Nat Cell Biol. 16:47–54. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Thorburn J, Andrysik Z, Staskiewicz L,
Gump J, Maycotte P, Oberst A, Green DR, Espinosa JM and Thorburn A:
Autophagy controls the kinetics and extent of mitochondrial
apoptosis by regulating PUMA levels. Cell Rep. 7:45–52. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|