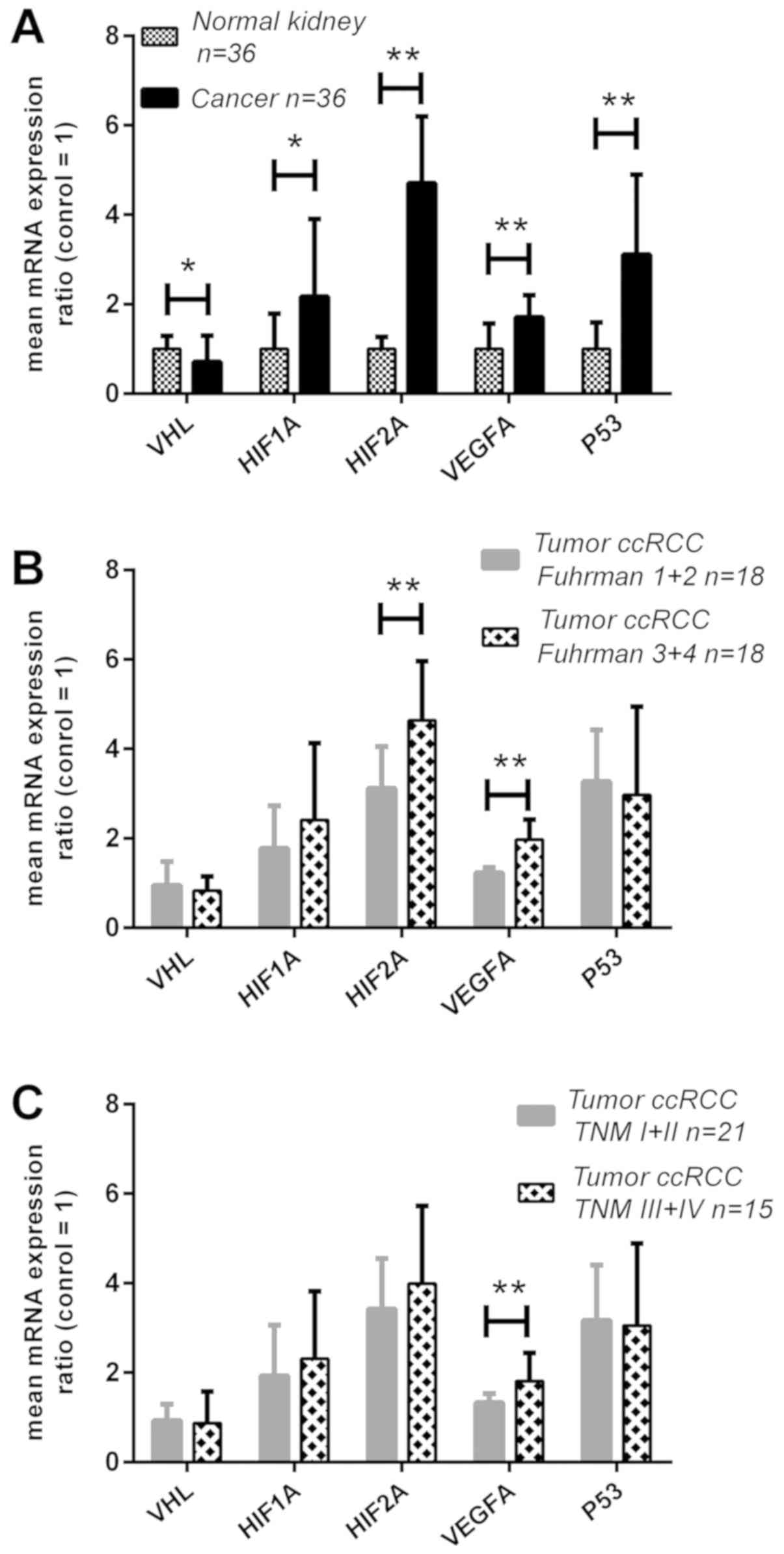
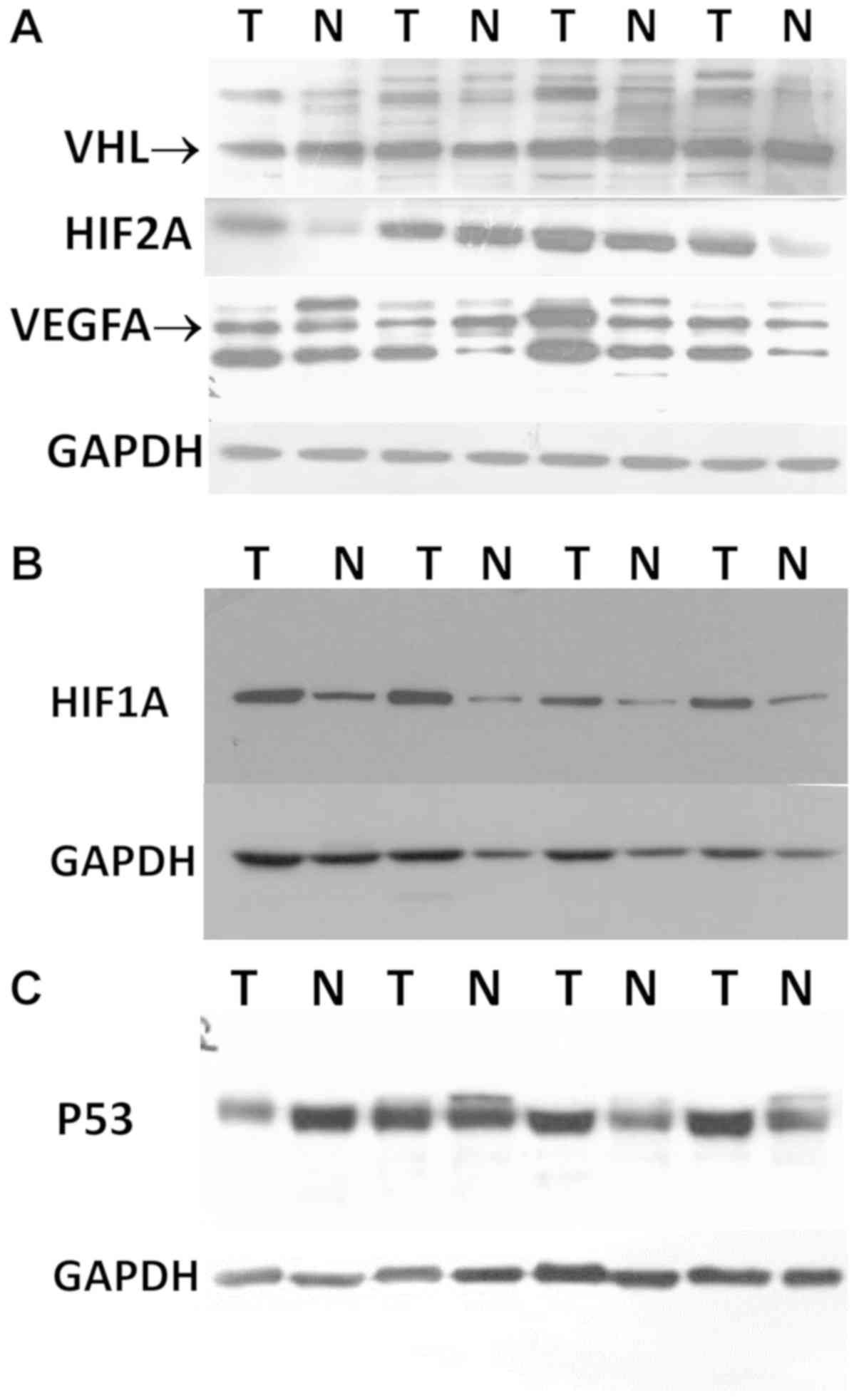
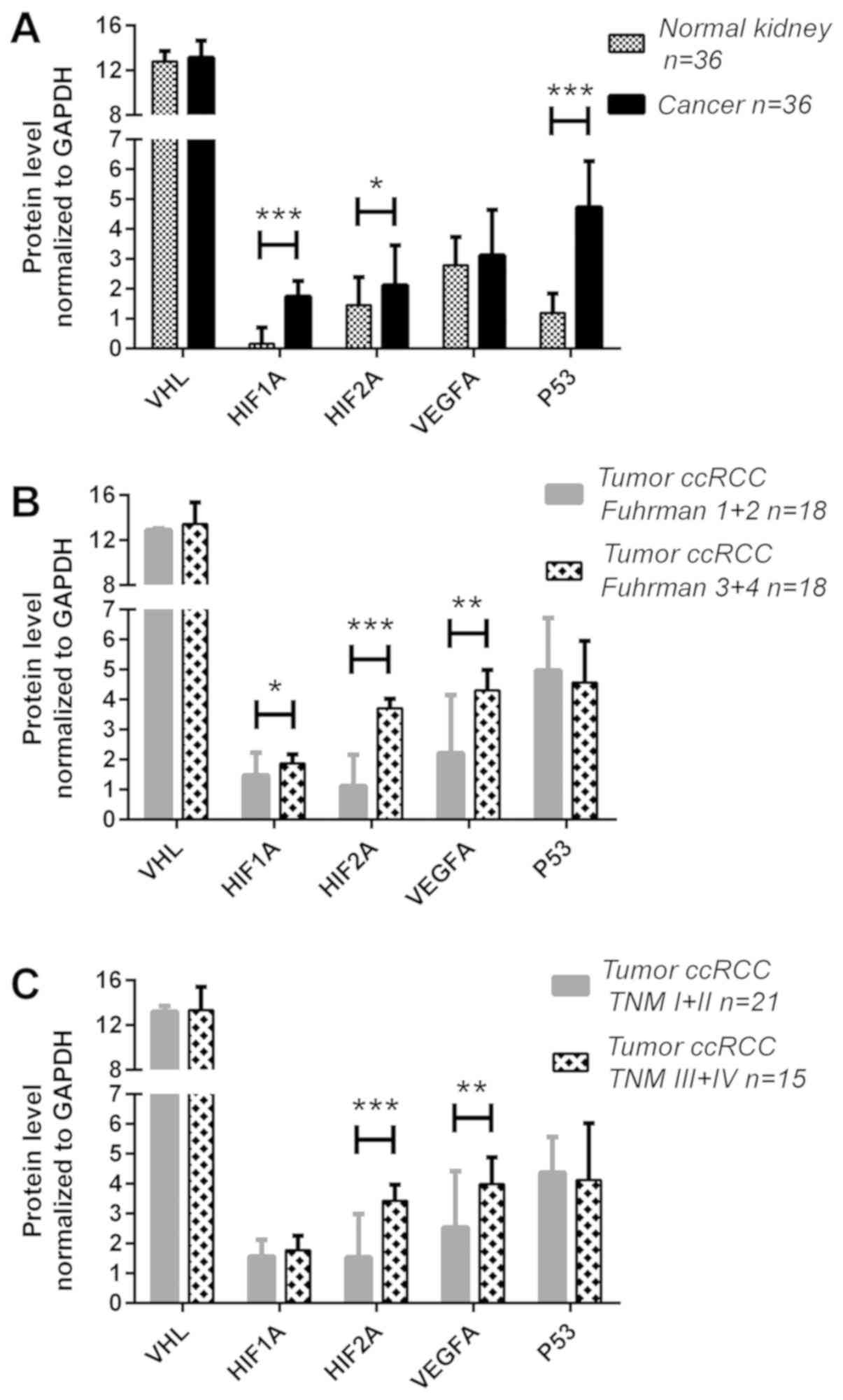
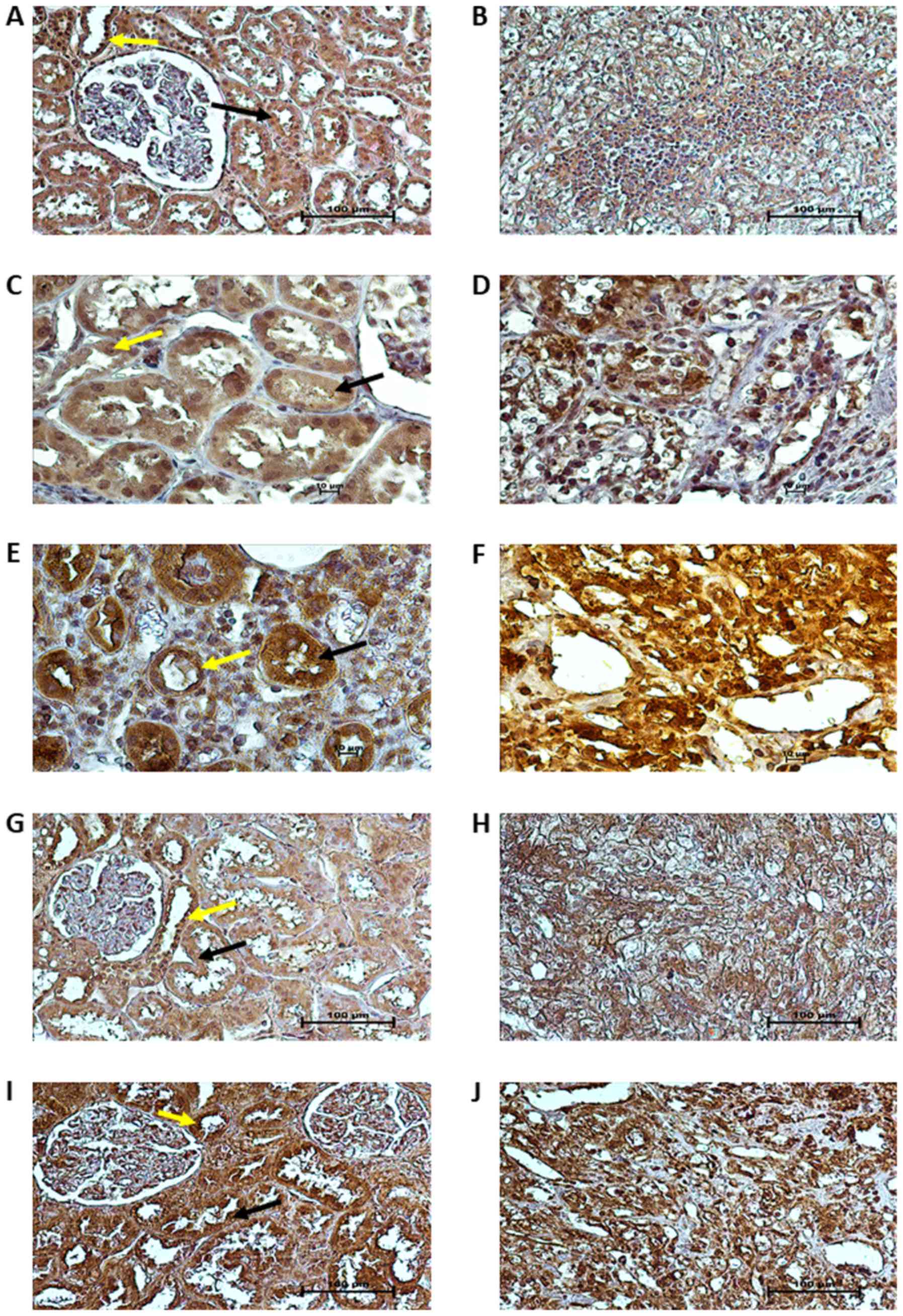
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schödel J, Grampp S, Maher ER, Moch H,
Ratcliffe PJ, Russo P and Mole DR: Hypoxia, hypoxia-inducible
transcription factors, and renal cancer. Eur Urol. 69:646–657.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Weinstock M and McDermott D: Targeting
PD-1/PD-L1 in the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma.
Ther Adv Urol. 7:365–377. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yu SS, Quinn DI and Dorff TB: Clinical use
of cabozantinib in the treatment of advanced kidney cancer:
Efficacy, safety, and patient selection. OncoTargets Ther.
9:5825–5837. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Dagher J, Kammerer-Jacquet SF, Dugay F,
Beaumont M, Lespagnol A, Cornevin L, Verhoest G, Bensalah K,
Rioux-Leclercq N and Belaud-Rotureau MA: Clear cell renal cell
carcinoma: A comparative study of histological and chromosomal
characteristics between primary tumors and their corresponding
metastases. Virchows Arch. 471:107–115. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen YL, Ge GJ, Qi C, Wang H, Wang HL, Li
LY, Li GH and Xia LQ: A five-gene signature may predict sunitinib
sensitivity and serve as prognostic biomarkers for renal cell
carcinoma. J Cell Physiol. 233:6649–6660. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang JY, Peng SH, Li T, Ning XH, Liu SJ,
Hong BA, Liu JY, Wu PJ, Zhou BW, Zhou JC, et al: Risk factors for
survival in patients with von Hippel-Lindau disease. J Med Genet.
55:322–328. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hasumi H and Yao M: Hereditary kidney
cancer syndromes: Genetic disorders driven by alterations in
metabolism and epigenome regulation. Cancer Sci. 109:581–586. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kondo K, Klco J, Nakamura E, Lechpammer M
and Kaelin WG Jr: Inhibition of HIF is necessary for tumor
suppression by the von Hippel-Lindau protein. Cancer Cell.
1:237–246. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Singh D, Arora R, Kaur P, Singh B, Mannan
R and Arora S: Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor and
metabolic pathways: Possible targets of cancer. Cell Biosci.
7:622017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ravi R, Mookerjee B, Bhujwalla ZM, Sutter
CH, Artemov D, Zeng Q, Dillehay LE, Madan A, Semenza GL and Bedi A:
Regulation of tumor angiogenesis by p53-induced degradation of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Genes Dev. 14:34–44.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Joshi S, Singh AR and Durden DL: MDM2
regulates hypoxic hypoxia-inducible factor 1α stability in an E3
ligase, proteasome, and PTEN-phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase-AKT-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. 289:22785–22797. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rybarczyk A, Klacz J, Wronska A,
Matuszewski M, Kmiec Z and Wierzbicki PM: Overexpression of the
YAP1 oncogene in clear cell renal cell carcinoma is associated with
poor outcome. Oncol Rep. 38:427–439. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shenoy N and Pagliaro L: Sequential
pathogenesis of metastatic VHL mutant clear cell renal cell
carcinoma: Putting it together with a translational perspective.
Ann Oncol. 27:1685–1695. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Elvidge GP, Glenny L, Appelhoff RJ,
Ratcliffe PJ, Ragoussis J and Gleadle JM: Concordant regulation of
gene expression by hypoxia and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase
inhibition: The role of HIF-1alpha, HIF-2alpha, and other pathways.
J Biol Chem. 281:15215–15226. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hori Y, Ito K, Hamamichi S, Ozawa Y,
Matsui J, Umeda IO and Fujii H: Functional characterization of
VEGF- and FGF-induced tumor blood vessel models in human cancer
xenografts. Anticancer Res. 37:6629–6638. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hutson TE and Figlin RA: Evolving role of
novel targeted agents in renal cell carcinoma. Oncology (Williston
Park). 21:1175–1180; discussion 1184-1187, 1190. 2007.
|
|
18
|
Hsieh JJ, Purdue MP, Signoretti S, Swanton
C, Albiges L, Schmidinger M, Heng DY, Larkin J and Ficarra V: Renal
cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 3:170092017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shibasaki N, Yamasaki T, Kanno T, Arakaki
R, Sakamoto H, Utsunomiya N, Inoue T, Tsuruyama T, Nakamura E,
Ogawa O, et al: Role of IL13RA2 in sunitinib resistance in clear
cell renal cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 10:e01309802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun M, Marconi L, Eisen T, Escudier B,
Giles RH, Haas NB, Harshman LC, Quinn DI, Larkin J, Pal SK, et al:
Adjuvant vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy in
renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and pooled analysis. Eur
Urol. 74:611–620. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lim SH, Hwang IG, Ji JH, Oh SY, Yi JH, Lim
DH, Lim HY, Lee SJ and Park SH: Intrinsic resistance to sunitinib
in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Asia Pac J Clin
Oncol. 13:61–67. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Mehdi A and Riazalhosseini Y: Epigenome
aberrations: Emerging driving factors of the clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 18:182017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Xiao-Fen W, Ting C, Jie L, Deng-Yang M,
Qing-Feng Z and Xin L: Correlation analysis of VHL and Jade-1 gene
expression in human renal cell carcinoma. Open Med (Wars).
11:226–230. 2016.
|
|
24
|
Wan L, Huang J, Chen J, Wang R, Dong C, Lu
S and Wu X: Expression and significance of FOXP1, HIF-1a and VEGF
in renal clear cell carcinoma. J BUON. 20:188–195. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gstalder C, Ader I and Cuvillier O: FTY720
(fingolimod) inhibits HIF1 and HIF2 signaling, promotes vascular
remodeling, and chemosensitizes in renal cell carcinoma animal
model. Mol Cancer Ther. 15:2465–2474. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Du W, Zhang L, Brett-Morris A, Aguila B,
Kerner J, Hoppel CL, Puchowicz M, Serra D, Herrero L, Rini BI, et
al: HIF drives lipid deposition and cancer in ccRCC via repression
of fatty acid metabolism. Nat Commun. 8:17692017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ebru T, Fulya OP, Hakan A, Vuslat YC,
Necdet S, Nuray C and Filiz O: Analysis of various potential
prognostic markers and survival data in clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Int Braz J Urol. 43:440–454. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Turner KJ, Moore JW, Jones A, Taylor CF,
Cuthbert-Heavens D, Han C, Leek RD, Gatter KC, Maxwell PH,
Ratcliffe PJ, et al: Expression of hypoxia-inducible factors in
human renal cancer: Relationship to angiogenesis and to the von
Hippel-Lindau gene mutation. Cancer Res. 62:2957–2961.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qin C, Chen J, Li J, Ju X, Zhang S, Cao Q,
Han Z, Li P, Shao P, Wang M, et al: Variants in
angiogenesis-related genes and the risk of clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Mutagenesis. 29:419–425. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Godlewski J, Krazinski BE, Kowalczyk AE,
Kiewisz J, Kiezun J, Kwiatkowski P, Sliwińska-Jewsiewicka A,
Wierzbicki PW and Kmieć Z: Expression and prognostic significance
of EP300, TP53 and BAX in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
Anticancer Res. 37:2927–2937. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yuan L, Chen L, Qian K, Qian G, Wu CL,
Wang X and Xiao Y: Co-expression network analysis identified six
hub genes in association with progression and prognosis in human
clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). Genom Data. 14:132–140.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Klacz J, Wierzbicki PM, Wronska A, et al:
Decreased expression of RASSF1A tumor suppressor gene is associated
with worse prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Manuskrypt
wysłany do European Urology. 21.07.2015. 2015.
|
|
33
|
Klacz J, Wierzbicki PM, Wronska A,
Rybarczyk A, Stanislawowski M, Slebioda T, Olejniczak A,
Matuszewski M and Kmiec Z: Decreased expression of RASSF1A tumor
suppressor gene is associated with worse prognosis in clear cell
renal cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 48:55–66. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang LE, Arany Z, Livingston DM and Bunn
HF: Activation of hypoxia-inducible transcription factor depends
primarily upon redox-sensitive stabilization of its alpha subunit.
J Biol Chem. 271:32253–32259. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Avădănei ER, Wierzbicki PM, Giuşcă SE,
Grigoraş A, Amălinei C and Căruntu ID: Macrophage profile in
primary versus secondary liver tumors. Folia Histochem Cytobiol.
52:112–123. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Escudier B and Kataja V; ESMO Guidelines
Working Group: Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice
Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol.
21(Suppl 5): v137–v139. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C; International Union Against Cancer: TNM Classification of
Malignant Tumours Chichester. West Sussex, Hoboken, NJ:
Wiley-Blackwell; 2010
|
|
39
|
Delahunt B, Sika-Paotonu D, Bethwaite PB,
William Jordan T, Magi-Galluzzi C, Zhou M, Samaratunga H and
Srigley JR: Grading of clear cell renal cell carcinoma should be
based on nucleolar prominence. Am J Surg Pathol. 35:1134–1139.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dzik C, Reis ST, Viana NI, Brito G,
Paloppi I, Nahas W, Srougi M and Leite KRM: Gene expression profile
of renal cell carcinomas after neoadjuvant treatment with
sunitinib: New pathways revealed. Int J Biol Markers. 32:e210–e217.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Klacz J, Wierzbicki PM, Wronska A,
Rybarczyk A, Stanislawowski M, Slebioda T, Olejniczak A,
Matuszewski M and Kmiec Z: Decreased expression of RASSF1A tumor
suppressor gene is associated with worse prognosis in clear cell
renal cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 48:55–66. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
42
|
Akhtar M, Al-Bozom IA and Al Hussain T:
Molecular and metabolic basis of clear cell carcinoma of the
kidney. Adv Anat Pathol. 25:189–196. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Duran I, Lambea J, Maroto P,
González-Larriba JL, Flores L, Granados-Principal S, Graupera M,
Sáez B, Vivancos A and Casanovas O: Resistance to targeted
therapies in renal cancer: The importance of changing the mechanism
of action. Target Oncol. 12:19–35. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Molina R, Ciocca DR, Tandon AK, Allred DC,
Clark GM, Chamness GC, Gullick WJ and McGuire WL: Expression of
HER-2/neu oncoprotein in human breast cancer: A comparison of
immunohistochemical and western blot techniques. Anticancer Res.
12B:B1965–B1971. 1992.
|
|
45
|
Ratajczak-Wielgomas K, Grzegrzolka J,
Piotrowska A, Matkowski R, Wojnar A, Rys J, Ugorski M and Dziegiel
P: Expression of periostin in breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
51:1300–1310. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yang L, Sun X and Meng X: Differences in
the expression profiles of claudin proteins in human gastric
carcinoma compared with non-neoplastic mucosa. Mol Med Rep.
18:1271–1278. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Parra ER, Villalobos P, Mino B and
Rodriguez-Canales J: Comparison of different antibody clones for
immunohistochemistry detection of programmed cell death ligand 1
(PD-L1) on non-small cell lung carcinoma. Appl Immunohistochem Mol
Morphol. 26:83–93. 2018.
|
|
48
|
Gao W, Li W, Xiao T, Liu XS and Kaelin WG
Jr: Inactivation of the PBRM1 tumor suppressor gene amplifies the
HIF-response in VHL−/− clear cell renal carcinoma. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:1027–1032. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Tarade D and Ohh M: The HIF and other
quandaries in VHL disease. Oncogene. 37:139–147. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Morris MR and Latif F: The epigenetic
landscape of renal cancer. Nat Rev Nephrol. 13:47–60. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Gossage L, Eisen T and Maher ER: VHL, the
story of a tumour suppressor gene. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:55–64. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Pantuck AJ, An J, Liu H and Retting MB:
NF-kappaB-dependent plasticity of the epithelial to mesenchymal
transition induced by von Hippel-Lindau inactivation in renal cell
carcinomas. Cancer Res. 70:752–761. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Roe JS, Kim H, Lee SM, Kim ST, Cho EJ and
Youn HD: p53 stabilization and transactivation by a von
Hippel-Lindau protein. Mol Cell. 22:395–405. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang T, Niu X, Liao L, Cho EA and Yang H:
The contributions of HIF-target genes to tumor growth in RCC. PLoS
One. 8:e805442013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Godlewski J, Kiezun J, Krazinski BE,
Kozielec Z, Wierzbicki PM and Kmiec Z: The immunoexpression of YAP1
and LATS1 proteins in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Impact on
patients' survival. BioMed Res Int. 2018:26536232018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Högner A, Krause H, Jandrig B, Kasim M,
Fuller TF, Schostak M, Erbersdobler A, Patzak A and Kilic E: PBRM1
and VHL expression correlate in human clear cell renal cell
carcinoma with differential association with patient's overall
survival. Urol Oncol. 36:94 e91–94 e14. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Girgis AH, Iakovlev VV, Beheshti B, Bayani
J, Squire JA, Bui A, Mankaruos M, Youssef Y, Khalil B, Khella H, et
al: Multilevel whole-genome analysis reveals candidate biomarkers
in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 72:5273–5284. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Patard JJ, Rioux-Leclercq N, Masson D,
Zerrouki S, Jouan F, Collet N, Dubourg C, Lobel B, Denis M and
Fergelot P: Absence of VHL gene alteration and high VEGF expression
are associated with tumour aggressiveness and poor survival of
renal-cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 101:1417–1424. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Beroukhim R, Brunet JP, Di Napoli A, Mertz
KD, Seeley A, Pires MM, Linhart D, Worrell RA, Moch H, Rubin MA, et
al: Patterns of gene expression and copy-number alterations in
von-hippel lindau disease-associated and sporadic clear cell
carcinoma of the kidney. Cancer Res. 69:4674–4681. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Song Y, Huang J, Shan L and Zhang HT:
Analyses of potential predictive markers and response to targeted
therapy in patients with advanced clear-cell renal cell carcinoma.
Chin Med J (Engl). 128:2026–2033. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Dornbusch J, Zacharis A, Meinhardt M,
Erdmann K, Wolff I, Froehner M, Wirth MP, Zastrow S and Fuessel S:
Analyses of potential predictive markers and survival data for a
response to sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell
carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e763862013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Beuselinck B, Verbiest A, Couchy G, Job S,
de Reynies A, Meiller C, Albersen M, Verkarre V, Lerut E, Méjean A,
et al: Pro-angiogenic gene expression is associated with better
outcome on sunitinib in metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma.
Acta Oncol. 57:498–508. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Sur S, Maurya AK, Roy A, Sharp TV, Pal DK
and Panda CK: Over expression of HIF1α is associated with
inactivation of both LimD1 and VHL in renal cell carcinoma:
Clinical importance. Pathol Res Pract. 213:1477–1481. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Gervais ML, Henry PC, Saravanan A, Burry
TN, Gallie BL, Jewwet MA, Hill RP, Evans AJ and Ohh M: Nuclear
E-cadherin and VHL immunoreactivity are prognostic indicators of
clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Lab Invest. 87:2152–1264. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Baldewijns MM, van Vlodrop IJH, Vermeulen
PB, Soetekouw PMMB, van Engeland M and de Bruïne AP: VHL and HIF
signalling in renal cell carcinogenesis. J Pathol. 221:125–138.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Nyhan MJ, El Mashad SM, O'Donovan TR,
Ahmad S, Collins C, Sweeney P, Rogers E, O'Sullivan GC and McKenna
SL: VHL genetic alteration in CCRCC does not determine
de-regulation of HIF, CAIX, hnRNP A2/B1 and osteopontin. Cell Oncol
(Dordr). 34:225–234. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Damjanovic SS, Ilic BB, Beleslin Cokic BB,
Antic JA, Bankovic JZ, Milicevic IT, Rodic GS, Ilic DS, Todorovic
VN, Puskas N, et al: Tuberous sclerosis complex protein 1
expression is affected by VHL Gene alterations and HIF-1α
production in sporadic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Exp Mol
Pathol. 101:323–331. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Muriel López C, Esteban E, Berros JP,
Pardo P, Astudillo A, Izquierdo M, Crespo G, Sanmamed M, Fonseca PJ
and Martínez-Camblor P: Prognostic factors in patients with
advanced renal cell carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 10:262–270.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Shen C, Beroukhim R, Schumacher SE, Zhou
J, Chang M, Signoretti S and Kaelin WG Jr: Genetic and functional
studies implicate HIF1α as a 14q kidney cancer suppressor gene.
Cancer Discov. 1:222–235. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Lidgren A, Hedberg Y, Grankvist K,
Rasmuson T, Vasko J and Ljungberg B: The expression of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is a favorable independent
prognostic factor in renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
11:1129–1135. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Mandriota SJ, Turner KJ, Davies DR, Murray
PG, Morgan NV, Sowter HM, Wykoff CC, Maher ER, Harris AL, Ratcliffe
PJ, et al: HIF activation identifies early lesions in VHL kidneys:
Evidence for site-specific tumor suppressor function in the
nephron. Cancer Cell. 1:459–468. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Martínez-Sáez O, Gajate Borau P,
Alonso-Gordoa T, Molina-Cerrillo J and Grande E: Targeting HIF-2 α
in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: A promising therapeutic
strategy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 111:117–123. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Raval RR, Lau KW, Tran MGB, Sowter HM,
Mandriota SJ, Li JL, Pugh CW, Maxwell PH, Harris AL and Ratcliffe
PJ: Contrasting properties of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1)
and HIF-2 in von Hippel-Lindau-associated renal cell carcinoma. Mol
Cell Biol. 25:5675–5686. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zimmer M, Doucette D, Siddiqui N and
Iliopoulos O: Inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor is sufficient
for growth suppression of VHL−/− tumors. Mol Cancer Res.
2:89–95. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Philips GK and Atkins MB: New agents and
new targets for renal cell carcinoma. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book.
34:e222–e227. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Maroto P, Esteban E, Parra EF,
Mendez-Vidal MJ, Domenech M, Pérez-Valderrama B, Calderero V,
Pérez-Gracia JL, Grande E and Algaba F: HIF pathway and c-Myc as
biomarkers for response to sunitinib in metastatic clear-cell renal
cell carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 10:4635–4643. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Wong SC, Cheng W, Hamilton H, Nicholas AL,
Wakefield DH, Almeida A, Blokhin AV, Carlson J, Neal ZC, Subbotin
V, et al: HIF2α-targeted RNAi therapeutic inhibits clear cell renal
cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 17:140–149. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Kamai T, Tokura Y, Uematsu T, Sakamoto K,
Suzuki I, Takei K, Narimatsu T, Kambara T, Yuki H, Betsunoh H, et
al: Elevated serum levels of cardiovascular biomarkers are
associated with progression of renal cancer. Open Heart.
5:e0006662018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Cuvillier O: The therapeutic potential of
HIF-2 antagonism in renal cell carcinoma. Transl Androl Urol.
6:131–133. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Chen W, Hill H, Christie A, Kim MS,
Holloman E, Pavia-Jimenez A, Homayoun F, Ma Y, Patel N, Yell P, et
al: Targeting renal cell carcinoma with a HIF-2 antagonist. Nature.
539:112–117. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Wehn PM, Rizzi JP, Dixon DD, Grina JA,
Schlachter ST, Wang B, Xu R, Yang H, Du X, Han G, et al: Design and
activity of specific hypoxia-inducible factor-2α (HIF-2α)
inhibitors for the treatment of clear cell renal cell carcinoma:
Discovery of clinical candidate
(S)-3-((2,2-Difluoro-1-hydroxy-7-(methylsulfonyl)-
2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-4-yl)oxy)-5-fluorobenzonitrile (PT2385). J Med
Chem. 61:9691–9721. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Burris H, Rodon J, Sharma S, Herbst RS,
Tabernero J, Infante JR, Silva A, Demanse D, Hackl W and Baselga J:
First-in-human phase I study of the oral PI3K inhibitor BEZ235 in
patients (pts) with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 28(Suppl
15): 282010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Wang X, Zhang J, Wang Y, Tu M, Wang Y and
Shi G: Upregulated VEGFAand DLL4 act as potential prognostic genes
for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther.
11:1697–1706. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Veselaj F, Manxhuka-Kerliu S, Neziri A,
Shahini L, Xharra S, Selmani L, Kerliu L and Kavaja F: Prognostic
value of vascular endothelial growth factor A in the prediction of
the tumor aggressiveness in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Open
Access Maced J Med Sci. 5:167–172. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Phuoc NB, Ehara H, Gotoh T, Nakano M,
Kamei S, Deguchi T and Hirose Y: Prognostic value of the
co-expression of carbonic anhydrase IX and vascular endothelial
growth factor in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
Oncol Rep. 20:525–530. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Shi ZG, Li SQ, Li ZJ, Zhu XJ, Xu P and Liu
G: Expression of vimentin and survivin in clear cell renal cell
carcinoma and correlation with p53. Clin Transl Oncol. 17:65–73.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Zhu Y, Xu L, Zhang J, Hu X, Liu Y, Yin H,
Lv T, Zhang H, Liu L, An H, et al: Sunitinib induces cellular
senescence via p53/Dec1 activation in renal cell carcinoma cells.
Cancer Sci. 104:1052–1061. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Busch J, Seidel C, Weikert S, Wolff I,
Kempkensteffen C, Weinkauf L, Hinz S, Magheli A, Miller K and
Grünwald V: Intrinsic resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors is
associated with poor clinical outcome in metastatic renal cell
carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 11:2952011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Giuliano S, Cormerais Y, Dufies M, Grépin
R, Colosetti P, Belaid A, Parola J, Martin A, Lacas-Gervais S,
Mazure NM, et al: Resistance to sunitinib in renal clear cell
carcinoma results from sequestration in lysosomes and inhibition of
the autophagic flux. Autophagy. 11:1891–1904. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Butz H, Ding Q, Nofech-Mozes R, Lichner Z,
Ni H and Yousef GM: Elucidating mechanisms of sunitinib resistance
in renal cancer: An integrated pathological-molecular analysis.
Oncotarget. 9:4661–4674. 2017.
|
|
91
|
Kamli H, Glenda GC, Li L, Vesey DA and
Morais C: Characterisation of the morphological, functional and
molecular changes in sunitinib-resistant renal cell carcinoma
cells. J Kidney Cancer VHL. 5:1–9. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|