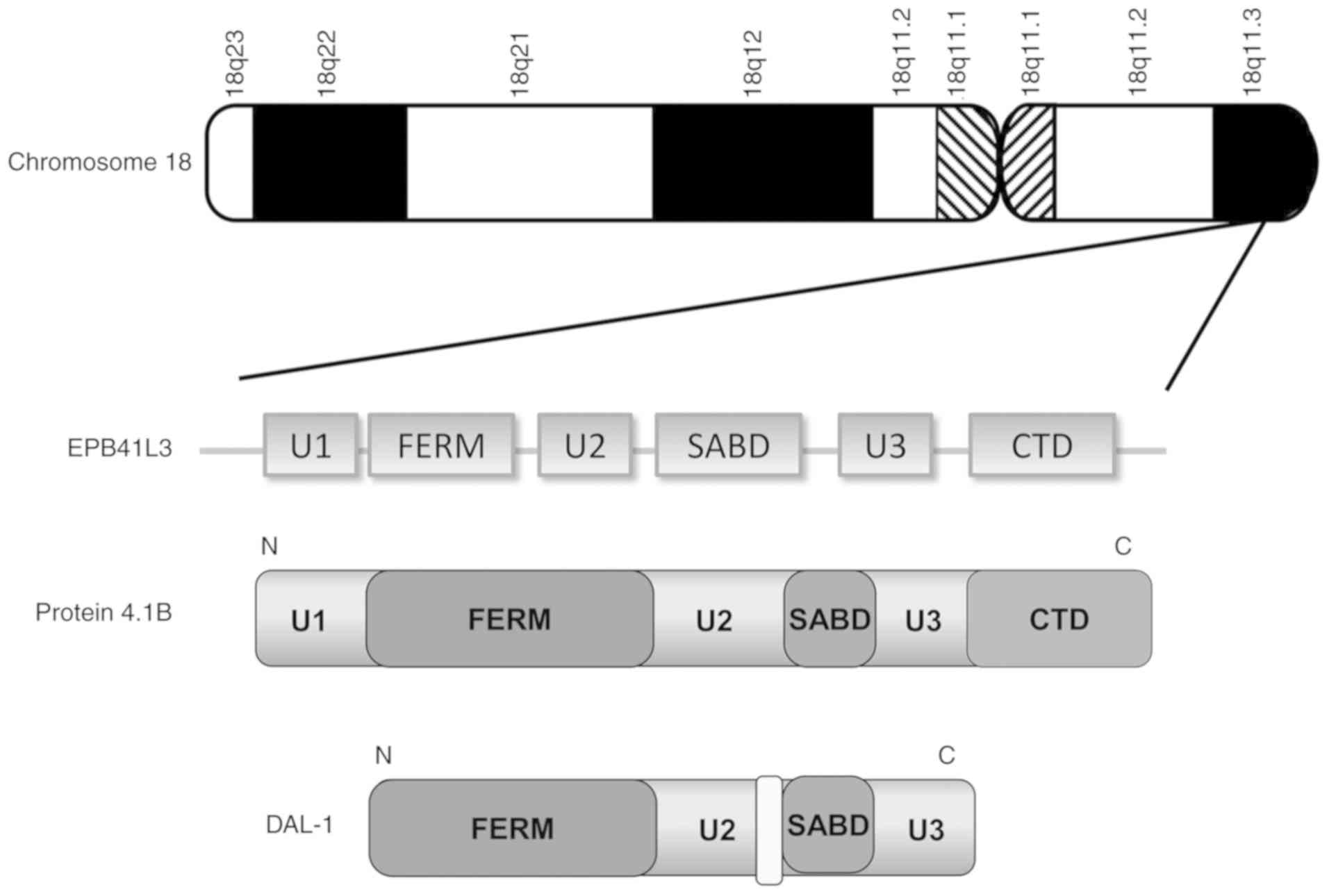
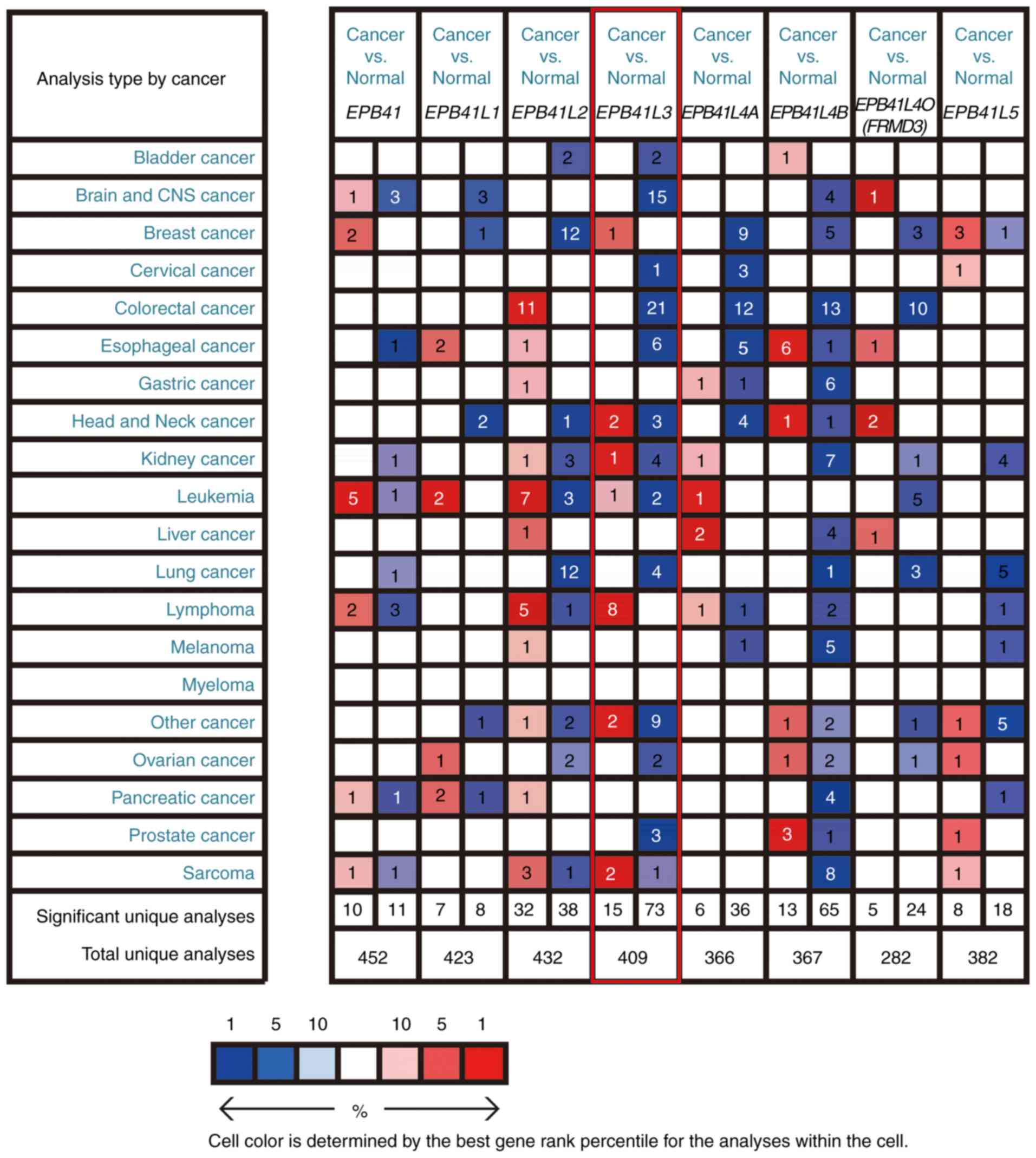
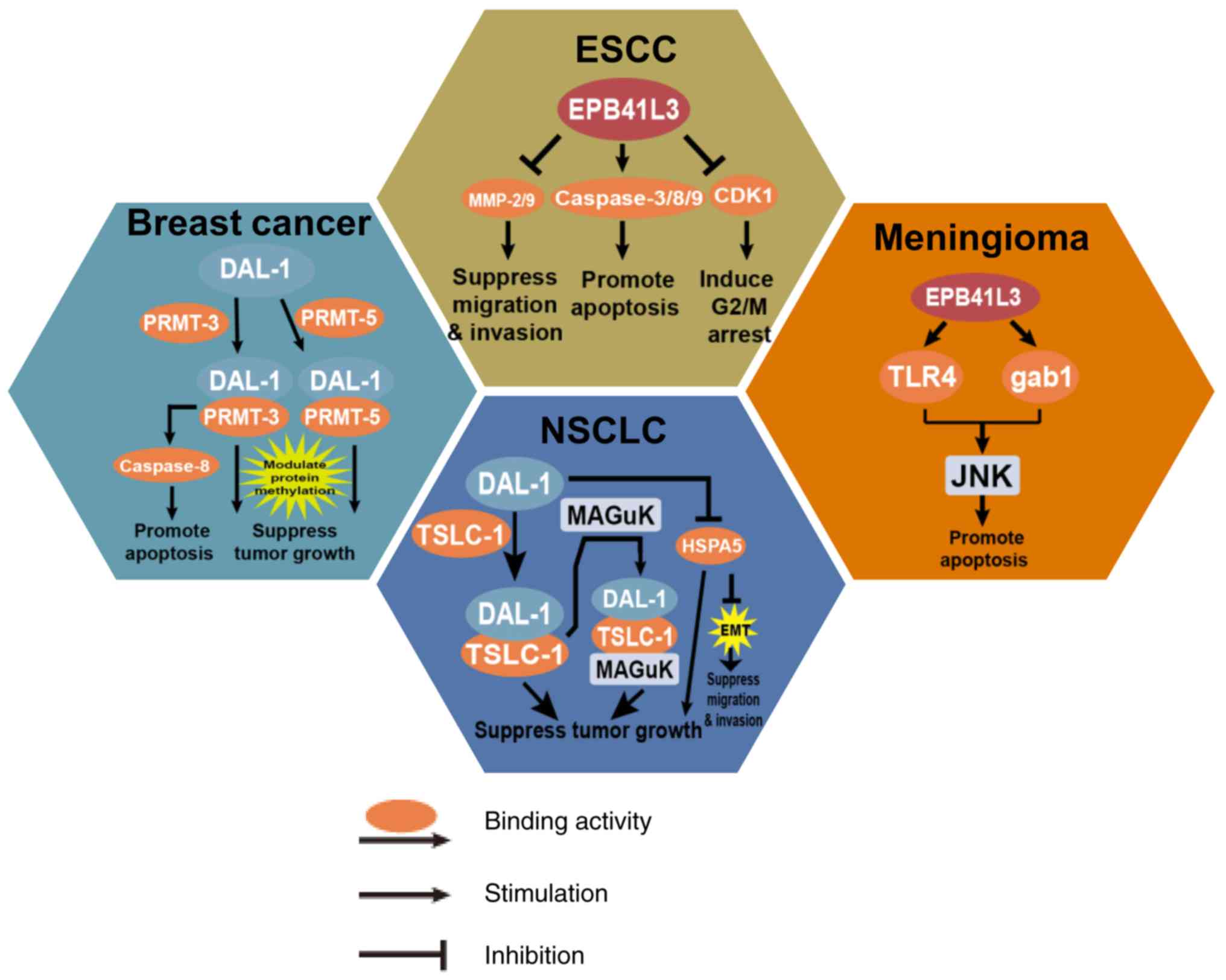
|
1
|
Cifuentes-Diaz C, Chareyre F, Garcia M,
Devaux J, Carnaud M, Levasseur G, Niwa-Kawakita M, Harroch S,
Girault JA, Giovannini M and Goutebroze L: Protein 4.1B contributes
to the organization of peripheral myelinated axons. PLoS One.
6:e250432011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hoover KB and Bryant PJ: The genetics of
the protein 4.1 family: Organizers of the membrane and
cytoskeleton. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 12:229–234. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Diakowski W, Grzybek M and Sikorski AF:
Protein 4.1, a component of the erythrocyte membrane skeleton and
its related homologue proteins forming the protein 4.1/FERM
superfamily. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 44:231–248. 2006.
|
|
4
|
Takeuchi K, Kawashima A, Nagafuchi A and
Tsukita S: Structural diversity of band 4.1 superfamily members. J
Cell Sci. 107:1921–1928. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sun CX, Robb VA and Gutmann DH: Protein
4.1 tumor suppressors: Getting a FERM grip on growth regulation. J
Cell Sci. 115:3991–4000. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chishti AH, Kim AC, Marfatia SM, Lutchman
M, Hanspal M, Jindal H, Liu SC, Low PS, Rouleau GA, Mohandas N, et
al: The FERM domain: A unique module involved in the linkage of
cytoplasmic proteins to the membrane. Trends Biochem Sci.
23:281–282. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Parra M, Gee S, Chan N, Ryaboy D, Dubchak
I, Mohandas N, Gascard PD and Conboy JG: Differential domain
evolution and complex RNA processing in a family of paralogous
EPB41 (protein 4.1) genes facilitate expression of diverse
tissue-specific isoforms. Genomics. 84:637–646. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tran YK, Bögler O, Gorse KM, Wieland I,
Green MR and Newsham IF: A novel member of the NF2/ERM/4.1
superfamily with growth suppressing properties in lung cancer.
Cancer Res. 59:35–43. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kikuchi S, Yamada D, Fukami T, Masuda M,
Sakurai-Yageta M, Williams YN, Maruyama T, Asamura H, Matsuno Y,
Onizuka M and Murakami Y: Promoter methylation of DAL-1/4.1B
predicts poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 11:2954–2961. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liang H, Yan X, Pan Y, Wang Y, Wang N, Li
L, Liu Y, Chen X, Zhang CY, Gu H and Zen K: MicroRNA-223 delivered
by platelet-derived microvesicles promotes lung cancer cell
invasion via targeting tumor suppressor EPB41L3. Mol Cancer.
14:582015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yageta M, Kuramochi M, Masuda M, Fukami T,
Fukuhara H, Maruyama T, Shibuya M and Murakami Y: Direct
association of TSLC1 and DAL-1, two distinct tumor suppressor
proteins in lung cancer. Cancer Res. 62:5129–5133. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gutmann DH, Donahoe J, Perry A, Lemke N,
Gorse K, Kittiniyom K, Rempel SA, Gutierrez JA and Newsham IF: Loss
of DAL-1, a protein 4.1-related tumor suppressor, is an important
early event in the pathogenesis of meningiomas. Hum Mol Genet.
9:1495–1500. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tran Y, Benbatoul K, Gorse K, Rempel S,
Futreal A, Green M and Newsham I: Novel regions of allelic deletion
on chromosome 18p in tumors of the lung, brain and breast.
Oncogene. 17:3499–3505. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Nunes F, Shen Y, Niida Y, Beauchamp R,
Stemmer- Rachamimov AO, Ramesh V, Gusella J and MacCollin M:
Inactivation patterns of NF2 and DAL-1/4.1B (EPB41L3) in sporadic
meningioma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 162:135–139. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Robb VA, Gerber MA, Hart-Mahon EK and
Gutmann DH: Membrane localization of the U2 domain of Protein 4.1B
is necessary and sufficient for meningioma growth suppression.
Oncogene. 24:1946–1957. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gerber MA, Bahr SM and Gutmann DH: Protein
4.1B/differentially expressed in adenocarcinoma of the lung-1
functions as a growth suppressor in meningioma cells by activating
Rac1-dependent c-Jun-NH(2)-kinase signaling. Cancer Res.
66:5295–5303. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kittiniyom K, Mastronardi M, Roemer M,
Wells WA, Greenberg ER, Titus-Ernstoff L and Newsham IF:
Allele-specific loss of heterozygosity at the DAL-1/4.1B (EPB41L3)
tumor-suppressor gene locus in the absence of mutation. Genes
Chromosomes Cancer. 40:190–203. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kittiniyom K, Gorse KM, Dalbegue F, Lichy
JH, Taubenberger JK and Newsham IF: Allelic loss on chromosome band
18p11.3 occurs early and reveals heterogeneity in breast cancer
progression. Breast Cancer Res. 3:192–198. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dafou D, Grun B, Sinclair J, Lawrenson K,
Benjamin EC, Hogdall E, Kruger-Kjaer S, Christensen L, Sowter HM,
Al-Attar A, et al: Microcell-mediated chromosome transfer
identifies EPB41L3 as a functional suppressor of epithelial ovarian
cancers. Neoplasia. 12:579–589. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bernkopf DB and Williams ED: Potential
role of EPB41L3 (protein 4.1B/Dal-1) as a target for treatment of
advanced prostate cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 12:845–853.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wong SY, Haack H, Kissil JL, Barry M,
Bronson RT, Shen SS, Whittaker CA, Crowley D and Hynes RO: Protein
4.1B suppresses prostate cancer progression and metastasis. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:12784–12789. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Z, Zhang J, Ye M, Zhu M, Zhang B, Roy
M, Liu J and An X: Tumor suppressor role of protein 4.1B/DAL-1.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 71:4815–4830. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Holzwarth G, Yu J and Steck TL:
Heterogeneity in the conformation of different protein fractions
from the human erythrocyte membrane. J Supramol Struct. 4:161–168.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Parra M, Gascard P, Walensky LD, Gimm JA,
Blackshaw S, Chan N, Takakuwa Y, Berger T, Lee G, Chasis JA, et al:
Molecular and functional characterization of protein 4.1B, a novel
member of the protein 4.1 family with high level, focal expression
in brain. J Biol Chem. 275:3247–3255. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Leto TL and Marchesi VT: A structural
model of human erythrocyte protein 4.1. J Biol Chem. 259:4603–4608.
1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Busam RD, Thorsell AG, Flores A,
Hammarström M, Persson C, Öbrink B and Hallberg BM: Structural
basis of tumor suppressor in lung cancer 1 (TSLC1) binding to
differentially expressed in adenocarcinoma of the lung
(DAL-1/4.1B). J Biol Chem. 286:4511–4516. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Nagata M, Sakurai-Yageta M, Yamada D, Goto
A, Ito A, Fukuhara H, Kume H, Morikawa T, Fukayama M, Homma Y and
Murakami Y: Aberrations of a cell adhesion molecule CADM4 in renal
clear cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 130:1329–1337. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sakurai-Yageta M, Masuda M, Tsuboi Y, Ito
A and Murakami Y: Tumor suppressor CADM1 is involved in epithelial
cell structure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 390:977–982. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Singh V, Miranda TB, Jiang W, Frankel A,
Roemer ME, Robb VA, Gutmann DH, Herschman HR, Clarke S and Newsham
IF: DAL-1/4.1B tumor suppressor interacts with protein arginine
N-methyltransferase 3 (PRMT3) and inhibits its ability to methylate
substrates in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 23:7761–7771. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiang W, Roemer ME and Newsham IF: The
tumor suppressor DAL-1/4.1B modulates protein arginine
N-methyltransferase 5 activity in a substrate-specific manner.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 329:522–530. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Horresh I, Bar V, Kissil JL and Peles E:
Organization of myelinated axons by Caspr and Caspr2 requires the
cytoskeletal adapter protein 4.1B. J Neurosci. 30:2480–2489. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yu T, Robb VA, Singh V, Gutmann DH and
Newsham IF: The 4.1/ezrin/radixin/moesin domain of the
DAL-1/Protein 4.1B tumour suppressor interacts with 14-3-3
proteins. Biochem J. 365:783–789. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gimm JA, An X, Nunomura W and Mohandas N:
Functional characterization of spectrin-actin-binding domains in
4.1 family of proteins. Biochemistry. 41:7275–7282. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Discher DE, Winardi R, Schischmanoff PO,
Parra M, Conboy JG and Mohandas N: Mechanochemistry of protein
4.1's spectrin-actin-binding domain: Ternary complex interactions,
membrane binding, network integration, structural strengthening. J
Cell Biol. 130:897–907. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Discher D, Parra M, Conboy JG and Mohandas
N: Mechanochemistry of the alternatively spliced spectrin-actin
binding domain in membrane skeletal protein 4.1. J Biol Chem.
268:7186–7195. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos A, Huang SC
and Benz EJ Jr: A nonerythroid isoform of protein 4.1R interacts
with components of the contractile apparatus in skeletal myofibers.
Mol Biol Cell. 11:3805–3817. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
McCarty JH, Cook AA and Hynes RO: An
interaction between {alpha}v{beta}8 integrin and Band 4.1B via a
highly conserved region of the Band 4.1 C-terminal domain. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:13479–13483. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang Y, Xu R, Li G, Xie X, Long J and
Wang H: Loss of expression of the differentially expressed in
adenocarcinoma of the lung (DAL-1) protein is associated with
metastasis of non-small cell lung carcinoma cells. Tumour Biol.
33:1915–1925. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Charboneau AL, Singh V, Yu T and Newsham
IF: Suppression of growth and increased cellular attachment after
expression of DAL-1 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer.
100:181–188. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Qiu X, Guan X, Liu W and Zhang Y: DAL-1
attenuates epithelial to mesenchymal transition and metastasis by
suppressing HSPA5 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol
Rep. 38:3103–3113. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen X, Guan X, Zhang H, Xie X, Wang H,
Long J, Cai T, Li S, Liu Z and Zhang Y: DAL-1 attenuates
epithelial-to mesenchymal transition in lung cancer. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 34:32015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yu F, Yang H, Zhang Z, Wang Z and Xiong J:
DAL-1/4.1B contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition via
regulation of transforming growth factor-β in lung cancer cell
lines. Mol Med Rep. 12:6072–6078. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Heller G, Fong KM, Girard L, Seidl S,
End-Pfützenreuter A, Lang G, Gazdar AF, Minna JD, Zielinski CC and
Zöchbauer-Müller S: Expression and methylation pattern of TSLC1
cascade genes in lung carcinomas. Oncogene. 25:959–968. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Martín-Sánchez E, Pernaut-Leza E, Mendaza
S, Cordoba A, Vicente-Garcia F, Monreal-Santesteban I, Vizcaino JP,
De Cerio MJ, Perez-Janices N, Blanco-Luquin I, et al: Gene promoter
hypermethylation is found in sentinel lymph nodes of breast cancer
patients, in samples identified as positive by one-step nucleic
acid amplification of cytokeratin 19 mRNA. Virchows Arch.
469:51–59. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jiang W and Newsham IF: The tumor
suppressor DAL-1/4.1B and protein methylation cooperate in inducing
apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 5:42006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Schulz WA, Alexa A, Jung V, Hader C,
Hoffmann MJ, Yamanaka M, Fritzsche S, Wlazlinski A, Müller M,
Lengauer T, et al: Factor interaction analysis for chromosome 8 and
DNA methylation alterations highlights innate immune response
suppression and cytoskeletal changes in prostate cancer. Mol
Cancer. 6:142007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Schulz WA, Ingenwerth M, Djuidje CE, Hader
C, Rahnenführer J and Engers R: Changes in cortical cytoskeletal
and extracellular matrix gene expression in prostate cancer are
related to oncogenic ERG deregulation. BMC Cancer. 10:5052010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Vasiljević N, Ahmad AS, Carter PD, Fisher
G, Berney DM, Foster CS, Cuzick J and Lorincz AT: DNA methylation
of PITX2 predicts poor survival in men with prostate cancer.
Biomark Med. 8:1143–1150. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Schulz WA and Hoffmann MJ: Epigenetic
mechanisms in the biology of prostate cancer. Semin Cancer Biol.
19:172–180. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li X, Zhou F, Jiang C, Wang Y, Lu Y, Yang
F, Wang N, Yang H, Zheng Y and Zhang J: Identification of a DNA
methylome profile of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and
potential plasma epigenetic biomarkers for early diagnosis. PLoS
One. 9:e1031622014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Maher SG, Gillham CM, Duggan SP, Smyth PC,
Miller N, Muldoon C, O'Byrne KJ, Sheils OM, Hollywood D and
Reynolds JV: Gene expression analysis of diagnostic biopsies
predicts pathological response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy of
esophageal cancer. Ann Surg. 250:729–737. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zeng R, Huang JP, Li XF, Xiong WB, Wu G,
Jiang ZJ, Song SJ, Li JQ, Zheng YF and Zhang JR: Epb41l3 suppresses
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma invasion and inhibits MMP2 and
MMP9 expression. Cell Biochem Funct. 34:133–141. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zeng R, Liu Y, Jiang ZJ, Huang JP, Wang Y,
Li XF, Xiong WB, Wu XC, Zhang JR, Wang QE and Zheng YF: EPB41L3 is
a potential tumor suppressor gene and prognostic indicator in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. Mar 14–2018.Epub
ahead of print.
|
|
54
|
Verlaat W, Van Leeuwen RW, Novianti PW,
Schuuring E, Meijer CJLM, Van Der Zee AGJ, Snijders PJF, Heideman
DAM, Steenbergen RDM and Wisman GBA: Host-cell DNA methylation
patterns during high-risk HPV-induced carcinogenesis reveal a
heterogeneous nature of cervical pre-cancer. Epigenetics.
13:769–778. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Vasiljević N, Scibior-Bentkowska D,
Brentnall AR, Cuzick J and Lorincz AT: Credentialing of DNA
methylation assays for human genes as diagnostic biomarkers of
cervical intraepithelial neoplasia in high-risk HPV positive women.
Gynecol Oncol. 132:709–714. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Brentnall AR, Vasiljević N,
Scibior-Bentkowska D, Cadman L, Austin J, Szarewski A, Cuzick J and
Lorincz AT: A DNA methylation classifier of cervical precancer
based on human papillomavirus and human genes. Int J Cancer.
135:1425–1432. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Boers A, Wang R, van Leeuwen RW, Klip HG,
de Bock GH, Hollema H, van Criekinge W, de Meyer T, Denil S, van
der Zee AGJ, et al: Discovery of new methylation markers to improve
screening for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2/3. Clin
Epigenetics. 8:292016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Louvanto K, Franco EL, Ramanakumar AV,
Vasiljević N, Scibior-Bentkowska D, Koushik A, Cuzick J, Coutlée F
and Lorincz AT; Biomarkers of Cervical Cancer Risk Study Team:
Methylation of viral and host genes and severity of cervical
lesions associated with human papillomavirus type 16. Int J Cancer.
136:E638–E645. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Kelly HA, Chikandiwa A, Warman R, Segondy
M, Sawadogo B, Vasiljević N, Didelot MN, Meda N, Weiss HA,
Delany-Moretlwe S, et al: Associations of human gene EPB41L3 DNA
methylation and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia in women living
with HIV-1 in Africa. AIDS. 32:2227–2236. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Clarke MA, Luhn P, Gage JC, Bodelon C,
Dunn ST, Walker J, Zuna R, Hewitt S, Killian JK, Yan L, et al:
Discovery and validation of candidate host DNA methylation markers
for detection of cervical precancer and cancer. Int J Cancer.
141:701–710. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Cuschieri K, Ronco G, Lorincz A, Smith L,
Ogilvie G, Mirabello L, Carozzi F, Cubie H, Wentzensen N, Snijders
P, et al: Eurogin roadmap 2017: Triage strategies for the
management of HPV-positive women in cervical screening programs.
Int J Cancer. 143:735–745. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lorincz AT, Brentnall AR,
Scibior-Bentkowska D, Reuter C, Banwait R, Cadman L, Austin J,
Cuzick J and Vasiljević N: Validation of a DNA methylation HPV
triage classifier in a screening sample. Int J Cancer.
138:2745–2751. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Nedjai B, Reuter C, Ahmad A, Banwait R,
Warman R, Carton J, Boer S, Cuzick J and Lorincz AT: Molecular
progression to cervical precancer, epigenetic switch or sequential
model? Int J Cancer. Apr 21–2018.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Huisman C, van der Wijst MG, Falahi F,
Overkamp J, Karsten G, Terpstra MM, Kok K, van der Zee AG,
Schuuring E, Wisman GB and Rots MG: Prolonged re-expression of the
hypermethylated gene EPB41L3 using artificial transcription factors
and epigenetic drugs. Epigenetics. 10:384–396. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Brentnall AR, Vasiljević N,
Scibior-Bentkowska D, Cadman L, Austin J, Cuzick J and Lorincz AT:
HPV33 DNA methylation measurement improves cervical pre-cancer risk
estimation of an HPV16, HPV18, HPV31 and \textit{EPB41L3}
methylation classifier. Cancer Biomark. 15:669–675. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Lorincz AT: Virtues and weaknesses of DNA
methylation as a test for cervical cancer prevention. Acta Cytol.
60:501–512. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
van Leeuwen RW, Ostrbenk A, Poljak M, van
der Zee AGJ, Schuuring E and Wisman GBA: DNA methylation markers as
a triage test for identification of cervical lesions in a high risk
human papillomavirus positive screening cohort. Int J Cancer.
144:746–754. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
68
|
Eijsink JJ, Lendvai Á, Deregowski V, Klip
HG, Verpooten G, Dehaspe L, de Bock GH, Hollema H, van Criekinge W,
Schuuring E, et al: A four-gene methylation marker panel as triage
test in high-risk human papillomavirus positive patients. Int J
Cancer. 130:1861–1869. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Lendvai Á, Johannes F, Grimm C, Eijsink
JJ, Wardenaar R, Volders HH, Klip HG, Hollema H, Jansen RC,
Schuuring E, et al: Genome-wide methylation profiling identifies
hypermethylated biomarkers in high-grade cervical intraepithelial
neoplasia. Epigenetics. 7:1268–1278. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Perez-Janices N, Blanco-Luquin I, Tuñón
MT, Barba-Ramos E, Ibáñez B, Zazpe-Cenoz I, Martinez-Aguillo M,
Hernandez B, Martínez-Lopez E, Fernández AF, et al: EPB41L3, TSP-1
and RASSF2 as new clinically relevant prognostic biomarkers in
diffuse gliomas. Oncotarget. 6:368–380. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ohno N, Terada N, Murata S, Yamakawa H,
Newsham IF, Katoh R, Ohara O and Ohno S: Immunolocalization of
protein 4.1B/DAL-1 during neoplastic transformation of mouse and
human intestinal epithelium. Histochem Cell Biol. 122:579–586.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Kume H, Muraoka S, Kuga T, Adachi J,
Narumi R, Watanabe S, Kuwano M, Kodera Y, Matsushita K, Fukuoka J,
et al: Discovery of colorectal cancer biomarker candidates by
membrane proteomic analysis and subsequent verification using
selected reaction monitoring (SRM) and tissue microarray (TMA)
analysis. Mol Cell Proteomics. 13:1471–1484. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Niwa T, Tsukamoto T, Toyoda T, Mori A,
Tanaka H, Maekita T, Ichinose M, Tatematsu M and Ushijima T:
Inflammatory processes triggered by Helicobacter pylori infection
cause aberrant DNA methylation in gastric epithelial cells. Cancer
Res. 70:1430–1440. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Sugimoto K, Ito T, Hulbert A, Chen C,
Orita H, Maeda M, Moro H, Fukagawa T, Ushijima T, Katai H, et al:
DNA methylation genome-wide analysis in remnant and primary gastric
cancers. Gastric Cancer. Mar 12–2019. View Article : Google Scholar : Epub ahead of
print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Terada N, Ohno N, Yamakawa H, Baba T,
Fujii Y, Christofori G, Ohara O and Ohno S: Protein 4.1B in mouse
islets of Langerhans and beta-cell tumorigenesis. Histochem Cell
Biol. 120:277–283. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zhu L, Yang N, Chen J, Zeng T, Yan S, Liu
Y, Yu G, Chen Q, Du G, Pan W, et al: LINC00052 upregulates EPB41L3
to inhibit migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by
binding miR-452-5p. Oncotarget. 8:63724–63737. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Giuliano AR, Nedjai B, Lorincz AT, Schell
MJ, Rahman S, Banwait R, Boulware D, Sirak B, Martin-Gomez L,
Abrahamsen M, et al: Methylation of HPV 16 and EPB41L3 in oral
gargles: Associations with oropharyngeal cancer detection and tumor
characteristics. Int J Cancer. Jul 15–2019.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Lorincz AT, Nathan M, Reuter C, Warman R,
Thaha MA, Sheaff M, Vasiljević N, Ahmad A, Cuzick J and Sasieni P:
Methylation of HPV and a tumor suppressor gene reveals anal cancer
and precursor lesions. Oncotarget. 8:50510–50520. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Yamada D, Kikuchi S, Williams YN,
Sakurai-Yageta M, Masuda M, Maruyama T, Tomita K, Gutmann DH,
Kakizoe T, Kitamura T, et al: Promoter hypermethylation of the
potential tumor suppressor DAL-1/4.1B gene in renal clear cell
carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 118:916–923. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Jiang SS, Chen CH, Tseng KY, Tsai FY, Wang
MJ, Chang IS, Lin JL and Lin S: Gene expression profiling suggests
a pathological role of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem
cells in aging-related skeletal diseases. Aging (Albany NY).
3:672–684. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Heller G, Geradts J, Ziegler B, Newsham I,
Filipits M, Markis-Ritzinger EM, Kandioler D, Berger W, Stiglbauer
W, Depisch D, et al: Downregulation of TSLC1 and DAL-1 expression
occurs frequently in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
103:283–291. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Li L, Li S, Cai T, Wang H, Xie X, Liu Z
and Zhang Y: The targeted inhibitory effects of human amniotic
fluid stem cells carrying CXCR4 promoter and DAL-1 on non-small
cell lung carcinoma growth. Gene Ther. 23:214–222. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|