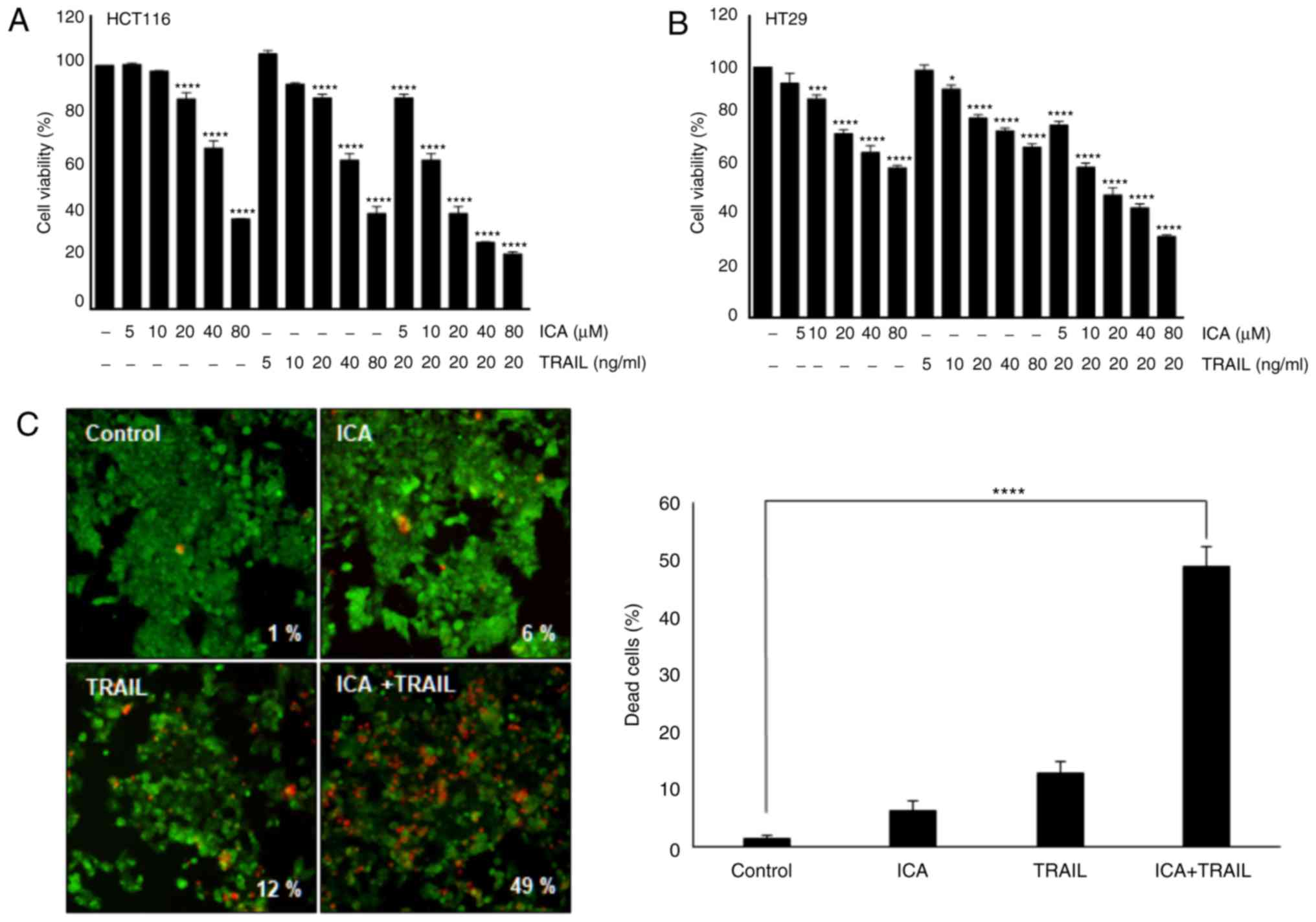
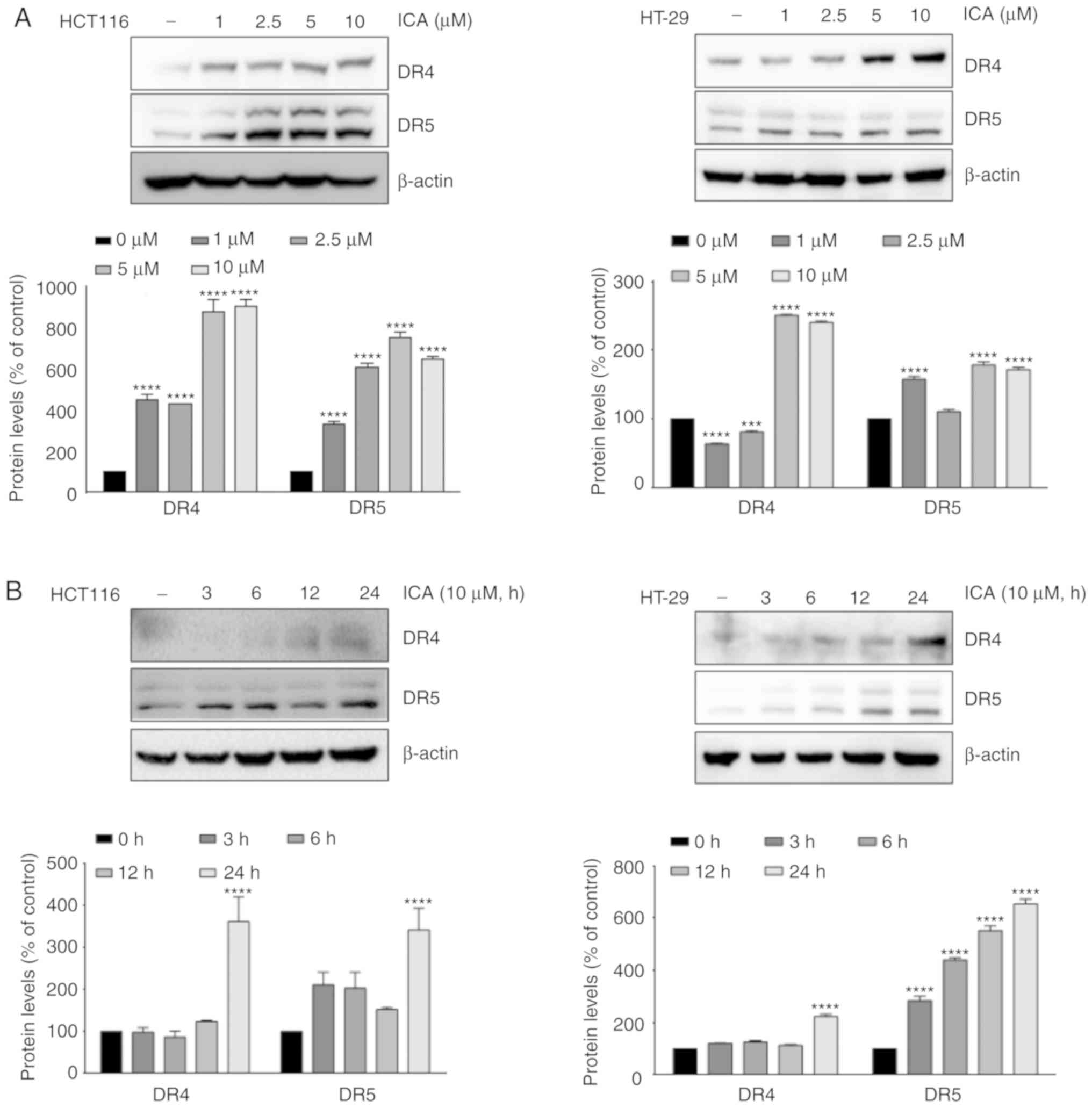
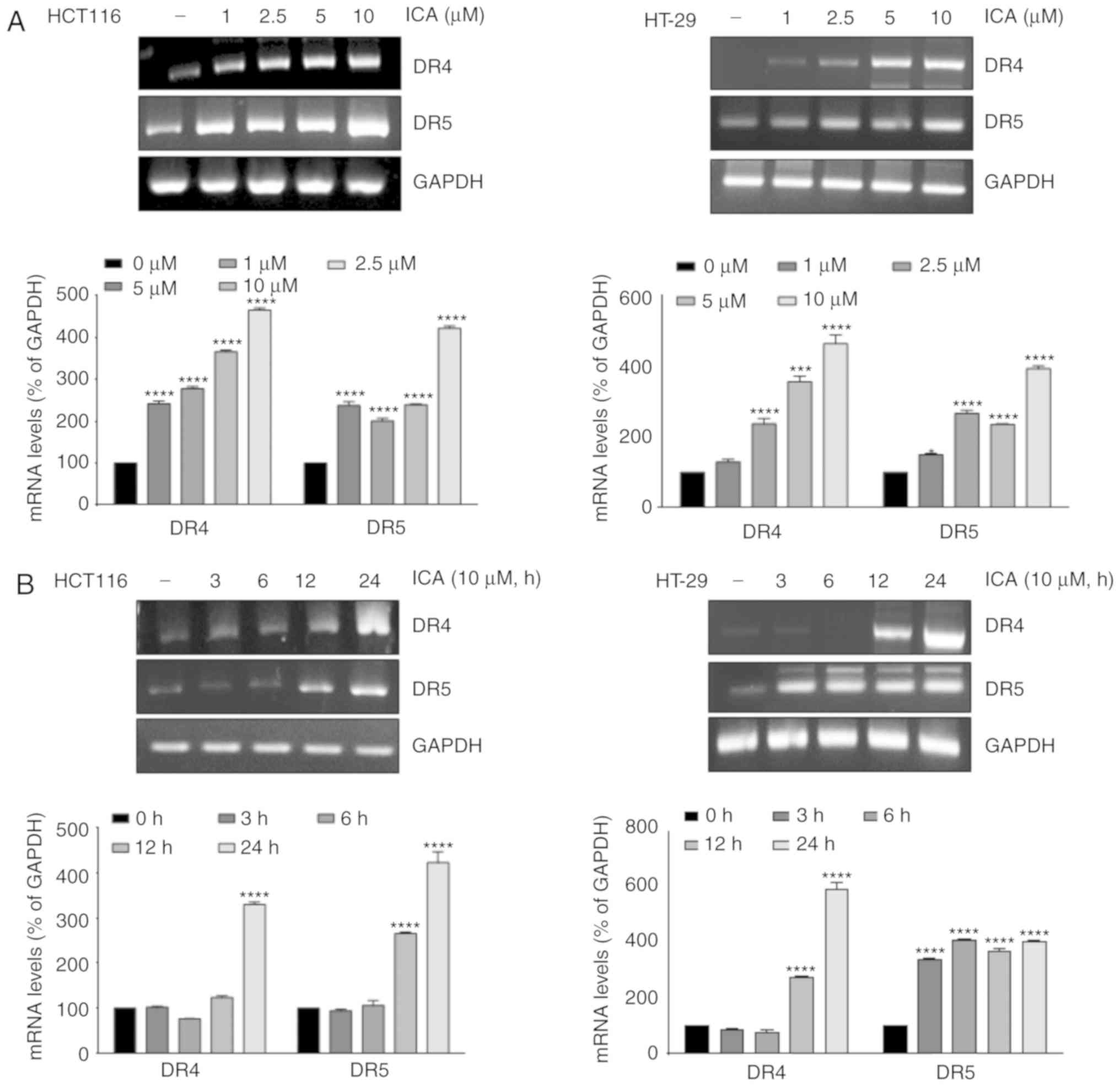
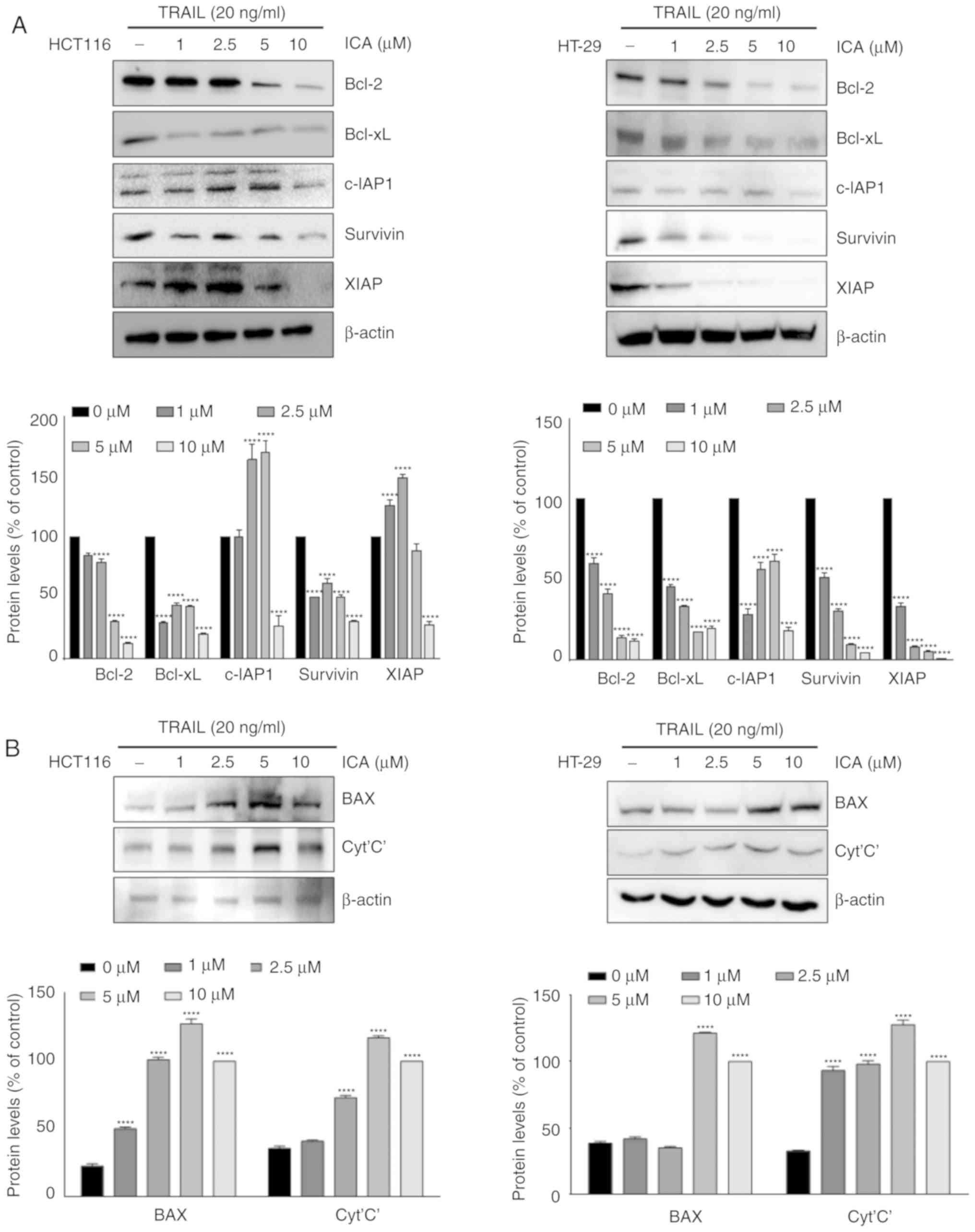
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hamilton SR: Characterizing the killer
colorectal carcinomas. Cancer Cell. 33:7–9. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lemke J, von Karstedt S, Zinngrebe J and
Walczak H: Getting TRAIL back on track for cancer therapy. Cell
Death Differ. 21:1350–1364. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kischkel FC, Lawrence DA, Chuntharapai A,
Schow P, Kim KJ and Ashkenazi A: Apo2L/TRAIL-dependent recruitment
of endogenous FADD and caspase-8 to death receptors 4 and 5.
Immunity. 12:611–620. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mühlethaler-Mottet A, Bourloud KB,
Auderset K, Joseph JM and Gross N: Drug-mediated sensitization to
TRAIL-induced apoptosis in caspase-8-complemented neuroblastoma
cells proceeds via activation of intrinsic and extrinsic pathways
and caspase-dependent cleavage of XIAP, Bcl-xL and RIP. Oncogene.
23:5415–5425. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zinonos I, Labrinidis A, Lee M, Liapis V,
Hay S, Ponomarev V, Diamond P, Zannettino AC, Findlay DM and
Evdokiou A: Apomab, a fully human agonistic antibody to DR5,
exhibits potent antitumor activity against primary and metastatic
breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:2969–2980. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Byun HS, Zhou W, Park I, Kang K, Lee SR,
Piao X, Park JB, Kwon TK, Na M and Hur GM: C-27-carboxylated
oleanane triterpenoids up-regulate TRAIL DISC assembly via p38 MAPK
and CHOP-mediated DR5 expression in human glioblastoma cells.
Biochem Pharmacol. 158:243–260. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kimberley FC and Screaton GR: Following a
TRAIL: Update on a ligand and its five receptors. Cell Res.
14:359–372. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ola MS, Nawaz M and Ahsan H: Role of Bcl-2
family proteins and caspases in the regulation of apoptosis. Mol
Cell Biochem. 351:41–58. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yadav VR, Prasad S and Aggarwal BB:
Cardamonin sensitizes tumour cells to TRAIL through ROS- and
CHOP-mediated up-regulation of death receptors and down-regulation
of survival proteins. Br J Pharmacol. 165:741–753. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Fruehauf JP and Meyskens FL Jr: Reactive
oxygen species: A breath of life or death? Clin Cancer Res.
13:789–794. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yip NC, Fombon IS, Liu P, Brown S,
Kannappan V, Armesilla AL, Xu B, Cassidy J, Darling JL and Wang W:
Disulfiram modulated ROS-MAPK and NFκB pathways and targeted breast
cancer cells with cancer stem cell-like properties. Br J Cancer.
104:1564–1574. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sze SC, Tong Y, Ng TB, Cheng CL and Cheung
HP: Herba Epimedii: Anti-oxidative properties and its medical
implications. Molecules. 15:7861–7870. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li S, Dong P, Wang J, Zhang J, Gu J, Wu X,
Wu W, Fei X, Zhang Z, Wang Y, et al: Icariin, a natural flavonol
glycoside, induces apoptosis in human hepatoma SMMC-7721 cells via
a ROS/JNK-dependent mitochondrial pathway. Cancer Lett.
298:222–230. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou J, Wu J, Chen X, Fortenbery N,
Eksioglu E, Kodumudi KN, Pk EB, Dong J, Djeu JY and Wei S: Icariin
and its derivative, ICT, exert anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor
effects, and modulate myeloid derived suppressive cells (MDSCs)
functions. Int Immunopharmacol. 11:890–898. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Z, Zhang X, Wang H, Qi L and Lou Y:
Neuroprotective effects of icaritin against beta amyloid-induced
neurotoxicity in primary cultured rat neuronal cells via
estrogen-dependent pathway. Neuroscience. 145:911–922. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang L, Lu D, Guo J, Meng X, Zhang G and
Wang F: Icariin from epimedium brevicornum maxim promotes the
biosynthesis of estrogen by aromatase (CYP19). J Ethnopharmacol.
145:715–721. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang Y, Dong H, Zhu M, Ou Y, Zhang J, Luo
H, Luo R, Wu J, Mao M, Liu X, et al: Icariin exterts negative
effects on human gastric cancer cell invasion and migration by
vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein via Rac1 pathway. Eur J
Pharmacol. 635:40–48. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun Y, Sun XH, Fan WJ, Jiang XM and Li AW:
Icariin induces S-phase arrest and apoptosis in medulloblastoma
cells. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 62:123–129. 2016.
|
|
20
|
Kim B, Lee KY and Park B: Icariin
abrogates osteoclast formation through the regulation of the
RANKL-mediated TRAF6/NF-κB/ERK signaling pathway in Raw264.7 cells.
Phytomedicine. 51:181–190. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jung KJ, Min KJ, Bae JH and Kwon TK:
Carnosic acid sensitized TRAIL-mediated apoptosis through
down-regulation of c-FLIP and Bcl-2 expression at the post
translational levels and CHOP-dependent up-regulation of DR5, Bim,
and PUMA expression in human carcinoma caki cells. Oncotarget.
6:1556–1568. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sung B, Prasad S, Ravindran J, Yadav VR
and Aggarwal BB: Capsazepine, a TRPV1 antagonist, sensitizes
colorectal cancer cells to apoptosis by TRAIL through
ROS-JNK-CHOP-mediated upregulation of death receptors. Free Radic
Biol Med. 53:1977–1987. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang X, Xue Q, Wu L, Wang B and Liang H:
Dasatinib promotes TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by upregulating
CHOP-dependent death receptor 5 in gastric cancer. FEBS Open Bio.
8:732–742. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yi L, Zongyuan Y, Cheng G, Lingyun Z,
Guilian Y and Wei G: Quercetin enhances apoptotic effect of tumor
necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) in
ovarian cancer cells through reactive oxygen species (ROS) mediated
CCAAT enhancer-binding protein homologous protein (CHOP)-death
receptor 5 pathway. Cancer Sci. 105:520–527. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jayasooriya RG, Choi YH, Hyun JW and Kim
GY: Camptothecin sensitizes human hepatoma Hep3B cells to
TRAIL-mediated apoptosis via ROS-dependent death receptor 5
upregulation with the involvement of MAPKs. Environ Toxicol
Pharmacol. 38:959–967. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yodkeeree S, Sung B, Limtrakul P and
Aggarwal BB: Zerumbone enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis through the
induction of death receptors in human colon cancer cells: Evidence
for an essential role of reactive oxygen species. Cancer Res.
69:6581–6589. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Do MT, Na M, Kim HG, Khanal T, Choi JH,
Jin SW, Oh SH, Hwang IH, Chung YC, Kim HS, et al: Ilimaquinone
induces death receptor expression and sensitizes human colon cancer
cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through activation of ROS-ERK/p38
MAPK-CHOP signaling pathways. Food Chem Toxicol. 71:51–59. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gupta SC, Francis SK, Nair MS, Mo YY and
Aggarwal BB: Azadirone, a limonoid tetranortriterpene, induces
death receptors and sensitizes human cancer cells to tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) through a p53
protein-independent mechanism: evidence for the role of the
ROS-ERK-CHOP-death receptor pathway. J Biol Chem. 288:32343–32356.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gupta SC, Hevia D, Patchva S, Park B, Koh
W and Aggarwal BB: Upsides and downsides of reactive oxygen species
for cancer: The roles of reactive oxygen species in tumorigenesis,
prevention, and therapy. Antioxid Redox Signal. 16:1295–1322. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Tao F, Qian C, Guo W, Luo Q, Xu Q and Sun
Y: Inhibition of Th1/Th17 responses via suppression of STAT1 and
STAT3 activation contributes to the amelioration of murine
experimental colitis by a natural flavonoid glucoside icariin.
Biochem Pharmacol. 85:798–807. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Reuss DE, Mucha J, Hagenlocher C, Ehemann
V, Kluwe L, Mautner V and von Deimling A: Sensitivity of malignant
peripheral nerve sheath tumor cells to TRAIL is augmented by loss
of NF1 through modulation of MYC/MAD and is potentiated by curcumin
through induction of ROS. PLoS One. 8:e571522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tian X, Ye J, Alonso-Basanta M, Hahn SM,
Koumenis C and Dorsey JF: Modulation of CCAAT/enhancer binding
protein homologous protein (CHOP)-dependent DR5 expression by
nelfinavir sensitizes glioblastoma multiforme cells to tumor
necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). J Biol
Chem. 286:29408–29416. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ravi R and Bedi A: Sensitization of tumor
cells to Apo2 ligand/TRAIL-induced apoptosis by inhibition of
casein kinase II. Cancer Res. 62:4180–4185. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yoon MJ, Kang YJ, Kim IY, Kim EH, Lee JA,
Lim JH, Kwon TK and Choi KS: Monensin, a polyether ionophore
antibiotic, overcomes TRAIL resistance in glioma cells via
endoplasmic reticulum stress, DR5 upregulation and c-FLIP
downregulation. Carcinogenesis. 34:1918–1928. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Park SK, Sanders BG and Kline K:
Tocotrienols induce apoptosis in breast cancer cell lines via an
endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent increase in extrinsic death
receptor signaling. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 124:361–375. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Stolfi C, Caruso R, Franzè E, Rizzo A,
Rotondi A, Monteleone I, Fantini MC, Pallone F and Monteleone G:
2-methoxy-5-amino-N-hydroxybenzamide sensitizes colon cancer cells
to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by regulating death receptor 5 and
survivin expression. Mol Cancer Ther. 10:1969–1981. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|