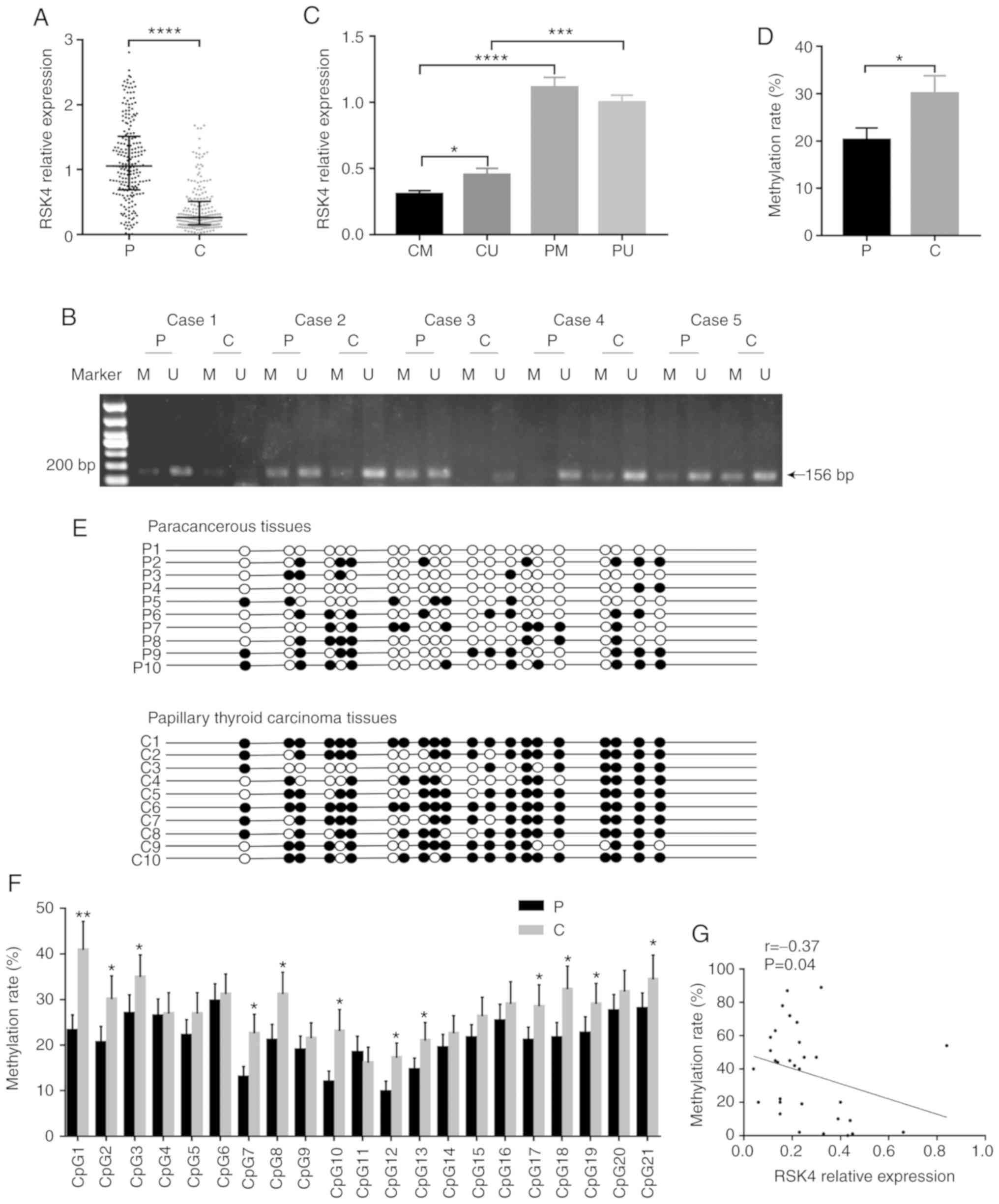
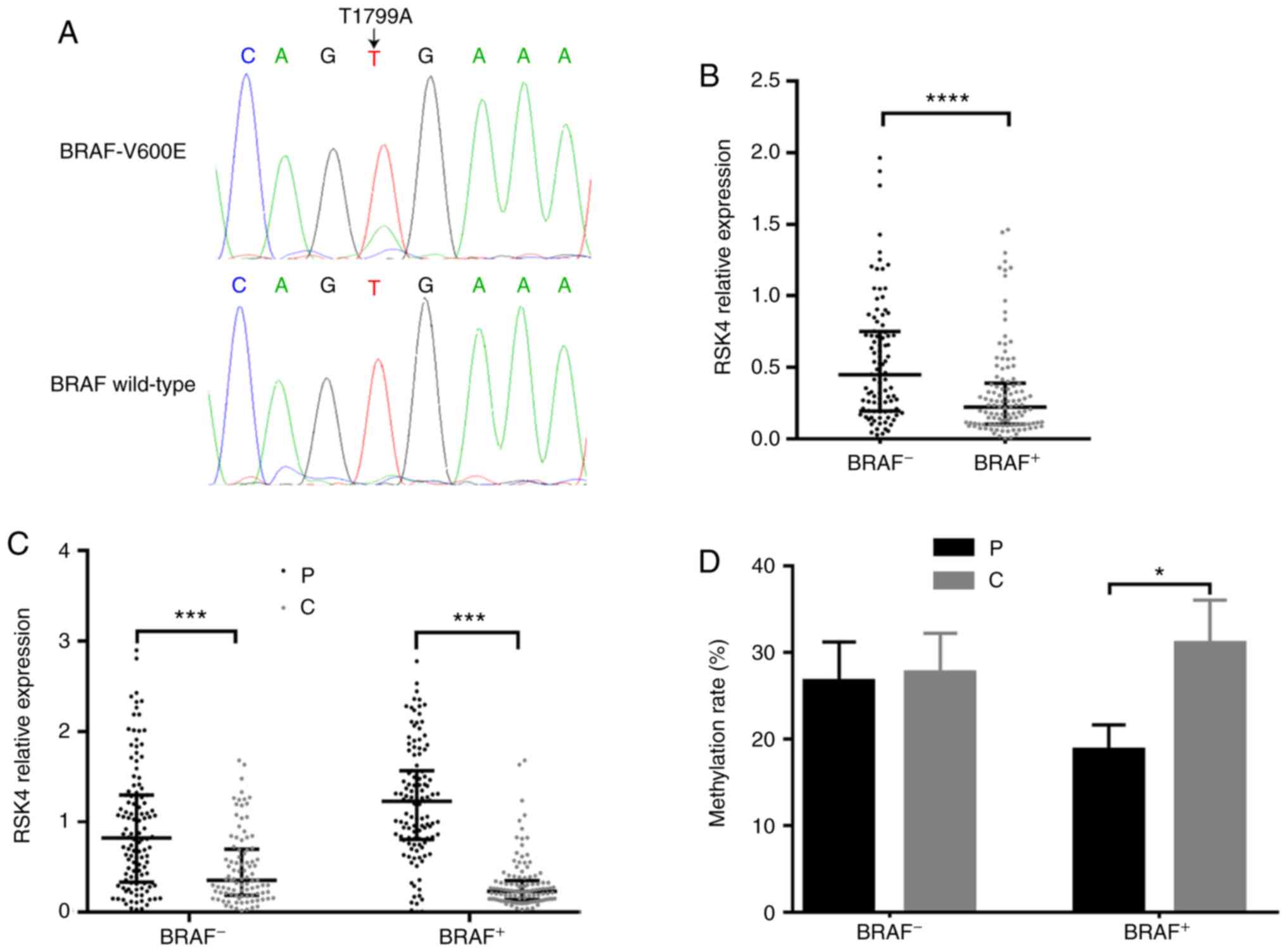
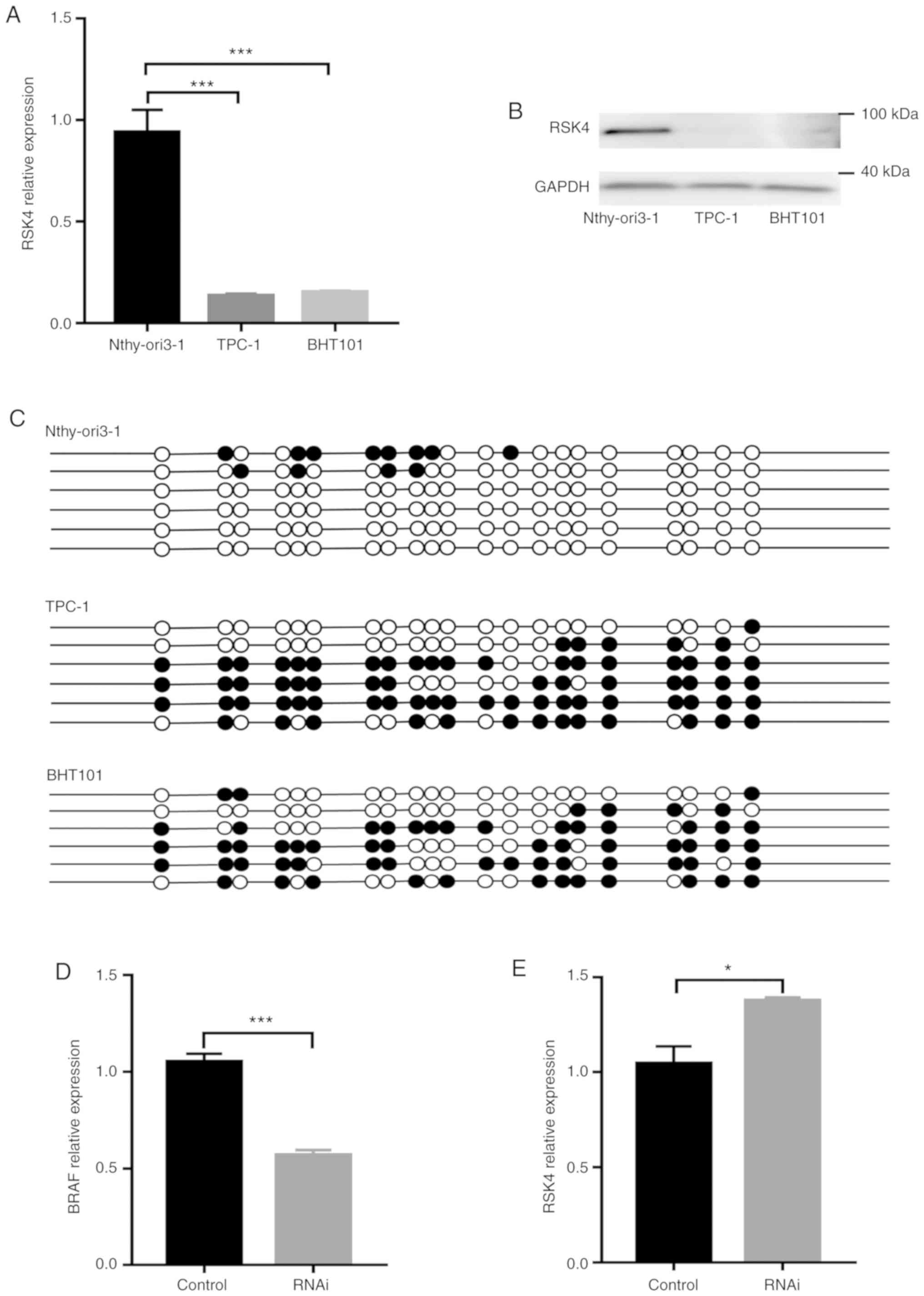
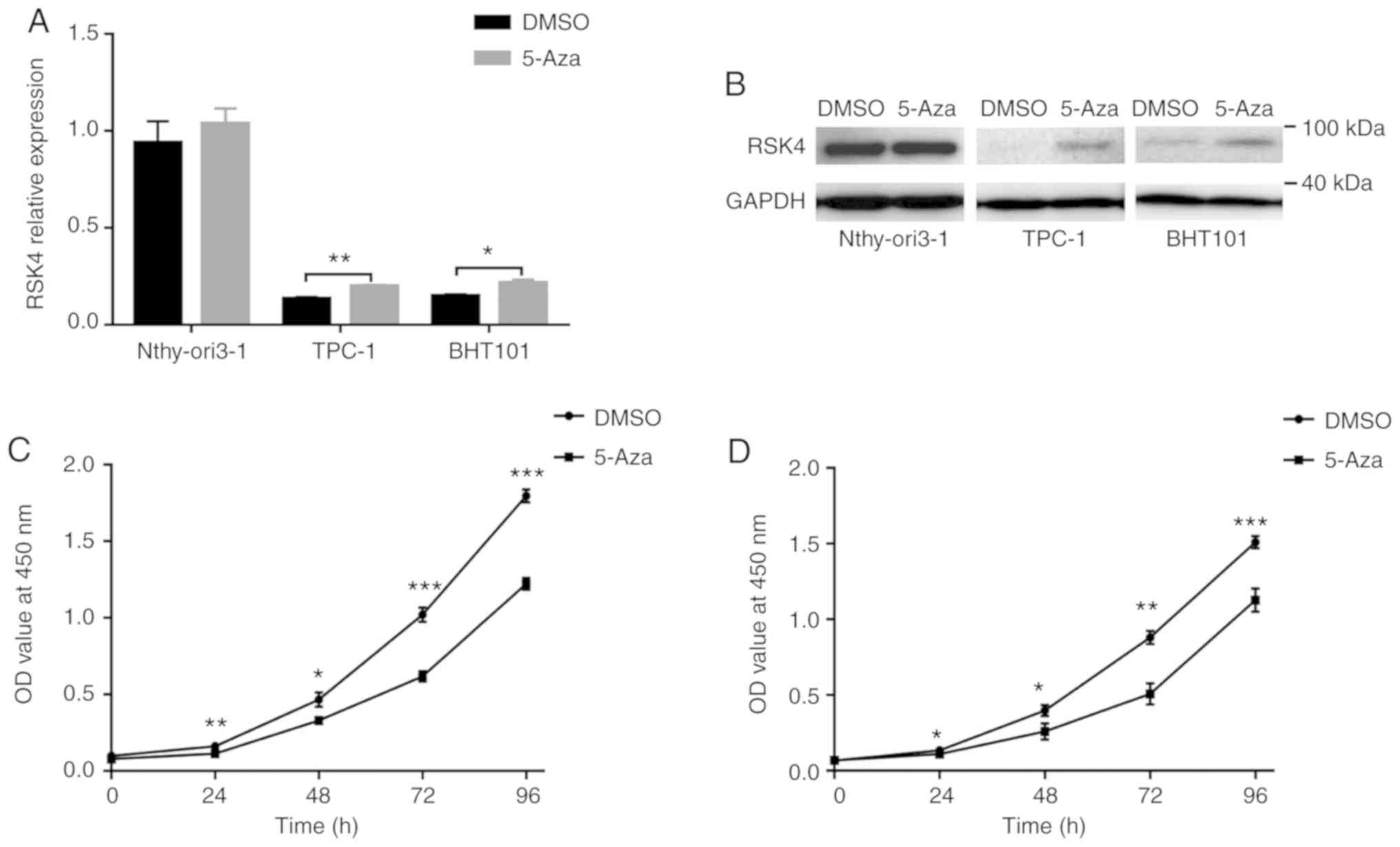
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, Doherty
GM, Mandel SJ, Nikiforov YE, Pacini F, Randolph GW, Sawka AM,
Schlumberger M, et al: 2015 American thyroid association management
guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and
differentiated thyroid cancer: The American thyroid association
guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid
cancer. Thyroid. 26:1–133. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Cabanillas ME, McFadden DG and Durante C:
Thyroid cancer. Lancet. 388:2783–2795. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tuttle RM, Ball DW, Byrd D, Dilawari RA,
Doherty GM, Duh QY, Ehya H, Farrar WB, Haddad RI, Kandeel F, et al:
Thyroid carcinoma. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 8:1228–1274. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Riesco-Eizaguirre G and Santisteban P:
ENDOCRINE TUMOURS: Advances in the molecular pathogenesis of
thyroid cancer: Lessons from the cancer genome. Eur J Endocrinol.
175:R203–R217. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
López-Vicente L, Pons B, Coch L, Teixidó
C, Hernández-Losa J, Armengol G, Ramon Y and Cajal S: RSK4
inhibition results in bypass of stress-induced and oncogene-induced
senescence. Carcinogenesis. 32:470–476. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lopez-Vicente L, Armengol G, Pons B, Coch
L, Argelaguet E, Lleonart M, Hernandez-Losa J, de Torres I and
Ramon y Cajal S: Regulation of replicative and stress-induced
senescence by RSK4, which is down-regulated in human tumors. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:4546–4553. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Arechavaleta-Velasco F, Zeferino-Toquero
M, Estrada-Moscoso I, Imani-Razavi FS, Olivares A, Perez-Juarez CE
and Diaz-Cueto L: Ribosomal S6 kinase 4 (RSK4) expression in
ovarian tumors and its regulation by antineoplastic drugs in
ovarian cancer cell lines. Med Oncol. 33:112016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dewdney SB, Rimel BJ, Thaker PH, Thompson
DM Jr, Schmidt A, Huettner P, Mutch DG, Gao F and Goodfellow PJ:
Aberrant methylation of the X-linked ribosomal S6 kinase RPS6KA6
(RSK4) in endometrial cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 17:2120–2129. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jiang Y, Ye X, Ji Y, Zhou X, Yang H, Wei W
and Li Q: Aberrant expression of RSK4 in breast cancer and its role
in the regulation of tumorigenicity. Int J Mol Med. 40:883–890.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Anjum R and Blenis J: The RSK family of
kinases: Emerging roles in cellular signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 9:747–758. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xing M: Molecular pathogenesis and
mechanisms of thyroid cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:184–199. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin JD, Fu SS, Chen JY, Lee CH, Chau WK,
Cheng CW, Wang YH, Lin YF, Fang WF and Tang KT: Clinical
manifestations and gene expression in patients with conventional
papillary thyroid carcinoma carrying the BRAF(V600E) mutation and
BRAF pseudogene. Thyroid. 26:691–704. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xing M: Genetic-guided risk assessment and
management of thyroid cancer. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am.
48:109–124. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang T, Chen C, Pan NF, Sun LY, Jiang XL,
Li JN, Tang Y and Jiang Y: BRAF V600E mutation and TERT promoter
mutation in papillary thyroid carcinomas and their association with
clinicopathological characteristics. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue
Ban. 50:919–924. 2019.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Myers AP, Corson LB, Rossant J and Baker
JC: Characterization of mouse Rsk4 as an inhibitor of fibroblast
growth factor-RAS-extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling.
Mol Cell Biol. 24:4255–4266. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Peixoto P, Grandvallet C, Feugeas JP,
Guittaut M and Hervouet E: Epigenetic control of autophagy in
cancer cells: A key process for cancer-related phenotypes. Cells.
8:E16562019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Skvortsova K, Stirzaker C and Taberlay P:
The DNA methylation landscape in cancer. Essays Biochem.
63:797–811. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Curtis CD and Goggins M: DNA methylation
analysis in human cancer. Methods Mol Med. 103:123–136. 2005.
|
|
20
|
Kubista M, Andrade JM, Bengtsson M,
Forootan A, Jonak J, Lind K, Sindelka R, Sjöback R, Sjögreen B,
Strömbom L, et al: The real-time polymerase chain reaction. Mol
Aspects Med. 27:95–125. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Niskakoski A, Kaur S, Staff S,
Renkonen-Sinisalo L, Lassus H, Järvinen HJ, Mecklin JP, Bützow R
and Peltomäki P: Epigenetic analysis of sporadic and
Lynch-associated ovarian cancers reveals histology-specific
patterns of DNA methylation. Epigenetics. 9:1577–1587. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Mao Y and Xing M: Recent incidences and
differential trends of thyroid cancer in the USA. Endocr Relat
Cancer. 23:313–322. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu R, Bishop J, Zhu G, Zhang T, Ladenson
PW and Xing M: Mortality risk stratification by combining BRAF
V600E and TERT promoter mutations in papillary thyroid cancer:
Genetic duet of BRAF and TERT promoter mutations in thyroid cancer
mortality. JAMA Oncol. 3:202–208. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Tsumagari K, Abd Elmageed ZY, Sholl AB,
Friedlander P, Abdraboh M, Xing M, Boulares AH and Kandil E:
Simultaneous suppression of the MAP kinase and NF-kB pathways
provides a robust therapeutic potential for thyroid cancer. Cancer
Lett. 368:46–53. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu D, Yang C, Bojdani E, Murugan AK and
Xing M: Identification of RASALl as a major tumor suppressor gene
in thyroid cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 105:1617–1627. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Khalaileh A, Dreazen A, Khatib A, Apel R,
Swisa A, Kidess-Bassir N, Maitra A, Meyuhas O, Dor Y and Zamir G:
Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 attenuates DNA damage and
tumor suppression during development of pancreatic cancer. Cancer
Res. 73:1811–1820. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li Q, Jiang Y, Wei W, Ji Y, Gao H and Liu
J: Frequent epigenetic inactivation of RSK4 by promoter methylation
in cancerous and non-cancerous tissues of breast cancer. Med Oncol.
31:7932014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Rafiee M, Keramati MR, Ayatollahi H,
Sadeghian MH, Barzegar M, Asgharzadeh A and Alinejad M:
Down-regulation of ribosomal S6 kinase RPS6KA6 in acute myeloid
leukemia patients. Cell J. 18:159–164. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
LLeonart ME, Vidal F, Gallardo D,
Diaz-Fuertes M, Rojo F, Cuatrecasas M, López-Vicente L, Kondoh H,
Blanco C, Carnero A, et al: New p53 related genes in human tumors:
Significant downregulation in colon and lung carcinomas. Oncol Rep.
16:603–608. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xiao K, Yu Z, Shi DT, Lei Z, Chen H, Cao
J, Tian W, Chen W and Zhang HT: Inactivation of BLU is associated
with methylation of Sp1-binding site of BLU promoter in gastric
cancer. Int J Oncol. 47:621–631. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Foy JP, Pickering CR, Papadimitrakopoulou
VA, Jelinek J, Lin SH, William WN Jr, Frederick MJ, Wang J, Lang W,
Feng L, et al: New DNA methylation markers and global DNA
hypomethylation are associated with oral cancer development. Cancer
Prev Res (Phila). 8. pp. 1027–1035. 2015, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Xing M, Alzahrani AS, Carson KA, Shong YK,
Kim TY, Viola D, Elisei R, Bendlova B, Yip L, Mian C, et al:
Association between BRAF V600E mutation and recurrence of papillary
thyroid cancer. J Clin Oncol. 33:42–50. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Xing M, Westra WH, Tufano RP, Cohen Y,
Rosenbaum E, Rhoden KJ, Carson KA, Vasko V, Larin A, Tallini G, et
al: BRAF mutation predicts a poorer clinical prognosis for
papillary thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 90:6373–6379.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang F, Zhao S, Shen X, Zhu G, Liu R,
Viola D, Elisei R, Puxeddu E, Fugazzola L, Colombo C, et al: braf
V600E confers male sex disease-specific mortality risk in patients
with papillary thyroid cancer. J Clin Oncol. 36:2787–2795. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kimura ET, Nikiforova MN, Zhu Z, Knauf JA,
Nikiforov YE and Fagin JA: High prevalence of BRAF mutations in
thyroid cancer: Genetic evidence for constitutive activation of the
RET/PTC-RAS-BRAF signaling pathway in papillary thyroid carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 63:1454–1457. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|