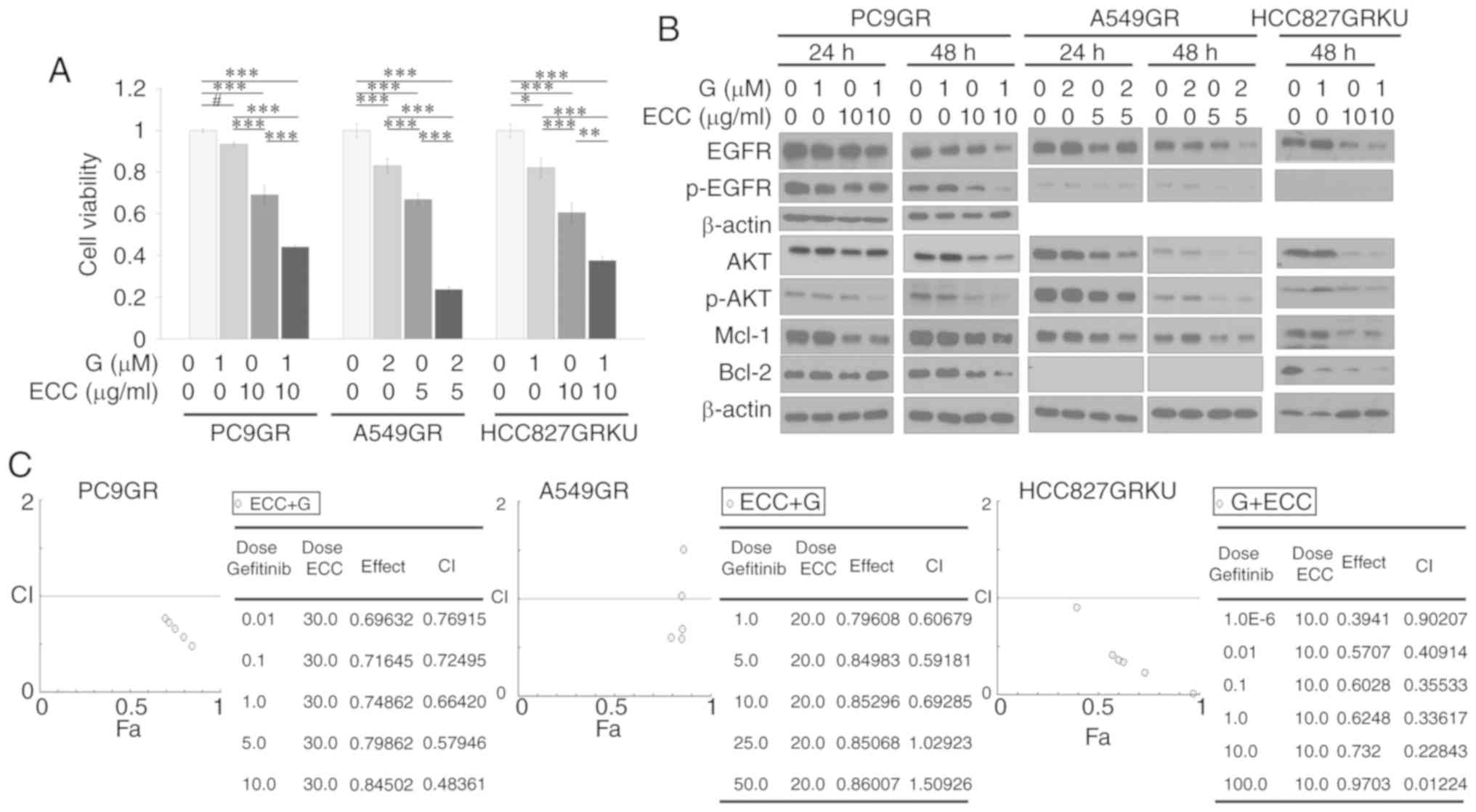
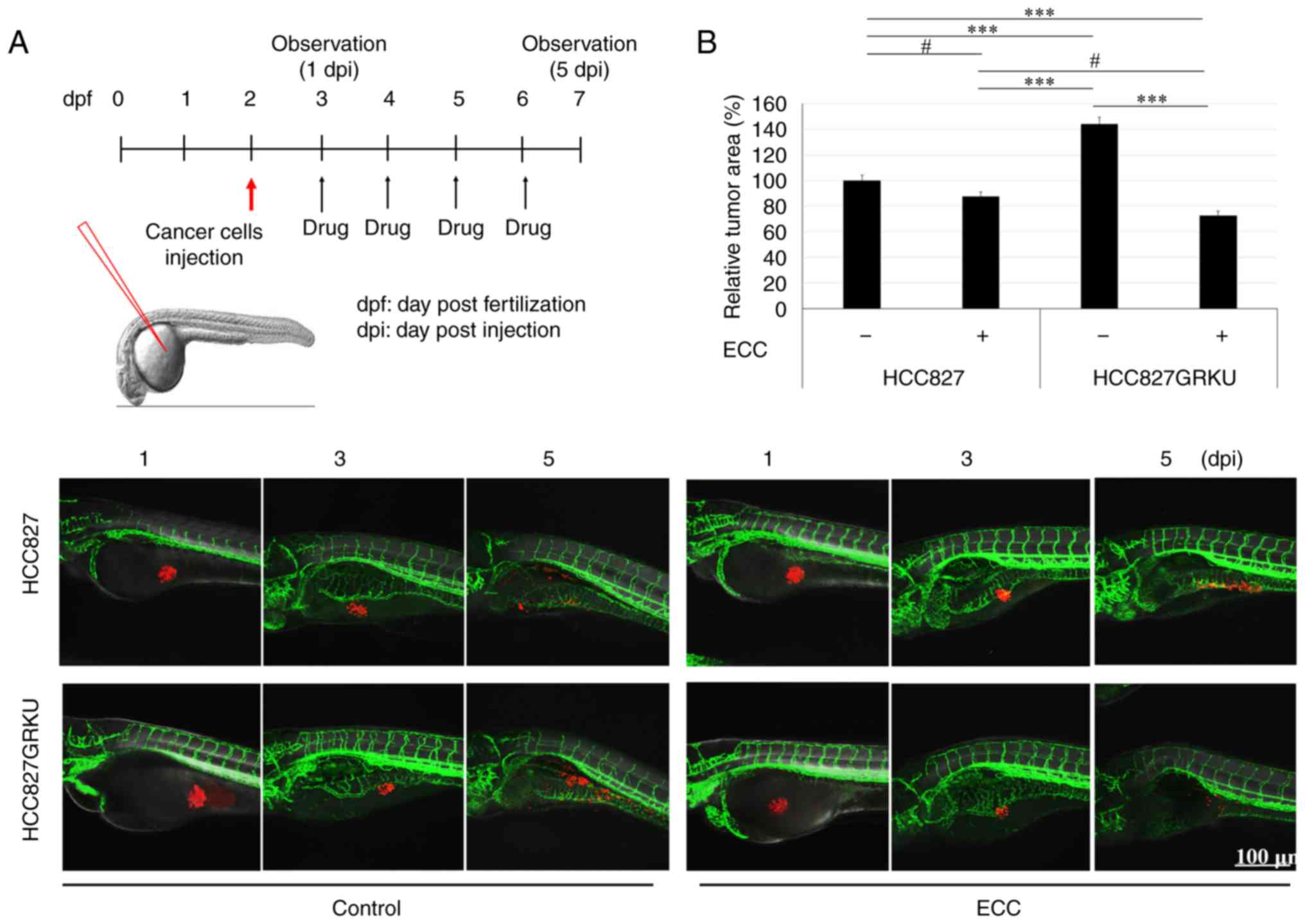
|
1
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fernald K and Kurokawa M: Evading
apoptosis in cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 23:620–633. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lin Y, Wang X and Jin H: EGFR-TKI
resistance in NSCLC patients: Mechanisms and strategies. Am J
Cancer Res. 4:411–435. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huang L and Fu L: Mechanisms of resistance
to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Acta Pharm Sin B. 5:390–401.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ng KP, Hillmer AM, Chuah CT, Juan WC, Ko
TK, Teo AS, Ariyaratne PN, Takahashi N, Sawada K, Fei Y, et al: A
common BIM deletion polymorphism mediates intrinsic resistance and
inferior responses to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer. Nat
Med. 18:521–528. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao M, Zhang Y, Cai W, Li J, Zhou F,
Cheng N, Ren R, Zhao C, Li X, Ren S, et al: The Bim deletion
polymorphism clinical profile and its relation with tyrosine kinase
inhibitor resistance in Chinese patients with non-small cell lung
cancer. Cancer. 120:2299–2307. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu SG, Liu YN, Yu CJ, Yang PC and Shih JY:
Association of BIM deletion polymorphism with intrinsic resistance
to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with lung
adenocarcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 2:826–828. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Costa DB, Halmos B, Kumar A, Schumer ST,
Huberman MS, Boggon TJ, Tenen DG and Kobayashi S: BIM mediates EGFR
tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced apoptosis in lung cancers with
oncogenic EGFR mutations. PLoS Med. 4:1669–1680. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pandey MK, Prasad S, Tyagi AK, Deb L,
Huang J, Karelia DN, Amin SG and Aggarwal BB: Targeting cell
survival proteins for cancer cell death. Pharmaceuticals (Basel).
9. pii: E11. 2016, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Delbridge AR and Strasser A: The BCL-2
protein family, BH3-mimetics and cancer therapy. Cell Death Differ.
22:1071–1080. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang TM, Barbone D, Fennell DA and
Broaddus VC: Bcl-2 family proteins contribute to apoptotic
resistance in lung cancer multicellular spheroids. Am J Respir Cell
Mol Biol. 41:14–23. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Martin B, Paesmans M, Berghmans T, Branle
F, Ghisdal L, Mascaux C, Meert AP, Steels E, Vallot F, Verdebout
JM, et al: Role of Bcl-2 as a prognostic factor for survival in
lung cancer: A systematic review of the literature with
meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. 89:55–64. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tang F, Mei W, Tian D and Huang D: An
evidence-based perspective of Coptis chinensis (Chinese Goldthread)
for cancer patients. Evidence-based anticancer materia medica. Cho
WCS: Springer; NY: pp. 111–130. 2011, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li J, Ni L, Li B, Wang M, Ding Z, Xiong C
and Lu X: Coptis chinensis affects the function of glioma cells
through the down-regulation of phosphorylation of STAT by reducing
HDAC3. BMC Complement Altern Med. 17:5242017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Auyeung K and Ko J: Coptis chinensis
inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth through nonsteroidal
anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene activation. Int J Mol Med.
24:571–577. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lulu N, Jiangan L, Weixing Z, Zhiyi Z, Hui
L, Jianhui T, Haizhou L and Hongli R: Coptis chinensis inhibits
growth and metastasis and induces cell apoptosis in non-small cell
lung cancer cells. Int J Clin Exp Med. 10:16037–16048. 2017.
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Park SH, Kim JH, Ko E, Kim JY, Park MJ,
Kim MJ, Seo H, Li S and Lee JY: Resistance to gefitinib and
cross-resistance to irreversible EGFR-TKIs mediated by disruption
of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in human lung cancer cells. FASEB J.
32:5862–5873. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Rho JK, Choi YJ, Lee JK, Ryoo BY, Na II,
Yang SH, Kim CH and Lee JC: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition
derived from repeated exposure to gefitinib determines the
sensitivity to EGFR inhibitors in A549, a non-small cell lung
cancer cell line. Lung Cancer. 63:219–226. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Rho JK, Choi YJ, Lee JK, Ryoo BY, Na II,
Yang SH, Lee SS, Kim CH, Yoo YD and Lee JC: The role of MET
activation in determining the sensitivity to epidermal growth
factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Mol Cancer Res.
7:1736–1743. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chou TC and Martin N: CompuSyn software
for drug combinations and for general dose-effect analysis, and
user's guide. ComboSyn, Inc.; Paramus, NJ: 2007
|
|
22
|
Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A and
Adams JM: Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family:
Implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
15:49–63. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wertz IE, Kusam S, Lam C, Okamoto T,
Sandoval W, Anderson DJ, Helgason E, Ernst JA, Eby M, Liu J, et al:
Sensitivity to antitubulin chemotherapeutics is regulated by MCL1
and FBW7. Nature. 471:110–114. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wei G, Margolin AA, Haery L, Brown E,
Cucolo L, Julian B, Shehata S, Kung AL, Beroukhim R and Golub TR:
Chemical genomics identifies small-molecule MCL1 repressors and
BCL-xL as a predictor of MCL1 dependency. Cancer Cell. 21:547–562.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Karnak D and Xu L: Chemosensitization of
prostate cancer by modulating Bcl-2 family proteins. Curr Drug
Targets. 11:699–707. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu DW, Chen CY, Chu CL and Lee H: Paxillin
confers resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutant
lung cancers via modulating BIM and Mcl-1 protein stability.
Oncogene. 35:621–630. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Belmar J and Fesik SW: Small molecule
Mcl-1 inhibitors for the treatment of cancer. Pharmacol Ther.
145:76–84. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Brumatti G and Ekert PG: Seeking a MCL-1
inhibitor. Cell Death Differ. 20:1440–1441. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pan R, Ruvolo VR, Wei J, Konopleva M, Reed
JC, Pellecchia M, Andreeff M and Ruvolo PP: Inhibition of Mcl-1
with the pan-Bcl-2 family inhibitor (-)BI97D6 overcomes ABT-737
resistance in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 126:363–372. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Song L, Coppola D, Livingston S, Cress D
and Haura EB: Mcl-1 regulates survival and sensitivity to diverse
apoptotic stimuli in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer
Biol Ther. 4:267–276. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Toge M, Yokoyama S, Kato S, Sakurai H,
Senda K, Doki Y, Hayakawa Y, Yoshimura N and Saiki I: Critical
contribution of MCL-1 in EMT-associated chemo-resistance in A549
non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Oncol. 46:1844–1848. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang H, Guttikonda S, Roberts L, Uziel T,
Semizarov D, Elmore SW, Leverson JD and Lam LT: Mcl-1 is critical
for survival in a subgroup of non-small-cell lung cancer cell
lines. Oncogene. 30:1963–1968. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhang J, Wang S, Wang L, Wang R, Chen S,
Pan B, Sun Y and Chen H: Prognostic value of Bcl-2 expression in
patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis and
systemic review. Onco Targets Ther. 8:3361–3369. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lohinai Z, Hoda MA, Fabian K, Ostoros G,
Raso E, Barbai T, Timar J, Kovalszky I, Cserepes M, Rozsas A, et
al: Distinct epidemiology and clinical consequence of classic
versus rare EGFR mutations in lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol.
10:738–746. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li K, Yang M, Liang N and Li S:
Determining EGFR-TKI sensitivity of G719X and other uncommon EGFR
mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: Perplexity and solution
(Review). Oncol Rep. 37:1347–1358. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|