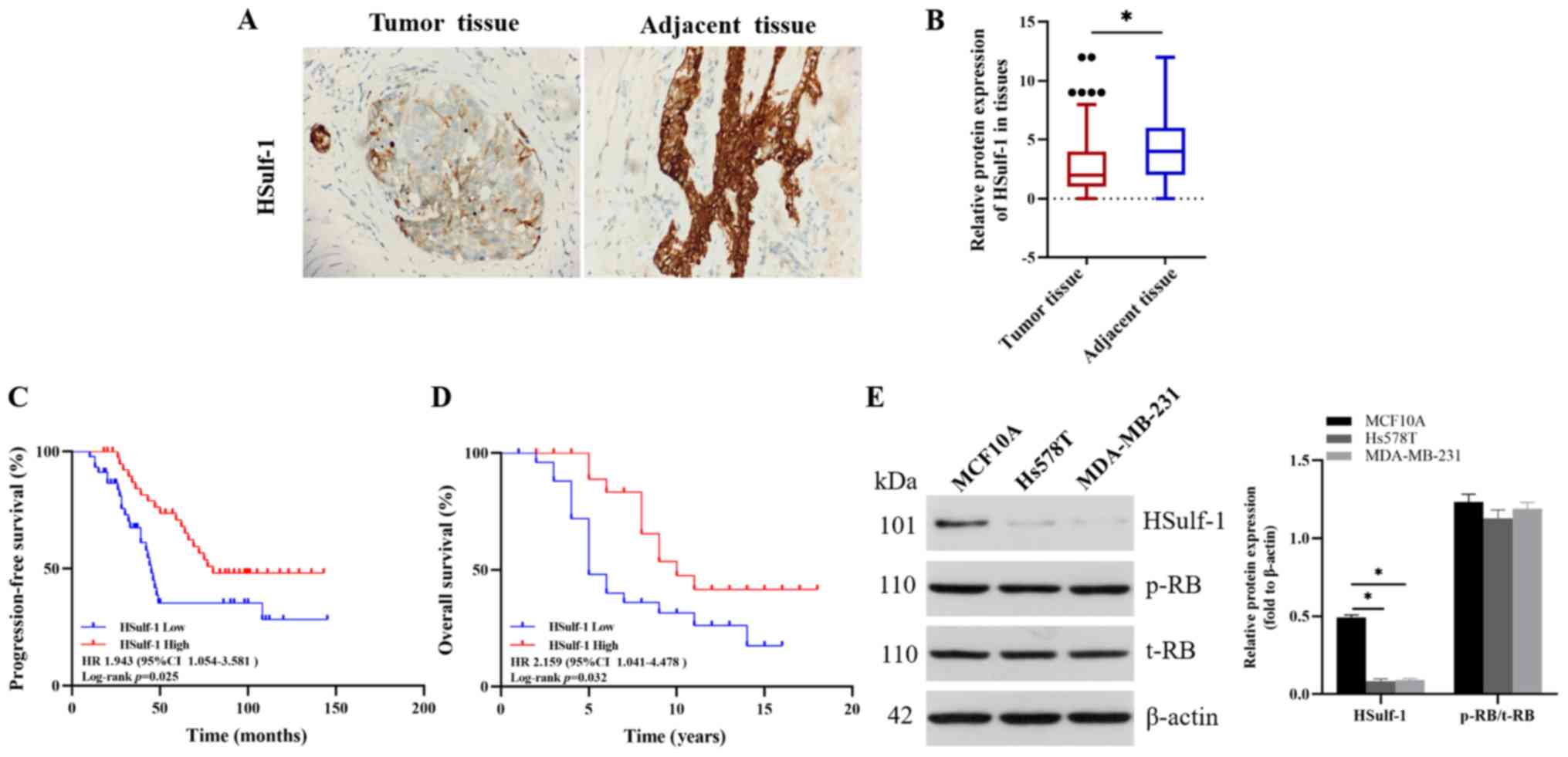
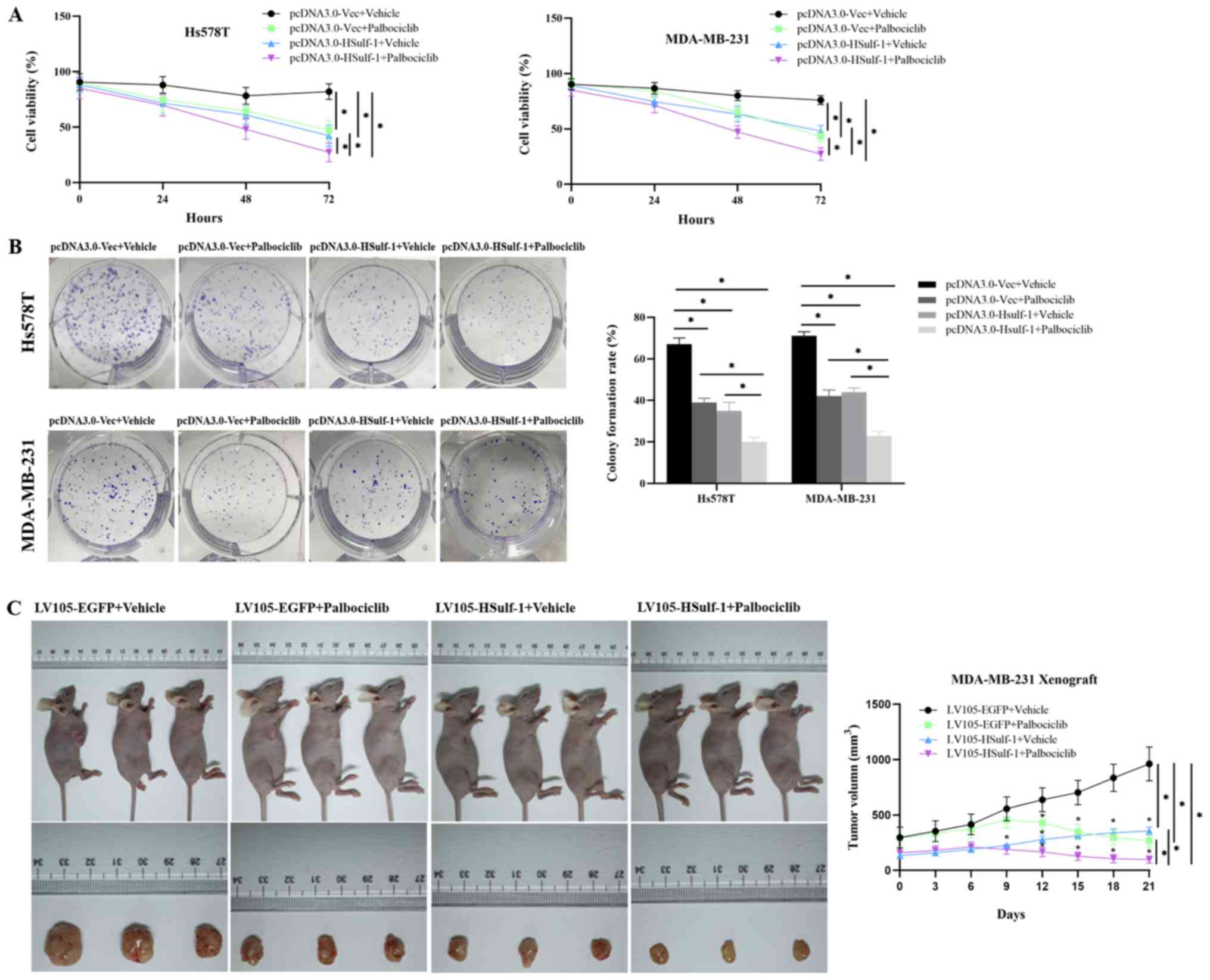
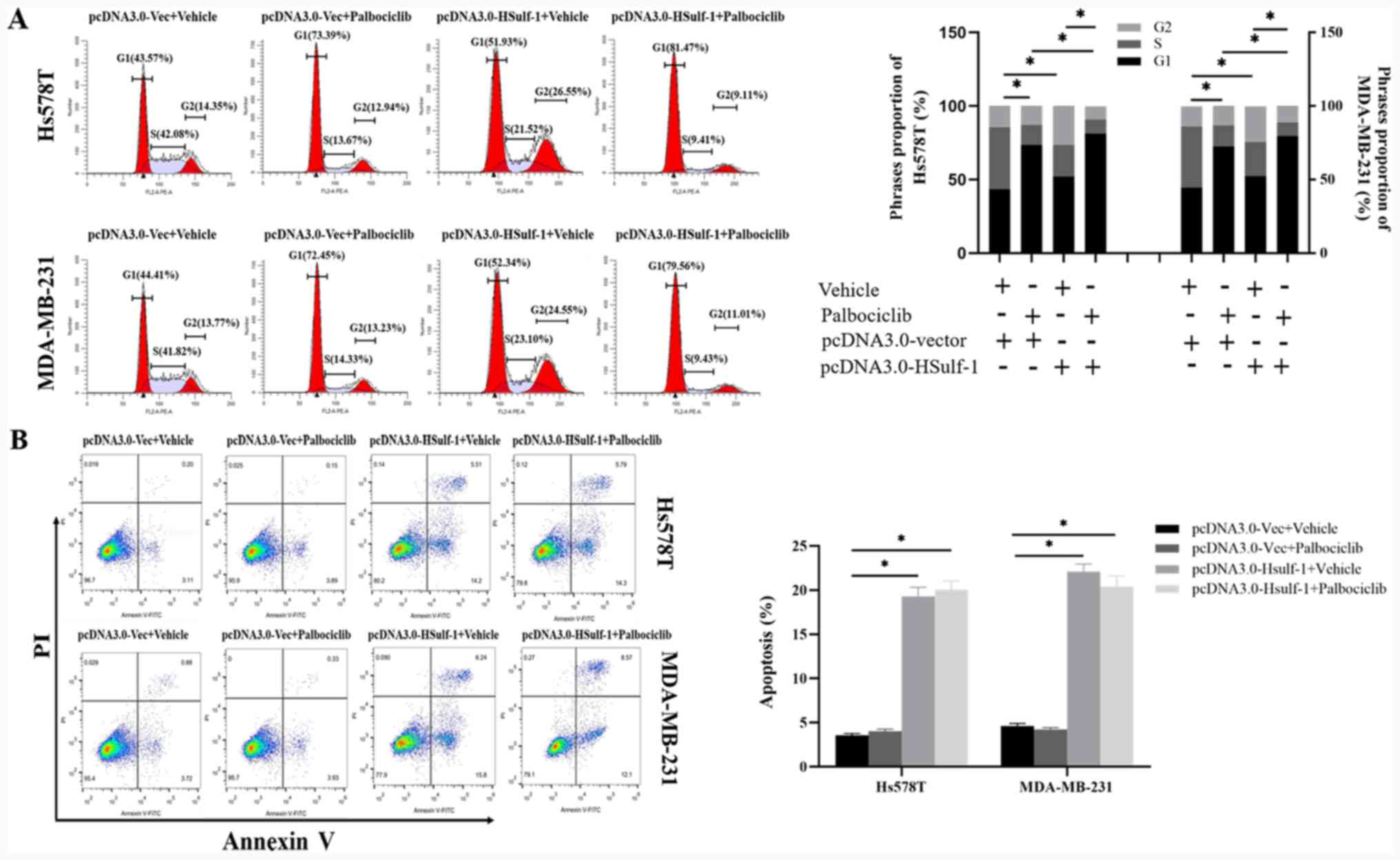
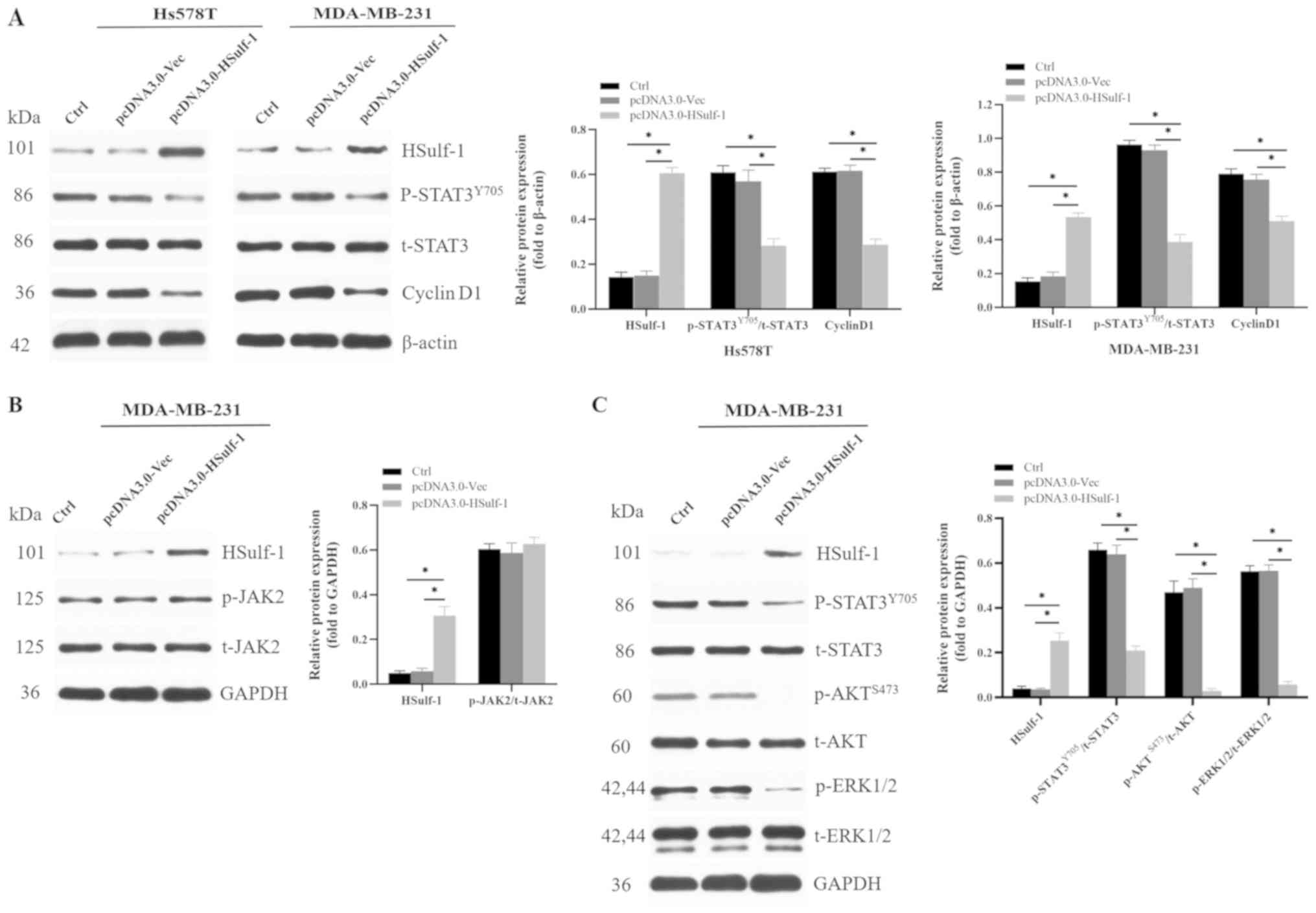
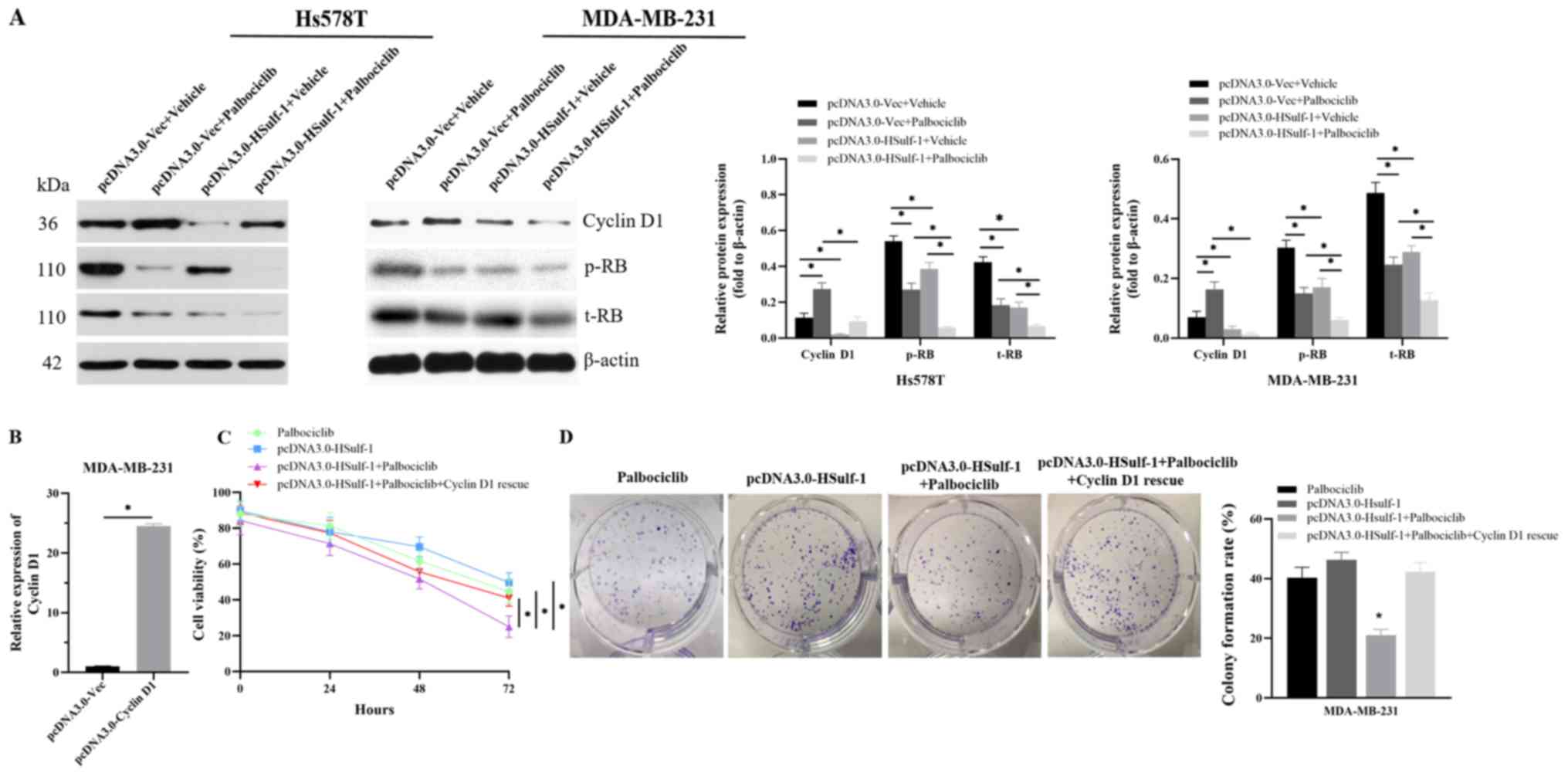
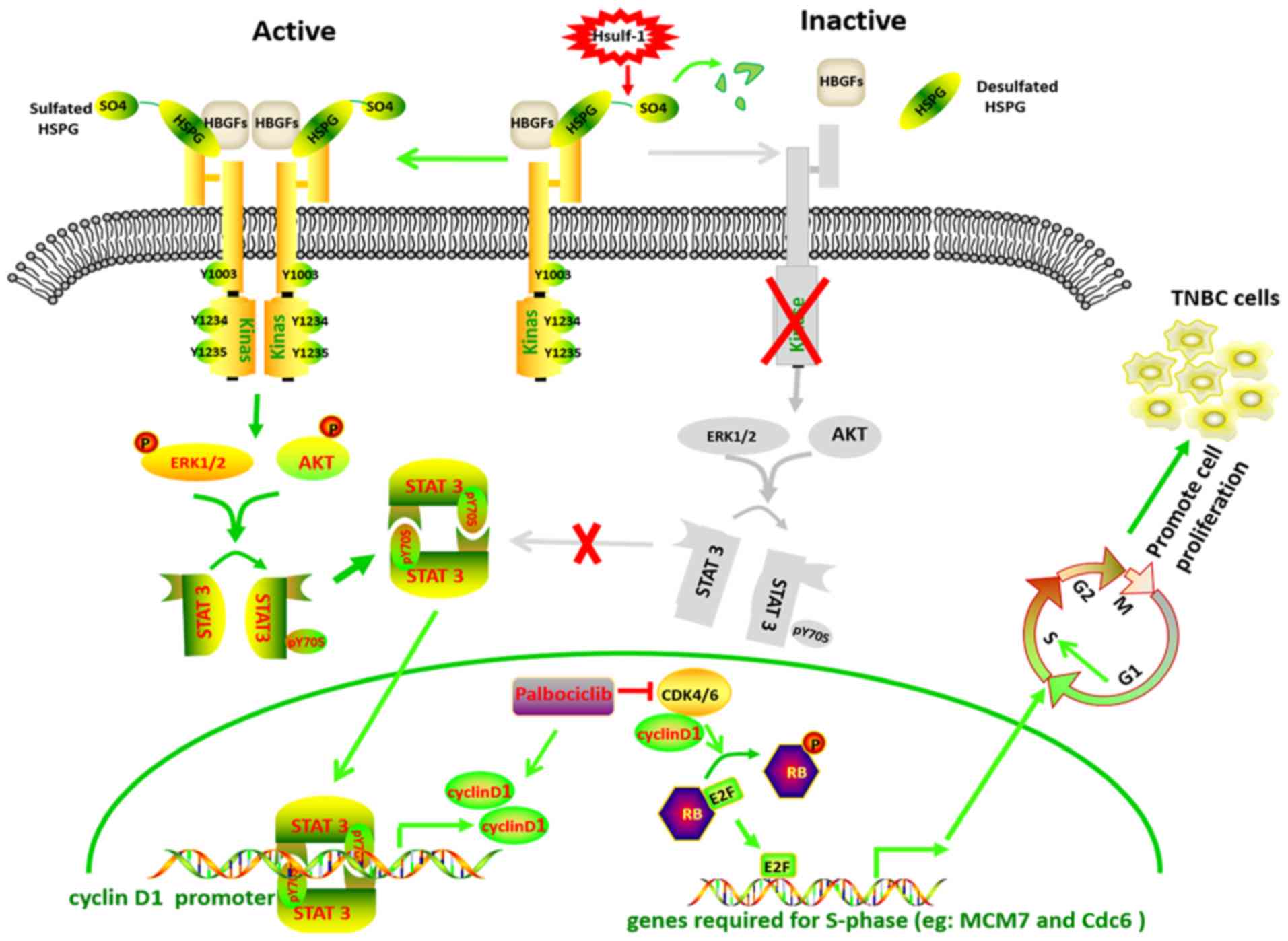
|
1
|
Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, Van De Rijn
M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA,
et al: Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature.
406:747–752. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network: Comprehensive
molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 490:61–70.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rakha EA, El-Rehim DA, Paish C, Green AR,
Lee AH, Robertson JF, Blamey RW, Macmillan D and Ellis IO: Basal
phenotype identifies a poor prognostic subgroup of breast cancer of
clinical importance. Eur J Cancer. 42:3149–3156. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Haffty BG, Yang Q, Reiss M, Kearney T,
Higgins SA, Weidhaas J, Harris L, Hait W and Toppmeyer D:
Locoregional relapse and distant metastasis in conservatively
managed triple negative early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
24:5652–5657. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM,
Kahn HK, Sawka CA, Lickley LA, Rawlinson E, Sun P and Narod SA:
Triple-negative breast cancer: Clinical features and patterns of
recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4429–4434. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR, André F,
Tordai A, Mejia JA, Symmans WF, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Hennessy B,
Green M, et al: Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term
survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 26:1275–1281. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Carey LA, Dees EC, Sawyer L, Gatti L,
Moore DT, Collichio F, Ollila DW, Sartor CI, Graham ML and Perou
CM: The triple negative paradox: Primary tumor chemosensitivity of
breast cancer subtypes. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2329–2334. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Robson M, Im SA, Senkus E, Xu B, Domchek
SM, Masuda N, Delaloge S, Li W, Tung N, Armstrong A, et al:
Olaparib for metastatic breast cancer in patients with a germline
BRCA mutation. N Engl J Med. 377:523–533. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Winter C, Nilsson MP, Olsson E, George AM,
Chen Y, Kvist A, Törngren T, Vallon-Christersson J, Hegardt C,
Häkkinen J, et al: Targeted sequencing of BRCA1 and BRCA2 across a
large unselected breast cancer cohort suggests that one-third of
mutations are somatic. Ann Oncol. 27:1532–1538. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Atchley DP, Albarracin CT, Lopez A, Valero
V, Amos CI, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Hortobagyi GN and Arun BK: Clinical
and pathologic characteristics of patients with BRCA-positive and
BRCA-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 26:4282–4288. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer. Cell. 100:57–70. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
O'Leary B, Finn RS and Turner NC: Treating
cancer with selective CDK4/6 inhibitors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
13:417–430. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Finn RS, Crown JP, Lang I, Boer K,
Bondarenko IM, Kulyk SO, Ettl J, Patel R, Pinter T, Schmidt M, et
al: The cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib in
combination with letrozole versus letrozole alone as first-line
treatment of oestrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative, advanced
breast cancer (PALOMA-1/TRIO-18): A randomised phase 2. study
Lancet Oncol. 16:25–35. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Turner NC, Ro J, André F, Loi S, Verma S,
Iwata H, Harbeck N, Loibl S, Huang Bartlett C, Zhang K, et al:
Palbociclib in hormone-receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. N
Engl J Med. 373:209–219. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Finn RS, Martin M, Rugo HS, Jones S, Im
SA, Gelmon K, Harbeck N, Lipatov ON, Walshe JM, Moulder S, et al:
Palbociclib and letrozole in advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med.
375:1925–1936. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hortobagyi GN, Stemmer SM, Burris HA, Yap
YS, Sonke GS, Paluch-Shimon S, Campone M, Blackwell KL, André F,
Winer EP, et al: Ribociclib as first-line therapy for HR-positive,
advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 375:1738–1748. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tripathy D, Im SA, Colleoni M, Franke F,
Bardia A, Harbeck N, Hurvitz SA, Chow L, Sohn J, Lee KS, et al:
Ribociclib plus endocrine therapy for premenopausal women with
hormone-receptor-positive, advanced breast cancer (MONALEESA-7): A
randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 19:904–915. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sledge GW Jr, Toi M, Neven P, Sohn J,
Inoue K, Pivot X, Burdaeva O, Okera M, Masuda N, Kaufman PA, et al:
MONARCH 2: Abemaciclib in combination with fulvestrant in women
with HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer who had progressed while
receiving endocrine therapy. J Clin Oncol. 35:2875–2884. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Finn RS, Dering J, Conklin D, Kalous O,
Cohen DJ, Desai AJ, Ginther C, Atefi M, Chen I, Fowst C, et al: PD
0332991, a selective cyclin D kinase 4/6 inhibitor, preferentially
inhibits proliferation of luminal estrogen receptor-positive human
breast cancer cell lines in vitro. Breast Cancer Res. 11:R772009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
DeMichele A, Clark AS, Tan KS, Heitjan DF,
Gramlich K, Gallagher M, Lal P, Feldman M, Zhang P, Colameco C, et
al: CDK 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib (PD0332991) in Rb+ advanced
breast cancer: Phase II activity, safety, and predictive biomarker
assessment. Clin Cancer Res. 21:995–1001. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lehmann BD, Bauer JA, Chen X, Sanders ME,
Chakravarthy AB, Shyr Y and Pietenpol JA: Identification of human
triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for
selection of targeted therapies. J Clin Invest. 121:2750–2767.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Witkiewicz AK and Knudsen ES:
Retinoblastoma tumor suppressor pathway in breast cancer:
Prognosis, precision medicine, and therapeutic interventions.
Breast Cancer Res. 16:2072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Treré D, Brighenti E, Donati G, Ceccarelli
C, Santini D, Taffurelli M, Montanaro L and Derenzini M: High
prevalence of retinoblastoma protein loss in triple-negative breast
cancers and its association with a good prognosis in patients
treated with adjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Oncol. 20:1818–1823. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Witkiewicz AK, Ertel A, McFalls J,
Valsecchi ME, Schwartz G and Knudsen ES: RB-pathway disruption is
associated with improved response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in
breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 18:5110–5122. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lamanna WC, Frese MA, Balleininger M and
Dierks T: Sulf loss influences N-, 2-O-, and 6-O-sulfation of
multiple heparan sulfate proteoglycans and modulates fibroblast
growth factor signaling. J Biol Chem. 283:27724–27735. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dhoot GK, Gustafsson MK, Ai X, Sun W,
Standiford DM and Emerson CP Jr: Regulation of Wnt signaling and
embryo patterning by an extracellular sulfatase. Science.
293:1663–1666. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Takashima Y, Keino-Masu K, Yashiro H, Hara
S, Suzuki T, van Kuppevelt TH, Masu M and Nagata M: Heparan sulfate
6-O-endosulfatases, Sulf1 and Sulf2, regulate glomerular integrity
by modulating growth factor signaling. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
310:F395–F408. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen Z, Fan JQ, Li J, Li QS, Yan Z, Jia
XK, Liu WD, Wei LJ, Zhang FZ, Gao H, et al: Promoter
hypermethylation correlates with the Hsulf-1 silencing in human
breast and gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 124:739–744. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Staub J, Chien J, Pan Y, Qian X, Narita K,
Aletti G, Scheerer M, Roberts LR, Molina J and Shridhar V:
Epigenetic silencing of HSulf-1 in ovarian cancer: Implications in
chemoresistance. Oncogene. 26:4969–4978. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lai JP, Sandhu DS, Shire AM and Roberts
LR: The tumor suppressor function of human sulfatase 1 (SULF1) in
carcinogenesis. J Gastrointest Cancer. 39:149–158. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Marotta LL, Almendro V, Marusyk A,
Shipitsin M, Schemme J, Walker SR, Bloushtain-Qimron N, Kim JJ,
Choudhury SA, Maruyama R, et al: The JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway
is required for growth of CD44(+)CD24(-) stem cell-like breast
cancer cells in human tumors. J Clin Invest. 121:2723–2735. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dai Y, Yang Y, MacLeod V, Yue X, Rapraeger
AC, Shriver Z, Venkataraman G, Sasisekharan R and Sanderson RD:
HSulf-1 and HSulf-2 are potent inhibitors of myeloma tumor growth
in vivo. J Biol Chem. 280:40066–40073. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lai JP, Chien JR, Moser DR, Staub JK,
Aderca I, Montoya DP, Matthews TA, Nagorney DM, Cunningham JM,
Smith DI, et al: hSulf1 Sulfatase promotes apoptosis of
hepatocellular cancer cells by decreasing heparin-binding growth
factor signaling. Gastroenterology. 126:231–248. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lai JP, Chien J, Strome SE, Staub J,
Montoya DP, Greene EL, Smith DI, Roberts LR and Shridhar V: HSulf-1
modulates HGF-mediated tumor cell invasion and signaling in head
and neck squamous carcinoma. Oncogene. 23:1439–1447. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Roy D, Mondal S, Wang C, He X, Khurana A,
Giri S, Hoffmann R, Jung DB, Kim SH, Chini EN, et al: Loss of
HSulf-1 promotes altered lipid metabolism in ovarian cancer. Cancer
Metab. 2:132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Narita K, Staub J, Chien J, Meyer K, Bauer
M, Friedl A, Ramakrishnan S and Shridhar V: HSulf-1 inhibits
angiogenesis and tumorigenesis in vivo. Cancer Res. 66:6025–6032.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lai J, Chien J, Staub J, Avula R, Greene
EL, Matthews TA, Smith DI, Kaufmann SH, Roberts LR and Shridhar V:
Loss of HSulf-1 up-regulates heparin-binding growth factor
signaling in cancer. J Biol Chem. 278:23107–23117. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Khurana A, Liu P, Mellone P, Lorenzon L,
Vincenzi B, Datta K, Yang B, Linhardt RJ, Lingle W, Chien J, et al:
HSulf-1 modulates FGF2- and hypoxia-mediated migration and invasion
of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 71:2152–2161. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Narita K, Chien J, Mullany SA, Staub J,
Qian X, Lingle WL and Shridhar V: Loss of HSulf-1 expression
enhances autocrine signaling mediated by amphiregulin in breast
cancer. J Biol Chem. 282:14413–14420. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Böcker W: WHO Classification of Breast
Tumors and Tumors of the Female Genital Organs: Pathology and
Genetics. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 86:116–119. 2002.
|
|
41
|
Amin MB, Edge S, Greene F, Byrd DR,
Brookland RK, Washington MK, Gershenwald JE, Compton CC, Hess KR,
Sullivan DC, et al: AJCC cancer staging manual. 8th ed. New York:
Springer; 2017, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Dean JL, McClendon AK and Knudsen ES:
Modification of the DNA damage response by therapeutic CDK4/6
inhibition. J Biol Chem. 287:29075–29087. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Asghar US, Barr AR, Cutts R, Beaney M,
Babina I, Sampath D, Giltnane J, Lacap JA, Crocker L, Young A, et
al: Single-cell dynamics determines response to CDK4/6 inhibition
in triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 23:5561–5572.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Yamamoto T, Kanaya N, Somlo G and Chen S:
Synergistic anti-cancer activity of CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib
and dual mTOR kinase inhibitor MLN0128 in pRb-expressing
ER-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 174:615–625.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Foidart P, Yip C, Radermacher J, Blacher
S, Lienard M, Montero-Ruiz L, Maquoi E, Montaudon E,
Château-Joubert S, Collignon J, et al: Expression of MT4-MMP, EGFR,
and RB in triple-negative breast cancer strongly sensitizes tumors
to erlotinib and palbociclib combination therapy. Clin Cancer Res.
25:1838–1850. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Liu CY, Lau KY, Hsu CC, Chen JL, Lee CH,
Huang TT, Chen YT, Huang CT, Lin PH and Tseng LM: Combination of
palbociclib with enzalutamide shows in vitro activity in RB
proficient and androgen receptor positive triple negative breast
cancer cells. PLoS One. 12:e01890072017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lamb R, Lehn S, Rogerson L, Clarke RB and
Landberg G: Cell cycle regulators cyclin D1 and CDK4/6 have
estrogen receptor-dependent divergent functions in breast cancer
migration and stem cell-like activity. Cell cycle. 12:2384–2394.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhong Z, Yeow WS, Zou C, Wassell R, Wang
C, Pestell RG, Quong JN and Quong AA: Cyclin D1/cyclin-dependent
kinase 4 interacts with filamin A and affects the migration and
invasion potential of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
70:2105–2114. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liu T, Yu J, Deng M, Yin Y, Zhang H, Luo
K, Qin B, Li Y, Wu C, Ren T, et al: CDK4/6-dependent activation of
DUB3 regulates cancer metastasis through SNAIL1. Nat Commun.
8:139232017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Qin G, Xu F, Qin T, Zheng Q, Shi D, Xia W,
Tian Y, Tang Y, Wang J, Xiao X, et al: Palbociclib inhibits
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in breast cancer
via c-Jun/COX-2 signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 6:41794–41808. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tsai JH and Yang J: Epithelial-mesenchymal
plasticity in carcinoma metastasis. Genes Dev. 27:2192–2206. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kang Y and Massague J:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: Twist in development and
metastasis. Cell. 118:277–279. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ye X and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity: A central regulator of cancer
progression. Trends Cell Biol. 25:675–686. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liu L, Ding F, Chen J, Wang B and Liu Z:
hSulf-1 inhibits cell proliferation and migration and promotes
apoptosis by suppressing stat3 signaling in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 7:963–969. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Banerjee K and Resat H: Constitutive
activation of STAT3 in breast cancer cells: A review. Int J Cancer.
138:2570–2578. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
58
|
Bao L, Yan Y, Xu C, Ji W, Shen S, Xu G,
Zeng Y, Sun B, Qian H, Chen L, et al: MicroRNA-21 suppresses PTEN
and hSulf-1 expression and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma
progression through AKT/ERK pathways. Cancer Lett. 337:226–236.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Liu H, Fu X, Ji W, Liu K, Bao L, Yan Y, Wu
M, Yang J and Su C: Human sulfatase-1 inhibits the migration and
proliferation of SMMC-7721 hepatocellular carcinoma cells by
downregulating the growth factor signaling. Hepatol Res.
43:516–525. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Xu G, Ji W, Su Y, Xu Y, Yan Y, Shen S, Li
X, Sun B, Qian H, Chen L, et al: Sulfatase 1 (hSulf-1) reverses
basic fibroblast growth factor-stimulated signaling and inhibits
growth of hepatocellular carcinoma in animal model. Oncotarget.
5:5029–5039. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhang H, Newman DR and Sannes PL: HSULF-1
inhibits ERK and AKT signaling and decreases cell viability in
vitro in human lung epithelial cells. Respir Res. 13:692012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Corsetti G, Yuan Z, Romano C,
Chen-Scarabelli C, Fanzani A, Pasini E, Dioguardi FS, Onorati F,
Linardi D, Knight R, et al: Urocortin induces phosphorylation of
distinct residues of signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3 (STAT3) via different signaling pathways. Med Sci
Monit Basic Res. 25:139–152. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Malanga D, De Marco C, Guerriero I,
Colelli F, Rinaldo N, Scrima M, Mirante T, De Vitis C, Zoppoli P,
Ceccarelli M, et al: The Akt1/IL-6/STAT3 pathway regulates growth
of lung tumor initiating cells. Oncotarget. 6:42667–42686. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Long F, He Y, Fu H, Li Y, Bao X, Wang Q,
Wang Y, Xie C and Lou L: Preclinical characterization of SHR6390, a
novel CDK 4/6 inhibitor, in vitro and in human tumor xenograft
models. Cancer Sci. 110:1420–1430. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Burstein MD, Tsimelzon A, Poage GM,
Covington KR, Contreras A, Fuqua SA, Savage MI, Osborne CK,
Hilsenbeck SG, Chang JC, et al: Comprehensive genomic analysis
identifies novel subtypes and targets of triple-negative breast
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 21:1688–1698. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
66
|
Asghar U, Herrera-Abreu MT, Cutts R,
Babina I, Pearson A and Turner NC: Identification of subtypes of
triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) that are sensitive to CDK4/6
inhibition. J Clin Oncol. 33:110982015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Rein DT, Breidenbach M and Curiel DT:
Current developments in adenovirus-based cancer gene therapy.
Future Oncol. 2:137–143. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Maruyama TH, Harada Y, Matsumura T, Satoh
E, Cui F, Iwai M, Kita M, Hibi S, Imanishi J, Sawada T and Mazda O:
Effective suicide gene therapy in vivo by EBV-based plasmid vector
coupled with polyamidoamine dendrimer. Gene Ther. 7:53–60. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Kursa M, Walker GF, Roessler V, Ogris M,
Roedl W, Kircheis R and Wagner E: Novel shielded
transferrin-polyethylene glycol-polyethylenimine/DNA complexes for
systemic tumor-targeted gene transfer. Bioconjug Chem. 14:222–231.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Griffin JM, Fackelmeier B, Clemett CA,
Fong DM, Mouravlev A, Young D and O'Carroll SJ: Astrocyte-selective
AAV-ADAMTS4 gene therapy combined with hindlimb rehabilitation
promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol.
327:1132322020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Salameh JW, Zhou L, Ward SM, Chalaarca CF,
Emrick T and Figueiredo ML: Polymer-mediated gene therapy: Recent
advances and merging of delivery techniques. Wiley Interdiscip Rev
Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 1:e15982020.
|
|
72
|
Selva EM and Perrimon N: Role of heparan
sulfate proteoglycans in cell signaling and cancer. Adv Cancer Res.
83:67–80. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Rubin JS, Day RM, Breckenridge D, Atabey
N, Taylor WG, Stahl SJ, Wingfield PT, Kaufman JD, Schwall R and
Bottaro DP: Dissociation of heparan sulfate and receptor binding
domains of hepatocyte growth factor reveals that heparan
sulfate-c-met interaction facilitates signaling. J Biol Chem.
276:32977–32983. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G,
Zhao Y, Pestell RG, Albanese C and Darnell JE Jr: Stat3 as an
oncogene. Cell. 98:295–303. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Herrera-Abreu MT, Palafox M, Asghar U,
Rivas MA, Cutts RJ, Garcia-Murillas I, Pearson A, Guzman M,
Rodriguez O, Grueso J, et al: Early adaptation and acquired
resistance to CDK4/6 inhibition in estrogen receptor-positive
breast cancer. Cancer Res. 76:2301–2313. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Michaloglou C, Crafter C, Siersbaek R,
Delpuech O, Curwen JO, Carnevalli LS, Staniszewska AD, Polanska UM,
Cheraghchi-Bashi A, Lawson M, et al: Combined inhibition of mTOR
and CDK4/6 is required for optimal blockade of E2F function and
long-term growth inhibition in estrogen receptor-positive breast
cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 17:908–920. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Javle MM, Shroff RT, Xiong H, Varadhachary
GA, Fogelman D, Reddy SA, Davis D, Zhang Y, Wolff RA and Abbruzzese
JL: Inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in
advanced pancreatic cancer: Results of two phase II studies. BMC
Cancer. 10:3682010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Kettner NM, Vijayaraghavan S, Durak MG,
Bui T, Kohansal M, Ha MJ, Liu B, Rao X, Wang J, Yi M, et al:
Combined inhibition of STAT3 and DNA repair in
palbociclib-resistant ER-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
25:3996–4013. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|