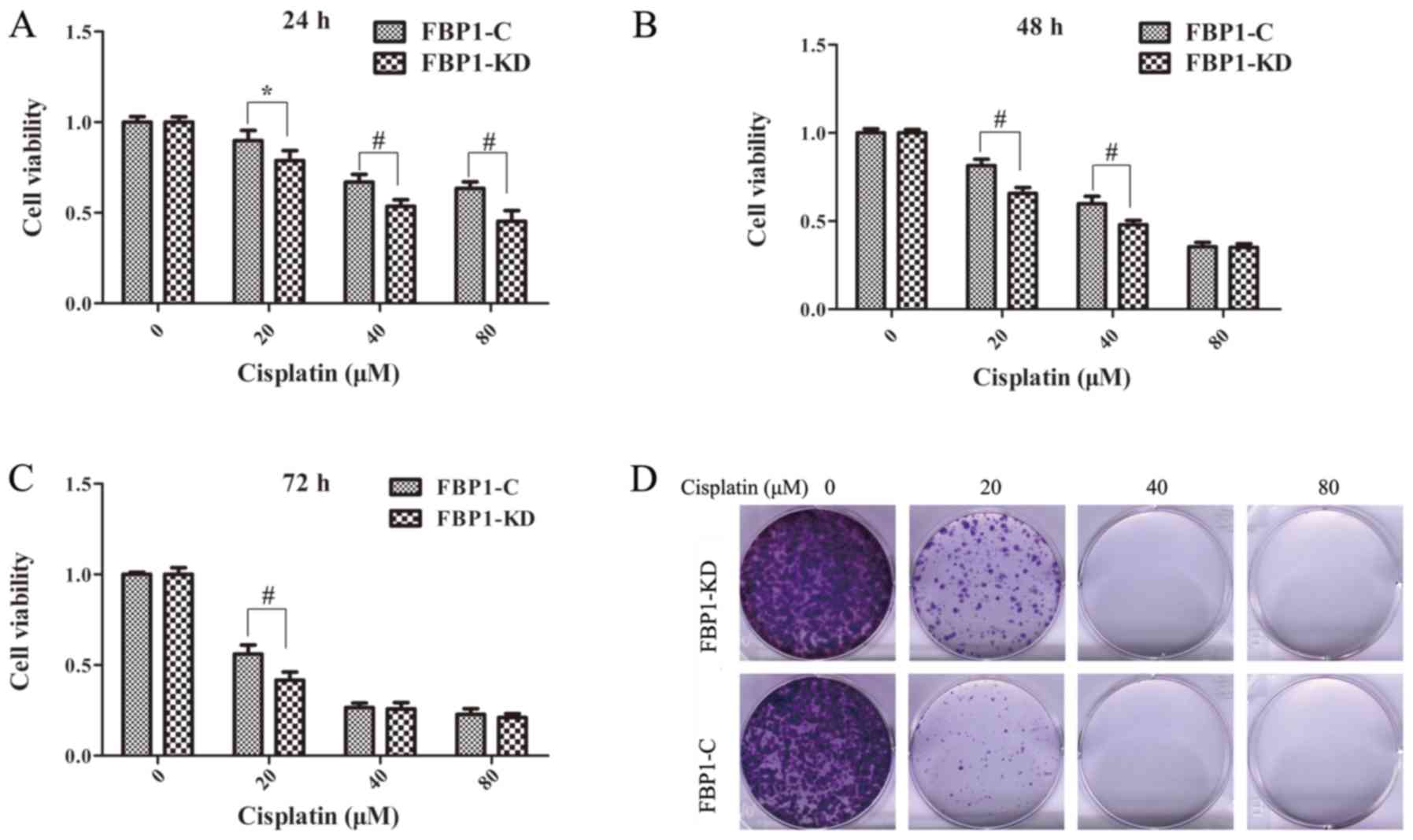
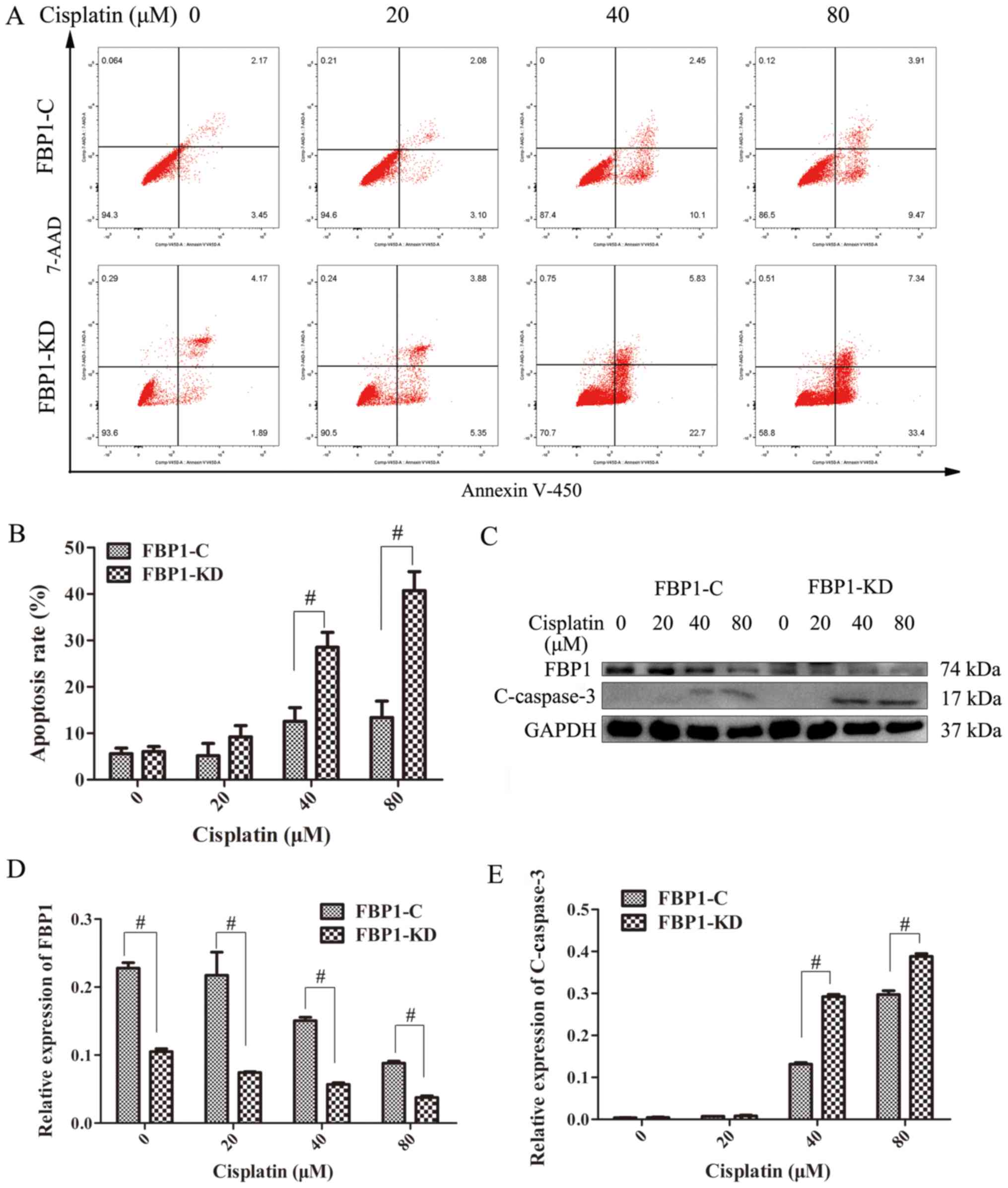
|
1
|
Tobin NP, Harrell JC, Lövrot J, Egyhazi
Brage S, Frostvik Stolt M, Carlsson L, Einbeigi Z, Linderholm B,
Loman N, Malmberg M, et al: TEX Trialists Group: Molecular subtype
and tumor characteristics of breast cancer metastases as assessed
by gene expression significantly influence patient post‑relapse
survival. Ann Oncol. 26:81–88. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Omarini C, Guaitoli G, Pipitone S,
Moscetti L, Cortesi L, Cascinu S and Piacentini F: Neoadjuvant
treatments in triple-negative breast cancer patients: Where we are
now and where we are going. Cancer Manag Res. 10:91–103. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hurvitz S and Mead M: Triple-negative
breast cancer: Advancements in characterization and treatment
approach. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 28:59–69. 2016.
|
|
4
|
Chalakur-Ramireddy NKR and Pakala SB:
Combined drug therapeutic strategies for the effective treatment of
Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Biosci Rep. 38:382018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Pénzváltó Z, Lánczky A, Lénárt J,
Meggyesházi N, Krenács T, Szoboszlai N, Denkert C, Pete I and
Győrffy B: MEK1 is associated with carboplatin resistance and is a
prognostic biomarker in epithelial ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer.
14:8372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Loibl S, O'Shaughnessy J, Untch M, Sikov
WM, Rugo HS, McKee MD, Huober J, Golshan M, von Minckwitz G, Maag
D, et al: Addition of the PARP inhibitor veliparib plus carboplatin
or carboplatin alone to standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy in
triple-negative breast cancer (BrighTNess): A randomised, phase 3
trial. Lancet Oncol. 19:497–509. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
von Minckwitz G, Schneeweiss A, Loibl S,
Salat C, Denkert C, Rezai M, Blohmer JU, Jackisch C, Paepke S,
Gerber B, et al: Neoadjuvant carboplatin in patients with
triple-negative and HER2-positive early breast cancer (GeparSixto;
GBG 66): A randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 15:pp. 747–756.
2014, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Poggio F, Bruzzone M, Ceppi M, Pondé NF,
La Valle G, Del Mastro L, de Azambuja E and Lambertini M:
Platinum-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast
cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Oncol.
29:1497–1508. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tutt A, Tovey H, Cheang MCU, Kernaghan S,
Kilburn L, Gazinska P, Owen J, Abraham J, Barrett S, Barrett-Lee P,
et al: Carboplatin in BRCA1/2-mutated and triple-negative breast
cancer BRCAness subgroups: The TNT Trial. Nat Med. 24:628–637.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ahmad S: Platinum-DNA interactions and
subsequent cellular processes controlling sensitivity to anticancer
platinum complexes. Chem Biodivers. 7:543–566. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim H and D'Andrea AD: Regulation of DNA
cross-link repair by the Fanconi anemia/BRCA pathway. Genes Dev.
26:pp. 1393–1408. 2012, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Debaize L and Troadec MB: The master
regulator FUBP1: Its emerging role in normal cell function and
malignant development. Cell Mol Life Sci. 76:259–281. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Steiner M, Schneider L, Yillah J, Gerlach
K, Kuvardina ON, Meyer A, Maring A, Bonig H, Seifried E, Zörnig M,
et al: FUSE binding protein 1 (FUBP1) expression is upregulated by
T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia protein 1 (TAL1) and required for
efficient erythroid differentiation. PLoS One. 14:pp. e02105152019,
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Malz M, Bovet M, Samarin J, Rabenhorst U,
Sticht C, Bissinger M, Roessler S, Bermejo JL, Renner M, Calvisi
DF, et al: Overexpression of far upstream element (FUSE) binding
protein (FBP)-interacting repressor (FIR) supports growth of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 60:1241–1250. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Venturutti L, Cordo Russo RI, Rivas MA,
Mercogliano MF, Izzo F, Oakley RH, Pereyra MG, De Martino M,
Proietti CJ, Yankilevich P, et al: MiR-16 mediates trastuzumab and
lapatinib response in ErbB-2-positive breast and gastric cancer via
its novel targets CCNJ and FUBP1. Oncogene. 35:6189–6202. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu ZH, Hu JL, Liang JZ, Zhou AJ, Li MZ,
Yan SM, Zhang X, Gao S, Chen L, Zhong Q, et al: Far upstream
element-binding protein 1 is a prognostic biomarker and promotes
nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression. Cell Death Dis. 6:pp.
e19202015, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang J and Chen QM: Far upstream element
binding protein 1: A commander of transcription, translation and
beyond. Oncogene. 32:2907–2916. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)). Method Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Duncan R, Bazar L, Michelotti G, Tomonaga
T, Krutzsch H, Avigan M and Levens D: A sequence-specific,
single-strand binding protein activates the far upstream element of
c-myc and defines a new DNA‑binding motif. Genes Dev. 8:pp.
465–480. 1994, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rodríguez D, Morrison CJ and Overall CM:
Matrix metalloproteinases: What do they not do? New substrates and
biological roles identified by murine models and proteomics.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1803:39–54. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jia Y, Chen Y, Wang Q, Jayasinghe U, Luo
X, Wei Q, Wang J, Xiong H, Chen C, Xu B, et al: Exosome: Emerging
biomarker in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 8:41717–41733. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang L, Zhu JY, Zhang JG, Bao BJ, Guan CQ,
Yang XJ, Liu YH, Huang YJ, Ni RZ and Ji LL: Far upstream
element-binding protein 1 (FUBP1) is a potential c-Myc regulator in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and its expression
promotes ESCC progression. Tumour Biol. 37:4115–4126. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ding Z, Liu X, Liu Y, Zhang J, Huang X,
Yang X, Yao L, Cui G and Wang D: Expression of far upstream element
(FUSE) binding protein 1 in human glioma is correlated with c-Myc
and cell proliferation. Mol Carcinog. 54:405–415. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Xiong X, Zhang J, Hua X, Cao W, Qin S, Dai
L, Liu W, Zhang Z, Li X and Liu Z: FBP1 promotes ovarian cancer
development through the acceleration of cell cycle transition and
metastasis. Oncol Lett. 16:1682–1688. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Talmadge JE and Fidler IJ: AACR centennial
series: the biology of cancer metastasis: historical perspective.
Cancer Res. 70:5649–5669. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Massagué J and Obenauf AC: Metastatic
colonization by circulating tumour cells. Nature. 529:298–306.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Butler GS and Overall CM: Updated
biological roles for matrix metalloproteinases and new
'intracellular' substrates revealed by degradomics. Biochemistry.
48:10830–10845. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zitka O, Kukacka J, Krizkova S, Huska D,
Adam V, Masarik M, Prusa R and Kizek R: Matrix metalloproteinases.
Curr Med Chem. 17:3751–3768. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell.
141:52–67. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vincenti MP and Brinckerhoff CE: Signal
transduction and cell‑type specific regulation of matrix
metalloproteinase gene expression: Can MMPs be good for you? J Cell
Physiol. 213:355–364. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li Z, Guo Y, Jiang H, Zhang T, Jin C,
Young CY and Yuan H: Differential regulation of MMPs by E2F1, Sp1
and NF-kappa B controls the small cell lung cancer invasive
phenotype. BMC Cancer. 14:2762014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jameson GS, Petricoin EF, Sachdev J,
Liotta LA, Loesch DM, Anthony SP, Chadha MK, Wulfkuhle JD,
Gallagher RI, Reeder KA, et al: A pilot study utilizing multi-omic
molecular profiling to find potential targets and select
individualized treatments for patients with previously treated
metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 147:579–588.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|