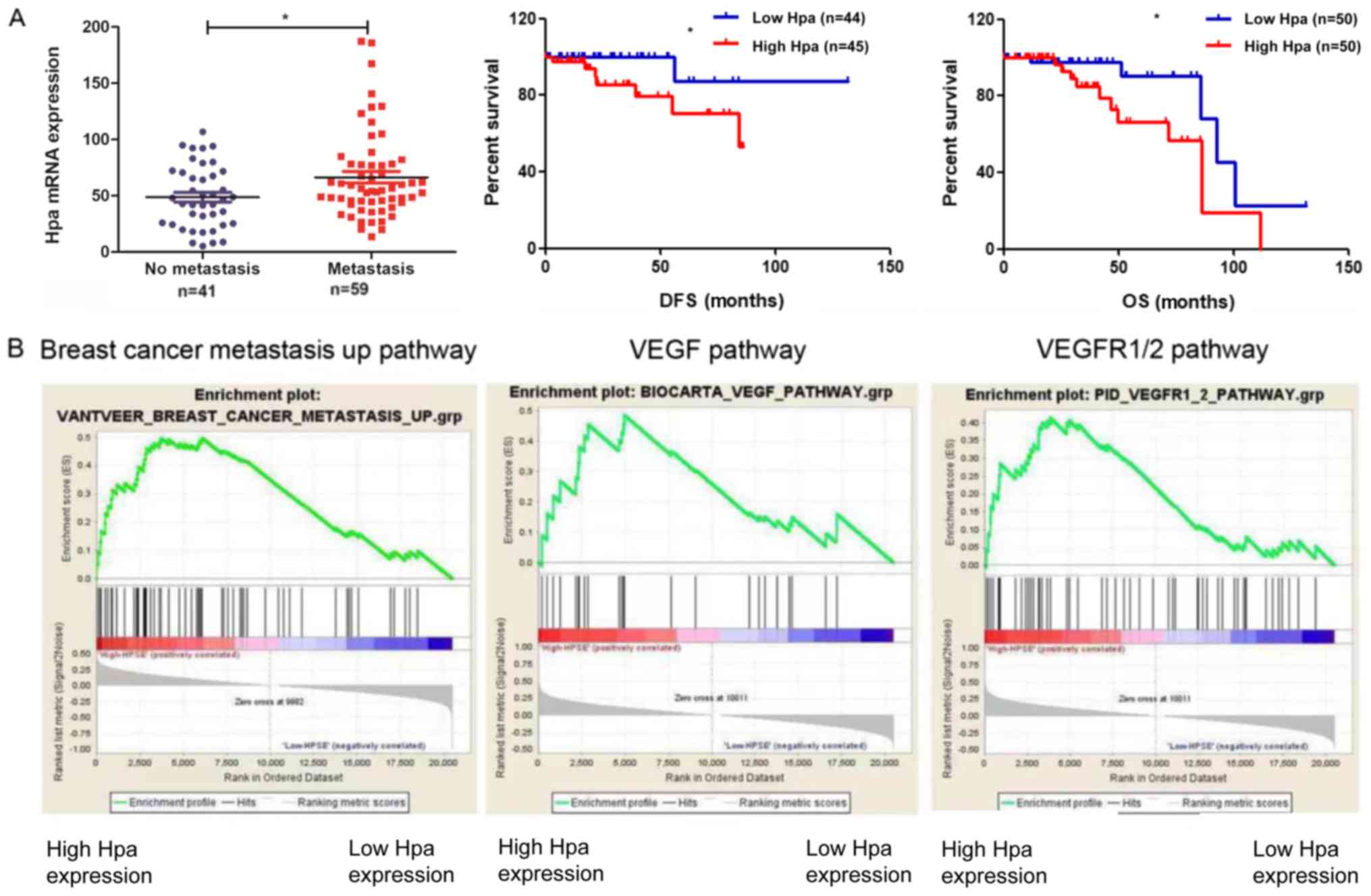
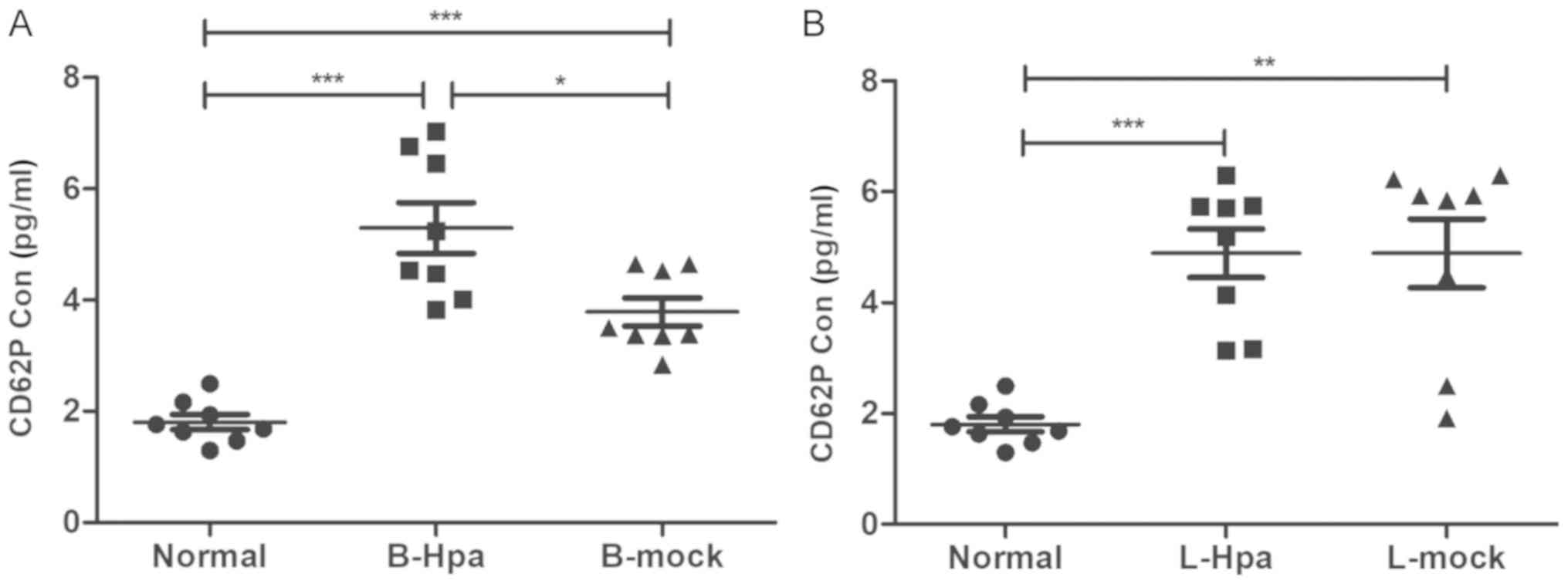
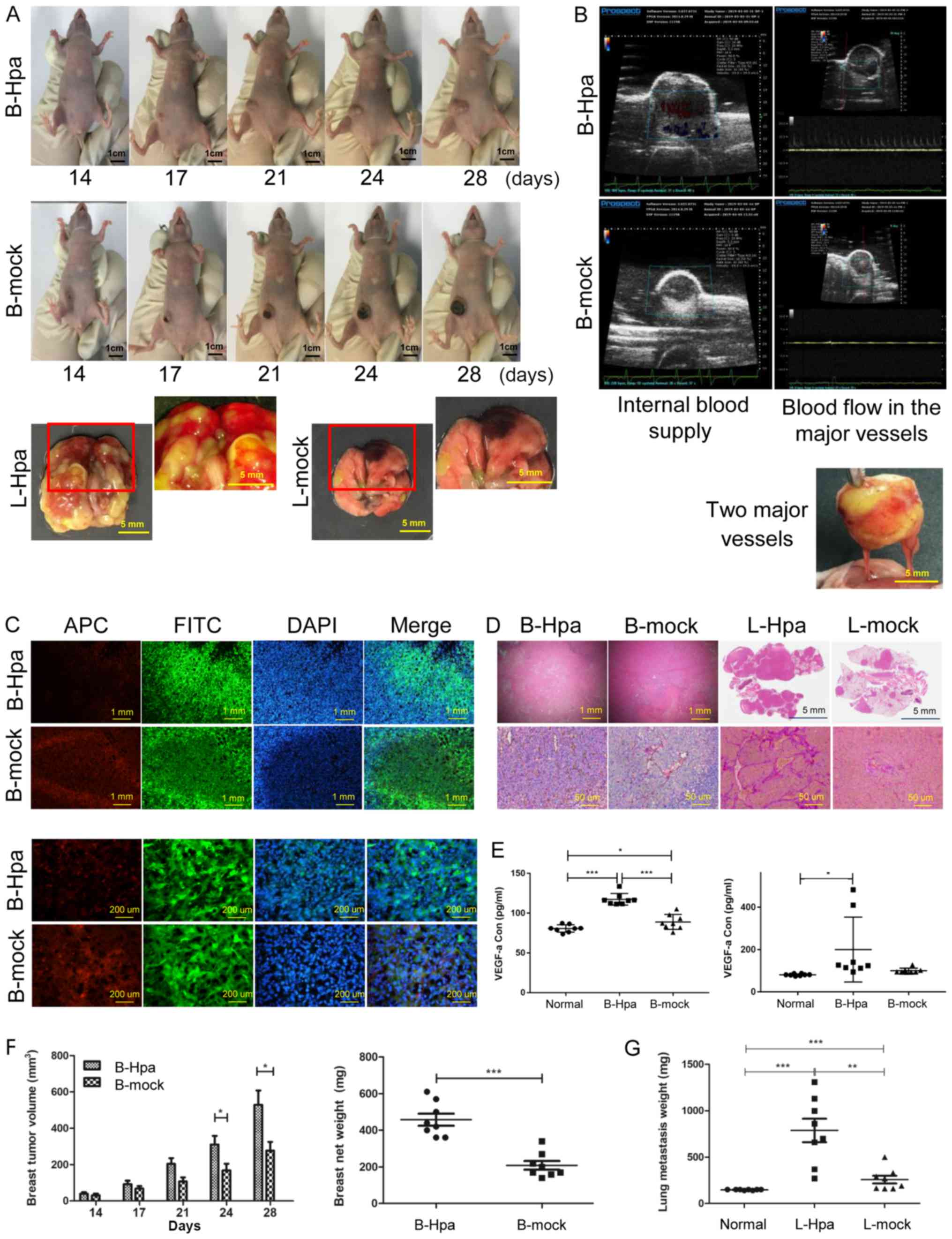
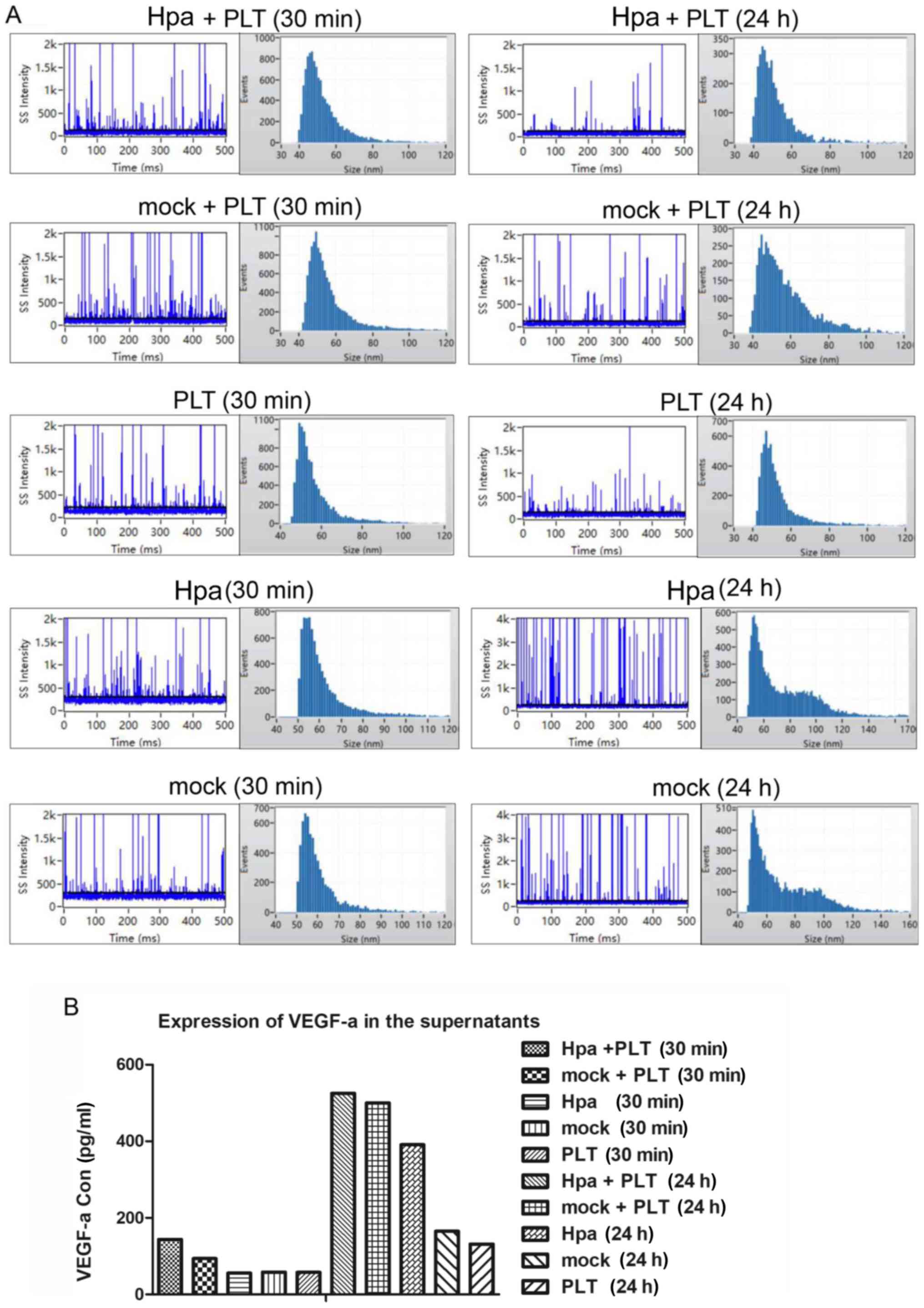
|
1
|
Elsawaf Z and Sinn H: Triple-negative
breast cancer: Clinical and histological correlations. Breast Care.
6:273–278. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bianchini G, Balko JM, Mayer IA, Sanders
ME and Gianni L: Triple-negative breast cancer: Challenges and
opportunities of a heterogeneous disease. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
13:674–690. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sharma D, Brummel-Ziedins KE, Bouchard BA
and Holmes CE: Platelets in tumor progression: A host factor that
offers multiple potential targets in the treatment of cancer. J
Cell Physiol. 229:1005–1015. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cross MJ and Claesson-Welsh L: FGF and
VEGF function in angiogenesis: Signalling pathways, biological
responses and therapeutic inhibition. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
22:201–207. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pinedo HM, Verheul H, D'Amato RJ and
Folkman J: Involvement of platelets in tumour angiogenesis? Lancet.
352:1775–1777. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
LeCouter J, Gerber H and Ferrara N: The
biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 9:669–676. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gil-Bernabé AM, Lucotti S and Muschel RJ:
Coagulation and metastasis: What does the experimental literature
tell us? Brit J Haematol. 162:433–441. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gay LJ and Felding-Habermann B:
Contribution of platelets to tumour metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:123–134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Erpenbeck L and Schön MP: Deadly allies:
The fatal interplay between platelets and metastasizing cancer
cells. Blood. 115:3427–3436. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Leblanc R, Lee S, David M, Bordet JC,
Norman DD, Patil R, Miller D, Sahay D, Ribeiro J, Clézardin P, et
al: Interaction of platelet-derived autotaxin with tumor integrin
aVb3 controls metastasis of breast cancer cells to bone. Blood.
124:3141–3150. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Peterson JE, Zurakowski D, Italiano JE Jr,
Michel LV, Fox L, Klement GL and Folkman J: Normal ranges of
angiogenesis regulatory proteins in human platelets. Am J Hematol.
85:487–493. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wojtukiewicz MZ, Sierko E, Klement P and
Rak J: The hemostatic system and angiogenesis in malignancy.
Neoplasia. 3:371–384. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bambace NM and Holmes CE: The platelet
contribution to cancer progression. J Thromb Haemost. 9:237–249.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Buergy D, Wenz F, Groden C and Brockmann
MA: Tumor-platelet interaction in solid tumors. Int J Cancer.
130:2747–2760. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li J, Meng X, Hu J, Zhang Y, Dang Y, Wei L
and Shi M: Heparanase promotes radiation resistance of cervical
cancer by upregulating hypoxia inducible factor 1. Am J Cancer Res.
7:234–244. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kelly T, Miao HQ, Yang Y, Navarro E,
Kussie P, Huang Y, MacLeod V, Casciano J, Joseph L, Zhan F, et al:
High heparanase activity in multiple myeloma is associated with
elevated microvessel density. Cancer Res. 63:8749–8756.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vlodavsky I, Friedmann Y, Elkin M, Aingorn
H, Atzmon R, Ishai-Michaeli R, Bitan M, Pappo O, Peretz T and
Michal I: Mammalian heparanase: Gene cloning, expression and
function in tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med. 5:793–802.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vornicova O, Boyango I, Feld S, Naroditsky
I, Kazarin O, Zohar Y, Tiram Y, Ilan N, Ben-Izhak O, Vlodavsky I
and Bar-Sela G: The prognostic significance of heparanase
expression in metastatic melanoma. Oncotarget. 7:74678–74685. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang L, Sullivan P, Suyama J and
Marchetti D: Epidermal growth factor-induced heparanase nucleolar
localization augments DNA topoisomerase I activity in brain
metastatic breast cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 8:278–290. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gomes AM, Stelling MP and Pavão MSG:
Heparan sulfate and heparanase as modulators of breast cancer
progression. Biomed Res Int. 2013:1–11. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sanderson RD, Yang Y, Suva LJ and Kelly T:
Heparan sulfate proteoglycans and heparanase-partners in osteolytic
tumor growth and metastasis. Matrix Biol. 23:341–352. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Edovitsky E, Elkin M, Zcharia E, Peretz T
and Vlodavsky I: Heparanase gene silencing, tumor invasiveness,
angiogenesis, and metastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 96:1219–1230.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang Y, MacLeod V, Bendre M, Huang Y,
Theus AM, Miao HQ, Kussie P, Yaccoby S, Epstein J, Suva LJ, et al:
Heparanase promotes the spontaneous metastasis of myeloma cells to
bone. Blood. 105:1303–1309. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Parish CR, Freeman C and Hulett MD:
Heparanase: A key enzyme involved in cell invasion. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1471:M99–M108. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vreys V and David G: Mammalian heparanase:
What is the message? J Cell Mol Med. 11:427–452. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vlodavsky I, Gross-Cohen M, Weissmann M,
Ilan N and Sanderson RD: Opposing functions of heparanase-1 and
hepa-ranase-2 in cancer progression. Trends Biochem Sci. 43:18–31.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ilan N, Elkin M and Vlodavsky I:
Regulation, function and clinical significance of heparanase in
cancer metastasis and angiogenesis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
38:2018–2039. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vlodavsky I, Beckhove P, Lerner I, Pisano
C, Meirovitz A, Ilan N and Elkin M: Significance of heparanase in
cancer and inflammation. Cancer Microenviron. 5:115–132. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Hammond E, Khurana A, Shridhar V and
Dredge K: The role of heparanase and sulfatases in the modification
of heparan sulfate proteoglycans within the tumor microenvironment
and opportunities for novel cancer therapeutics. Front Oncol.
4:1952014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Freeman C, Browne AM and Parish CR:
Evidence that platelet and tumour heparanases are similar enzymes.
Biochem J. 342:361–368. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cui H, Tan YX, Österholm C, Zhang X, Hedin
U, Vlodavsky I and Li JP: Heparanase expression upregulates
platelet adhesion activity and thrombogenicity. Oncotarget.
7:39486–39496. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Da ML, Ledaki I, Purshouse K, Haider S, De
Bastiani MA, Baban D, Morotti M, Steers G, Wigfield S, Bridges E,
et al: The BET inhibitor JQ1 selectively impairs tumour response to
hypoxia and downregulates CA9 and angiogenesis in triple nega-tive
breast cancer. Oncogene. 36:122–132. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Vaupel P: The role of hypoxia-induced
factors in tumor progression. Oncologist. 9(Suppl 5): S10–S17.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Chen X, Iliopoulos D, Zhang Q, Tang Q,
Greenblatt MB, Hatziapostolou M, Lim E, Tam WL, Ni M, Chen Y, et
al: XBP1 promotes triple-negative breast cancer by controlling the
HIF1α pathway. Nature. 508:103–107. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Harris AL: Hypoxia-a key regulatory factor
in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:38–47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yamamoto Y, Ibusuki M, Okumura Y, Kawasoe
T, Kai K, Iyama K and Iwase H: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is
closely linked to an aggressive phenotype in breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 110:465–475. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Schindl M, Schoppmann SF, Samonigg H,
Hausmaninger H, Kwasny W, Gnant M, Jakesz R, Kubista E, Birner P
and Oberhuber G; Austrian Breast and Colorectal Cancer Study Group:
Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is associated
with an unfavorable prognosis in lymph node-positive breast cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 8:1831–1837. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rankin EB and Giaccia AJ: The role of
hypoxia-inducible factors in tumorigenesis. Cell Death Differ.
15:678–685. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
He X, Brenchley PEC, Jayson GC, Hampson L,
Davies J and Hampson IN: Hypoxia increases heparanase-dependent
tumor cell invasion, which can be inhibited by antiheparanase
anti-bodies. Cancer Res. 64:3928–3933. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Saha SK, Lee SB, Won J, Choi HY, Kim K,
Yang GM, Dayem AA and Cho SG: Correlation between oxidative stress,
nutrition, and cancer initiation. Int J Mol Sci. 18:15442017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Leontieva OV and Blagosklonny MV:
Yeast-like chronological senescence in mammalian cells: Phenomenon,
mechanism and pharmacological suppression. Aging (Albany NY).
3:1078–1091. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Dewhirst MW: Concepts of oxygen transport
at the microcirculatory level. Semin Radiat Oncol. 8:143–150. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Vaupel P and Mayer A: Hypoxia in cancer:
Significance and impact on clinical outcome. Cancer Metast Rev.
26:225–239. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible factors in
physiology and medicine. Cell. 399–408. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yao KS, Clayton M and O'Dwyer PJ:
Apoptosis in human adenocarcinoma HT29 cells induced by exposure to
hypoxia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 87:117–122. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Graeber T, Peterson J, Tsai M, Monica K,
Fornace AJ Jr and Giaccia AJ: Hypoxia induces accumulation of p53
protein, but activation of a G1-Phase Checkpoint by Low-oxygen
conditions is independent of p53 Statust. Mol Cell Biol.
14:6264–6277. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shimizu S, Eguchi Y, Kosaka H, Kamiike W,
Matsuda H and Tsujimoto Y: Prevention of hypoxia-induced cell death
by Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL. Nature. 374:811–813. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Schmaltz C, Hardenbergh PH, Wells A and
Fisher DE: Regulation of proliferation-survival decisions during
tumor cell hypoxia. Mol Cell Biol. 18:2845–2854. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Coquelle A, Toledo F, Stern S, Bieth A and
Debatisse M: A new role for hypoxia in tumor Progression: Induction
of fragile site triggering genomic Rearrangements and formation of
complex DMs and HSRs. Mol Cell. 2:259–265. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
De Bock K, Mazzone M and Carmeliet P:
Antiangiogenic therapy, hypoxia, and metastasis: Risky liaisons, or
not? Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 8:393–404. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RYJ and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Vaupel P and Multhoff G: Fatal alliance of
hypoxia-/HIF-1α-driven microenvironmental traits promoting cancer
progression. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1232:169–176. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Sullivan R and Graham CH: Hypoxia prevents
etoposide-induced DNA damage in cancer cells through a mechanism
involving hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:1702–1713.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Helczynska K, Kronblad A, Jögi A, Nilsson
E, Beckman S, Landberg G and Påhlman S: Hypoxia promotes a
dedifferentiated phenotype in ductal breast carcinoma in situ.
Cancer Res. 63:1441–1444. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Graeber TG, Osmanian C, Jacks T, Housman
DE, Koch CJ, Lowe SW and Giaccia AJ: Hypoxia-mediated selection of
cells with diminished apoptotic potential in solid tumours. Nature.
379:88–91. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Rokavec M, Öner MG and Hermeking H:
Lnflammation-induced epigenetic switches in cancer. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 73:23–39. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Knelson EH, Nee JC and Blobe GC: Heparan
sulfate signaling in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci. 39:277–288. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yue W and Chen Z: Does vasculogenic
mimicry exist in astrocytoma? J Histochem Cytochem. 53:997–1002.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Clemente M, Pérez-Alenza MD, Illera JC and
Peña L: Histological, immunohistological, and ultrastructural
description of vasculogenic mimicry in canine mammary cancer. Vet
Pathol. 47:265–274. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Sun B, Zhang D, Zhang S, Zhang W, Guo H
and Zhao X: Hypoxia influences vasculogenic mimicry channel
formation and tumor invasion-related protein expression in
melanoma. Cancer Lett. 249:188–197. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Sood AK, Seftor EA, Fletcher MS, Gardner
LM, Heidger PM, Buller RE, Seftor RE and Hendrix MJ: Molecular
determinants of ovarian cancer plasticity. Am J Pathol.
158:1279–1288. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kirschmann DA, Seftor EA, Hardy KM, Seftor
REB and Hendrix MJC: Molecular pathways: Vasculogenic mimicry in
tumor cells: Diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Clin Cancer
Res. 18:2726–2732. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Seftor RE, Hess AR, Seftor EA, Kirschmann
DA, Hardy KM, Margaryan NV and Hendrix MJ: Tumor cell vasculogenic
mimicry. Am J Pathol. 181:1115–1125. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Passalidou E, Trivella M, Singh N,
Ferguson M, Hu J, Cesario A, Granone P, Nicholson AG, Goldstraw P,
Ratcliffe C, et al: Vascular phenotype in angiogenic and
non-angiogenic lung non-small cell carcinomas. Br J Cancer.
86:244–249. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Folberg R, Hendrix MJ and Maniotis AJ:
Vasculogenic mimicry and tumor angiogenesis. Am J Pathol.
156:361–381. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Semenza GL: Defining the role of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in cancer biology and therapeutics.
Oncogene. 29:625–634. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
67
|
Semenza GL: HIF-1 mediates metabolic
responses to intratumoral hypoxia and oncogenic mutations. J Clin
Invest. 123:3664–3671. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Maxwell PH, Dachs GU, Gleadle JM, Nicholls
LG, Harris AL, Stratford IJ, Hankinson O, Pugh CW and Ratcliffe PJ:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 modulates gene expression in solid
tumors and influences both angiogenesis and tumor growth. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 94:8104–8109. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Wenger RH, Stiehl DP and Camenisch G:
Integration of oxygen signaling at the consensus HRE. Sci Stke.
2005:re122005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Chen Z, He X, Xia W, Huang Q, Zhang Z, Ye
J, Ni C, Wu P, Wu D, Xu J, et al: Prognostic value and
clinicopathological differences of HIFs in colorectal cancer:
Evidence from meta-analysis. PLoS One. 8:e803372013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Fan L, Dong W, Jiang C, Qian Q and Yu Q:
Role of Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and Survivin in colorectal
carcinoma progression. Int J Colorectal Dis. 23:1057–1064. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Semenza GL: Targeting HIF-1 for cancer
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:721–732. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Tseng W, Yang S, Lai C and Tang C: Hypoxia
induces BMP-2 expression via ILK, Akt, mTOR, and HIF-1 pathways in
osteoblasts. J Cell Physiol. 223:810–818. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Pugh CW and Ratcliffe PJ: Regulation of
angiogenesis by hypoxia: Role of the HIF system. Nat Med.
9:677–684. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Manalo DJ, Rowan A, Lavoie T, Natarajan L,
Kelly BD, Ye SQ, Garcia JG and Semenza GL: Transcriptional
regulation of vascular endothelial cell responses to hypoxia by
HIF-1. Blood. 105:659–669. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Gao J, Su L, Qin R, Chang Q, Huang T and
Feng Y: Transfection of antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits
heparanase gene expression and invasive ability of human pancreatic
cancer cell in vitro. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci.
26:72–74. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|