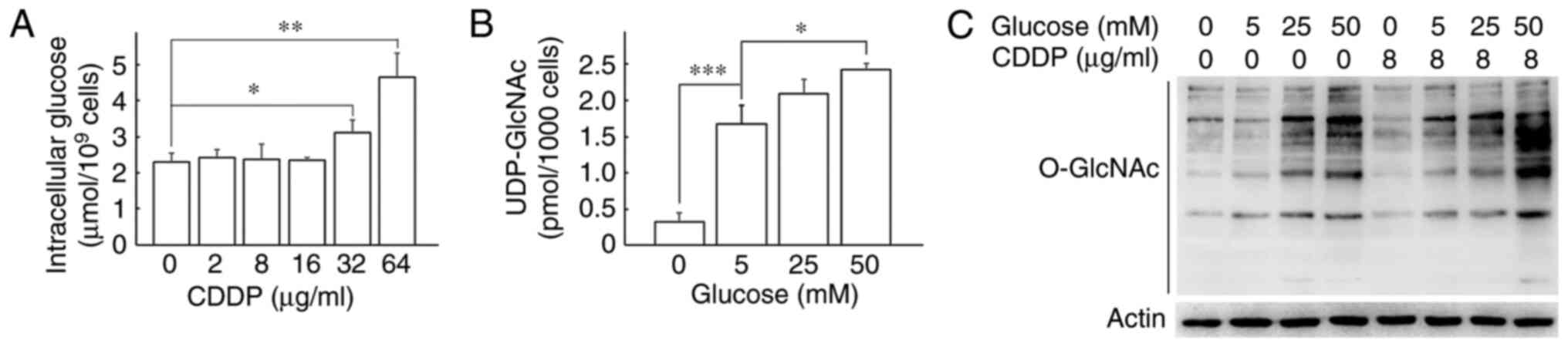
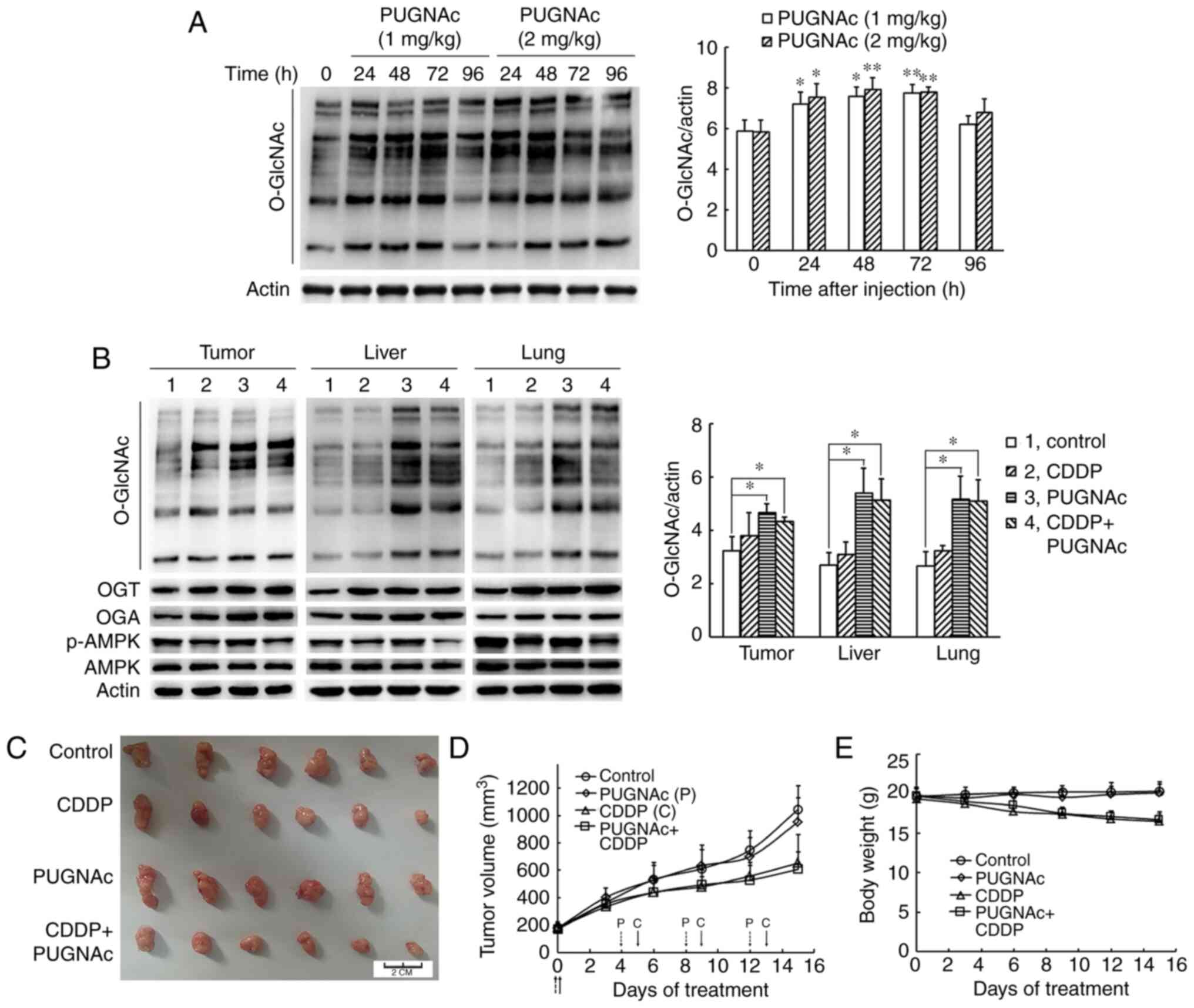
|
1
|
Wells L and Hart GW: O-GlcNAc turns
twenty: Functional implications for post-translational modification
of nuclear and cytosolic proteins with a sugar. FEBS Lett.
546:154–158. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Joiner CM, Li H, Jiang J and Walker S:
Structural characterization of the O-GlcNAc cycling enzymes:
Insights into substrate recognition and catalytic mechanisms. Curr
Opin Struct Biol. 56:97–106. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nie H and Yi W: O-GlcNAcylation, a sweet
link to the pathology of diseases. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B.
20:437–448. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hanover JA, Chen W and Bond MR: O-GlcNAc
in cancer: An Oncometabolism-fueled vicious cycle. J Bioenerg
Biomembr. 50:155–173. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hart GW: Nutrient regulation of signaling
and transcription. J Biol Chem. 294:2211–2231. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Martinez MR, Dias TB, Natov PS and Zachara
NE: Stress-induced O-GlcNAcylation: an adaptive process of injured
cells. Biochem Soc Trans. 45:237–249. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee A, Miller D, Henry R, Paruchuri VD,
O'Meally RN, Boronina T, Cole RN and Zachara NE: Combined
anti-body/Lectin enrichment identifies extensive changes in the
O-GlcNAc sub-proteome upon oxidative stress. J Proteome Res.
15:4318–4336. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Groves JA, Maduka AO, O'Meally RN, Cole RN
and Zachara NE: Fatty acid synthase inhibits the O-GlcNAcase during
oxidative stress. J Biol Chem. 292:6493–6511. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zachara NE, Molina H, Wong KY, Pandey A
and Hart GW: The dynamic stress-induced 'O-GlcNAc-ome' highlights
functions for O-GlcNAc in regulating DNA damage/repair and other
cellular pathways. Amino Acids. 40:793–808. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chen SH and Chang JY: New insights into
mechanisms of cisplatin resistance: From tumor cell to
microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. 20:41362019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Chen W, Do KC, Saxton B, Leng S, Filipczak
P, Tessema M, Belinsky SA and Lin Y: Inhibition of the hexosamine
biosynthesis pathway potentiates cisplatin cytotoxicity by
decreasing BiP expression in non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Mol
Carcinog. 58:1046–1055. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou F, Yang X, Zhao H, Liu Y, Feng Y, An
R, Lv X, Li J and Chen B: Down-regulation of OGT promotes cisplatin
resistance by inducing autophagy in ovarian cancer. Theranostics.
8:5200–5212. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kang JG, Park SY, Ji S, Jang I, Park S,
Kim HS, Kim SM, Yook JI, Park YI, Roth J and Cho JW: O-GlcNAc
protein modification in cancer cells increases in response to
glucose deprivation through glycogen degradation. J Biol Chem.
284:34777–34784. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Taylor RP, Geisler TS, Chambers JH and
McClain DA: Up-regulation of O-GlcNAc transferase with glucose
deprivation in HepG2 cells is mediated by decreased hexosamine
pathway flux. J Biol Chem. 284:3425–3432. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Eguchi S, Oshiro N, Miyamoto T, Yoshino K,
Okamoto S, Ono T, Kikkawa U and Yonezawa K: AMP-activated protein
kinase phosphorylates glutamine: Fructose-6-phosphate
amidotransferase 1 at Ser243 to modulate its enzymatic activity.
Genes Cells. 14:179–189. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nöt LG, Brocks CA, Vámhidy L, Marchase RB
and Chatham JC: Increased O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine levels
on proteins improves survival, reduces inflammation and organ
damage 24 h after trauma-hemorrhage in rats. Crit Care Med.
38:562–571. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chen R, Lai LA, Sullivan Y, Wong M, Wang
L, Riddell J, Jung L, Pillarisetty VG, Brentnall TA and Pan S:
Disrupting glutamine metabolic pathways to sensitize
gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer. Sci Rep. 7:79502017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Asthana A, Ramakrishnan P, Vicioso Y,
Zhang K and Parameswaran R: Hexosamine biosynthetic pathway
inhibition leads to AML cell differentiation and cell death. Mol
Cancer Ther. 17:2226–2237. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zibrova D, Vandermoere F, Göransson O,
Peggie M, Mariño KV, Knierim A, Spengler K, Weigert C, Viollet B,
Morrice NA, et al: GFAT1 phosphorylation by AMPK promotes
VEGF-induced angiogenesis. Biochem J. 474:983–1001. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lin SC and Hardie DG: AMPK: Sensing
glucose as well as cellular energy status. Cell Metab. 27:299–313.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Patel BA, D'Amico TL and Blagg BSJ:
Natural products and other inhibitors of F1FO
ATP synthase. Eur J Med Chem. 207:1127792020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhou W and Faraldo-Gómez JD: Membrane
plasticity facilitates recognition of the inhibitor oligomycin by
the mitochondrial ATP synthase rotor. Biochim Biophys Acta
Bioenerg. 1859:789–796. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zachara NE, O'Donnell N, Cheung WD, Mercer
JJ, Marth JD and Hart GW: Dynamic O-GlcNAc modification of
nucleocytoplasmic proteins in response to stress. A survival
response of mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 279:30133–30142. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pan X, Wilson M, Mirbahai L, McConville C,
Arvanitis TN, Griffin JL, Kauppinen RA and Peet AC: In vitro
metabonomic study detects increases in UDP-GlcNAc and UDP-GalNAc,
as early phase markers of cisplatin treatment response in brain
tumor cells. J Proteome Res. 10:3493–3500. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Duarte IF, Ladeirinha AF, Lamego I, Gil
AM, Carvalho L, Carreira IM and Melo JB: Potential markers of
cisplatin treatment response unveiled by NMR metabolomics of human
lung cells. Mol Pharm. 10:4242–4251. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Duarte IF, Lamego I, Marques J, Marques
MP, Blaise BJ and Gil AM: Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) study of
the effect of cisplatin on the metabolic profile of MG-63
osteosarcoma cells. J Proteome Res. 9:5877–5886. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang C, Peng P, Li L, Shao M, Zhao J, Wang
L, Duan F, Song S, Wu H, Zhang J, et al: High expression of GFAT1
predicts poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer. Sci
Rep. 6:390442016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li L, Shao M, Peng P, Yang C, Song S, Duan
F, Jia D, Zhang M, Zhao J, Zhao R, et al: High expression of GFAT1
predicts unfavorable prognosis in patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:19205–19217. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chang Q, Su K, Baker JR, Yang X, Paterson
AJ and Kudlow JE: Phosphorylation of human glutamine:
Fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase by cAMP-dependent protein
kinase at serine 205 blocks the enzyme activity. J Biol Chem.
275:21981–21987. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sharma NS, Gupta VK, Garrido VT, Hadad R,
Durden BC, Kesh K, Giri B, Ferrantella A, Dudeja V, Saluja A and
Banerjee S: Targeting tumor-intrinsic hexosamine biosynthesis
sensitizes pancreatic cancer to anti-PD1 therapy. J Clin Invest.
130:451–465. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Lemberg KM, Vornov JJ, Rais R and Slusher
BS: We're Not 'DON' Yet: Optimal dosing and prodrug delivery of
6-Diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine. Mol Cancer Ther. 17:1824–1832. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Laczy B, Fülöp N, Onay-Besikci A, Des
Rosiers C and Chatham JC: Acute regulation of cardiac metabolism by
the hexosamine biosynthesis pathway and protein O-GlcNAcylation.
PLoS One. 6:e184172011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hudson CD, Savadelis A, Nagaraj AB, Joseph
P, Avril S, DiFeo A and Avril N: Altered glutamine metabolism in
platinum resistant ovarian cancer. Oncotarget. 7:41637–41649. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao JG, Ren KM and Tang J: Overcoming
5-Fu resistance in human non-small cell lung cancer cells by the
combination of 5-Fu and cisplatin through the inhibition of glucose
metabolism. Tumour Biol. 35:12305–12315. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yang X and Qian K: Protein
O-GlcNAcylation: Emerging mechanisms and functions. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 18:452–465. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Haltiwanger RS, Grove K and Philipsberg
GA: Modulation of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine levels on nuclear
and cytoplasmic proteins in vivo using the peptide
O-GlcNAc-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase inhibitor
O-(2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucopyranosylidene)
amino-N-phenylcarbamate. J Biol Chem. 273:3611–3617. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang L, Chen S, Zhang Z, Zhang J, Mao S,
Zheng J, Xuan Y, Liu M, Cai K, Zhang W, et al: Suppressed OGT
expression inhibits cell proliferation while inducing cell
apoptosis in bladder cancer. BMC Cancer. 18:11412018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|