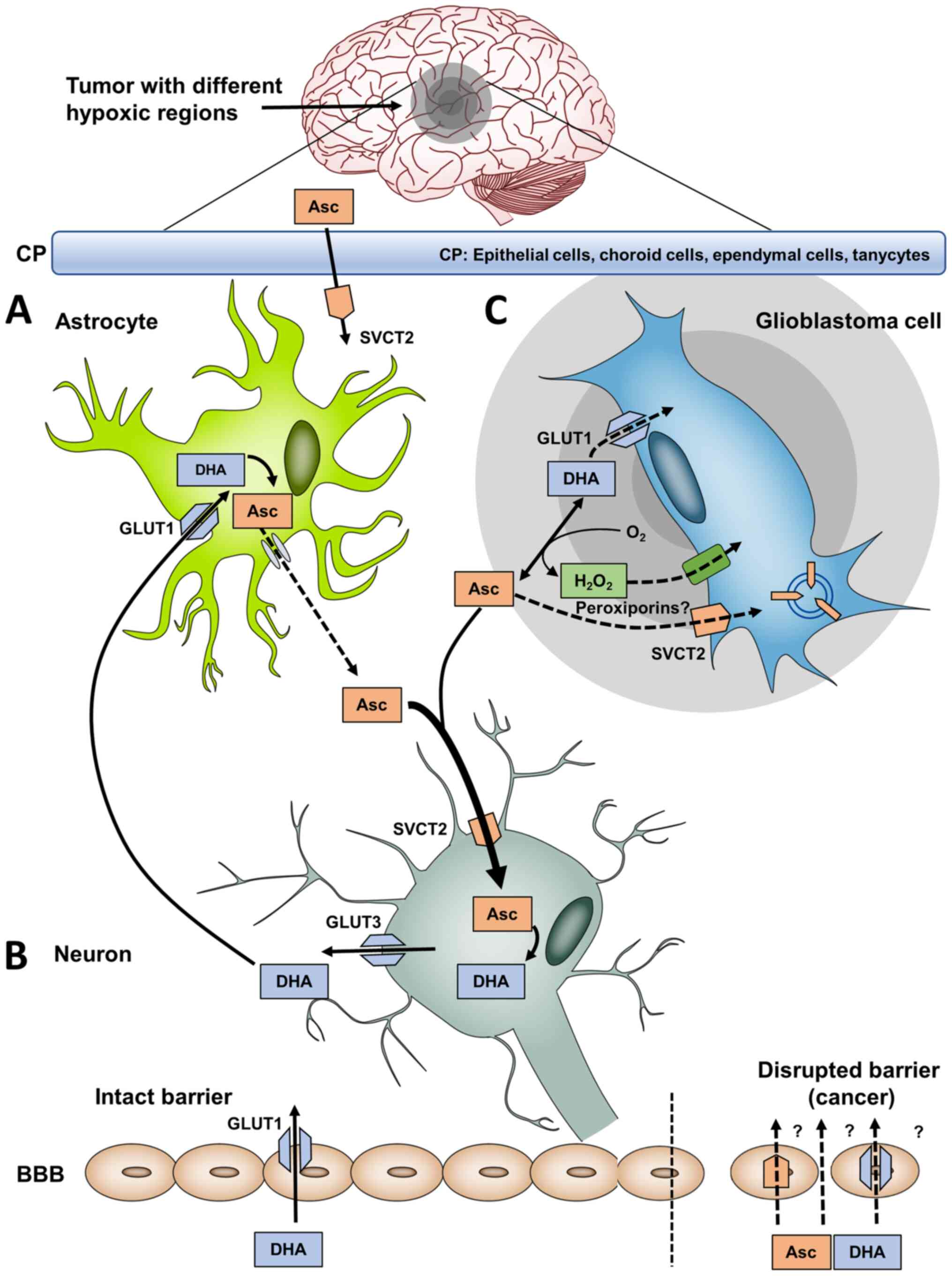
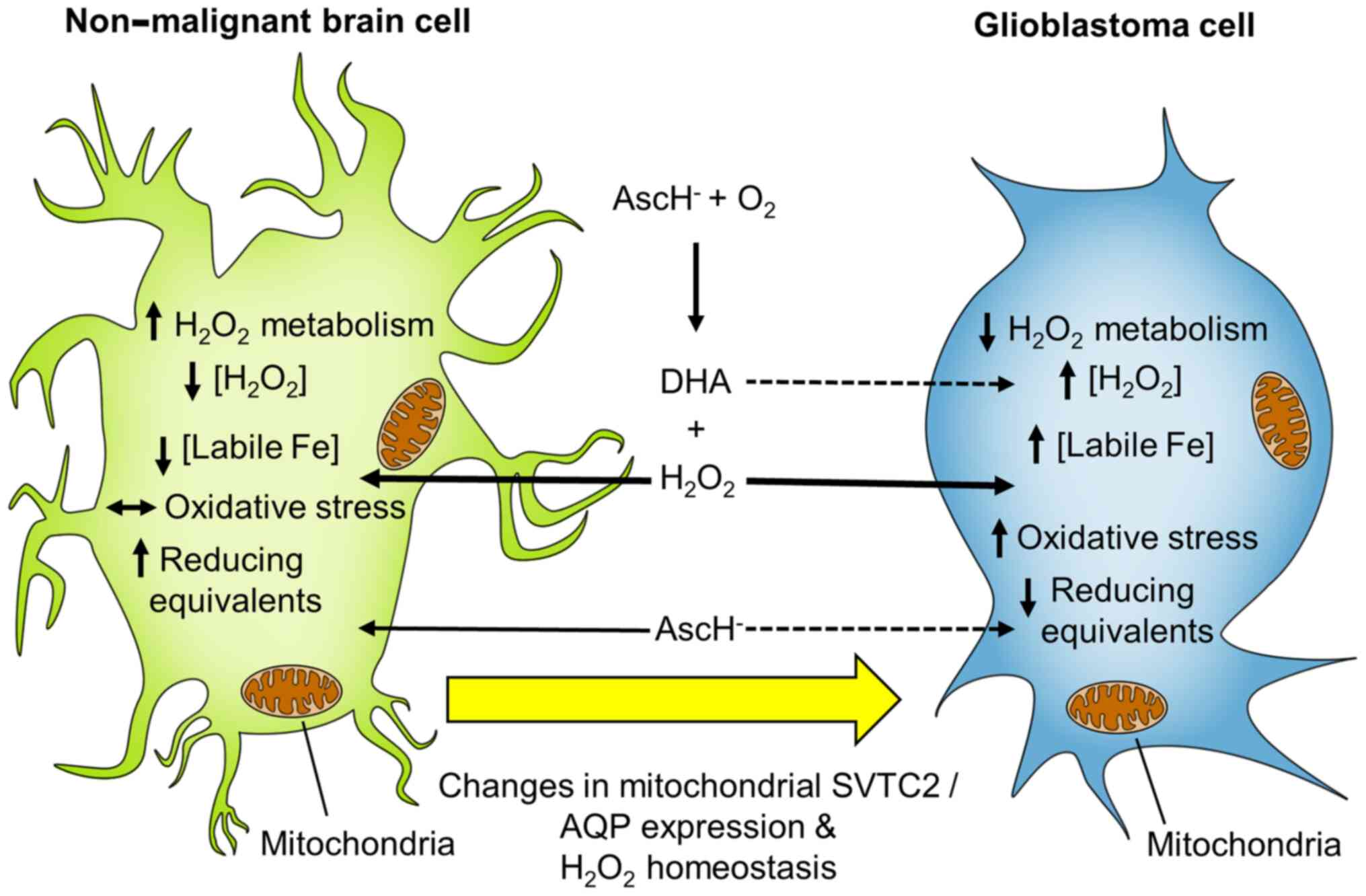
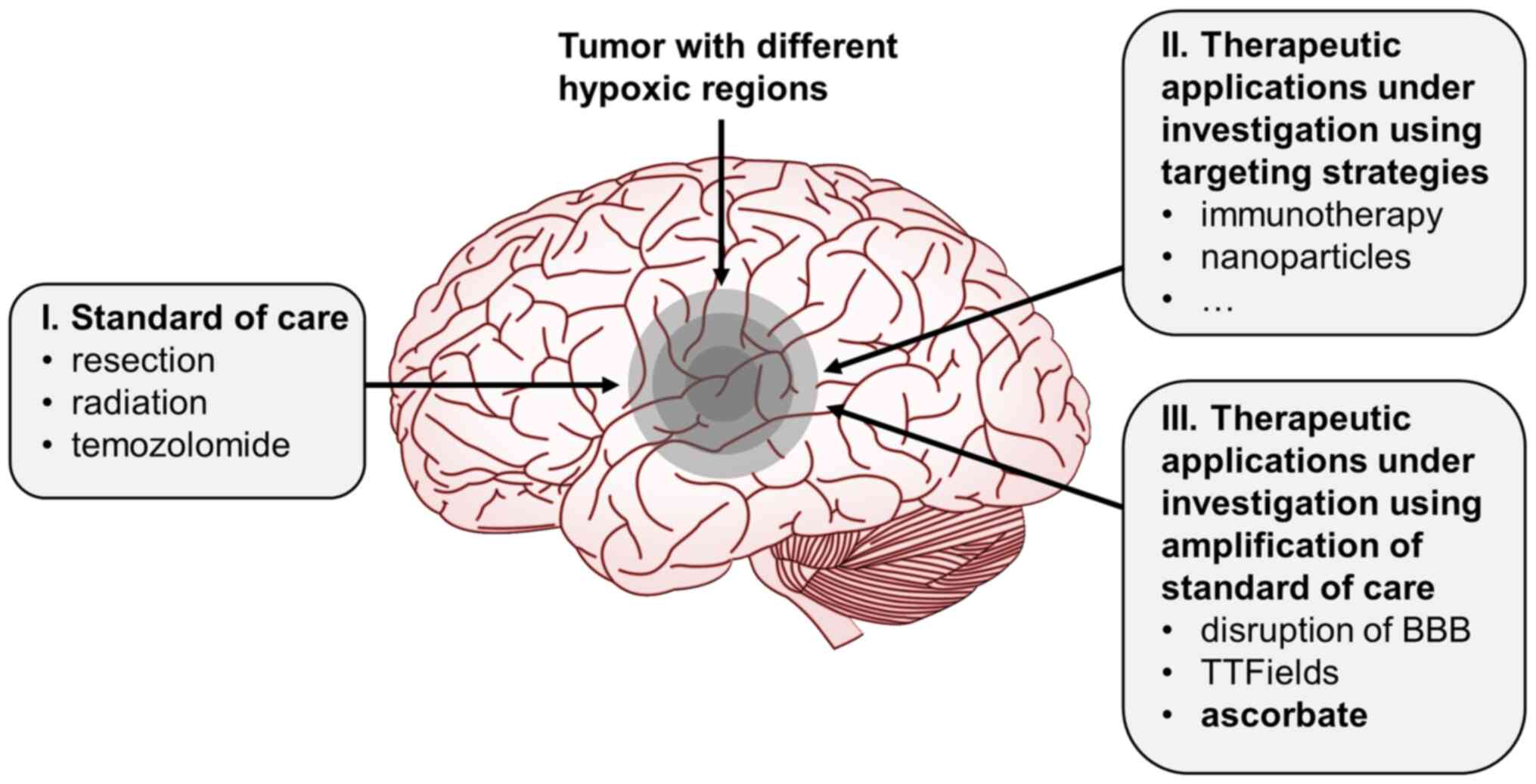
|
1
|
Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von
Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD,
Kleihues P and Ellison DW: The 2016 world health organization
classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary.
Acta Neuropathol. 131:803–820. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Silantyev AS, Falzone L, Libra M, Gurina
OI, Kardashova KS, Nikolouzakis TK, Nosyrev AE, Sutton CW, Mitsias
PD and Tsatsakis A: Current and future trends on diagnosis and
prognosis of glioblastoma: From molecular biology to proteomics.
Cells. 8:8632019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Candido S, Lupo G, Pennisi M, Basile MS,
Anfuso CD, Petralia MC, Gattuso G, Vivarelli S, Spandidos DA, Libra
M and Falzone L: The analysis of miRNA expression profiling
datasets reveals inverse microRNA patterns in glioblastoma and
Alzheimer's disease. Oncol Rep. 42:911–922. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Armento A, Ehlers J, Schötterl S and
Naumann U: Molecular mechanisms of glioma cell motility.
Glioblastoma. De Vleeschouwer S: Codon Publications; Brisbane:
2017, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Tabatabai G and Wakimoto H: Glioblastoma:
State of the Art and future perspectives. Cancers (Basel).
11:10912019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ohgaki H and Kleihues P: Epidemiology and
etiology of gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 109:93–108. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Stetson L, Virk S
and Barnholtz-Sloan JS: Epidemiology of intracranial gliomas. Prog
Neurol Surg. 30:1–11. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide
for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Weller M, Butowski N, Tran DD, Recht LD,
Lim M, Hirte H, Ashby L, Mechtler L, Goldlust SA, Iwamoto F, et al:
Rindopepimut with temozolomide for patients with newly diagnosed,
EGFRvIII-expressing glioblastoma (ACT IV): A randomised,
double-blind, international phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol.
18:1373–1385. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tian M, Ma W, Chen Y, Yu Y, Zhu D, Shi J
and Zhang Y: Impact of gender on the survival of patients with
glioblastoma. Biosci Rep. Nov 7–2018.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Brat DJ, Aldape K, Colman H, Holland EC,
Louis DN, Jenkins RB, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Perry A,
Reifenberger G, Stupp R, et al: cIMPACT-NOW update 3: Recommended
diagnostic criteria for 'Diffuse astrocytic glioma, IDH-wildtype,
with molecular features of glioblastoma, WHO grade IV'. Acta
Neuropathol. 136:805–810. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhao H, Zhu H, Huang J, Zhu Y, Hong M, Zhu
H, Zhang J, Li S, Yang L, Lian Y, et al: The synergy of vitamin C
with decitabine activates TET2 in leukemic cells and significantly
improves overall survival in elderly patients with acute myeloid
leukemia. Leuk Res. 66:1–7. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
García MG, Carella A, Urdinguio RG, Bayón
GF, Lopez V, Tejedor JR, Sierra MI, García-Toraño E, Santamarina P,
Perez RF, et al: Epigenetic dysregulation of TET2 in human
glioblastoma. Oncotarget. 9:25922–25934. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Mansouri A, Hachem LD, Mansouri S, Nassiri
F, Laperriere NJ, Xia D, Lindeman NI, Wen PY, Chakravarti A, Mehta
MP, et al: MGMT promoter methylation status testing to guide
therapy for glioblastoma: Refining the approach based on emerging
evidence and current challenges. Neuro Oncol. 21:167–178. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Stummer W, Pichlmeier U, Meinel T,
Wiestler OD, Zanella F and Reulen HJ; ALA-Glioma Study Group:
Fluorescence-guided surgery with 5-aminolevulinic acid for
resection of malignant glioma: A randomised controlled multicentre
phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 7:392–401. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pichlmeier U, Bink A and Schackert G:
Resection and survival in glioblastoma multiforme: An RTOG
recursive partitioning analysis of ALA study patients. Neuro Oncol.
10:1025–1034. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Abd-El-Barr MM and Chiocca EA: How much is
enough? The question of extent of resection in glioblastoma
multiforme. World Neurosurg. 82:e109–e110. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ryken TC, Parney I, Buatti J, Kalkanis SN
and Olson JJ: The role of radiotherapy in the management of
patients with diffuse low grade glioma: A systematic review and
evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J Neurooncol.
125:551–583. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Niyazi M, Brada M, Chalmers AJ, Combs SE,
Erridge SC, Fiorentino A, Grosu AL, Lagerwaard FJ, Minniti G,
Mirimanoff RO, et al: ESTRO-ACROP guideline 'target delineation of
glioblastomas'. Radiother Oncol. 118:35–42. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wick W, Platten M, Meisner C, Felsberg J,
Tabatabai G, Simon M, Nikkhah G, Papsdorf K, Steinbach JP, Sabel M,
et al: Temozolomide chemotherapy alone versus radiotherapy alone
for malignant astrocytoma in the elderly: The NOA-08 randomised,
phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 13:707–715. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rusthoven CG, Koshy M and Sher DJ:
Radiation plus temozolomide in patients with glioblastoma. N Engl J
Med. 376:2195–2197. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Perry JR, Laperriere N, O'Callaghan CJ,
Brandes AA, Menten J, Phillips C, Fay M, Nishikawa R, Cairncross
JG, Roa W, et al: Short-course radiation plus temozolomide in
elderly patients with glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 376:1027–1037.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
McGranahan T, Therkelsen KE, Ahmad S and
Nagpal S: Current state of immunotherapy for treatment of
glioblastoma. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 20:242019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rominiyi O, Vanderlinden A, Clenton SJ,
Bridgewater C, Al-Tamimi Y and Collis SJ: Tumour treating fields
therapy for glioblastoma: Current advances and future directions.
Br J Cancer. 124:697–709. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Geletneky K, Hajda J, Angelova AL, Leuchs
B, Capper D, Bartsch AJ, Neumann JO, Schöning T, Hüsing J, Beelte
B, et al: Oncolytic H-1 parvovirus shows safety and signs of
immunogenic activity in a first phase I/IIa glioblastoma trial. Mol
Ther. 25:2620–2634. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen Q, Espey MG, Krishna MC, Mitchell JB,
Corpe CP, Buettner GR, Shacter E and Levine M: Pharmacologic
ascorbic acid concentrations selectively kill cancer cells: Action
as a prodrug to deliver hydrogen peroxide to tissues. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:13604–13609. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chen Q, Espey MG, Sun AY, Lee JH, Krishna
MC, Shacter E, Choyke PL, Pooput C, Kirk KL, Buettner GR and Levine
M: Ascorbate in pharmacologic concentrations selectively generates
ascorbate radical and hydrogen peroxide in extracellular fluid in
vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:8749–8754. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schoenfeld JD, Sibenaller ZA, Mapuskar KA,
Wagner BA, Cramer-Morales KL, Furqan M, Sandhu S, Carlisle TL,
Smith MC, Abu Hejleh T, et al: O2− and
H2O2-mediated disruption of fe metabolism
causes the differential susceptibility of NSCLC and GBM cancer
cells to pharmacological ascorbate. Cancer Cell. 32:2682017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Klingelhoeffer C, Kämmerer U, Koospal M,
Mühling B, Schneider M, Kapp M, Kübler A, Germer CT and Otto C:
Natural resistance to ascorbic acid induced oxidative stress is
mainly mediated by catalase activity in human cancer cells and
catalase-silencing sensitizes to oxidative stress. BMC Complement
Altern Med. 12:612012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sauberlich HE: Pharmacology of vitamin C.
Annu Rev Nutr. 14:371–391. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nishikimi M and Yagi K: Molecular basis
for the deficiency in humans of gulonolactone oxidase, a key enzyme
for ascorbic acid biosynthesis. Am J Clin Nutr. 54(Suppl 6):
1203S–1208S. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Padayatty SJ and Levine M: Vitamin C: The
known and the unknown and goldilocks. Oral Dis. 22:463–493. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Carr A and Frei B: Does vitamin C act as a
pro-oxidant under physiological conditions? FASEB J. 13:1007–1024.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Levine M, Wang Y, Katz A, Eck P, Kwon O,
Chen S, Lee JH and Padayatty SJ: Ideal vitamin C intake.
Biofactors. 15:71–74. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Carr AC and Lykkesfeldt J: Discrepancies
in global vitamin C recommendations: A review of RDA criteria and
underlying health perspectives. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 61:742–755.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Levine M, Conry-Cantilena C, Wang Y, Welch
RW, Washko PW, Dhariwal KR, Park JB, Lazarev A, Graumlich JF, King
J and Cantilena LR: Vitamin C pharmacokinetics in healthy
volunteers: Evidence for a recommended dietary allowance. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 93:3704–3709. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hoffer LJ, Levine M, Assouline S,
Melnychuk D, Padayatty SJ, Rosadiuk K, Rousseau C, Robitaille L and
Miller WH Jr: Phase I clinical trial of i.v. ascorbic acid in
advanced malignancy. Ann Oncol. 19:1969–1974. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Padayatty SJ, Sun AY, Chen Q, Espey MG,
Drisko J and Levine M: Vitamin C: Intravenous use by complementary
and alternative medicine practitioners and adverse effects. PLoS
One. 5:e114142010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nielsen TK, Højgaard M, Andersen JT,
Poulsen HE, Lykkesfeldt J and Mikines KJ: Elimination of ascorbic
acid after high-dose infusion in prostate cancer patients: A
pharmacokinetic evaluation. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol.
116:343–348. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Stephenson CM, Levin RD, Spector T and Lis
CG: Phase I clinical trial to evaluate the safety, tolerability,
and pharmacokinetics of high-dose intravenous ascorbic acid in
patients with advanced cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
72:139–146. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Torun M, Yardim S, Gönenç A, Sargin H,
Menevşe A and Símşek B: Serum beta-carotene, vitamin E, vitamin C
and malondialdehyde levels in several types of cancer. J Clin Pharm
Ther. 20:259–263. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mahdavi R, Faramarzi E, Seyedrezazadeh E,
Mohammad-Zadeh M and Pourmoghaddam M: Evaluation of oxidative
stress, antioxidant status and serum vitamin C levels in cancer
patients. Biol Trace Elem Res. 130:1–6. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sharma A, Tripathi M, Satyam A and Kumar
L: Study of antioxidant levels in patients with multiple myeloma.
Leuk Lymphoma. 50:809–815. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Emri S, Kilickap S, Kadilar C, Halil MG,
Akay H and Besler T: Serum levels of alpha-tocopherol, vitamin C,
beta-carotene, and retinol in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:3025–3029. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Mehdi WA, Zainulabdeen JA and Mehde AA:
Investigation of the antioxidant status in multiple myeloma
patients: Effects of therapy. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
14:3663–3667. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Huijskens MJ, Wodzig WK, Walczak M,
Germeraad WT and Bos GM: Ascorbic acid serum levels are reduced in
patients with hematological malignancies. Results Immunol. 6:8–10.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Fain O, Mathieu E and Thomas M: Scurvy in
patients with cancer. BMJ. 316:1661–1662. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mayland CR, Bennett MI and Allan K:
Vitamin C deficiency in cancer patients. Palliat Med. 19:17–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Riordan HD, Riordan NH, Jackson JA,
Casciari JJ, Hunninghake R, González MJ, Mora EM, Miranda-Massari
JR, Rosario N and Rivera A: Intravenous vitamin C as a
chemo-therapy agent: A report on clinical cases. P R Health Sci J.
23:115–118. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hoffer LJ, Robitaille L, Zakarian R,
Melnychuk D, Kavan P, Agulnik J, Cohen V, Small D and Miller WH Jr:
High-dose intravenous vitamin C combined with cytotoxic
chemotherapy in patients with advanced cancer: A phase I-II
clinical trial. PLoS One. 10:e01202282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Liu M, Ohtani H, Zhou W, Ørskov AD,
Charlet J, Zhang YW, Shen H, Baylin SB, Liang G, Grønbæk K and
Jones PA: Vitamin C increases viral mimicry induced by
5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:10238–10244.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Shenoy N, Bhagat T, Nieves E, Stenson M,
Lawson J, Choudhary GS, Habermann T, Nowakowski G, Singh R, Wu X,
et al: Upregulation of TET activity with ascorbic acid induces
epigenetic modulation of lymphoma cells. Blood Cancer J.
7:e5872017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Anthony HM and Schorah CJ: Severe
hypovitaminosis C in lung-cancer patients: The utilization of
vitamin C in surgical repair and lymphocyte-related host
resistance. Br J Cancer. 46:354–367. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ramaswamy G and Krishnamoorthy L: Serum
carotene, vitamin A, and vitamin C levels in breast cancer and
cancer of the uterine cervix. Nutr Cancer. 25:173–177. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Khanzode SS, Muddeshwar MG, Khanzode SD
and Dakhale GN: Antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxidation in
different stages of breast cancer. Free Radic Res. 38:81–85. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Popa-Wagner A, Mitran S, Sivanesan S,
Chang E and Buga AM: ROS and brain diseases: The good, the bad, and
the ugly. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013:9635202013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Levine M, Padayatty SJ and Espey MG:
Vitamin C: A concentration-function approach yields pharmacology
and therapeutic discoveries. Adv Nutr. 2:78–88. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
58
|
Du J, Cullen JJ and Buettner GR: Ascorbic
acid: Chemistry, biology and the treatment of cancer. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1826:443–457. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Harrison FE and May JM: Vitamin C function
in the brain: Vital role of the ascorbate transporter SVCT2. Free
Radic Biol Med. 46:719–730. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kaźmierczak-Barańska J, Boguszewska K,
Adamus-Grabicka A and Karwowski BT: Two faces of vitamin
C-antioxidative and pro-oxidative agent. Nutrients. 12:15012020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Lykkesfeldt J and Tveden-Nyborg P: The
pharmacokinetics of vitamin C. Nutrients. 11:24122019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
62
|
Abbott NJ: Dynamics of CNS barriers:
Evolution, differentiation, and modulation. Cell Mol Neurobiol.
25:5–23. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Nualart F, Mack L, García A, Cisternas P,
Bongarzone ER, Heitzer M, Jara N, Martínez F, Ferrada L, Espinoza
F, et al: Vitamin C transporters, recycling and the bystander
effect in the nervous system: SVCT2 versus gluts. J Stem Cell Res
Ther. 4:2092014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Angelow S, Haselbach M and Galla HJ:
Functional characterisation of the active ascorbic acid transport
into cerebrospinal fluid using primary cultured choroid plexus
cells. Brain Res. 988:105–113. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Haselbach M, Wegener J, Decker S,
Engelbertz C and Galla HJ: Porcine choroid plexus epithelial cells
in culture: Regulation of barrier properties and transport
processes. Microsc Res Tech. 52:137–152. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Shi LZ, Li GJ, Wang S and Zheng W: Use of
Z310 cells as an in vitro blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier model:
Tight junction proteins and transport properties. Toxicol In Vitro.
22:190–199. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Strazielle N and Ghersi-Egea JF:
Demonstration of a coupled metabolism-efflux process at the choroid
plexus as a mechanism of brain protection toward xenobiotics. J
Neurosci. 19:6275–6289. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Sotiriou S, Gispert S, Cheng J, Wang Y,
Chen A, Hoogstraten-Miller S, Miller GF, Kwon O, Levine M,
Guttentag SH and Nussbaum RL: Ascorbic-acid transporter Slc23a1 is
essential for vitamin C transport into the brain and for perinatal
survival. Nat Med. 8:514–517. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Tsukaguchi H, Tokui T, Mackenzie B, Berger
UV, Chen XZ, Wang Y, Brubaker RF and Hediger MA: A family of
mammalian Na+-dependent L-ascorbic acid transporters. Nature.
399:70–75. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Daruwala R, Song J, Koh WS, Rumsey SC and
Levine M: Cloning and functional characterization of the human
sodium-dependent vitamin C transporters hSVCT1 and hSVCT2. FEBS
Lett. 460:480–484. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Wang D, Christensen K, Chawla K, Xiao G,
Krebsbach PH and Franceschi RT: Isolation and characterization of
MC3T3-E1 preosteoblast subclones with distinct in vitro and in vivo
differentiation/mineralization potential. J Bone Miner Res.
14:893–903. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Wang Y, Mackenzie B, Tsukaguchi H,
Weremowicz S, Morton CC and Hediger MA: Human vitamin C (L-ascorbic
acid) transporter SVCT1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 267:488–494.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wohlrab C, Phillips E and Dachs GU:
Vitamin C transporters in cancer: Current understanding and gaps in
knowledge. Front Oncol. 7:742017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Agus DB, Gambhir SS, Pardridge WM,
Spielholz C, Baselga J, Vera JC and Golde DW: Vitamin C crosses the
blood-brain barrier in the oxidized form through the glucose
transporters. J Clin Invest. 100:2842–2848. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Ho HTB, Dahlin A and Wang J: Expression
profiling of solute carrier gene families at the blood-CSF barrier.
Front Pharmacol. 3:1542012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Bürzle M, Suzuki Y, Ackermann D, Miyazaki
H, Maeda N, Clémençon B, Burrier R and Hediger MA: The
sodium-dependent ascorbic acid transporter family SLC23. Mol
Aspects Med. 34:436–454. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Rice ME: Ascorbate regulation and its
neuroprotective role in the brain. Trends Neurosci. 23:209–216.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Spector R, Keep RF, Robert Snodgrass S,
Smith QR and Johanson CE: A balanced view of choroid plexus
structure and function: Focus on adult humans. Exp Neurol.
267:78–86. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Mun GH, Kim MJ, Lee JH, Kim HJ, Chung YH,
Chung YB, Kang JS, Hwang YI, Oh SH, Kim JG, et al:
Immunohistochemical study of the distribution of sodium-dependent
vitamin C trans-porters in adult rat brain. J Neurosci Res.
83:919–928. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Ulloa V, García-Robles M, Martínez F,
Salazar K, Reinicke K, Pérez F, Godoy DF, Godoy AS and Nualart F:
Human choroid plexus papilloma cells efficiently transport glucose
and vitamin C. J Neurochem. 127:403–414. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Rice M and Russo-Menna I: Differential
compartmentalization of brain ascorbate and glutathione between
neurons and glia. Neuroscience. 82:1213–1223. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Castro M, Caprile T, Astuya A, Millán C,
Reinicke K, Vera JC, Vásquez O, Aguayo LG and Nualart F:
High-affinity sodium-vitamin C co-transporters (SVCT) expression in
embryonic mouse neurons. J Neurochem. 78:815–823. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Nualart FJ, Rivas CI, Montecinos VP, Godoy
AS, Guaiquil VH, Golde DW and Vera JC: Recycling of vitamin C by a
bystander effect. J Biol Chem. 278:10128–10133. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Kaufman S: Coenzymes and hydroxylases:
Ascorbate and dopamine-beta-hydroxylase; tetrahydropteridines and
phenyl-alanine and tyrosine hydroxylases. Pharmacol Rev. 18:61–69.
1966.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Eipper BA, Milgram SL, Husten EJ, Yun HY
and Mains RE: Peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase: A
multifunctional protein with catalytic, processing, and routing
domains. Protein Sci. 2:489–497. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Eldridge CF, Bunge MB, Bunge RP and Wood
PM: Differentiation of axon-related Schwann cells in vitro. I.
Ascorbic acid regulates basal lamina assembly and myelin formation.
J Cell Biol. 105:1023–1034. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Qiu S, Li L, Weeber EJ and May JM:
Ascorbate transport by primary cultured neurons and its role in
neuronal function and protection against excitotoxicity. J Neurosci
Res. 85:1046–1056. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Rebec GV and Pierce RC: A vitamin as
neuromodulator: Ascorbate release into the extracellular fluid of
the brain regulates dopaminergic and glutamatergic transmission.
Prog Neurobiol. 43:537–565. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Pastor P, Cisternas P, Salazar K,
Silva-Alvarez C, Oyarce K, Jara N, Espinoza F, Martínez AD and
Nualart F: SVCT2 vitamin C transporter expression in progenitor
cells of the post-natal neurogenic niche. Front Cell Neurosci.
7:1192013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Oyarce K, Bongarzone ER and Nualart F:
Unconventional neurogenic niches and neurogenesis modulation by
vitamins. J Stem Cell Res Ther. 4:1842014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Davson H and Oldendorf WH: Symposium on
membrane transport. Transport in the central nervous system. Proc R
Soc Med. 60:326–329. 1967.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Reiber H, Ruff M and Uhr M: Ascorbate
concentration in human cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and serum.
Intrathecal accumulation and CSF flow rate. Clinica Chimica Acta.
217:163–173. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Cameron E and Pauling L: Supplemental
ascorbate in the supportive treatment of cancer: Prolongation of
survival times in terminal human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
73:3685–3689. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Creagan ET, Moertel CG, O'Fallon JR,
Schutt AJ, O'Connell MJ, Rubin J and Frytak S: Failure of high-dose
vitamin C (ascorbic acid) therapy to benefit patients with advanced
cancer. A controlled trial. N Engl J Med. 301:687–690. 1979.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Moertel CG, Fleming TR, Creagan ET, Rubin
J, O'Connell MJ and Ames MM: High-dose vitamin C versus placebo in
the treatment of patients with advanced cancer who have had no
prior chemotherapy. A randomized double-blind comparison. N Engl J
Med. 312:137–141. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Monti DA, Mitchell E, Bazzan AJ, Littman
S, Zabrecky G, Yeo CJ, Pillai MV, Newberg AB, Deshmukh S and Levine
M: Phase I evaluation of intravenous ascorbic acid in combination
with gemcitabine and erlotinib in patients with metastatic
pancreatic cancer. PLoS One. 7:e297942012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Welsh JL, Wagner BA, van't Erve TJ, Zehr
PS, Berg DJ, Halfdanarson TR, Yee NS, Bodeker KL, Du J, Roberts LJ
II, et al: Pharmacological ascorbate with gemcitabine for the
control of metastatic and node-positive pancreatic cancer (PACMAN):
Results from a phase I clinical trial. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
71:765–775. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Herst PM, Broadley KWR, Harper JL and
McConnell MJ: Pharmacological concentrations of ascorbate
radiosensitize glio-blastoma multiforme primary cells by increasing
oxidative DNA damage and inhibiting G2/M arrest. Free Radic Biol
Med. 52:1486–1493. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Ma Y, Chapman J, Levine M, Polireddy K,
Drisko J and Chen Q: High-dose parenteral ascorbate enhanced
chemosensitivity of ovarian cancer and reduced toxicity of
chemotherapy. Sci Transl Med. 6:222ra182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Fritz H, Flower G, Weeks L, Cooley K,
Callachan M, McGowan J, Skidmore B, Kirchner L and Seely D:
Intravenous vitamin C and cancer: A systematic review. Integr
Cancer Ther. 13:280–300. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Carr AC and Cook J: Intravenous vitamin C
for cancer therapy-identifying the current gaps in our knowledge.
Front Physiol. 9:11822018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Violet PC and Levine M: Pharmacologic
ascorbate in myeloma treatment: Doses matter. EBioMedicine.
18:9–10. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Schoenfeld JD, Alexander MS, Waldron TJ,
Sibenaller ZA, Spitz DR, Buettner GR, Allen BG and Cullen JJ:
Pharmacological ascorbate as a means of sensitizing cancer cells to
radio-chemo-therapy while protecting normal tissue. Semin Radiat
Oncol. 29:25–32. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Bienert GP, Schjoerring JK and Jahn TP:
Membrane transport of hydrogen peroxide. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1758:994–1003. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Bienert GP, Møller AL, Kristiansen KA,
Schulz A, Møller IM, Schjoerring JK and Jahn TP: Specific
aquaporins facilitate the diffusion of hydrogen peroxide across
membranes. J Biol Chem. 282:1183–1192. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Erudaitius D, Huang A, Kazmi S, Buettner
GR and Rodgers VG: Peroxiporin expression is an important factor
for cancer cell susceptibility to therapeutic
H2O2: Implications for pharmacological
ascorbate therapy. PLoS One. 12:e01704422017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Deubzer B, Mayer F, Kuçi Z, Niewisch M,
Merkel G, Handgretinger R and Bruchelt G: H(2)O(2)-mediated
cytotoxicity of pharmacologic ascorbate concentrations to
neuroblastoma cells: Potential role of lactate and ferritin. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 25:767–774. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Olney KE, Du J, van 't Erve TJ, Witmer JR,
Sibenaller ZA, Wagner BA, Buettner GR and Cullen JJ: Inhibitors of
hydroperoxide metabolism enhance ascorbate-induced cytotoxicity.
Free Radic Res. 47:154–163. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
109
|
Du J, Martin SM, Levine M, Wagner BA,
Buettner GR, Wang S, Taghiyev AF, Du C, Knudson CM and Cullen JJ:
Mechanisms of ascorbate-induced cytotoxicity in pancreatic cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 16:509–520. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Ibrahim WH, Habib HM, Kamal H, St Clair DK
and Chow CK: Mitochondrial superoxide mediates labile iron level:
Evidence from Mn-SOD-transgenic mice and heterozygous knockout mice
and isolated rat liver mitochondria. Free Radic Biol Med.
65:143–149. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Doskey CM, Buranasudja V, Wagner BA,
Wilkes JG, Du J, Cullen JJ and Buettner GR: Tumor cells have
decreased ability to metabolize H2O2:
Implications for pharmacological ascorbate in cancer therapy. Redox
Biol. 10:274–284. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Sinnberg T, Noor S, Venturelli S, Berger
A, Schuler P, Garbe C and Busch C: The ROS-induced cytotoxicity of
ascorbate is attenuated by hypoxia and HIF-1alpha in the NCI60
cancer cell lines. J Cell Mol Med. 18:530–541. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
113
|
Du J, Cieslak JA III, Welsh JL, Sibenaller
ZA, Allen BG, Wagner BA, Kalen AL, Doskey CM, Strother RK, Button
AM, et al: Pharmacological ascorbate radiosensitizes pancreatic
cancer. Cancer Res. 75:3314–3326. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Torti SV and Torti FM: Iron and cancer:
More ore to be mined. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:342–355. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Uetaki M, Tabata S, Nakasuka F, Soga T and
Tomita M: Metabolomic alterations in human cancer cells by vitamin
C-induced oxidative stress. Sci Rep. 5:138962015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
El Banna N, Hatem E, Heneman-Masurel A,
Léger T, Baïlle D, Vernis L, Garcia C, Martineau S, Dupuy C, Vagner
S, et al: Redox modifications of cysteine-containing proteins, cell
cycle arrest and translation inhibition: Involvement in vitamin
C-induced breast cancer cell death. Redox Biol. 26:1012902019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Frömberg A, Gutsch D, Schulze D,
Vollbracht C, Weiss G, Czubayko F and Aigner A: Ascorbate exerts
anti-proliferative effects through cell cycle inhibition and
sensitizes tumor cells towards cytostatic drugs. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 67:1157–1166. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
118
|
Marklund SL, Westman NG, Lundgren E and
Roos G: Copper- and zinc-containing superoxide dismutase,
manganese-containing superoxide dismutase, catalase, and
glutathione peroxidase in normal and neoplastic human cell lines
and normal human tissues. Cancer Res. 42:1955–1961. 1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Johnson RM, Ho YS, Yu DY, Kuypers FA,
Ravindranath Y and Goyette GW: The effects of disruption of genes
for peroxire-doxin-2, glutathione peroxidase-1, and catalase on
erythrocyte oxidative metabolism. Free Radic Biol Med. 48:519–525.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Vaupel P, Höckel M and Mayer A: Detection
and characterization of tumor hypoxia using pO2 histography.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 9:1221–1235. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Moulder JE and Rockwell S: Hypoxic
fractions of solid tumors: Experimental techniques, methods of
analysis, and a survey of existing data. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 10:695–712. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Vaupel P, Mayer A and Höckel M: Tumor
hypoxia and malignant progression. Methods Enzymol. 381:335–354.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Zeng W, Liu P, Pan W, Singh SR and Wei Y:
Hypoxia and hypoxia inducible factors in tumor metabolism. Cancer
Lett. 356:263–267. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Korkolopoulou P, Patsouris E,
Konstantinidou AE, Pavlopoulos PM, Kavantzas N, Boviatsis E,
Thymara I, Perdiki M, Thomas-Tsagli E, Angelidakis D, et al:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha/vascular endothelial growth factor
axis in astrocytomas. Associations with microvessel morphometry,
proliferation and prognosis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol.
30:267–278. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Mashiko R, Takano S, Ishikawa E, Yamamoto
T, Nakai K and Matsumura A: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α expression
is a prognostic biomarker in patients with astrocytic tumors
associated with necrosis on MR image. J Neurooncol. 102:43–50.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Søndergaard KL, Hilton DA, Penney M,
Ollerenshaw M and Demaine AG: Expression of hypoxia-inducible
factor 1alpha in tumours of patients with glioblastoma. Neuropathol
Appl Neurobiol. 28:210–217. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Bao L, Chen Y, Lai HT, Wu SY, Wang JE,
Hatanpaa KJ, Raisanen JM, Fontenot M, Lega B, Chiang CM, et al:
Methylation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α by G9a/GLP
inhibits HIF-1 transcriptional activity and cell migration. Nucleic
Acids Res. 46:6576–6591. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Campbell EJ, Dachs GU, Morrin HR, Davey
VC, Robinson BA and Vissers MCM: Activation of the hypoxia pathway
in breast cancer tissue and patient survival are inversely
associated with tumor ascorbate levels. BMC Cancer. 19:3072019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Camarena V and Wang G: The epigenetic role
of vitamin C in health and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci.
73:1645–1658. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Satheesh NJ, Samuel SM and Büsselberg D:
Combination therapy with vitamin c could eradicate cancer stem
cells. Biomolecules. 10:792020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
131
|
O'Leary BR, Houwen FK, Johnson CL, Allen
BG, Mezhir JJ, Berg DJ, Cullen JJ and Spitz DR: Pharmacological
ascorbate as an adjuvant for enhancing radiation-chemotherapy
responses in gastric adenocarcinoma. Radiat Res. 189:456–465. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Espey MG, Chen P, Chalmers B, Drisko J,
Sun AY, Levine M and Chen Q: Pharmacologic ascorbate synergizes
with gemcitabine in preclinical models of pancreatic cancer. Free
Radic Biol Med. 50:1610–1619. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Moser JC, Rawal M, Wagner BA, Du J, Cullen
JJ and Buettner GR: Pharmacological ascorbate and ionizing
radiation (IR) increase labile iron in pancreatic cancer. Redox
Biol. 2:22–27. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Chen Q, Espey MG, Sun AY, Pooput C, Kirk
KL, Krishna MC, Khosh DB, Drisko J and Levine M: Pharmacologic
doses of ascorbate act as a prooxidant and decrease growth of
aggressive tumor xenografts in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:11105–11109. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Lu YX, Wu QN, Chen DL, Chen LZ, Wang ZX,
Ren C, Mo HY, Chen Y, Sheng H, Wang YN, et al: Pharmacological
ascorbate suppresses growth of gastric cancer cells with GLUT1
overexpression and enhances the efficacy of oxaliplatin through
redox modulation. Theranostics. 8:1312–1326. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Oka N, Komuro A, Amano H, Dash S, Honda M,
Ota K, Nishimura S, Ueda T, Akagi M and Okada H: Ascorbate
sensitizes human osteosarcoma cells to the cytostatic effects of
cisplatin. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 8:e006322020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Kanter M and Akpolat M: Vitamin C protects
against ionizing radiation damage to goblet cells of the ileum in
rats. Acta Histochem. 110:481–490. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Ito Y, Kinoshita M, Yamamoto T, Sato T,
Obara T, Saitoh D, Seki S and Takahashi Y: A combination of pre-
and post-exposure ascorbic acid rescues mice from radiation-induced
lethal gastrointestinal damage. Int J Mol Sci. 14:19618–19635.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Vollbracht C, Schneider B, Leendert V,
Weiss G, Auerbach L and Beuth J: Intravenous vitamin C
administration improves quality of life in breast cancer patients
during chemo-/radiotherapy and aftercare: Results of a
retrospective, multicentre, epidemiological cohort study in
Germany. In Vivo. 25:983–990. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Polireddy K, Dong R, Reed G, Yu J, Chen P,
Williamson S, Violet PC, Pessetto Z, Godwin AK, Fan F, et al: High
dose parenteral ascorbate inhibited pancreatic cancer growth and
metastasis: Mechanisms and a phase I/IIa study. Sci Rep.
7:171882017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Nauman G, Gray JC, Parkinson R, Levine M
and Paller CJ: Systematic review of intravenous ascorbate in cancer
clinical trials. Antioxidants (Basel). 7:892018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Nielsen TK, Højgaard M, Andersen JT,
Jørgensen NR, Zerahn B, Kristensen B, Henriksen T, Lykkesfeldt J,
Mikines KJ and Poulsen HE: Weekly ascorbic acid infusion in
castration-resistant prostate cancer patients: A single-arm phase
II trial. Transl Androl Urol. 6:517–528. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Wang F, He MM, Wang ZX, Li S, Jin Y, Ren
C, Shi SM, Bi BT, Chen SZ, Lv ZD, et al: Phase I study of high-dose
ascorbic acid with mFOLFOX6 or FOLFIRI in patients with metastatic
colorectal cancer or gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 19:4602019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Alexander MS, Wilkes JG, Schroeder SR,
Buettner GR, Wagner BA, Du J, Gibson-Corley K, O'Leary BR, Spitz
DR, Buatti JM, et al: Pharmacologic ascorbate reduces
radiation-induced normal tissue toxicity and enhances tumor
radiosensitization in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 78:6838–6851.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Ou J, Zhu X, Chen P, Du Y, Lu Y, Peng X,
Bao S, Wang J, Zhang X, Zhang T and Pang CLK: A randomized phase II
trial of best supportive care with or without hyperthermia and
vitamin C for heavily pretreated, advanced, refractory
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Adv Res. 24:175–182. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Allen BG, Bodeker KL, Smith MC, Monga V,
Sandhu S, Hohl R, Carlisle T, Brown H, Hollenbeck N, Vollstedt S,
et al: First-in-human phase I clinical trial of pharmacologic
ascorbate combined with radiation and temozolomide for newly
diagnosed glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 25:6590–6597. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Baillie N, Carr AC and Peng S: The use of
intravenous vitamin C as a supportive therapy for a patient with
glioblastoma multiforme. Antioxidants (Basel). 7:1152018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Cushing CM, Petronek MS, Bodeker KL,
Vollstedt S, Brown HA, Opat E, Hollenbeck NJ, Shanks T, Berg DJ,
Smith BJ, et al: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of
pharmacological ascorbate-induced iron redox state as a biomarker
in subjects undergoing radio-chemotherapy. Redox Biol.
38:1018042021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Padayatty SJ, Sun H, Wang Y, Riordan HD,
Hewitt SM, Katz A, Wesley RA and Levine M: Vitamin C
pharmacokinetics: Implications for oral and intravenous use. Ann
Intern Med. 140:533–537. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Fowler AA III, Syed AA, Knowlson S,
Sculthorpe R, Farthing D, DeWilde C, Farthing CA, Larus TL, Martin
E, Brophy DF, et al: Phase I safety trial of intravenous ascorbic
acid in patients with severe sepsis. J Transl Med. 12:322014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Zabet MH, Mohammadi M, Ramezani M and
Khalili H: Effect of high-dose ascorbic acid on vasopressor's
requirement in septic shock. J Res Pharm Pract. 5:94–100. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Tanaka H, Matsuda T, Miyagantani Y,
Yukioka T, Matsuda H and Shimazaki S: Reduction of resuscitation
fluid volumes in severely burned patients using ascorbic acid
administration: A randomized, prospective study. Arch Surg.
135:326–331. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Li G, Qin Z, Chen Z, Xie L, Wang R and
Zhao H: Tumor microenvironment in treatment of glioma. Open Med
(Wars). 12:247–251. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Ginhoux F, Greter M, Leboeuf M, Nandi S,
See P, Gokhan S, Mehler MF, Conway SJ, Ng LG, Stanley ER, et al:
Fate mapping analysis reveals that adult microglia derive from
primitive macrophages. Science. 330:841–845. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Charles NA, Holland EC, Gilbertson R,
Glass R and Kettenmann H: The brain tumor microenvironment. Glia.
60:502–514. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Poon CC, Sarkar S, Yong VW and Kelly JJP:
Glioblastoma-associated microglia and macrophages: Targets for
therapies to improve prognosis. Brain. 140:1548–1560. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Poon CC, Gordon PMK, Liu K, Yang R, Sarkar
S, Mirzaei R, Ahmad ST, Hughes ML, Yong VW and Kelly JJP:
Differential microglia and macrophage profiles in human IDH-mutant
and -wild type glioblastoma. Oncotarget. 10:3129–3143. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Tomaszewski W, Sanchez-Perez L, Gajewski
TF and Sampson JH: Brain tumor microenvironment and host state:
Implications for immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 25:4202–4210.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Hwang SY, Yoo BC, Jung J, Oh ES, Hwang JS,
Shin JA, Kim SY, Cha SH and Han IO: Induction of glioma apoptosis
by microglia-secreted molecules: The role of nitric oxide and
cathepsin B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1793:1656–1668. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Chicoine MR, Zahner M, Won EK, Kalra RR,
Kitamura T, Perry A and Higashikubo R: The in vivo antitumoral
effects of lipopolysaccharide against glioblastoma multiforme are
mediated in part by Toll-like receptor 4. Neurosurgery. 60:372–381.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Martins TA, Schmassmann P, Shekarian T,
Boulay JL, Ritz MF, Zanganeh S, vom Berg J and Hutter G:
Microglia-centered combinatorial strategies against glioblastoma.
Front Immunol. 11:5719512020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Gupta K and Burns TC: Radiation-induced
alterations in the recurrent glioblastoma microenvironment:
Therapeutic implications. Front Oncol. 8:5032018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Yoshimura M, Itasaka S, Harada H and
Hiraoka M: Micro-environment and radiation therapy. Biomed Res Int.
2013:6853082013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
164
|
Bellail AC, Hunter SB, Brat DJ, Tan C and
van Meir EG: Microregional extracellular matrix heterogeneity in
brain modulates glioma cell invasion. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
36:1046–1069. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Wild-Bode C, Weller M, Rimner A, Dichgans
J and Wick W: Sublethal irradiation promotes migration and
invasiveness of glioma cells: Implications for radiotherapy of
human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 61:2744–2750. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Shankar A, Kumar S, Iskander AS, Varma NR,
Janic B, deCarvalho A, Mikkelsen T, Frank JA, Ali MM, Knight RA, et
al: Subcurative radiation significantly increases cell
proliferation, invasion, and migration of primary glioblastoma
multiforme in vivo. Chin J Cancer. 33:148–158. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
167
|
Wank M, Schilling D, Reindl J, Meyer B,
Gempt J, Motov S, Alexander F, Wilkens JJ, Schlegel J, Schmid TE
and Combs SE: Evaluation of radiation-related invasion in primary
patient-derived glioma cells and validation with established cell
lines: Impact of different radiation qualities with differing LET.
J Neurooncol. 139:583–590. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Wank M, Schilling D, Schmid TE, Meyer B,
Gempt J, Barz M, Schlegel J, Liesche F, Kessel KA, Wiestler B, et
al: Human glioma migration and infiltration properties as a target
for personalized radiation medicine. Cancers (Basel). 10:4562018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
169
|
Zhang X, Wang X, Xu R, Ji J, Xu Y, Han M,
Wei Y, Huang B, Chen A, Zhang Q, et al: YM155 decreases
radiation-induced invasion and reverses epithelial-mesenchymal
transition by targeting STAT3 in glioblastoma. J Transl Med.
16:792018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Gupta K, Vuckovic I, Zhang S, Xiong Y,
Carlson BL, Jacobs J, Olson I, Petterson XM, Macura SI, Sarkaria J
and Burns TC: Radiation induced metabolic alterations associate
with tumor aggressiveness and poor outcome in glioblastoma. Front
Oncol. 10:5352020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Dixit S, Bernardo A, Walker JM, Kennard
JA, Kim GY, Kessler ES and Harrison FE: Vitamin C deficiency in the
brain impairs cognition, increases amyloid accumulation and
deposition, and oxidative stress in APP/PSEN1 and normally aging
mice. ACS Chem Neurosci. 6:570–581. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Portugal CC, Socodato R and Relvas JB: The
ascorbate transporter SVCT2 to target microglia-dependent
inflammation. Oncotarget. 8:99217–99218. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Azzolini C, Fiorani M, Cerioni L,
Guidarelli A and Cantoni O: Sodium-dependent transport of ascorbic
acid in U937 cell mitochondria. IUBMB Life. 65:149–153. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Muñoz-Montesino C, Roa FJ, Peña E,
González M, Sotomayor K, Inostroza E, Muñoz CA, González I,
Maldonado M, Soliz C, et al: Mitochondrial ascorbic acid transport
is mediated by a low-affinity form of the sodium-coupled ascorbic
acid transporter-2. Free Radic Biol Med. 70:241–254. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Peña E, Roa FJ, Inostroza E, Sotomayor K,
González M, Gutierrez-Castro FA, Maurin M, Sweet K, Labrousse C,
Gatica M, et al: Increased expression of mitochondrial
sodium-coupled ascorbic acid transporter-2 (mitSVCT2) as a central
feature in breast cancer. Free Radic Biol Med. 135:283–292. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Roa FJ, Peña E, Gatica M, Escobar-Acuña K,
Saavedra P, Maldonado M, Cuevas ME, Moraga-Cid G, Rivas CI and
Muñoz-Montesino C: Therapeutic use of vitamin C in cancer:
Physiological considerations. Front Pharmacol. 11:2112020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
McCaffrey G, Staatz WD, Quigley CA, Nametz
N, Seelbach MJ, Campos CR, Brooks TA, Egleton RD and Davis TP:
Tight junctions contain oligomeric protein assembly critical for
maintaining blood-brain barrier integrity in vivo. J Neurochem.
103:2540–2555. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Kook SY, Lee KM, Kim Y, Cha MY, Kang S,
Baik SH, Lee H, Park R and Mook-Jung I: High-dose of vitamin C
supplementation reduces amyloid plaque burden and ameliorates
pathological changes in the brain of 5XFAD mice. Cell Death Dis.
5:e10832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Dubois LG, Campanati L, Righy C,
D'Andrea-Meira I, Spohr TC, Porto-Carreiro I, Pereira CM,
Balça-Silva J, Kahn SA, DosSantos MF, et al: Gliomas and the
vascular fragility of the blood brain barrier. Front Cell Neurosci.
8:4182014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
180
|
Prata C, Hrelia S and Fiorentini D:
Peroxiporins in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 20:13712019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
181
|
Henzler T and Steudle E: Transport and
metabolic degradation of hydrogen peroxide in Chara corallina:
Model calculations and measurements with the pressure probe suggest
transport of H(2)O(2) across water channels. J Exp Bot.
51:2053–2066. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
182
|
Noell S, Ritz R, Wolburg-Buchholz K,
Wolburg H and Fallier-Becker P: An allograft glioma model reveals
the depen-dence of aquaporin-4 expression on the brain
microenvironment. PLoS One. 7:e365552012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
183
|
Warth A, Kröger S and Wolburg H:
Redistribution of aqua-porin-4 in human glioblastoma correlates
with loss of agrin immunoreactivity from brain capillary basal
laminae. Acta Neuropathol. 107:311–318. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Markert JM, Fuller CM, Gillespie GY,
Bubien JK, McLean LA, Hong RL, Lee K, Gullans SR, Mapstone TB and
Benos DJ: Differential gene expression profiling in human brain
tumors. Physiol Genomics. 5:21–33. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Papadopoulos MC and Saadoun S: Key roles
of aquaporins in tumor biology. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1848:2576–2583. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
186
|
Labak CM, Wang PY, Arora R, Guda MR,
Asuthkar S, Tsung AJ and Velpula KK: Glucose transport: Meeting the
metabolic demands of cancer, and applications in glioblastoma
treatment. Am J Cancer Res. 6:1599–1608. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Castro MA, Pozo M, Cortés C, García Mde L,
Concha II and Nualart F: Intracellular ascorbic acid inhibits
transport of glucose by neurons, but not by astrocytes. J
Neurochem. 102:773–782. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Azzalin A, Nato G, Parmigiani E, Garello
F, Buffo A and Magrassi L: Inhibitors of GLUT/SLC2A enhance the
action of BCNU and temozolomide against high-grade gliomas.
Neoplasia. 19:364–373. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Astuya A, Caprile T, Castro M, Salazar K,
García Mde L, Reinicke K, Rodríguez F, Vera JC, Millán C, Ulloa V,
et al: Vitamin C uptake and recycling among normal and tumor cells
from the central nervous system. J Neurosci Res. 79:146–156. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
190
|
Chen S, Roffey DM, Dion CA, Arab A and Wai
EK: Effect of perioperative vitamin C supplementation on
postoperative pain and the incidence of chronic regional pain
syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin J Pain.
32:179–185. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
191
|
Salazar K, Martínez F, Pérez-Martín M,
Cifuentes M, Trigueros L, Ferrada L, Espinoza F, Saldivia N,
Bertinat R, Forman K, et al: SVCT2 expression and function in
reactive astrocytes is a common event in different brain
pathologies. Mol Neurobiol. 55:5439–5452. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
192
|
Heneka MT, Carson MJ, El Khoury J,
Landreth GE, Brosseron F, Feinstein DL, Jacobs AH, Wyss-Coray T,
Vitorica J, Ransohoff RM, et al: Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's
disease. Lancet Neurol. 14:388–405. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Berger UV, Lu XC, Liu W, Tang Z, Slusher
BS and Hediger MA: Effect of middle cerebral artery occlusion on
mRNA expression for the sodium-coupled vitamin C transporter SVCT2
in rat brain. J Neurochem. 86:896–906. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Savini I, Rossi A, Catani MV, Ceci R and
Avigliano L: Redox regulation of vitamin C transporter SVCT2 in
C2C12 myotubes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 361:385–390. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Reuter S, Gupta SC, Chaturvedi MM and
Aggarwal BB: Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: How are
they linked? Free Radic Biol Med. 49:1603–1616. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Harris HR, Orsini N and Wolk A: Vitamin C
and survival among women with breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Eur J
Cancer. 50:1223–1231. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Wilson MK, Baguley BC, Wall C, Jameson MB
and Findlay MP: Review of high-dose intravenous vitamin C as an
anticancer agent. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 10:22–37. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Hunnisett A, Davies S, McLaren-Howard J,
Gravett P, Finn M and Gueret-Wardle D: Lipoperoxides as an index of
free radical activity in bone marrow transplant recipients.
Preliminary observations. Biol Trace Elem Res. 47:125–132. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Nan-Ya K, Kajihara M, Kojima N and Degawa
M: Usefulness of urinary kidney injury molecule-1 (Kim-1) as a
biomarker for cisplatin-induced sub-chronic kidney injury. J Appl
Toxicol. 35:124–132. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
200
|
Schoenfeld JD, Sibenaller ZA, Mapuskar KA,
Wagner BA, Cramer-Morales KL, Furqan M, Sandhu S, Carlisle TL,
Smith MC, Abu Hejleh T, et al: O2− and
H2O2-mediated disruption of fe metabolism
causes the differential susceptibility of NSCLC and GBM cancer
cells to pharmacological ascorbate. Cancer Cell. 31:487–500.e8.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
201
|
Attia M, Essa EA, Zaki RM and Elkordy AA:
An overview of the antioxidant effects of ascorbic acid and alpha
lipoic acid (in liposomal forms) as adjuvant in cancer treatment.
Antioxidants (Basel). 9:3592020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
202
|
Milletti F: Cell-penetrating peptides:
Classes, origin, and current landscape. Drug Discov Today.
17:850–860. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Hultqvist G, Syvänen S, Fang XT, Lannfelt
L and Sehlin D: Bivalent brain shuttle increases antibody uptake by
monovalent binding to the transferrin receptor. Theranostics.
7:308–318. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Staquicini FI, Ozawa MG, Moya CA, Driessen
WH, Barbu EM, Nishimori H, Soghomonyan S, Flores LG, Liang X II,
Paolillo V, et al: Systemic combinatorial peptide selection yields
a non-canonical iron-mimicry mechanism for targeting tumors in a
mouse model of human glioblastoma. J Clin Invest. 121:161–173.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
205
|
Tong HI, Kang W, Davy PM, Shi Y, Sun S,
Allsopp RC and Lu Y: Monocyte trafficking, engraftment, and
delivery of nanoparticles and an exogenous gene into the acutely
inflamed brain tissue-evaluations on monocyte-based delivery system
for the central nervous system. PLoS One. 11:e01540222016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
206
|
Di Tacchio M, Macas J, Weissenberger J,
Sommer K, Bähr O, Steinbach JP, Senft C, Seifert V, Glas M,
Herrlinger U, et al: Tumor vessel normalization, immunostimulatory
reprogramming, and improved survival in glioblastoma with combined
inhibition of PD-1, angiopoietin-2, and VEGF. Cancer Immunol Res.
7:1910–1927. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Przystal JM, Waramit S, Pranjol MZI, Yan
W, Chu G, Chongchai A, Samarth G, Olaciregui NG, Tabatabai G,
Carcaboso AM, et al: Efficacy of systemic temozolomide-activated
phage-targeted gene therapy in human glioblastoma. EMBO Mol Med.
11:e84922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Carr A, Wohlrab C, Young P and Bellomo R:
Stability of intravenous vitamin C solutions: A technical report.
Crit Care Resusc. 20:180–181. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|