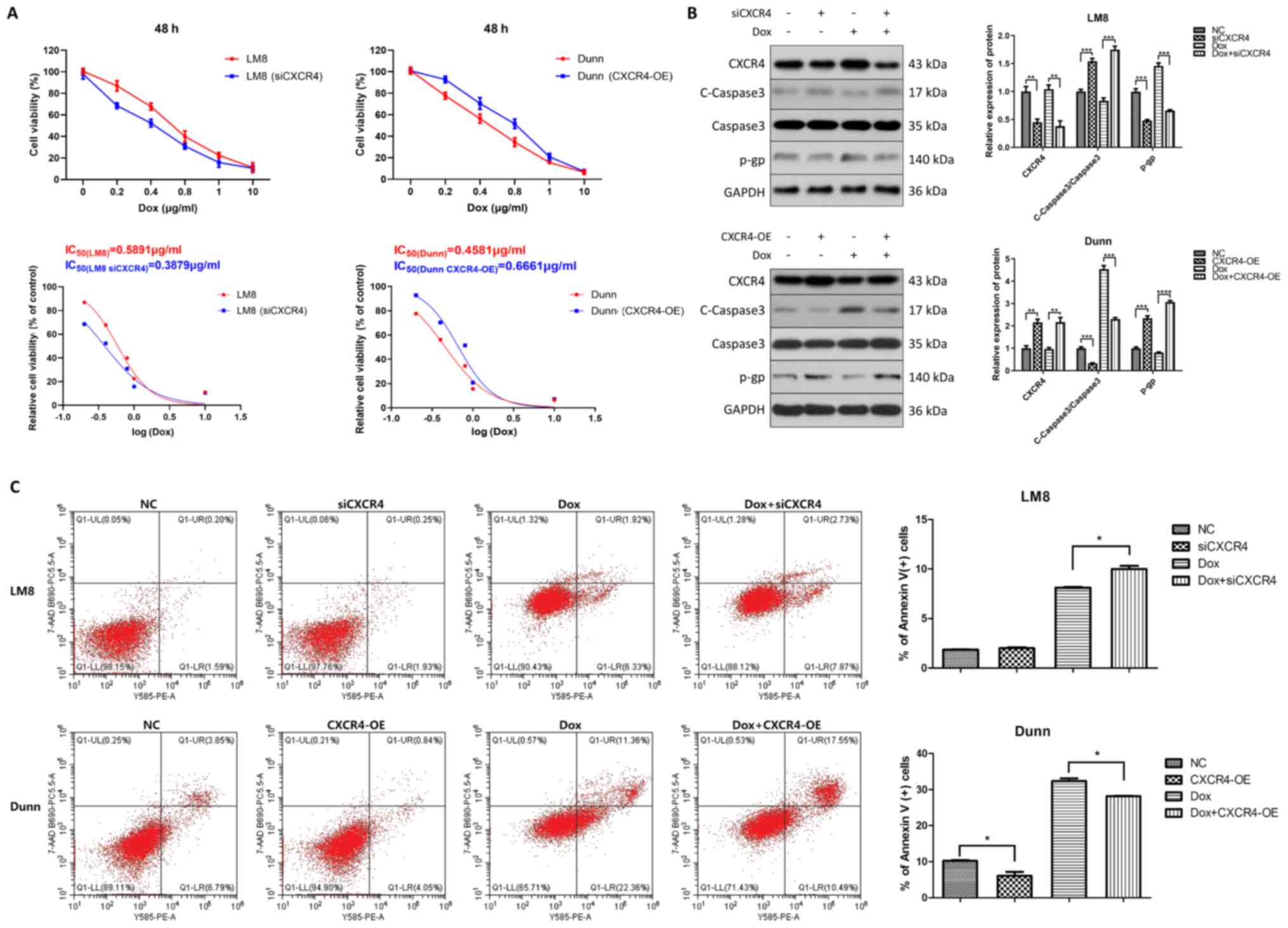
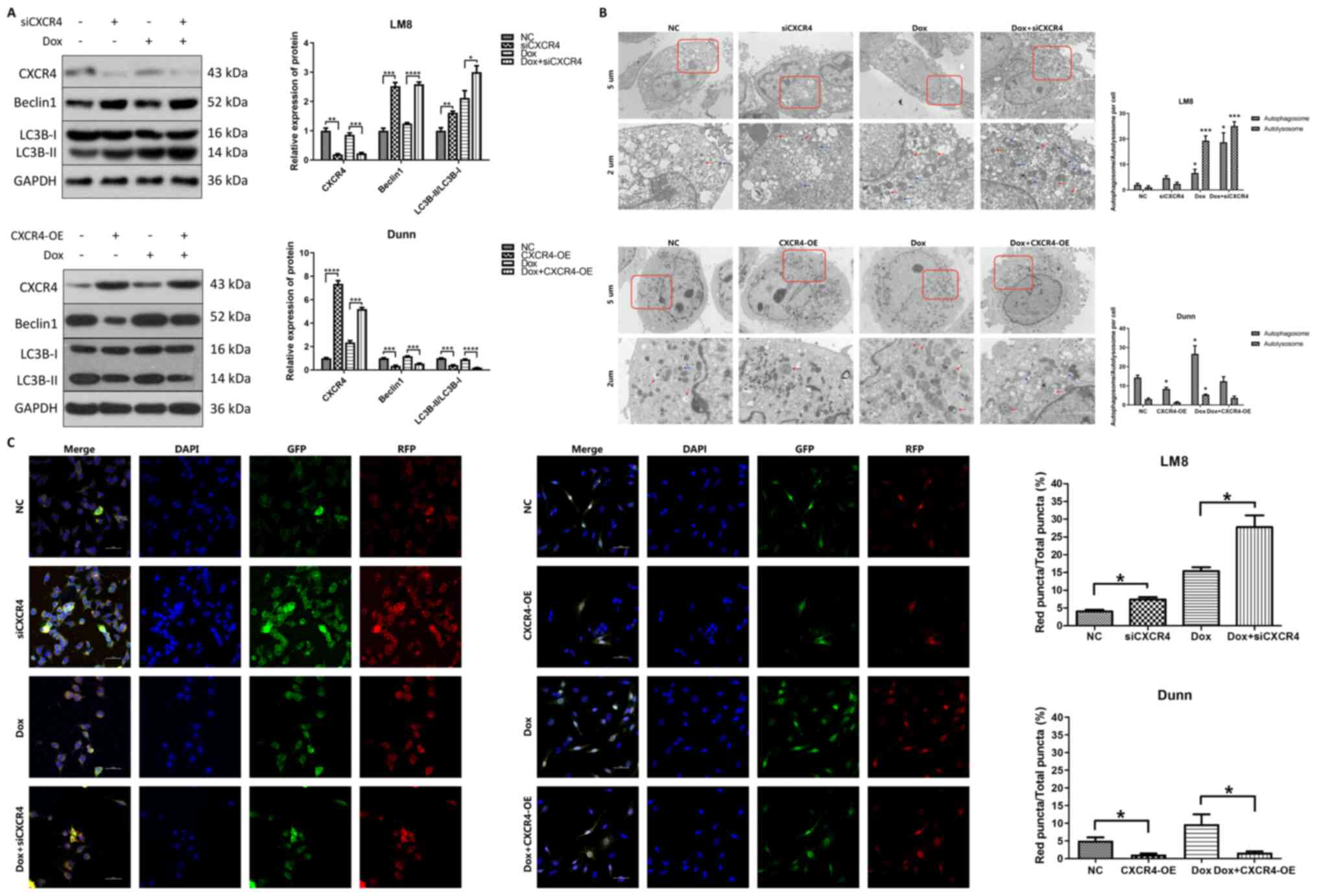
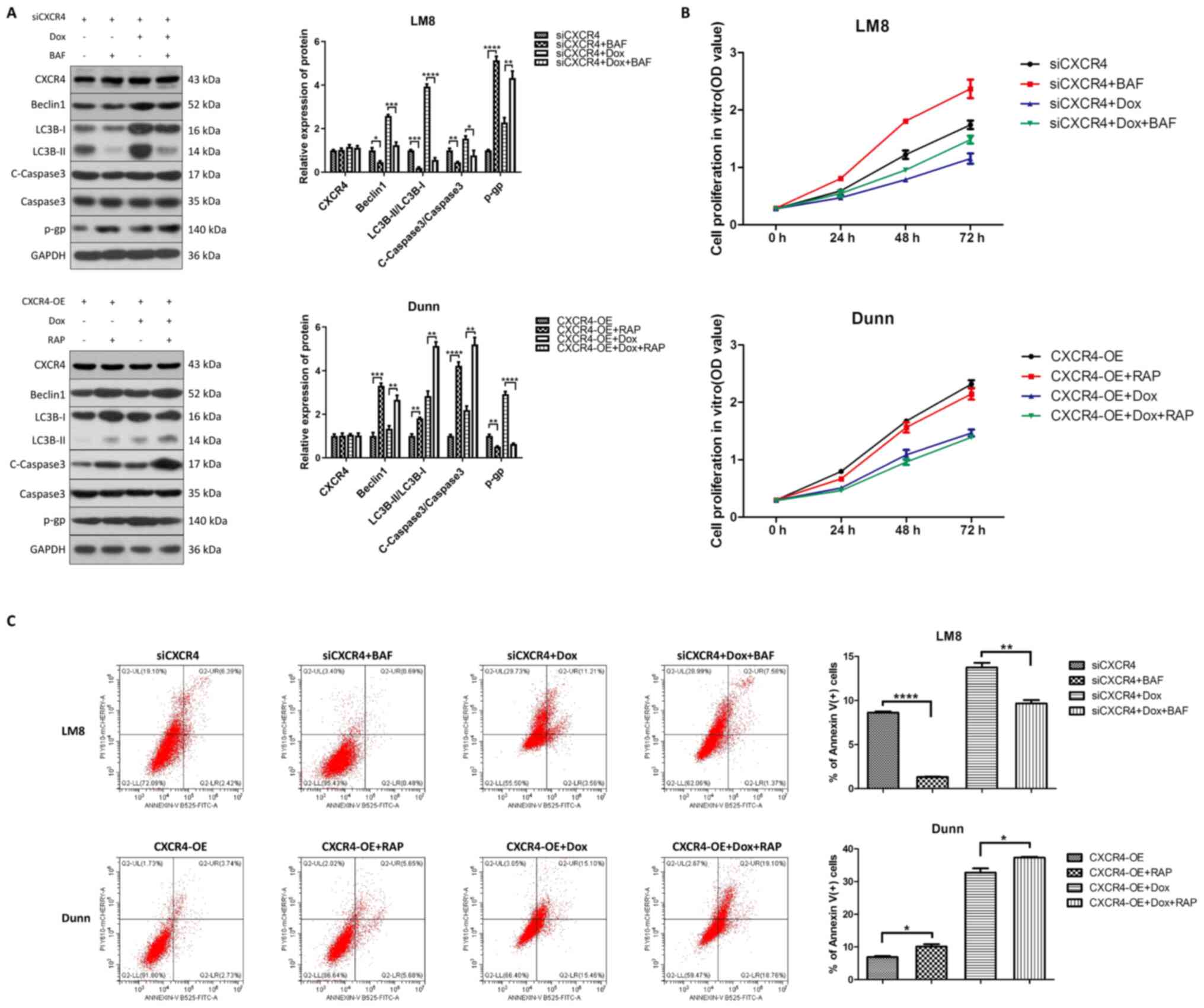
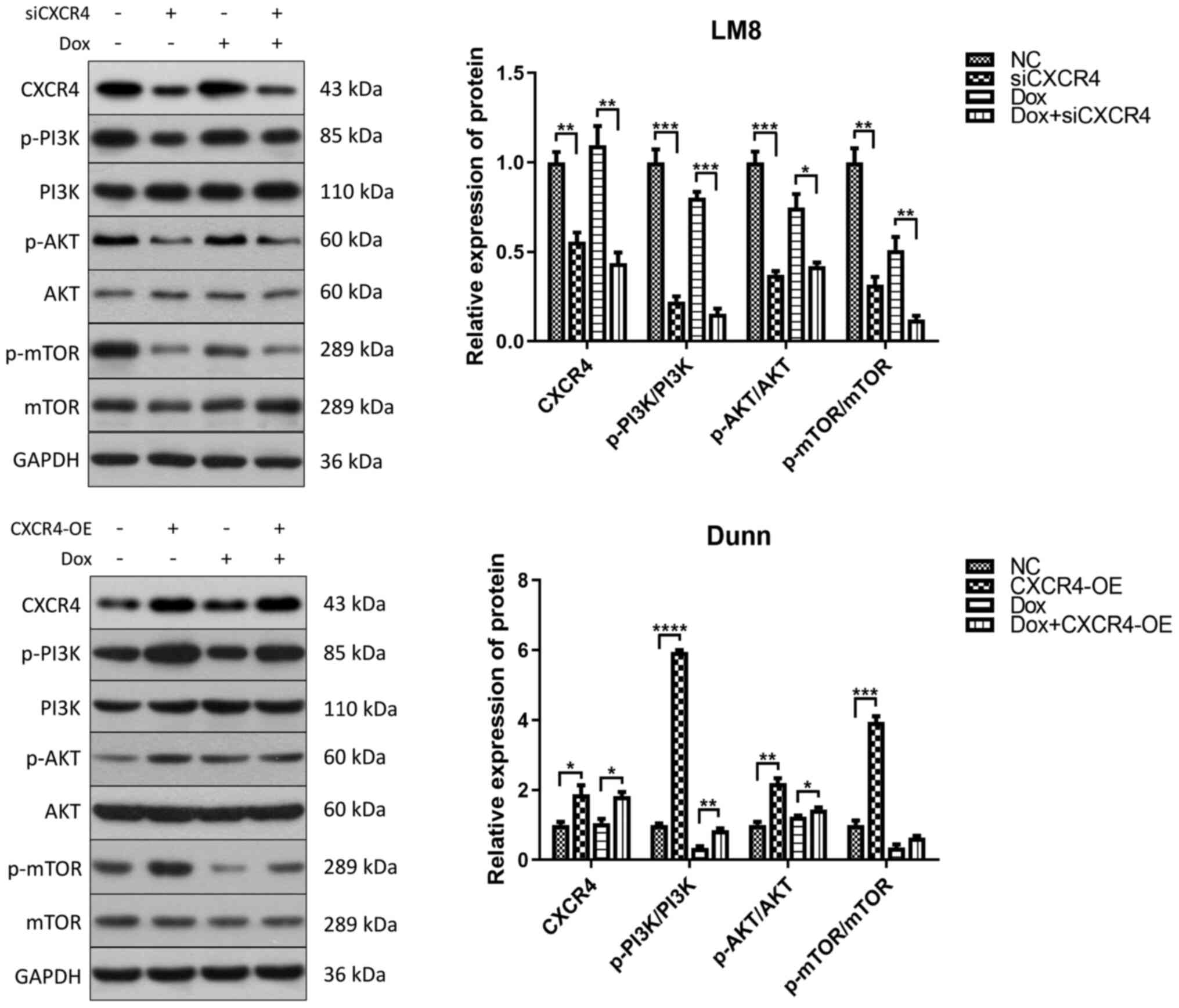
|
1
|
Morrow JJ, Bayles I, Funnell APW, Miller
TE, Saiakhova A, Lizardo MM, Bartels CF, Kapteijn MY, Hung S,
Mendoza A, et al: Positively selected enhancer elements endow
osteosarcoma cells with metastatic competence. Nat Med. 24:176–185.
2018. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Isakoff MS, Bielack SS, Meltzer P and
Gorlick R: Osteosarcoma: Current treatment and a collaborative
pathway to success. J Clin Oncol. 33:3029–3035. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Buondonno I, Gazzano E, Tavanti E, Chegaev
K, Kopecka J, Fanelli M, Rolando B, Fruttero R, Gasco A, Hattinger
C, et al: Endoplasmic reticulum-targeting doxorubicin: A new tool
effective against doxorubicin-resistant osteosarcoma. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 76:609–625. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Gazzano E, Buondonno I, Marengo A, Rolando
B, Chegaev K, Kopecka J, Saponara S, Sorge M, Hattinger CM, Gasco
A, et al: Hyaluronated liposomes containing H2S-releasing
doxorubicin are effective against
P-glycoprotein-positive/doxorubicin-resistant osteosarcoma cells
and xenografts. Cancer Lett. 456:29–39. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu J, Wang H, Hu Y, Zhang YS, Wen L, Yin
F, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Li S, Miao Y, et al: Inhibition of CaMKIIα
activity enhances antitumor effect of fullerene C60 nanocrystals by
suppression of autophagic degradation. Adv Sci (Weinh).
6:18012332019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chen R, Wang G, Zheng Y, Hua Y and Cai Z:
Drug resistance-related microRNAs in osteosarcoma: Translating
basic evidence into therapeutic strategies. J Cell Mol Med.
23:2280–2292. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Roundhill EA, Jabri S and Burchill SA:
ABCG1 and Pgp identify drug resistant, self-renewing osteosarcoma
cells. Cancer Lett. 453:142–157. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liao YX, Zhou CH, Zeng H, Zuo DQ, Wang ZY,
Yin F, Hua YQ and Cai ZD: The role of the CXCL12-CXCR4/CXCR7 axis
in the progression and metastasis of bone sarcomas (Review). Int J
Mol Med. 32:1239–1246. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liao YX, Fu ZZ, Zhou CH, Shan LC, Wang ZY,
Yin F, Zheng LP, Hua YQ and Cai ZD: AMD3100 reduces CXCR4-mediated
survival and metastasis of osteosarcoma by inhibiting JNK and Akt,
but not p38 or Erk1/2, pathways in in vitro and mouse experiments.
Oncol Rep. 34:33–42. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhu Y, Tang L, Zhao S, Sun B, Cheng L,
Tang Y, Luo Z, Lin Z, Zhu J, Zhu W, et al: CXCR4-mediated
osteosarcoma growth and pulmonary metastasis is suppressed by
MicroRNA-613. Cancer Sci. 109:2412–2422. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pollino S, Palmerini E, Dozza B,
Bientinesi E, Piccinni-Leopardi M, Lucarelli E, Righi A, Benassi MS
and Pazzaglia L: CXCR4 in human osteosarcoma malignant progression.
The response of osteosarcoma cell lines to the fully human CXCR4
antibody MDX1338. J Bone Oncol. 17:1002392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li YJ, Dai YL, Zhang WB, Li SJ and Tu CQ:
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of chemokine
receptor CXCR4 in patients with bone and soft tissue sarcoma: A
meta-analysis. Clin Exp Med. 17:59–69. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chen Z, Teo AE and McCarty N: ROS-Induced
CXCR4 signaling regulates mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) cell survival
and drug resistance in the bone marrow microenvironment via
autophagy. Clin Cancer Res. 22:187–199. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Dragoj M, Milosevic Z, Bankovic J, Tanic
N, Pesic M and Stankovic T: Targeting CXCR4 and FAK reverses
doxorubicin resistance and suppresses invasion in non-small cell
lung carcinoma. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 40:47–62. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hu X, Mei S, Meng W, Xue S, Jiang L, Yang
Y, Hui L, Chen Y and Guan MX: CXCR4-mediated signaling regulates
autophagy and influences acute myeloid leukemia cell survival and
drug resistance. Cancer Lett. 425:1–12. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu Y, Liang HM, Lv YQ, Tang SM and Cheng
P: Blockade of SDF-1/CXCR4 reduces adhesion-mediated
chemoresistance of multiple myeloma cells via interacting with
interleukin-6. J Cell Physiol. 234:19702–19714. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liao YX, Yu HY, Lv JY, Cai YR, Liu F, He
ZM and He SS: Targeting autophagy is a promising therapeutic
strategy to overcome chemoresistance and reduce metastasis in
osteosarcoma. Int J Oncol. 55:1213–1222. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lenna S, Bellotti C, Duchi S, Martella E,
Columbaro M, Dozza B, Ballestri M, Guerrini A, Sotgiu G, Frisoni T,
et al: Mesenchymal stromal cells mediated delivery of photoactive
nanoparticles inhibits osteosarcoma growth in vitro and in a murine
in vivo ectopic model. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 39:402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Han XG, Du L, Qiao H, Tu B, Wang YG, Qin
A, Dai KR, Fan QM and Tang TT: CXCR1 knockdown improves the
sensitivity of osteosarcoma to cisplatin. Cancer Lett. 369:405–415.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Robey RW, Pluchino KM, Hall MD, Fojo AT,
Bates SE and Gottesman MM: Revisiting the role of ABC transporters
in multidrug-resistant cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 18:452–464. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Z, Wang C, Zuo D, Zhang T, Yin F,
Zhou Z, Wang H, Xu J, Mao M, Wang G, et al: Attenuation of STAT3
phosphorylation promotes apoptosis and chemosensitivity in Human
osteosarcoma induced by raddeanin A. Int J Biol Sci. 15:668–679.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Amaravadi RK, Kimmelman AC and Debnath J:
Targeting autophagy in cancer: Recent advances and future
directions. Cancer Discov. 9:1167–1181. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang J, Liu K, Yu Y, Xie M, Kang R,
Vernon P, Cao L, Tang D and Ni J: Targeting HMGB1-mediated
autophagy as a novel therapeutic strategy for osteosarcoma.
Autophagy. 8:275–277. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim M, Jung JY, Choi S, Lee H, Morales LD,
Koh JT, Kim SH, Choi YD, Choi C, Slaga TJ, et al: GFRA1 promotes
cisplatin-induced chemoresistance in osteosarcoma by inducing
autophagy. Autophagy. 13:149–168. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Marino G, Niso-Santano M, Baehrecke EH and
Kroemer G: Self-consumption: The interplay of autophagy and
apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:81–94. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang H, Li W, Xu J, Zhang T, Zuo D, Zhou
Z, Lin B, Wang G, Wang Z, Sun W, et al: NDRG1 inhibition sensitizes
osteosarcoma cells to combretastatin A-4 through targeting
autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 8:e30482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Z, Yin F, Xu J, Zhang T, Wang G, Mao
M, Wang Z, Sun W, Han J, Yang M, et al: CYT997(Lexibulin) induces
apoptosis and autophagy through the activation of mutually
reinforced ER stress and ROS in osteosarcoma. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 38:442019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang K, Chen Y, Zhang R, Wu Y, Ma Y, Fang
X and Shen S: Honokiol induces apoptosis and autophagy via the
ROS/ERK1/2 signaling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells in vitro
and in vivo. Cell Death Dis. 9:1572018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yen JH, Huang ST, Huang HS, Fong YC, Wu
YY, Chiang JH and Su YC: HGK-sestrin 2 signaling-mediated autophagy
contributes to antitumor efficacy of Tanshinone IIA in human
osteosarcoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 9:10032018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yue Z, Guan X, Chao R, Huang C, Li D, Yang
P, Liu S, Hasegawa T, Guo J and Li M: Diallyl disulfide induces
apoptosis and autophagy in Human osteosarcoma MG-63 cells through
the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Molecules. 24:26652019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Wauson EM, Dbouk HA, Ghosh AB and Cobb MH:
G protein-coupled receptors and the regulation of autophagy. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 25:274–282. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu F, Li J, Xie Y, Sleightholm RL and
Oupicky D: Polymeric chloroquine as an inhibitor of cancer cell
migration and experimental lung metastasis. J Control Release.
244:347–356. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Coly PM, Perzo N, Le Joncour V, Lecointre
C, Schouft MT, Desrues L, Tonon MC, Wurtz O, Gandolfo P, Castel H
and Morin F: Chemotactic G protein-coupled receptors control cell
migration by repressing autophagosome biogenesis. Autophagy.
12:2344–2362. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang J, Tannous BA, Poznansky MC and Chen
H: CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 (plerixafor): From an impurity to a
therapeutic agent. Pharmacol Res. 159:1050102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|