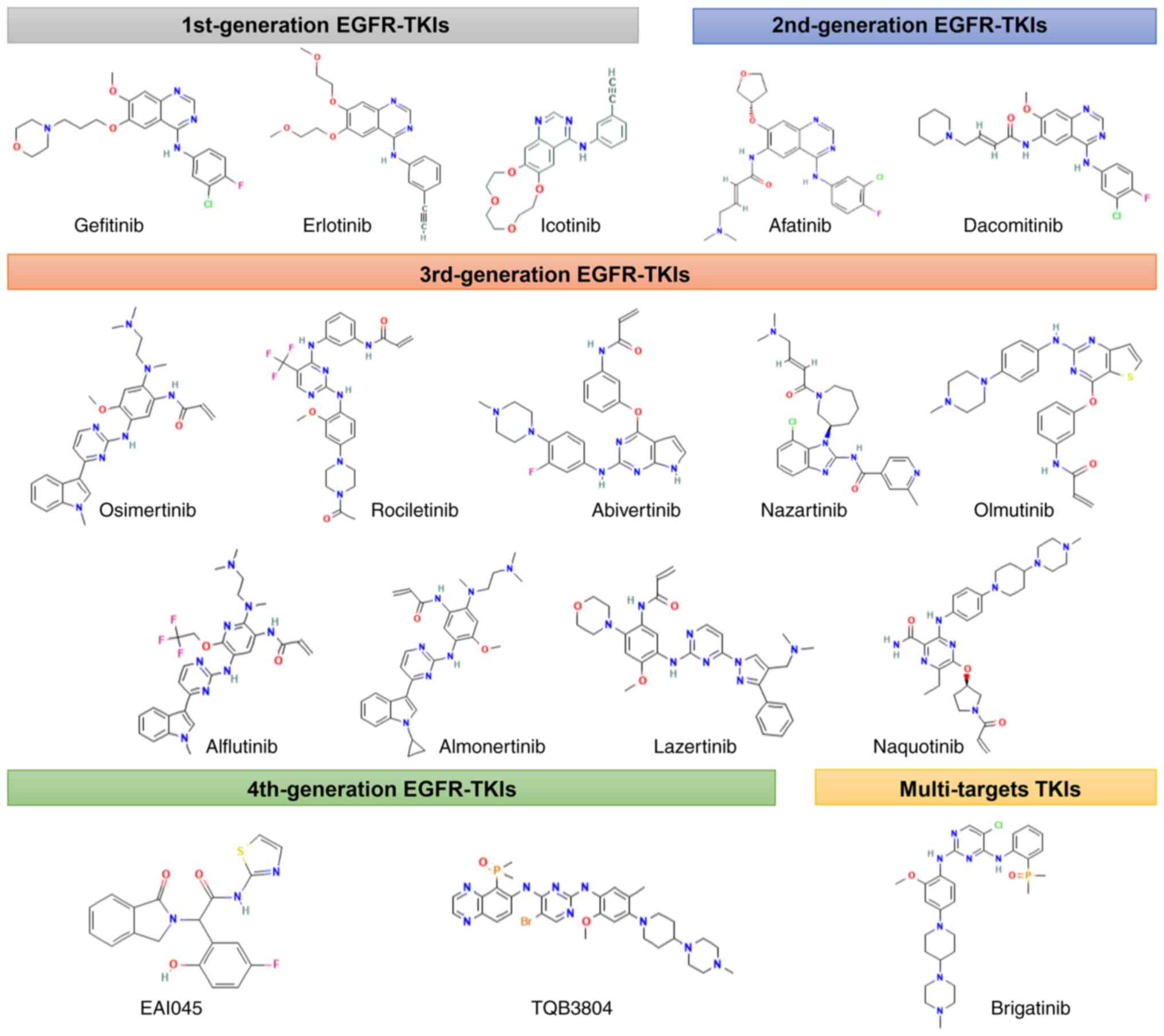
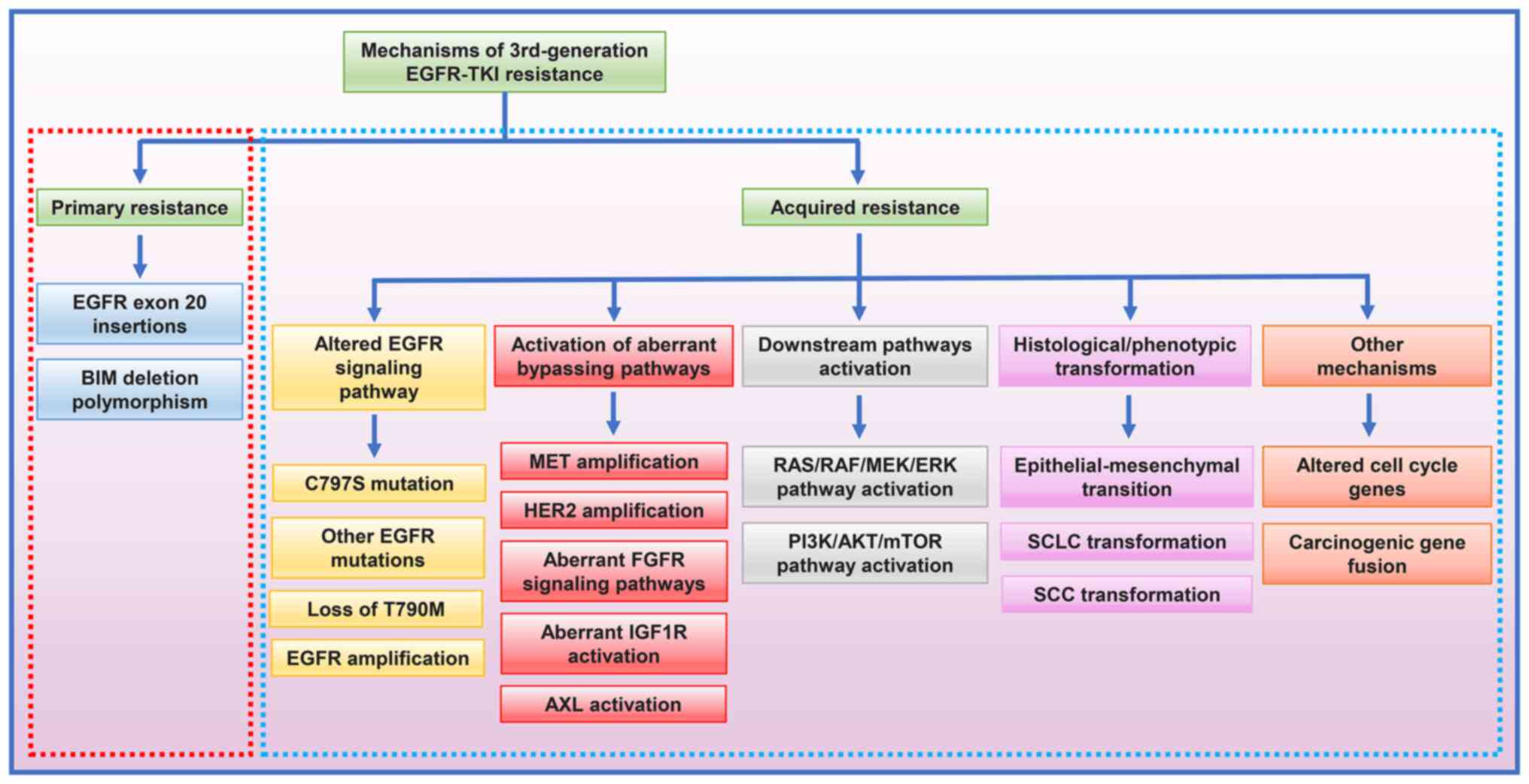
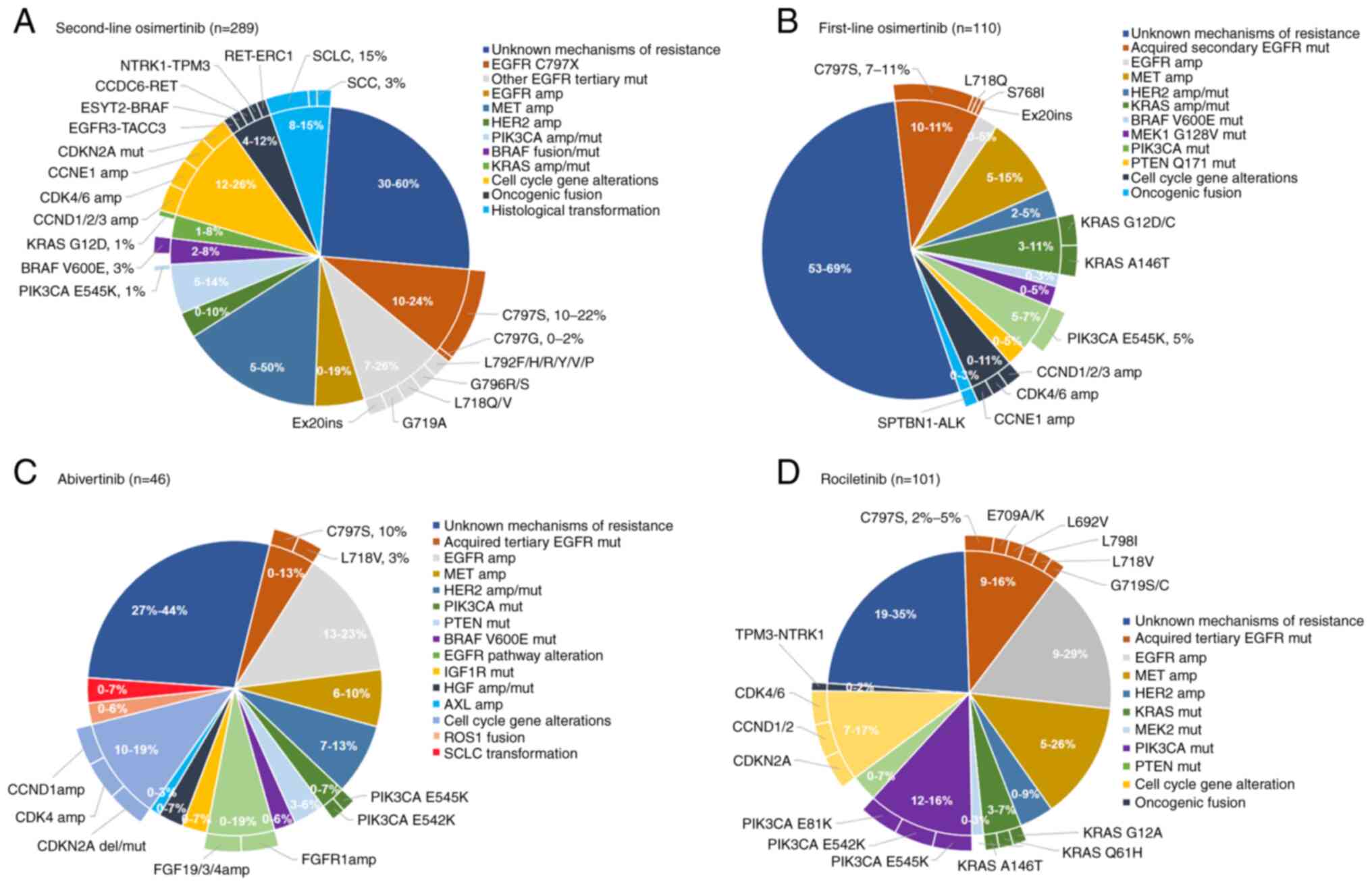
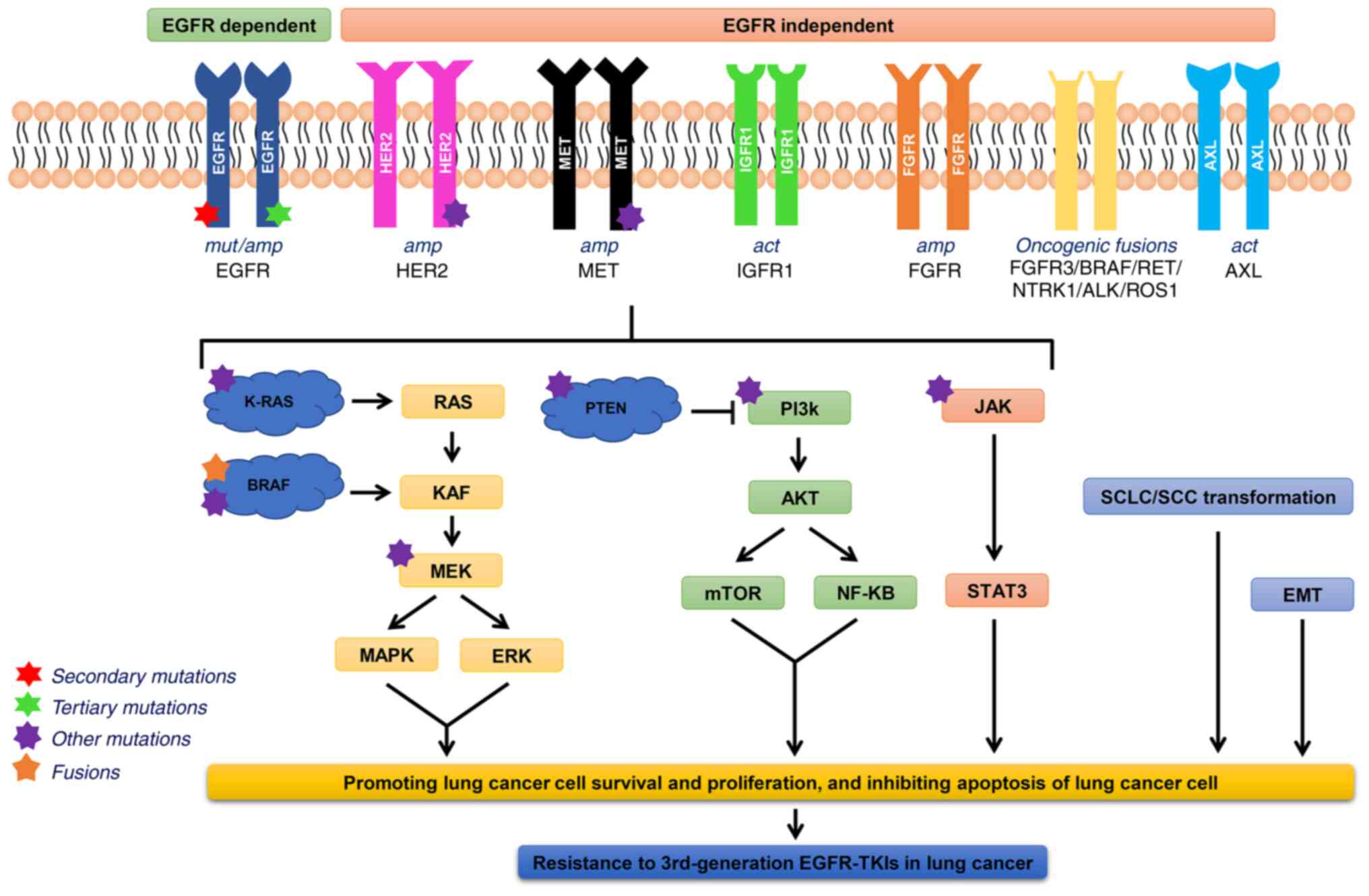
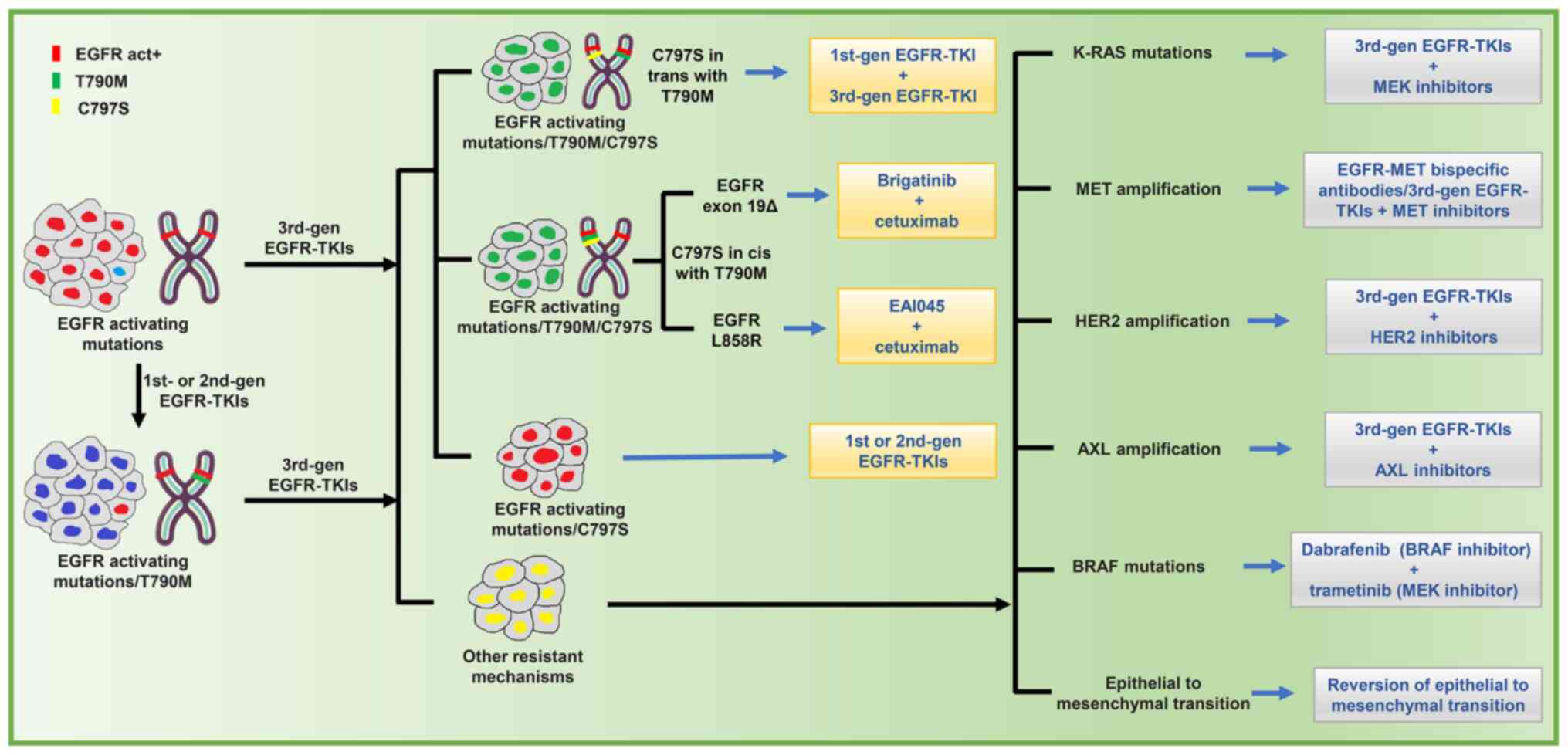
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:7–30. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Testa U, Castelli G and Pelosi E: Lung
cancers: Molecular characterization, clonal heterogeneity and
evolution, and cancer stem cells. Cancers (Basel). 10:2482018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Rosell R, Moran T, Queralt C, Porta R,
Cardenal F, Camps C, Majem M, Lopez-Vivanco G, Isla D, Provencio M,
et al: Screening for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in
lung cancer. New Engl J Med. 361:958–967. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
da Cunha Santos G, Shepherd FA and Tsao
MS: EGFR mutations and lung cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:49–69. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Roskoski R Jr: Small molecule inhibitors
targeting the EGFR/ErbB family of protein-tyrosine kinases in human
cancers. Pharmacol Res. 139:395–411. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Huang L and Fu L: Mechanisms of resistance
to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Acta Pharm Sin B. 5:390–401.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH,
Chu DT, Saijo N, Sunpaweravong P, Han B, Margono B, Ichinose Y, et
al: Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary
adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 361:947–957. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kazandjian D, Blumenthal GM, Yuan W, He K,
Keegan P and Pazdur R: FDA approval of gefitinib for the treatment
of patients with metastatic EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell
lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 22:1307–1312. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R,
Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, Palmero R, Garcia-Gomez R,
Pallares C, Sanchez JM, et al: Erlotinib versus standard
chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with
advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer
(EURTAC): A multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial.
Lancet Oncol. 13:239–246. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shi YK, Wang L, Han BH, Li W, Yu P, Liu
YP, Ding CM, Song X, Ma ZY, Ren XL, et al: First-line icotinib
versus cisplatin/pemetrexed plus pemetrexed maintenance therapy for
patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma
(CONVINCE): A phase 3, open-label, randomized study. Ann Oncol.
28:2443–2450. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Park K, Tan EH, O'Byrne K, Zhang L, Boyer
M, Mok T, Hirsh V, Yang JC, Lee KH, Lu S, et al: Afatinib versus
gefitinib as first-line treatment of patients with EGFR
mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (LUX-Lung 7): A phase
2B, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol.
17:577–589. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu YL, Cheng Y, Zhou X, Lee KH, Nakagawa
K, Niho S, Tsuji F, Linke R, Rosell R, Corral J, et al: Dacomitinib
versus gefitinib as first-line treatment for patients with
EGFR-mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARCHER 1050): A
randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 18:1454–1466.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Miller VA, Hirsh V, Cadranel J, Chen YM,
Park K, Kim SW, Zhou C, Su WC, Wang M, Sun Y, et al: Afatinib
versus placebo for patients with advanced, metastatic
non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of erlotinib, gefitinib,
or both, and one or two lines of chemotherapy (LUX-Lung 1): A phase
2b/3 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 13:528–538. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ellis PM, Shepherd FA, Millward M, Perrone
F, Seymour L, Liu G, Sun S, Cho BC, Morabito A, Leighl NB, et al:
Dacomitinib compared with placebo in pretreated patients with
advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NCIC CTG BR.26):
A double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol.
15:1379–1388. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Westover D, Zugazagoitia J, Cho BC, Lovly
CM and Paz-Ares L: Mechanisms of acquired resistance to first- and
second-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Ann Oncol.
29(Suppl-1): i10–i19. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Passaro A, Guerini-Rocco E, Pochesci A,
Vacirca D, Spitaleri G, Catania CM, Rappa A, Barberis M and de
Marinis F: Targeting EGFR T790M mutation in NSCLC: From biology to
evaluation and treatment. Pharmacol Res. 117:406–415. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mok TS, Wu YL, Ahn MJ, Garassino MC, Kim
HR, Ramalingam SS, Shepherd FA, He Y, Akamatsu H, Theelen WS, et
al: Osimertinib or platinum-pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-positive lung
cancer. New Engl J Med. 376:629–640. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Cross DA, Ashton SE, Ghiorghiu S, Eberlein
C, Nebhan CA, Spitzler PJ, Orme JP, Finlay MR, Ward RA, Mellor MJ,
et al: AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated
resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discov.
4:1046–1061. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J,
Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, Dechaphunkul A, Imamura
F, Nogami N, Kurata T, et al: Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. New Engl J Med. 378:113–125.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sequist LV, Soria JC and Camidge DR:
Update to rociletinib data with the RECIST confirmed response rate.
New Engl J Med. 374:2296–2297. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yun J, Hong MH, Kim SY, Park CW, Kim S,
Yun MR, Kang HN, Pyo KH, Lee SS, Koh JS, et al: YH25448, an
irreversible EGFR-TKI with potent intracranial activity in EGFR
mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 25:2575–2587.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu X, Mao L, Xu W, Tang W, Zhang X, Xi B,
Xu R, Fang X, Liu J, Fang C, et al: AC0010, an irreversible EGFR
inhibitor selectively targeting mutated EGFR and overcoming
T790M-induced resistance in animal models and lung cancer patients.
Mol Cancer Ther. 15:2586–2597. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jia Y, Juarez J, Li J, Manuia M, Niederst
MJ, Tompkins C, Timple N, Vaillancourt MT, Pferdekamper AC,
Lockerman EL, et al: EGF816 exerts anticancer effects in non-small
cell lung cancer by irreversibly and selectively targeting primary
and acquired activating mutations in the EGF receptor. Cancer Res.
76:1591–1602. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu HA, Spira A, Horn L, Weiss J, West H,
Giaccone G, Evans T, Kelly RJ, Desai B, Krivoshik A, et al: A phase
I, dose escalation study of oral ASP8273 in patients with non-small
cell lung cancers with epidermal growth factor receptor mutations.
Clin Cancer Res. 23:7467–7473. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Park K, Lee JS, Lee KH, Kim JH, Min YJ,
Cho JY, Han JY, Kim BS, Kim JS, Lee DH, et al: Updated safety and
efficacy results from phase I/II study of HM61713 in patients (pts)
with EGFR mutation positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who
failed previous EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI). J Clin Oncol.
33(Suppl 15): S80842015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sequist LV, Rolfe L and Allen AR:
Rociletinib in EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer. New Engl J
Med. 373:578–579. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang H, Pan R, Zhang X, Si X, Wang M and
Zhang L: Abivertinib in patients with T790M-positive advanced NSCLC
and its subsequent treatment with osimertinib. Thorac Cancer.
11:594–602. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tan DS, Leighl NB, Riely GJ, Yang JC,
Sequist LV, Wolf J, Seto T, Felip E, Aix SP, Jonnaert M, et al:
Safety and efficacy of nazartinib (EGF816) in adults with
EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung carcinoma: A multicentre,
open-label, phase 1 study. Lancet Resp Med. 8:561–572. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kim DW, Lee DH, Han JY, Lee J, Cho BC,
Kang JH, Lee KH, Cho EK, Kim JS, Min YJ, et al: Safety,
tolerability, and anti-tumor activity of olmutinib in non-small
cell lung cancer with T790M mutation: A single arm, open label,
phase 1/2 trial. Lung Cancer. 135:66–72. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shi Y, Zhang S, Hu X, Feng J, Ma Z, Zhou
J, Yang N, Wu L, Liao W, Zhong D, et al: Safety, clinical activity,
and pharmacokinetics of alflutinib (AST2818) in patients with
advanced NSCLC With EGFR T790M mutation. J Thorac Oncol.
15:1015–1026. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang JC, Camidge DR, Yang CT, Zhou J, Guo
R, Chiu CH, Chang GC, Shiah HS, Chen Y, Wang CC, et al: Safety,
efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of almonertinib (HS-10296) in
pretreated patients with EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC: A
multicenter, open-label, phase 1 Trial. J Thorac Oncol.
15:1907–1918. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ahn MJ, Han JY, Lee KH, Kim SW, Kim DW,
Lee YG, Cho EK, Kim JH, Lee GW, Lee JS, et al: Lazertinib in
patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung
cancer: Results from the dose escalation and dose expansion parts
of a first-in-human, open-label, multicentre, phase 1-2 study.
Lancet Oncol. 20:1681–1690. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kelly RJ, Shepherd FA, Krivoshik A, Jie F
and Horn L: A phase III, randomized, open-label study of ASP8273
versus erlotinib or gefitinib in patients with advanced stage
IIIB/IV non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 30:1127–1133. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mezquita L, Varga A and Planchard D:
Safety of osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer.
Expert Opin Drug Saf. 17:1239–1248. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ramalingam SS, Vansteenkiste J, Planchard
D, Cho BC, Gray JE, Ohe Y, Zhou C, Reungwetwattana T, Cheng Y,
Chewaskulyong B, et al: Overall Survival with Osimertinib in
Untreated, -Mutated Advanced NSCLC. New Engl J Med. 382:41–50.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Reungwetwattana T, Nakagawa K, Cho BC,
Cobo M, Cho EK, Bertolini A, Bohnet S, Zhou C, Lee KH, Nogami N, et
al: CNS response to osimertinib versus standard epidermal growth
factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with
untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin
Oncol. Aug 28–2018.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Saito H, Fukuhara T, Furuya N, Watanabe K,
Sugawara S, Iwasawa S, Tsunezuka Y, Yamaguchi O, Okada M, Yoshimori
K, et al: Erlotinib plus bevacizumab versus erlotinib alone in
patients with EGFR-positive advanced non-squamous non-small-cell
lung cancer (NEJ026): Interim analysis of an open-label,
randomised, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 20:625–635.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Goldberg SB, Redman MW, Lilenbaum R,
Politi K, Stinchcombe TE, Horn L, Chen EH, Mashru SH, Gettinger SN,
Melnick MA, et al: Randomized trial of afatinib plus cetuximab
versus afatinib alone for first-line treatment of -mutant
non-small-cell lung cancer: Final results from SWOG S1403. J Clin
Oncol. 38:4076–4085. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Oxnard GR, Yang JC, Yu H, Kim SW, Saka H,
Horn L, Goto K, Ohe Y, Mann H, Thress KS, et al: TATTON: A
multi-arm, phase Ib trial of osimertinib combined with selumetinib,
savolitinib, or durvalumab in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Ann Oncol.
31:507–516. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sequist LV, Piotrowska Z, Niederst MJ,
Heist RS, Digumarthy S, Shaw AT and Engelman JA: Osimertinib
responses after disease progression in patients who had been
receiving rociletinib. JAMA Oncol. 2:541–543. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nagasaka M, Zhu VW, Lim SM, Greco M, Wu F
and Ou SI: Beyond osimertinib: The development of third-generation
EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors for advanced EGFR+
NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 16:740–763. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ma Y, Zheng X, Zhao H, Fang W, Zhang Y, Ge
J, Wang L, Wang W, Jiang J, Chuai S, et al: First-in-human phase I
study of AC0010, a mutant-selective EGFR inhibitor in non-small
cell lung cancer: Safety, efficacy, and potential mechanism of
resistance. J Thorac Oncol. 13:968–977. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang H, Zhang L, Hu P, Zheng X, Si X,
Zhang X and Wang M: Penetration of the blood-brain barrier by
avitinib and its control of intra/extra-cranial disease in
non-small cell lung cancer harboring the T790M mutation. Lung
Cancer. 122:1–6. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kim ES: Olmutinib: First global approval.
Drugs. 76:1153–1157. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Arcila ME, Nafa K, Chaft JE, Rekhtman N,
Lau C, Reva BA, Zakowski MF, Kris MG and Ladanyi M: EGFR exon 20
insertion mutations in lung adenocarcinomas: Prevalence, molecular
heterogeneity, and clinicopathologic characteristics. Mol Cancer
Ther. 12:220–229. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Robichaux JP, Elamin YY, Tan Z, Carter BW,
Zhang S, Liu S, Li S, Chen T, Poteete A, Estrada-Bernal A, et al:
Mechanisms and clinical activity of an EGFR and HER2 exon
20-selective kinase inhibitor in non-small cell lung cancer. Nat
Med. 24:638–646. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Qin Y, Jian H, Tong X, Wu X, Wang F, Shao
YW and Zhao X: Variability of EGFR exon 20 insertions in 24 468
Chinese lung cancer patients and their divergent responses to EGFR
inhibitors. Mol Oncol. 14:1695–1704. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
van Veggel B, Madeira R, Santos JFV,
Hashemi SMS, Paats MS, Monkhorst K, Heideman DAM, Groves M, Radonic
T, Smit EF, et al: Osimertinib treatment for patients with EGFR
exon 20 mutation positive non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
141:9–13. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li X, Wang S, Li B, Wang Z, Shang S, Shao
Y, Sun X and Wang L: BIM deletion polymorphism confers resistance
to osimertinib in EGFR T790M lung cancer: A case report and
literature review. Target Oncol. 13:517–523. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhao M, Zhang Y, Cai W, Li J, Zhou F,
Cheng N, Ren R, Zhao C, Li X, Ren S, et al: The Bim deletion
polymorphism clinical profile and its relation with tyrosine kinase
inhibitor resistance in Chinese patients with non-small cell lung
cancer. Cancer. 120:2299–2307. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tanimoto A, Takeuchi S, Arai S, Fukuda K,
Yamada T, Roca X, Ong ST and Yano S: Histone deacetylase 3
inhibition overcomes BIM deletion polymorphism-mediated osimertinib
resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
23:3139–3149. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Isobe K, Hata Y, Tochigi N, Kaburaki K,
Kobayashi H, Makino T, Otsuka H, Sato F, Ishida F, Kikuchi N, et
al: Clinical significance of BIM deletion polymorphism in
non-small-cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor
mutation. J Thorac Oncol. 9:483–487. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liu SY, Zhou JY, Li WF, Sun H, Zhang YC,
Yan HH, Chen ZH, Chen CX, Ye JY, Yang JJ, et al: Concomitant
genetic alterations having greater impact on the clinical benefit
of EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-mutant advanced NSCLC than BIM deletion
polymorphism. Clin Transl Med. 10:337–345. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Papadimitrakopoulou VA, Wu YL, Han JY, Ahn
MJ, Ramalingam SS, John T, Okamoto I, Yang JCH, Bulusu KC, Laus G,
et al: Analysis of resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in patients
with EGFR T790M advanced NSCLC from the AURA3 study. Ann Oncol.
29(Suppl 8): VIII7412018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Yang Z, Yang N, Ou Q, Xiang Y, Jiang T, Wu
X, Bao H, Tong X, Wang X, Shao YW, et al: Investigating novel
resistance mechanisms to third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase
inhibitor osimertinib in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Clin
Cancer Res. 24:3097–3107. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Le X, Puri S, Negrao MV, Nilsson MB,
Robichaux J, Boyle T, Hicks JK, Lovinger KL, Roarty E,
Rinsurongkawong W, et al: Landscape of EGFR-dependent and
-independent resistance mechanisms to osimertinib and continuation
therapy beyond progression in -mutant NSCLC. Clin Cancer Res.
24:6195–6203. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Oxnard GR, Hu Y, Mileham KF, Husain H,
Costa DB, Tracy P, Feeney N, Sholl LM, Dahlberg SE, Redig AJ, et
al: Assessment of resistance mechanisms and clinical implications
in patients with EGFR T790M-positive lung cancer and acquired
resistance to osimertinib. JAMA Oncol. 4:1527–1534. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lin CC, Shih JY, Yu CJ, Ho CC, Liao WY,
Lee JH, Tsai TH, Su KY, Hsieh MS, Chang YL, et al: Outcomes in
patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and acquired Thr790Met
mutation treated with osimertinib: A genomic study. Lancet Resp
Med. 6:107–116. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Ramalingam SS, Cheng Y, Zhou C, Ohe Y,
Imamura F, Cho BC, Lin MC, Majem M, Shah R, Rukazenkov Y, et al:
Mechanisms of acquired resistance to first-line osimertinib:
Preliminary data from the phase III FLAURA study. Ann Oncol.
29(Suppl 8): viii7402018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Ramalingam SS, Yang JC, Lee CK, Kurata T,
Kim DW, John T, Nogami N, Ohe Y, Mann H, Rukazenkov Y, et al:
Osimertinib as first-line treatment of EGFR mutation-positive
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 36:841–849.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Zhang YC, Chen ZH, Zhang XC, Xu CR, Yan
HH, Xie Z, Chuai SK, Ye JY, Han-Zhang H, Zhang Z, et al: Analysis
of resistance mechanisms to abivertinib, a third-generation EGFR
tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with EGFR T790M-positive
non-small cell lung cancer from a phase I trial. EBioMedicine.
43:180–187. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Chabon JJ, Simmons AD, Lovejoy AF,
Esfahani MS, Newman AM, Haringsma HJ, Kurtz DM, Stehr H, Scherer F,
Karlovich CA, et al: Circulating tumour DNA profiling reveals
heterogeneity of EGFR inhibitor resistance mechanisms in lung
cancer patients. Nat Commun. 7:118152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Helman E, Nguyen M, Karlovich CA, Despain
D, Choquette AK, Spira AI, Yu HA, Camidge DR, Harding TC, Lanman RB
and Simmons AD: Cell-Free DNA next-generation sequencing prediction
of response and resistance to third-generation EGFR inhibitor. Clin
Lung Cancer. 19:530.e72018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Ercan D, Choi HG, Yun CH, Capelletti M,
Xie T, Eck MJ, Gray NS and Jänne PA: EGFR mutations and resistance
to irreversible pyrimidine-based EGFR inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res.
21:3913–3923. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Song HN, Jung KS, Yoo KH, Cho J, Lee JY,
Lim SH, Kim HS, Sun JM, Lee SH, Ahn JS, et al: Acquired C797S
mutation upon treatment with a T790M-specific third-generation EGFR
inhibitor (HM61713) in non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol.
11:e45–e47. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Park S, Ku BM, Jung HA, Sun JM, Ahn JS,
Lee SH, Park K and Ahn MJ: EGFR C797S as a resistance mechanism of
lazertinib in non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR T790M mutation.
Cancer Res Treat. 52:1288–1290. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Oztan A, Fischer S, Schrock AB, Erlich RL,
Lovly CM, Stephens PJ, Ross JS, Miller V, Ali SM, Ou SI and Raez
LE: Emergence of EGFR G724S mutation in EGFR-mutant lung
adenocarcinoma post progression on osimertinib. Lung Cancer.
111:84–87. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Fassunke J, Muller F, Keul M, Michels S,
Dammert MA, Schmitt A, Plenker D, Lategahn J, Heydt C, Bragelmann
J, et al: Overcoming EGFRG724S-mediated osimertinib
resistance through unique binding characteristics of
second-generation EGFR inhibitors. Nat Commun. 9:46552018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Bersanelli M, Minari R, Bordi P, Gnetti L,
Bozzetti C, Squadrilli A, Lagrasta CA, Bottarelli L, Osipova G,
Capelletto E, et al: L718Q mutation as new mechanism of acquired
resistance to AZD9291 in EGFR-Mutated NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol 11:
e121-e123,. 2016.
|
|
70
|
Zhao S, Li X, Zhao C, Jiang T, Jia Y, Shi
J, He Y, Li J, Zhou F, Gao G, et al: Loss of T790M mutation is
associated with early progression to osimertinib in Chinese
patients with advanced NSCLC who are harboring EGFR T790M. Lung
Cancer. 128:33–39. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Piotrowska Z, Niederst MJ, Karlovich CA,
Wakelee HA, Neal JW, Mino-Kenudson M, Fulton L, Hata AN, Lockerman
EL, Kalsy A, et al: Heterogeneity underlies the emergence of
EGFRT790 wild-type clones following treatment of T790M-positive
cancers with a third-generation EGFR inhibitor. Cancer Discov.
5:713–722. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Knebel FH, Bettoni F, Shimada AK, Cruz M,
Alessi JV, Negrão MV, Reis LFL, Katz A and Camargo AA: Sequential
liquid biopsies reveal dynamic alterations of EGFR driver mutations
and indicate EGFR amplification as a new mechanism of resistance to
osimertinib in NSCLC. Lung Cancer. 108:238–241. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wang Q, Yang S, Wang K and Sun SY: MET
inhibitors for targeted therapy of EGFR TKI-resistant lung cancer.
J Hematol Oncol. 12:632019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Drilon A, Cappuzzo F, Ou SI and Camidge
DR: Targeting MET in lung cancer: Will expectations finally Be MET?
J Thorac Oncol. 12:15–26. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
75
|
Hsu CC, Liao BC, Liao WY, Markovets A,
Stetson D, Thress K and Yang JC: Exon 16-Skipping HER2 as a Novel
Mechanism of Osimertinib Resistance in EGFR L858R/T790M-positive
non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 15:50–61. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Desai A and Adjei AA: FGFR signaling as a
target for lung cancer therapy. J Thorac Oncol. 11:9–20. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Kim TM, Song A, Kim DW, Kim S, Ahn YO,
Keam B, Jeon YK, Lee SH, Chung DH and Heo DS: Mechanisms of
acquired resistance to AZD9291: A mutation-selective, irreversible
EGFR inhibitor. J Thorac Oncol. 10:1736–1744. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Ou SI, Horn L, Cruz M, Vafai D, Lovly CM,
Spradlin A, Williamson MJ, Dagogo-Jack I, Johnson A, Miller VA, et
al: Emergence of FGFR3-TACC3 fusions as a potential by-pass
resistance mechanism to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR
mutated NSCLC patients. Lung Cancer. 111:61–64. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Hayakawa D, Takahashi F, Mitsuishi Y,
Tajima K, Hidayat M, Winardi W, Ihara H, Kanamori K, Matsumoto N,
Asao T, et al: Activation of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor
confers acquired resistance to osimertinib in non-small cell lung
cancer with EGFR T790M mutation. Thorac Cancer. 11:140–149. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Manabe T, Yasuda H, Terai H, Kagiwada H,
Hamamoto J, Ebisudani T, Kobayashi K, Masuzawa K, Ikemura S, Kawada
I, et al: IGF2 Autocrine-Mediated IGF1R activation is a clinically
relevant mechanism of osimertinib resistance in lung cancer. Mol
Cancer Res. 18:549–559. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Taniguchi H, Yamada T, Wang R, Tanimura K,
Adachi Y, Nishiyama A, Tanimoto A, Takeuchi S, Araujo LH, Boroni M,
et al: AXL confers intrinsic resistance to osimertinib and advances
the emergence of tolerant cells. Nat Commun. 10:2592019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Namba K, Shien K, Takahashi Y, Torigoe H,
Sato H, Yoshioka T, Takeda T, Kurihara E, Ogoshi Y, Yamamoto H, et
al: Activation of AXL as a preclinical acquired resistance
mechanism against osimertinib treatment in EGFR-mutant non-small
cell lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 17:499–507. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Nakatani K, Yamaoka T, Ohba M, Fujita KI,
Arata S, Kusumoto S, Taki-Takemoto I, Kamei D, Iwai S, Tsurutani J
and Ohmori T: KRAS and EGFR amplifications mediate resistance to
rociletinib and osimertinib in acquired afatinib-resistant NSCLC
harboring exon 19 deletion/T790M in. Mol Cancer Ther. 18:112–126.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Marcoux N, Gettinger SN, O'Kane G, Arbour
KC, Neal JW, Husain H, Evans TL, Brahmer JR, Muzikansky A, Bonomi
PD, et al: EGFR-mutant adenocarcinomas that transform to small-cell
lung cancer and other neuroendocrine carcinomas: Clinical outcomes.
J Clin Oncol. 37:278–285. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Schoenfeld AJ, Chan JM, Kubota D, Sato H,
Rizvi H, Daneshbod Y, Chang JC, Paik PK, Offin M, Arcila ME, et al:
Tumor analyses reveal squamous transformation and off-target
alterations as early resistance mechanisms to first-line
osimertinib in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
26:2654–2663. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Dongre A and Weinberg RA: New insights
into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
implications for cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:69–84. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Nukaga S, Yasuda H, Tsuchihara K, Hamamoto
J, Masuzawa K, Kawada I, Naoki K, Matsumoto S, Mimaki S, Ikemura S,
et al: Amplification of EGFR wild-type alleles in non-small cell
lung cancer cells confers acquired resistance to mutation-selective
EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer Res. 77:2078–2089. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Weng CH, Chen LY, Lin YC, Shih JY, Lin YC,
Tseng RY, Chiu AC, Yeh YH, Liu C, Lin YT, et al:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) beyond EGFR mutations per
se is a common mechanism for acquired resistance to EGFR TKI.
Oncogene. 38:455–468. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Schrock AB, Zhu VW, Hsieh WS, Madison R,
Creelan B, Silberberg J, Costin D, Bharne A, Bonta I, Bosemani T,
et al: Receptor tyrosine kinase fusions and BRAF kinase fusions are
rare but actionable resistance mechanisms to EGFR tyrosine kinase
inhibitors. J Thorac Oncol. 13:1312–1323. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Batra U, Sharma M, Amrith BP, Mehta A and
Jain P: EML4-ALK fusion as a resistance mechanism to osimertinib
and its successful management with osimertinib and alectinib: Case
report and review of the literature. Clin Lung Cancer.
21:e597–e600. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Jia Y, Yun CH, Park E, Ercan D, Manuia M,
Juarez J, Xu C, Rhee K, Chen T, Zhang H, et al: Overcoming
EGFR(T790M) and EGFR(C797S) resistance with mutant-selective
allosteric inhibitors. Nature. 534:129–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Uchibori K, Inase N, Araki M, Kamada M,
Sato S, Okuno Y, Fujita N and Katayama R: Brigatinib combined with
anti-EGFR antibody overcomes osimertinib resistance in EGFR-mutated
non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat Commun. 8:147682017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Schalm SS, Dineen T, Lim SM, Park CW,
Hsieh J, Woessner R, Zhang Z, Wilson K, Eno M, Wilson D, et al:
1296P BLU-945, a highly potent and selective 4th generation EGFR
TKI for the treatment of EGFR T790M/C797S resistant NSCLC. Ann
Oncol. 31(Suppl 6): S1386–S1406. 2020.
|
|
94
|
Liu X, Zhang X, Yang L, Tian X, Dong T,
Ding CZ, Hu L, Wu L, Zhao L, Mao J, et al: Abstract 1320:
Preclinical evaluation of TQB3804, a potent EGFR C797S inhibitor.
79(Suppl 13): S13202019.
|
|
95
|
Kim DW, Tiseo M, Ahn MJ, Reckamp KL,
Hansen KH, Kim SW, Huber RM, West HL, Groen HJ, Hochmair MJ, et al:
Brigatinib in patients with crizotinib-refractory anaplastic
lymphoma kinase-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: A randomized,
multicenter phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 35:2490–2498. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Wang Y, Yang N, Zhang Y, Li L, Han R, Zhu
M, Feng M, Chen H, Lizaso A, Qin T, et al: Effective treatment of
lung adenocarcinoma harboring EGFR-activating mutation, T790M, and
cis-C797S triple mutations by brigatinib and cetuximab combination
therapy. J Thorac Oncol. 15:1369–1375. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Zhao J, Zou M, Lv J, Han Y and Wang G and
Wang G: Effective treatment of pulmonary adenocarcinoma harboring
triple EGFR mutations of L858R, T790M, and -C797S by osimertinib,
bevacizumab, and brigatinib combination therapy: A case report.
Onco Targets Ther. 11:5545–5550. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
98
|
Arulananda S, Do H, Musafer A, Mitchell P,
Dobrovic A and John T: Combination osimertinib and gefitinib in
C797S and T790M EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac
Oncol. 12:1728–1732. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Giroux-Leprieur E, Dumenil C and Chinet T:
Combination of crizotinib and osimertinib or erlotinib might
overcome MET-mediated resistance to EGFR Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
in EGFR-mutated adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol. 13:e232–e234. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Sequist LV, Han JY, Ahn MJ, Cho BC, Yu H,
Kim SW, Yang JC, Lee JS, Su WC, Kowalski D, et al: Osimertinib plus
savolitinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive, MET-amplified,
non-small-cell lung cancer after progression on EGFR tyrosine
kinase inhibitors: Interim results from a multicentre, open-label,
phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol. 21:373–386. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Odogwu L, Mathieu L, Blumenthal G, Larkins
E, Goldberg KB, Griffin N, Bijwaard K, Lee EY, Philip R, Jiang X,
et al: FDA approval summary: Dabrafenib and trametinib for the
treatment of metastatic non-small cell lung cancers harboring BRAF
V600E mutations. Oncologist. 23:740–745. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Oh DK, Ji WJ, Kim WS, Choi CM, Yoon SK,
Rho JK and Lee JC: Efficacy, safety, and resistance profile of
osimertinib in T790M mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer
in real-world practice. PLoS One. 14:e02102252019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Piotrowska Z, Isozaki H, Lennerz JK,
Gainor JF, Lennes IT, Zhu VW, Marcoux N, Banwait MK, Digumarthy SR,
Su W, et al: Landscape of acquired resistance to osimertinib in
EGFR-Mutant NSCLC and clinical validation of combined EGFR and RET
inhibition with osimertinib and BLU-667 for acquired fusion. Cancer
Discov. 8:1529–1539. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Han R, Hao S, Lu C, Zhang C, Lin C, Li L,
Wang Y, Hu C and He Y: Aspirin sensitizes osimertinib-resistant
NSCLC cells in vitro and in vivo via Bim-dependent apoptosis
induction. Mol Oncol. 14:1152–1169. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Niederst MJ, Hu H, Mulvey HE, Lockerman
EL, Garcia AR, Piotrowska Z, Sequist LV and Engelman JA: The
allelic context of the C797S mutation acquired upon treatment with
third-generation EGFR inhibitors impacts sensitivity to subsequent
treatment strategies. Clin Cancer Res. 21:3924–3933. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Wang Z, Yang JJ, Huang J, Ye JY, Zhang XC,
Tu HY, Han-Zhang H and Wu YL: Lung Adenocarcinoma Harboring EGFR
T790M and in trans C797S responds to combination therapy of first-
and third-generation EGFR TKIs and shifts allelic configuration at
resistance. J Thorac Oncol. 12:1723–1727. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Rotow JK, Costa DB, Paweletz CP, Awad MM,
Marcoux P, Rangachari D, Barbie DA, Sands J, Cheng ML, Johnson BE,
et al: Concurrent osimertinib plus gefitinib for first-line
treatment of EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J
Clin Oncol. 38:95072020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Chic N, Mayo-de-Las-Casas C and Reguart N:
Successful treatment with gefitinib in advanced non-small cell lung
cancer after acquired resistance to osimertinib. J Thorac Oncol.
12:e78–e80. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Rangachari D, To C, Shpilsky JE,
VanderLaan PA, Kobayashi SS, Mushajiang M, Lau CJ, Paweletz CP,
Oxnard GR, Jänne PA and Costa DB: EGFR-mutated lung cancers
resistant to osimertinib through EGFR C797S respond to
first-generation reversible EGFR inhibitors but eventually acquire
EGFR T790M/C797S in preclinical models and clinical samples. J
Thorac Oncol. 14:1995–2002. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Yang X, Huang C, Chen R and Zhao J:
Resolving resistance to osimertinib therapy with afatinib in an
NSCLC patient with EGFR L718Q mutation. Clin Lung Cancer.
21:e258–e260. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Romaniello D, Mazzeo L, Mancini M,
Marrocco I, Noronha A, Kreitman M, Srivastava S, Ghosh S, Lindzen
M, Salame TM, et al: A combination of approved antibodies overcomes
resistance of lung cancer to osimertinib by blocking bypass
pathways. Clin Cancer Res. 24:5610–5621. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Yu HA, Baik CS, Gold K, Hayashi H, Johnson
M, Koczywas M, Murakami H, Nishio M, Steuer C, Su WC, et al: LBA62
Efficacy and safety of patritumab deruxtecan (U3-1402), a novel
HER3 directed antibody drug conjugate, in patients (pts) with
EGFR-mutated (EGFRm) NSCLC. Ann Oncol. 31:S1189–S1190. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Cho BC, Lee KH, Cho EK, Kim DW, Lee JS,
Han JY, Kim SW, Spira A, Haura EB, Sabari JK, et al: 1258O
Amivantamab (JNJ-61186372), an EGFR-MET bispecific antibody, in
combination with lazertinib, a 3rd-generation tyrosine kinase
inhibitor (TKI), in advanced EGFR NSCLC. Ann Oncol. 31(Suppl 4):
S8132020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Okura N, Nishioka N, Yamada T, Taniguchi
H, Tanimura K, Katayama Y, Yoshimura A, Watanabe S, Kikuchi T,
Shiotsu S, et al: ONO-7475, a Novel AXL inhibitor, suppresses the
adaptive resistance to initial EGFR-TKI treatment in -mutated
non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 26:2244–2256. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Kim D, Bach DH, Fan YH, Luu TT, Hong JY,
Park HJ and Lee SK: AXL degradation in combination with EGFR-TKI
can delay and overcome acquired resistance in human non-small cell
lung cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 10:3612019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Yang YM, Jang Y, Lee SH, Kang B and Lim
SM: AXL/MET dual inhibitor, CB469, has activity in non-small cell
lung cancer with acquired resistance to EGFR TKI with AXL or MET
activation. Lung Cancer. 46:70–77. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Shi P, Oh YT, Deng L, Zhang G, Qian G,
Zhang S, Ren H, Wu G, Legendre B Jr, Anderson E, et al: Overcoming
acquired resistance to AZD9291, A third-generation EGFR inhibitor,
through modulation of MEK/ERK-dependent Bim and Mcl-1 Degradation.
Clin Cancer Res. 23:6567–6579. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Gu J, Yao W, Shi P, Zhang G, Owonikoko TK,
Ramalingam SS and Sun SY: MEK or ERK inhibition effectively
abrogates emergence of acquired osimertinib resistance in the
treatment of epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung cancers.
Cancer. 126:3788–3799. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Xie Z, Gu Y, Xie X, Lin X, Ouyang M, Qin
Y, Zhang J, Lizaso A, Chen S and Zhou C: Lung adenocarcinoma
harboring concomitant EGFR mutations and BRAF V600E responds to a
combination of osimertinib and vemurafenib to overcome osimertinib
resistance. Clin Lung Cancer. 22:e390–e394. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Raoof S, Mulford IJ, Frisco-Cabanos H,
Nangia V, Timonina D, Labrot E, Hafeez N, Bilton SJ, Drier Y, Ji F,
et al: Targeting FGFR overcomes EMT-mediated resistance in EGFR
mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 38:6399–6413. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Yochum ZA, Cades J, Wang H, Chatterjee S,
Simons BW, O'Brien JP, Khetarpal SK, Lemtiri-Chlieh G, Myers KV,
Huang EH, et al: Targeting the EMT transcription factor TWIST1
overcomes resistance to EGFR inhibitors in EGFR-mutant
non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 38:656–670. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Yang JC, Schuler M, Popat S, Miura S,
Heeke S, Park K, Märten A and Kim ES: Afatinib for the treatment of
NSCLC harboring uncommon EGFR mutations: A database of 693 cases. J
Thorac Oncol. 15:803–815. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Fang W, Huang Y, Gan J, Shao YW and Zhang
L: Durable response of low-dose afatinib plus cetuximab in an
adenocarcinoma patient with a novel EGFR exon 20 insertion
mutation. J Thorac Oncol. 14:e220–e221. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Hasegawa H, Yasuda H, Hamamoto J, Masuzawa
K, Tani T, Nukaga S, Hirano T, Kobayashi K, Manabe T, Terai H, et
al: Efficacy of afatinib or osimertinib plus cetuximab combination
therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with EGFR exon 20 insertion
mutations. Lung Cancer. 127:146–152. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
van Veggel B, de Langen AJ, Hashemi SMS,
Monkhorst K, Heideman DAM, Thunnissen E and Smit EF: Afatinib and
cetuximab in four patients with EGFR exon 20 insertion-positive
advanced NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 13:1222–1226. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Yun J, Lee SH, Kim SY, Jeong SY, Kim JH,
Pyo KH, Park CW, Heo SG, Yun MR, Lim S, et al: Antitumor activity
of amivantamab (JNJ-61186372), an EGFR-MET bispecific antibody, in
diverse models of exon 20 insertion-driven NSCLC. Cancer Discov.
10:1194–1209. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Riely GJ, Neal JW, Camidge DR, Spira A,
Piotrowska Z, Horn L, Costa DB, Tsao A, Patel J, Gadgeel S, et al:
1261MO Updated results from a phase I/II study of mobocertinib
(TAK-788) in NSCLC with EGFR exon 20 insertions (exon20ins). Ann
Oncol. 31:S815–S816. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Nakahara Y, Kato T, Isomura R, Seki N,
Furuya N, Naoki K, Yamanaka T and Okamoto H: A multicenter, open
label, randomized phase II study of osimertinib plus ramucirumab
versus osimertinib alone as initial chemotherapy for EGFR
mutation-positive non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer:
TORG1833. J Clin Oncol. 37:TPS91202019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Yu HA, Schoenfeld AJ, Makhnin A, Kim R,
Rizvi H, Tsui D, Falcon C, Houck-Loomis B, Meng F, Yang JL, et al:
Effect of osimertinib and bevacizumab on progression-free survival
for patients with metastatic EGFR-mutant lung cancers: A Phase 1/2
single-group open-label trial. JAMA Oncol. 6:1048–1054. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Kobayashi N, Hashimoto H, Kamimaki C,
Nagasawa R, Tanaka K, Kubo S, Katakura S, Chen H, Hirama N, Ushio
R, et al: Afatinib + bevacizumab combination therapy in EGFR-mutant
NSCLC patients with osimertinib resistance: Protocol of an
open-label, phase II, multicenter, single-arm trial. Thorac Cancer.
11:2125–2129. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Lisberg A, Cummings A, Goldman JW,
Bornazyan K, Reese N, Wang T, Coluzzi P, Ledezma B, Mendenhall M,
Hunt J, et al: A phase II study of pembrolizumab in EGFR-Mutant,
PD-L1+, tyrosine kinase inhibitor naïve patients with
advanced NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 13:1138–1145. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Ahn MJ, Yang J, Yu H, Saka H, Ramalingam
S, Goto K, Kim SW, Yang L, Walding A and Oxnard GR: 136O:
Osimertinib combined with durvalumab in EGFR-mutant non-small cell
lung cancer: Results from the TATTON phase Ib trial. J Thorac
Oncol. 11:S1152016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Zhou J, Zhou F, Xie H, Wu Y, Zhao J and Su
C: An advanced non-small cell lung cancer patient with epidermal
growth factor receptor sensitizing mutation responded to
toripalimab in combination with chemotherapy after resistance to
osimertinib: A case report. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 9:354–359.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Zhang YC, Zhou Q and Wu YL: Clinical
management of third-generation EGFR inhibitor-resistant patients
with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: Current status and future
perspectives. Cancer Lett. 459:240–247. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Wu YL, Planchard D, Lu S, Sun H, Yamamoto
N, Kim DW, Tan DSW, Yang JC, Azrif M, Mitsudomi T, et al: Pan-Asian
adapted clinical practice guidelines for the management of patients
with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: A CSCO-ESMO initiative
endorsed by JSMO, KSMO, MOS, SSO and TOS. Ann Oncol. 30:171–210.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Version 4. NCCN
Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. 2021, https://www.nccn.org. Accessed at 25 Jun 2021.
|
|
137
|
Jang J, To C, De Clercq DJH, Park E,
Ponthier CM, Shin BH, Mushajiang M, Nowak RP, Fischer ES, Eck MJ,
et al: Mutant-selective allosteric EGFR degraders are effective
against a broad range of drug-resistant mutations. Angew Chem Int
Ed Engl. 59:14481–14489. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
To C, Jang J, Chen T, Park E, Mushajiang
M, De Clercq DJH, Xu M, Wang S, Cameron MD, Heppner DE, et al:
Single and dual targeting of mutant EGFR with an allosteric
inhibitor. Cancer Discov. 9:926–943. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|