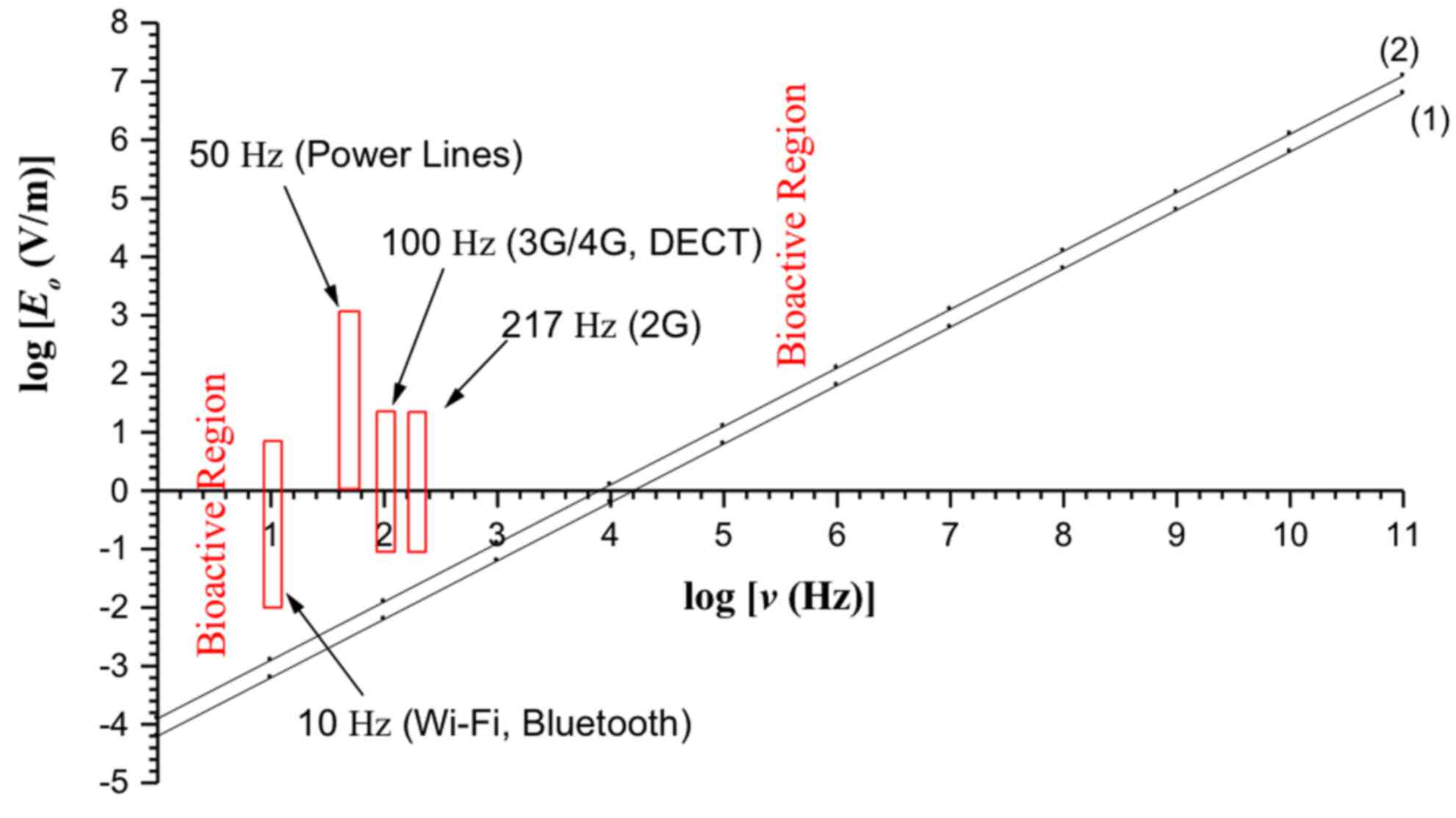
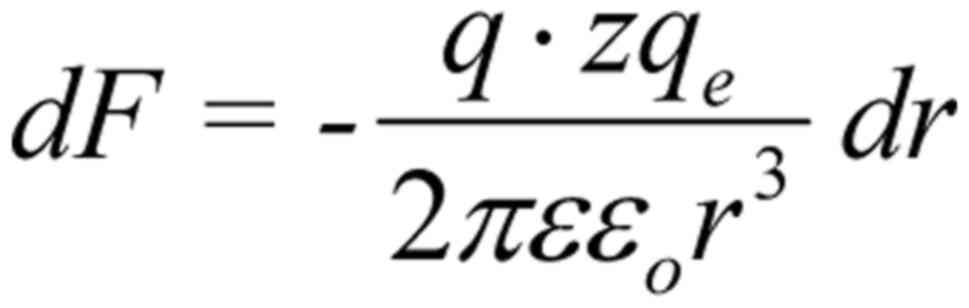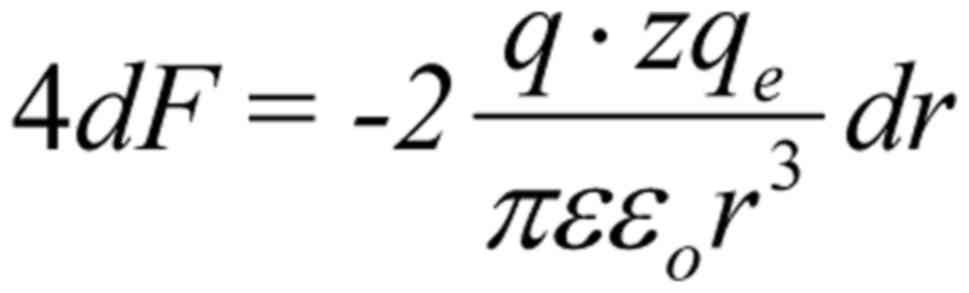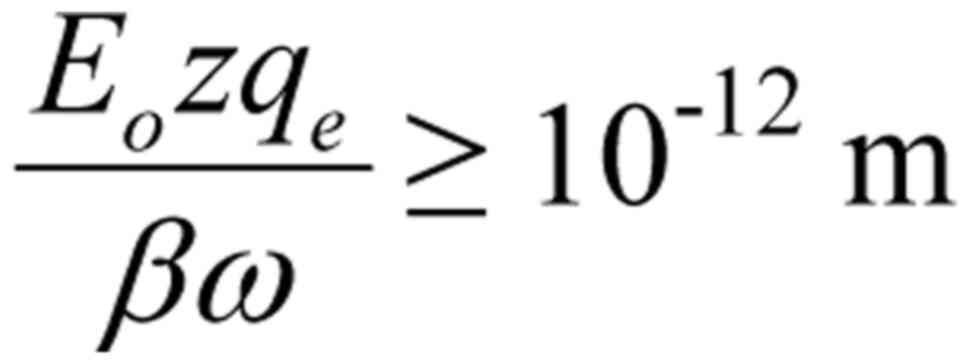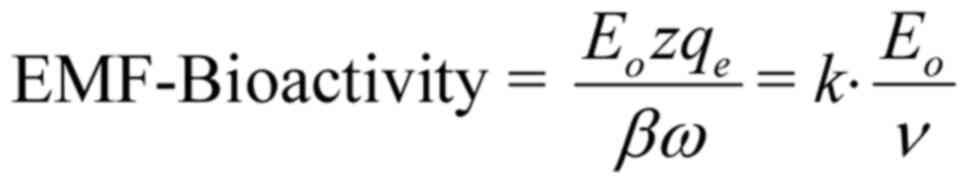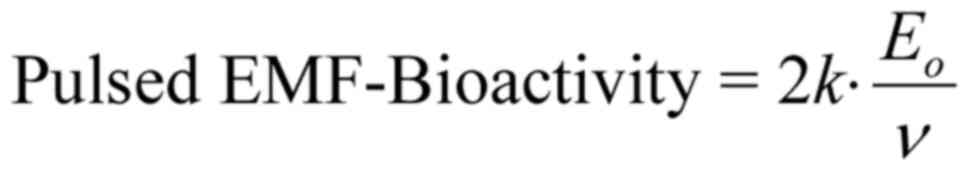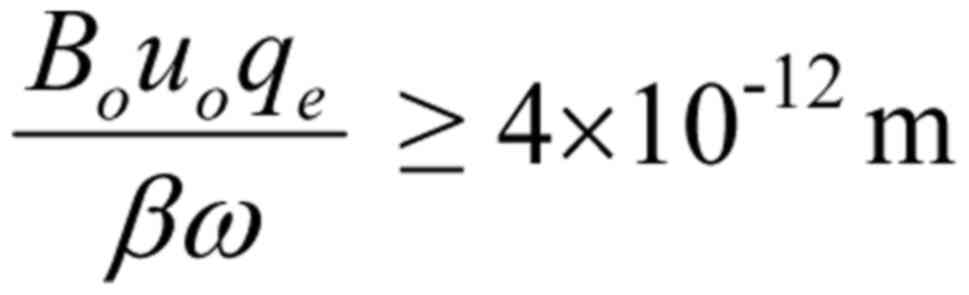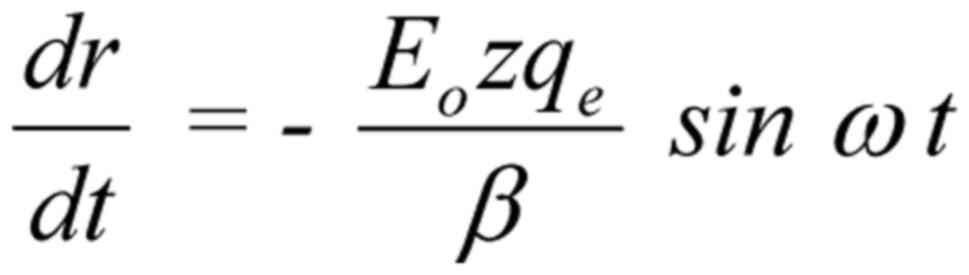|
1
|
Goodman EM, Greenebaum B and Marron MT:
Effects of electromagnetic fields on molecules and cells. Int Rev
Cytol. 158:279–338. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Santini MT, Ferrante A, Rainaldi G,
Indovina P and Indovina PL: Extremely low frequency (ELF) magnetic
fields and apoptosis: A review. Int J Radiat Biol. 81:1–11. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Phillips JL, Singh NP and Lai H:
Electromagnetic fields and DNA damage. Pathophysiology. 16:79–88.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Panagopoulos DJ: Comparing DNA damage
induced by mobile telephony and other types of man-made
electromagnetic fields. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 781:53–62. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Delgado JMR: Biological effects of
extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields. J Bioelectricity.
4:75–92. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Garaj-Vrhovac V, Horvat D and Koren Z: The
effect of microwave radiation on the cell genome. Mutat Res.
243:87–93. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Garaj-Vrhovac V, Horvat D and Koren Z: The
relationship between colony-forming ability, chromosome aberrations
and incidence of micronuclei in V79 Chinese hamster cells exposed
to microwave radiation. Mutat Res. 263:143–149. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Garaj-Vrhovac V, Fucić A and Horvat D: The
correlation between the frequency of micronuclei and specific
chromosome aberrations in human lymphocytes exposed to microwave
radiation in vitro. Mutat Res. 281:181–186. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma TH and Chu KC: Effect of the extremely
low frequency (ELF) electromagnetic field (EMF) on developing
embryos of the fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster L.). Mutat Res.
303:35–39. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sarkar S, Ali S and Behari J: Effect of
low power microwave on the mouse genome: A direct DNA analysis.
Mutat Res. 320:141–147. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lai H and Singh NP: Acute low-intensity
microwave exposure increases DNA single-strand breaks in rat brain
cells. Bioelectromagnetics. 16:207–210. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lai H and Singh NP: Single- and
double-strand DNA breaks in rat brain cells after acute exposure to
radiofrequency electro-magnetic radiation. Int J Radiat Biol.
69:513–521. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lai H and Singh NP: Acute exposure to a 60
Hz magnetic field increases DNA strand breaks in rat brain cells.
Bioelectromagnetics. 18:156–165. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Svedenstål BM, Johanson KJ and Mild KH:
DNA damage induced in brain cells of CBA mice exposed to magnetic
fields. In Vivo. 13:551–552. 1999.
|
|
15
|
Koana T, Okada MO, Takashima Y, Ikehata M
and Miyakoshi J: Involvement of eddy currents in the mutagenicity
of ELF magnetic fields. Mutat Res. 476:55–62. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ivancsits S, Diem E, Pilger A, Rüdiger HW
and Jahn O: Induction of DNA strand breaks by intermittent exposure
to extremely-low-frequency electromagnetic fields in human diploid
fibroblasts. Mutat Res. 519:1–13. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ivancsits S, Diem E, Jahn O and Rüdiger
HW: Intermittent extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields
cause DNA damage in a dose-dependent way. Int Arch Occup Environ
Health. 76:431–436. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Winker R, Ivancsits S, Pilger A, Adlkofer
F and Rüdiger HW: Chromosomal damage in human diploid fibroblasts
by intermittent exposure to extremely low-frequency electromagnetic
fields. Mutat Res. 585:43–49. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Diem E, Schwarz C, Adlkofer F, Jahn O and
Rüdiger H: Non-thermal DNA breakage by mobile-phone radiation (1800
MHz) in human fibroblasts and in transformed GFSH-R17 rat granulosa
cells in vitro. Mutat Res. 583:178–183. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mausset-Bonnefont AL, Hirbec H, Bonnefont
X, Privat A, Vignon J and de Sèze R: Acute exposure to GSM 900-MHz
electromagnetic fields induces glial reactivity and biochemical
modifications in the rat brain. Neurobiol Dis. 17:445–454. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ji S, Oh E, Sul D, Choi JW, Park H and Lee
E: DNA damage of lymphocytes in volunteers after 4 h use of mobile
phone. J Prev Med Public Health. 37:373–380. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hong R, Zhang Y, Liu Y and Weng EQ:
Effects of extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields on DNA of
testicular cells and sperm chromatin structure in mice. Zhonghua
Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 23:414–417. 2005.In
Chinese.
|
|
23
|
Belyaev IY, Hillert L, Protopopova M, Tamm
C, Malmgren LO, Persson BR, Selivanova G and Harms-Ringdahl M: 915
MHz microwaves and 50 Hz magnetic field affect chromatin
conformation and 53BP1 foci in human lymphocytes from
hypersensitive and healthy persons. Bioelectromagnetics.
26:173–184. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Markovà E, Hillert L, Malmgren L, Persson
BR and Belyaev IY: Microwaves from GSM mobile telephones affect
53BP1 and gamma-H2AX foci in human lymphocytes from hypersensitive
and healthy persons. Environ Health Perspect. 113:1172–1177. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Aitken RJ, Bennetts LE, Sawyer D, Wiklendt
AM and King BV: Impact of radio frequency electromagnetic radiation
on DNA integrity in the male germline. Int J Androl. 28:171–179.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nikolova T, Czyz J, Rolletschek A,
Blyszczuk P, Fuchs J, Jovtchev G, Schuderer J, Kuster N and Wobus
AM: Electromagnetic fields affect transcript levels of
apoptosis-related genes in embryonic stem cell-derived neural
progenitor cells. FASEB J. 19:1686–1688. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang DY, Xu ZP, Chiang H, Lu DQ and Zeng
QL: Effects of GSM 1800 MHz radiofrequency electromagnetic fields
on DNA damage in Chinese hamster lung cells. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi
Xue Za Zhi. 40:149–152. 2006.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lixia S, Yao K, Kaijun W, Deqiang L,
Huajun H, Xiangwei G, Baohong W, Wei Z, Jianling L and Wei W:
Effects of 1.8 GHz radiofrequency field on DNA damage and
expression of heat shock protein 70 in human lens epithelial cells.
Mutat Res. 602:135–142. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ferreira AR, Knakievicz T, Pasquali MA,
Gelain DP, Dal-Pizzol F, Fernández CE, de Salles AA, Ferreira HB
and Moreira JC: Ultra high frequency-electromagnetic field
irradiation during pregnancy leads to an increase in erythrocytes
micronuclei incidence in rat offspring. Life Sci. 80:43–50. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Panagopoulos DJ, Chavdoula ED, Nezis IP
and Margaritis LH: Cell death induced by GSM 900-MHz and DCS
1800-MHz mobile telephony radiation. Mutat Res. 626:69–78. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yan JG, Agresti M, Bruce T, Yan YH,
Granlund A and Matloub HS: Effects of cellular phone emissions on
sperm motility in rats. Fertil Steril. 88:957–964. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yao K, Wu W, Wang K, Ni S, Ye P, Yu Y, Ye
J and Sun L: Electromagnetic noise inhibits radiofrequency
radiation-induced DNA damage and reactive oxygen species increase
in human lens epithelial cells. Mol Vis. 14:964–969.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yadav AS and Sharma MK: Increased
frequency of micronucleated exfoliated cells among humans exposed
in vivo to mobile telephone radiations. Mutat Res. 650:175–180.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sokolovic D, Djindjic B, Nikolic J,
Bjelakovic G, Pavlovic D, Kocic G, Krstic D, Cvetkovic T and
Pavlovic V: Melatonin reduces oxidative stress induced by chronic
exposure of microwave radiation from mobile phones in rat brain. J
Radiat Res. 49:579–586. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee KS, Choi JS, Hong SY, Son TH and Yu K:
Mobile phone electromagnetic radiation activates MAPK signaling and
regulates viability in Drosophila. Bioelectromagnetics. 29:371–379.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
De Iuliis GN, Newey RJ, King BV and Aitken
RJ: Mobile phone radiation induces reactive oxygen species
production and DNA damage in human spermatozoa in vitro. PLoS One.
4:e64462009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Agarwal A, Desai NR, Makker K, Varghese A,
Mouradi R, Sabanegh E and Sharma R: Effects of radiofrequency
electromagnetic waves (RF-EMW) from cellular phones on human
ejaculated semen: An in vitro pilot study. Fertil Steril.
92:1318–1325. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Mailankot M, Kunnath AP, Jayalekshmi H,
Koduru B and Valsalan R: Radio frequency electromagnetic radiation
(RF-EMR) from GSM (0.9/1.8 GHz) mobile phones induces oxidative
stress and reduces sperm motility in rats. Clinics (Sao Paulo).
64:561–565. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Luukkonen J, Hakulinen P, Mäki-Paakkanen
J, Juutilainen J and Naarala J: Enhancement of chemically induced
reactive oxygen species production and DNA damage in human SH-SY5Y
neuroblastoma cells by 872 MHz radiofrequency radiation. Mutat Res.
662:54–58. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Panagopoulos DJ, Chavdoula ED and
Margaritis LH: Bioeffects of mobile telephony radiation in relation
to its intensity or distance from the antenna. Int J Radiat Biol.
86:345–357. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chavdoula ED, Panagopoulos DJ and
Margaritis LH: Comparison of biological effects between continuous
and intermittent exposure to GSM-900-MHz mobile phone radiation.
Detection of apoptotic cell death features Mutat Res. 700:51–61.
2010.
|
|
42
|
Guler G, Tomruk A, Ozgur E and Seyhan N:
The effect of radio-frequency radiation on DNA and lipid damage in
non-pregnant and pregnant rabbits and their newborns. Gen Physiol
Biophys. 29:59–66. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tomruk A, Guler G and Dincel AS: The
influence of 1800 MHz GSM-like signals on hepatic oxidative DNA and
lipid damage in nonpregnant, pregnant, and newly born rabbits. Cell
Biochem Biophys. 56:39–47. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Franzellitti S, Valbonesi P, Ciancaglini
N, Biondi C, Contin A, Bersani F and Fabbri E: Transient DNA damage
induced by high-frequency electromagnetic fields (GSM 1.8 GHz) in
the human trophoblast HTR-8/SVneo cell line evaluated with the
alkaline comet assay. Mutat Res. 683:35–42. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Campisi A, Gulino M, Acquaviva R, Bellia
P, Raciti G, Grasso R, Musumeci F, Vanella A and Triglia A:
Reactive oxygen species levels and DNA fragmentation on astrocytes
in primary culture after acute exposure to low intensity microwave
electromagnetic field. Neurosci Lett. 473:52–55. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Panagopoulos DJ: Effect of microwave
exposure on the ovarian development of Drosophila melanogaster.
Cell Biochem Biophys. 63:121–132. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Panagopoulos DJ, Karabarbounis A and
Lioliousis C: ELF alternating magnetic field decreases reproduction
by DNA damage induction. Cell Biochem Biophys. 67:703–716. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liu C, Gao P, Xu SC, Wang Y, Chen CH, He
MD, Yu ZP, Zhang L and Zhou Z: Mobile phone radiation induces
mode-dependent DNA damage in a mouse spermatocyte-derived cell
line: A protective role of melatonin. Int J Radiat Biol.
89:993–1001. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Pesnya DS and Romanovsky AV: Comparison of
cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of plutonium-239 alpha particles
and mobile phone GSM 900 radiation in the Allium cepa test. Mutat
Res. 750:27–33. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Mihai CT, Rotinberg P, Brinza F and
Vochita G: Extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields cause DNA
strand breaks in normal cells. J Environ Health Sci Eng. 12:152014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Daroit NB, Visioli F, Magnusson AS, Vieira
GR and Rados PV: Cell phone radiation effects on cytogenetic
abnormalities of oral mucosal cells. Braz Oral Res. 29:1–8. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Banerjee S, Singh NN, Sreedhar G and
Mukherjee S: Analysis of the genotoxic effects of mobile phone
radiation using buccal micronucleus assay: A comparative
evaluation. J Clin Diagn Res. 10:ZC82–ZC85. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
D'Silva MH, Swer RT, Anbalagan J and
Rajesh B: Effect of radiofrequency radiation emitted from 2G and 3G
cell phone on developing liver of chick embryo-a comparative study.
J Clin Diagn Res. 11:AC05–AC09. 2017.
|
|
54
|
Panagopoulos DJ: Chromosome damage in
human cells induced by UMTS mobile telephony radiation. Gen Physiol
Biophys. 38:445–454. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Panagopoulos DJ: Comparing chromosome
damage induced by mobile telephony radiation and a high caffeine
dose: Effect of combination and exposure duration. Gen Physiol
Biophys. 39:531–544. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Magras IN and Xenos TD: RF
radiation-induced changes in the prenatal development of mice.
Bioelectromagnetics. 18:455–461. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Panagopoulos DJ, Karabarbounis A and
Margaritis LH: Effect of GSM 900-MHz mobile phone radiation on the
reproductive capacity of Drosophila melanogaster. Electromagn Biol
Med. 23:29–43. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Panagopoulos DJ, Chavdoula ED,
Karabarbounis A and Margaritis LH: Comparison of bioactivity
between GSM 900 MHz and DCS 1800 MHz mobile telephony radiation.
Electromagn Biol Med. 26:33–44. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wdowiak A, Wdowiak L and Wiktor H:
Evaluation of the effect of using mobile phones on male fertility.
Ann Agric Environ Med. 14:169–172. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Agarwal A, Deepinder F, Sharma RK, Ranga G
and Li J: Effect of cell phone usage on semen analysis in men
attending infertility clinic: An observational study. Fertil
Steril. 89:124–128. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Batellier F, Couty I, Picard D and
Brillard JP: Effects of exposing chicken eggs to a cell phone in
'call' position over the entire incubation period. Theriogenology.
69:737–745. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Gul A, Celebi H and Uğraş S: The effects
of microwave emitted by cellular phones on ovarian follicles in
rats. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 280:729–733. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Sharma VP and Kumar NR: Changes in honey
bee behaviour and biology under the influence of cell phone
radiations. Curr Sci. 98:1376–1378. 2010.
|
|
64
|
La Vignera S, Condorelli RA, Vicardi E,
D'Agata R and Calogero AE: Effects of the exposure to mobile phones
on male reproduction: A review of the literature. J Androl.
33:350–356. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Balmori A: Possible effects of
electromagnetic fields from phone masts on a population of white
stork (Ciconia ciconia). Electromagn Biol Med. 24:109–119. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Balmori A and Hallberg O: The urban
decline of the house sparrow (Passer domesticus): A possible link
with electromagnetic radiation. Electromagn Biol Med. 26:141–151.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Everaert J and Bauwens D: A possible
effect of electromagnetic radiation from mobile phone base stations
on the number of breeding house sparrows (Passer domesticus).
Electromagn Biol Med. 26:63–72. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Bacandritsos N, Granato A, Budge G,
Papanastasiou I, Roinioti E, Caldon M, Falcaro C, Gallina A and
Mutinelli F: Sudden deaths and colony population decline in Greek
honey bee colonies. J Invertebr Pathol. 105:335–340. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Cucurachi S, Tamis WL, Vijver MG,
Peijnenburg WJ, Bolte JF and de Snoo GR: A review of the ecological
effects of radio-frequency electromagnetic fields (RF-EMF). Environ
Int. 51:116–140. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Balmori A: The incidence of
electromagnetic pollution on the amphibian decline: Is this an
important piece of the puzzle? Toxicol Environ Chem. 88:287–299.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Balmori A: Mobile phone mast effects on
common frog (Rana temporaria) tadpoles: The city turned into a
laboratory. Electromagn Biol Med. 29:31–35. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Wertheimer N and Leeper E: Electrical
wiring configurations and childhood cancer. Am J Epidemiol.
109:273–284. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Savitz DA, Wachtel H, Barnes F, John EM
and Tvrdik JG: Case-control study of childhood cancer and exposure
to 60-Hz magnetic fields. Am J Epidemiol. 128:21–38. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Coleman MP, Bell CM, Taylor HL and
Primic-Zakelj M: Leukaemia and residence near electricity
transmission equipment: A case-control study. Br J Cancer.
60:793–798. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Feychting M and Ahlbom A: Magnetic fields
and cancer in children residing near Swedish high-voltage power
lines. Am J Epidemiol. 138:467–481. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Feychting M and Ahlbom A: Magnetic fields,
leukemia, and central nervous system tumors in Swedish adults
residing near high-voltage power lines. Epidemiology. 5:501–509.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Feychting M and Ahlbom A: Childhood
leukemia and residential exposure to weak extremely low frequency
magnetic fields. Environ Health Perspect. 103(Suppl 2): S59–S62.
1995.
|
|
78
|
Coghill RW, Steward J and Philips A: Extra
low frequency electric and magnetic fields in the bed place of
children diagnosed with leukaemia: A case-control study. Eur J
Cancer Prev. 5:153–158. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Ahlbom A, Day N, Feychting M, Roman E,
Skinner J, Dockerty J, Linet M, McBride M, Michaelis J, Olsen JH,
et al: A pooled analysis of magnetic fields and childhood
leukaemia. Br J Cancer. 83:692–698. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Greenland S, Sheppard AR, Kaune WT, Poole
C and Kelsh MA: A pooled analysis of magnetic fields, wire codes,
and childhood leukemia. Childhood leukemia-EMF study group
Epidemiology. 11:624–634. 2000.
|
|
81
|
Draper G, Vincent T, Kroll ME and Swanson
J: Childhood cancer in relation to distance from high voltage power
lines in England and Wales: A case-control study. BMJ.
330:12902005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Kheifets L, Ahlbom A, Crespi CM, Draper G,
Hagihara J, Lowenthal RM, Mezei G, Oksuzyan S, Schüz J, Swanson J,
et al: Pooled analysis of recent studies on magnetic fields and
childhood leukaemia. Br J Cancer. 103:1128–1135. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Hallberg O and Johansson O: Melanoma
incidence and frequency modulation (FM) broadcasting. Arch Environ
Health. 57:32–40. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Gulati S, Yadav A, Kumar N, Kanupriya,
Aggarwal NK, Kumar R and Gupta R: Effect of GSTM1 and GSTT1
polymorphisms on genetic damage in humans populations exposed to
radiation from mobile towers. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol.
70:615–625. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Zothansiama, Zosangzuali M, Lalramdinpuii
M and Jagetia GC: Impact of radiofrequency radiation on DNA damage
and anti-oxidants in peripheral blood lymphocytes of humans
residing in the vicinity of mobile phone base stations. Electromagn
Biol Med. 36:295–305. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M, Söderqvist F, Mild
KH and Morgan LL: Long-term use of cellular phones and brain
tumours: Increased risk associated with use for > or =10 years.
Occup Environ Med. 64:626–632. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M and Hansson Mild K:
Epidemiological evidence for an association between use of wireless
phones and tumor diseases. Pathophysiology. 16:113–122. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Khurana VG, Teo C, Kundi M, Hardell L and
Carlberg M: Cell phones and brain tumors: A review including the
long-term epidemiologic data. Surg Neurol. 72:205–214. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Hardell L and Carlberg M: Mobile phones,
cordless phones and the risk for brain tumours. Int J Oncol.
35:5–17. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M, Söderqvist F and
Mild KH: Pooled analysis of case-control studies on acoustic
neuroma diagnosed 1997-2003 and 2007-2009 and use of mobile and
cordless phones. Int J Oncol. 43:1036–1044. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M, Söderqvist F and
Mild KH: Case-control study of the association between malignant
brain tumours diagnosed between 2007 and 2009 and mobile and
cordless phone use. Int J Oncol. 43:1833–1845. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M and Hansson Mild K:
Use of mobile phones and cordless phones is associated with
increased risk for glioma and acoustic neuroma. Pathophysiology.
20:85–110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Wang Y and Guo X: Meta-analysis of
association between mobile phone use and glioma risk. J Cancer Res
Ther. 12(Suppl): C298–C300. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Carlberg M and Hardell L: Evaluation of
mobile phone and cordless phone use and glioma risk using the
bradford hill viewpoints from 1965 on association or causation.
Biomed Res Int. 2017:92184862017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Hardell L: Effects of mobile phones on
children's and adolescents' health: A commentary. Child Dev.
89:137–140. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Momoli F, Siemiatycki J, McBride ML,
Parent MÉ, Richardson L, Bedard D, Platt R, Vrijheid M, Cardis E
and Krewski D: Probabilistic multiple-bias modelling applied to the
Canadian data from the INTERPHONE study of mobile phone use and
risk of glioma, meningioma, acoustic neuroma, and parotid gland
tumors. Am J Epidemiol. 186:885–893. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Miller AB, Morgan LL, Udasin I and Davis
DL: Cancer epidemiology update following the 2011 IARC evaluation
of radiofrequency electromagnetic fields (Monograph 102). Environ
Res. 167:673–683. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Miller AB, Sears ME, Morgan LL, Davis DL,
Hardell L, Oremus M and Soskolne CL: Risks to health and well-being
from radio-frequency radiation emitted by cell phones and other
wireless devices. Front Public Health. 7:2232019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Santini R, Santini P, Danze JM, Le Ruz P
and Seigne M: Study of the health of people living in the vicinity
of mobile phone base stations: I. Influences of distance and sex
Pathol Biol. 50:369–373. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Navarro A, Garcia JS, Portoles M and
Gómez-Perretta G: The microwave syndrome: A preliminary study in
Spain. Electromagn Biol Med. 22:161–169. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Salama OE and Abou El Naga RM: Cellular
phones: Are they detrimental? J Egypt Public Health Assoc.
79:197–223. 2004.
|
|
102
|
Hutter HP, Moshammer H, Wallner P and
Kundi M: Subjective symptoms, sleeping problems, and cognitive
performance in subjects living near mobile phone base stations.
Occup Environ Med. 63:307–313. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Abdel-Rassoul G, El-Fateh OA, Salem MA,
Michael A, Farahat F, El-Batanouny M and Salem E: Neurobehavioral
effects among inhabitants around mobile phone base stations.
Neurotoxicology. 28:434–440. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Blettner M, Schlehofer B, Breckenkamp J,
Kowall B, Schmiedel S, Reis U, Potthoff P, Schüz J and
Berg-Beckhoff G: Mobile phone base stations and adverse health
effects: Phase 1 of a population-based, cross-sectional study in
Germany. Occup Environ Med. 66:118–123. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Viel JF, Clerc S, Barrera C, Rymzhanova R,
Moissonnier M, Hours M and Cardis E: Residential exposure to
radiofrequency fields from mobile phone base stations, and
broadcast transmitters: A population-based survey with personal
meter. Occup Environ Med. 66:550–556. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Kundi M and Hutter HP: Mobile phone base
stations-effects on wellbeing and health. Pathophysiology.
16:123–135. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Shahbazi-Gahrouei D, Karbalae M, Moradi HA
and Baradaran-Ghahfarokhi M: Health effects of living near mobile
phone base transceiver station (BTS) antennae: A report from
Isfahan, Iran. Electromagn Biol Med. 33:206–210. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Irigaray P, Caccamo D and Belpomme D:
Oxidative stress in electrohypersensitivity self-reporting
patients: Results of a prospective in vivo investigation with
comprehensive molecular analysis. Int J Mol Med. 42:1885–1898.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Yakymenko I, Tsybulin O, Sidorik E,
Henshel D, Kyrylenko O and Kyrylenko S: Oxidative mechanisms of
biological activity of low-intensity radiofrequency radiation.
Electromagn Biol Med. 35:186–202. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Tillmann T, Ernst H, Streckert J, Zhou Y,
Taugner F, Hansen V and Dasenbrock C: Indication of cocarcinogenic
potential of chronic UMTS-modulated radiofrequency exposure in an
ethylnitrosourea mouse model. Int J Radiat Biol. 86:529–541. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Lerchl A, Klose M, Grote K, Wilhelm AF,
Spathmann O, Fiedler T, Streckert J, Hansen V and Clemens M: Tumor
promotion by exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields
below exposure limits for humans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
459:585–590. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
National Toxicology Program: Toxicology
and carcinogenesis studies in Sprague Dawley (Hsd:Sprague Dawley
SD) rats exposed to whole-body radio frequency radiation at a
frequency (900 MHz) and modulations (GSM and CDMA) used by cell
phones. Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser: NTP-TR-595. 2018.
|
|
113
|
Smith-Roe SL, Wyde ME, Stout MD, Winters
JW, Hobbs CA, Shepard KG, Green AS, Kissling GE, Shockley KR, Tice
RR, et al: Evaluation of the genotoxicity of cell phone
radiofrequency radiation in male and female rats and mice following
subchronic exposure. Environ Mol Mutagen. 61:276–290. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
114
|
Falcioni L, Bua L, Tibaldi E, Lauriola M,
De Angelis L, Gnudi F, Mandrioli D, Manservigi M, Manservisi F,
Manzoli I, et al: Report of final results regarding brain and heart
tumors in Sprague-Dawley rats exposed from prenatal life until
natural death to mobile phone radiofrequency field representative
of a 1.8 GHz GSM base station environmental emission. Environ Res.
165:496–503. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
International Commission on Non-Ionizing
Radiation Protection: Guidelines for limiting exposure to
time-varying electric and magnetic fields (1 Hz to 100 kHz). Health
Phys. 99:818–836. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
International Commission on Non-Ionizing
Radiation Protection: Guidelines for limiting exposure to
electromagnetic fields (100 kHz to 300 GHz). Health Phys.
118:483–524. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
IARC: Non-ionizing radiation, part 1:
Static and extremely low-frequency (ELF) electric and magnetic
fields. 80. World Health Organization. IARC Press; Lyon: 2002
|
|
118
|
IARC: Non-Ionizing Radiation, Part 2:
Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields. 102. IARC Press; Lyon:
2013
|
|
119
|
Baan R, Grosse Y, Lauby-Secretan B, El
Ghissassi F, Bouvard V, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Guha N, Islami F and
Galichet L: Carcinogenicity of radiofrequency electromagnetic
fields. Lancet Oncol. 12:624–626. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Verschaeve L: Misleading scientific papers
on health effects from wireless communication devices. Microwave
Effects on DNA and Proteins. Geddes CD: Springer; Cham: pp.
159–233. 2017, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Panagopoulos DJ, Johansson O and Carlo GL:
Real versus simulated mobile phone exposures in experimental
studies. Biomed Res Int. 2015:6070532015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Panagopoulos DJ: Mobile telephony
radiation effects on insect ovarian cells. The necessity for real
exposures bioactivity assessment The key role of polarization, and
the 'ion forced-oscillation mechanism'. Microwave Effects on DNA
and Proteins. Geddes CD: Springer; Cham: pp. 1–48. 2017
|
|
123
|
Manna D and Ghosh R: Effect of
radiofrequency radiation in cultured mammalian cells: A review.
Electromagn Biol Med. 35:265–301. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Leach V, Weller S and Redmayne M: A novel
database of bio-effects from non-ionizing radiation. Rev Environ
Health. 33:273–280. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Karipidis K, Mate R, Urban D, Tinker R and
Wood A: 5G mobile networks and health-a state-of-the-science review
of the research into low-level RF fields above 6 GHz. J Expo Sci
Environ Epidemiol. 31:585–605. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Hardell L and Nyberg R: Appeals that
matter or not on a moratorium on the deployment of the fifth
generation, 5G, for microwave radiation. Mol Clin Oncol.
12:247–257. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Hardell L and Carlberg M: Health risks
from radiofrequency radiation, including 5G, should be assessed by
experts with no conflicts of interest. Oncol Lett.
20:152020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Metaxas AC: Microwave heating. Power Eng.
5:237–247. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Panagopoulos DJ: Comments on Pall's
'Millimeter (MM) wave and microwave frequency radiation produce
deeply penetrating effects: The biology and the physics'. Rev
Environ Health. Jul 12–2021, https://doi.org/10.1515/reveh-2021-0090. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Ames BN: Endogenous DNA damage as related
to cancer and aging. Mutat Res. 214:41–46. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Lieber MR: Pathological and physiological
double-strand breaks: Roles in cancer, aging, and the immune
system. Am J Pathol. 153:1323–1332. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Helleday T, Loc J, van Gentd DC and
Engelward BP: DNA double-strand break repair: From mechanistic
understanding to cancer treatment. DNA Repair (Amst). 6:923–935.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Lahtz C and Pfeifer GP: Epigenetic changes
of DNA repair genes in cancer. J Mol Cell Biol. 3:51–58. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Yao Y and Dai W: Genomic instability and
cancer. J Carcinog Mutagen. 5:10001652014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Bernstein C, Prasad AR, Nfonsam V and
Bernstein H: DNA damage, DNA repair and cancer. New Research
Directions in DNA Repair. Clarc C: InTech; Rijeka: pp. 413–465.
2013
|
|
136
|
Basu AK: DNA damage, mutagenesis and
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 19:9702018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
137
|
von Zglinicki T, Saretzki G, Ladhoff J,
d'Adda di Fagagna F and Jackson SP: Human cell senescence as a DNA
damage response. Mech Ageing Dev. 126:111–117. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Shah DJ, Sachs RK and Wilson DJ:
Radiation-induced cancer: A modern view. Br J Radiol.
85:e1166–e1173. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Rodgers K and McVey M: Error-prone repair
of DNA double-strand breaks. J Cell Physiol. 231:15–24. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Nadler DL and Zurbenko IG: Estimating
cancer latency times using a weibull model. Adv Epidemiol.
2014:7467692014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Francis G: Ionization Phenomena in Gases.
Butterworths Scientific Publications; London: 1960
|
|
142
|
Gomer R: Field Emission and Field
Ionization. Harvard University Press; Cambridge: 1961
|
|
143
|
Panagopoulos DJ, Johansson O and Carlo GL:
Polarization: A key difference between man-made and natural
electromagnetic fields, in regard to biological activity. Sci Rep.
5:149142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Panagopoulos DJ, Messini N, Karabarbounis
A, Filippetis AL and Margaritis LH: A mechanism for action of
oscillating electric fields on cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
272:634–640. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Panagopoulos DJ, Karabarbounis A and
Margaritis LH: Mechanism for action of electromagnetic fields on
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 298:95–102. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Panagopoulos DJ, Balmori A and Chrousos
GP: On the biophysical mechanism of sensing upcoming earthquakes by
animals. Sci Total Environ. 717:1369892020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M,
Roberts K and Walter P: Molecular Biology of the Cell. Garland
Publishing, Inc; New York: 1994
|
|
148
|
Stryer L: Biochemistry. 4th edition.
Freeman WH: Freeman and Company; New York, NY: 1995
|
|
149
|
Halgamuge MN and Abeyrathne CD: Behavior
of charged particles in a biological cell exposed to AC-DC
electromagnetic fields. Environ Eng Sci. 28:1–10. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
Panagopoulos DJ and Karabarbounis A:
Comments on study of charged particle's behavior in a biological
cell exposed to AC-DC electromagnetic fields, and on comparison
between two models of interaction between electric and magnetic
fields and proteins in cell membranes. Environ Eng Sci. 28:749–751.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Bawin SM, Kaczmarek LK and Adey WR:
Effects of modulated VHF fields, on the central nervous system. Ann
N Y Acad Sci. 247:74–81. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Bawin SM, Adey WR and Sabbot IM: Ionic
factors in release of 45Ca2+ from chicken
cerebral tissue by electromagnetic fields. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
75:6314–6318. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
153
|
Blackman CF, Benane SG, Elder JA, House
DE, Lampe JA and Faulk JM: Induction of calcium-ion efflux from
brain tissue by radiofrequency radiation: Effect of sample number
and modulation frequency on the power density window.
Bioelectromagnetics. 1:35–43. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Frei M, Jauchem J and Heinmets F:
Physiological effects of 2.8 GHz radio-frequency radiation: A
comparison of pulsed and continuous-wave radiation. J Microw Power
Electromagn Energy. 23:85–93. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Bolshakov MA and Alekseev SI: Bursting
responses of Lymnea neurons to microwave radiation.
Bioelectromagnetics. 13:119–129. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Penafiel LM, Litovitz T, Krause D, Desta A
and Mullins JM: Role of modulation on the effect of microwaves on
ornithine decarboxylase activity in L929 cells.
Bioelectromagnetics. 18:132–141. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Huber R, Treyer V, Borbély AA, Schuderer
J, Gottselig JM, Landolt HP, Werth E, Berthold T, Kuster N, Buck A
and Achermann P: Electromagnetic fields, such as those from mobile
phones, alter regional cerebral blood flow and sleep and waking
EEG. J Sleep Res. 11:289–295. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Höytö A, Luukkonen J, Juutilainen J and
Naarala J: Proliferation, oxidative stress and cell death in cells
exposed to 872 MHz radio-frequency radiation and oxidants. Radiat
Res. 170:235–243. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
Mohammed HS, Fahmy HM, Radwan NM and
Elsayed AA: Non-thermal continuous and modulated electromagnetic
radiation fields effects on sleep EEG of rats. J Adv Res.
4:181–187. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Noda M, Ikeda T, Kayano T, Suzuki H,
Takeshima H, Kurasaki M, Takahashi H and Numa S: Existence of
distinct sodium channel messenger RNAs in rat brain. Nature.
320:188–192. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Liman ER, Hess P, Weaver F and Koren G:
Voltage-sensing residues in the S4 region of a mammalian
K+ channel. Nature. 353:752–756. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Tombola F, Pathak MM and Isacoff EY: How
does voltage open an ion channel? Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 22:23–52.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Schmidt WF and Thomas CG: More precise
model of α-helix and transmembrane α-helical peptide backbone
structure. J Biophy Chem. 3:295–303. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
164
|
Miller C: An overview of the potassium
channel family. Genome Biol. 1:REVIEWS00042000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
165
|
Zhang XC, Yang H, Liu Z and Sun F:
Thermodynamics of voltage-gated ion channels. Biophys Rep.
4:300–319. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
166
|
DeCoursey TE: Interactions between NADPH
oxidase and voltage-gated proton channels: Why electron transport
depends on proton transport. FEBS Lett. 555:57–61. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Seredenina T, Demaurex N and Krause KH:
Voltage-gated proton channels as novel drug targets: From NADPH
oxidase regulation to sperm biology. Antioxid Redox Sign.
23:490–513. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
168
|
Panagopoulos DJ, Johansson O and Carlo GL:
Evaluation of specific absorption rate as a dosimetric quantity for
electromagnetic fields bioeffects. PLoS One. 8:e626632013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Creasey WA and Goldberg RB: A new twist on
an old mechanism for EMF bioeffects? EMF Health Rep. 9:1–11.
2001.
|
|
170
|
Belyaev IY: Non-thermal biological effects
of microwaves. Microw Rev. 11:13–29. 2005.
|
|
171
|
Zhou R, Xiong Y, Xing G, Sun L and Ma J:
ZiFi: Wireless LAN discovery via ZigBee interference signatures.
MobiCom'10. In: September 20-24; Chicago, Illinois, USA. 2010
Proceedings of the 16th Annual International Conference on Mobile
Computing and Networking; View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
172
|
Piacentini R, Ripoli C, Mezzogori D,
Azzena GB and Grassi C: Extremely low-frequency electromagnetic
fields promote in vitro neurogenesis via upregulation of
Ca(v)1-channel activity. J Cell Physiol. 215:129–139. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
173
|
Cecchetto C, Maschietto M, Boccaccio P and
Vassanelli S: Electromagnetic field affects the voltage-dependent
potassium channel Kv1.3. Electromagn Biol Med. 39:316–322. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Zheng Y, Xia P, Dong L, Tian L and Xiong
C: Effects of modulation on sodium and potassium channel currents
by extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields stimulation on
hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. Electromagn Biol Med. 40:274–285.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Batcioglu K, Uyumlu AB, Satilmis B,
Yildirim B, Yucel N, Demirtas H, Onkal R, Guzel RM and Djamgoz MB:
Oxidative stress in the in vivo DMBA rat model of breast cancer:
Suppression by a voltage-gated sodium channel inhibitor (RS100642).
Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 111:137–141. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Ramírez A, Vázquez-Sánchez AY,
Carrión-Robalino N and Camacho J: Ion channels and oxidative stress
as a potential link for the diagnosis or treatment of liver
diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:39287142016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
O'Hare Doig RL, Chiha W, Giacci MK, Yates
NJ, Bartlett CA, Smith NM, Hodgetts SI, Harvey AR and Fitzgerald M:
Specific ion channels contribute to key elements of pathology
during secondary degeneration following neurotrauma. BMC Neurosci.
18:622017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Akbarali HI: Oxidative stress and ion
channels. Systems Biology of Free Radicals and Antioxidants. Lahers
I: Springer; Berlin, Heidelberg: pp. 355–373. 2014, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
179
|
Kourie JI: Interaction of reactive oxygen
species with ion transport mechanisms. Am J Physiol. 275:C1–C24.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Lushchak VI: Free radicals, reactive
oxygen species, oxidative stress and its classification. Chem Biol
Interact. 224:164–175. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Pacher P, Beckman JS and Liaudet L: Nitric
oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol Rev.
87:315–424. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MT,
Mazur M and Telser J: Free radicals and antioxidants in normal
physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
39:44–84. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
183
|
Halliwell B: Biochemistry of oxidative
stress. Biochem Soc Trans. 35:1147–1150. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Balasubramanian B, Pogozelski WK and
Tullius TD: DNA strand breaking by the hydroxyl radical is governed
by the accessible surface areas of the hydrogen atoms of the DNA
backbone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:9738–9743. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Cadet J, Delatour T, Douki T, Gasparutto
D, Pouget JP, Ravanat JL and Sauvaigo S: Hydroxyl radicals and DNA
base damage. Mutat Res. 1424:9–21. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
186
|
Cadet J and Wagner JR: DNA base damage by
reactive oxygen species, oxidizing agents, and UV radiation. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 5:a0125592013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Tsunoda M, Sakaue T, Naito S, Sunami T,
Abe N, Ueno Y, Matsuda A and Takénaka A: Insights into the
structures of DNA damaged by hydroxyl radical: Crystal structures
of DNA duplexes containing 5-formyluracil. J Nucleic Acids.
2010:1072892010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Cooke MS, Evans MD, Dizdaroglu M and Lunec
J: Oxidative DNA damage: Mechanisms, mutation, and disease. FASEB
J. 17:1195–1214. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Barzilai A and Yamamoto K: DNA damage
responses to oxidative stress. DNA Repair (Amst). 3:1109–1115.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
190
|
Pall ML: Electromagnetic fields act via
activation of voltage-gated calcium channels to produce beneficial
or adverse effects. J Cell Mol Med. 17:958–965. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Liburdy RP: Calcium signaling in
lymphocytes and ELF fields. Evidence for an electric field metric
and a site of interaction involving the calcium ion channel. FEBS
Lett. 301:53–59. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Walleczek J: Electromagnetic field effects
on cells of the immune system: The role of calcium signaling. FASEB
J. 6:3177–3185. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Brookes PS, Yoon Y, Robotham JL, Anders MW
and Sheu SS: Calcium, ATP, and ROS: A mitochondrial love-hate
triangle. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 287:C817–C833. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Lang F, Föller M, Lang KS, Lang PA, Ritter
M, Gulbins E, Vereninov A and Huber SM: Ion channels in cell
proliferation and apoptotic cell death. J Membr Biol. 205:147–157.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Görlach A, Bertram K, Hudecova S and
Krizanova O: Calcium and ROS: A mutual interplay. Redox Biol.
6:260–271. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Lombardi AA, Gibb AA, Arif E, Kolmetzky
DW, Tomar D, Luongo TS, Jadiya P, Murray EK, Lorkiewicz PK,
Hajnóczky G, et al: Mitochondrial calcium exchange links metabolism
with the epigenome to control cellular differentiation. Nat Commun.
10:45092019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Lowe SW and Lin AW: Apoptosis in cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 21:485–495. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Ikwegbue PC, Masamba P, Oyinloye BE and
Kappo AP: Roles of heat shock proteins in apoptosis, oxidative
stress, human inflammatory diseases, and cancer. Pharmaceuticals
(Basel). 11:22017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
199
|
Becchetti A: Ion channels and transporters
in cancer. 1. Ion channels and cell proliferation in cancer. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 301:C255–C265. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Gaasch JA, Geldenhuys WJ, Lockman PR,
Allen DD and Van der Schyf CJ: Voltage-gated calcium channels
provide an alternate route for iron uptake in neuronal cell
cultures. Neurochem Res. 32:1686–1693. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Chattipakorn N, Kumfu S, Fucharoen S and
Chattipakorn S: Calcium channels and iron uptake into the heart.
World J Cardiol. 3:215–218. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Salsbury G, Cambridge EL, McIntyre Z,
Arends MJ, Karp NA, Isherwood C, Shannon C, Hooks Y; Sanger Mouse
Genetics Project; Ramirez-Solis R, et al: Disruption of the
potassium channel regulatory subunit KCNE2 causes iron-deficient
anemia. Exp Hematol. 42:1053–1058.e1. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
203
|
Gamaley I, Augsten K and Berg H:
Electrostimulation of macrophage NADPH oxidase by modulated
high-frequency electromagnetic fields. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg.
38:415–418. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
204
|
Panday A, Sahoo MK, Osorio D and Batra S:
NADPH oxidases: An overview from structure to innate
immunity-associated pathologies. Cell Mol Immunol. 12:5–23. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
205
|
Henderson LM: NADPH oxidase subunit
gp91phox: A proton pathway. Protoplasma. 217:37–42. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Musset B, Cherny VV, Morgan D and
DeCoursey TE: The intimate and mysterious relationship between
proton channels and NADPH oxidase. FEBS Lett. 583:7–12. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
207
|
DeCoursey T, Morgan D and Cherny V: The
voltage dependence of NADPH oxidase reveals why phagocytes need
proton channels. Nature. 422:531–534. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Friedman J, Kraus S, Hauptman Y, Schiff Y
and Seger R: Mechanism of short-term ERK activation by
electromagnetic fields at mobile phone frequencies. Biochem J.
405:559–568. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Pratt RD, Brickman CR, Cottrill CL,
Shapiro JI and Liu J: The Na/K-ATPase signaling: from specific
ligands to general reactive oxygen species. Int J Mol Sci.
19:26002018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
210
|
Nitahara JA, Cheng W, Liu Y, Li B, Leri A,
Li P, Mogul D, Gambert SR, Kajstura J and Anversa P: Intracellular
calcium, DNase activity and myocyte apoptosis in aging Fischer 344
rats. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 30:519–535. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Fenton HJH: Oxidation of tartaric acid in
presence of iron. J Chem Soc Trans. 65:899–911. 1894. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
212
|
Bawin SM and Adey WR: Sensitivity of
calcium binding in cerebral tissue to weak environmental electric
fields oscillating at low frequency. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
73:1999–2003. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Jackson JD: Classical Electrodynamics. 2nd
edition. John Wiley & Sons, Inc; New York, NY: 1975
|
|
214
|
Barr R, Llanwyn Jones D and Rodger CJ: ELF
and VLF radio waves. J Atmos Sol-Terr Phys. 62:1689–1718. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
215
|
McLeod KJ, Lee RC and Ehrlich HP:
Frequency dependence of electric field modulation of fibroblast
protein synthesis. Science. 236:1465–1469. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Cleary SF, Liu LM, Graham R and Diegelmann
RF: Modulation of tendon fibroplasia by exogenous electric
currents. Bioelectromagnetics. 9:183–194. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Lee RC, Canaday DJ and Doong H: A review
of the biophysical basis for the clinical application of electric
fields in soft-tissue repair. J Burn Care Rehabil. 14:319–335.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Sandipan C and Baron C: Basic mechanisms
of voltage sensing. Handbook of Ion Channels. Zheng J and Trudeau
MC: CRC Press; London: pp. 25–39. 2015
|
|
219
|
Groome JR and Bayless-Edwards L: Roles for
countercharge in the voltage sensor domain of ion channels. Front
Pharmacol. 11:1602020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Shi YP, Thouta S and Claydon TW:
Modulation of hERG K+ channel deactivation by voltage
sensor relaxation. Front Pharmacol. 11:1392020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
221
|
Villalba-Galea CA and Chiem AT: Hysteretic
behavior in voltage-gated channels. Front Pharmacol. 11:5795962020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Panagopoulos DJ and Margaritis LH: The
identification of an intensity 'window' on the bioeffects of mobile
telephony radiation. Int J Radiat Biol. 86:358–366. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Panagopoulos DJ and Balmori A: On the
biophysical mechanism of sensing atmospheric discharges by living
organisms. Sci Total Environ. 599-600:2026–2034. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Liboff AR: Cyclotron resonance in membrane
transport. Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Cells.
Chiabrera A, Nicolini C and Schwan HP: Plenum Press; London: pp.
281–296. 1985
|
|
225
|
Bianco B, Chiabrera A, Morro A and Parodi
M: Effects of magnetic exposure on ions in electric fields.
Ferroelectrics. 86:159–168. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
226
|
Balcavage WX, Alvager T, Swez J, Goff CW,
Fox MT, Abdullyava S and King MW: A mechanism for action of
extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields on biological
systems. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 222:374–378. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Zhadin MN: Combined action of static and
alternating magnetic fields on ion motion in a macromolecule:
Theoretical aspects. Bioelectromagnetics. 19:279–292. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Liboff AR: Ion cyclotron resonance in
biological systems: Experimental evidence. Biological Effects of
Electromagnetic Fields. Stavroulakis P: Springer; Berlin: pp.
76–113. 2003
|
|
229
|
Lednev VV: Possible mechanism for the
influence of weak magnetic fields on biological systems.
Bioelectromagnetics. 12:71–75. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Kirschvink JL: Magnetite biomineralization
and geomagnetic sensitivity in higher animals: An update and
recommendations for future study. Bioelectromagnetics. 10:239–259.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Brocklehurst B and McLauchlan KA: Free
radical mechanism for the effects of environmental electromagnetic
fields on biological systems. Int J Radiat Biol. 69:3–24. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Sheppard AR, Swicord ML and Balzano Q:
Quantitative evaluations of mechanisms of radiofrequency
interactions with biological molecules and processes. Health Phys.
93:365–396. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
233
|
Hall EJ and Giaccia AJ: Radiobiology for
the Radiologist. 6th edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;
Philadelphia, PA: 2006
|
|
234
|
Coggle JE: Biological Effects of
Radiation. Taylor & Francis; 1983
|
|
235
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer. Cell. 100:57–70. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
236
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
237
|
Blank M and Goodman R: Electromagnetic
fields stress living cells. Pathophysiology. 16:71–78. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
238
|
Blank M and Goodman R: DNA is a fractal
antenna in electromagnetic fields. Int J Radiat Biol. 87:409–415.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|