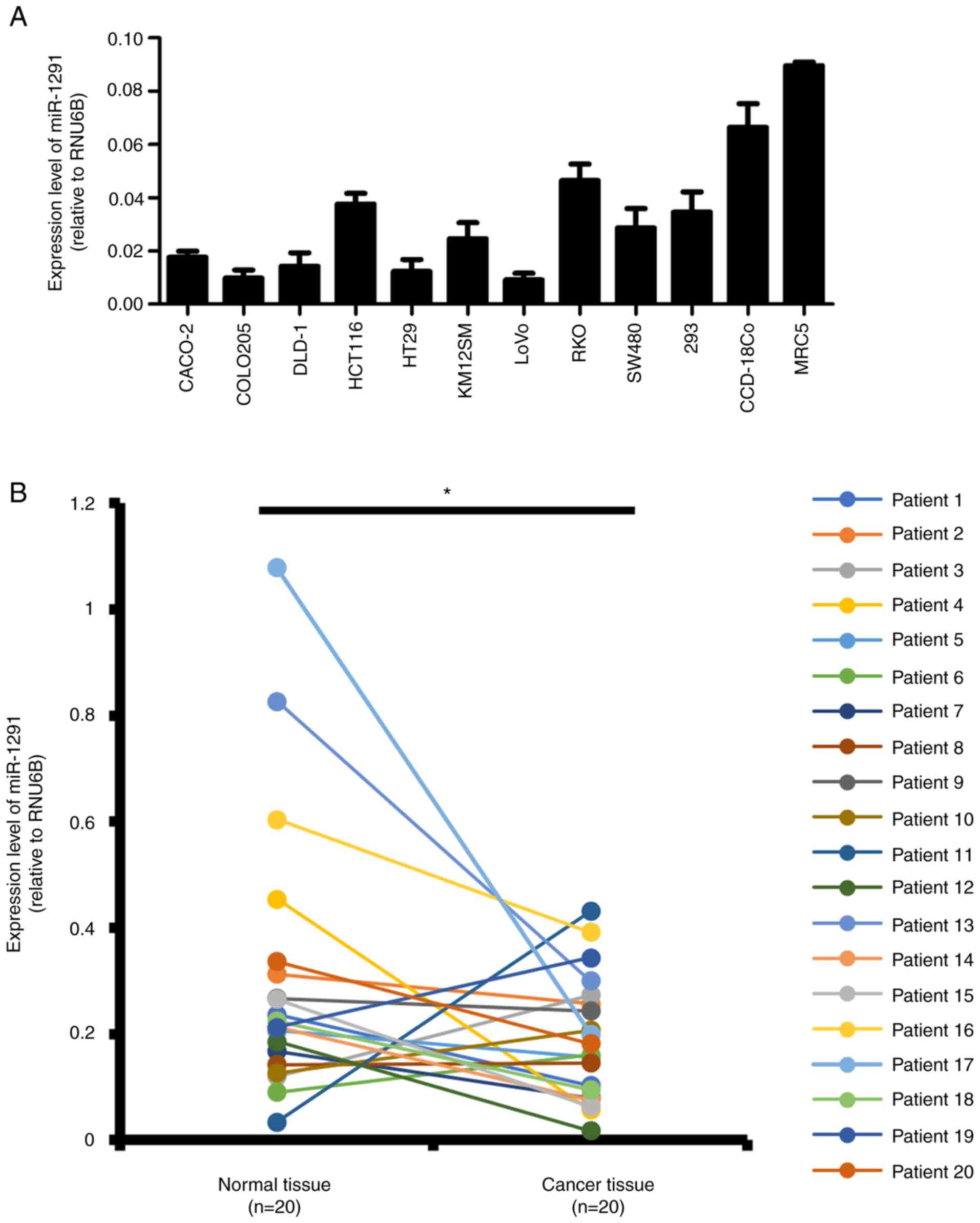
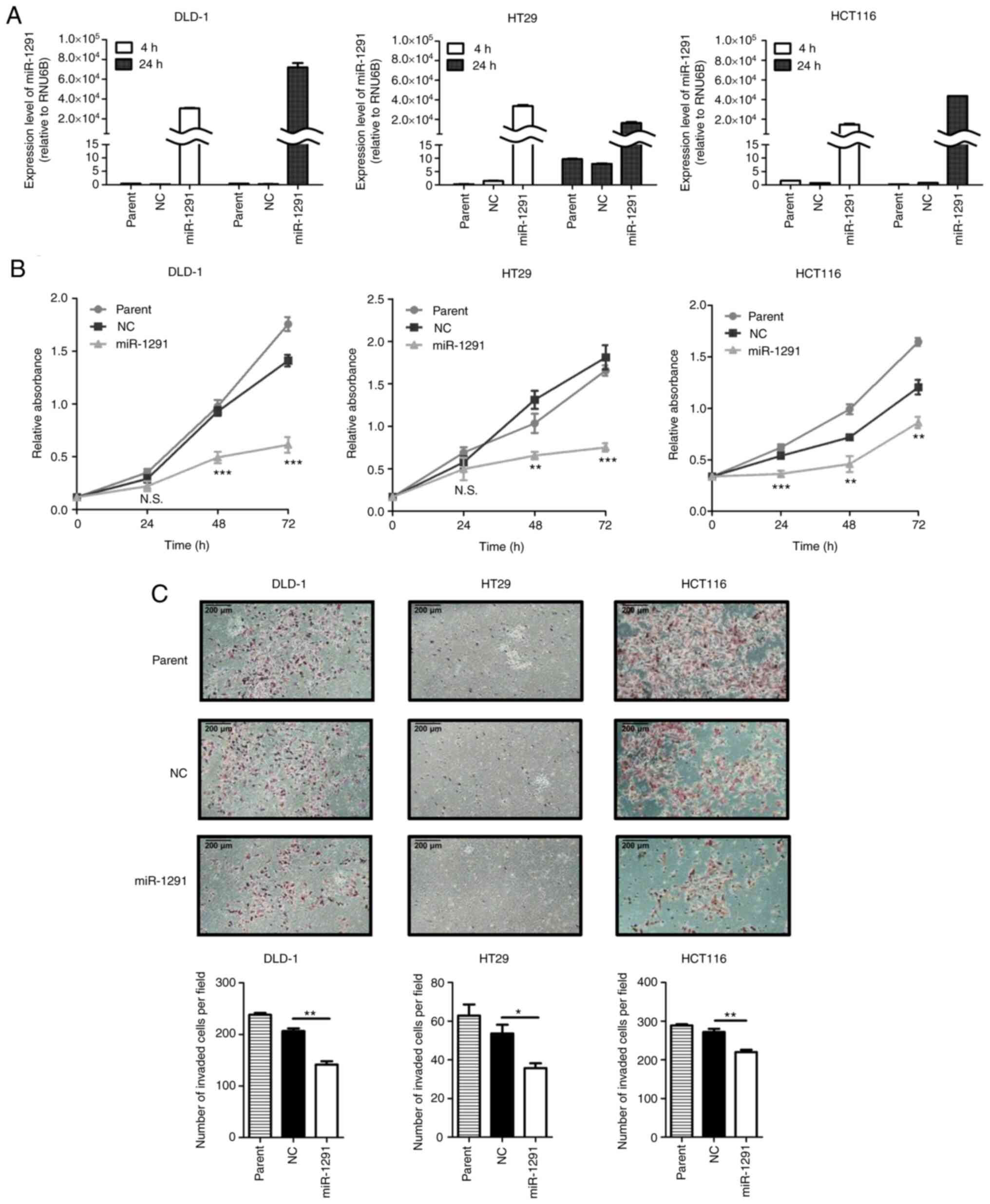
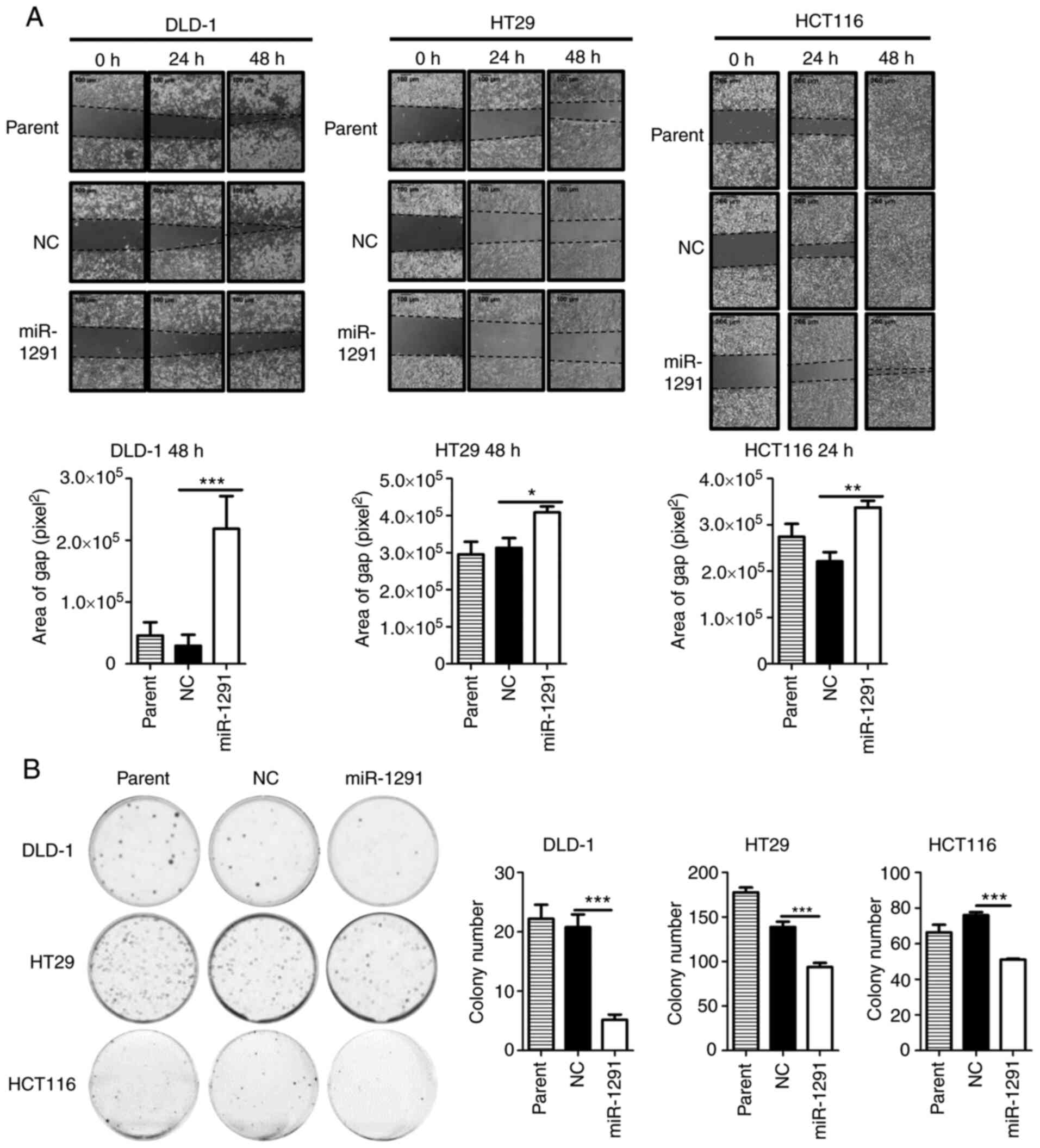
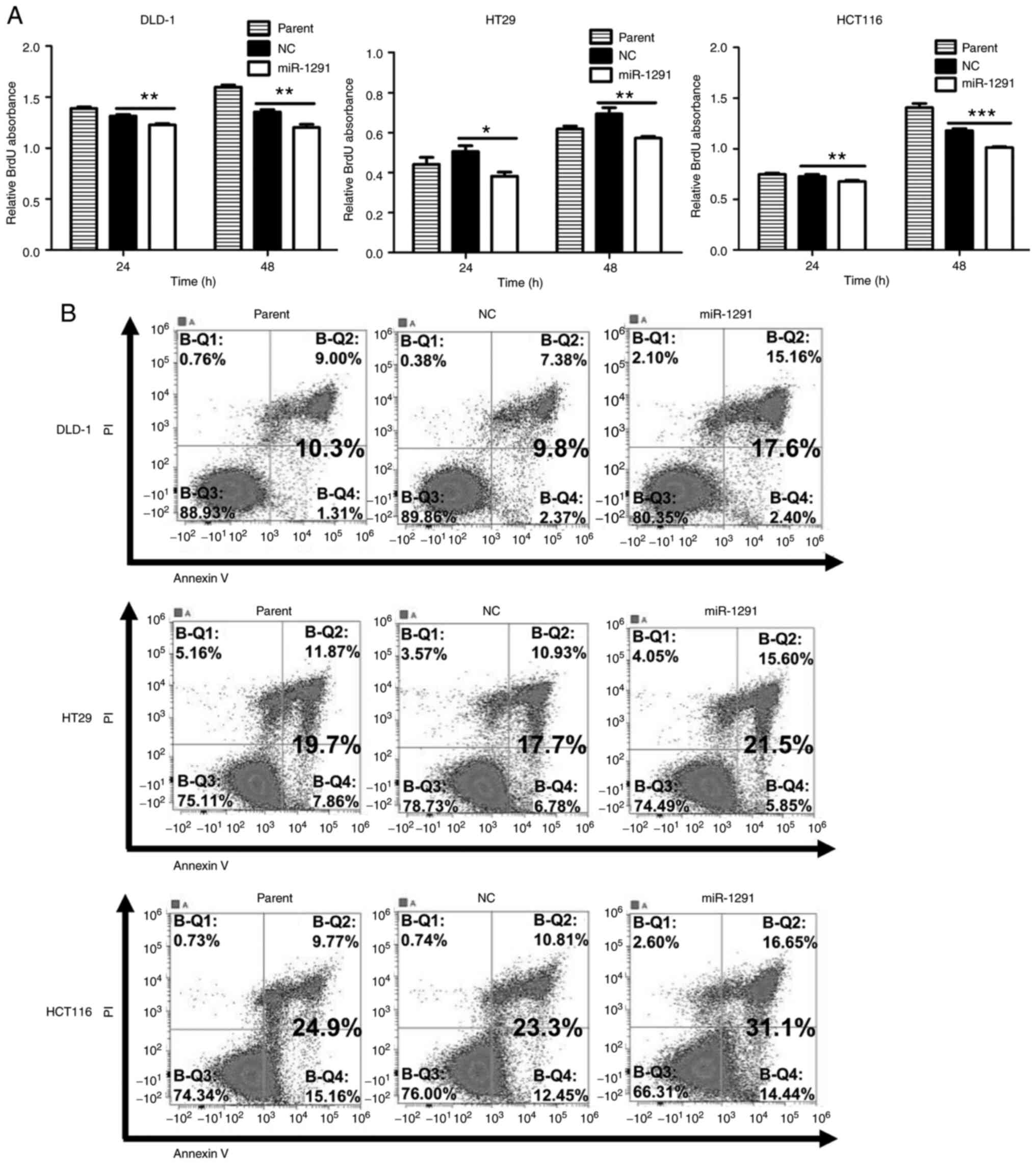
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rawla P, Sunkara T and Barsouk A:
Epidemiology of colorectal cancer: Incidence, mortality, survival,
and risk factors. Prz Gastroenterol. 14:89–103. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brenner H, Kloor M and Pox CP: Colorectal
cancer. Lancet. 383:1490–1502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Graham JS and Cassidy J: Adjuvant therapy
in colon cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 12:99–109. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Rupaimoole R and Slack FJ: MicroRNA
therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and
other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16:203–222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fischer SE: RNA Interference and
MicroRNA-mediated silencing. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. Oct 1. pp.
201Epub ahead of print 0.1002/0471142727.mb2601s112.
|
|
7
|
Mehta A and Baltimore D: MicroRNAs as
regulatory elements in immune system logic. Nat Rev Immunol.
16:279–294. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pons-Espinal M, de Luca E, Marzi MJ,
Beckervordersandforth R, Armirotti A, Nicassio F, Fabel K,
Kempermann G and De Pietri Tonelli D: Synergic functions of miRNAs
determine neuronal fate of adult neural stem cells. Stem Cell
Reports. 8:1046–1061. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Aghaei M, Khodadadian A, Elham KN, Nazari
M and Babakhanzadeh E: Major miRNA involved in insulin secretion
and production in beta-cells. Int J Gen Med. 13:89–97. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ali Syeda Z, Langden SSS, Munkhzul C, Lee
M and Song SJ: Regulatory mechanism of MicroRNA expression in
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 21:17232020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Lee YS and Dutta A: MicroRNAs in cancer.
Annu Rev Pathol. 4:199–227. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Li VS, Ng SS, Boersema PJ, Low TY,
Karthaus WR, Gerlach JP, Mohammed S, Heck AJ, Maurice MM, Mahmoudi
T and Clevers H: Wnt signaling through inhibition of β-catenin
degradation in an intact Axin1 complex. Cell. 149:1245–1256. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Spano JP, Lagorce C, Atlan D, Milano G,
Domont J, Benamouzig R, Attar A, Benichou J, Martin A, Morere JF,
et al: Impact of EGFR expression on colorectal cancer patient
prognosis and survival. Ann Oncol. 16:102–108. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Markowitz S, Wang J, Myeroff L, Parsons R,
Sun L, Lutterbaugh J, Fan RS, Zborowska E, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein
B, et al: Inactivation of the type II TGF-beta receptor in colon
cancer cells with microsatellite instability. Science.
268:1336–1338. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Baker SJ, Fearon ER, Nigro JM, Hamilton
SR, Preisinger AC, Jessup JM, vanTuinen P, Ledbetter DH, Barker DF,
Nakamura Y, et al: Chromosome 17 deletions and p53 gene mutations
in colorectal carcinomas. Science. 244:217–221. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelialmesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hiraki M, Nishimura J, Takahashi H, Wu X,
Takahashi Y, Miyo M, Nishida N, Uemura M, Hata T, Takemasa I, et
al: Concurrent Targeting of KRAS and AKT by MiR-4689 is a novel
treatment against mutant KRAS Colorectal cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic
Acids. 4:e2312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Inoue A, Mizushima T, Wu X, Okuzaki D,
Kambara N, Ishikawa S, Wang J, Qian Y, Hirose H, Yokoyama Y, et al:
miR-29b byproduct sequence exhibits potent tumour-suppressive
activities via inhibition of NF-κB signaling in KRAS-mutant colon
cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 17:977–987. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tazawa H, Tsuchiya N, Izumiya M and
Nakagama H: Tumor-suppressive miR-34a induces senescence-like
growth arrest through modulation of the E2F pathway in human colon
cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:15472–15477. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Morimoto Y, Mizushima T, Wu X, Okuzaki D,
Yokoyama Y, Inoue A, Hata T, Hirose H, Qian Y, Wang J, et al:
miR-4711-5p regulates cancer stemness and cell cycle progression
via KLF5, MDM2 and TFDP1 in colon cancer cells. Br J Cancer.
122:1037–1049. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ayob AZ and Ramasamy TS: Cancer stem cells
as key drivers of tumour progression. J Biomed Sci. 25:202018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao J: Cancer stem cells and
chemoresistance: The smartest survives the raid. Pharmacol Ther.
160:145–58. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
de Sousa e Melo F, Kurtova AV, Harnoss JM,
Kljavin N, Hoeck JD, Hung J, Anderson JE, Storm EE, Modrusan Z,
Koeppen H, et al: A distinct role for Lgr5+ stem cells
in primary and metastatic colon cancer. Nature. 543:676–680. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vermeulen L, Todaro M, de Sousa Mello F,
Sprick MR, Kemper K, Perez Alea M, Richel DJ, Stassi G and Medema
JP: Single-cell cloning of colon cancer stem cells reveals a
multi-lineage differentiation capacity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:13427–1332. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ren F, Sheng WQ and Du X: CD133: A cancer
stem cells Marker, is used in colorectal cancers. World J
Gastroenterol. 19:2603–2611. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Soheilifar MH, Moshtaghian A, Maadi H,
Izadi F and Saidijam M: BMI1 roles in cancer stem cells and its
association with MicroRNAs dysregulation in cancer: Emphasis on
colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer Manag. 11:92018.
|
|
27
|
Nakanishi Y, Seno H, Fukuoka A, Ueo T,
Yamaga Y, Maruno T, Nakanishi N, Kanda K, Komekado H, Kawada M, et
al: Dclk1 distinguishes between tumor and normal stem cells in the
intestine. Nat Genet. 45:98–103. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Chandrakesan P, Weygant N, May R, Qu D,
Chinthalapally HR, Sureban SM, Ali N, Lightfoot SA, Umar S and
Houchen CW: DCLK1 facilitates intestinal tumor growth via enhancing
pluripotency and epithelial mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget.
5:9269–9280. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Makino S, Takahashi H, Okuzaki D, Miyoshi
N, Haraguchi N, Hata T, Matsuda C, Yamamoto H, Mizushima T, Mori M,
et al: DCLK1 integrates induction of TRIB3, EMT, drug resistance
and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis.
41:303–312. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Westphalen CB, Takemoto Y, Tanaka T,
Macchini M, Jiang Z, Renz BW, Chen X, Ormanns S, Nagar K, Tailor Y,
et al: Dclk1 defines quiescent pancreatic progenitors that promote
injury-induced regeneration and tumorigenesis. Cell Stem Cell.
18:441–455. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Weygant N, Qu D, May R, Tierney RM, Berry
WL, Zhao L, Agarwal S, Chandrakesan P, Chinthalapally HR, Murphy
NT, et al: DCLK1 is a broadly dysregulated target against
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, focal adhesion, and stemness in
clear cell renal carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:2193–2205. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Adikrisna R, Tanaka S, Muramatsu S, Aihara
A, Ban D, Ochiai T, Irie T, Kudo A, Nakamura N, Yamaoka S and Arii
S: Identification of pancreatic cancer stem cells and selective
toxicity of chemotherapeutic agents. Gastroenterology.
143:234–245.e7. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Munakata K, Uemura M, Tanaka S, Kawai K,
Kitahara T, Miyo M, Kano Y, Nishikawa S, Fukusumi T, Takahashi Y,
et al: Cancer stem-like properties in colorectal cancer cells with
low proteasome activity. Clin Cancer Res. 22:5277–5286. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Qian Y, Wu X, Yokoyama Y, Okuzaki D,
Taguchi M, Hirose H, Wang J, Hata T, Inoue A, Hiraki M, et al:
E-cadherin-Fc chimera protein matrix enhances cancer stem-like
properties and induces mesenchymal features in colon cancer cells.
Cancer Sci. 110:3520–3532. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pan YZ, Zhou A, Hu Z and Yu AM: Small
nucleolar RNA-derived microRNA hsa-miR-1291 modulates cellular drug
disposition through direct targeting of ABC transporter ABCC1. Drug
Metab Dispos. 41:1744–1751. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Peng L, Chun-Guang Q, Bei-Fang L, Xue-Zhi
D, Zi-Hao W, Yun-Fu L, Yan-Ping D, Yang-Gui L, Wei-Guo L, Tian-Yong
H and Zhen-Wen H: Clinical impact of circulating miR-133, miR-1291
and miR-663b in plasma of patients with acute myocardial
infarction. Diagn Pathol. 9:892014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Qiu L, Zhang L, Qi R, Gao X, Chen H and
Xiao T: miR-1291 Functions as a potential serum biomarker for
bullous pemphigoid. Dis Markers. 2020:95053122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen Z, Wang X, Li L, Han M, Wang M, Li Z,
Xie X, Du H, Xie Z and Zhang H: Construction of an autophagy
interaction network based on competitive endogenous RNA reveals the
key pathways and central genes of SARS-CoV-2 infection in vivo.
Microb Pathog. 158:1050512021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hagag NA, Ali YB, Elsharawy AA and Talaat
RM: Clinical impact of circulated miR-1291 in plasma of patients
with liver cirrhosis (LC) and Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC):
Implication on Glypican-3 Expression. J Gastrointest Cancer.
51:234–241. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Maurel M, Dejeans N, Taouji S, Chevet E
and Grosset CF: MicroRNA-1291-mediated silencing of IRE1alpha
enhances Glypican-3 expression. RNA. 19:778–788. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tu MJ, Duan Z, Liu Z, Zhang C, Bold RJ,
Gonzalez FJ, Kim EJ and Yu AM: MicroRNA-1291-5p sensitizes
pancreatic carcinoma cells to arginine deprivation and chemotherapy
through the regulation of arginolysis and glycolysis. Mol
Pharmacol. 98:686–694. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tu MJ, Ho PY, Zhang QY, Jian C, Qiu JX,
Kim EJ, Bold RJ, Gonzalez FJ, Bi H and Yu AM: Bioengineered
miRNA-1291 prodrug therapy in pancreatic cancer cells and
patient-derived xenograft mouse models. Cancer Lett. 442:82–90.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Tu MJ, Pan YZ, Qiu JX, Kim EJ and Yu AM:
MicroRNA-1291 targets the FOXA2-AGR2 pathway to suppress pancreatic
cancer cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. Oncotarget.
7:45547–45561. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yamasaki T, Seki N, Yoshino H, Itesako T,
Yamada Y, Tatarano S, Hidaka H, Yonezawa T, Nakagawa M and Enokida
H: Tumor-suppressive microRNA-1291 directly regulates glucose
transporter 1 in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 104:1411–149.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Luo H, Guo W, Wang F, You Y, Wang J, Chen
X, Wang J, Wang Y, Du Y, Chen X, et al: miR-1291 targets mucin 1
inhibiting cell proliferation and invasion to promote cell
apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep.
34:2665–2673. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cai Q, Zhao A, Ren L, Chen J, Liao K, Wang
Z and Zhang W: MicroRNA-1291 mediates cell proliferation and
tumorigenesis by downregulating MED1 in prostate cancer. Oncol
Lett. 17:3253–3260. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Salehi Z, Hadadi P and Tavallaei O:
Prediction of biomarker miRNAs signature in colorectal cancer
metastasis to liver cancer. Electron J Gen Med. 16:em1002019.
|
|
48
|
Morikawa K, Walker SM, Nakajima M, Pathak
S, Jessup JM and Fidler IJ: Influence of organ environment on the
growth, selection, and metastasis of human colon carcinoma cells in
nude mice. Cancer Res. 48:6863–6871. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Jin H, Li XJ, Park MH and Kim SM:
FOXM1-mediated downregulation of uPA and MMP9 by
3,3′-diindolylmethane inhibits migration and invasion of human
colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 33:3171–3177. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Jung H, Kim HS, Lee JH, Lee JJ and Park
HS: Wound healing promoting activity of tonsil-derived stem cells
on 5-Fluorouracil-Induced oral mucositis model. Tissue Eng Regen
Med. 17:105–119. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wu X, Yamamoto H, Nakanishi H, Yamamoto Y,
Inoue A, Tei M, Hirose H, Uemura M, Nishimura J, Hata T, et al:
Innovative delivery of siRNA to solid tumors by super carbonate
apatite. PLoS One. 10:e01160222015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ogawa H, Wu X, Kawamoto K, Nishida N,
Konno M, Koseki J, Matsui H, Noguchi K, Gotoh N, Yamamoto T, et al:
MicroRNAs induce epigenetic reprogramming and suppress malignant
phenotypes of human colon cancer cells. PLoS One. 10:e01271192015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Takeyama H, Yamamoto H, Yamashita S, Wu X,
Takahashi H, Nishimura J, Haraguchi N, Miyake Y, Suzuki R, Murata
K, et al: Decreased miR-340 expression in bone marrow is associated
with liver metastasis of colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer Ther.
13:976–985. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Fukata T, Mizushima T, Nishimura J,
Okuzaki D, Wu X, Hirose H, Yokoyama Y, Kubota Y, Nagata K,
Tsujimura N, et al: The Supercarbonate Apatite-MicroRNA complex
inhibits dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. Mol Ther Nucleic
Acids. 12:658–671. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
SCJ (Science Council of Japan): Guidelines
for Proper Conduct of Animal Experiments. 2006.
|
|
57
|
UCI Office of Research: Euthanasia of
Research Animals. Assessment Criteria for Confirmation of Death.
2014.
|
|
58
|
Mogavero A, Maiorana MV, Zanutto S,
Varinelli L, Bozzi F, Belfiore A, Volpi CC, Gloghini A, Pierotti MA
and Gariboldi M: Metformin transiently inhibits colorectal cancer
cell proliferation as a result of either AMPK activation or
increased ROS production. Sci Rep. 7:159922017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Gharib E, Nasri Nasrabadi P and Reza Zali
M: miR-497-5p mediates starvation-induced death in colon cancer
cells by targeting acyl-CoA synthetase-5 and modulation of lipid
metabolism. J Cell Physiol. 235:5570–5589. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zou P, Zhu M, Lian C, Wang J, Chen Z,
Zhang X, Yang Y, Chen X, Cui X and Liu J: miR-192-5p suppresses the
progression of lung cancer bone metastasis by targeting TRIM44. Sci
Rep. 9:196192019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Weng J, Zhang H, Wang C, Liang J, Chen G,
Li W, Tang H and Hou J: miR-373-3p targets DKK1 to promote
EMT-Induced metastasis via the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway in tongue
squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed Res Int. 2017:60109262017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Forterre A, Komuro H, Aminova S and Harada
M: A Comprehensive review of cancer MicroRNA therapeutic delivery
strategies. Cancers (Basel). 12:18522020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Abd-Aziz N, Kamaruzman NI and Poh CL:
Development of MicroRNAs as Potential Therapeutics against Cancer.
J Oncol. 2020:80297212020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Merhautova J, Demlova R and Slaby O:
MicroRNA-Based therapy in animal models of selected
gastrointestinal cancers. Front Pharmacol. 7:3292016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Takahashi RU, Prieto-Vila M, Kohama I and
Ochiya T: Development of miRNA-based therapeutic approaches for
cancer patients. Cancer Sci. 110:1140–1147. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Sadanandam A, Lyssiotis CA, Homicsko K,
Collisson EA, Gibb WJ, Wullschleger S, Ostos LC, Lannon WA,
Grotzinger C, Del Rio M, et al: A colorectal cancer classification
system that associates cellular phenotype and responses to therapy.
Nat Med. 19:619–625. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Yeung TM, Gandhi SC, Wilding JL, Muschel R
and Bodmer WF: Cancer stem cells from colorectal cancer-derived
cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:3722–3727. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Chen KL, Pan F, Jiang H, Chen JF, Pei L,
Xie FW and Liang HJ: Highly enriched CD133(+)CD44(+) stem-like
cells with CD133(+) CD44(high) metastatic subset in HCT116 colon
cancer cells. Clin Exp Metastasis. 28:751–763. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Dexter DL, Barbosa JA and Calabresi P: N,
N-dimethylformamide-induced alteration of cell culture
characteristics and loss of tumorigenicity in cultured human colon
carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 39:1020–1025. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Miyamoto M, Sawada K, Nakamura K,
Yoshimura A, Ishida K, Kobayashi M, Shimizu A, Yamamoto M, Kodama
M, Hashimoto K and Kimura T: Paclitaxel exposure downregulates
miR-522 expression and its downregulation induces paclitaxel
resistance in ovarian cancer cells. Sci Rep. 10:167552020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Seki Y, Yamamoto H, Ngan CY, Yasui M,
Tomita N, Kitani K, Takemasa I, Ikeda M, Sekimoto M, Matsuura N, et
al: Construction of a novel DNA decoy that inhibits the oncogenic
beta-catenin/T-cell factor pathway. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:985–994.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
O'Connell MR, Sarkar S, Luthra GK, Okugawa
Y, Toiyama Y, Gajjar AH, Qiu S, Goel A and Singh P: Epigenetic
changes and alternate promoter usage by human colon cancers for
expressing DCLK1-isoforms: Clinical implications. Sci Rep.
5:149832015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Sarkar S, O'Connell MR, Okugawa Y, Lee BS,
Toiyama Y, Kusunoki M, Daboval RD, Goel A and Singh P: FOXD3
Regulates CSC Marker, DCLK1-S, and invasive potential: Prognostic
implications in colon cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 15:1678–1691. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Manhas J, Bhattacharya A, Agrawal SK,
Gupta B, Das P, Deo SV, Pal S and Sen S: Characterization of cancer
stem cells from different grades of human colorectal cancer. Tumour
Biol. 37:14069–14081. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Kantara C, O'Connell M, Sarkar S, Moya S,
Ullrich R and Singh P: Curcumin promotes autophagic survival of a
subset of colon cancer stem cells, which are ablated by
DCLK1-siRNA. Cancer Res. 74:2487–2498. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Ji D, Zhan T, Li M, Yao Y, Jia J, Yi H,
Qiao M, Xia J, Zhang Z, Ding H, et al: Enhancement of sensitivity
to Chemo/Radiation therapy by using miR-15b against DCLK1 in
colorectal cancer. Stem Cell Reports. 11:1506–1522. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Abukhdeir AM and Park BH: P21 and p27:
Roles in carcinogenesis and drug resistance. Expert Rev Mol Med.
10:e192008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Slingerland J and Pagano M: Regulation of
the Cdk Inhibitor p27 and Its Deregulation in Cancer. J Cell
Physiol. 183:10–17. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
LaBaer J, Garrett MD, Stevenson LF,
Slingerland JM, Sandhu C, Chou HS, Fattaey A and Harlow E: New
functional activities for the p21 family of CDK inhibitors. Genes
Dev. 11:847–862. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Wang Y, Ji P, Liu J, Broaddus RR, Xue F
and Zhang W: Centrosome-associated regulators of the G(2)/M
checkpoint as targets for cancer therapy. Mol Cancer. 8:82009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
To KK, Tong CW, Wu M and Cho WC: MicroRNAs
in the prognosis and therapy of colorectal cancer: From bench to
bedside. World J Gastroenterol. 24:2949–2973. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Chi Y and Zhou D: MicroRNAs in colorectal
carcinoma-from pathogenesis to therapy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
35:432016. View Article : Google Scholar
|