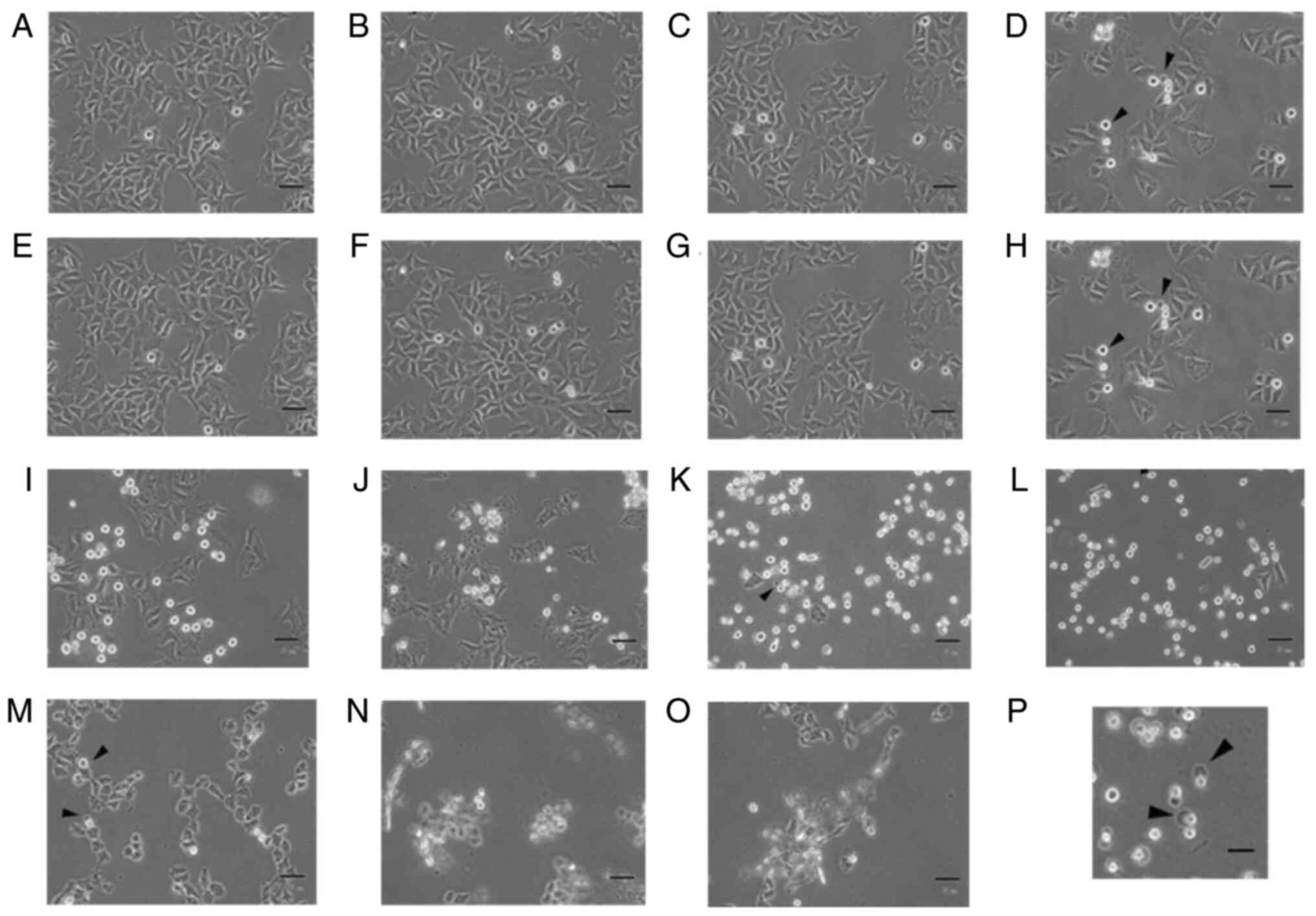
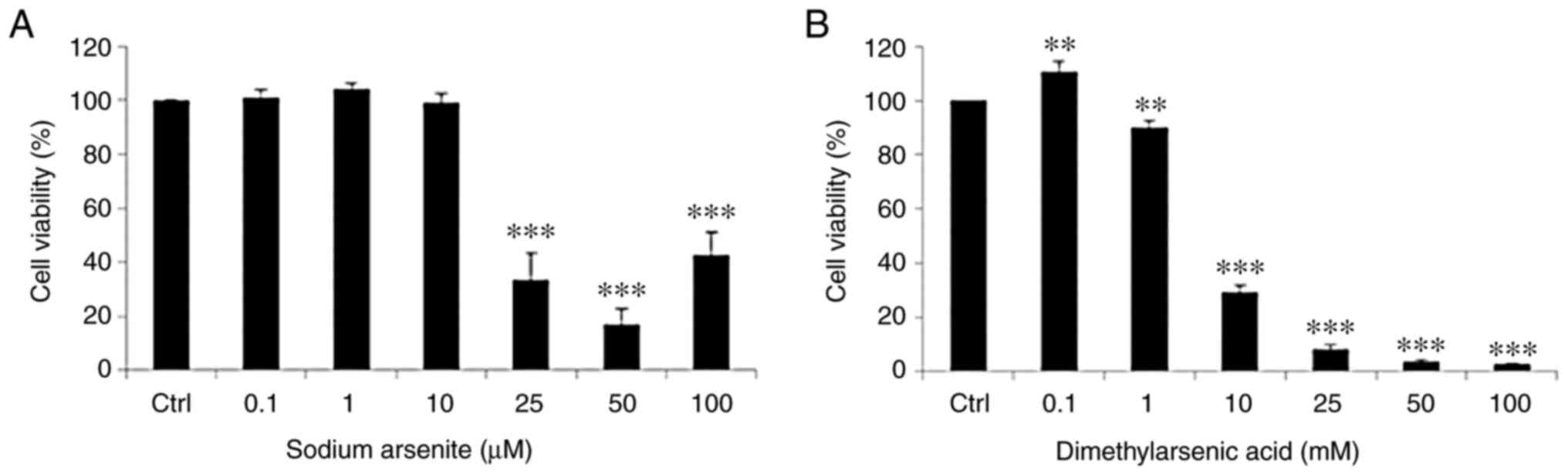
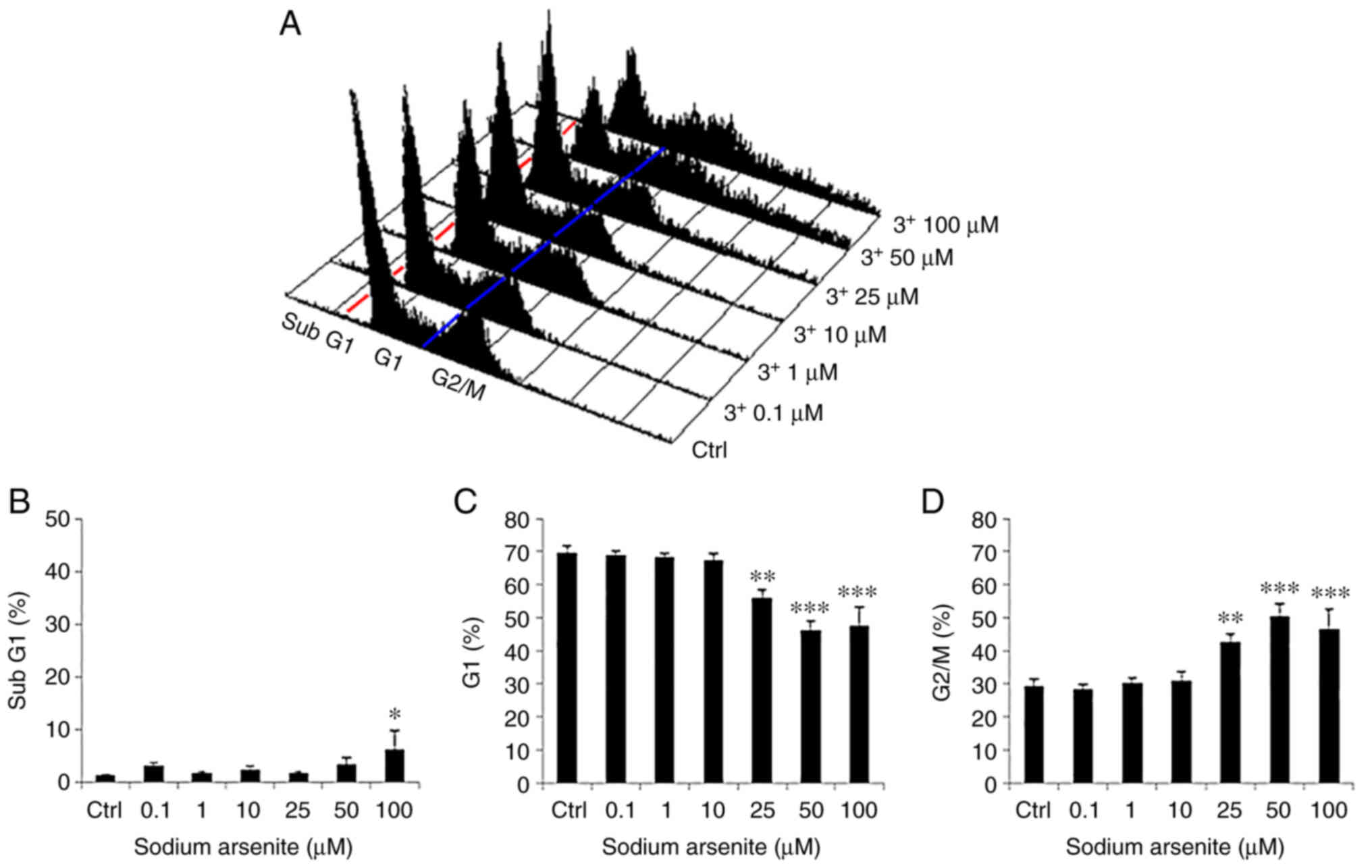
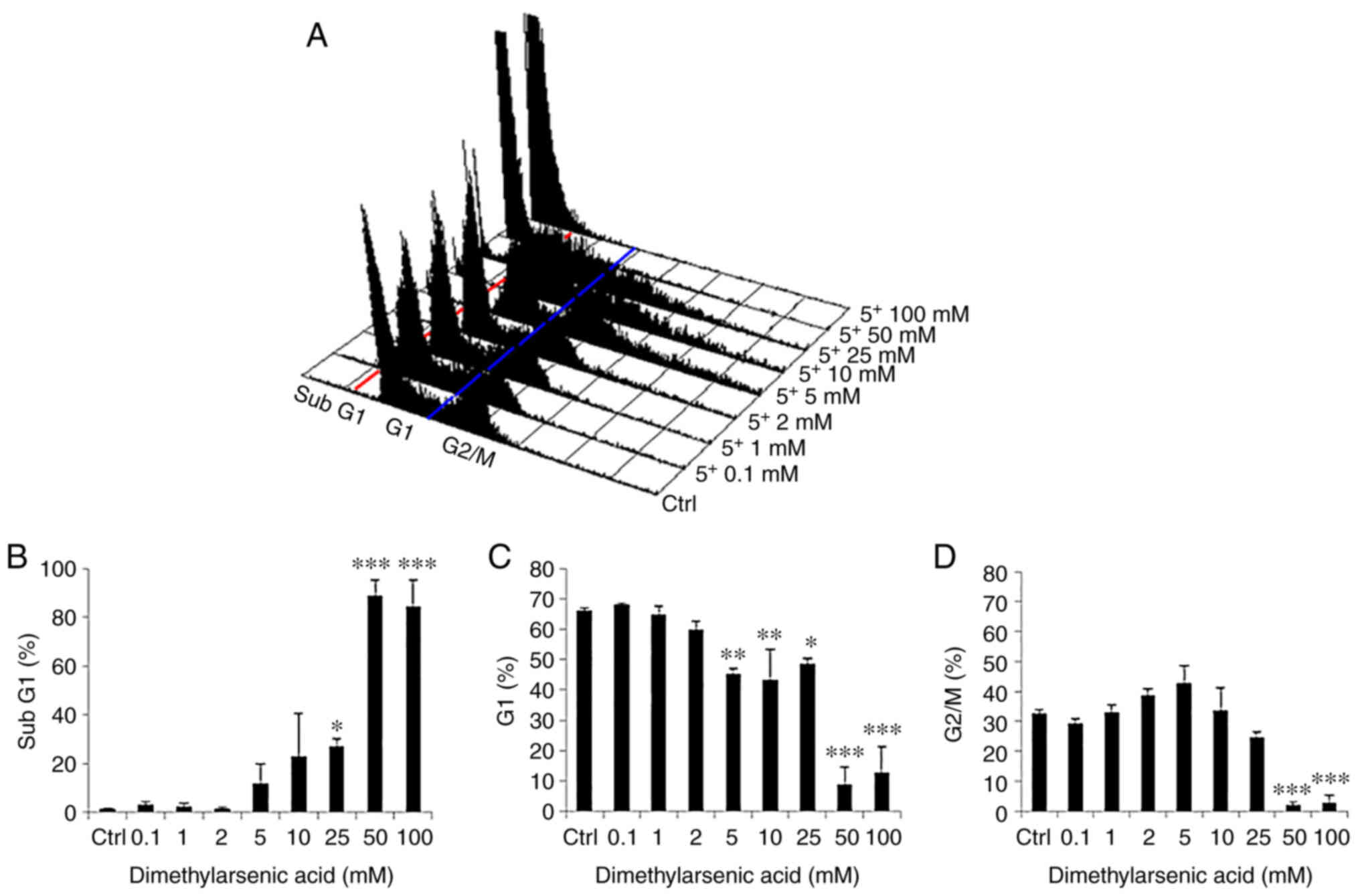
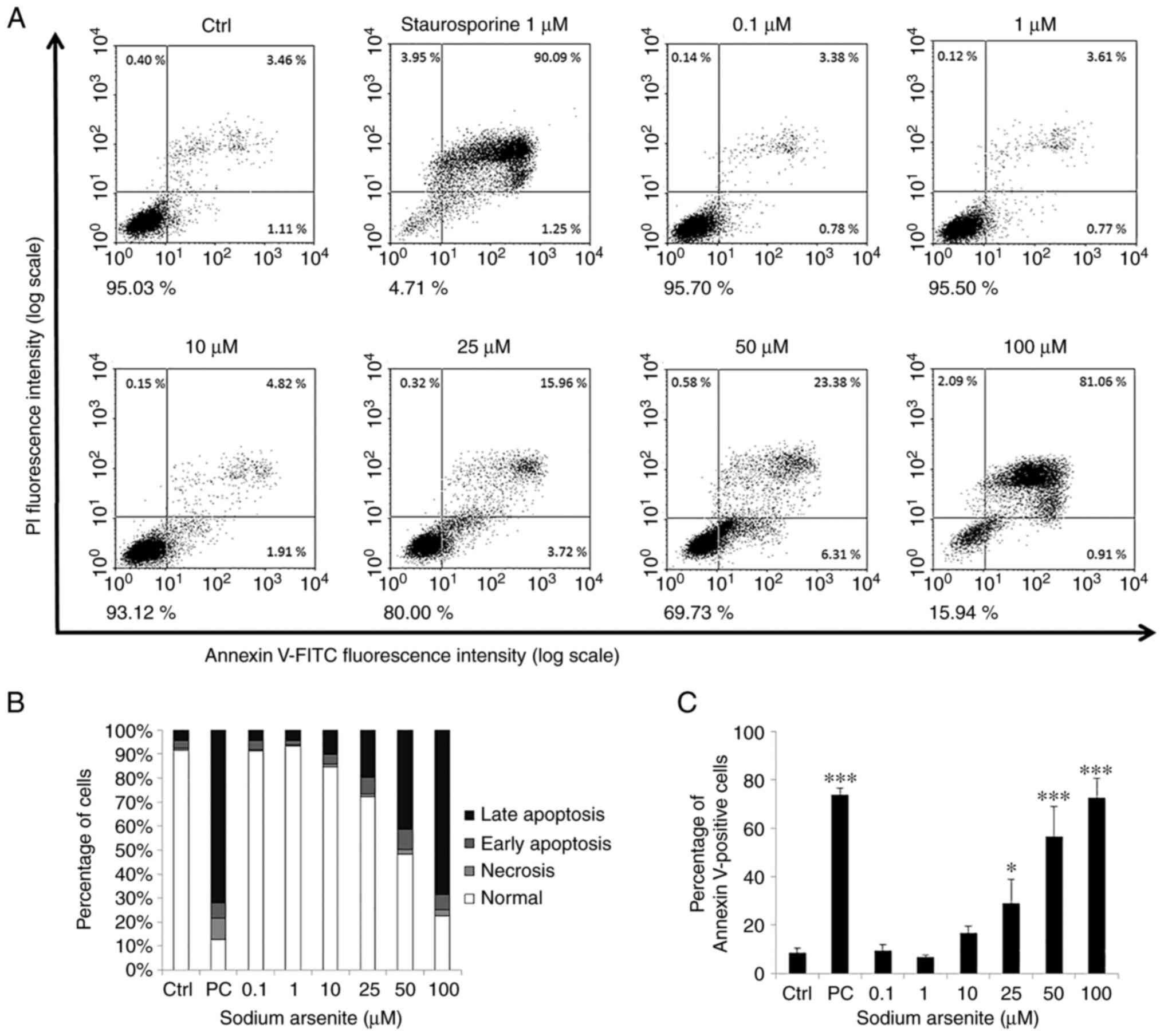
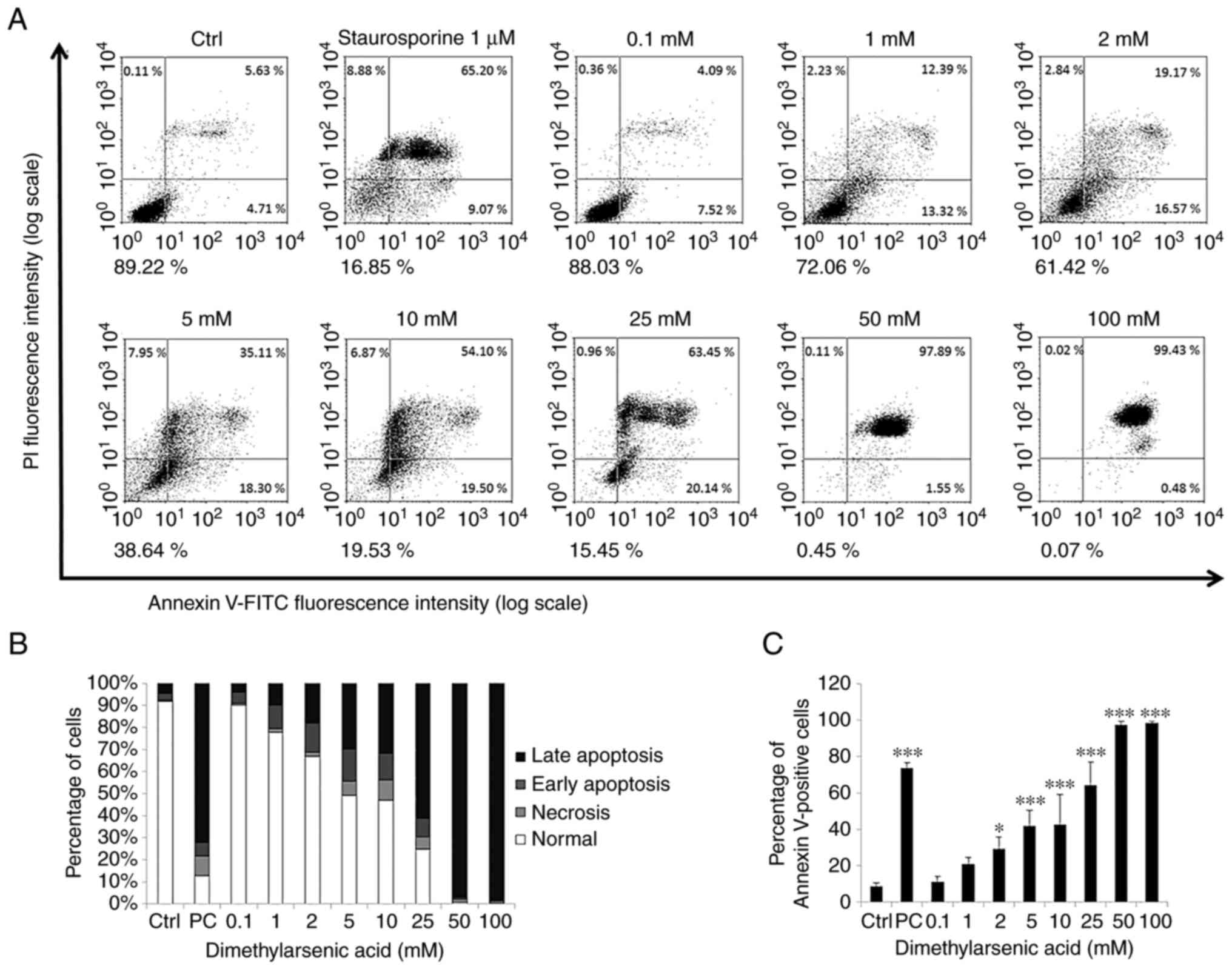
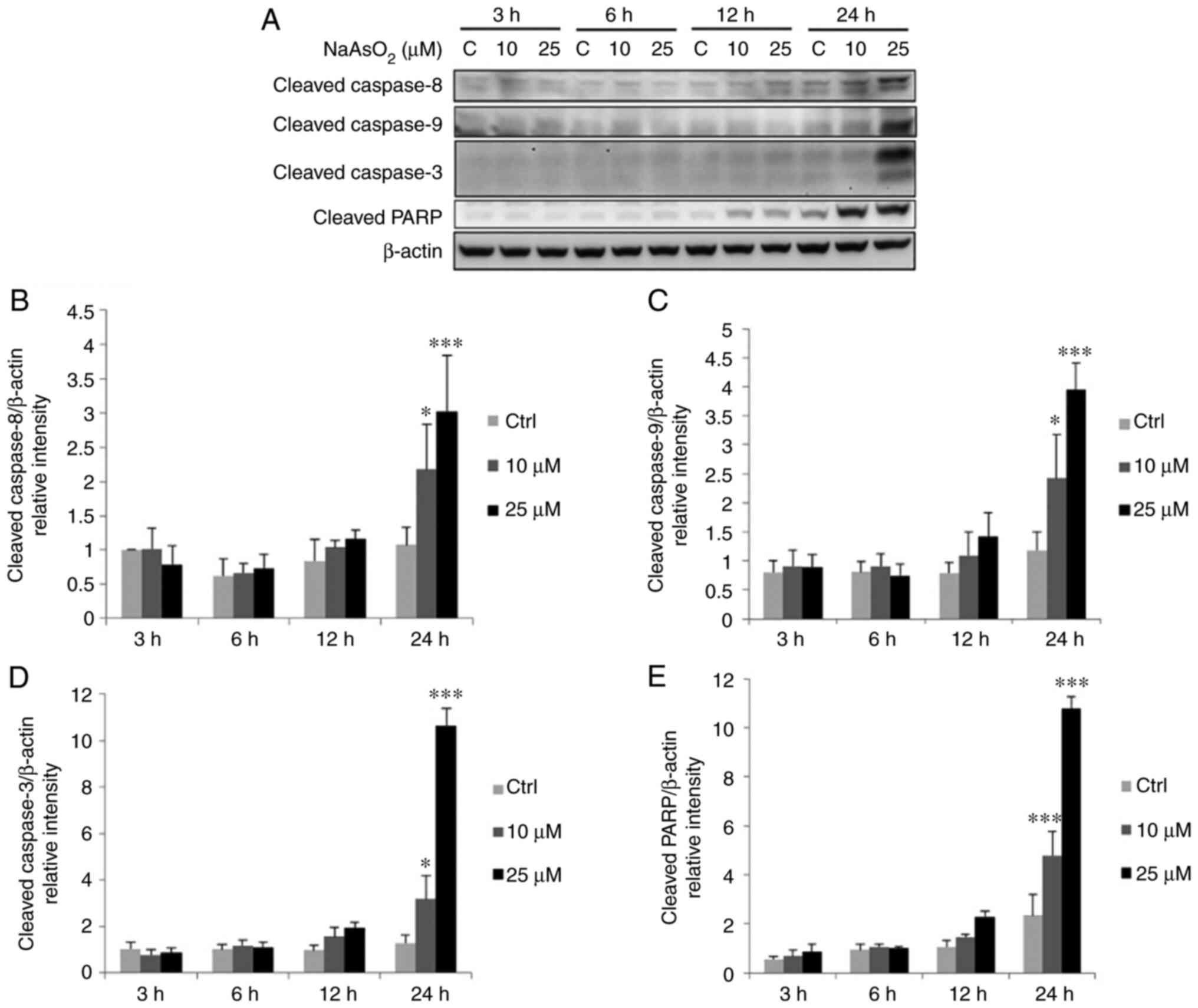
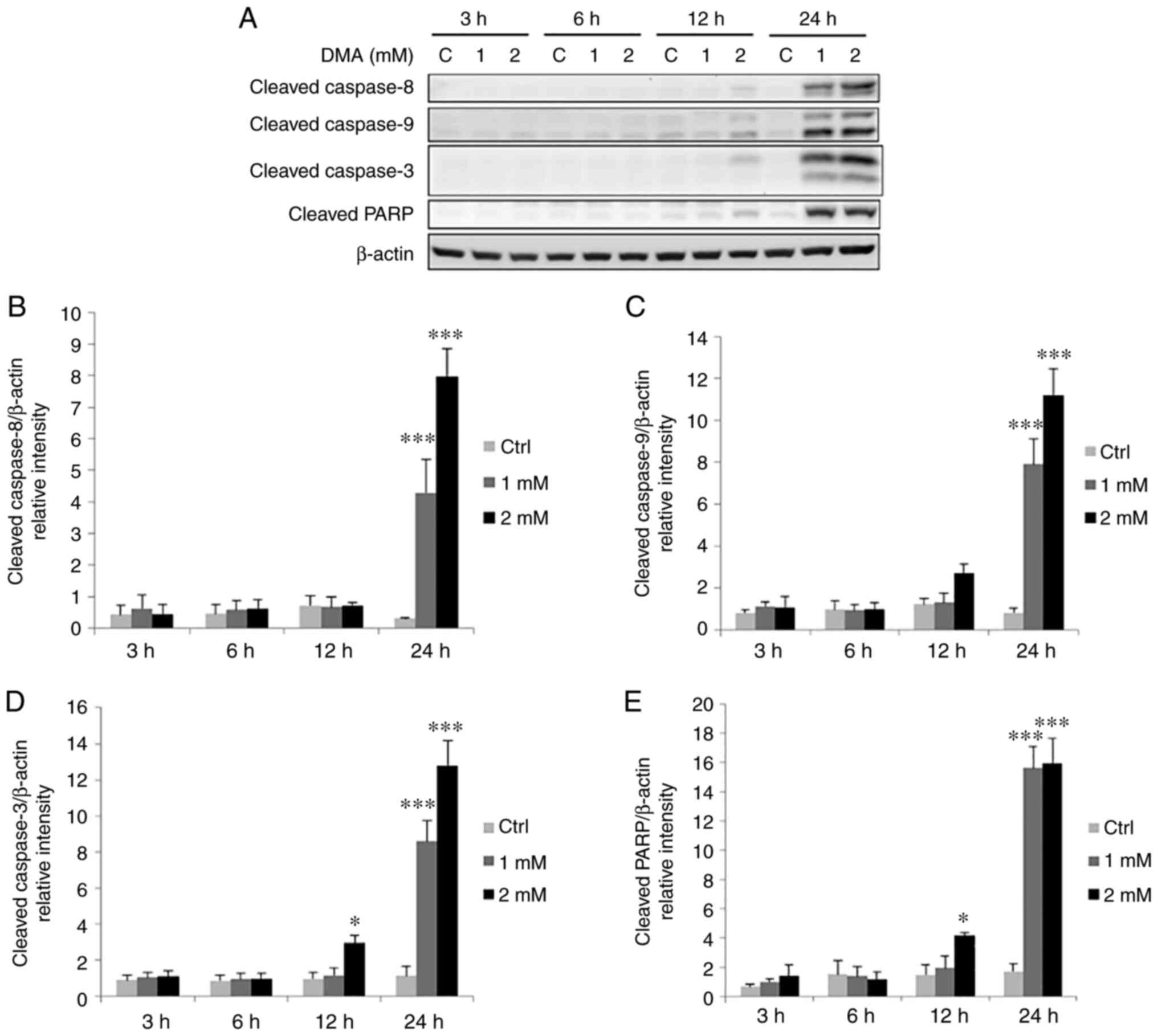
|
1
|
David MC, Randal SW and Stephen YL: Head
and neck cancer. Cancer. 113 (Suppl 7):S1911–S1932. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Laraway DC, Lakshmiah R, Lowe D, Roe B and
Rogers SN: Quality of life in older people with oral cancer. Br J
Oral Maxillofac Surg. 50:715–720. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sabio JM, Pasquau J and Jiménez-Alonso J:
Human papillomavirus infection as a risk factor for squamous-cell
carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 345:376–377. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ko YC, Huang YL, Lee CH, Chen MJ, Lin LM
and Tsai CC: Betel quid chewing, cigarette smoking and alcohol
consumption related to oral cancer in Taiwan. J Oral Pathol Med.
24:450–453. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bernier J and Cooper JS: Chemoradiation
after surgery for high-risk head and neck cancer patients: How
strong is the evidence? Oncologist. 10:215–224. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen CJ, You SL, Lin LH, Hsu WL and Yang
YW: Cancer epidemiology and control in Taiwan: A brief review. Jpn
J Clin Oncol. 32 (Suppl):S66–S81. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mandal BK and Suzuki KT: Arsenic round the
world: A review. Talanta. 58:201–235. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Calatayud M, Devesa V and Vélez D:
Differential toxicity and gene expression in Caco-2 cells exposed
to arsenic species. Toxicol Lett. 218:70–80. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shen ZX, Chen GQ, Ni JH, Li XS, Xiong SM,
Qiu QY, Zhu J, Tang W, Sun GL, Yang KQ, et al: Use of arsenic
trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute
promyelocytic leukemia (APL): II. Clinical efficacy and
pharmacokinetics in relapsed patients. Blood. 89:3354–3360. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yedjou C, Tchounwou P, Jenkins J and
McMurray R: Basic mechanisms of arsenic trioxide (ATO)-induced
apoptosis in human leukemia (HL-60) cells. J Hematol Oncol.
3:282010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu Q, Hilsenbeck S and Gazitt Y: Arsenic
trioxide-induced apoptosis in myeloma cells: p53-dependent G1 or
G2/M cell cycle arrest, activation of caspase-8 or caspase-9, and
synergy with APO2/TRAIL. Blood. 101:4078–4087. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mandegary A, Torshabi M, Seyedabadi M,
Amirheidari B, Sharif E and Ghahremani MH: Indomethacin-enhanced
anticancer effect of arsenic trioxide in A549 cell line:
Involvement of apoptosis and phospho-ERK and p38 MAPK pathways.
Biomed Res Int. 2013:2375432013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim MJ, Jung JH, Lee WS, Yun JW, Lu JN, Yi
SM, Kim HJ, Chang SH, Kim GS, Hong SC and Ha WS: Arsenic hexoxide
enhances TNF-α-induced anticancer effects by inhibiting NF-κB
activity at a safe dose in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Oncol
Rep. 31:2305–2311. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mann KK, Wallner B, Lossos IS and Miller
WH Jr: Darinaparsin: A novel organic arsenical with promising
anticancer activity. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 18:1727–1734.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jaeschke H and Bajt ML: Intracellular
signaling mechanisms of acetaminophen-induced liver cell death.
Toxicol Sci. 89:31–41. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kuwabara M, Asanuma T, Niwa K and Inanami
O: Regulation of cell survival and death signals induced by
oxidative stress. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 43:51–57. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Vandenabeele P,
Abrams J, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV, El-Deiry WS,
Golstein P, Green DR, et al: Classification of cell death:
Recommendations of the nomenclature committee on cell death 2009.
Cell Death Differ. 16:3–11. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Danial NN and Korsmeyer SJ: Cell death:
Critical control points. Cell. 116:205–219. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wilson TR, Johnston PG and Longley DB:
Anti-apoptotic mechanisms of drug resistance in cancer. Curr Cancer
Drug Targets. 9:307–319. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kasibhatla S and Tseng B: Why target
apoptosis in cancer treatment? Mol Cancer Ther. 2:573–580.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang Y, Chen X, Gueydan C and Han J:
Plasma membrane changes during programmed cell deaths. Cell Res.
28:9–21. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Carneiro BA and El-Deiry WS: Targeting
apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 17:395–417. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
O' Reilly E, Tirincsi A, Logue SE and
Szegezdi E: The Janus face of death receptor signaling during tumor
immunoediting. Front Immunol. 7:4462016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ashkenazi A and Dixit VM: Death receptors:
Signaling and modulation. Science. 281:1305–1308. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu H, Li J, Yuan W, Hao S, Wang M, Wang F
and Xuan H: Bioactive components and mechanisms of poplar propolis
in inhibiting proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2
cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 144:1123642021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Patwardhan GA, Beverly LJ and Siskind LJ:
Sphingolipids and mitochondrial apoptosis. J Bioenerg Biomembr.
48:153–168. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Akao Y, Nakagawa Y and Akiyama K: Arsenic
trioxide induces apoptosis in neuroblastoma cell lines through the
activation of caspase 3 in vitro. FEBS Lett. 455:59–62. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen GQ, Zhu J, Shi XG, Ni JN, Zhong HJ,
Si GY, Jin XL, Tang W, Li XS, Xong SM, et al: In vitro studies on
cellular and molecular mechanisms of arsenic trioxide
(As2O3) in the treatment of acute
promyelocytic leukemia: As2O3 induces NB4
cell apoptosis with downregulation of Bcl-2 expression and
modulation of PML-RAR alpha/PML proteins. Blood. 88:1052–1061.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wada T and Penninger JM: Mitogen-activated
protein kinases in apoptosis regulation. Oncogene. 23:2838–2849.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hayakawa J, Ohmichi M, Kurachi H, Ikegami
H, Kimura A, Matsuoka T, Jikihara H, Mercola D and Murata Y:
Inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase or
c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase cascade, differentially activated
by cisplatin, sensitizes human ovarian cancer cell line. J Biol
Chem. 274:31648–31654. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kang YH and Lee SJ: The role of p38 MAPK
and JNK in arsenic trioxide-induced mitochondrial cell death in
human cervical cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 217:23–33. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Foo NP, Ko CL, Chu CY, Wang CY, So EC and
Huang BM: Arsenic compounds activate the MAPK and caspase pathways
to induce apoptosis in OEC-M1 gingival epidermal carcinoma. Oncol
Rep. 44:2701–2714. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rangan SR: A new human cell line (FaDu)
from a hypopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer. 29:117–121. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wu WC, Hsiao JR, Lian YY, Lin CY and Huang
BM: The apoptotic effect of cordycepin on human OEC-M1 oral cancer
cell line. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 60:103–111. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mu YF, Chen YH, Chang MM, Chen YC and
Huang BM: Arsenic compounds induce apoptosis through caspase
pathway activation in MA-10 Leydig tumor cells. Oncol Lett.
18:944–954. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Berridge MV and Tan AS: Characterization
of the cellular reduction of
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT):
Subcellular localization, substrate dependence, and involvement of
mitochondrial electron transport in MTT reduction. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 303:474–482. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kang FC, Wang SC, So EC, Chang MM, Wong
KL, Cheng KS, Chen YC and Huang BM: Propofol may increase caspase
and MAPK pathways, and suppress the Akt pathway to induce apoptosis
in MA-10 mouse Leydig tumor cells. Oncol Rep. 41:3565–3574.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kang FC, Chen YC, Wang SC, So EC and Huang
BM: Propofol induces apoptosis by activating caspases and the MAPK
pathways, and inhibiting the Akt pathway in TM3 mouse Leydig
stem/progenitor cells. Int J Mol Med. 46:439–448. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nicoletti I, Migliorati G, Pagliacci MC,
Grignani F and Riccardi C: A rapid and simple method for measuring
thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow
cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 139:271–279. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chang MM, Lai MS, Hong SY, Pan BS, Huang
H, Yang SH, Wu CC, Sun HS, Chuang JI, Wang CY and Huang BM:
FGF9/FGFR2 increase cell proliferation by activating ERK1/2,
Rb/E2F1, and cell cycle pathways in mouse Leydig tumor cells.
Cancer Sci. 109:3503–3518. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chang MM, Pan BS, Wang CY and Huang BM:
Cordycepin-induced unfolded protein response-dependent cell death,
and AKT/MAPK-mediated drug resistance in mouse testicular tumor
cells. Cancer Med. 8:3949–3964. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
van Engeland M, Ramaekers FC, Schutte B
and Reutelingsperger CP: A novel assay to measure loss of plasma
membrane asymmetry during apoptosis of adherent cells in culture.
Cytometry. 24:131–139. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lan YY, Chen YH, Liu C, Tung KL, Wu YT,
Lin SC, Wu CH, Chang HY, Chen YC and Huang BM: Role of JNK
activation in paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in human head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 22:7052021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chang MM, Hong SY, Yang SH, Wu CC, Wang CY
and Huang BM: Anti-cancer effect of cordycepin on FGF9-induced
testicular tumorigenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 21:83362020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chang MM, Wu SZ, Yang SH, Wu CC, Wang CY
and Huang BM: FGF9/FGFR1 promotes cell proliferation,
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, M2 macrophage infiltration and
liver metastasis of lung cancer. Transl Oncol. 14:1012082021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shu CH, Yang WK, Shih YL, Kuo ML and Huang
TS: Cell cycle G2/M arrest and activation of cyclin-dependent
kinases associated with low-dose paclitaxel-induced sub-G1
apoptosis. Apoptosis. 2:463–470. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tyagi AK, Singh RP, Agarwal C, Chan DC and
Agarwal R: Silibinin strongly synergizes human prostate carcinoma
DU145 cells to doxorubicin-induced growth Inhibition, G2-M arrest,
and apoptosis. Clin Cancer Res. 8:3512–3519. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang TD, Chen GQ, Wang ZG, Wang ZY, Chen
SJ and Chen Z: Arsenic trioxide, a therapeutic agent for APL.
Oncogene. 20:7146–7153. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Nakagawa Y, Akao Y, Morikawa H, Hirata I,
Katsu K, Naoe T, Ohishi N and Yagi K: Arsenic trioxide-induced
apoptosis through oxidative stress in cells of colon cancer cell
lines. Life Sci. 70:2253–2269. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li X, Ding X and Adrian TE: Arsenic
trioxide induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells via changes
in cell cycle, caspase activation, and GADD expression. Pancreas.
27:174–179. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li W and Chou IN: Effects of sodium
arsenite on the cytoskeleton and cellular glutathione levels in
cultured cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 114:132–139. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ochi T, Nakajima F and Fukumori N:
Different effects of inorganic and dimethylated arsenic compounds
on cell morphology, cytoskeletal organization, and DNA synthesis in
cultured Chinese hamster V79 cells. Arch Toxicol. 72:566–573. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zuk A, Targosz-Korecka M and Szymonski M:
Effect of selected drugs used in asthma treatment on morphology and
elastic properties of red blood cells. Int J Nanomedicin.
6:249–257. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Hartwell LH and Weinert TA: Checkpoints:
Controls that ensure the order of cell cycle events. Science.
246:629–634. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yih LH, Wu YC, Hsu NC and Kuo HH: Arsenic
trioxide induces abnormal mitotic spindles through a PIP4KIIγ/Rho
pathway. Toxicol Sci. 128:115–125. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ling YH, Jiang JD, Holland JF and
Perez-Soler R: Arsenic trioxide produces polymerization of
microtubules and mitotic arrest before apoptosis in human tumor
cell lines. Mol Pharmacol. 62:529–538. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Concin N, Stimpfl M, Zeillinger C, Wolff
U, Hefler L, Sedlak J, Leodolter S and Zeillinger R: Role of p53 in
G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in response to
gamma-irradiation in ovarian carcinoma cell lines. Int J Oncol.
22:51–57. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Brown JM and Attardi LD: The role of
apoptosis in cancer development and treatment response. Nat Rev
Cancer. 5:231–237. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Fan TJ, Han LH, Cong RS and Liang J:
Caspase family proteases and apoptosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 37:719–727. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Nguyen TTM, Gillet G and Popgeorgiev N:
Caspases in the developing central nervous system: Apoptosis and
beyond. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:7024042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Cheng B, Yang X, Han Z, An L and Liu S:
Arsenic trioxide induced the apoptosis of laryngeal cancer via
down-regulation of survivin mRNA. Auris Nasus Larynx. 35:95–101.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Jiang XH, Wong BC, Yuen ST, Jiang SH, Cho
CH, Lai KC, Lin MC, Kung HF and Lam SK: Arsenic trioxide induces
apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells through up-regulation of
p53 and activation of caspase-3. Int J Cancer. 91:173–179. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Buckley CD, Pilling D, Henriquez NV,
Parsonage G, Threlfall K, Scheel-Toellner D, Simmons DL, Akbar AN,
Lord JM and Salmon M: RGD peptides induce apoptosis by direct
caspase-3 activation. Nature. 397:534–539. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Goping IS, Barry M, Liston P, Sawchuk T,
Constantinescu G, Michalak KM, Shostak I, Roberts DL, Hunter AM,
Korneluk R and Bleackley RC: Granzyme B-induced apoptosis requires
both direct caspase activation and relief of caspase inhibition.
Immunity. 18:355–365. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Hitomi J, Katayama T, Taniguchi M, Honda
A, Imaizumi K and Tohyama M: Apoptosis induced by endoplasmic
reticulum stress depends on activation of caspase-3 via caspase-12.
Neurosci Lett. 357:127–130. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Minden A, Lin A, McMahon M, Lange-Carter
C, Dérijard B, Davis RJ, Johnson GL and Karin M: Differential
activation of ERK and JNK mitogen-activated protein kinases by
Raf-1 and MEKK. Science. 266:1719–1723. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Westwick JK, Bielawska AE, Dbaibo G,
Hannun YA and Brenner DA: Ceramide activates the stress-activated
protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 270:22689–22692. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Davison K, Mann KK, Waxman S and Miller WH
Jr: JNK activation is a mediator of arsenic trioxide-induced
apoptosis in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Blood.
103:3496–3502. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Kim YH, Lee DH, Jeong JH, Guo ZS and Lee
YJ: Quercetin augments TRAIL-induced apoptotic death: Involvement
of the ERK signal transduction pathway. Biochem Pharmacol.
75:1946–1958. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Tewari R, Sharma V, Koul N and Sen E:
Involvement of miltefosine-mediated ERK activation in glioma cell
apoptosis through Fas regulation. J Neurochem. 107:616–627. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Eguchi R, Fujimori Y, Takeda H, Tabata C,
Ohta T, Kuribayashi K, Fukuoka K and Nakano T: Arsenic trioxide
induces apoptosis through JNK and ERK in human mesothelioma cells.
J Cell Physiol. 226:762–768. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Alvarado-Kristensson M, Melander F,
Leandersson K, Rönnstrand L, Wernstedt C and Andersson T: p38-MAPK
signals survival by phosphorylation of caspase-8 and caspase-3 in
human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 199:449–458. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Grethe S, Ares MP, Andersson T and
Pörn-Ares MI: p38 MAPK mediates TNF-induced apoptosis in
endothelial cells via phosphorylation and downregulation of
Bcl-x(L). Exp Cell Res. 298:632–642. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Kim D, Park NY, Kang K, Calderwood SK, Cho
DH, Bae IJ and Bunch H: Arsenic hexoxide has differential effects
on cell proliferation and genome-wide gene expression in human
primary mammary epithelial and MCF7 cells. Sci Rep. 11:37612021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Sönksen M, Kerl K and Bunzen H: Current
status and future prospects of nanomedicine for arsenic trioxide
delivery to solid tumors. Med Res Rev. 42:374–398. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Eyvani H, Moghaddaskho F, Kabuli M, Zekri
A, Momeny M, Tavakkoly-Bazzaz J, Alimoghaddam K, Ghavamzadeh A and
Ghaffari SH: Arsenic trioxide induces cell cycle arrest and alters
DNA methylation patterns of cell cycle regulatory genes in
colorectal cancer cells. Life Sci. 167:67–77. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|