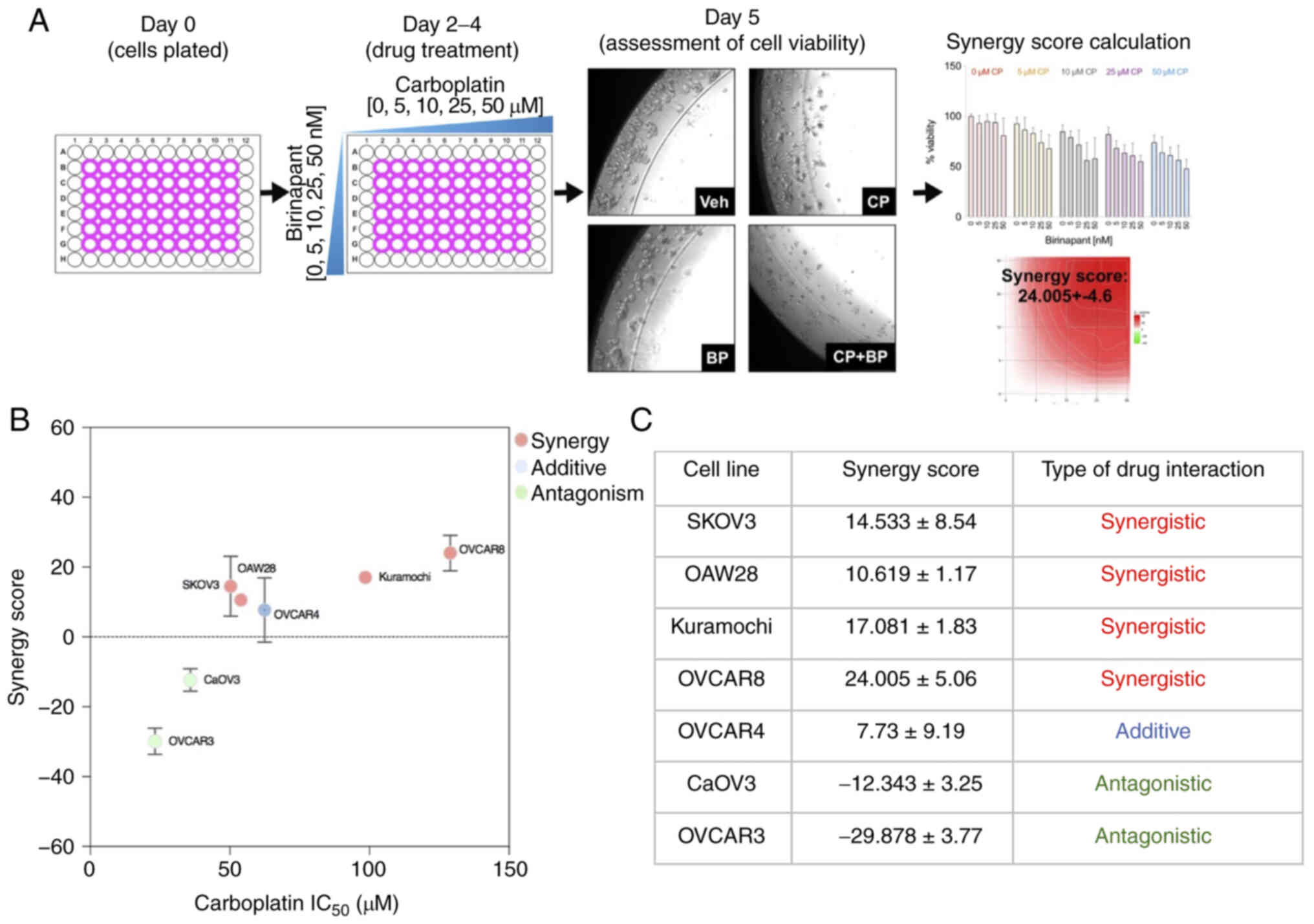
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:7–33. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Desai A, Xu J, Aysola K, Qin Y, Okoli C,
Hariprasad R, Chinemerem U, Gates C, Reddy A, Danner O, et al:
Epithelial ovarian cancer: An overview. World J Transl Med. 3:1–8.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kurnit KC, Fleming GF and Lengyel E:
Updates and new options in advanced epithelial ovarian cancer
treatment. Obstet Gynecol. 137:108–121. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kaplan DA: Overview of the Updated NCCN
Guidelines on Ovarian Cancer. 6:2020.
|
|
5
|
Berek JS, Crum C and Friedlander M: Cancer
of the ovary, fallopian tube, and peritoneum. Int J Gynaecol
Obstet. 119(Suppl 2): S118–S129. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Baert T, Ferrero A, Sehouli J, O'Donnell
DM, González-Martín A, Joly F, van der Velden J, Blecharz P, Tan
DSP, Querleu D, et al: The systemic treatment of recurrent ovarian
cancer revisited. Ann Oncol. 32:710–725. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang Y, Yang Y, Yang J, Zhao X and Wei X:
Tumor microenvironment in ovarian cancer: Function and therapeutic
strategy. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8:7582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhou J, Kang Y, Chen L, Wang H, Liu J,
Zeng S and Yu L: The drug-resistance mechanisms of five
platinum-based antitumor agents. Front Pharmacol. 11:3432020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dubrez L, Berthelet J and Glorian V: IAP
proteins as targets for drug development in oncology. Onco Targets
Ther. 9:1285–1304. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Finlay D, Teriete P, Vamos M, Cosford NDP
and Vuori K: Inducing death in tumor cells: Roles of the inhibitor
of apoptosis proteins. F1000Res. 6:5872017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pluta P, Jeziorski A, Cebula-Obrzut AP,
Wierzbowska A, Piekarski J and Smolewski P: Expression of IAP
family proteins and its clinical importance in breast cancer
patients. Neoplasma. 62:666–673. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hofmann HS, Simm A, Hammer A, Silber RE
and Bartling B: Expression of inhibitors of apoptosis (IAP)
proteins in non-small cell human lung cancer. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 128:554–560. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Imoto I, Tsuda H, Hirasawa A, Miura M,
Sakamoto M, Hirohashi S and Inazawa J: Expression of cIAP1, a
target for 11q22 amplification, correlates with resistance of
cervical cancers to radiotherapy. Cancer Res. 62:4860–4866.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Miyamoto M, Takano M, Iwaya K, Shinomiya
N, Kato M, Aoyama T, Sasaki N, Goto T, Suzuki A, Hitrata J and
Furuya K: X-chromosome-linked inhibitor of apoptosis as a key
factor for chemoresistance in clear cell carcinoma of the ovary. Br
J Cancer. 110:2881–2886. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cai Y, Ma W, Huang X, Cao L, Li H, Jiang
Y, Lu N and Yin Y: Effect of survivin on tumor growth of colorectal
cancer in vivo. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:13267–13272. 2015.
|
|
16
|
Zhao G, Wang Q, Wu Z, Tian X, Yan H, Wang
B, Dong P, Watari H, Pfeffer LM, Guo Y, et al: Ovarian primary and
metastatic tumors suppressed by survivin knockout or a novel
survivin inhibitor. Mol Cancer Ther. 18:2233–2245. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Park E, Gang EJ, Hsieh YT, Schaefer P,
Chae S, Klemm L, Huantes S, Loh M, Conway EM, Kang ES, et al:
Targeting survivin overcomes drug resistance in acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Blood. 118:2191–2199. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moriai R, Tsuji N, Moriai M, Kobayashi D
and Watanabe N: Survivin plays as a resistant factor against
tamoxifen-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 117:261–271. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Span PN, Sweep FCGJ, Wiegerinck ET,
Tjan-Heijnen VC, Manders P, Beex LV and de Kok JB: Survivin is an
independent prognostic marker for risk stratification of breast
cancer patients. Clin Chem. 50:1986–1993. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sui L, Dong Y, Ohno M, Watanabe Y,
Sugimoto K and Tokuda M: Survivin expression and its correlation
with cell proliferation and prognosis in epithelial ovarian tumors.
Int J Oncol. 21:315–320. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Morrish E, Brumatti G and Silke J: Future
therapeutic directions for Smac-Mimetics. Cells. 9:4062020.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Eytan DF, Snow GE, Carlson S, Derakhshan
A, Saleh A, Schiltz S, Cheng H, Mohan S, Cornelius S, Coupar J, et
al: SMAC mimetic birinapant plus radiation eradicates human head
and neck cancers with genomic amplifications of cell death genes
FADD and BIRC2. Cancer Res. 76:5442–5454. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lalaoui N, Merino D, Giner G, Vaillant F,
Chau D, Liu L, Kratina T, Pal B, Whittle JR, Etemadi N, et al:
Targeting triple-negative breast cancers with the Smac-mimetic
birinapant. Cell Death Differ. 27:2768–2780. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xie X, Lee J, Liu H, Pearson T, Lu AY,
Tripathy D, Devi GR, Bartholomeusz C and Ueno NT: Birinapant
enhances gemcitabine's antitumor efficacy in triple-negative breast
cancer by inducing intrinsic pathway-dependent apoptosis. Mol
Cancer Ther. 20:296–306. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Colombo M, Marabese M, Vargiu G, Broggini
M and Caiola E: Activity of birinapant, a SMAC mimetic compound,
alone or in combination in NSCLCs with different mutations. Front
Oncol. 10:5322922020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hernandez LF, Dull AB, Korrapati S and
Annunziata CM: Smac-mimetic enhances antitumor effect of standard
chemotherapy in ovarian cancer models via Caspase 8-independent
mechanism. Cell Death Discov. 7:1342021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Noonan AM, Bunch KP, Chen JQ, Herrmann MA,
Lee JM, Kohn EC, O'Sullivan CC, Jordan E, Houston N, Takebe N, et
al: Pharmacodynamic markers and clinical results from the phase II
Study of the SMAC-Mimetic birinapant in women with relapsed
platinum-resistant or refractory epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer.
122:588–597. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Phan N, Hong JJ, Tofig B, Mapua M,
Elashoff D, Moatamed NA, Huang J, Memarzadeh S, Damoiseaux R and
Soragni A: A simple high-throughput approach identifies actionable
drug sensitivities in patient-derived tumor organoids. Commun Biol.
2:782019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nguyen HTL and Soragni A: Patient-derived
tumor organoid rings for histologic characterization and
high-throughput screening. STAR Protoc. 1:1000562020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ianevski A, Giri AK and Aittokallio T:
SynergyFinder 2.0: Visual analytics of multi-drug combination
synergies. Nucleic Acids Res. 48(W1): W488–W493. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
National Cancer Institute: Oxaliplatin.
Accessed September 15, 2021. Available from: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/drugs/oxaliplatin.
|
|
32
|
National Cancer Institute: Cisplatin.
Accessed September 15, 2021. Available from: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/drugs/cisplatin.
|
|
33
|
National Cancer Institute:
Discovery-Cisplatin and The Treatment of Testicular and Other
Cancers. Accessed September 15, 2021. Available from: https://www.cancer.gov/research/progress/discovery/cisplatin.
|
|
34
|
Decatris MP, Sundar S and O'Byrne KJ:
Platinum-based chemotherapy in metastatic breast cancer: Current
status. Cancer Treat Rev. 30:53–81. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Burstein HJ, Mangu PB, Somerfield MR,
Schrag D, Samson D, Holt L, Zelman D and Ajani JA; American Society
of Clinical Oncology: American Society of Clinical Oncology
clinical practice guideline update on the use of chemotherapy
sensitivity and resistance assays. J Clin Oncol. 29:3328–3330.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Haley J, Tomar S, Pulliam N, Xiong S,
Perkins SM, Karpf AR, Mitra S, Nephew KP and Mitra AK: Functional
characterization of a panel of high-grade serous ovarian cancer
cell lines as representative experimental models of the disease.
Oncotarget. 7:32810–32820. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Beaufort CM, Helmijr JC, Piskorz AM,
Hoogstraat M, Ruigrok-Ritstier K, Besselink N, Murtaza M, van
IJcken WF, Heine AA, Smid M, et al: Ovarian cancer cell line panel
(OCCP): Clinical importance of in vitro morphological subtypes.
PLoS One. 9:e1039882014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kopper O, de Witte CJ, Lõhmussaar K,
Valle-Inclan JE, Hami N, Kester L, Balgobind AV, Korving J, Proost
N, Begthel H, et al: An organoid platform for ovarian cancer
captures intra- and interpatient heterogeneity. Nat Med.
25:838–849. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
LaCasse EC, Mahoney DJ, Cheung HH,
Plenchette S, Baird S and Korneluk RG: IAP-targeted therapies for
cancer. Oncogene. 27:6252–6275. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Thibault B, Genre L, Le Naour A, Broca C,
Mery E, Vuagniaux G, Delord JP, Wiedemann N and Couderc B: DEBIO
1143, an IAP inhibitor, reverses carboplatin resistance in ovarian
cancer cells and triggers apoptotic or necroptotic cell death. Sci
Rep. 8:178622018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rabik CA and Dolan ME: Molecular
mechanisms of resistance and toxicity associated with platinating
agents. Cancer Treat Rev. 33:9–23. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
42
|
Vince JE, Wong WW, Khan N, Feltham R, Chau
D, Ahmed AU, Benetatos CA, Chunduru SK, Condon SM, McKinlay M, et
al: IAP Antagonists Target cIAP1 to Induce TNFα-Dependent
Apoptosis. Cell. 131:682–693. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Probst BL, Liu L, Ramesh V, Li L, Sun H,
Minna JD and Wang L: Smac mimetics increase cancer cell response to
chemotherapeutics in a TNF-α-dependent manner. Cell Death Differ.
17:1645–1654. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Amaravadi RK, Senzer NN, Martin LP,
Schilde RJ, LoRusso P, Papadopoulos KP, Weng DE, Graham M and Adjei
AA: A phase I study of birinapant (TL32711) combined with multiple
chemotherapies evaluating tolerability and clinical activity for
solid tumor patients. J Clin Oncol. 31(Suppl 15): S25042013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Fichtner M, Bozkurt E, Salvucci M, McCann
C, McAllister KA, Halang L, Düssmann H, Kinsella S, Crawford N,
Sessler T, et al: Molecular subtype-specific responses of colon
cancer cells to the SMAC mimetic Birinapant. Cell Death Dis.
11:10202020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Eytan DF, Snow GE, Carlson SG, Schiltz S,
Chen Z and Van Waes C: Combination effects of SMAC mimetic
birinapant with TNFα, TRAIL, and docetaxel in preclinical models of
HNSCC. Laryngoscope. 125:E118–E124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Michie J, Beavis PA, Freeman AJ, Vervoort
SJ, Ramsbottom KM, Narasimhan V, Lelliott EJ, Lalaoui N, Ramsay RG,
Johnstone RW, et al: Antagonism of IAPs Enhances CAR T-cell
Efficacy. Cancer Immunol Res. 7:183–192. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zinngrebe J, Schlichtig F, Kraus JM, Meyer
M, Boldrin E, Kestler HA, Meyer LH, Fischer-Posovszky P and Debatin
KM: Biomarker profile for prediction of response to SMAC mimetic
monotherapy in pediatric precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Int J Cancer. 146:3219–3231. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
McCann C, Matveeva A, McAllister K, Van
Schaeybroeck S, Sessler T, Fichtner M, Carberry S, Rehm M, Prehn
JHM and Longley DB: Development of a protein signature to enable
clinical positioning of IAP inhibitors in colorectal cancer. FEBS
J. 288:5374–5388. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|