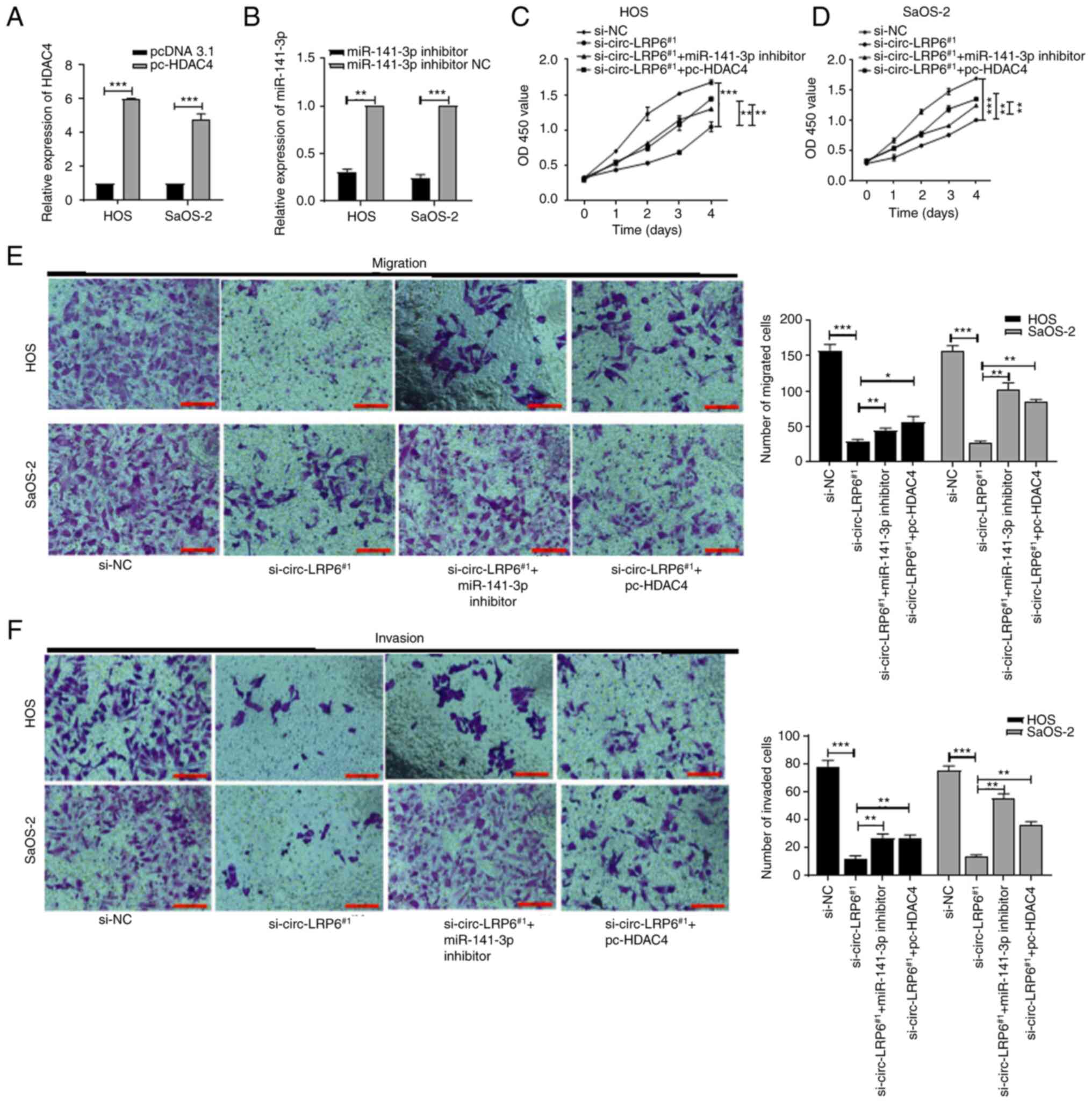
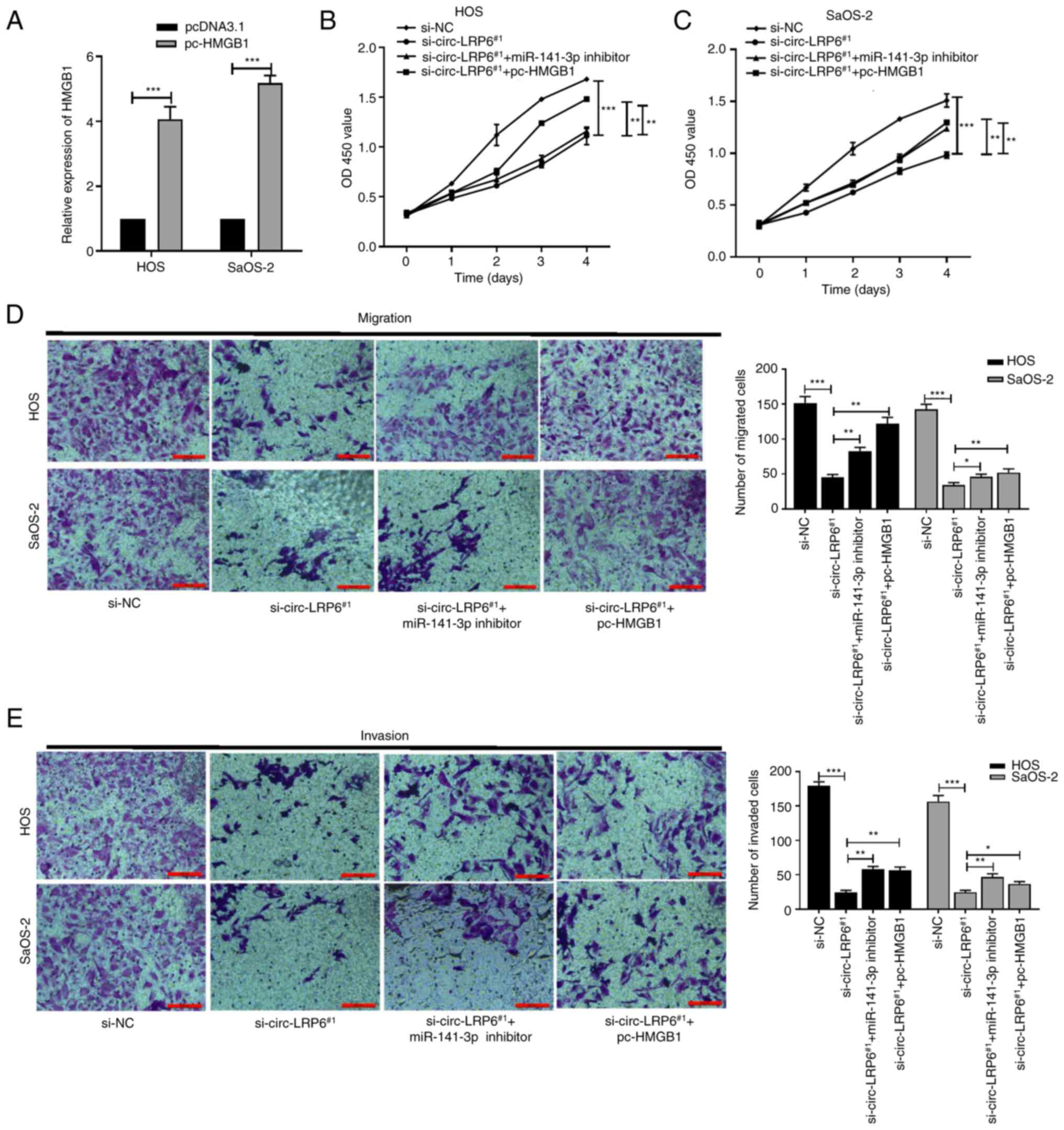
|
1
|
Sangle NA and Layfield LJ: Telangiectatic
osteosarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 136:572–576. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Strobel O, Neoptolemos J, Jäger D and
Büchler MW: Optimizing the outcomes of pancreatic cancer surgery.
Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 16:11–26. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Harrison DJ, Geller DS, Gill JD, Lewis VO
and Gorlick R: Current and future therapeutic approaches for
osteosarcoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 18:39–50. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Li Z, Ruan Y, Zhang H, Shen Y, Li T and
Xiao B: Tumor-suppressive circular RNAs: Mechanisms underlying
their suppression of tumor occurrence and use as therapeutic
targets. Cancer Sci. 110:3630–3638. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhang F, Zhang R, Zhang X, Wu Y, Li X,
Zhang S, Hou W, Ding Y, Tian J, Sun L and Kong X: Comprehensive
analysis of circRNA expression pattern and circRNA-miRNA-mRNA
network in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis in rabbits. Aging
(Albany NY). 10:2266–2283. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Xu Y, Xu X, Ocansey DKW, Cao H, Qiu W, Tu
Q and Mao F: CircRNAs as promising biomarkers of inflammatory bowel
disease and its associated-colorectal cancer. Am J Transl Res.
13:1580–1593. 2021.
|
|
7
|
Wu F, Han B, Wu S, Yang L, Leng S, Li M,
Liao J, Wang G, Ye Q, Zhang Y, et al: Circular RNA TLK1 aggravates
neuronal injury and neurological deficits after ischemic stroke via
miR-335-3p/TIPARP. J Neurosci. 39:7369–7393. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ma W, Xue N, Zhang J, Wang D, Yao X, Lin L
and Xu Q: circUBAP2 regulates osteosarcoma progression via the
miR-204-3p/HMGA2 axis. Int J Oncol. 58:298–311. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu S, Zhang J, Zheng T, Mou X and Xin W:
Circ_WWC3 overexpression decelerates the progression of
osteosarcoma by regulating miR-421/PDE7B axis. Open Life Sci.
16:229–241. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Huo S and Dou D: Circ_0056285 regulates
proliferation, apop- tosis and glycolysis of osteosarcoma cells via
miR-1244/TRIM44 axis. Cancer Manag Res. 13:1257–1270. 20210.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wen Y, Li B, He M, Teng S, Sun Y and Wang
G: circHIPK3 promotes proliferation and migration and invasion via
regulation of miR-637/HDAC4 signaling in osteosarcoma cells. Oncol
Rep. 45:169–179. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen Z, Xu W, Zhang D, Chu J, Shen S, Ma
Y, Wang Q, Liu G, Yao T, Huang Y, et al: circCAMSAP1 promotes
osteosarcoma progression and metastasis by sponging miR-145-5p and
regulating FLI1 expression. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 23:1120–1135.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hall IF, Climent M, Quintavalle M, Farina
FM, Schorn T, Zani S, Carullo P, Kunderfranco P, Civilini E,
Condorelli G and Elia L: Circ_Lrp6, a circular RNA enriched in
vascular smooth muscle cells, acts as a sponge regulating miRNA-145
function. Circ Res. 124:498–510. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zheng S, Qian Z, Jiang F, Ge D, Tang J,
Chen H, Yang J, Yao Y, Yan J, Zhao L, et al: CircRNA LRP6 promotes
the development of osteosarcoma via negatively regulating KLF2 and
APC levels. Am J Transl Res. 11:4126–4138. 2019.
|
|
15
|
Zhang Q, Jiang C, Ren W, Li S, Zheng J,
Gao Y, Zhi K and Gao L: Circ-LRP6 mediates epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and autophagy in oral squamous cell carcinomas. J Oral
Pathol Med. 50:660–667. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang J, Zhu W, Tao G and Wang W: Circular
RNA circ-LRP6 facilitates Myc-driven tumorigenesis in esophageal
squamous cell cancer. Bioengineered. 11:932–938. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu Y, Wang L, Li Z, Zheng Y, Shi Z and
Wang G: Long noncoding RNA CRNDE functions as a diagnostic and
prognostic biomarker in osteosarcoma, as well as promotes its
progression via inhibition of miR-335-3p. J Biochem Mol Toxicol.
35:e227342021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gulino R, Forte S, Parenti R, Memeo L and
Gulisano M: MicroRNA and pediatric tumors: Future perspectives.
Acta Histochem. 117:339–354. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu Y, Wang Y, Yang H, Zhao L, Song R, Tan
H and Wang L: MicroRNA-873 targets HOXA9 to inhibit the aggressive
pheno- type of osteosarcoma by deactivating the Wnt/β-catenin
pathway. Int J Oncol. 54:1809–1820. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gao S, Wang J, Tian S and Luo J: miR-9
depletion suppresses the proliferation of osteosarcoma cells by
targeting p16. Int J Oncol. 54:1921–1932. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Feng T, Zhu Z, Jin Y, Wang H, Mao X, Liu
D, Li Y, Lu L and Zuo G: The microRNA-708-5p/ZEB1/EMT axis mediates
the metastatic potential of osteosarcoma. Oncol Rep. 43:491–502.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun X, Xu Y, Zhang S, Li X and Wang Y,
Zhang Y, Zhao X, Li Y and Wang Y: MicroRNA-183 suppresses the
vitality, invasion and migration of human osteosarcoma cells by
targeting metastasis-associated protein 1. Exp Ther Med.
15:5058–5064. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao X, Xu Y, Sun X, Ma Y, Zhang Y and
Wang Y, Guan H, Jia Z, Li Y and Wang Y: miR-17-5p promotes
proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human
osteosarcoma cells by targeting SRC kinase signaling inhibitor 1. J
Cell Biochem. 120:5495–5504. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wang N, Li P, Liu W, Wang N, Lu Z, Feng J,
Zeng X, Yang J, Wang Y and Zhao W: miR-141-3p suppresses
proliferation and promotes apoptosis by targeting GLI2 in
osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Rep. 39:747–754. 2018.
|
|
25
|
Wang L: MiR-141-3p overexpression
suppresses the malignancy of osteosarcoma by targeting FUS to
degrade LDHB. Biosci Rep. Jun 26–2020.Epub ahead of print.
|
|
26
|
Liang Z, Li X, Liu S, Li C, Wang X and
Xing J: MiR-141-3p inhibits cell proliferation, migration and
invasion by targeting TRAF5 in colorectal cancer. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 514:699–705. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou Y, Zhong JH, Gong FS and Xiao J:
MiR-141-3p suppresses gastric cancer induced transition of normal
fibroblast and BMSC to cancer-associated fibroblasts via targeting
STAT4. Exp Mol Pathol. 107:85–94. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Jiang J, Sun Y, Xu G, Wang H and Wang L:
The role of miRNA, lncRNA and circRNA in the development of
intervertebral disk degeneration (review). Exp Ther Med.
21:5552021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Chen F, He L, Qiu L, Zhou Y, Li Z, Chen G,
Xin F, Dong X, Xu H, Wang G, et al: Circular RNA CircEPB41L2
functions as tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma through
sponging miR-590-5p. Cancer Manag Res. 13:2969–2981. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang C, Cao J, Lv W and Mou H:
CircRNA_100395 carried by exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal
stem cells inhibits the malignant transformation of non-small cell
lung carcinoma through the miR-141-3p-LATS2 axis. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 9:6631472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huang XY, Huang ZL, Zhang PB, Huang XY,
Huang J, Wang HC, Xu B, Zhou J and Tang ZY: CircRNA-100338 is
associated with mTOR signaling pathway and poor prognosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol. 9:3922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chao F, Song Z, Wang S, Ma Z, Zhuo Z, Meng
T, Xu G and Chen G: Novel circular RNA circSOBP governs amoeboid
migration through the regulation of the miR-141-3p/MYPT1/p-MLC2
axis in prostate cancer. Clin Transl Med. 11:e3602021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ma J, Wu Y and He Y: Silencing circRNA
LRP6 down-regulates PRMT1 to improve the streptozocin-induced
pancreatic β-cell injury and insulin secretion by sponging
miR-9-5p. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 53:333–342. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xue J, Chen C, Luo F, Pan X, Xu H, Yang P,
Sun Q, Liu X, Lu L, Yang Q, et al: CircLRP6 regulation of ZEB1 via
miR-455 is involved in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition during
arsenite-induced malignant transformation of human keratinocytes.
Toxicol Sci. 162:450–461. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cai JY, Xu TT, Wang Y, Chang JJ, Li J,
Chen XY, Chen X, Yin YF and Ni XJ: Histone deacetylase HDAC4
promotes the proliferation and invasion of glioma cells. Int J
Oncol. 53:2758–2768. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xiao Q, Huang L, Zhang Z, Chen X, Luo J,
Zhang Z, Chen S, Shu Y, Han Z and Cao K: Overexpression of miR-140
inhibits proliferation of osteosarcoma cells via suppression of
histone deacetylase 4. Oncol Res. 25:267–275. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zeng LS, Yang XZ, Wen YF, Mail SJ, Wang
MH, Zhang MY, Zheng XF and Wang HY: Overexpressed HDAC4 is
associated with poor survival and promotes tumor progression in
esophageal carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY). 8:1236–1249. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Cao K, Wang H, Fang Y, Wang Y, Wei L, Chen
X, Jiang Z, Wei X and Hu Y: Histone deacetylase 4 promotes
osteosarcoma cell proliferation and invasion by regulating
expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Front Oncol.
9:8702019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wang H, Feng L, Zheng Y, Li W, Liu L, Xie
S, Zhou Y, Chen C and Cheng D: LINC00680 promotes the progression
of non-small cell lung cancer and functions as a sponge of
miR-410-3p to enhance HMGB1 expression. Onco Targets Ther.
13:8183–8196. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang H, Wang J, Li J, Zhou X, Yin L, Wang
Y, Gu Y, Niu X, Yang Y, Ji H and Zhang Q: HMGB1 is a key factor for
tamoxifen resistance and has the potential to predict the efficacy
of CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 112:1603–1613.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nakamura T, Okui T, Hasegawa K, Ryumon S,
Ibaragi S, Ono K, Kunisada Y, Obata K, Masui M, Shimo T and Sasaki
A: High mobility group box 1 induces bone pain associated with bone
invasion in a mouse model of advanced head and neck cancer. Oncol
Rep. 44:2547–2558. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
42
|
Zhu X, Sun L and Wang Y: High mobility
group box 1 (HMGB1) is upregulated by the Epstein-Barr virus
infection and promotes the proliferation of human nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cells. Acta Otolaryngol. 136:87–94. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Yuan C and Yang L: Long non-coding RNA
PITPNA-AS1 accelerates the progression of colorectal cancer through
miR-129-5p/HMGB1 axis. Cancer Manag Res. 12:12497–12507. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
44
|
Guan H, Liu J, Lv P, Zhou L, Zhang J and
Cao W: MicroRNA-590 inhibits migration, invasion and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma by targeting low-density lipoprotein receptor-related
protein 6. Oncol Rep. 44:1385–1392. 2020.
|
|
45
|
Zhang F, Cheng N, Du J, Zhang H and Zhang
C: MicroRNA-200b-3p promotes endothelial cell apoptosis by
targeting HDAC4 in atherosclerosis. BMC Cardiovasc Disord.
21:1722021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lu Z, Wang D, Wang X, Zou J, Sun J and Bi
Z: MiR-206 regulates the progression of osteoporosis via targeting
HDAC4. Eur J Med Res. 26:82021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gondaliya P, P Dasare A, Jash K, Tekade
RK, Srivastava A and Kalia K: miR-29b attenuates histone
deacetylase-4 mediated podocyte dysfunction and renal fibrosis in
diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 19:13–27. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Malavika D, Shreya S, Raj Priya V, Rohini
M, He Z, Partridge NC and Selvamurugan N: miR-873-3p targets HDAC4
to stimulate matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression upon
parathyroid hormone exposure in rat osteoblasts. J Cell Physiol.
235:7996–8009. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhang Y, Chu X and Wei Q: MiR-451 Promotes
cell apoptosis and inhibits autophagy in pediatric acute myeloid
leukemia by targeting HMGB1. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol.
40:45–53. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Feng XE: miR-548b suppresses melanoma cell
growth, migration, and invasion by negatively regulating its target
gene HMGB1. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 36:189–201. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Shen H, Xu L, You C, Tang H, Wu H, Zhang Y
and Xie M: miR-665 is downregulated in glioma and inhibits tumor
cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting high
mobility group box 1. Oncol Lett. 21:1562021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Dong H and Song J: miR-142-3p reduces the
viability of human cervical cancer cells by negatively regulating
the cytoplasmic localization of HMGB1. Exp Ther Med. 21:2122021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Qiu M, Liu D and Fu Q: MiR-129-5p shuttled
by human synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes relieves
IL-1β induced osteoarthritis via targeting HMGB1. Life Sci.
269:1189872021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Liu W, Zhang J, Zou C, Xie X, Wang Y, Wang
B, Zhao Z, Tu J, Wang X, Li H, et al: Microarray expression profile
and functional analysis of circular RNAs in osteosarcoma. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 43:969–985. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Guan H, Mei Y, Mi Y, Li C, Sun X, Zhao X,
Liu J, Cao W, Li Y and Wang Y: Downregulation of lncRNA ANRIL
suppresses growth and metastasis in human osteosarcoma cells. Onco
Targets Ther. 11:4893–4899. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Lei S and Xiang L: Up-regulation of
circRNA hsa_circ_0003074 expression is a reliable diagnostic and
prognostic biomarker in patients with osteosarcoma. Cancer Manag
Res. 12:9315–9325. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Nie WB, Zhao LM, Guo R, Wang MX and Ye FG:
Circular RNA circ-NT5C2 acts as a potential novel biomarker for
prognosis of osteosarcoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:6239–6244.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kun-Peng Z, Chun-Lin Z, Jian-Ping H and
Lei Z: A novel circulating hsa_circ_0081001 act as a potential
biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of osteosarcoma. Int J Biol
Sci. 14:1513–1520. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wang Z, Deng M, Chen L, Wang W, Liu G, Liu
D, Han Z and Zhou Y: Circular RNA Circ-03955 promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in osteosarcoma by regulating
miR-3662/metadherin pathway. Front Oncol. 10:5454602020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
61
|
Wan J, Liu Y, Long F, Tian J and Zhang C:
circPVT1 promotes osteosarcoma glycolysis and metastasis by
sponging miR-423-5p to activate Wnt5a/Ror2 signaling. Cancer Sci.
112:1707–1722. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Yi Y, Liu Y, Wu W, Wu K and Zhang W:
Reconstruction and analysis of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in the
pathology of cervical cancer. Oncol Rep. 41:2209–2225.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zhang J, Yang Y, Yang T, Liu Y, Li A, Fu
S, Wu M, Pan Z and Zhou W: microRNA-22, downregulated in
hepatocellular carcinoma and correlated with prognosis, suppresses
cell proliferation and tumourigenicity. Br J Cancer. 103:1215–1220.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Hsieh TH, Hsu CY, Tsai CF, Long CY, Chai
CY, Hou MF, Lee JN, Wu DC, Wang SC and Tsai EM: miR-125a-5p is a
prognostic biomarker that targets HDAC4 to suppress breast
tumorigenesis. Oncotarget. 6:494–509. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Shen YF, Wei AM, Kou Q, Zhu QY and Zhang
L: Histone deacetylase 4 increases progressive epithelial ovarian
cancer cells via repression of p21 on fibrillar collagen matrices.
Oncol Rep. 35:948–954. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Zhang Y, Lv F, Qiao L and Zhao Q: MiR-505
inhibits prostate cancer cell invasion, metastasis and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through targeting HMGB-1. J
BUON. 25:2036–2044. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Luan X, Ma C, Wang P and Lou F: HMGB1 is
negatively correlated with the development of endometrial carcinoma
and prevents cancer cell invasion and metastasis by inhibiting the
process of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Onco Targets Ther.
10:1389–1402. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
68
|
Meng Q, Zhao J, Liu H, Zhou G, Zhang W, Xu
X and Zheng M: HMGB1 promotes cellular proliferation and invasion,
suppresses cellular apoptosis in osteosarcoma. Tumour Biol.
35:12265–12274. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|