|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Duma N, Santana-Davila R and Molina JR:
Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, screening, diagnosis, and
treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 94:1623–1640. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:7–30. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Garon EB, Rizvi NA, Hui R, Leighl N,
Balmanoukian AS, Eder JP, Patnaik A, Aggarwal C, Gubens M, Horn L,
et al: Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung
cancer. New Engl J Med. 372:2018–2028. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gandhi L, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Gadgeel S,
Esteban E, Felip E, De Angelis F, Domine M, Clingan P, Hochmair MJ,
Powell SF, et al: Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic
non-small-cell lung cancer. New Engl J Med. 378:2078–2092. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brahmer J, Reckamp KL, Baas P, Crinò L,
Eberhardt WE, Poddubskaya E, Antonia S, Pluzanski A, Vokes EE,
Holgado E, et al: Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced
squamous-cell non-small-cell lung cancer. New Engl J Med.
373:123–135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Borghaei H, Paz-Ares L, Horn L, Spigel DR,
Steins M, Ready NE, Chow LQ, Vokes EE, Felip E, Holgado E, et al:
Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell
lung cancer. New Engl J Med. 373:1627–1639. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qin S, Xu L, Yi M, Yu S, Wu K and Luo S:
Novel immune checkpoint targets: Moving beyond PD-1 and CTLA-4. Mol
Cancer. 18:1552019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Postow MA, Sidlow R and Hellmann MD:
Immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint
blockade. New Engl J Med. 378:158–168. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Postow MA, Callahan MK and Wolchok JD:
Immune checkpoint blockade in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol.
33:1974–1982. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shukuya T and Carbone DP: Predictive
markers for the efficacy of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in lung
cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 11:976–988. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Reck M, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG,
Hui R, Csőszi T, Fülöp A, Gottfried M, Peled N, Tafreshi A, Cuffe
S, et al: Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1-positive
non-small-cell lung cancer. New Engl J Med. 375:1823–1833. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Herbst RS, Giaccone G, de Marinis F,
Reinmuth N, Vergnenegre A, Barrios CH, Morise M, Felip E, Andric Z,
Geater S, et al: Atezolizumab for first-line treatment of
PD-L1-selected patients with NSCLC. New Engl J Med. 383:1328–1339.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rizvi H, Sanchez-Vega F, La K, Chatila W,
Jonsson P, Halpenny D, Plodkowski A, Long N, Sauter JL, Rekhtman N,
et al: Molecular determinants of response to anti-programmed cell
death (PD)-1 and anti-programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) blockade in
patients with non-small-cell lung cancer profiled with targeted
next-generation sequencing. J Clin Oncol. 36:633–641. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shirasawa M, Yoshida T, Shimoda Y,
Takayanagi D, Shiraishi K, Kubo T, Mitani S, Matsumoto Y, Masuda K,
Shinno Y, et al: Differential immune-related microenvironment
determines programmed cell death protein-1/programmed death-ligand
1 blockade efficacy in patients with advanced NSCLC. J Thorac
Oncol. 16:2078–2090. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mansfield AS, Murphy SJ, Peikert T, Yi ES,
Vasmatzis G, Wigle DA and Aubry MC: Heterogeneity of programmed
cell death ligand 1 expression in multifocal lung cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 22:2177–2182. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Sacher AG and Gandhi L: Biomarkers for the
clinical use of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in non-small-cell lung
cancer: A review. JAMA Oncol. 2:1217–1222. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Havel JJ, Chowell D and Chan TA: The
evolving landscape of biomarkers for checkpoint inhibitor
immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 19:133–150. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Daud AI, Wolchok JD, Robert C, Hwu WJ,
Weber JS, Ribas A, Hodi FS, Joshua AM, Kefford R, Hersey P, et al:
Programmed death-ligand 1 expression and response to the
anti-programmed death 1 antibody pembrolizumab in melanoma. J Clin
Oncol. 34:4102–4109. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Forman BM, Goode E, Chen J, Oro AE,
Bradley DJ, Perlmann T, Noonan DJ, Burka LT, McMorris T, Lamph WW,
et al: Identification of a nuclear receptor that is activated by
farnesol metabolites. Cell. 81:687–693. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lu TT, Makishima M, Repa JJ, Schoonjans K,
Kerr TA, Auwerx J and Mangelsdorf DJ: Molecular basis for feedback
regulation of bile acid synthesis by nuclear receptors. Mol Cell.
6:507–515. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang YD, Chen WD, Moore DD and Huang W:
FXR: A metabolic regulator and cell protector. Cell Res.
18:1087–1095. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang F, Huang X, Yi T, Yen Y, Moore DD and
Huang W: Spontaneous development of liver tumors in the absence of
the bile acid receptor farnesoid X receptor. Cancer Res.
67:863–867. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
De Gottardi A, Touri F, Maurer CA, Perez
A, Maurhofer O, Ventre G, Bentzen CL, Niesor EJ and Dufour JF: The
bile acid nuclear receptor FXR and the bile acid binding protein
IBABP are differently expressed in colon cancer. Dig Dis Sci.
49:982–989. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guan B, Li H, Yang Z, Hoque A and Xu X:
Inhibition of farnesoid X receptor controls esophageal cancer cell
growth in vitro and in nude mouse xenografts. Cancer.
119:1321–1329. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Journe F, Durbecq V, Chaboteaux C, Rouas
G, Laurent G, Nonclercq D, Sotiriou C, Body JJ and Larsimont D:
Association between farnesoid X receptor expression and cell
proliferation in estrogen receptor-positive luminal-like breast
cancer from postmenopausal patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
115:523–535. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
You W, Chen B, Liu X, Xue S, Qin H and
Jiang H: Farnesoid X receptor, a novel proto-oncogene in non-small
cell lung cancer, promotes tumor growth via directly
transactivating CCND1. Sci Rep. 7:5912017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
You W, Li L, Sun D, Liu X, Xia Z, Xue S,
Chen B, Qin H, Ai J and Jiang H: Farnesoid X receptor constructs an
immunosuppressive microenvironment and sensitizes
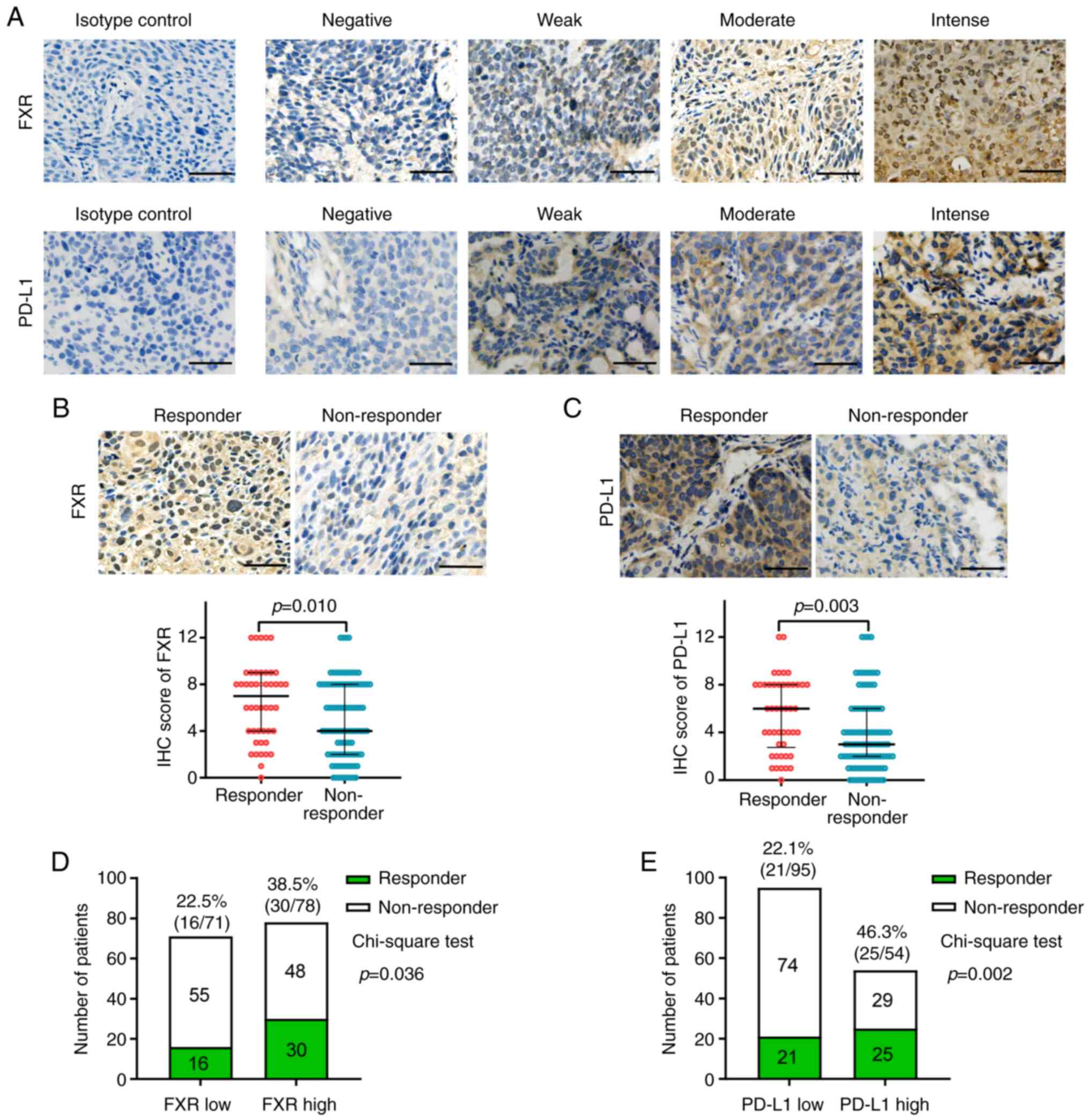
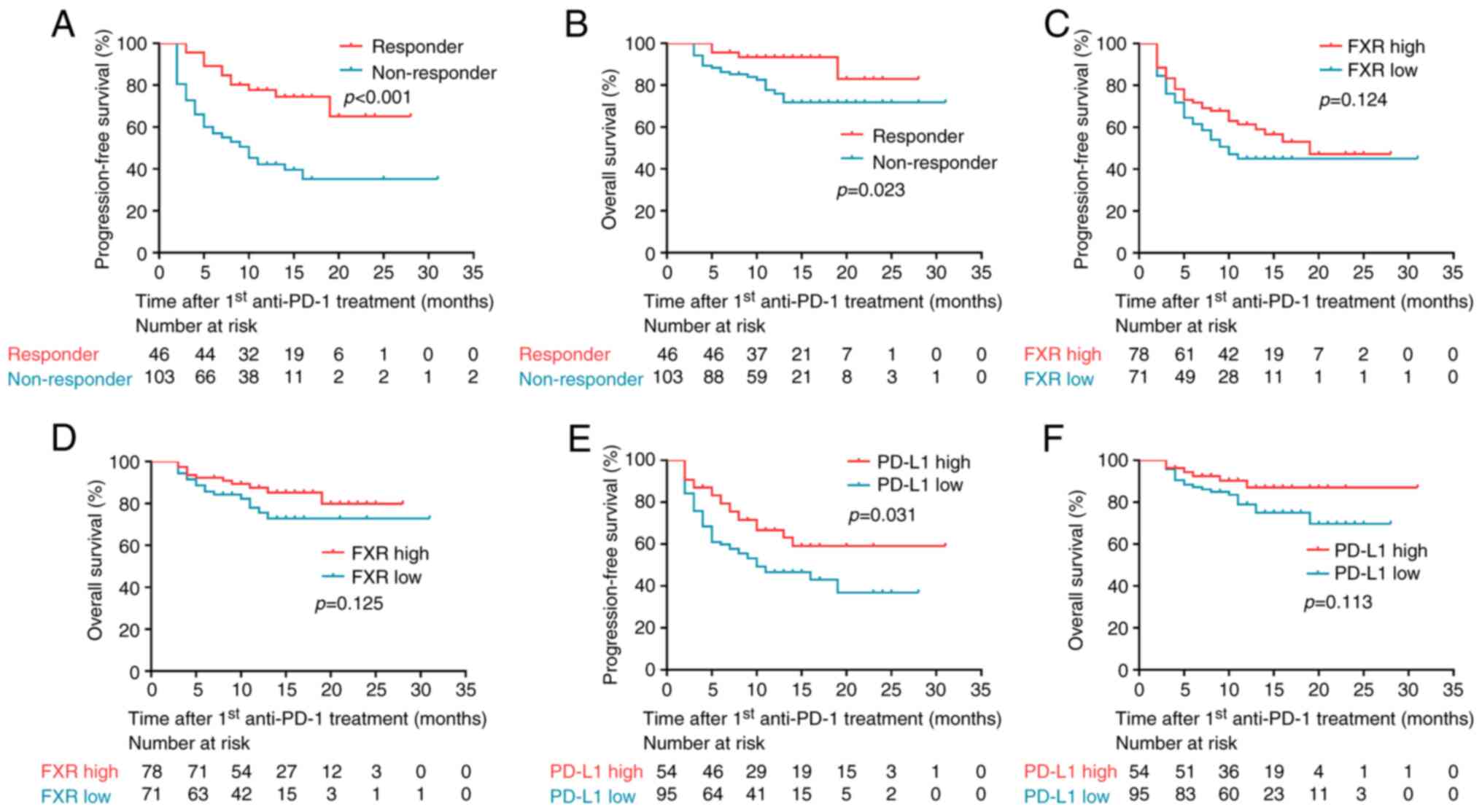
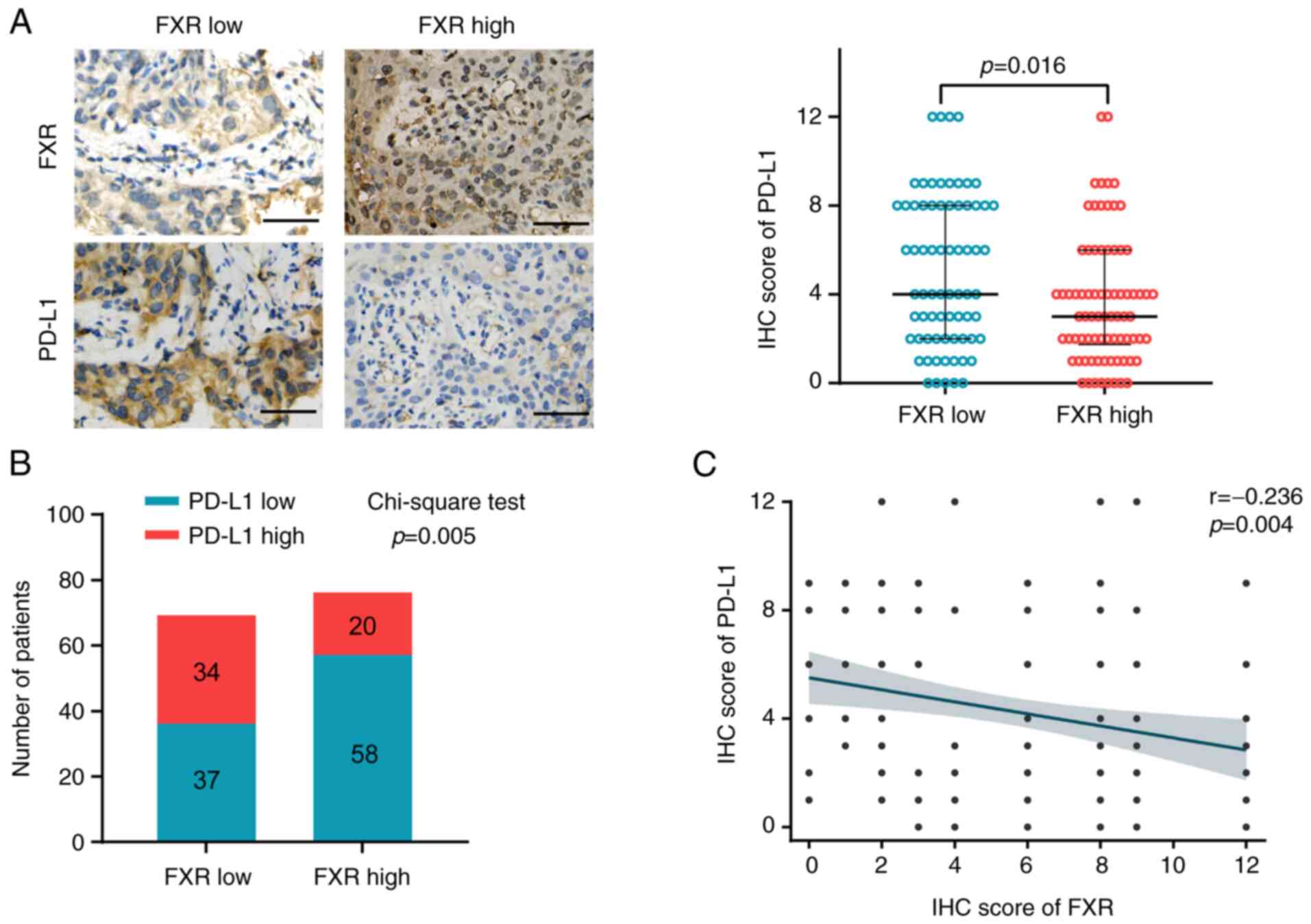
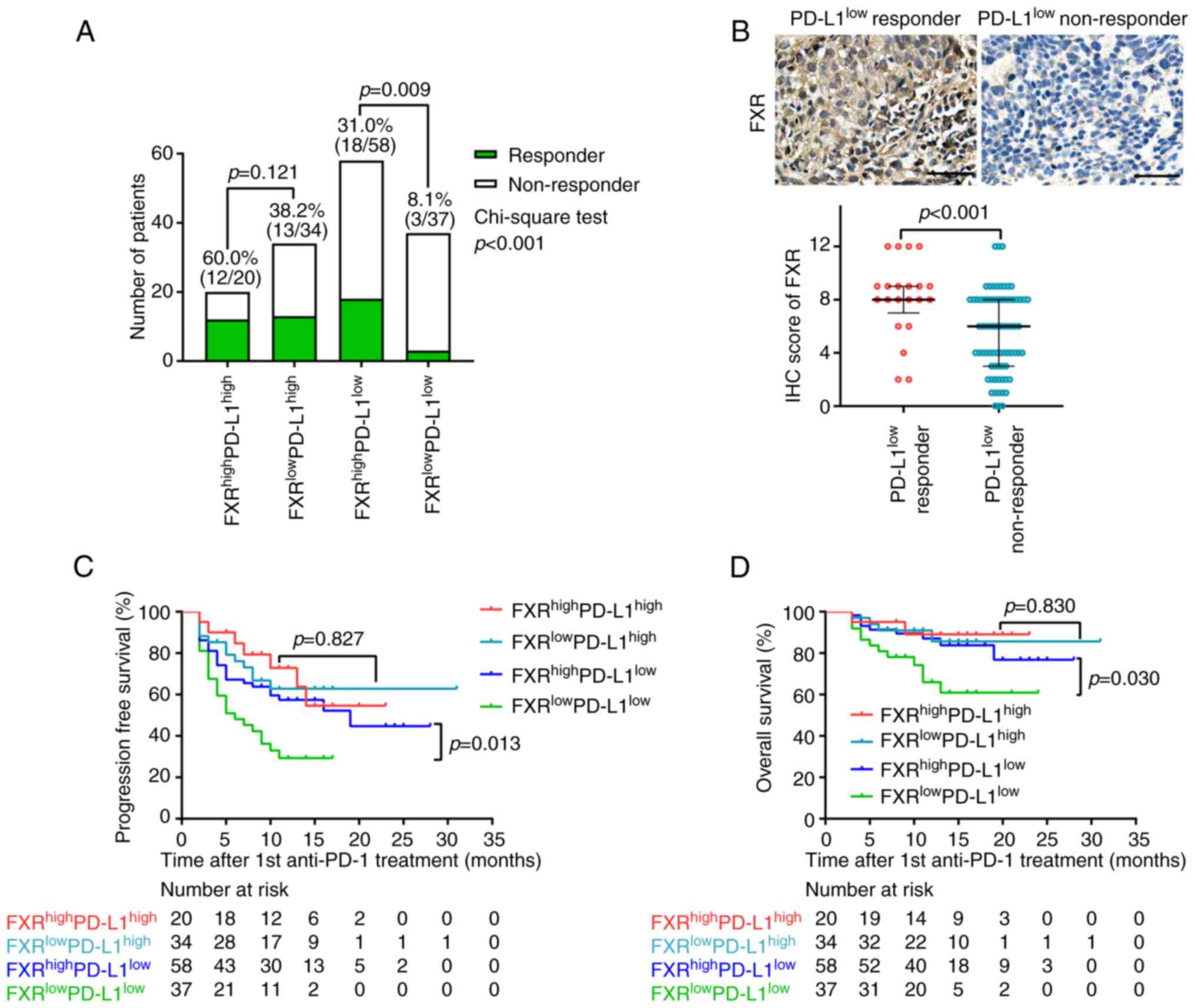
FXRhighPD-L1low NSCLC to anti-PD-1
immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol Res. 7:990–1000. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, Horton J,
Davis TE, McFadden ET and Carbone PP: Toxicity and response
criteria of the Eastern cooperative oncology group. Am J Clin
Oncol. 5:649–655. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cortellini A, Ricciuti B, Facchinetti F,
Alessi JVM, Venkatraman D, Dall'Olio FG, Cravero P, Vaz VR,
Ottaviani D, Majem M, et al: Antibiotic-exposed patients with
non-small-cell lung cancer preserve efficacy outcomes following
first-line chemo-immunotherapy. Ann Oncol. 32:1391–1399. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lantuejoul S, Sound-Tsao M, Cooper WA,
Girard N, Hirsch FR, Roden AC, Lopez-Rios F, Jain D, Chou TY, Motoi
N, et al: PD-L1 testing for lung cancer in 2019: Perspective from
the IASLC pathology committee. J Thorac Oncol. 15:499–519. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Nakayama Y, Mimura K, Tamaki T, Shiraishi
K, Kua LF, Koh V, Ohmori M, Kimura A, Inoue S, Okayama H, et al:
Phospho-STAT1 expression as a potential biomarker for
anti-PD-1/anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy for breast cancer. Int J Oncol.
54:2030–2038. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Weigelin B, Krause M and Friedl P:
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte migration and effector function in the tumor
microenvironment. Immunol Lett. 138:19–21. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Blank C and Mackensen A: Contribution of
the PD-L1/PD-1 pathway to T-cell exhaustion: An update on
implications for chronic infections and tumor evasion. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 56:739–745. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lee JY, Lee KT, Lee JK, Lee KH, Jang KT,
Heo JS, Choi SH, Kim Y and Rhee JC: Farnesoid X receptor,
overexpressed in pancreatic cancer with lymph node metastasis
promotes cell migration and invasion. Br J Cancer. 104:1027–1037.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Das A, Yaqoob U, Mehta D and Shah VH: FXR
promotes endothelial cell motility through coordinated regulation
of FAK and MMP-9. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:562–570. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang W, Zhan M, Li Q, Chen W, Chu H, Huang
Q, Hou Z, Man M and Wang J: FXR agonists enhance the sensitivity of
biliary tract cancer cells to cisplatin via SHP dependent
inhibition of Bcl-xL expression. Oncotarget. 7:34617–34629. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Guo J, Zheng J, Mu M, Chen Z, Xu Z, Zhao
C, Yang K, Qin X, Sun X and Yu J: GW4064 enhances the
chemosensitivity of colorectal cancer to oxaliplatin by inducing
pyroptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 548:60–66. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fusi A, Festino L, Botti G, Masucci G,
Melero I, Lorigan P and Ascierto PA: PD-L1 expression as a
potential predictive biomarker. Lancet Oncol. 16:1285–1287. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Carbone DP, Reck M, Paz-Ares L, Creelan B,
Horn L, Steins M, Felip E, van den Heuvel MM, Ciuleanu TE, Badin F,
et al: First-line nivolumab in stage IV or recurrent non-small-cell
lung cancer. New Engl J Med. 376:2415–2426. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Herbst RS, Soria JC, Kowanetz M, Fine GD,
Hamid O, Gordon MS, Sosman JA, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Gettinger
SN, et al: Predictive correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1
antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature. 515:563–567. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kang DH, Park CK, Chung C, Oh IJ, Kim YC,
Park D, Kim J, Kwon GC, Kwon I, Sun P, et al: Baseline serum
interleukin-6 levels predict the response of patients with advanced
non-small cell lung cancer to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. Immune Netw.
20:e272020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Botta GP, Kato S, Patel H, Fanta P, Lee S,
Okamura R and Kurzrock R: SWI/SNF complex alterations as a
biomarker of immunotherapy efficacy in pancreatic cancer. JCI
Insight. 6:e1504532021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ayers M, Lunceford J, Nebozhyn M, Murphy
E, Loboda A, Kaufman DR, Albright A, Cheng JD, Kang SP, Shankaran
V, et al: IFN-γ-related mRNA profile predicts clinical response to
PD-1 blockade. J Clin Invest. 127:2930–2940. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|