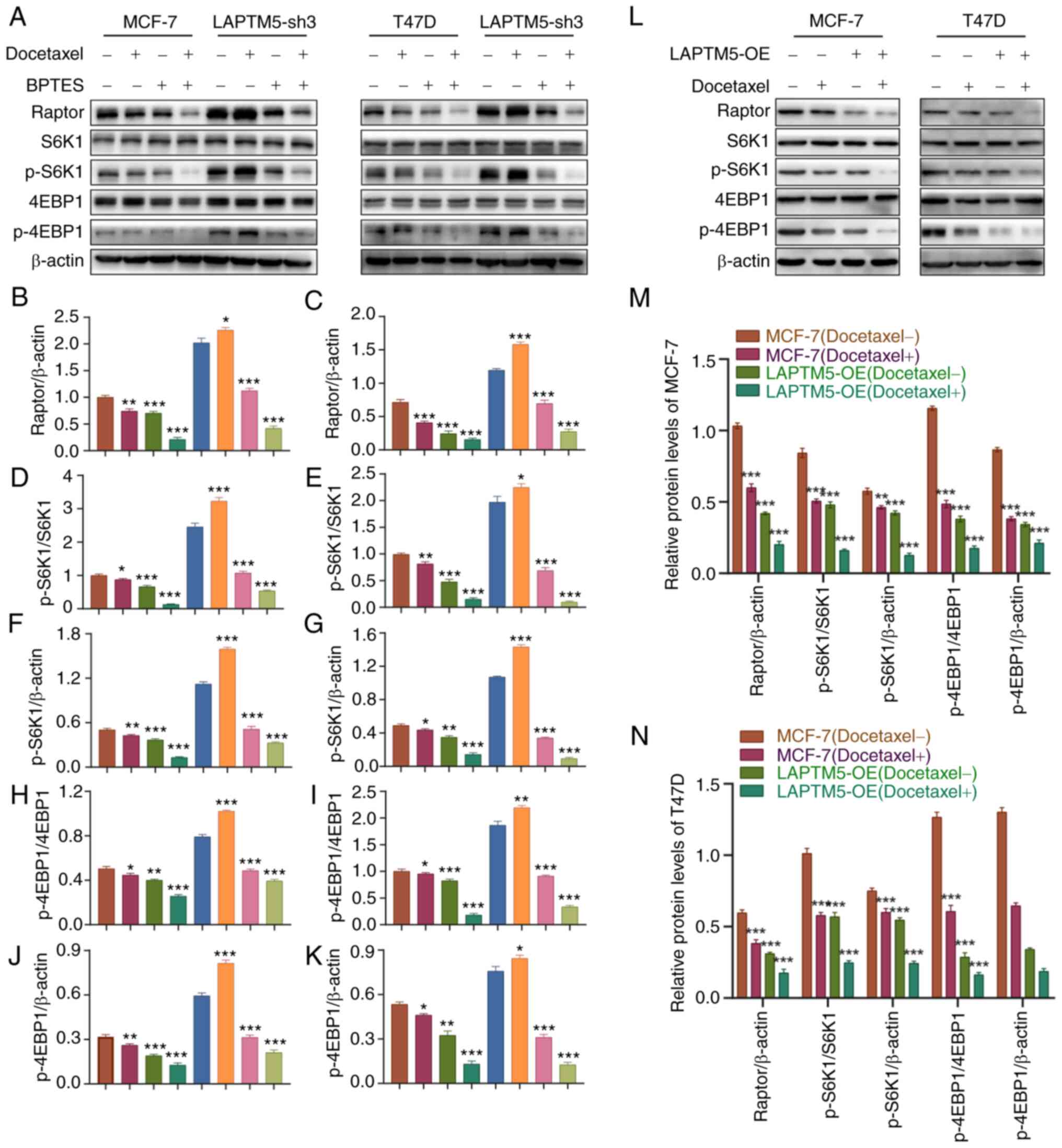
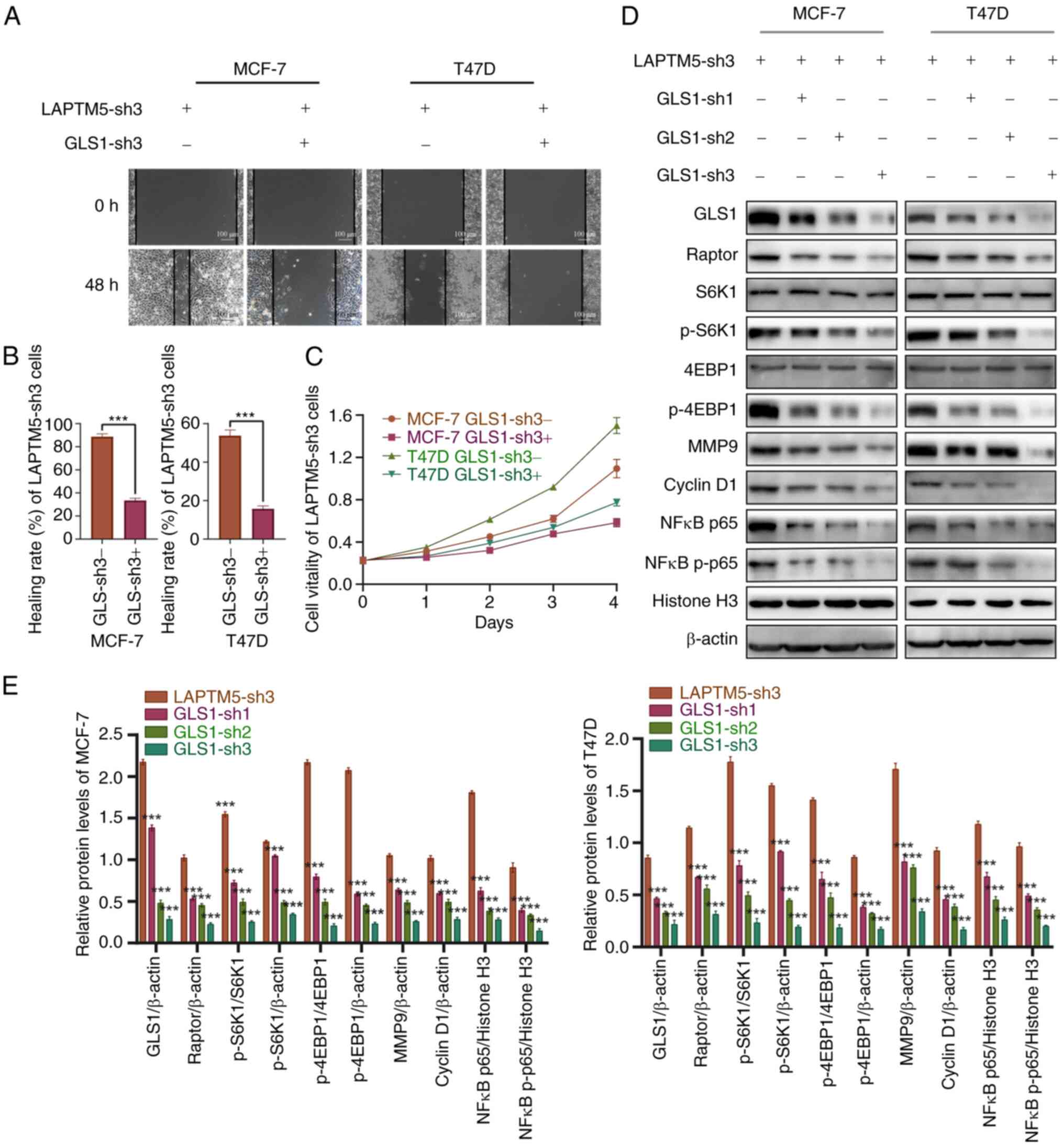
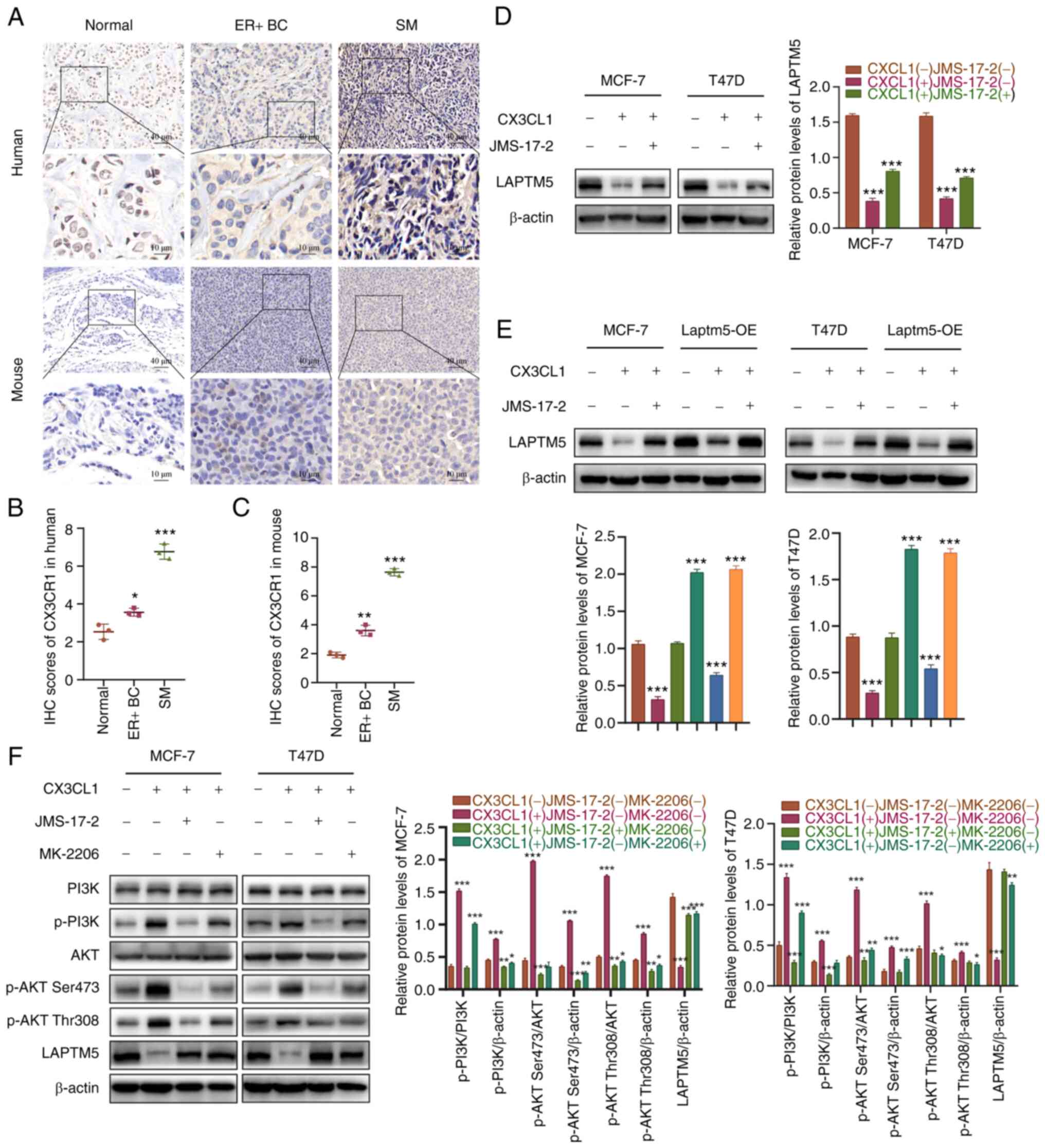
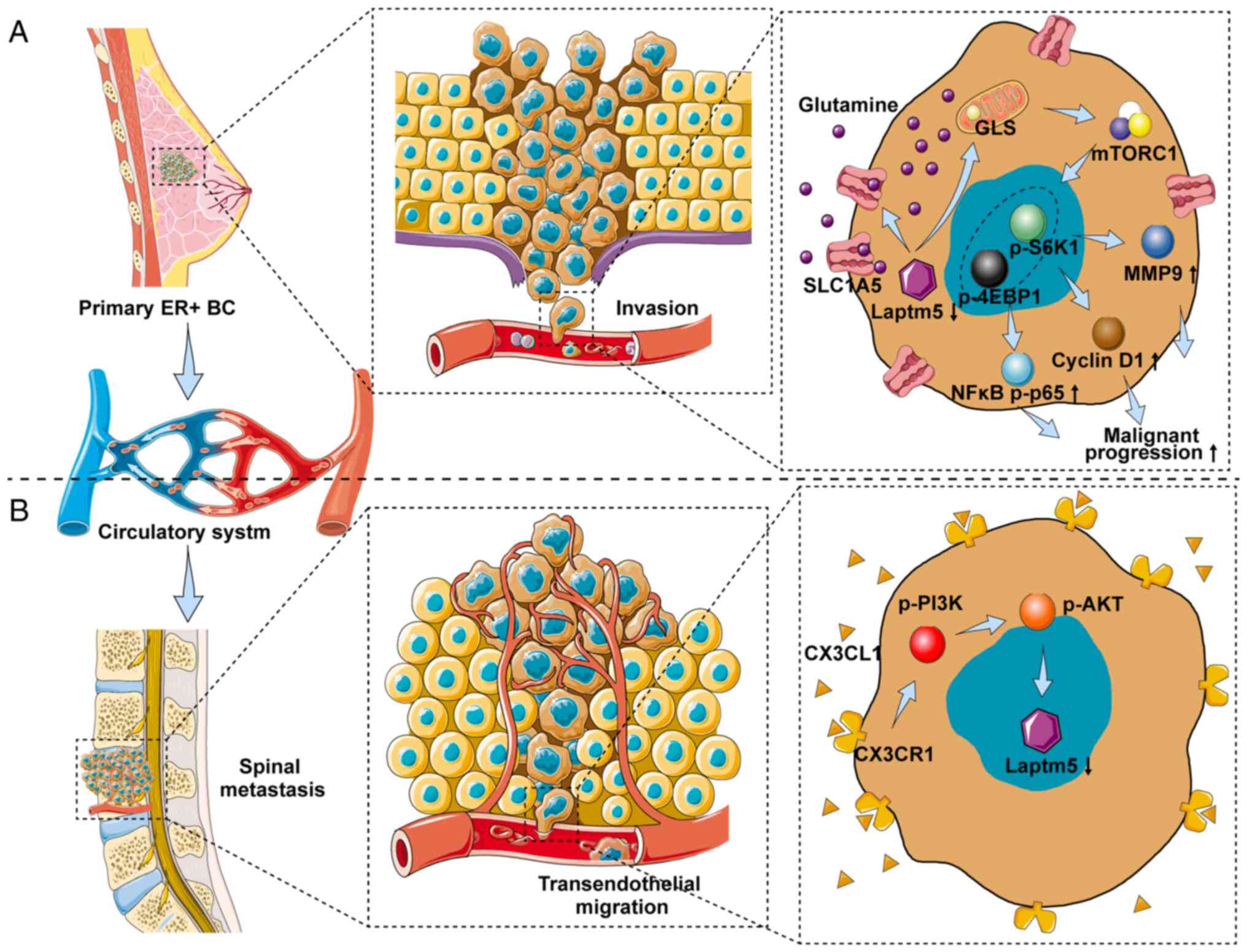
|
1
|
Akram M, Iqbal M, Daniyal M and Khan AU:
Awareness and current knowledge of breast cancer. Biol Res.
50:332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liang Y, Zhang H, Song X and Yang Q:
Metastatic heterogeneity of breast cancer: Molecular mechanism and
potential therapeutic targets. Semin Cancer Biol. 60:14–27. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Scully OJ, Bay BH, Yip G and Yu Y: Breast
cancer metastasis. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 9:311–320.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Turner NC, Neven P, Loibl S and Andre F:
Advances in the treatment of advanced oestrogen-receptor-positive
breast cancer. Lancet. 389:2403–2414. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chen WZ, Shen JF, Zhou Y, Chen XY, Liu JM
and Liu ZL: Clinical characteristics and risk factors for
developing bone metastases in patients with breast cancer. Sci Rep.
7:113252017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ma RY, Zhang H, Li XF, Zhang CB, Selli C,
Tagliavini G, Lam AD, Prost S, Sims AH, Hu HY, et al:
Monocyte-derived macrophages promote breast cancer bone metastasis
outgrowth. J Exp Med. 217:e201918202020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tahara RK, Brewer TM, Theriault RL and
Ueno NT: Bone metastasis of breast cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol.
1152:105–129. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Glowacka WK, Alberts P, Ouchida R, Wang JY
and Rotin D: LAPTM5 protein is a positive regulator of
proinflammatory signaling pathways in macrophages. J Biol Chem.
287:27691–27702. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu X, Shang X, Li J and Zhang S: The
prognosis and immune checkpoint blockade efficacy prediction of
tumor-infiltrating immune cells in lung cancer. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 9:7071432021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang L, Zhang M, Chen X, He Y, Chen R,
Zhang J, Huang J, Ouyang C and Shi G: Identification of the
tubulointerstitial infiltrating immune cell landscape and immune
marker related molecular patterns in lupus nephritis using
bioinformatics analysis. Ann Transl Med. 8:15962020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Berberich A, Bartels F, Tang Z, Knoll M,
Pusch S, Hucke N, Kessler T, Dong Z, Wiestler B, Winkler F, et al:
LAPTM5-CD40 crosstalk in glioblastoma invasion and temozolomide
resistance. Front Oncol. 10:7472020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Nuylan M, Kawano T, Inazawa J and Inoue J:
Down-regulation of LAPTM5 in human cancer cells. Oncotarget.
7:28320–28328. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mossmann D, Park S and Hall MN: mTOR
signalling and cellular metabolism are mutual determinants in
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 18:744–757. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vander Heiden MG and DeBerardinis RJ:
Understanding the intersections between metabolism and cancer
biology. Cell. 168:657–669. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Reinfeld BI, Madden MZ, Wolf MM, Chytil A,
Bader JE, Patterson AR, Sugiura A, Cohen AS, Ali A and Do BT: et al
Cell-programmed nutrient partitioning in the tumour
microenvironment. Nature. 593:282–288. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cha YJ, Kim ES and Koo JS: Amino acid
transporters and glutamine metabolism in breast cancer. Int J Mol
Sci. 19:9072018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
van Geldermalsen M, Wang Q, Nagarajah R,
Marshall AD, Thoeng A, Gao D, Ritchie W, Feng Y, Bailey CG and Deng
N: et al ASCT2/SLC1A5 controls glutamine uptake and tumour growth
in triple-negative basal-like breast cancer. Oncogene.
35:3201–3208. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Kodama M, Oshikawa K, Shimizu H, Yoshioka
S, Takahashi M, Izumi Y, Bamba T, Tateishi C, Tomonaga T, Matsumoto
M and Nakayama KI: A shift in glutamine nitrogen metabolism
contributes to the malignant progression of cancer. Nat Commun.
11:13202020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Feng M, Xiong G, Cao Z, Yang G, Zheng S,
Qiu J, You L, Zheng L, Zhang T and Zhao Y: LAT2 regulates
glutamine-dependent mTOR activation to promote glycolysis and
chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
37:2742018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ramapriyan R, Caetano MS, Barsoumian HB,
Mafra ACP, Zambalde EP, Menon H, Tsouko E, Welsh JW and Cortez MA:
Altered cancer metabolism in mechanisms of immunotherapy
resistance. Pharmacol Ther. 195:162–171. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Korbecki J, Simińska D, Kojder K, Grochans
S, Gutowska I, Chlubek D and Baranowska-Bosiacka I:
Fractalkine/CX3CL1 in neoplastic processes. Int J Mol Sci.
21:37232020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Liang Y, Yi L, Liu P, Jiang L, Wang H, Hu
A, Sun C and Dong J: CX3CL1 involves in breast cancer metastasizing
to the spine via the Src/FAK signaling pathway. J Cancer.
9:3603–3612. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang G, Wang H, Huang D, Wu Y, Ding W,
Zhou Q, Ding Q, Zhang N, Na R and Xu K: The clinical implications
and molecular mechanism of CX3CL1 expression in urothelial bladder
cancer. Front Oncol. 11:7528602021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang K, Jiang L, Hu A, Sun C, Zhou L,
Huang Y, Chen Q, Dong J, Zhou X and Zhang F: Vertebral-specific
activation of the CX3CL1/ICAM-1 signaling network mediates
non-small-cell lung cancer spinal metastasis by engaging tumor
cell-vertebral bone marrow endothelial cell interactions.
Theranostics. 11:4770–4789. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive
functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lichter JG, Carruth E, Mitchell C, Barth
AS, Aiba T, Kass DA, Tomaselli GF, Bridge JH and Sachse FB:
Remodeling of the sarcomeric cytoskeleton in cardiac ventricular
myocytes during heart failure and after cardiac resynchronization
therapy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 72:186–195. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Xiang Y, Stine ZE, Xia J, Lu Y, O'Connor
RS, Altman BJ, Hsieh AL, Gouw AM, Thomas AG and Gao P: et al
Targeted inhibition of tumor-specific glutaminase diminishes
cell-autonomous tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest. 125:2293–2306. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shen F, Zhang Y, Jernigan DL, Feng X, Yan
J, Garcia FU, Meucci O, Salvino JM and Fatatis A: Novel
small-molecule CX3CR1 antagonist impairs metastatic seeding and
colonization of breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 14:518–527.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Montaudon E, Nikitorowicz-Buniak J, Sourd
L, Morisset L, El Botty R, Huguet L, Dahmani A, Painsec P, Nemati F
and Vacher S: et al PLK1 inhibition exhibits strong anti-tumoral
activity in CCND1-driven breast cancer metastases with acquired
palbociclib resistance. Nat Commun. 11:40532020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu W, Jiang L, Bian C, Liang Y, Xing R,
Yishakea M and Dong J: Role of CX3CL1 in diseases. Arch Immunol
Ther Exp (Warsz). 64:371–383. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Sun C, Hu A, Wang S, Tian B, Jiang L,
Liang Y, Wang H and Dong J: ADAM17-regulated CX3CL1 expression
produced by bone marrow endothelial cells promotes spinal
metastasis from hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 57:249–263.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yi L, Liang Y, Zhao Q, Wang H and Dong J:
CX3CL1 induces vertebral microvascular barrier dysfunction via the
Src/P115-RhoGEF/ROCK signaling pathway. Front Cell Neurosci.
14:962020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tu J, Kuang Z, Xie X, Wu S, Wu T and Chen
S: Prognostic and predictive value of a mRNA signature in
peripheral T-cell lymphomas: A mRNA expression analysis. J Cell Mol
Med. 25:84–95. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zouali M: Transcriptional and metabolic
pre-B cell receptor-mediated checkpoints: Implications for
autoimmune diseases. Mol Immunol. 62:315–320. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cory JG and Cory AH: Critical roles of
glutamine as nitrogen donors in purine and pyrimidine nucleotide
synthesis: Asparaginase treatment in childhood acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. In Vivo. 20:587–589. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Metallo CM, Gameiro PA, Bell EL, Mattaini
KR, Yang J, Hiller K, Jewell CM, Johnson ZR, Irvine DJ and Guarente
L: et al Reductive glutamine metabolism by IDH1 mediates
lipogenesis under hypoxia. Nature. 481:380–384. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Karunakaran S, Ramachandran S,
Coothankandaswamy V, Elangovan S, Babu E, Periyasamy-Thandavan S,
Gurav A, Gnanaprakasam JP, Singh N and Schoenlein PV: et al SLC6A14
(ATB0,+) protein, a highly concentrative and broad specific amino
acid transporter, is a novel and effective drug target for
treatment of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. J Biol Chem.
286:31830–31838. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Matés JM, Campos-Sandoval JA,
Santos-Jiménez JL and Márquez J: Dysregulation of glutaminase and
glutamine synthetase in cancer. Cancer Lett. 467:29–39. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jewell JL, Kim YC, Russell RC, Yu FX, Park
HW, Plouffe SW, Tagliabracci VS and Guan KL: Metabolism.
Differential regulation of mTORC1 by leucine and glutamine.
Science. 347:194–198. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Meng D, Yang Q, Wang H, Melick CH, Navlani
R, Frank AR and Jewell JL: Glutamine and asparagine activate mTORC1
independently of Rag GTPases. J Biol Chem. 295:2890–2899. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Csibi A, Fendt SM, Li C, Poulogiannis G,
Choo AY, Chapski DJ, Jeong SM, Dempsey JM, Parkhitko A and Morrison
T: et al The mTORC1 pathway stimulates glutamine metabolism and
cell proliferation by repressing SIRT4. Cell. 153:840–854. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hua H, Kong Q, Zhang H, Wang J, Luo T and
Jiang Y: Targeting mTOR for cancer therapy. J Hematol Oncol.
12:712019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhen Y, Liu J, Huang Y, Wang Y, Li W and
Wu J: miR-133b inhibits cell growth, migration, and invasion by
targeting MMP9 in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Res.
25:1109–1116. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Shi Q and Li Y, Li S, Jin L, Lai H, Wu Y,
Cai Z, Zhu M, Li Q and Li Y: et al LncRNA DILA1 inhibits cyclin D1
degradation and contributes to tamoxifen resistance in breast
cancer. Nat Commun. 11:55132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ling J and Kumar R: Crosstalk between NFkB
and glucocorticoid signaling: A potential target of breast cancer
therapy. Cancer Lett. 322:119–126. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|