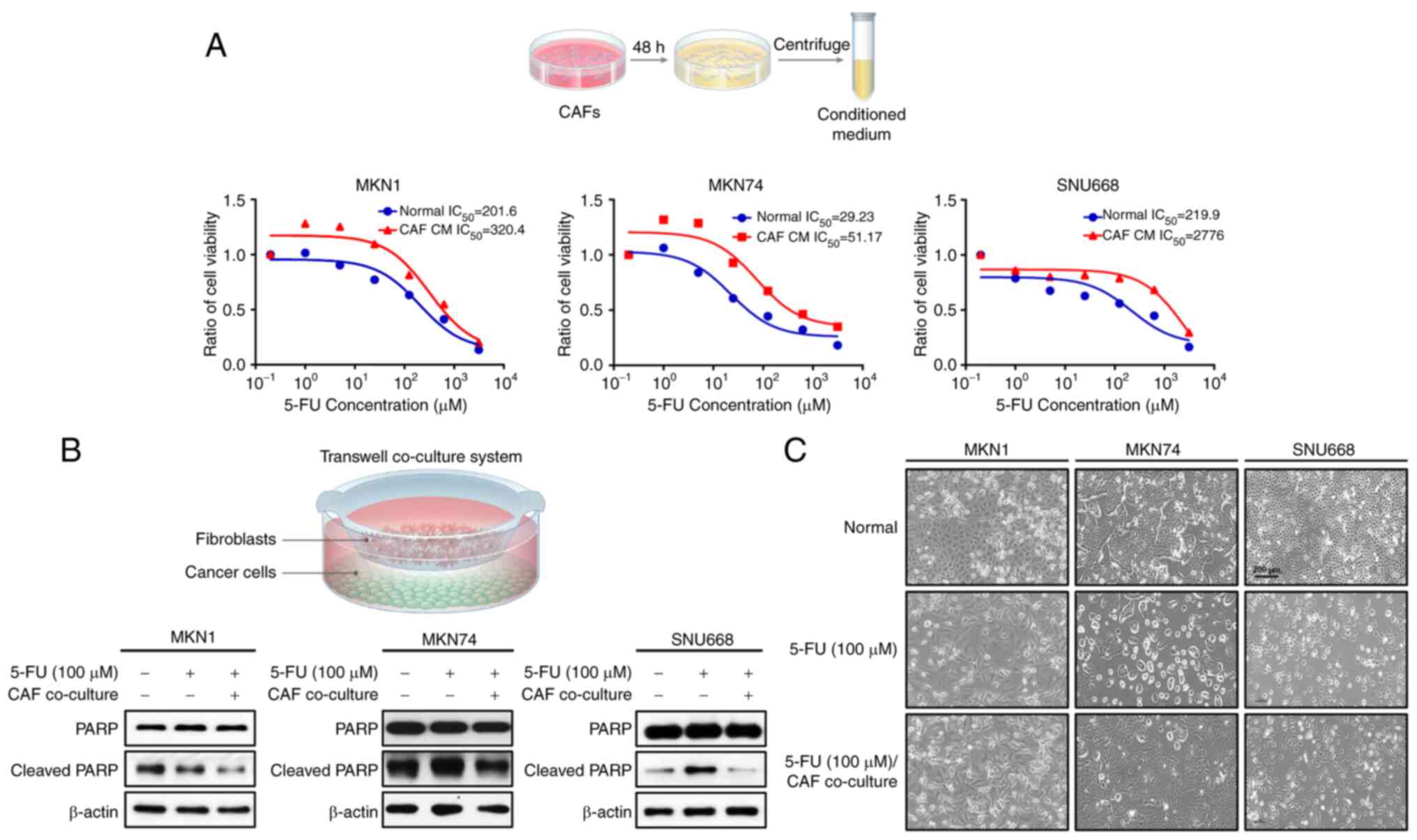
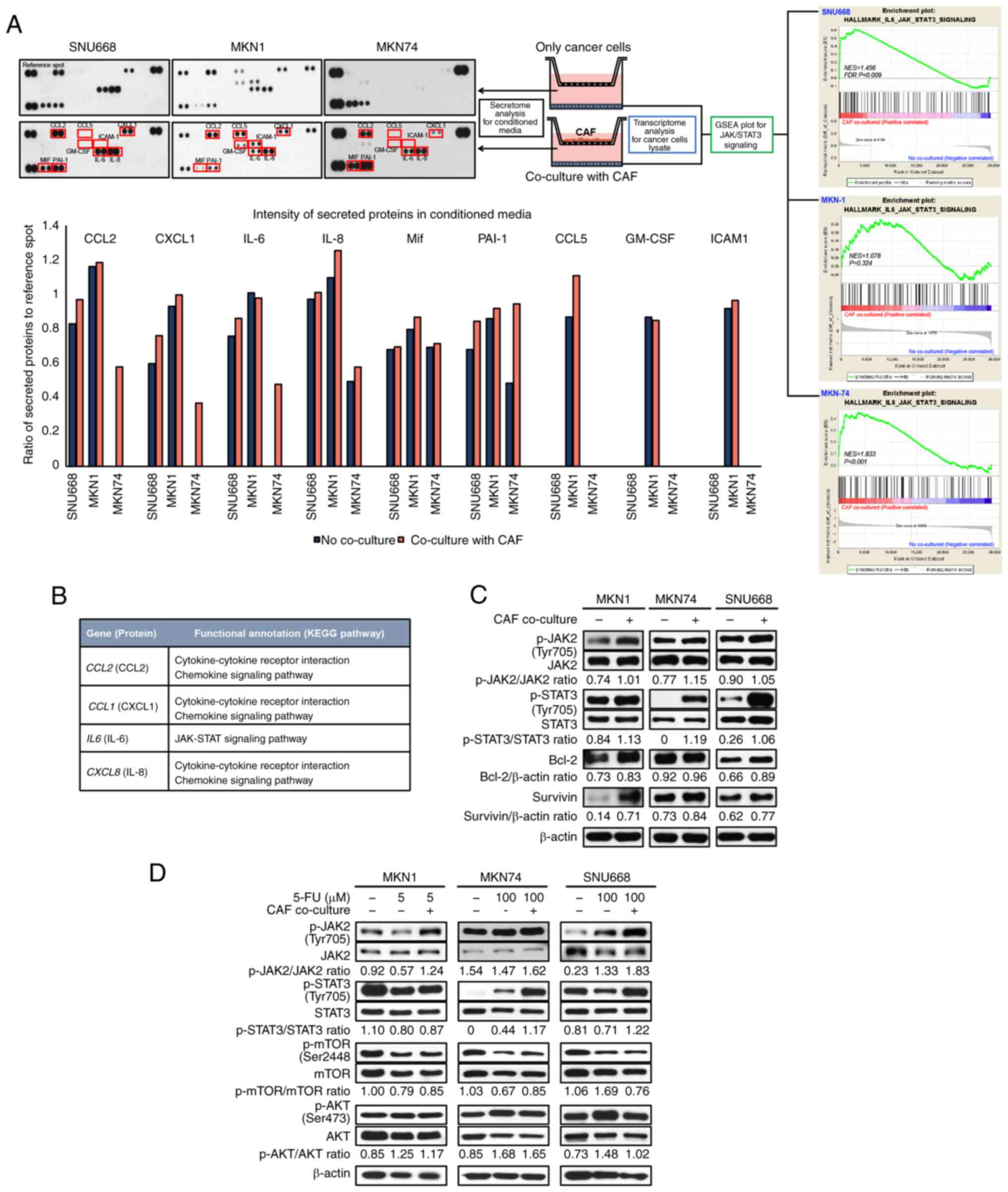
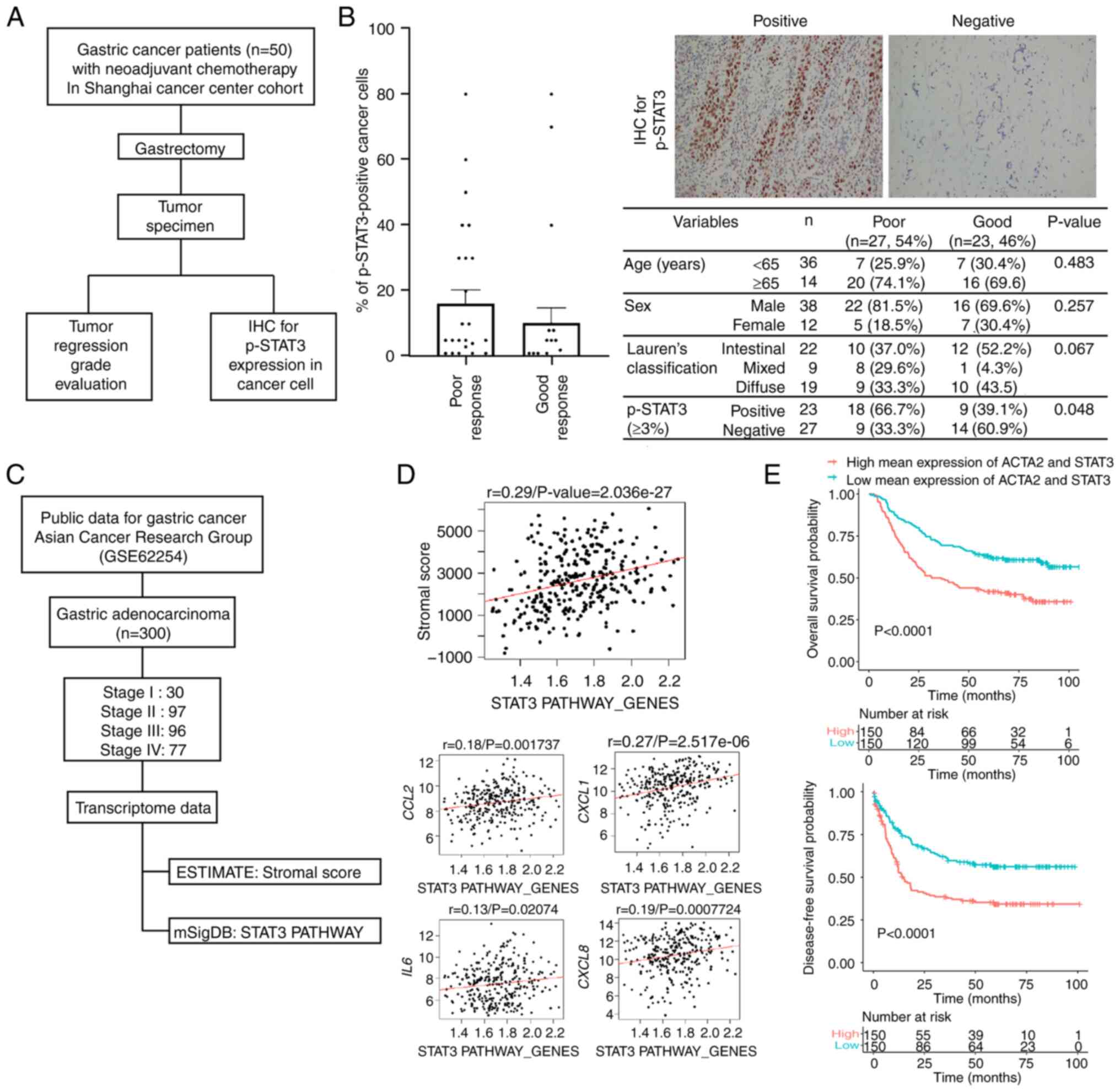
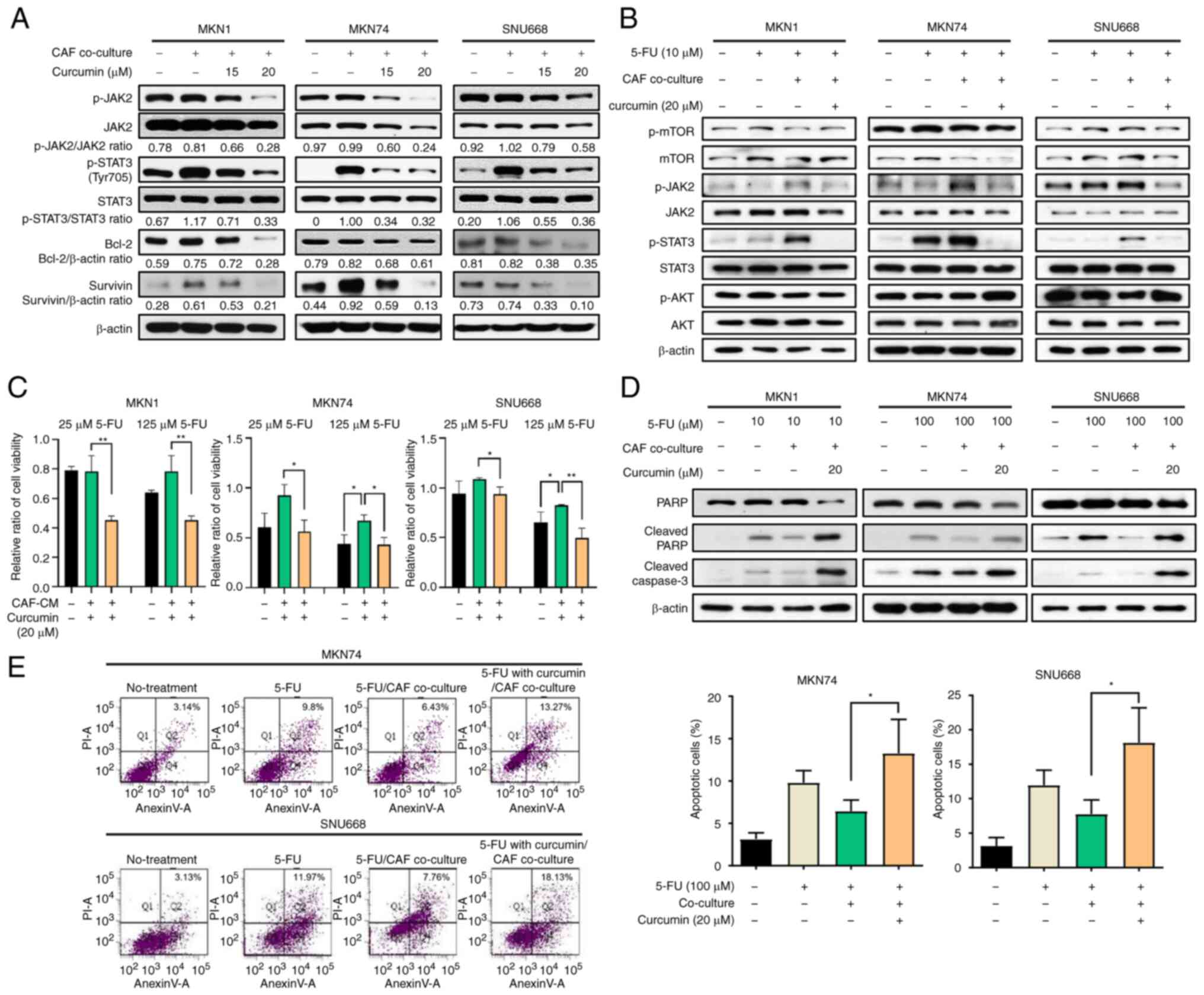
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wagner AD, Grothe W, Haerting J, Kleber G,
Grothey A and Fleig WE: Chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis based on aggregate data. J Clin
Oncol. 24:2903–2909. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Guideline Committee of the Korean Gastric
Cancer Association (KGCA), Development Working Group & Review
Panel: Korean practice guideline for gastric cancer 2018: An
evidence-based, multi-disciplinary approach. J Gastric Cancer.
19:1–48. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Japanese Gastric Cancer Association:
Japanese gastric cancer treatment guidelines 2018 (5th edition).
Gastric Cancer. 24:1–21. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wu Y, Grabsch H, Ivanova T, Tan IB, Murray
J, Ooi CH, Wright AI, West NP, Hutchins GG, Wu J, et al:
Comprehensive genomic meta-analysis identifies intra-tumoural
stroma as a predictor of survival in patients with gastric cancer.
Gut. 62:1100–1111. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lei Z, Tan IB, Das K, Deng N, Zouridis H,
Pattison S, Chua C, Feng Z, Guan YK, Ooi CH, et al: Identification
of molecular subtypes of gastric cancer with different responses to
PI3-kinase inhibitors and 5-fluorouracil. Gastroenterology.
145:554–565. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ma J, Song X, Xu X and Mou Y:
Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote the chemo-resistance in
gastric cancer through secreting IL-11 targeting JAK/STAT3/Bcl2
pathway. Cancer Res Treat. 51:194–210. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ham IH, Oh HJ, Jin H, Bae CA, Jeon SM,
Choi KS, Son SY, Han SU, Brekken RA, Lee D and Hur H: Targeting
interleukin-6 as a strategy to overcome stroma-induced resistance
to chemotherapy in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 18:682019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kalluri R: The biology and function of
fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 16:582–598. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kalluri R and Zeisberg M: Fibroblasts in
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:392–401. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kuzet SE and Gaggioli C: Fibroblast
activation in cancer: When seed fertilizes soil. Cell Tissue Res.
365:607–619. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Resemann HK, Watson CJ and Lloyd-Lewis B:
The Stat3 paradox: A killer and an oncogene. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
382:603–611. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Aaronson DS and Horvath CM: A road map for
those who don't know JAK-STAT. Science. 296:1653–1655. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Sweet K, Hazlehurst L, Sahakian E, Powers
J, Nodzon L, Kayali F, Hyland K, Nelson A and Pinilla-Ibarz J: A
phase I clinical trial of ruxolitinib in combination with nilotinib
in chronic myeloid leukemia patients with molecular evidence of
disease. Leuk Res. 74:89–96. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
McLornan DP, Khan AA and Harrison CN:
Immunological consequences of JAK inhibition: Friend or foe? Curr
Hematol Malig Rep. 10:370–379. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wake MS and Watson CJ: STAT3 the
oncogene-still eluding therapy? FEBS J. 282:2600–2611. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Gupta SC, Patchva S, Koh W and Aggarwal
BB: Discovery of curcumin, a component of golden spice, and its
miraculous biological activities. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
39:283–299. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lee WH, Bebawy M, Loo CY, Luk F, Mason RS
and Rohanizadeh R: Fabrication of curcumin micellar nanoparticles
with enhanced anti-cancer activity. J Biomed Nanotechnol.
11:1093–1105. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lee WH, Loo CY, Young PM, Rohanizadeh R
and Traini D: Curcumin nanoparticles attenuate production of
pro-inflammatory markers in lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophages.
Pharm Res. 33:315–327. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lee WH, Loo CY, Young PM, Traini D, Mason
RS and Rohanizadeh R: Recent advances in curcumin nanoformulation
for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 11:1183–1201. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wong TF, Takeda T, Li B, Tsuiji K,
Kitamura M, Kondo A and Yaegashi N: Curcumin disrupts uterine
leiomyosarcoma cells through AKT-mTOR pathway inhibition. Gynecol
Oncol. 122:141–148. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Byun SY, Kim DB and Kim E: Curcumin
ameliorates the tumor-enhancing effects of a high-protein diet in
an azoxymethane-induced mouse model of colon carcinogenesis. Nutr
Res. 35:726–735. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yang CL, Liu YY, Ma YG, Xue YX, Liu DG,
Ren Y, Liu XB, Li Y and Li Z: Curcumin blocks small cell lung
cancer cells migration, invasion, angiogenesis, cell cycle and
neoplasia through Janus kinase-STAT3 signalling pathway. PLoS One.
7:e379602012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lee D, Ham IH, Son SY, Han SU, Kim YB and
Hur H: Intratumor stromal proportion predicts aggressive phenotype
of gastric signet ring cell carcinomas. Gastric Cancer. 20:591–601.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ryan R, Gibbons D, Hyland JM, Treanor D,
White A, Mulcahy HE, O'Donoghue DP, Moriarty M, Fennelly D and
Sheahan K: Pathological response following long-course neoadjuvant
chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced rectal cancer.
Histopathology. 47:141–146. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Cristescu R, Lee J, Nebozhyn M, Kim KM,
Ting JC, Wong SS, Liu J, Yue YG, Wang J, Yu K, et al: Molecular
analysis of gastric cancer identifies subtypes associated with
distinct clinical outcomes. Nat Med. 21:449–456. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang H, Wu X and Chen Y: Stromal-immune
score-based gene signature: A prognosis stratification tool in
gastric cancer. Front Oncol. 9:12122019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Tsuyada A, Chow A, Wu J, Somlo G, Chu P,
Loera S, Luu T, Li AX, Wu X, Ye W, et al: CCL2 mediates cross-talk
between cancer cells and stromal fibroblasts that regulates breast
cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 72:2768–2779. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wu J, Gao FX, Wang C, Qin M, Han F, Xu T,
Hu Z, Long Y, He XM, Deng X, et al: IL-6 and IL-8 secreted by
tumour cells impair the function of NK cells via the STAT3 pathway
in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
38:3212019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
O'Shea JJ, Holland SM and Staudt LM: JAKs
and STATs in immunity, immunodeficiency, and cancer. N Engl J Med.
368:161–170. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Quintás-Cardama A and Verstovsek S:
Molecular pathways: Jak/STAT pathway: Mutations, inhibitors, and
resistance. Clin Cancer Res. 19:1933–1940. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Birner P, Toumangelova-Uzeir K, Natchev S
and Guentchev M: STAT3 tyrosine phosphorylation influences survival
in glioblastoma. J Neurooncol. 100:339–343. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Qin A, Yu Q, Gao Y, Tan J, Huang H, Qiao Z
and Qian W: Inhibition of STAT3/cyclinD1 pathway promotes
chemotherapeutic sensitivity of colorectal caner. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 457:681–687. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Spitzner M, Roesler B, Bielfeld C, Emons
G, Gaedcke J, Wolff HA, Rave-Fränk M, Kramer F, Beissbarth T, Kitz
J, et al: STAT3 inhibition sensitizes colorectal cancer to
chemoradiotherapy in vitro and in vivo. Int J Cancer. 134:997–1007.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Stella S, Tirrò E, Conte E, Stagno F, Di
Raimondo F, Manzella L and Vigneri P: Suppression of survivin
induced by a BCR-ABL/JAK2/STAT3 pathway sensitizes
imatinib-resistant CML cells to different cytotoxic drugs. Mol
Cancer Ther. 12:1085–1098. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wen K, Fu Z, Wu X, Feng J, Chen W and Qian
J: Oct-4 is required for an antiapoptotic behavior of
chemoresistant colorectal cancer cells enriched for cancer stem
cells: Effects associated with STAT3/survivin. Cancer Lett.
333:56–65. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Brambilla L, Genini D, Laurini E, Merulla
J, Perez L, Fermeglia M, Carbone GM, Pricl S and Catapano CV:
Hitting the right spot: Mechanism of action of OPB-31121, a novel
and potent inhibitor of the signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3 (STAT3). Mol Oncol. 9:1194–1206. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Redell MS, Ruiz MJ, Alonzo TA, Gerbing RB
and Tweardy DJ: Stat3 signaling in acute myeloid leukemia:
Ligand-dependent and -independent activation and induction of
apoptosis by a novel small-molecule Stat3 inhibitor. Blood.
117:5701–5709. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Okusaka T, Ueno H, Ikeda M, Mitsunaga S,
Ozaka M, Ishii H, Yokosuka O, Ooka Y, Yoshimoto R, Yanagihara Y and
Okita K: Phase 1 and pharmacological trial of OPB-31121, a signal
transducer and activator of transcription-3 inhibitor, in patients
with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 45:1283–1291.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Beebe JD, Liu JY and Zhang JT: Two decades
of research in discovery of anticancer drugs targeting STAT3, how
close are we? Pharmacol Ther. 191:74–91. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Kunnumakkara AB, Anand P and Aggarwal BB:
Curcumin inhibits proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis and
metastasis of different cancers through interaction with multiple
cell signaling proteins. Cancer Lett. 269:199–225. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Bill MA, Fuchs JR, Li C, Yui J, Bakan C,
Benson DM Jr, Schwartz EB, Abdelhamid D, Lin J, Hoyt DG, et al: The
small molecule curcumin analog FLLL32 induces apoptosis in melanoma
cells via STAT3 inhibition and retains the cellular response to
cytokines with anti-tumor activity. Mol Cancer. 9:1652010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Onimoe GI, Liu A, Lin L, Wei CC, Schwartz
EB, Bhasin D, Li C, Fuchs JR, Li PK, Houghton P, et al: Small
molecules, LLL12 and FLLL32, inhibit STAT3 and exhibit potent
growth suppressive activity in osteosarcoma cells and tumor growth
in mice. Invest New Drugs. 30:916–926. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Yan J, Wang Q, Zou K, Wang L, Schwartz EB,
Fuchs JR, Zheng Z and Wu J: Inhibition of the JAK2/STAT3 signaling
pathway exerts a therapeutic effect on osteosarcoma. Mol Med Rep.
12:498–502. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|