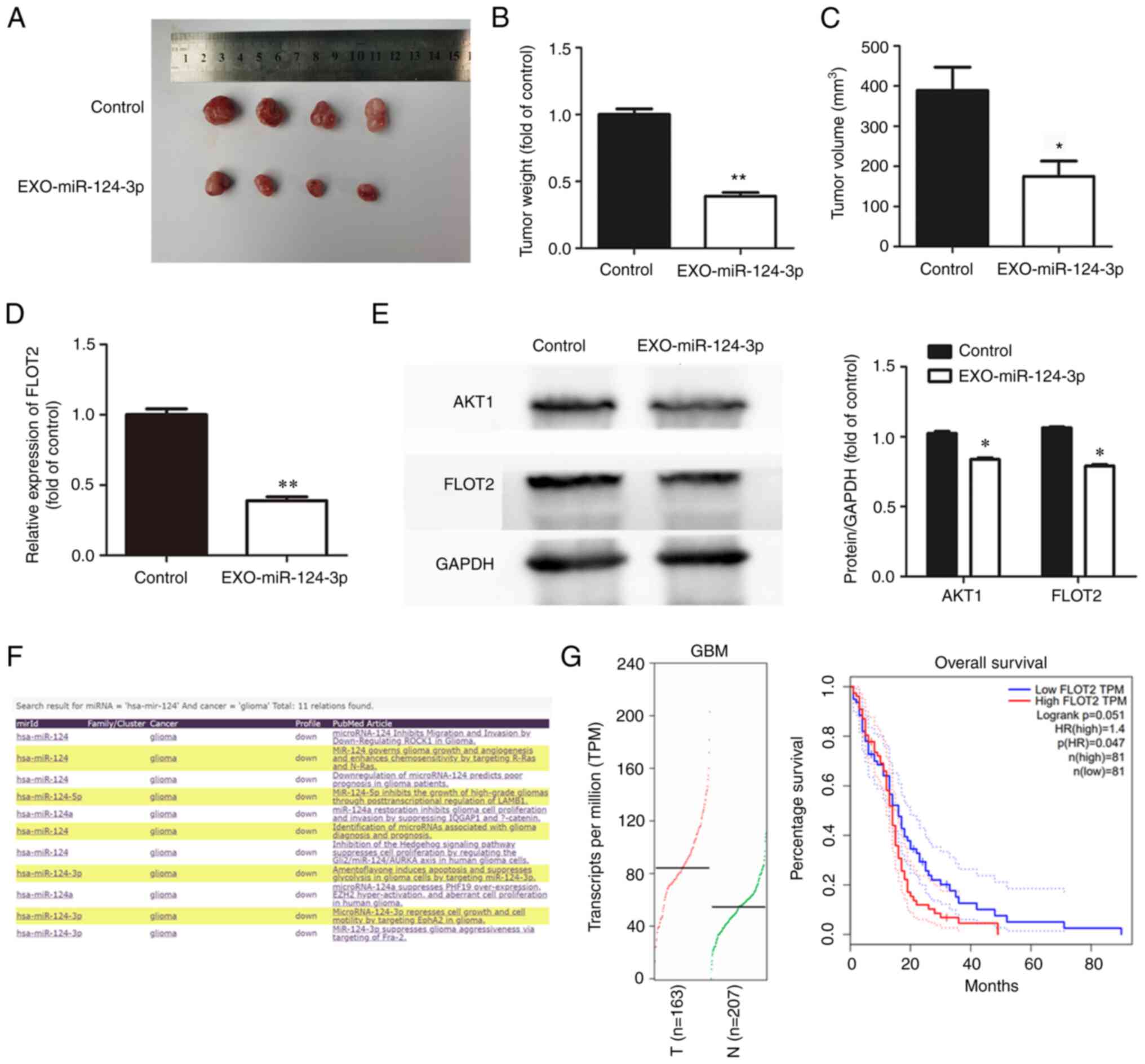
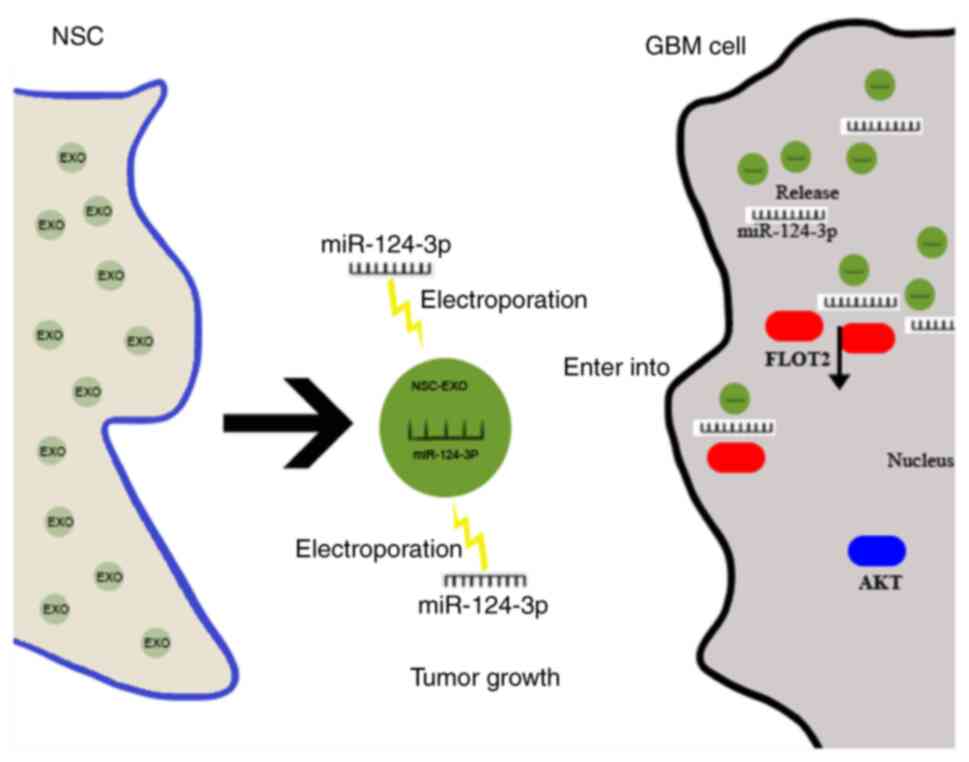
|
1
|
Lapointe S, Perry A and Butowski NA:
Primary brain tumours in adults. Lancet. 392:432–446. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wen PY and Kesari S: Malignant gliomas in
adults. N Engl J Med. 359:492–507. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bedard PL, Hyman DM, Davids MS and Siu LL:
Small molecules, big impact: 20 years of targeted therapy in
oncology. Lancet. 395:1078–1088. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Reifenberger G, Wirsching HG,
Knobbe-Thomsen CB and Weller M: Advances in the molecular genetics
of gliomas-implications for classification and therapy. Nat Rev
Clin Oncol. 14:434–452. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ammirati M, Chotai S, Newton H, Lamki T,
Wei L and Grecula J: Hypofractionated intensity modulated
radiotherapy with temozolomide in newly diagnosed glioblastoma
multiforme. J Clin Neurosci. 21:633–637. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bond AM, Ming GL and Song H: Adult
mammalian neural stem cells and neurogenesis: Five decades later.
Cell Stem Cell. 17:385–395. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bagó JR, Alfonso-Pecchio A, Okolie O,
Dumitru R, Rinkenbaugh A, Baldwin AS, Miller CR, Magness ST and
Hingtgen SD: Therapeutically engineered induced neural stem cells
are tumour-homing and inhibit progression of glioblastoma. Nat
Commun. 7:105932016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mutukula N and Elkabetz Y: 'Neural killer'
cells: Autologous cytotoxic neural stem cells for fighting glioma.
Cell Stem Cell. 20:426–428. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cheng Y, Morshed R, Cheng SH, Tobias A,
Auffinger B, Wainwright DA, Zhang L, Yunis C, Han Y, Chen CT, et
al: Nanoparticle-programmed self-destructive neural stem cells for
glioblastoma targeting and therapy. Small. 9:4123–4129. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Portnow J, Synold TW, Badie B, Tirughana
R, Lacey SF, D'Apuzzo M, Metz MZ, Najbauer J, Bedell V, Vo T, et
al: Neural stem cell-based anticancer gene therapy: A
first-in-human study in recurrent high-grade glioma patients. Clin
Cancer Res. 23:2951–2960. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Marban E: The secret life of exosomes:
What bees can teach us about next-generation therapeutics. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 71:193–200. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
van Niel G, D'Angelo G and Raposo G:
Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 19:213–228. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mathieu M, Martin-Jaular L, Lavieu G and
Thery C: Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and
other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat
Cell Biol. 21:9–17. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zeng Z, Li Y, Pan Y, Lan X, Song F, Sun J,
Zhou K, Liu X, Ren X, Wang F, et al: Cancer-derived exosomal
miR-25-3p promotes pre-metastatic niche formation by inducing
vascular permeability and angiogenesis. Nat Commun. 9:53952018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yue X, Lan F and Xia T: Hypoxic glioma
cell-secreted exosomal miR-301a activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling
and promotes radiation resistance by targeting TCEAL7. Mol Ther.
27:1939–1949. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen G, Huang AC, Zhang W, Zhang G, Wu M,
Xu W, Yu Z, Yang J, Wang B, Sun H, et al: Exosomal PD-L1
contributes to immunosuppression and is associated with anti-PD-1
response. Nature. 560:382–386. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ:
Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:259–269. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cheng H, Zhao H, Xiao X, Huang Q, Zeng W,
Tian B, Ma T, Lu D, Jin Y and Li Y: Long non-coding RNA MALAT1
upregulates ZEB2 expression to promote malignant progression of
glioma by attenuating miR-124. Mol Neurobiol. 58:1006–1016. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Shi Z, Chen Q, Li C, Wang L, Qian X, Jiang
C, Liu X, Wang X, Li H, Kang C, et al: MiR-124 governs glioma
growth and angiogenesis and enhances chemosensitivity by targeting
R-Ras and N-Ras. Neuro Oncol. 16:1341–1353. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang G, Chen L, Khan AA, Li B, Gu B, Lin
F, Su X and Yan J: miRNA-124-3p/neuropilin-1(NRP-1) axis plays an
important role in mediating glioblastoma growth and angiogenesis.
Int J Cancer. 143:635–644. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang G, Chen L, Guo X, Wang H, Chen W, Wu
G, Gu B, Miao W, Kong J, Jin X, et al: Comparative analysis of
microRNA expression profiles of exosomes derived from normal and
hypoxic preconditioning human neural stem cells by next generation
sequencing. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 14:1075–1089. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang G, Zhu Z, Wang H, Yu Y, Chen W,
Waqas A, Wang Y and Chen L: Exosomes derived from human neural stem
cells stimulated by interferon gamma improve therapeutic ability in
ischemic stroke model. J Adv Res. 24:435–445. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Théry C, Witwer KW, Aikawa E, Alcaraz MJ,
Anderson JD, Andriantsitohaina R, Antoniou A, Arab T, Archer F,
Atkin-Smith GK, et al: Minimal information for studies of
extra-cellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of
the international society for extracellular vesicles and update of
the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 7:15357502018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Saadatpour L, Fadaee E, Fadaei S, Nassiri
Mansour R, Mohammadi M, Mousavi SM, Goodarzi M, Verdi J and Mirzaei
H: Glioblastoma: Exosome and microRNA as novel diagnosis
biomarkers. Cancer Gene Ther. 23:415–418. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Skog J, Würdinger T, van Rijn S, Meijer
DH, Gainche L, Sena-Esteves M, Curry WT Jr, Carter BS, Krichevsky
AM and Breakefield XO: Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and
proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic
biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol. 10:1470–1476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang J, Liu J, Sun G, Meng H, Wang J, Guan
Y, Yin Y, Zhao Z, Dong X, Yin S, et al: Glioblastoma extracellular
vesicles induce the tumour-promoting transformation of neural stem
cells. Cancer Lett. 466:1–12. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Katakowski M and Chopp M: Exosomes as
tools to suppress primary brain tumor. Cell Mol Neurobiol.
36:343–352. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Guo S, Chen J, Chen F, Zeng Q, Liu WL and
Zhang G: Exosomes derived from Fusobacterium nucleatum-infected
colorectal cancer cells facilitate tumour metastasis by selectively
carrying miR-1246/92b-3p/27a-3p and CXCL16. Gut. Nov 10–2020.Epub
ahead of print.
|
|
30
|
Wu H, Mu X, Liu L, Wu H, Hu X, Chen L, Liu
J, Mu Y, Yuan F, Liu W and Zhao Y: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem
cells-derived exosomal microRNA-193a reduces cisplatin resistance
of non-small cell lung cancer cells via targeting LRRC1. Cell Death
Dis. 11:8012020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huang S, Xue P, Han X, Zhang C, Yang L,
Liu L, Wang X, Li H, Fu J and Zhou Y: Exosomal miR-130b-3p targets
SIK1 to inhibit medulloblastoma tumorigenesis. Cell Death Dis.
11:4082020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Munson PB, Hall EM, Farina NH, Pass HI and
Shukla A: Exosomal miR-16-5p as a target for malignant
mesothelioma. Sci Rep. 9:116882019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Qin EY, Cooper DD, Abbott KL, Lennon J,
Nagaraja S, Mackay A, Jones C, Vogel H, Jackson PK and Monje M:
Neural precursor-derived pleiotrophin mediates subventricular zone
invasion by glioma. Cell. 170:845–859.e19. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hazarika P, McCarty MF, Prieto VG, George
S, Babu D, Koul D, Bar-Eli M and Duvic M: Up-regulation of
Flotillin-2 is associated with melanoma progression and modulates
expression of the thrombin receptor protease activated receptor 1.
Cancer Res. 64:7361–7369. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang X, Yang Q, Guo L, Li XH, Zhao XH,
Song LB and Lin HX: Flotillin-2 is associated with breast cancer
progression and poor survival outcomes. J Transl Med. 11:1902013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang CH, Zhu XD, Ma DN, Sun HC, Gao DM,
Zhang N, Qin CD, Zhang YY, Ye BG, Cai H, et al: Flot2 promotes
tumor growth and metastasis through modulating cell cycle and
inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res. 7:1068–1083. 2017.
|
|
37
|
Song M, Bode AM, Dong Z and Lee MH: AKT as
a therapeutic target for cancer. Cancer Res. 79:1019–1031. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hoxhaj G and Manning BD: The PI3K-AKT
network at the interface of oncogenic signalling and cancer
metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 20:74–88. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|