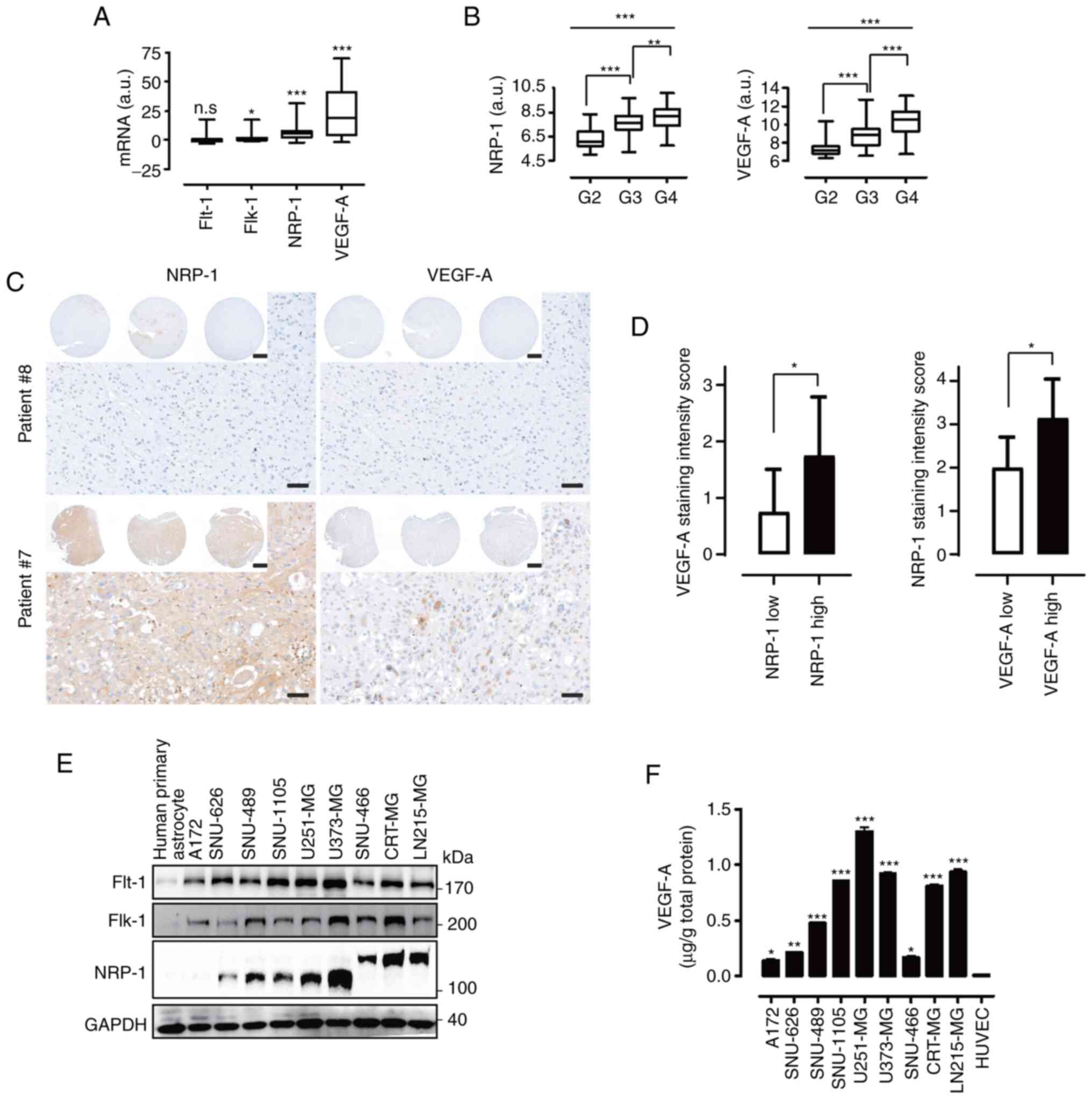
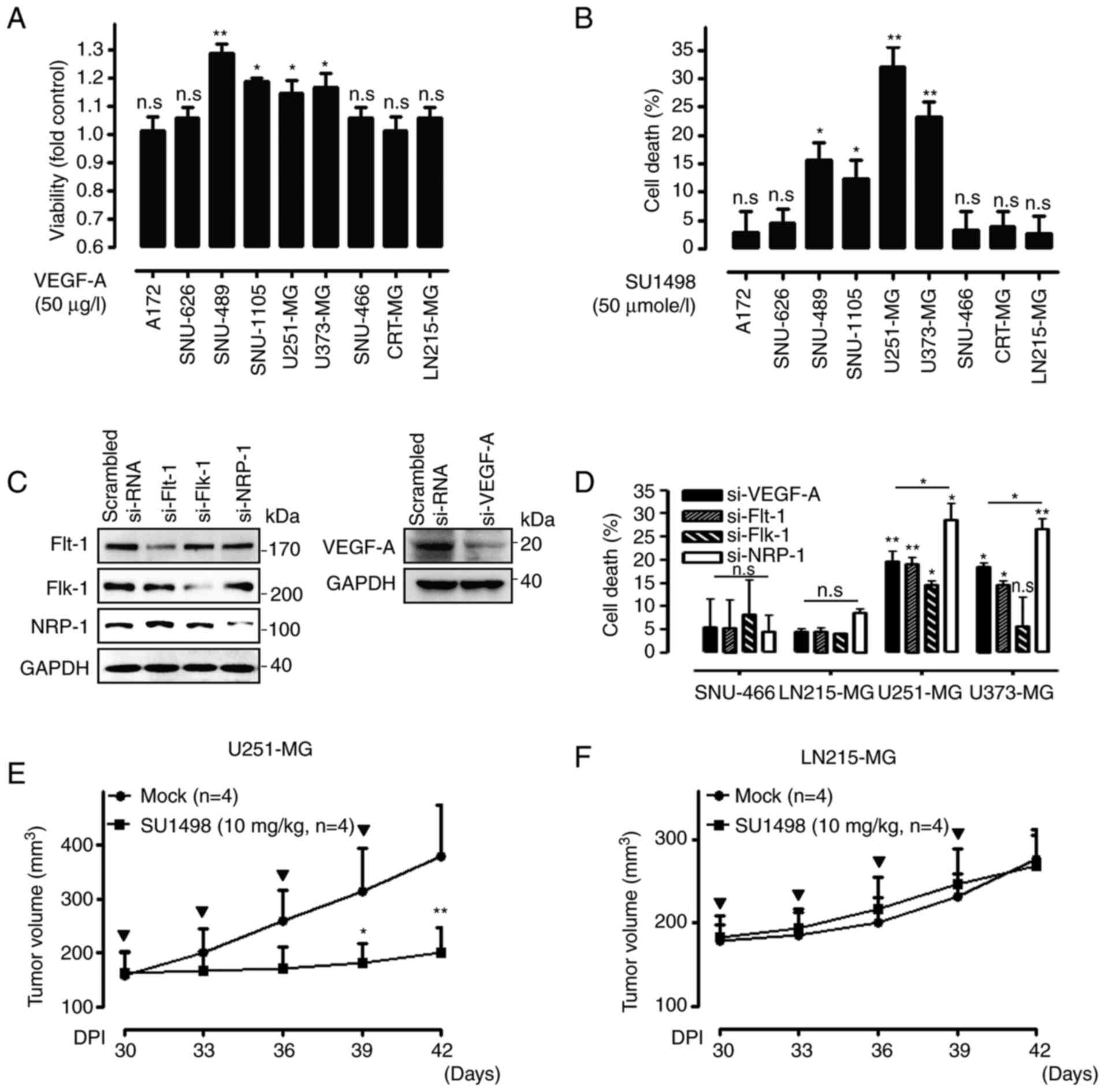
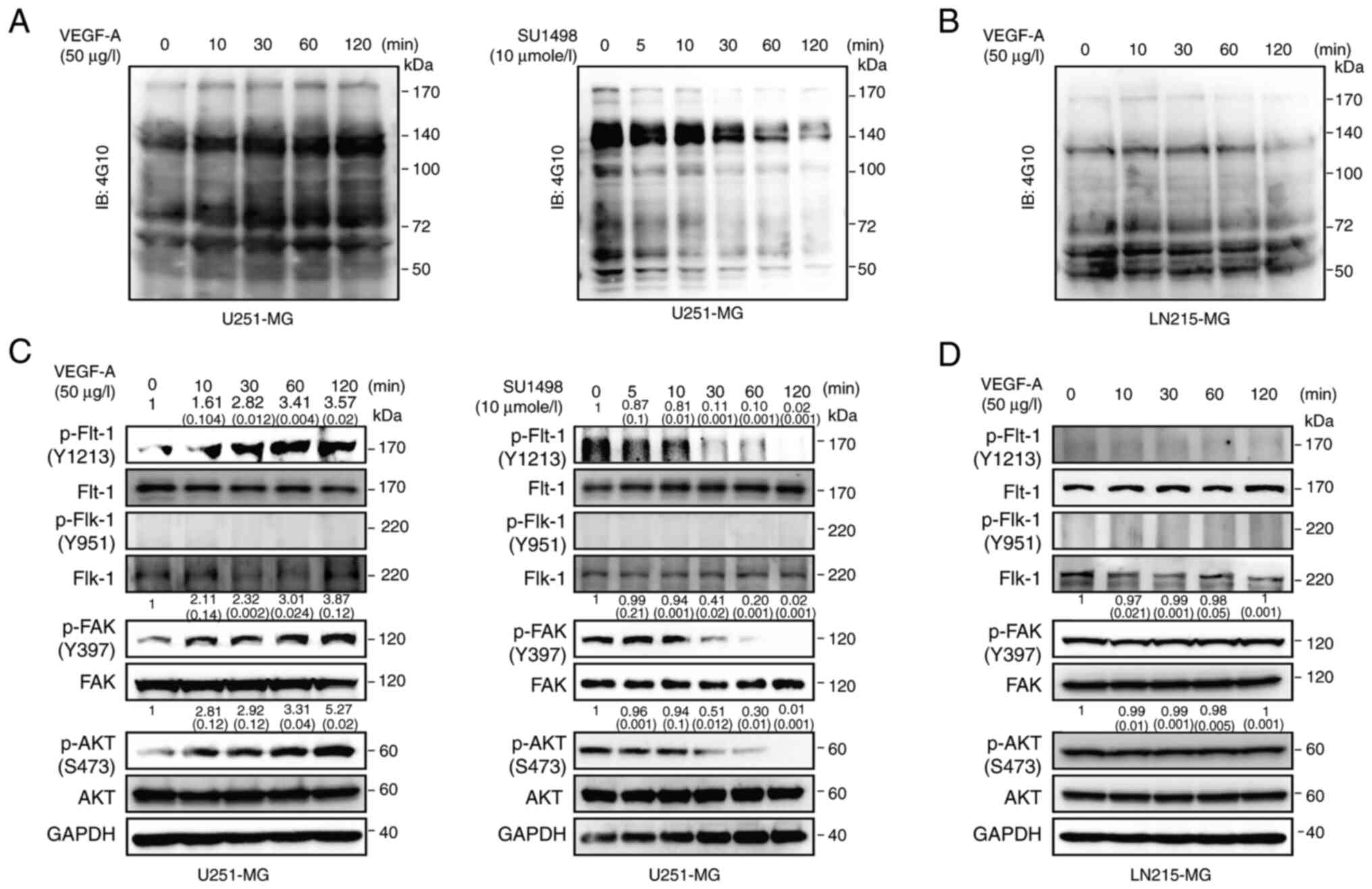
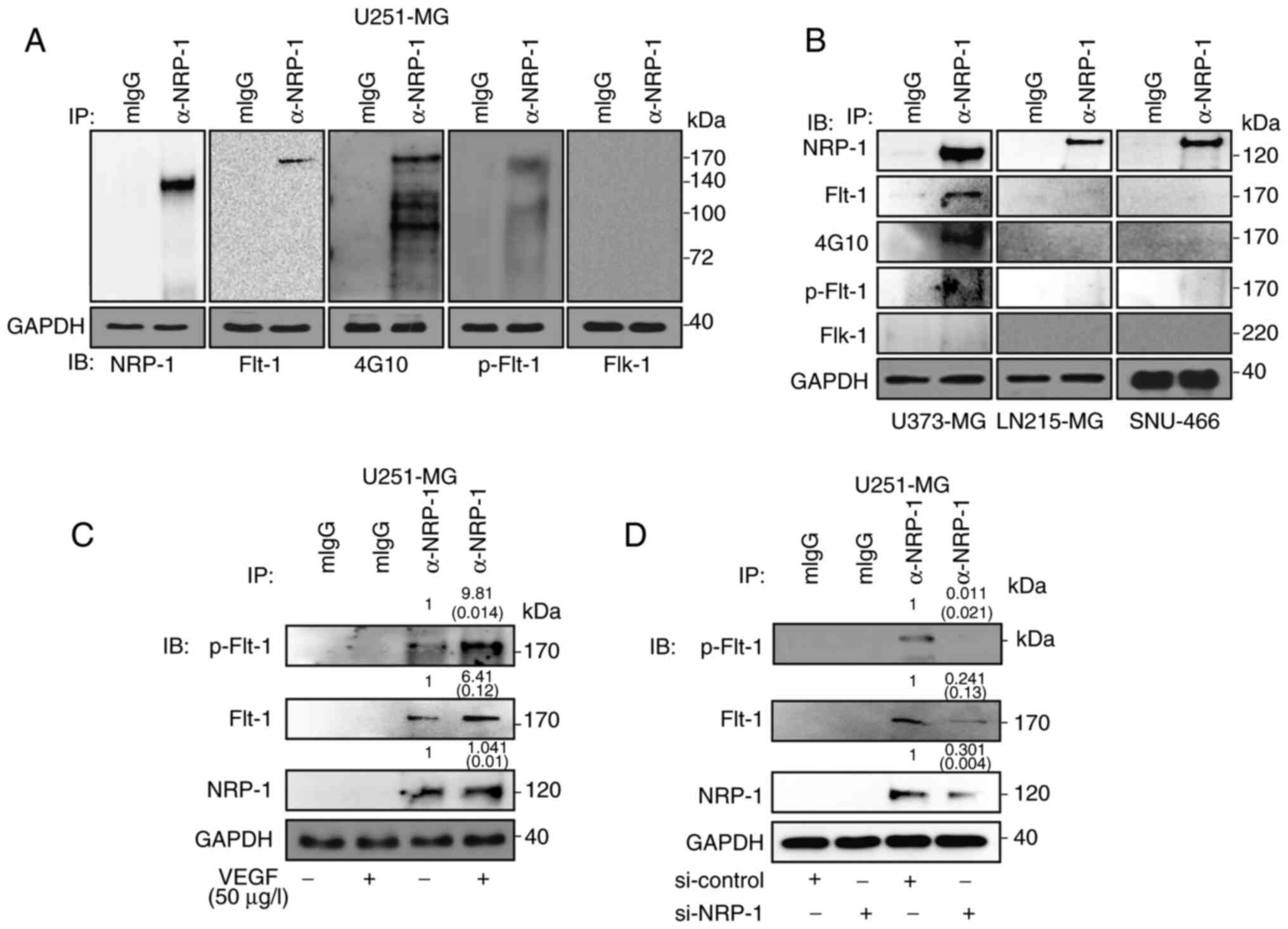
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide
for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Westphal M and Lamszus K: The neurobiology
of gliomas: From cell biology to the development of therapeutic
approaches. Nat Rev Neurosci. 12:495–508. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee
WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW and Kleihues P: The 2007
WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta
Neuropathol. 114:97–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ohgaki H and Kleihues P: Population-based
studies on incidence, survival rates, and genetic alterations in
astrocytic and oligodendroglial gliomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.
64:479–489. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Miller CR and Perry A: Glioblastoma. Arch
Pathol Lab Med. 131:397–406. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Newton HB: Primary brain tumors: Review of
etiology, diagnosis and treatment. Am Fam Physician. 49:787–797.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Soker S, Takashima S, Miao HQ, Neufeld G
and Klagsbrun M: Neuropilin-1 is expressed by endothelial and tumor
cells as an isoform-specific receptor for vascular endothelial
growth factor. Cell. 92:735–745. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gu C, Rodriguez ER, Reimert DV, Shu T,
Fritzsch B, Richards LJ, Kolodkin AL and Ginty DD: Neuropilin-1
conveys semaphorin and VEGF signaling during neural and
cardiovascular development. Dev Cell. 5:45–57. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hu B, Guo P, Bar-Joseph I, Imanishi Y,
Jarzynka MJ, Bogler O, Mikkelsen T, Hirose T, Nishikawa R and Cheng
SY: Neuropilin-1 promotes human glioma progression through
potentiating the activity of the HGF/SF autocrine pathway.
Oncogene. 26:5577–5586. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ellis LM: The role of neuropilins in
cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:1099–1107. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Evans IM, Yamaji M, Britton G, Pellet-Many
C, Lockie C, Zachary IC and Frankel P: Neuropilin-1 signaling
through p130Cas tyrosine phosphorylation is essential for growth
factor-dependent migration of glioma and endothelial cells. Mol
Cell Biol. 31:1174–1185. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Frankel P, Pellet-Many C, Lehtolainen P,
D'Abaco GM, Tickner ML, Cheng L and Zachary IC: Chondroitin
sulphate-modified neuropilin 1 is expressed in human tumour cells
and modulates 3D invasion in the U87MG human glioblastoma cell line
through a p130Cas-mediated pathway. EMBO Rep. 9:983–989. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Miao HQ, Lee P, Lin H, Soker S and
Klagsbrun M: Neuropilin-1 expression by tumor cells promotes tumor
angiogenesis and progression. FASEB J. 14:2532–2539. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Parikh AA, Fan F, Liu WB, Ahmad SA,
Stoeltzing O, Reinmuth N, Bielenberg D, Bucana CD, Klagsbrun M and
Ellis LM: Neuropilin-1 in human colon cancer: Expression,
regulation, and role in induction of angiogenesis. Am J Pathol.
164:2139–2151. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shintani Y, Takashima S, Asano Y, Kato H,
Liao Y, Yamazaki S, Tsukamoto O, Seguchi O, Yamamoto H, Fukushima
T, et al: Glycosaminoglycan modification of neuropilin-1 modulates
VEGFR2 signaling. EMBO J. 25:3045–3055. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kjellen L and Lindahl U: Proteoglycans:
Structures and interactions. Annu Rev Biochem. 60:443–475. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Theocharis AD, Tsolakis I, Tzanakakis GN
and Karamanos NK: Chondroitin sulfate as a key molecule in the
development of atherosclerosis and cancer progression. Adv
Pharmacol. 53:281–295. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lee J, Ku T, Yu H, Chong K, Ryu SW, Choi K
and Choi C: Blockade of VEGF-A suppresses tumor growth via
inhibition of autocrine signaling through FAK and AKT. Cancer Lett.
318:221–225. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Piccolo SR, Withers MR, Francis OE, Bild
AH and Johnson WE: Multiplatform single-sample estimates of
transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:17778–17783. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F,
Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U and Speed TP:
Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density
oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 4:249–264.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dai M, Wang P, Boyd AD, Kostov G, Athey B,
Jones EG, Bunney WE, Myers RM, Speed TP, Akil H, et al: Evolving
gene/transcript definitions significantly alter the interpretation
of GeneChip data. Nucleic Acids Res. 33:e1752005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee J, Lee J, Yun JH, Choi C, Cho S, Kim
SJ and Kim JH: Autocrine DUSP28 signaling mediates pancreatic
cancer malignancy via regulation of PDGF-A. Scientific reports.
7:127602017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee J, Lee J, Sim W and Kim JH: Soluble
TGFBI aggravates the malignancy of cholangiocarcinoma through
activation of the ITGB1 dependent PPARγ signalling pathway. Cell
Oncol (Dordr). 45:275–291. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lee J, Kim DH and Kim JH: Combined
administration of naringenin and hesperetin with optimal ratio
maximizes the anti-cancer effect in human pancreatic cancer via
down regulation of FAK and p38 signaling pathway. Phytomedicine.
58:1527622019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee J, Lee J, Yun JH, Choi C, Cho S, Kim
SJ and Kim JH: Autocrine DUSP28 signaling mediates pancreatic
cancer malignancy via regulation of PDGF-A. Sci Rep. 7:127602017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Reddy SP, Britto R, Vinnakota K, Aparna H,
Sreepathi HK, Thota B, Kumari A, Shilpa BM, Vrinda M, Umesh S, et
al: Novel glioblastoma markers with diagnostic and prognostic value
identified through transcriptome analysis. Clin Cancer Res.
14:2978–2987. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vasudev NS and Reynolds AR:
Anti-angiogenic therapy for cancer: Current progress unresolved
questions and future directions. Angiogenesis. 17:471–494. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Batchelor TT, Sorensen AG, di Tomaso E,
Zhang WT, Duda DG, Cohen KS, Kozak KR, Cahill DP, Chen PJ, Zhu M,
et al: AZD2171, a pan-VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor,
normalizes tumor vasculature and alleviates edema in glioblastoma
patients. Cancer Cell. 11:83–95. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sabir A, Schor-Bardach R, Wilcox CJ,
Rahmanuddin S, Atkins MB, Kruskal JB, Signoretti S, Raptopoulos VD
and Goldberg SN: Perfusion MDCT enables early detection of
therapeutic response to antiangiogenic therapy. AJR Am J
Roentgenol. 191:133–139. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Galli R, Binda E, Orfanelli U, Cipelletti
B, Gritti A, De Vitis S, Fiocco R, Foroni C, Dimeco F and Vescovi
A: Isolation and characterization of tumorigenic, stem-like neural
precursors from human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 64:7011–7021. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q,
Hjelmeland AB, Dewhirst MW, Bigner DD and Rich JN: Glioma stem
cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA
damage response. Nature. 444:756–760. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chung AS, Lee J and Ferrara N: Targeting
the tumour vasculature: Insights from physiological angiogenesis.
Nat Rev Cancer. 10:505–514. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ferrara N: Role of vascular endothelial
growth factor in physiologic and pathologic angiogenesis:
Therapeutic implications. Semin Oncol. 29(6 Suppl 16): S10–S14.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wang ES, Teruya-Feldstein J, Wu Y, Zhu Z,
Hicklin DJ and Moore MA: Targeting autocrine and paracrine VEGF
receptor pathways inhibits human lymphoma xenografts in vivo.
Blood. 104:2893–2902. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Karp JE, Gojo I, Pili R, Gocke CD, Greer
J, Guo C, Qian D, Morris L, Tidwell M, Chen H and Zwiebel J:
Targeting vascular endothelial growth factor for relapsed and
refractory adult acute myelogenous leukemias: Therapy with
sequential 1-beta-d-arabinofuranosylcytosine, mitoxantrone, and
bevacizumab. Clin Cancer Res. 10:3577–3585. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Qi L, Robinson WA, Brady BM and Glode LM:
Migration and invasion of human prostate cancer cells is related to
expression of VEGF and its receptors. Anticancer Res. 23:3917–3922.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bates RC, Goldsmith JD, Bachelder RE,
Brown C, Shibuya M, Oettgen P and Mercurio AM: Flt-1-dependent
survival characterizes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of
colonic organoids. Curr Biol. 13:1721–1727. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Das B, Yeger H, Tsuchida R, Torkin R, Gee
MF, Thorner PS, Shibuya M, Malkin D and Baruchel S: A
hypoxia-driven vascular endothelial growth factor/Flt1 autocrine
loop interacts with hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha through
mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated
kinase 1/2 pathway in neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 65:7267–7275.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Steiner HH, Karcher S, Mueller MM,
Nalbantis E, Kunze S and Herold-Mende C: Autocrine pathways of the
vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in glioblastoma
multiforme: Clinical relevance of radiation-induced increase of
VEGF levels. J Neurooncol. 66:129–138. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bachelder RE, Crago A, Chung J, Wendt MA,
Shaw LM, Robinson G and Mercurio AM: Vascular endothelial growth
factor is an autocrine survival factor for neuropilin-expressing
breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 61:5736–5740. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Broholm H and Laursen H: Vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor neuropilin-1's
distribution in astrocytic tumors. APMIS. 112:257–263. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gray MJ, Wey JS, Belcheva A, McCarty MF,
Trevino JG, Evans DB, Ellis LM and Gallick GE: Neuropilin-1
suppresses tumorigenic properties in a human pancreatic
adenocarcinoma cell line lacking neuropilin-1 coreceptors. Cancer
Res. 65:3664–3670. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pan Q, Chanthery Y, Liang WC, Stawicki S,
Mak J, Rathore N, Tong RK, Kowalski J, Yee SF, Pacheco G, et al:
Blocking neuropilin-1 function has an additive effect with
anti-VEGF to inhibit tumor growth. Cancer Cell. 11:53–67. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kamiya T, Kawakami T, Abe Y, Nishi M,
Onoda N, Miyazaki N, Oida Y, Yamazaki H, Ueyama Y and Nakamura M:
The preserved expression of neuropilin (NRP) 1 contributes to a
better prognosis in colon cancer. Oncol Rep. 15:369–373.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hong X, Jiang F, Kalkanis SN, Zhang ZG,
Zhang X, Zheng X, Mikkelsen T, Jiang H and Chopp M: Decrease of
endogenous vascular endothelial growth factor may not affect glioma
cell proliferation and invasion. J Exp Ther Oncol. 6:219–229.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Jia H, Bagherzadeh A, Hartzoulakis B,
Jarvis A, Löhr M, Shaikh S, Aqil R, Cheng L, Tickner M, Esposito D,
et al: Characterization of a bicyclic peptide neuropilin-1 (NP-1)
antagonist (EG3287) reveals importance of vascular endothelial
growth factor exon 8 for NP-1 binding and role of NP-1 in KDR
signaling. J Biol Chem. 281:13493–13502. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Swendeman S, Mendelson K, Weskamp G,
Horiuchi K, Deutsch U, Scherle P, Hooper A, Rafii S and Blobel CP:
VEGF-A stimulates ADAM17-dependent shedding of VEGFR2 and crosstalk
between VEGFR2 and ERK signaling. Circ Res. 103:916–918. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lu Y, Xiang H, Liu P, Tong RR, Watts RJ,
Koch AW, Sandoval WN, Damico LA, Wong WL and Meng YG:
Identification of circulating neuropilin-1 and dose-dependent
elevation following anti-neuropilin-1 antibody administration.
MAbs. 1:364–369. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
Gagnon ML, Bielenberg DR, Gechtman Z, Miao
HQ, Takashima S, Soker S and Klagsbrun M: Identification of a
natural soluble neuropilin-1 that binds vascular endothelial growth
factor: In vivo expression and antitumor activity. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 97:2573–2578. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|