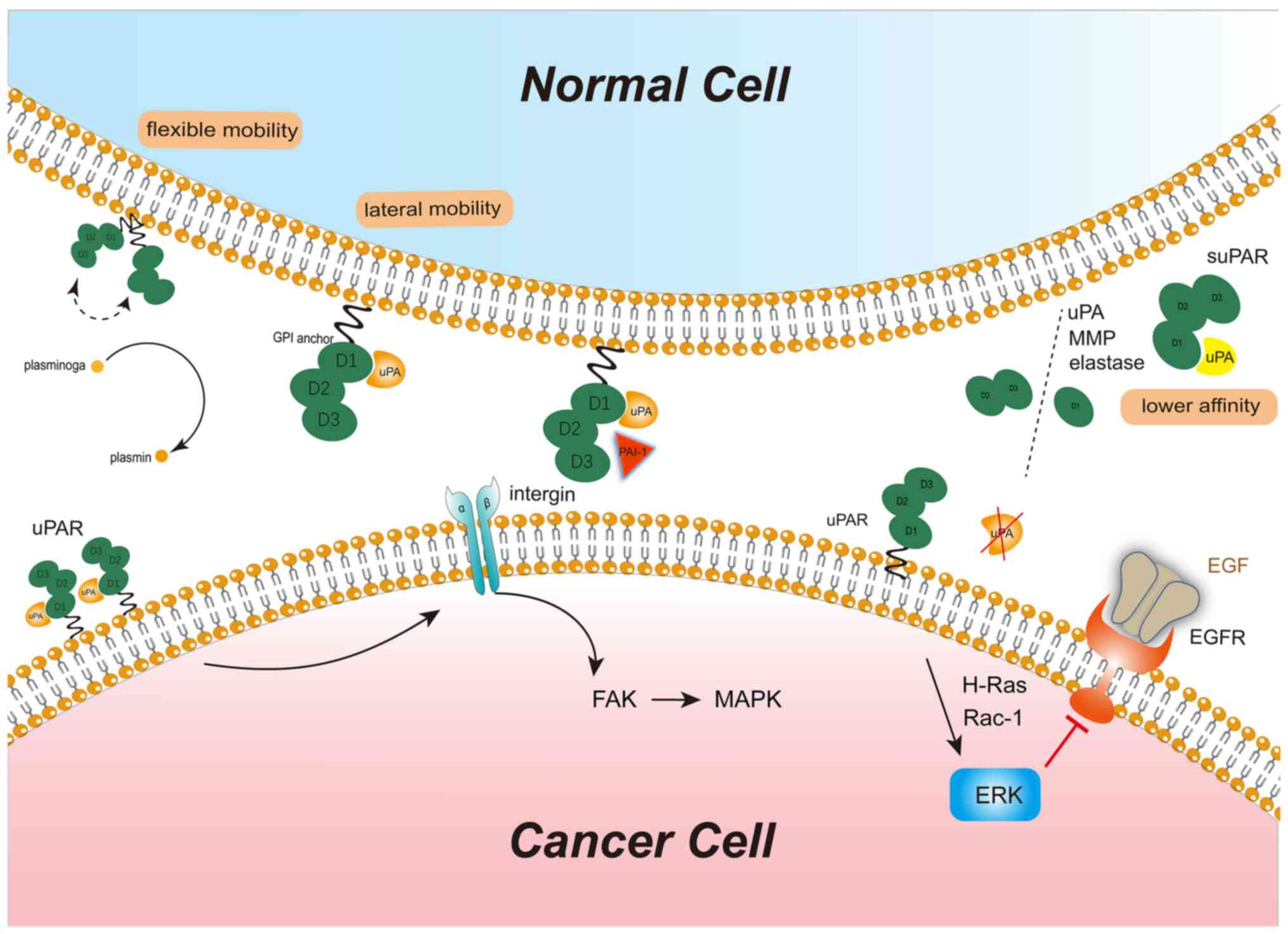
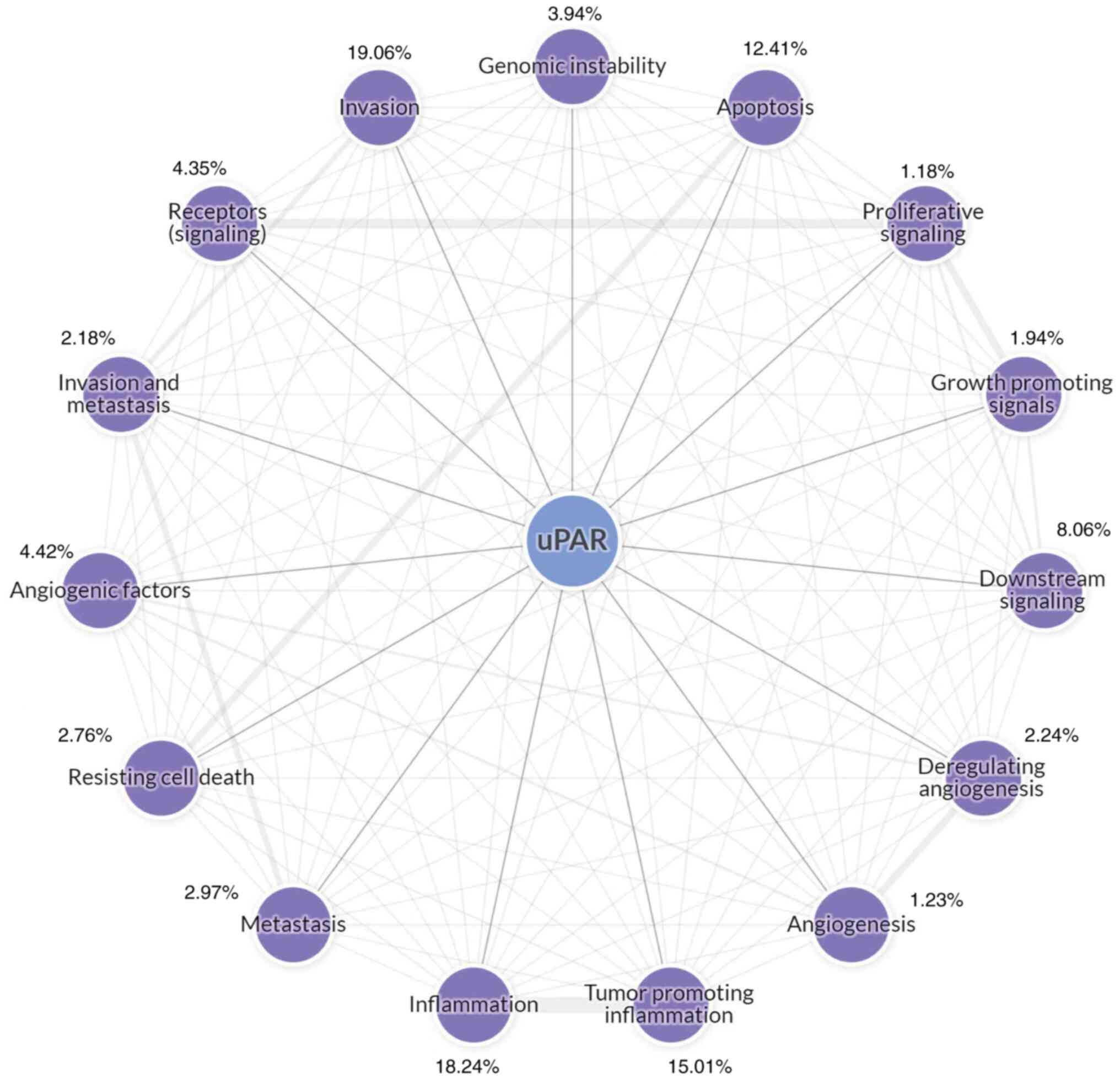
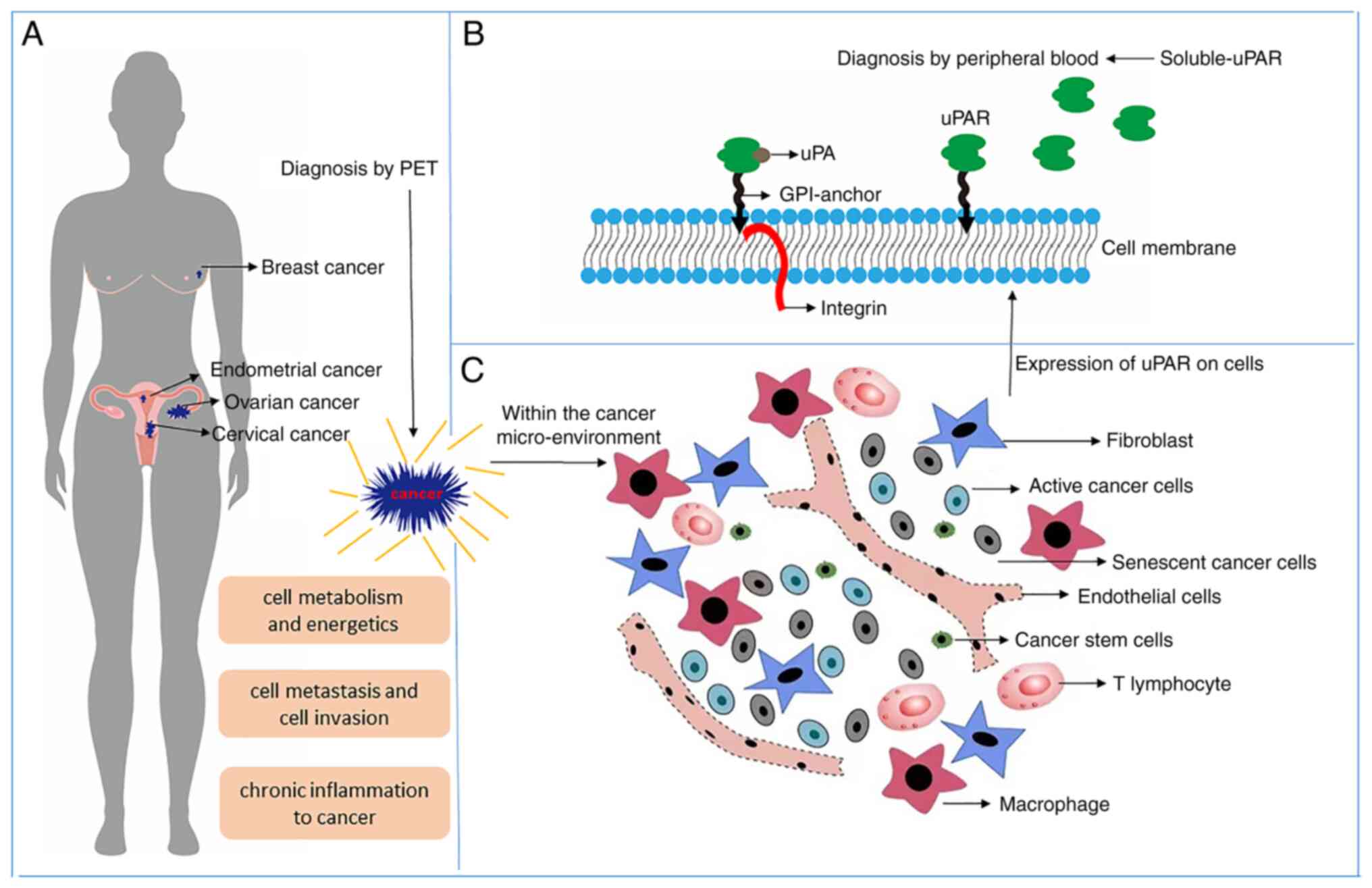
|
1
|
Vassalli JD, Baccino D and Belin D: A
cellular binding site for the Mr 55,000 form of the human
plasminogen activator, urokinase. J Cell Biol. 100:86–92. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Smith HW and Marshall CJ: Regulation of
cell signalling by uPAR. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 11:23–36. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gyetko MR, Libre EA, Fuller JA, Chen GH
and Toews G: Urokinase is required for T lymphocyte proliferation
and activation in vitro. J Lab Clin Med. 133:274–288. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Alfano M, Sidenius N, Panzeri B, Blasi F
and Poli G: Urokinase-urokinase receptor interaction mediates an
inhibitory signal for HIV-1 replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99:8862–8867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ploug MRE, Behrendt N, Jensen AL, Blasi F
and Danø K: Cellular receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator.
Carboxyl-terminal processing and membrane anchoring by
glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol. J Biol Chem. 266:1926–1933. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ploug M, Behrendt N, Løber D and Danø K:
Protein structure and membrane anchorage of the cellular receptor
for urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Semin Thromb Hemost.
17:183–193. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ellis V, Wun TC, Behrendt N, Rønne E and
Danø K: Inhibition of receptor-bound urokinase by
plasminogen-activator inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 265:9904–9908. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ploug M, Gårdsvoll H, Jørgensen TJ,
Lønborg Hansen L and Danø K: Structural analysis of the interaction
between urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its receptor: A
potential target for anti-invasive cancer therapy. Biochem Soc
Trans. 30:177–183. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Andreasen PA, Egelund R and Petersen HH:
The plasminogen activation system in tumor growth, invasion, and
metastasis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 57:25–40. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Danø K, Romer J, Nielsen BS, Bjørn S, Pyke
C, Rygaard J and Lund LR: Cancer invasion and tissue
remodeling-cooperation of protease systems and cell types. APMIS.
107:120–127. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Berkenblit A, Matulonis UA, Kroener JF,
Dezube BJ, Lam GN, Cuasay LC, Brünner N, Jones TR, Silverman MH and
Gold MA: A6, a urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA)-derived
peptide in patients with advanced gynecologic cancer: A phase I
trial. Gynecol Oncol. 99:50–57. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gold MA, Brady WE, Lankes HA, Rose PG,
Kelley JL, De Geest K, Crispens MA, Resnick KE and Howell SB: A
phase II study of a urokinase-derived peptide (A6) in the treatment
of persistent or recurrent epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or
primary peritoneal carcinoma: A gynecologic oncology group study.
Gynecol Oncol. 125:635–639. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ploug M: Structure-driven design of
radionuclide tracers for non-invasive imaging of uPAR and targeted
radiotherapy. The tale of a synthetic peptide antagonist.
Theranostics. 3:467–476. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Noh H, Hong S and Huang S: Role of
urokinase receptor in tumor progression and development.
Theranostics. 3:487–495. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
O'Halloran TV, Ahn R, Hankins P, Swindell
E and Mazar AP: The many spaces of uPAR: Delivery of theranostic
agents and nanobins to multiple tumor compartments through a single
target. Theranostics. 3:496–506. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhuang X, Zhang H and Hu G: Cancer and
microenvironment plasticity: Double-edged swords in metastasis.
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 40:419–429. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ishii G, Ochiai A and Neri S: Phenotypic
and functional heterogeneity of cancer-associated fibroblast within
the tumor microenvironment. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 99:186–196. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Najafi M, Goradel NH, Farhood B, Salehi E,
Solhjoo S, Toolee H, Kharazinejad E and Mortezaee K: Tumor
microenvironment: Interactions and therapy. J Cell Physiol.
234:5700–5721. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
D'Alessio S and Blasi F: The urokinase
receptor as an entertainer of signal transduction. Front Biosci
(Landmark Ed). 14:4575–4587. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dass K, Ahmad A, Azmi AS, Sarkar SH and
Sarkar FH: Evolving role of uPA/uPAR system in human cancers.
Cancer Treat Rev. 34:122–136. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ulisse S, Baldini E, Sorrenti S and
D'Armiento M: The urokinase plasminogen activator system: A target
for anti-cancer therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 9:32–71. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Blasi F and Sidenius N: The urokinase
receptor: Focused cell surface proteolysis, cell adhesion and
signaling. FEBS Lett. 584:1923–1930. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Paulick MG and Bertozzi CR: The
glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor: A complex membrane-anchoring
structure for proteins. Biochemistry. 47:6991–7000. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Eden G, Archinti M, Furlan F, Murphy R and
Degryse B: The urokinase receptor interactome. Curr Pharm Des.
17:1874–1889. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Eugen-Olsen J and Giamarellos-Bourboulis
EJ: suPAR: The unspecific marker for disease presence, severity and
prognosis. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 46 (Suppl 1):S33–S34. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Desmedt S, Desmedt V, Delanghe JR,
Speeckaert R and Speeckaert MM: The intriguing role of soluble
urokinase receptor in inflammatory diseases. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci.
54:117–133. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Loughner CL, Bruford EA, McAndrews MS,
Delp EE, Swamynathan S and Swamynathan SK: Organization, evolution
and functions of the human and mouse Ly6/uPAR family genes. Hum
Genomics. 10:102016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kong HK and Park JH: Characterization and
function of human Ly-6/uPAR molecules. BMB Rep. 45:595–603. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kriegbaum MC, Jacobsen B and Hald Aand
Ploug M: Expression of C4.4A, a structural uPAR homolog, reflects
squamous epithelial differentiation in the adult mouse and during
embryogenesis. J Histochem Cytochem. 59:188–201. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hansen LV, Gårdsvoll H, Nielsen BS, Lund
LR, Danø K, Jensen ON and Ploug M: Structural analysis and tissue
localization of human C4.4A: A protein homologue of the urokinase
receptor. Biochem J. 380:845–857. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Davidson B, Trope CG and Reich R: The role
of the tumor stroma in ovarian cancer. Front Oncol. 4:1042014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Baig MH, Adil M, Khan R, Dhadi S, Ahmad K,
Rabbani G, Bashir T, Imran MA, Husain FM, Lee EJ, et al: Enzyme
targeting strategies for prevention and treatment of cancer:
Implications for cancer therapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 56:1–11. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Myöhänen HT, Stephens RW, Hedman K,
Tapiovaara H, Rønne E, Høyer-Hansen G, Danø K and Vaheri A:
Distribution and lateral mobility of the urokinase-receptor complex
at the cell surface. J Histochem Cytochem. 41:1291–1301. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Eastman BM, Jo M, Webb DL, Takimoto S and
Gonias SL: A transformation in the mechanism by which the urokinase
receptor signals provides a selection advantage for estrogen
receptor-expressing breast cancer cells in the absence of estrogen.
Cell Signal. 24:1847–1855. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu D, Xu D, Liu M, Knabe WE, Yuan C, Zhou
D, Huang M and Meroueh SO: Small molecules engage hot spots through
cooperative binding to inhibit a tight protein-protein interaction.
Biochemistry. 56:1768–1784. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Høyer-Hansen G and Lund IK: Urokinase
receptor variants in tissue and body fluids. Adv Clin Chem.
44:65–102. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ahn SB, Mohamedali A, Anand S, Cheruku HR,
Birch D, Sowmya G, Cantor D, Ranganathan S, Inglis DW, Frank R, et
al: Characterization of the interaction between heterodimeric αvβ6
integrin and urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) using
functional proteomics. J Proteome Res. 13:5956–5964. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Aguirre Ghiso JA: Inhibition of FAK
signaling activated by urokinase receptor induces dormancy in human
carcinoma cells in vivo. Oncogene. 21:2513–2524. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kenny HA, Leonhardt P, Ladanyi A, Yamada
SD, Montag A, Im HK, Jagadeeswaran S, Shaw DE, Mazar AP and Lengyel
E: Targeting the urokinase plasminogen activator receptor inhibits
ovarian cancer metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 17:459–471. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A and
Balkwill F: Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 454:436–444. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gyetko MR, Sud S, Sonstein J, Polak T, Sud
A and Curtis JL: Cutting edge: Antigen-driven lymphocyte
recruitment to the lung is diminished in the absence of
urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) receptor, but is
independent of uPA. J Immunol. 167:5539–5542. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li S, Wei X, He J, Tian X, Yuan S and Sun
L: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in cancer research. Biomed
Pharmacother. 105:83–94. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ghosh AK and Vaughan DE: PAI-1 in tissue
fibrosis. J Cell Physiol. 227:493–507. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Olson D, Pöllänen J, Høyer-Hansen G, Rønne
E, Sakaguchi K, Wun TC, Appella E, Danø K and Blasi F:
Internalization of the urokinase-plasminogen activator inhibitor
type-1 complex is mediated by the urokinase receptor. J Biol Chem.
267:9129–9133. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Solberg H, Ploug M, Høyer-Hansen G,
Nielsen BS and Lund LR: The murine receptor for urokinase-type
plasminogen activator is primarily expressed in tissues actively
undergoing remodeling. J Histochem Cytochem. 49:237–246. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Conforti G, Dominguez-Jimenez C, Rønne E,
Høyer-Hansen G and Dejana E: Cell-surface plasminogen activation
causes a retraction of in vitro cultured human umbilical vein
endothelial cell monolayer. Blood. 83:994–1005. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gur-Wahnon D, Mizrachi T, Maaravi-Pinto
FY, Lourbopoulos A, Grigoriadis N, Higazi AA and Brenner T: The
plasminogen activator system: Involvement in central nervous system
inflammation and a potential site for therapeutic intervention. J
Neuroinflammation. 10:1242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Diaz A, Merino P, Manrique LG, Ospina JP,
Cheng L, Wu F, Jeanneret V and Yepes M: A cross talk between
neuronal urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and astrocytic
uPA receptor (uPAR) promotes astrocytic activation and synaptic
recovery in the ischemic brain. J Neurosci. 37:10310–10322. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hohensinner PJ, Takacs N, Kaun C, Thaler
B, Krychtiuk KA, Pfaffenberger S, Aliabadi A, Zuckermann A, Huber K
and Wojta J: Urokinase plasminogen activator protects cardiac
myocytes from oxidative damage and apoptosis via hOGG1 induction.
Apoptosis. 22:1048–1055. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ploug M, Plesner T, Rønne E, Ellis V,
Høyer-Hansen G, Hansen NE and Danø K: The receptor for
urokinase-type plasminogen activator is deficient on peripheral
blood leukocytes in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal
hemoglobinuria. Blood. 79:1447–1455. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sloand EM, Pfannes L, Scheinberg P, More
K, Wu CO, Horne M and Young NS: Increased soluble urokinase
plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR) is associated with
thrombosis and inhibition of plasmin generation in paroxysmal
nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) patients. Exp Hematol. 36:1616–1624.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liu W, Hsu AY, Wang Y, Lin T, Sun H,
Pachter JS, Groisman A, Imperioli M, Yungher FW, Hu L, et al:
Mitofusin-2 regulates leukocyte adhesion and β2 integrin
activation. J Leukoc Biol. 111:771–791. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gyetko MR, Sud S, Kendall T, Fuller JA,
Newstead MW and Standiford TJ: Urokinase receptor-deficient mice
have impaired neutrophil recruitment in response to pulmonary
Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. J Immunol. 165:1513–1519. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Puthusseri B, Marudamuthu A, Tiwari N, Fu
J, Idell S and Shetty S: Regulation of p53-mediated changes in the
uPA-fibrinolytic system and in lung injury by loss of surfactant
protein C expression in alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 312:L783–L796. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Stewart CE and Sayers I: Urokinase
receptor orchestrates the plasminogen system in airway epithelial
cell function. Lung. 191:215–225. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Beaufort N, Leduc D, Eguchi H, Mengele K,
Hellmann D, Masegi T, Kamimura T, Yasuoka S, Fend F, Chignard M and
Pidard D: The human airway trypsin-like protease modulates the
urokinase receptor (uPAR, CD87) structure and functions. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 292:L1263–L1272. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Shetty S, Padijnayayveetil J, Tucker T,
Stankowska D and Idell S: The fibrinolytic system and the
regulation of lung epithelial cell proteolysis, signaling, and
cellular viability. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
295:L967–L975. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Svenningsen P, Hinrichs GR, Zachar R,
Ydegaard R and Jensen BL: Physiology and pathophysiology of the
plasminogen system in the kidney. Pflugers Arch. 469:1415–1423.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hayek SS, Koh KH, Grams ME, Wei C, Ko YA,
Li J, Samelko B, Lee H, Dande RR, Lee HW, et al: A tripartite
complex of suPAR, APOL1 risk variants and
αvβ3 integrin on podocytes mediates chronic
kidney disease. Nat Med. 23:945–953. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Cheng Y, Hall TR, Xu X, Yung I, Souza D,
Zheng J, Schiele F, Hoffmann M, Mbow ML, Garnett JP and Li J:
Targeting uPA-uPAR interaction to improve intestinal epithelial
barrier integrity in inflammatory bowel disease. EBioMedicine.
75:1037582022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wang H, Yang L, Jamaluddin MS and Boyd DD:
The Kruppel-like KLF4 transcription factor, a novel regulator of
urokinase receptor expression, drives synthesis of this binding
site in colonic crypt luminal surface epithelial cells. J Biol
Chem. 279:22674–22683. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Amor C, Feucht J, Leibold J, Ho YJ, Zhu C,
Alonso-Curbelo D, Mansilla-Soto J, Boyer JA, Li X, Giavridis T, et
al: Senolytic CAR T cells reverse senescence-associated
pathologies. Nature. 583:127–132. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Lv T, Zhao Y, Jiang X, Yuan H, Wang H, Cui
X, Xu J, Zhao J and Wang J: uPAR: An essential factor for tumor
development. J Cancer. 12:7026–7040. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Laurenzana A, Chillà A, Luciani C,
Peppicelli S, Biagioni A, Bianchini F, Tenedini E, Torre E, Mocali
A, Calorini L, et al: uPA/uPAR system activation drives a
glycolytic phenotype in melanoma cells. Int J Cancer.
141:1190–1200. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Biagioni A, Laurenzana A, Chillà A, Del
Rosso M, Andreucci E, Poteti M, Bani D, Guasti D, Fibbi G and
Margheri F: uPAR knockout results in a deep glycolytic and OXPHOS
reprogramming in melanoma and colon carcinoma cell lines. Cells.
9:3082020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Flores-López LA, Martínez-Hernández MG,
Viedma-Rodríguez R, Díaz-Flores M and Baiza-Gutman LA: High glucose
and insulin enhance uPA expression, ROS formation and invasiveness
in breast cancer-derived cells. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 39:365–378.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Pastushenko I and Blanpain C: EMT
transition states during tumor progression and metastasis. Trends
Cell Biol. 29:212–226. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Csiszar A, Kutay B, Wirth S, Schmidt U,
Macho-Maschler S, Schreiber M, Alacakaptan M, Vogel GF, Aumayr K,
Huber LA and Beug H: Interleukin-like epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition inducer activity is controlled by proteolytic processing
and plasminogen-urokinase plasminogen activator receptor
system-regulated secretion during breast cancer progression. Breast
Cancer Res. 16:4332014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ragone C, Minopoli M, Ingangi V, Botti G,
Fratangelo F, Pessi A, Stoppelli MP, Ascierto PA, Ciliberto G,
Motti ML and Carriero MV: Targeting the cross-talk between
urokinase receptor and Formyl peptide receptor type 1 to prevent
invasion and trans-endothelial migration of melanoma cells. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 36:1802017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Qu M, Yu J, Liu H, Ren Y, Ma C, Bu X and
Lan Q: The candidate tumor suppressor gene SLC8A2 inhibits
invasion, angiogenesis and growth of glioblastoma. Mol Cells.
40:761–772. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Yang QX, Zhong S, He L, Jia XJ, Tang H,
Cheng ST, Ren JH, Yu HB, Zhou L, Zhou HZ, et al: PBK overexpression
promotes metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via activating
ETV4-uPAR signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 452:90–102. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ding Y, Zhang H, Lu A, Zhou Z, Zhong M,
Shen D, Wang X and Zhu Z: Effect of urokinase-type plasminogen
activator system in gastric cancer with peritoneal metastasis.
Oncol Lett. 11:4208–4216. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Su B, Su J, He H, Wu Y, Xia H, Zeng X, Dai
W, Ai X, Ling H, Jiang H and Su Q: Identification of potential
targets for diallyl disulfide in human gastric cancer MGC-803 cells
using proteomics approaches. Oncol Rep. 33:2484–2894. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Alpízar-Alpízar W, Skindersoe ME,
Rasmussen L, Kriegbaum MC, Christensen IJ, Lund IK, Illemann M,
Laerum OD, Krogfelt KA, Andersen LP and Ploug M: Helicobacter
pylori colonization drives urokinase receptor (uPAR) expression in
murine gastric epithelium during early pathogenesis.
Microorganisms. 8:10192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Beleva E, Stoencheva S, Deneva T, Nenova I
and Grudeva-Popova Z: Assessment of clinical utility and predictive
potential of pre-chemotherapy soluble urokinase plasminogen
activator receptor-observational single center study. Bosn J Basic
Med Sci. Sep 8–2022.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Bifulco K, Longanesi-Cattani I, Gala M, DI
Carluccio G, Masucci MT, Pavone V, Lista L, Arra C, Stoppelli MP
and Carriero MV: The soluble form of urokinase receptor promotes
angiogenesis through its Ser88-Arg-Ser-Arg-Tyr92 chemotactic
sequence. J Thromb Haemost. 8:2789–2799. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Poettler M, Unseld M, Mihaly-Bison J,
Uhrin P, Koban F, Binder BR, Zielinski CC and Prager GW: The
urokinase receptor (CD87) represents a central mediator of growth
factor-induced endothelial cell migration. Thromb Haemost.
108:357–366. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Boas SEM, Carvalho J, van den Broek M,
Weijers EM, Goumans MJ, Koolwijk P and Merks RMH: A local
uPAR-plasmin-TGFβ1 positive feedback loop in a qualitative
computational model of angiogenic sprouting explains the in vitro
effect of fibrinogen variants. PLoS Comput Biol. 14:e10062392018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Unseld M, Chilla A, Pausz C, Mawas R,
Breuss J, Zielinski C, Schabbauer G and Prager GW: PTEN expression
in endothelial cells is down-regulated by uPAR to promote
angiogenesis. Thromb Haemost. 114:379–389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Jing Y, Tong C, Zhang J, Nakamura T,
Iankov I, Russell SJ and Merchan JR: Tumor and vascular targeting
of a novel oncolytic measles virus retargeted against the urokinase
receptor. Cancer Res. 69:1459–1468. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Jing Y, Chavez V, Ban Y, Acquavella N,
El-Ashry D, Pronin A, Chen X and Merchan JR: Molecular effects of
stromal-selective targeting by uPAR-retargeted oncolytic virus in
breast cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 15:1410–1420. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Pyke C, Graem N, Ralfkiaer E, Rønne E,
Høyer-Hansen G, Brünner N and Danø K: Receptor for urokinase is
present in tumor-associated macrophages in ductal breast carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 53:1911–1915. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Berg D, Wolff C, Malinowsky K, Tran K,
Walch A, Bronger H, Schuster T, Höfler H and Becker KF: Profiling
signalling pathways in formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded breast
cancer tissues reveals cross-talk between EGFR, HER2, HER3 and
uPAR. J Cell Physiol. 227:204–212. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Li C, Cao S, Liu Z, Ye X, Chen L and Meng
S: RNAi-mediated downregulation of uPAR synergizes with targeting
of HER2 through the ERK pathway in breast cancer cells. Int J
Cancer. 127:1507–1516. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Desai A, Xu J, Aysola K, Qin Y, Okoli C,
Hariprasad R, Chinemerem U, Gates C, Reddy A, Danner O, et al:
Epithelial ovarian cancer: An overview. World J Transl Med. 3:1–8.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Kim S, Kim B and Song YS: Ascites
modulates cancer cell behavior, contributing to tumor heterogeneity
in ovarian cancer. Cancer Sci. 107:1173–1178. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Cho KR and Shih IeM: Ovarian cancer. Annu
Rev Pathol. 4:287–313. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Al-Hassan NN, Behzadian A, Caldwell R,
Ivanova VS, Syed V, Motamed K and Said NA: Differential roles of
uPAR in peritoneal ovarian carcinomatosis. Neoplasia. 14:259–270.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Chambers SK, Gertz RE Jr, Ivins CM and
Kacinski BM: The significance of urokinase-type plasminogen
activator, its inhibitors, and its receptor in ascites of patients
with epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer. 75:1627–1633. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
van Dam PA, Coelho A and Rolfo C: Is there
a role for urokinase-type plasminogen activator inhibitors as
maintenance therapy in patients with ovarian cancer? Eur J Surg
Oncol. 43:252–257. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Kuhn W, Schmalfeldt B, Reuning U, Pache L,
Berger U, Ulm K, Harbeck N, Späthe K, Dettmar P, Höfler H, et al:
Prognostic significance of urokinase (uPA) and its inhibitor PAI-1
for survival in advanced ovarian carcinoma stage FIGO IIIc. Br J
Cancer. 79:1746–1751. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Dorn J, Harbeck N, Kates R, Gkazepis A,
Scorilas A, Soosaipillai A, Diamandis E, Kiechle M, Schmalfeldt B
and Schmitt M: Impact of expression differences of
kallikrein-related peptidases and of uPA and PAI-1 between primary
tumor and omentum metastasis in advanced ovarian cancer. Ann Oncol.
22:877–883. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Du J, Li Y, Lv S, Wang Q, Sun C, Dong X,
He M, Ulain Q, Yuan Y, Tuo X, et al: Endometrial sampling devices
for early diagnosis of endometrial lesions. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 142:2515–2522. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Morice P, Leary A, Creutzberg C,
Abu-Rustum N and Darai E: Endometrial cancer. Lancet.
387:1094–1108. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Chiu HC, Li CJ, Yiang GT, Tsai AP and Wu
MY: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cell biology of
molecular regulation in endometrial carcinogenesis. J Clin Med.
8:4392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Sorosky JI: Endometrial cancer. Obstet
Gynecol. 120:383–397. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Prifti S, Zourab Y, Koumouridis A,
Bohlmann M, Strowitzki T and Rabe T: Role of integrins in invasion
of endometrial cancer cell lines. Gynecol Oncol. 84:12–20. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Memarzadeh S, Kozak KR, Chang L, Natarajan
S, Shintaku P, Reddy ST and Farias-Eisner R: Urokinase plasminogen
activator receptor: Prognostic biomarker for endometrial cancer.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:10647–10652. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Tecimer C, Doering DL, Goldsmith LJ, Meyer
JS, Abdulhay G and Wittliff JL: Clinical relevance of
urokinase-type plasminogen activator, its receptor, and its
inhibitor type 1 in endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 80:48–55.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Fredstorp-Lidebring M, Bendahl PO, Brünner
N, Casslén B, Högberg T, Långström-Einarsson E, Willén R and Fernö
M: Urokinase plasminogen activator and its inhibitor, PAI-1, in
association with progression-free survival in early stage
endometrial cancer. Eur J Cancer. 37:2339–2348. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Makieva S, Giacomini E, Ottolina J,
Sanchez AM, Papaleo E and Viganò P: Inside the endometrial cell
signaling subway: Mind the Gap(s). Int J Mol Sci. 19:24772018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Rider V, Isuzugawa K, Twarog M, Jones S,
Cameron B, Imakawa K and Fang J: Progesterone initiates
Wnt-beta-catenin signaling but estradiol is required for nuclear
activation and synchronous proliferation of rat uterine stromal
cells. J Endocrinol. 191:537–548. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Sahebali S, Van den Eynden G, Murta EF,
Michelin MA, Cusumano P, Petignat P and Bogers JJ: Stromal issues
in cervical cancer: A review of the role and function of basement
membrane, stroma, immune response and angiogenesis in cervical
cancer development. Eur J Cancer Prev. 19:204–215. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Smola S: Immunopathogenesis of
HPV-associated cancers and prospects for immunotherapy. Viruses.
9:254–270. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Jing J, Zheng S, Han C, Du L, Guo Y and
Wang P: Evaluating the value of uPAR of serum and tissue on
patients with cervical cancer. J Clin Lab Anal. 26:16–21. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Sasaki T, Nishi H, Nagata C, Nagai T,
Nagao T, Terauchi F and Isaka K: A retrospective study of
urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) as a
prognostic factor in cancer of the uterine cervix. Int J Clin
Oncol. 19:1059–1064. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Nishi H, Sasaki T, Nagamitsu Y, Terauchi
F, Nagai T, Nagao T and Isaka K: Hypoxia inducible factor-1
mediates upregulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator
receptor gene transcription during hypoxia in cervical cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 35:992–998. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Chaudary N and Hill RP: Increased
expression of metastasis-related genes in hypoxic cells sorted from
cervical and lymph nodal xenograft tumors. Lab Invest. 89:587–596.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Sato M, Kawana K, Adachi K, Fujimoto A,
Yoshida M, Nakamura H, Nishida H, Inoue T, Taguchi A, Takahashi J,
et al: Decreased expression of the plasminogen activator inhibitor
type 1 is involved in degradation of extracellular matrix
surrounding cervical cancer stem cells. Int J Oncol. 48:829–835.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Duriseti S, Goetz DH, Hostetter DR, LeBeau
AM, Wei Y and Craik CS: Antagonistic anti-urokinase plasminogen
activator receptor (uPAR) antibodies significantly inhibit
uPAR-mediated cellular signaling and migration. J Biol Chem.
285:26878–26888. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Xu X, Cai Y, Wei Y, Donate F, Juarez J,
Parry G, Chen L, Meehan EJ, Ahn RW, Ugolkov A, et al:
Identification of a new epitope in uPAR as a target for the cancer
therapeutic monoclonal antibody ATN-658, a structural homolog of
the uPAR binding integrin CD11b (αM). PLoS One. 9:e853492014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Van Buren G II, Gray MJ, Dallas NA, Xia L,
Lim SJ, Fan F, Mazar AP and Ellis LM: Targeting the urokinase
plasminogen activator receptor with a monoclonal antibody impairs
the growth of human colorectal cancer in the liver. Cancer.
115:3360–3368. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Rabbani SA, Ateeq B, Arakelian A,
Valentino ML, Shaw DE, Dauffenbach LM, Kerfoot CA and Mazar AP: An
anti-urokinase plasminogen activator receptor antibody (ATN-658)
blocks prostate cancer invasion, migration, growth, and
experimental skeletal metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Neoplasia.
12:778–788. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Wang L, Yang R, Zhao L, Zhang X, Xu T and
Cui M: Basing on uPAR-binding fragment to design chimeric antigen
receptors triggers antitumor efficacy against uPAR expressing
ovarian cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 117:1091732019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Qin L, Wang L, Zhang J, Zhou H, Yang Z,
Wang Y, Cai W, Wen F, Jiang X, Zhang T, et al: Therapeutic
strategies targeting uPAR potentiate anti-PD-1 efficacy in
diffuse-type gastric cancer. Sci Adv. 8:eabn37742022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Su M, Chang W, Cui M, Lin Y, Wu S and Xu
T: Expression and anticancer activity analysis of recombinant human
uPA1-43-melittin. IntJ Oncol. 46:619–626. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Hall WA and Vallera DA: Efficacy of
antiangiogenic targeted toxins against glioblastoma multiforme.
Neurosurg Focus. 20:E232006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Todhunter DA, Hall WA, Rustamzadeh E, Shu
Y, Doumbia SO and Vallera DA: A bispecific immunotoxin (DTAT13)
targeting human IL-13 receptor (IL-13R) and urokinase-type
plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) in a mouse xenograft model.
Protein Eng Des Sel. 17:157–164. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Vallera DA, Li C, Jin N,
Panoskaltsis-Mortari A and Hall WA: Targeting urokinase-type
plasminogen activator receptor on human glioblastoma tumors with
diphtheria toxin fusion protein DTAT. J Natl Cancer Inst.
94:597–606. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Sun Q, Xu Q, Dong X, Cao L, Huang X, Hu Q
and Hua ZC: A hybrid protein comprising ATF domain of pro-UK and
VAS, an angiogenesis inhibitor, is a potent candidate for targeted
cancer therapy. Int J Cancer. 123:942–950. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Takei Y, Mizukami H, Saga Y, Kobayashi H
and Suzuki M, Matsushita T, Ozawa K and Suzuki M: Overexpression of
a hybrid gene consisting of the amino-terminal fragment of
urokinase and carboxyl-terminal domain of bikunin suppresses
invasion and migration of human ovarian cancer cells in vitro. Int
J Cancer. 113:54–58. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Errico Provenzano A, Posteri R, Giansanti
F, Angelucci F, Flavell SU, Flavell DJ, Fabbrini MS, Porro D,
Ippoliti R, Ceriotti A, et al: Optimization of construct design and
fermentation strategy for the production of bioactive ATF-SAP, a
saporin based anti-tumoral uPAR-targeted chimera. Microb Cell Fact.
15:1942016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Liu X, Liu X, Sunchen S, Liu M, Shen C, Wu
J, Zhao W, Yu B and Liu J: A novel tumor-activated ALA fusion
protein for specific inhibition on the growth and invasion of
breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231. Drug Deliv. 24:1811–1817. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Schmitt M, Harbeck N, Brünner N, Jänicke
F, Meisner C, Mühlenweg B, Jansen H, Dorn J, Nitz U, Kantelhardt EJ
and Thomssen C: Cancer therapy trials employing level-of-evidence-1
disease forecast cancer biomarkers uPA and its inhibitor PAI-1.
Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 11:617–634. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Sharma S, Watanabe T, Nishimoto T,
Takihara T, Mlakar L, Nguyen XX, Sanderson M, Su Y, Chambers RA and
Feghali-Bostwick C: E4 engages uPAR and enolase-1 and activates
urokinase to exert antifibrotic effects. JCI Insight.
6:e1449352021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Gao N, Bozeman EN, Qian W, Wang L, Chen H,
Lipowska M, Staley CA, Wang YA, Mao H and Yang L: Tumor penetrating
theranostic nanoparticles for enhancement of targeted and
image-guided drug delivery into peritoneal tumors following
intraperitoneal delivery. Theranostics. 7:1689–16704. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Kriegbaum MC, Persson M, Haldager L,
Alpízar-Alpízar W, Jacobsen B, Gårdsvoll H, Kjær A and Ploug M:
Rational targeting of the urokinase receptor (uPAR): Development of
antagonists and non-invasive imaging probes. Curr Drug Targets.
12:1711–1728. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Carlsen EA, Loft M, Loft A, Berthelsen AK,
Langer SW, Knigge U and Kjaer A: Prospective phase II trial of
prognostication by 68Ga-NOTA-AE105 uPAR PET in patients
with neuroendocrine neoplasms: Implications for uPAR targeted
therapy. J Nucl Med. 63:1371–1377. 2022.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Oh F, Modiano JF, Bachanova V and Vallera
DA: Bispecific targeting of EGFR and urokinase receptor (uPAR)
using ligand-targeted toxins in solid tumors. Biomolecules.
10:9562020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Zhai BT, Tian H, Sun J, Zou JB, Zhang XF,
Cheng JX, Shi YJ, Fan Y and Guo DY: Urokinase-type plasminogen
activator receptor (uPAR) as a therapeutic target in cancer. J
Transl Med. 20:1352022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Metrangolo V, Ploug M and Engelholm LH:
The urokinase receptor (uPAR) as a ‘trojan horse’ in targeted
cancer therapy: Challenges and opportunities. Cancers (Basel).
13:53762021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|