|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global Cancer Statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sorlie T, Tibshirani R, Parker J, Hastie
T, Marron JS, Nobel A, Deng S, Johnsen H, Pesich R, Geisler S, et
al: Repeated observation of breast tumor subtypes in independent
gene expression data sets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:8418–8423.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hugh J, Hanson J, Cheang MC, Nielsen TO,
Perou CM, Dumontet C, Reed J, Krajewska M, Treilleux I, Rupin M, et
al: Breast cancer subtypes and response to docetaxel in
node-positive breast cancer: Use of an immunohistochemical
definition in the BCIRG 001 trial. J Clin Oncol. 27:1168–1176.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Prat A, Cheang MC, Martín M, Parker JS,
Carrasco E, Caballero R, Tyldesley S, Gelmon K, Bernard PS, Nielsen
TO, et al: Prognostic significance of progesterone
receptor-positive tumor cells within immunohistochemically defined
luminal A breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 31:203–209. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Raj-Kumar PK, Liu J, Hooke JA, Kovatich
AJ, Kvecher L, Shriver CD and Hu H: PCA-PAM50 improves consistency
between breast cancer intrinsic and clinical subtyping
reclassifying a subset of luminal A tumors as luminal B. Sci Rep.
9:79562019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nagini S: Breast cancer: Current molecular
therapeutic targets and new players. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
17:152–163. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Burstein HJ: The distinctive nature of
HER2-positive breast cancers. N Engl J Med. 353:1652–1654. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pernas S, Barroso-Sousa R and Tolaney SM:
Optimal treatment of early stage HER2-positive breast cancer.
Cancer. 124:4455–4466. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pellat A, Vaquero J and Fouassier L: Role
of ErbB/HER family of receptor tyrosine kinases in cholangiocyte
biology. Hepatology. 67:762–773. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
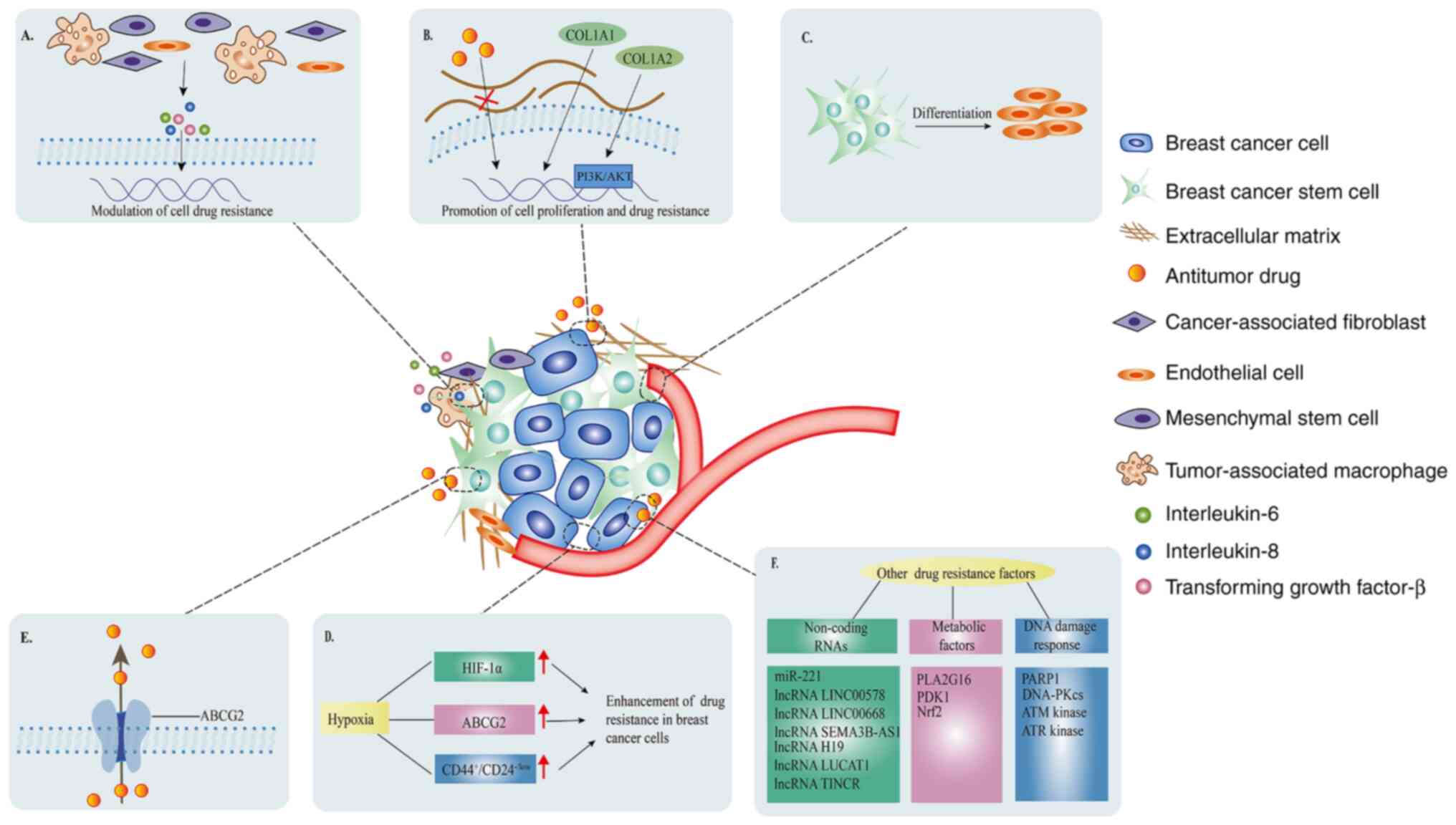
Reschke M, Mihic-Probst D, van der Horst
EH, Knyazev P, Wild PJ, Hutterer M, Meyer S, Dummer R, Moch H and
Ullrich A: HER3 is a determinant for poor prognosis in melanoma.
Clin Cancer Res. 14:5188–5197. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Saglam O, Xiong Y, Marchion DC, Strosberg
C, Wenham RM, Johnson JJ, Saeed-Vafa D, Cubitt C, Hakam A and
Magliocco AM: ERBB4 expression in ovarian serous carcinoma
resistant to platinum-based therapy. Cancer Control. 24:89–95.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang Z: ErbB receptors and cancer. Methods
Mol Biol. 1652:3–35. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Watanabe S, Yonesaka K, Tanizaki J,
Nonagase Y, Takegawa N, Haratani K, Kawakami H, Hayashi H, Takeda
M, Tsurutani J and Nakagawaet K: Targeting of the HER2/HER3
signaling axis overcomes ligand-mediated resistance to trastuzumab
in HER2-positive breast cancer. Cancer Med. 8:1258–1268. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cronin KA, Harlan LC, Dodd KW, Abrams JS
and Ballard-Barbash R: Population-based estimate of the prevalence
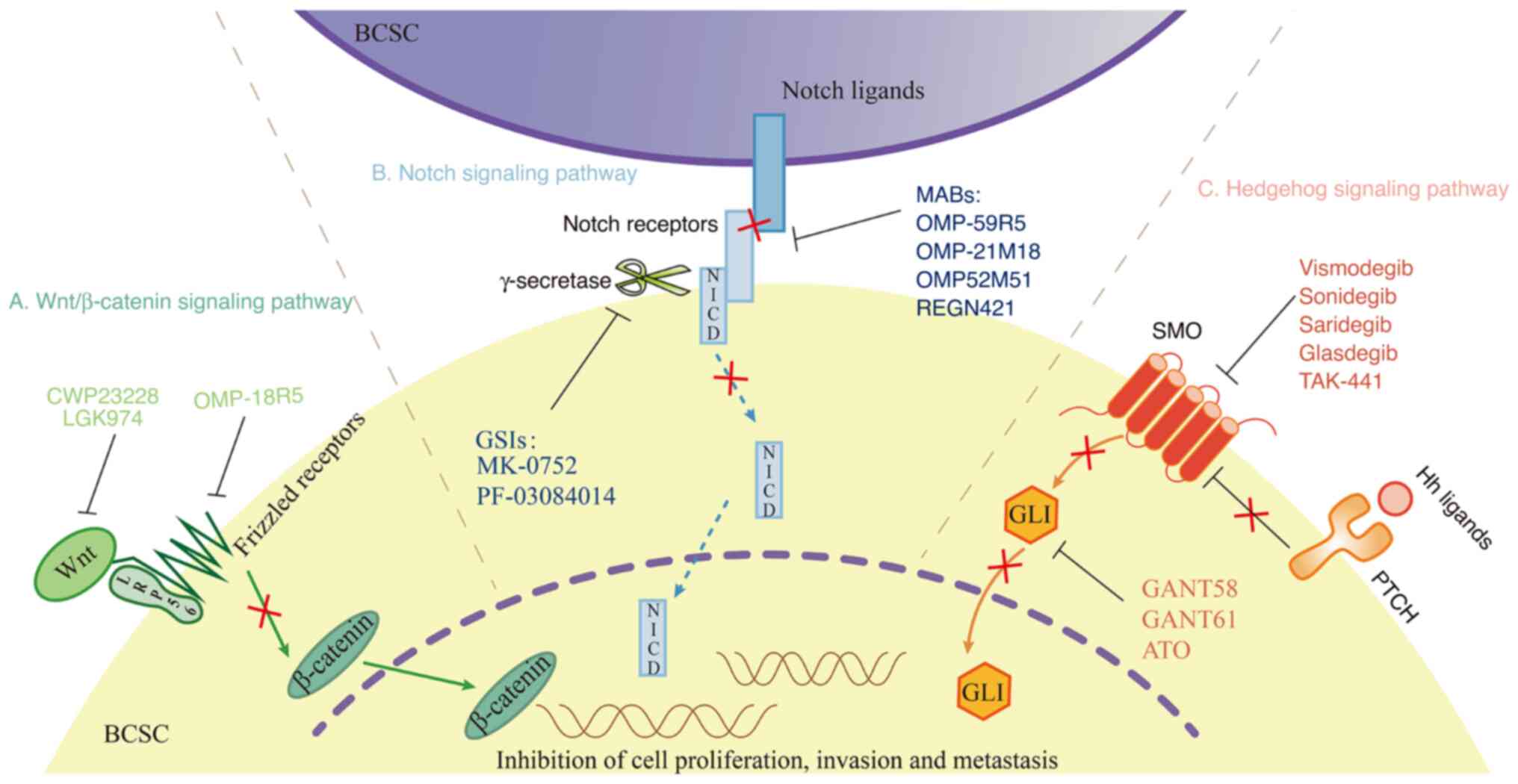
of HER-2 positive breast cancer tumors for early stage patients in
the US. Cancer Invest. 28:963–968. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Von Minckwitz G, Huang CS, Mano MS, Loibl
S, Mamounas EP, Untch M, Wolmark N, Rastogi P, Schneeweiss A,
Redondo A, et al: Trastuzumab Emtansine for residual invasive
HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 380:617–628. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Saura C, Oliveira M, Feng YH, Dai MS, Chen
SW, Hurvitz SA, Kim SB, Moy B, Delaloge S, Gradishar W, et al:
Neratinib plus capecitabine versus lapatinib plus capecitabine in
HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer previously treated with ≥2
HER2-directed regimens: Phase III NALA trial. J Clin Oncol.
38:3138–3149. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Piccart M, Procter M, Fumagalli D, de
Azambuja E, Clark E, Ewer MS, Restuccia E, Jerusalem G, Dent S,
Reaby L, et al: Adjuvant Pertuzumab and trastuzumab in early
HER2-positive breast cancer in the APHINITY trial: 6 Years'
follow-up. J Clin Oncol. 39:1448–1457. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nader-Marta G, Martins-Branco D and de
Azambuja E: How we treat patients with metastatic HER2-positive
breast cancer. ESMO Open. 7:1003432022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Figueroa-Magalhães MC, Jelovac D, Connolly
R and Wolff AC: Treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer. Breast.
23:128–136. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Qiu Y, Yang L, Liu H and Luo X: Cancer
stem cell-targeted therapeutic approaches for overcoming
trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer. Stem Cells.
39:1125–1136. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang Y: The root cause of drug resistance
in HER2-positive breast cancer and the therapeutic approaches to
overcoming the resistance. Pharmacol Ther. 218:1076772021.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Ross JS, Slodkowska EA, Symmans WF,
Pusztai L, Ravdin PM and Hortobagyi GN: The HER-2 receptor and
breast cancer: Ten years of targeted anti-HER-2 therapy and
personalized medicine. Oncologist. 14:320–368. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lambertini M, Pondé NF, Solinas C and de
Azambuja E: Adjuvant trastuzumab: A 10-year overview of its
benefit. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 17:61–74. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Valabrega G, Montemurro F and Aglietta M:
Trastuzumab: Mechanism of action, resistance and future
perspectives in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer. Ann Oncol.
18:977–984. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
McCormack PL: Pertuzumab: A review of its
use for first-line combination treatment of HER2-positive
metastatic breast cancer. Drugs. 73:1491–1502. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xia W, Mullin RJ, Keith BR, Liu LH, Ma H,
Rusnak DW, Owens G, Alligood KJ and Spector NL: Anti-tumor activity
of GW572016: A dual tyrosine kinase inhibitor blocks EGF activation
of EGFR/erbB2 and downstream Erk1/2 and AKT pathways. Oncogene.
21:6255–6263. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hegde PS, Rusnak D, Bertiaux M, Alligood
K, Strum J, Gagnon R and Gilmer TM: Delineation of molecular
mechanisms of sensitivity to lapatinib in breast cancer cell lines
using global gene expression profiles. Mol Cancer Ther.
6:1629–1640. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rabindran SK, Discafani CM, Rosfjord EC,
Baxter M, Floyd MB, Golas J, Hallett WA, Johnson BD, Nilakantan R,
Overbeek E, et al: Antitumor activity of HKI-272, an orally active,
irreversible inhibitor of the HER-2 tyrosine kinase. Cancer Res.
64:3958–3965. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mohd Nafi SN, Generali D, Kramer-Marek G,
Gijsen M, Strina C, Cappelletti M, Andreis D, Haider S, Li JL,
Bridges E, et al: Nuclear HER4 mediates acquired resistance to
trastuzumab and is associated with poor outcome in HER2 positive
breast cancer. Oncotarget. 5:5934–5949. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kourie HR, Chaix M, Gombos A, Aftimos P
and Awada A: Pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics and clinical
efficacy of neratinib in HER2-positive breast cancer and breast
cancer with HER2 mutations. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol.
12:947–957. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Borges VF, Ferrario C, Aucoin N, Falkson
C, Khan Q, Krop I, Welch S, Conlin A, Chaves J, Bedard PL, et al:
Tucatinib combined with Ado-trastuzumab emtansine in advanced
ERBB2/HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer: A phase 1b clinical
trial. JAMA Oncol. 4:1214–1220. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kulukian A, Lee P, Taylor J, Rosler R, de
Vries P, Watson D, Forero-Torres A and Peterson S: Preclinical
activity of HER2-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor tucatinib as a
single agent or in combination with trastuzumab or docetaxel in
solid tumor models. Mol Cancer Ther. 19:976–987. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Murthy RK, Loi S, Okines A, Paplomata E,
Hamilton E, Hurvitz SA, Lin NU, Borges V, Abramson V, Anders C, et
al: Tucatinib, trastuzumab, and capecitabine for HER2-positive
metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 382:597–609. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Junttila TT, Li G, Parsons K, Phillips GL
and Sliwkowski MX: Trastuzumab-DM1 (T-DM1) retains all the
mechanisms of action of trastuzumab and efficiently inhibits growth
of lapatinib insensitive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
128:347–356. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Li G, Guo J, Shen BQ, Yadav DB, Sliwkowski
MX, Crocker LM, Lacap JA and Phillips G: Mechanisms of acquired
resistance to trastuzumab emtansine in breast cancer cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 17:1441–1453. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nagai Y, Oitate M, Shiozawa H and Ando O:
Comprehensive preclinical pharmacokinetic evaluations of
trastuzumab deruxtecan (DS-8201a), a HER2-targeting antibody-drug
conjugate, in cynomolgus monkeys. Xenobiotica. 49:1086–1096. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ogitani Y, Aida T, Hagihara K, Yamaguchi
J, Ishii C, Harada N, Soma M, Okamoto H, Oitate M, Arakawa S, et
al: DS-8201a, A novel HER2-targeting ADC with a Novel DNA
topoisomerase I inhibitor, demonstrates a promising antitumor
efficacy with differentiation from T-DM1. Clin Cancer Res.
22:5097–5108. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Metzger-Filho O, Vora T and Awada A:
Management of metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer progression
after adjuvant trastuzumab therapy-current evidence and future
trends. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 19(Suppl 1): S31–S39. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Bonnet D and Dick JE: Human acute myeloid
leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a
primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med. 3:730–737. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kreso A and Dick JE: Evolution of the
cancer stem cell model. Cell Stem Cell. 14:275–291. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,
Morrison SJ and Clarke MF: Prospective identification of
tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:3983–3988. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim YJ, Sung D, Oh E, Cho Y, Cho TM,
Farrand L, Seo JH and Kim JY: Flubendazole overcomes trastuzumab
resistance by targeting cancer stem-like properties and HER2
signaling in HER2-positive breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 412:118–130.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Seo AN, Lee HJ, Kim EJ, Jang MH, Kim YJ,
Kim JH, Kim SW, Ryu HS, Park IA, Im SA, et al: Expression of breast
cancer stem cell markers as predictors of prognosis and response to
trastuzumab in HER2-positive breast cancer. Br J Cancer.
114:1109–1116. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ricardo S, Vieira AF, Gerhard R, Leitão D,
Pinto R, Cameselle-Teijeiro JF, Milanezi F, Schmitt F and Paredes
J: Breast cancer stem cell markers CD44, CD24 and ALDH1: Expression
distribution within intrinsic molecular subtype. J Clin Pathol.
64:937–946. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li X, Lewis MT, Huang J, Gutierrez C,
Osborne CK, Wu MF, Hilsenbeck SG, Pavlick A, Zhang X, Chamness GC,
et al: Intrinsic resistance of tumorigenic breast cancer cells to
chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 100:672–679. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bourguignon L: Matrix hyaluronan-CD44
interaction activates MicroRNA and LncRNA signaling associated with
chemoresistance, invasion, and tumor progression. Front Oncol.
9:4922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen Y, Song J, Jiang Y, Yu C and Ma Z:
Predictive value of CD44 and CD24 for prognosis and chemotherapy
response in invasive breast ductal carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:11287–11295. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liu S, Cong Y, Wang D, Sun Y, Deng L, Liu
Y, Martin-Trevino R, Shang L, McDermott SP, Landis MD, et al:
Breast cancer stem cells transition between epithelial and
mesenchymal states reflective of their normal counterparts. Stem
Cell Reports. 2:78–91. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Oliveras-Ferraros C, Vazquez-Martin A,
Martin-Castillo B, Cufí S, Del Barco S, Lopez-Bonet E, Brunet J and
Menendez JA: Dynamic emergence of the mesenchymal
CD44(pos)CD24(neg/low) phenotype in HER2-gene amplified breast
cancer cells with de novo resistance to trastuzumab (Herceptin).
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 397:27–33. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ginestier C, Hur MH, Charafe-Jauffret E,
Monville F, Dutcher J, Brown M, Jacquemier J, Viens P, Kleer CG,
Liu S, et al: ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human
mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell
Stem Cell. 1:555–567. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Liu C, Qiang J, Deng Q, Xia J, Deng L,
Zhou L, Wang D, He X, Liu Y, Zhao B, et al: ALDH1A1 activity in
tumor-initiating cells remodels myeloid-derived suppressor cells to
promote breast cancer progression. Cancer Res. 81:5919–5934. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Talukdar S, Bhoopathi P, Emdad L, Das S,
Sarkar D and Fisher PB: Dormancy and cancer stem cells: An enigma
for cancer therapeutic targeting. Adv Cancer Res. 141:43–84. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Duru N, Fan M, Candas D, Menaa C, Liu HC,
Nantajit D, Wen Y, Xiao K, Eldridge A, Chromy BA, et al:
HER2-associated radiore-sistance of breast cancer stem cells
isolated from HER2-negative breast cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res.
18:6634–6647. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Shao J, Fan W, Ma B and Wu Y: Breast
cancer stem cells expressing different stem cell markers exhibit
distinct biological characteristics. Mol Med Rep. 14:4991–4998.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Barzegar Behrooz A, Syahir A and Ahmad S:
CD133: Beyond a cancer stem cell biomarker. J Drug Target.
27:257–269. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Li Y, Chu J, Feng W, Yang M, Zhang Y,
Zhang Y, Qin Y, Xu J, Li J, Vasilatos SN, et al: EPHA5 mediates
trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive breast cancers through
regulating cancer stem cell-like properties. FASEB J. 33:4851–4865.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
He X, Semenov M, Tamai K and Zeng X: LDL
receptor-related proteins 5 and 6 in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling:
Arrows point the way. Development. 131:1663–1677. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wei B, Cao J, Tian JH, Yu CY, Huang Q, Yu
JJ, Ma R, Wang J, Xu F and Wang LB: Mortalin maintains breast
cancer stem cells stemness via activation of Wnt/GSK3β/β-catenin
signaling pathway. Am J Cancer Res. 11:2696–2716. 2021.
|
|
59
|
Wu Y, Ginther C, Kim J, Mosher N, Chung S,
Slamon D and Vadgama JV: Expression of Wnt3 activates Wnt/β-catenin
pathway and promotes EMT-like phenotype in trastuzumab-resistant
HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res.
10:1597–1606. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Choi HJ, Jin S, Cho H, Won HY, An HW,
Jeong GY, Park YU, Kim HY, Park MK, Son T, et al: CDK12 drives
breast tumor initiation and trastuzumab resistance via WNT and
IRS1-ErbB-PI3K signaling. EMBO Rep. 20:e480582019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
El Abbass KA, Abdellateif MS, Gawish AM,
Zekri AN, Malash I and Bahnassy AA: The role of breast cancer stem
cells and some related molecular biomarkers in metastatic and
nonmetastatic breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 20:e373–e384.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Shen Q and Reedijk M: Notch signaling and
the breast cancer microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1287:183–200.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Baker A, Wyatt D, Bocchetta M, Li J,
Filipovic A, Green A, Peiffer DS, Fuqua S, Miele L, Albain KS and
Osipo C: Notch-1-PTEN-ERK1/2 signaling axis promotes HER2+ breast
cancer cell proliferation and stem cell survival. Oncogene.
37:4489–4504. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Pandya K, Wyatt D, Gallagher B, Shah D,
Baker A, Bloodworth J, Zlobin A, Pannuti A, Green A, Ellis IO, et
al: PKCα attenuates Jagged-1-mediated notch signaling in
ErbB-2-positive breast cancer to reverse trastuzumab resistance.
Clin Cancer Res. 22:175–186. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
He M, Fu Y, Yan Y, Xiao Q, Wu H, Yao W,
Zhao H, Zhao L, Jiang Q, Yu Z, et al: The Hedgehog signalling
pathway mediates drug response of MCF-7 mammosphere cells in breast
cancer patients. Clin Sci (Lond). 129:809–822. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Liu S, Duan X, Xu L, Ye J, Cheng Y, Liu Q,
Zhang H, Zhang S, Zhu S, Li T and Liu Y: Nuclear Gli1 expression is
associated with pathological complete response and event-free
survival in HER2-positive breast cancer treated with
trastuzumab-based neoadjuvant therapy. Tumour Biol. 37:4873–4881.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Gupta P, Gupta N, Fofaria NM, Ranjan A and
Srivastava SK: HER2-mediated GLI2 stabilization promotes anoikis
resistance and metastasis of breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
442:68–81. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Doheny D, Sirkisoon S, Carpenter RL,
Aguayo NR, Regua AT, Anguelov M, Manore SG, Arrigo A, Jalboush SA,
Wong GL, et al: Combined inhibition of JAK2-STAT3 and
SMO-GLI1/tGLI1 pathways suppresses breast cancer stem cells, tumor
growth, and metastasis. Oncogene. 39:6589–6605. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Guo Z, Guo A and Zhou C: Breast cancer
stem cell-derived ANXA6-containing exosomes sustain paclitaxel
resistance and cancer aggressiveness in breast cancer. Front Cell
Dev Biol. 9:7187212021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Yousefnia S, Seyed Forootan F, Seyed
Forootan S, Nasr Esfahani MH, Gure AO and Ghaedi K: Mechanistic
pathways of malignancy in breast cancer stem cells. Front Oncol.
10:4522020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zhao Q, Liu Y, Wang T, Yang Y, Ni H, Liu
H, Guo Q, Xi T and Zheng L: MiR-375 inhibits the stemness of breast
cancer cells by blocking the JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Eur J Pharmacol.
884:1733592020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Hu Y, Guo R, Wei J, Zhou Y, Ji W, Liu J,
Zhi X and Zhang J: Effects of PI3K inhibitor NVP-BKM120 on
overcoming drug resistance and eliminating cancer stem cells in
human breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 6:e20202015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Yang L, Shi P, Zhao G, Xu J, Peng W, Zhang
J, Zhang G, Wang X, Dong Z, Chen F and Cui H: Targeting cancer stem
cell pathways for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
5:82020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Xing F, Kobayashi A, Okuda H, Watabe M,
Pai SK, Pandey PR, Hirota S, Wilber A, Mo YY, Moore BE, et al:
Reactive astrocytes promote the metastatic growth of breast cancer
stem-like cells by activating Notch signalling in brain. EMBO Mol
Med. 5:384–396. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhou N, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Lei Z, Hu R, Li
H, Mao Y, Wang X, Irwin DM, Niu G and Tan H: Exposure of
tumor-associated macrophages to apoptotic MCF-7 cells promotes
breast cancer growth and metastasis. Int J Mol Sci. 16:11966–11982.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Ko YS, Rugira T, Jin H, Joo YN and Kim HJ:
Radiotherapy-resistant breast cancer cells enhance tumor
progression by enhancing premetastatic niche formation through the
HIF-1α-LOX. Axis Int J Mol Sci. 21:80272020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Mao Y, Zhang Y, Qu Q, Zhao M, Lou Y, Liu
J, huang O, Chen X, Wu J and Shen K: Cancer-associated fibroblasts
induce trastuzumab resistance in HER2 positive breast cancer cells.
Mol Biosyst. 11:1029–1040. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Brown Y, Hua S and Tanwar PS:
Extracellular matrix-mediated regulation of cancer stem cells and
chemoresistance. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 109:90–104. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Liu J, Shen JX, Wu HT, Li XL, Wen XF, Du
CW and Zhang GJ: Collagen 1A1 (COL1A1) promotes metastasis of
breast cancer and is a potential therapeutic target. Discov Med.
25:211–223. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Hanker AB, Estrada MV, Bianchini G, Moore
PD, Zhao J, Cheng F, Koch JP, Gianni L, Tyson DR, Sánchez V, et al:
Extracellular matrix/integrin signaling promotes resistance to
combined inhibition of HER2 and PI3K in HER2+ Breast
Cancer. Cancer Res. 77:3280–3292. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Jokela TA and LaBarge MA: Integration of
mechanical and ECM microenvironment signals in the determination of
cancer stem cell states. Curr Stem Cell Rep. 7:39–47. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Li F, Xu J and Liu S: Cancer stem cells
and neovascularization. Cells. 10:10702021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Hori A, Shimoda M, Naoi Y, Kagara N, Tanei
T, Miyake T, Shimazu K, Kim SJ and Noguchi S: Vasculogenic mimicry
is associated with trastuzumab resistance of HER2-positive breast
cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 21:882019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Bussolati B, Grange C, Sapino A and
Camussi G: Endothelial cell differentiation of human breast tumour
stem/progenitor cells. J Cell Mol Med. 13:309–319. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
McClements L, Yakkundi A, Papaspyropoulos
A, Harrison H, Ablett MP, Jithesh PV, McKeen HD, Bennett R, Donley
C, Kissenpfennig A, et al: Targeting treatment-resistant breast
cancer stem cells with FKBPL and its peptide derivative, AD-01, via
the CD44 pathway. Clin Cancer Res. 19:3881–3893. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Li M, Pan M, You C, Zhao F, Wu D, Guo M,
Xu H, Shi F, Zheng D and Dou J: MiR-7 reduces the BCSC subset by
inhibiting XIST to modulate the miR-92b/Slug/ESA axis and inhibit
tumor growth. Breast Cancer Res. 22:262020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Sandiford OA, Donnelly RJ, El-Far MH,
Burgmeyer LM, Sinha G, Pamarthi SH, Sherman LS, Ferrer AI, DeVore
DE, Patel SA, et al: Mesenchymal stem cell-secreted extracellular
vesicles instruct stepwise dedifferentiation of breast cancer cells
into dormancy at the bone marrow perivascular region. Cancer Res.
81:1567–1582. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Kim SY, Kang JW, Song X, Kim BK, Yoo YD,
Kwon YT and Lee YJ: Role of the IL-6-JAK1-STAT3-Oct-4 pathway in
the conversion of non-stem cancer cells into cancer stem-like
cells. Cell Signal. 25:961–969. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Rodríguez CE, Berardi DE, Abrigo M, Todaro
LB, Bal de Kier Joffé ED and Fiszman GL: Breast cancer stem cells
are involved in Trastuzumab resistance through the HER2 modulation
in 3D culture. J Cell Biochem. 119:1381–1391. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Maroufi NF, Amiri M, Dizaji BF, Vahedian
V, Akbarzadeh M, Roshanravan N, Haiaty S, Nouri M and Rashidi MR:
Inhibitory effect of melatonin on hypoxia-induced vasculogenic
mimicry via suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in
breast cancer stem cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 881:1732822020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Lee KM, Giltnane JM, Balko JM, Schwarz LJ,
Guerrero-Zotano AL, Hutchinson KE, Nixon MJ, Estrada MV, Sánchez V,
Sanders ME, et al: MYC and MCL1 cooperatively promote
chemotherapy-resistant breast cancer stem cells via regulation of
mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Cell Metab. 26:633–647.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Park SJ, Kim JG, Kim ND, Yang K, Shim JW
and Heo K: Estradiol, TGF-β1 and hypoxia promote breast cancer
stemness and EMT-mediated breast cancer migration. Oncol Lett.
11:1895–1902. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Takegawa N, Nonagase Y, Yonesaka K, Sakai
K, Maenishi O, Ogitani Y, Tamura T, Nishio K, Nakagawa K and
Tsurutani J: DS-8201a, a new HER2-targeting antibody-drug conjugate
incorporating a novel DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor, overcomes
HER2-positive gastric cancer T-DM1 resistance. Int J Cancer.
141:1682–1689. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Chen K, Huang YH and Chen JL:
Understanding and targeting cancer stem cells: Therapeutic
implications and challenges. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 34:732–740. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Zhang YS, Yang C, Han L, Liu L and Liu YJ:
Expression of BCRP/ABCG2 Protein in invasive breast cancer and
response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Oncol Res Treat. 45:94–101.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Němcová-Fürstová V, Kopperová D,
Balušíková K, Ehrlichová M, Brynychová V, Václavíková R, Daniel P,
Souček P and Kovář J: Characterization of acquired paclitaxel
resistance of breast cancer cells and involvement of ABC
transporters. Toxicol Appl Pharm. 310:215–228. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Shi RZ, He YF, Wen J, Niu YN, Gao Y, Liu
LH, Zhang XP, Wang Y, Zhang XL, Zhang HF, et al: Epithelial cell
adhesion molecule promotes breast cancer resistance
protein-mediated multidrug resistance in breast cancer by inducing
partial epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell Biol Int.
45:1644–1653. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Ye X, Bai W, Zhu H, Zhang X, Chen Y, Wang
L, Yang A, Zhao J and Jia L: MiR-221 promotes
trastuzumab-resistance and metastasis in HER2-positive breast
cancers by targeting PTEN. BMB Rep. 47:268–273. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
99
|
Li X, Li Y, Yu X and Jin F: Identification
and validation of stemness-related lncRNA prognostic signature for
breast cancer. J Transl Med. 18:3312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Müller V, Oliveira-Ferrer L, Steinbach B,
Pantel K and Schwarzenbach H: Interplay of lncRNA H19/miR-675 and
lncRNA NEAT1/miR-204 in breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 13:1137–1149.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Zheng A, Song X, Zhang L, Zhao L, Mao X,
Wei M and Jin F: Long non-coding RNA LUCAT1/miR-5582-3p/TCF7L2 axis
regulates breast cancer stemness via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 38:3052019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Xu S, Kong D, Chen Q, Ping Y and Pang D:
Oncogenic long noncoding RNA landscape in breast cancer. Mol
Cancer. 16:1292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Pickard MR and Williams GT: Regulation of
apoptosis by long non-coding RNA GAS5 in breast cancer cells:
Implications for chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
145:359–370. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Ye XM, Zhu HY, Bai WD, Wang T, Wang L,
Chen Y, Yang AG and Jia LT: Epigenetic silencing of miR-375 induces
trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer by targeting
IGF1R. BMC Cancer. 14:1342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Liu S, Sun Y, Hou Y, Yang L, Wan X, Qin Y,
Liu Y, Wang R, Zhu P, Teng Y and Liuet M: A novel lncRNA
ROPM-mediated lipid metabolism governs breast cancer stem cell
properties. J Hematol Oncol. 14:1782021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Peng F, Wang JH, Fan WJ, Meng YT, Li MM,
Li TT, Cui B, Wang HF, Zhao Y, An F, et al: Glycolysis gatekeeper
PDK1 repro-grams breast cancer stem cells under hypoxia. Oncogene.
37:1062–1074. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Fox DB, Garcia N, McKinney BJ, Lupo R,
Noteware LC, Newcomb R, Liu J, Locasale JW, Hirschey MD and Alvarez
JV: NRF2 activation promotes the recurrence of dormant tumour cells
through regulation of redox and nucleotide metabolism. Nat Metab.
2:318–334. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Najafi M, Mortezaee K and Majidpoor J:
Cancer stem cell (CSC) resistance drivers. Life Sci.
234:1167812019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Abad E, Graifer D and Lyakhovich A: DNA
damage response and resistance of cancer stem cells. Cancer Lett.
474:106–117. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Oh KS, Nam AR, Bang JH, Seo HR, Kim JM,
Yoon J, Kim TY and Oh DY: A synthetic lethal strategy using PARP
and ATM inhibition for overcoming trastuzumab resistance in
HER2-positive cancers. Oncogene. 41:3939–3952. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Wengner AM, Scholz A and Haendler B:
Targeting DNA damage response in prostate and breast cancer. Int J
Mol Sci. 21:82732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Torres VI, Godoy JA and Inestrosa NC:
Modulating Wnt signaling at the root: Porcupine and Wnt acylation.
Pharmacol Ther. 198:34–45. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Yang Y, Li X, Wang T, Guo Q, Xi T and
Zheng L: Emerging agents that target signaling pathways in cancer
stem cells. J Hematol Oncol. 13:602020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Jang GB, Hong IS, Kim RJ, Lee SY, Park SJ,
Lee ES, Park JH, Yun CH, Chung JU, Lee KJ, et al: Wnt/β-Catenin
small-molecule inhibitor CWP232228 preferentially inhibits the
growth of breast cancer stem-like cells. Cancer Res. 75:1691–1702.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Gurney A, Axelrod F, Bond CJ, Cain J,
Chartier C, Donigan L, Fischer M, Chaudhari A, Ji M, Kapoun AM, et
al: Wnt pathway inhibition via the targeting of Frizzled receptors
results in decreased growth and tumorigenicity of human tumors.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:11717–11722. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Mu J, Hui T, Shao B, Li L, Du Z, Lu L, Ye
L, Li S, Li Q, Xiao Q, et al: Dickkopf-related protein 2 induces
G0/G1 arrest and apoptosis through suppressing Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and is frequently methylated in breast cancer.
Oncotarget. 8:39443–39459. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
An SM, Ding Q, Zhang J, Xie J and Li L:
Targeting stem cell signaling pathways for drug discovery: Advances
in the Notch and Wnt pathways. Sci China Life Sci. 57:575–580.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Schott AF, Landis MD, Dontu G, Griffith
KA, Layman RM, Krop I, Paskett LA, Wong H, Dobrolecki LE, Lewis MT,
et al: Preclinical and clinical studies of gamma secretase
inhibitors with docetaxel on human breast tumors. Clin Cancer Res.
19:1512–1524. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Takebe N, Nguyen D and Yang SX: Targeting
notch signaling pathway in cancer: Clinical development advances
and challenges. Pharmacol Ther. 141:140–149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
120
|
Yen WC, Fischer MM, Axelrod F, Bond C,
Cain J, Cancilla B, Henner WR, Meisner R, Sato A, Shah J, et al:
Targeting Notch signaling with a Notch2/Notch3 antagonist
(tarextumab) inhibits tumor growth and decreases tumor-initiating
cell frequency. Clin Cancer Res. 21:2084–2095. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Huang J, Hu W, Hu L, Previs RA, Dalton HJ,
Yang XY, Sun Y, McGuire M, Rupaimoole R, Nagaraja AS, et al: Dll4
inhibition plus aflibercept markedly reduces ovarian tumor growth.
Mol Cancer Ther. 15:1344–1352. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
McKeage MJ, Kotasek D, Markman B, Hidalgo
M, Millward MJ, Jameson MB, Harris DL, Stagg RJ, Kapoun AM, Xu L,
et al: Phase IB Trial of the Anti-cancer stem cell DLL4-binding
agent demcizumab with pemetrexed and carboplatin as First-line
treatment of metastatic non-squamous NSCLC. Target Oncol. 13:89–98.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Silkenstedt E, Arenas F, Colom-Sanmartí B,
Xargay-Torrent S, Higashi M, Giró A, Rodriguez V, Fuentes P,
Aulitzky WE, van der Kuip H, et al: Notch1 signaling in
NOTCH1-mutated mantle cell lymphoma depends on delta-like ligand 4
and is a potential target for specific antibody therapy. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 38:4462019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Hui M, Cazet A, Nair R, Watkins DN,
O'Toole SA and Swarbrick A: The Hedgehog signalling pathway in
breast development, carcinogenesis and cancer therapy. Breast
Cancer Res. 15:2032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Clara JA, Monge C, Yang Y and Takebe N:
Targeting signalling pathways and the immune microenvironment of
cancer stem cells-a clinical update. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
17:204–232. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Bhateja P, Cherian M, Majumder S and
Ramaswamy B: The hedgehog signaling pathway: A viable target in
breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). 11:11262019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Liu C, Qi M, Li L, Yuan Y, Wu X and Fu J:
Natural cordycepin induces apoptosis and suppresses metastasis in
breast cancer cells by inhibiting the Hedgehog pathway. Food Funct.
11:2107–2116. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Takebe N, Harris PJ, Warren RQ and Ivy SP:
Targeting cancer stem cells by inhibiting Wnt, Notch, and Hedgehog
pathways. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 8:97–106. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Sorrentino G, Ruggeri N, Specchia V,
Cordenonsi M, Mano M, Dupont S, Manfrin A, Ingallina E, Sommaggio
R, Piazza S, et al: Metabolic control of YAP and TAZ by the
mevalonate pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 16:357–366. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Haque S and Morris JC: Transforming growth
factor-β: A therapeutic target for cancer. Hum Vaccin Immunother.
13:1741–1750. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Wang T, Fahrmann JF, Lee H, Li YJ,
Tripathi SC, Yue C, Zhang C, Lifshitz V, Song J, Yuan Y, et al:
JAK/STAT3-regulated fatty acid β-oxidation is critical for breast
cancer stem cell self-renewal and chemoresistance. Cell Metab.
27:136–150. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Patel JS, Hu M, Sinha G, Walker ND,
Sherman LS, Gallagher A and Rameshwar P: Non-coding RNA as
mediators in microenvironment-breast cancer cell communication.
Cancer Lett. 380:289–295. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Liu Y, Zhang P, Wu Q, Fang H, Wang Y, Xiao
Y, Cong M, Wang T, He Y, Ma C, et al: Long non-coding RNA NR2F1-AS1
induces breast cancer lung metastatic dormancy by regulating NR2F1
and ΔNp63. Nat Commun. 12:52322021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
El Touny LH, Vieira A, Mendoza A, Khanna
C, Hoenerhoff MJ and Green JE: Combined SFK/MEK inhibition prevents
metastatic outgrowth of dormant tumor cells. J Clin Invest.
124:156–168. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
135
|
Puig I, Tenbaum SP, Chicote I, Arqués O,
Martínez-Quintanilla J, Cuesta-Borrás E, Ramírez L, Gonzalo P, Soto
A, Aguilar S, et al: TET2 controls chemoresistant slow-cycling
cancer cell survival and tumor recurrence. J Clin Invest.
128:3887–3905. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Ma HP, Chang HL, Bamodu OA, Yadav VK,
Huang TY, Wu A, Yeh CT, Tsai SH and Lee WH: Collagen 1A1 (COL1A1)
is a reliable biomarker and putative therapeutic target for
hepatocellular carcinogenesis and metastasis. Cancers (Basel).
11:7862019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Chen Q, Xu L, Chen J, Yang Z, Liang C,
Yang Y and Liu Z: Tumor vasculature normalization by orally fed
erlotinib to modulate the tumor microenvironment for enhanced
cancer nanomedicine and immunotherapy. Biomaterials. 148:69–80.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Kim JH, Verwilst P, Won M, Lee J, Sessler
JL, Han J and Kim JS: A small molecule strategy for targeting
cancer stem cells in hypoxic microenvironments and preventing
tumorigenesis. J Am Chem Soc. 143:14115–14124. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Fico F and Santamaria-Martínez A: TGFBI
modulates tumour hypoxia and promotes breast cancer metastasis. Mol
Oncol. 14:3198–3210. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Jiang B, Zhu H, Tang L, Gao T, Zhou Y,
Gong F, Tan Y, Xie L, Wu X and Li Y: Apatinib inhibits stem
properties and malignant biological behaviors of breast cancer stem
cells by blocking wnt/β-catenin signal pathway through
down-regulating LncRNA ROR. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
22:1723–1734. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Wu X, Zhang X, Sun L, Zhang H, Li L, Wang
X, Li W, Su P, Hu J, Gao P and Zhou G: Progesterone negatively
regulates BCRP in progesterone receptor-positive human breast
cancer cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 32:344–354. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Vannini I, Zoli W, Fabbri F, Ulivi P,
Tesei A, Carloni S, Brigliadori G and Amadori D: Role of efflux
Pump activity in Lapatinib/Caelyx combination in breast cancer cell
lines. Anticancer Drugs. 20:918–925. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Karbownik A, Sobańska K, Płotek W,
Grabowski T, Klupczynska A, Plewa S, Grześkowiak E and Szałek E:
The influence of the coadministration of the p-glycoprotein
modulator elacridar on the pharmacokinetics of lapatinib and its
distribution in the brain and cerebrospinal fluid. Invest New
Drugs. 38:574–583. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
144
|
Yi J, Chen S, Yi P, Luo J, Fang M, Du Y,
Zou L and Fan P: Pyrotinib sensitizes 5-fluorouracil-resistant HER2
breast cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil. Oncol Res. 28:519–531. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Cufi S, Corominas-Faja B, Vazquez-Martin
A, Oliveras-Ferraros C, Dorca J, Bosch-Barrera J, Martin-Castillo B
and Menendez JA: Metformin-induced preferential killing of breast
cancer initiating CD44+CD24-/low cells is sufficient to overcome
primary resistance to trastuzumab in HER2+ human breast cancer
xenografts. Oncotarget. 3:395–398. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Song CW, Lee H, Dings RP, Williams B,
Powers J, Santos TD, Choi BH and Park HJ: Metformin kills and
radiosensitizes cancer cells and preferentially kills cancer stem
cells. Sci Rep. 2:3622012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Singh JK, Simões BM, Clarke RB and Bundred
NJ: Targeting IL-8 signalling to inhibit breast cancer stem cell
activity. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 17:1235–1241. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Singh JK, Farnie G, Bundred NJ, Simões BM,
Shergill A, Landberg G, Howell SJ and Clarke RB: Targeting CXCR1/2
significantly reduces breast cancer stem cell activity and
increases the efficacy of inhibiting HER2 via HER2-dependent and
-independent mechanisms. Clin Cancer Res. 19:643–656. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Kim HJ, Min A, Im SA, Jang H, Lee KH, Lau
A, Lee M, Kim S, Yang Y, Kim J, et al: Anti-tumor activity of the
ATR inhibitor AZD6738 in HER2 positive breast cancer cells. Int J
Cancer. 140:109–119. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|