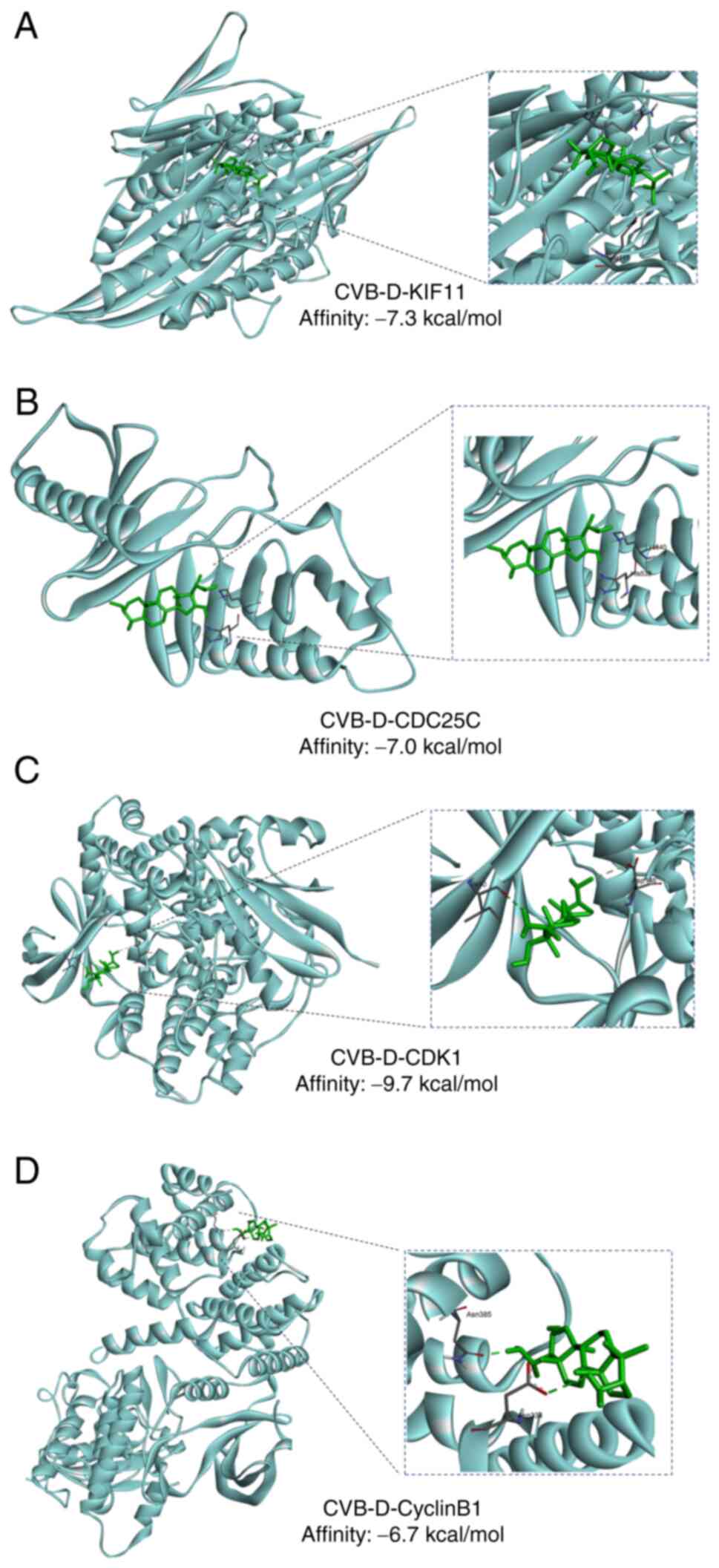
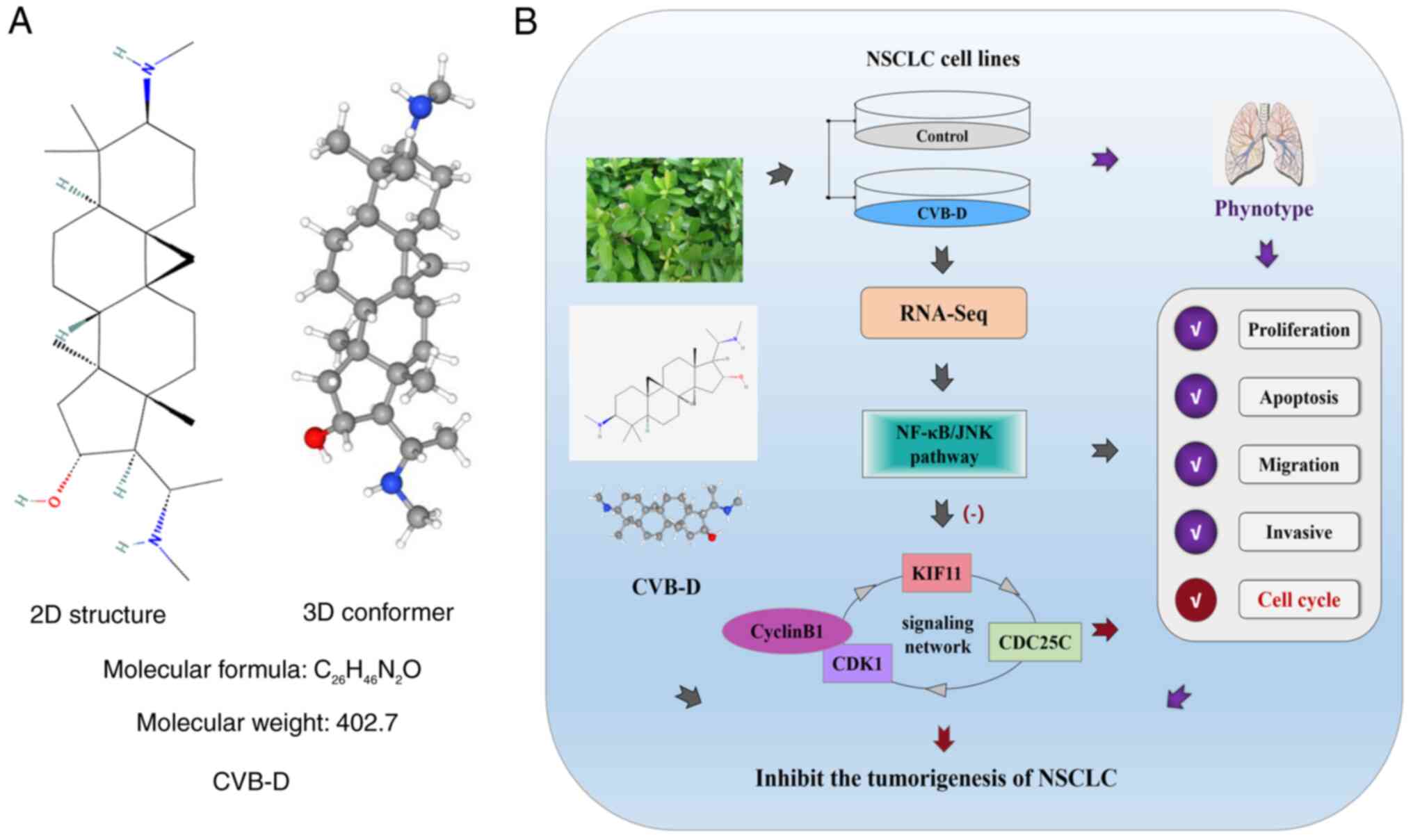
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Inamura K: Lung Cancer: Understanding its
molecular pathology and the 2015 WHO Classification. Front Oncol.
7:1932017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Burke AP, Marx A
and Nicholson AG: Introduction to the 2015 World Health
Organization Classification of tumors of the lung, pleura, thymus,
and heart. J Thorac Oncol. 10:1240–1242. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu WJ, Du Y, Wen R, Yang M and Xu J: Drug
resistance to targeted therapeutic strategies in Non-small cell
lung cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 206:1074382020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Garcia-Saez I and Skoufias DA: Eg5
targeting agents: From new anti-mitotic based inhibitor discovery
to cancer therapy and resistance. Biochem Pharmacol.
184:1143642021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wei D, Rui B, Qingquan F, Chen C, Ping HY,
Xiaoling S, Hao W and Jun G: KIF11 promotes cell proliferation via
ERBB2/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in gallbladder cancer. Int J Biol
Sci. 17:514–526. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Neska-Dlugosz I, Buchholz K, Durslewicz J,
Gagat M, Grzanka D, Tojek K and Klimaszewska-Wisniewska A:
Prognostic impact and functional annotations of KIF11 and KIF14
expression in patients with colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
22:97322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li TF, Zeng HJ, Shan Z, Ye RY, Cheang TY,
Zhang YJ, Lu SH, Zhang Q, Shao N and Lin Y: Overexpression of
kinesin super-family members as prognostic biomarkers of breast
cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 20:1232020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Schneider MA, Christopoulos P, Muley T,
Warth A, Klingmueller U, Thomas M, Herth FJ, Dienemann H, Mueller
NS, Theis F and Meister M: AURKA, DLGAP5, TPX2, KIF11 and CKAP5:
Five specific mitosis-associated genes correlate with poor
prognosis for non-small cell lung cancer patients. Int J Oncol.
50:365–372. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fu F, Zhang Y, Gao Z, Zhao Y, Wen Z, Han
H, Li Y and Chen H: Development and validation of a five-gene model
to predict post-operative brain metastasis in operable lung
adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer. 147:584–592. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li Z, Yu B, Qi F and Li F: KIF11 Serves as
an independent prognostic factor and therapeutic target for
patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol. 11:6702182021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu X, Liu X, Li J and Ren F:
Identification and integrated analysis of key biomarkers for
diagnosis and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Med Sci
Monit. 25:9280–9289. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Z, Ma L, Su M, Zhou Y, Mao K, Li C,
Peng G, Zhou C, Shen B and Dou J: Baicalin induces cellular
senescence in human colon cancer cells via upregulation of DEPP and
the activation of Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling. Cell Death Dis.
9:2172018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pricci M, Girardi B, Giorgio F, Losurdo G,
Ierardi E and Di Leo A: Curcumin and colorectal cancer: From basic
to clinical evidences. Int J Mol Sci. 21:23642020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rauf A, Imran M, Butt MS, Nadeem M, Peters
DG and Mubarak MS: Resveratrol as an anti-cancer agent: A review.
Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 58:1428–1447. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Erin N, Grahovac J, Brozovic A and Efferth
T: Tumor microenvironment and epithelial mesenchymal transition as
targets to overcome tumor multidrug resistance. Drug Resist Updat.
53:1007152020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jiang Z, Fu L, Xu Y, Hu X, Yang H, Zhang
Y, Luo H, Gan S, Tao L, Liang G and Shen X: Cyclovirobuxine D
protects against diabetic cardiomyopathy by activating
Nrf2-mediated antioxidant responses. Sci Rep. 10:64272020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou L, Tang H, Wang F, Ou S, Wu T, Fang
Y, Xu J and Guo K: Cyclovirobuxine D inhibits cell proliferation
and migration and induces apoptosis in human glioblastoma
multiforme and lowgrade glioma. Oncol Rep. 43:807–816.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang J, Chen Y, Lin J, Jia R, An T, Dong
T, Zhang Y and Yang X: Cyclovirobuxine D exerts anticancer effects
by suppressing the EGFR-FAK-AKT/ERK1/2-slug signaling pathway in
human hepatocellular carcinoma. DNA Cell Biol. 39:355–367. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jiang F, Chen Y, Ren S, Li Z, Sun K, Xing
Y, Zhu Y and Piao D: Cyclovirobuxine D inhibits colorectal cancer
tumorigenesis via the CTHRC1AKT/ERKSnail signaling pathway. Int J
Oncol. 57:183–196. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zeng C, Zou T, Qu J, Chen X, Zhang S and
Lin Z: Cyclovirobuxine D Induced-mitophagy through the
p65/BNIP3/LC3 axis potentiates its apoptosis-inducing effects in
lung cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 22:58202021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Creamer-Hente MA, Lao FK, Dragos ZP and
Waterman LL: Sex- and strain-related differences in the stress
response of mice to CO2 euthanasia. J Am Assoc Lab Anim
Sci. 57:513–519. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xie B, Wang S, Jiang N and Li JJ: Cyclin
B1/CDK1-regulated mitochondrial bioenergetics in cell cycle
progression and tumor resistance. Cancer Lett. 443:56–66. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Cardano M, Tribioli C and Prosperi E:
Targeting proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) as an effective
strategy to inhibit tumor cell proliferation. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 20:240–252. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Brabletz S, Schuhwerk H, Brabletz T and
Stemmler MP: Dynamic EMT: A multi-tool for tumor progression. EMBO
J. 40:e1086472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen Y, Liu P, Sun P, Jiang J, Zhu Y, Dong
T, Cui Y, Tian Y, An T, Zhang J, et al: Oncogenic MSH6-CXCR4-TGFB1
feedback loop: A novel therapeutic target of photothermal therapy
in glioblastoma multiforme. Theranostics. 9:1453–1473. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pinzi L and Rastelli G: Molecular docking:
Shifting paradigms in drug discovery. Int J Mol Sci. 20:43312019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Socinski MA, Obasaju C, Gandara D, Hirsch
FR, Bonomi P, Bunn P, Kim ES, Langer CJ, Natale RB, Novello S, et
al: Clinicopathologic features of advanced squamous NSCLC. J Thorac
Oncol. 11:1411–1422. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Duma N, Santana-Davila R and Molina JR:
Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, screening, diagnosis, and
treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 94:1623–1640. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Herbst RS, Morgensztern D and Boshoff C:
The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature.
553:446–454. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pastushenko I and Blanpain C: EMT
Transition states during tumor progression and metastasis. Trends
Cell Biol. 29:212–226. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Majidpoor J and Mortezaee K: Steps in
metastasis: An updated review. Med Oncol. 38:32021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gavet O and Pines J: Progressive
activation of CyclinB1-Cdk1 coordinates entry to mitosis. Dev Cell.
18:533–543. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hong M, Tao S, Zhang L, Diao LT, Huang X,
Huang S, Xie SJ, Xiao ZD and Zhang H: RNA sequencing: New
technologies and applications in cancer research. J Hematol Oncol.
13:1662020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Paczkowska M, Barenboim J, Sintupisut N,
Fox NS, Zhu H, Abd-Rabbo D, Mee MW, Boutros PC, Drivers P; PCAWG
Drivers and Functional Interpretation Working Group; et al:
Integrative pathway enrichment analysis of multivariate omics data.
Nat Commun. 11:7352020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Venere M, Horbinski C, Crish JF, Jin X,
Vasanji A, Major J, Burrows AC, Chang C, Prokop J, Wu Q, et al: The
mitotic kinesin KIF11 is a driver of invasion, proliferation, and
self-renewal in glioblastoma. Sci Transl Med. 7:304ra1432015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hu ZD, Jiang Y, Sun HM, Wang JW, Zhai LL,
Yin ZQ and Yan J: KIF11 promotes proliferation of hepatocellular
carcinoma among patients with liver cancers. Biomed Res Int.
2021:26767452021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu J, Tian Y, Yi L, Gao Z, Lou M and Yuan
K: High KIF11 expression is associated with poor outcome of NSCLC.
Tumori. 108:40–46. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yang Y, Zhang S and Guo L:
Characterization of cell cycle-related competing endogenous RNAs
using robust rank aggregation as prognostic biomarker in lung
adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol. 12:8073672022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li S, Xuan Y, Gao B, Sun X, Miao S, Lu T,
Wang Y and Jiao W: Identification of an eight-gene prognostic
signature for lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Manag Res. 10:3383–3392.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang L, Chen S, Luo Y, Yuan L, Peng T,
Qian K, Liu X, Xiao Y and Wang X: Identification of several cell
cycle relevant genes highly correlated with the progression and
prognosis of human bladder urothelial tumor. J Cell Physiol.
234:13439–13451. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Meng F, Zhang L, Ren Y and Ma Q:
Transcriptome analysis reveals key signature genes involved in the
oncogenesis of lung cancer. Cancer Biomark. 29:475–482. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gong K, Zhou H, Liu H, Xie T, Luo Y, Guo
H, Chen J, Tan Z, Yang Y and Xie L: Identification and integrate
analysis of key biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of non-small
cell lung cancer based on bioinformatics analysis. Technol Cancer
Res Treat. 20:153303382110602022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gao L, Xia S, Zhang K, Lin C, He X and
Zhang Y: Gene expression profile of THZ1-treated nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cell lines indicates its involvement in the inhibition of
the cell cycle. Transl Cancer Res. 10:445–460. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Guido BC, Ramos LM, Nolasco DO, Nobrega
CC, Andrade BY, Pic-Taylor A, Neto BA and Correa JR: Impact of
kinesin Eg5 inhibition by 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-one
derivatives on various breast cancer cell features. BMC Cancer.
15:2832015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Jiang M, Zhuang H, Xia R, Gan L, Wu Y, Ma
J, Sun Y and Zhuang Z: KIF11 is required for proliferation and
self-renewal of docetaxel resistant triple negative breast cancer
cells. Oncotarget. 8:92106–92118. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Thankamony AP, Murali R, Karthikeyan N,
Varghese BA, Teo WS, McFarland A, Roden DL, Holliday H, Konrad CV,
Cazet A, et al: Targeting the Id1-Kif11 Axis in triple-negative
breast cancer using combination therapy. Biomolecules. 10:12952020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kato T, Lee D, Wu L, Patel P, Young AJ,
Wada H, Hu HP, Ujiie H, Kaji M, Kano S, et al: Kinesin family
members KIF11 and KIF23 as potential therapeutic targets in
malignant pleural mesothelioma. Int J Oncol. 49:448–456. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhou Y, Yang L, Xiong L, Wang K, Hou X, Li
Q, Kong F, Liu X and He J: KIF11 is upregulated in colorectal
cancer and silencing of it impairs tumor growth and sensitizes
colorectal cancer cells to oxaliplatin via p53/GSK3beta signaling.
J Cancer. 12:3741–3753. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
51
|
Liu K, Zheng M, Lu R, Du J, Zhao Q, Li Z,
Li Y and Zhang S: The role of CDC25C in cell cycle regulation and
clinical cancer therapy: A systematic review. Cancer Cell Int.
20:2132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Takizawa CG and Morgan DO: Control of
mitosis by changes in the subcellular location of cyclin-B1-Cdk1
and Cdc25C. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 12:658–665. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang JN, Zhang ZR, Che Y, Yuan ZY, Lu ZL,
Li Y, Li N, Wan J, Sun HD, Sun N, et al: Acetyl-macrocalin B, an
ent-kaurane diterpenoid, initiates apoptosis through the
ROS-p38-caspase 9-dependent pathway and induces G2/M phase arrest
via the Chk1/2-Cdc25C-Cdc2/cyclin B axis in non-small cell lung
cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 19:609–621. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wu Q, Wu W, Jacevic V, Franca TCC, Wang X
and Kuca K: Selective inhibitors for JNK signalling: A potential
targeted therapy in cancer. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 35:574–583.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Bubici C and Papa S: JNK signalling in
cancer: In need of new, smarter therapeutic targets. Br J
Pharmacol. 171:24–37. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
56
|
Abdelrahman KS, Hassan HA, Abdel-Aziz SA,
Marzouk AA, Narumi A, Konno H and Abdel-Aziz M: JNK signaling as a
target for anticancer therapy. Pharmacol Rep. 73:405–434. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Song W, Ma Y, Wang J, Brantley-Sieders D
and Chen J: JNK signaling mediates EPHA2-dependent tumor cell
proliferation, motility, and cancer stem cell-like properties in
non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 74:2444–2454. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Dou Y, Jiang X, Xie H, He J and Xiao S:
The Jun N-terminal kinases signaling pathway plays a 'seesaw' role
in ovarian carcinoma: A molecular aspect. J Ovarian Res. 12:992019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Wang J and Tai G: Role of C-Jun N-terminal
kinase in hepatocellular carcinoma development. Target Oncol.
11:723–738. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Gutierrez GJ, Tsuji T, Cross JV, Davis RJ,
Templeton DJ, Jiang W and Ronai ZA: JNK-mediated phosphorylation of
Cdc25C regulates cell cycle entry and G(2)/M DNA damage checkpoint.
J Biol Chem. 285:14217–14228. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Udden SN, Kwak YT, Godfrey V, Khan MAW,
Khan S, Loof N, Peng L, Zhu H and Zaki H: NLRP12 suppresses
hepatocellular carcinoma via downregulation of cJun N-terminal
kinase activation in the hepatocyte. Elife. 8:e403962019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Han YH, Mun JG, Jeon HD, Park J, Kee JY
and Hong SH: Gomisin A ameliorates metastatic melanoma by
inhibiting AMPK and ERK/JNK-mediated cell survival and metastatic
phenotypes. Phytomedicine. 68:1531472020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Okada M, Shibuya K, Sato A, Seino S,
Watanabe E, Suzuki S, Seino M and Kitanaka C: Specific role of JNK
in the maintenance of the tumor-initiating capacity of A549 human
non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 30:1957–1964. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Cheng J, Li M, Tzeng CM, Gou X and Chen S:
Suppression of tumorigenicity 5 ameliorates tumor characteristics
of invasive breast cancer cells via ERK/JNK Pathway. Front Oncol.
11:6215002021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Baud V and Karin M: Is NF-kappaB a good
target for cancer therapy? Hopes and pitfalls. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
8:33–40. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Hoesel B and Schmid JA: The complexity of
NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer. 12:862013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Rasmi RR, Sakthivel KM and Guruvayoorappan
C: NF-κB inhibitors in treatment and prevention of lung cancer.
Biomed Pharmacother. 130:1105692020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Sarkar FH and Li Y: NF-kappaB: A potential
target for cancer chemoprevention and therapy. Front Biosci.
13:2950–2959. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Fouani L, Kovacevic Z and Richardson DR:
Targeting oncogenic nuclear factor Kappa B Signaling with
redox-active agents for cancer treatment. Antioxid Redox Signal.
30:1096–1123. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Suhail M, Tarique M, Muhammad N, Naz H,
Hafeez A, Zughaibi TA, Kamal MA and Rehan M: A critical
transcription factor NF-κB as a cancer therapeutic target and its
inhibitors as cancer treatment options. Curr Med Chem.
28:4117–4132. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Khan H, Ullah H, Castilho P, Gomila AS,
D'Onofrio G, Filosa R, Wang F, Nabavi SM, Daglia M, Silva AS, et
al: Targeting NF-κB signaling pathway in cancer by dietary
polyphenols. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 60:2790–2800. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Rajagopal C, Lankadasari MB, Aranjani JM
and Harikumar KB: Targeting oncogenic transcription factors by
polyphenols: A novel approach for cancer therapy. Pharmacol Res.
130:273–291. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ashrafizadeh M, Najafi M, Makvandi P,
Zarrabi A, Farkhondeh T and Samarghandian S: Versatile role of
curcumin and its derivatives in lung cancer therapy. J Cell
Physiol. 235:9241–9268. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Saijo T, Ishii G, Ochiai A, Yoh K, Goto K,
Nagai K, Kato H, Nishiwaki Y and Saijo N: Eg5 expression is closely
correlated with the response of advanced non-small cell lung cancer
to antimitotic agents combined with platinum chemotherapy. Lung
Cancer. 54:217–225. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Lv P, Man S, Xie L, Ma L and Gao W:
Pathogenesis and therapeutic strategy in platinum resistance lung
cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1876:1885772021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Wang LH, Li Y, Yang SN, Wang FY, Hou Y,
Cui W, Chen K, Cao Q, Wang S, Zhang TY, et al: Gambogic acid
synergistically potentiates cisplatin-induced apoptosis in
non-small-cell lung cancer through suppressing NF-κB and MAPK/HO-1
signalling. Br J Cancer. 110:341–352. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Wang J, Tian L, Khan MN, Zhang L, Chen Q,
Zhao Y, Yan Q, Fu L and Liu J: Ginsenoside Rg3 sensitizes hypoxic
lung cancer cells to cisplatin via blocking of NF-κB mediated
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stemness. Cancer Lett.
415:73–85. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Cui H, Arnst K, Miller DD and Li W: Recent
advances in elucidating paclitaxel resistance mechanisms in
non-small cell lung cancer and strategies to overcome drug
resistance. Curr Med Chem. 27:6573–6595. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Jiang N, Dong XP, Zhang SL, You QY, Jiang
XT and Zhao XG: Triptolide reverses the Taxol resistance of lung
adenocarcinoma by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway and the
expression of NF-κB-regulated drug-resistant genes. Mol Med Rep.
13:153–159. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Li DD, Qin XC, Yang Y, Chu HX, Li RL, Ma
LX, Ding HW and Zhao QC: Daurinoline suppressed the migration and
invasion of chemo-resistant human non-small cell lung cancer cells
by reversing EMT and Notch-1 and sensitized the cells to Taxol.
Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 66:109–115. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Li Y and Zhang H: Nanoparticle-based drug
delivery systems for enhanced tumor-targeting treatment. J Biomed
Nanotechnol. 15:1–27. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|