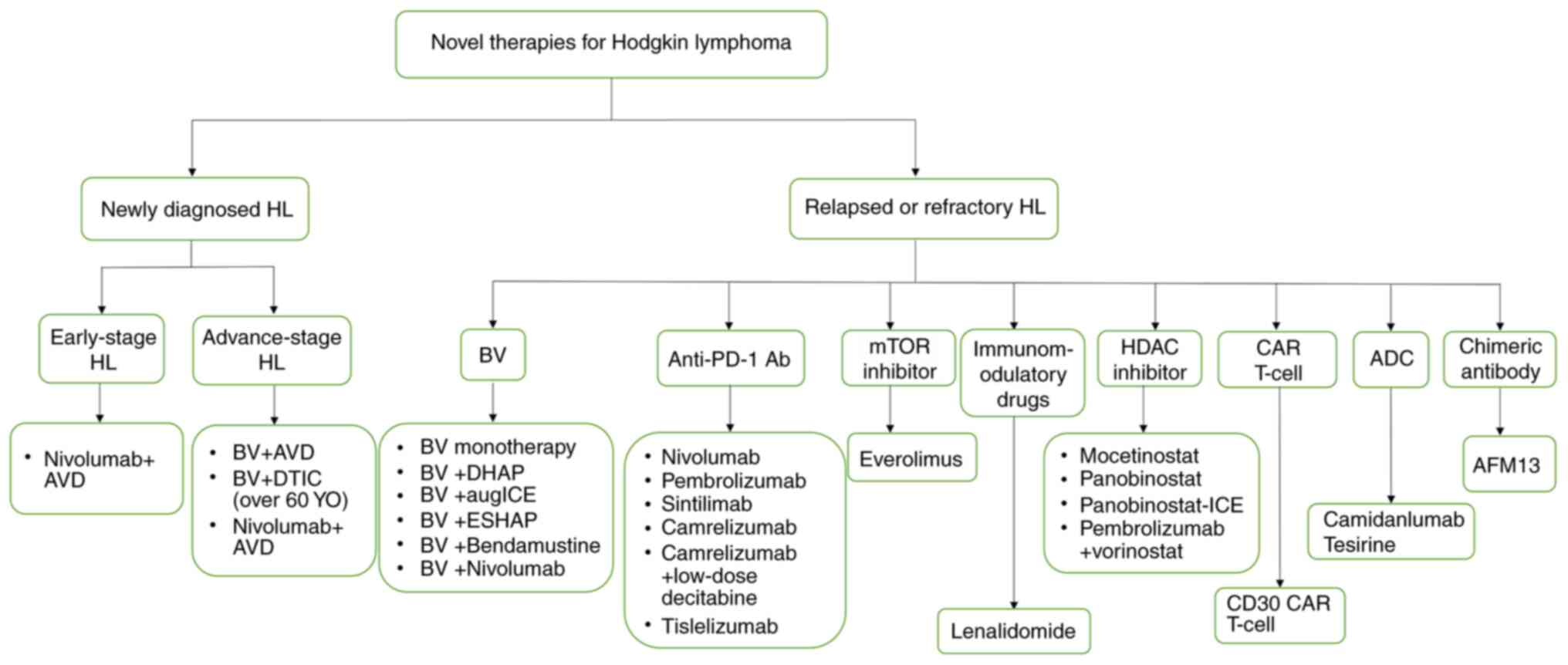
|
1
|
Hodgkin: On some morbid appearances of the
absorbent glands and spleen. Med Chir Trans. 17:68–114. 1832.
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:7–30. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Johnson P, Federico M, Kirkwood A, Fossa
A, Berkahn L, Carella A, d'Amore F, Enblad G, Franceschetto A,
Fulham M, et al: Adapted treatment guided by interim PET-CT scan in
advanced Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 374:2419–2429. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Viviani S, Zinzani PL, Rambaldi A,
Brusamolino E, Levis A, Bonfante V, Vitolo U, Pulsoni A, Liberati
AM, Specchia G, et al: ABVD versus BEACOPP for Hodgkin's lymphoma
when high-dose salvage is planned. N Engl J Med. 365:203–212. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Radford J, Illidge T, Counsell N, Hancock
B, Pettengell R, Johnson P, Wimperis J, Culligan D, Popova B, Smith
P, et al: Results of a trial of PET-directed therapy for
early-stage Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 372:1598–1607. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sureda A, Constans M, Iriondo A, Arranz R,
Caballero MD, Vidal MJ, Petit J, López A, Lahuerta JJ, Carreras E,
et al: Prognostic factors affecting long-term outcome after stem
cell transplantation in Hodgkin's lymphoma autografted after a
first relapse. Ann Oncol. 16:625–633. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Majhail NS, Weisdorf DJ, Defor TE, Miller
JS, McGlave PB, Slungaard A, Arora M, Ramsay NK, Orchard PJ,
MacMillan ML, et al: Long-term results of autologous stem cell
transplantation for primary refractory or relapsed Hodgkin's
lymphoma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 12:1065–1072. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sirohi B, Cunningham D, Powles R, Murphy
F, Arkenau T, Norman A, Oates J, Wotherspoon A and Horwich A:
Long-term outcome of autologous stem-cell transplantation in
relapsed or refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 19:1312–1319.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Smith SD, Moskowitz CH, Dean R, Pohlman B,
Sobecks R, Copelan E, Andresen S, Bolwell B, Maragulia JC, Vanak
JM, et al: Autologous stem cell transplant for early
relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: Results from two transplant
centres. Br J Haematol. 153:358–363. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shanbhag S and Ambinder RF: Hodgkin
lymphoma: A review and update on recent progress. CA Cancer J Clin.
68:116–132. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Durkop H, Latza U, Hummel M, Eitelbach F,
Seed B and Stein H: Molecular cloning and expression of a new
member of the nerve growth factor receptor family that is
characteristic for Hodgkin's disease. Cell. 68:421–427. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chiarle R, Podda A, Prolla G, Gong J,
Thorbecke GJ and Inghirami G: CD30 in normal and neoplastic cells.
Clin Immunol. 90:157–164. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Horie R and Watanabe T: CD30: Expression
and function in health and disease. Semin Immunol. 10:457–470.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schwab U, Stein H, Gerdes J, Lemke H,
Kirchner H, Schaadt M and Diehl V: Production of a monoclonal
antibody specific for Hodgkin and Sternberg-Reed cells of Hodgkin's
disease and a subset of normal lymphoid cells. Nature. 299:65–67.
1982. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hartmann F, Renner C, Jung W and
Pfreundschuh M: Anti-CD16/CD30 bispecific antibodies as possible
treatment for refractory Hodgkin's disease. Leuk Lymphoma.
31:385392. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Falini B, Bolognesi A, Flenghi L, Tazzari
PL, Broe MK, Stein H, Dürkop H, Aversa F, Corneli P, Pizzolo G, et
al: Response of refractory Hodgkin's disease to monoclonal
anti-CD30 immunotoxin. Lancet. 339:1195–116. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Schnell R, Staak O, Borchmann P, Schwartz
C, Matthey B, Hansen H, Schindler J, Ghetie V, Vitetta ES, Diehl V
and Engert A: A Phase I study with an anti-CD30 ricin A-chain
immunotoxin (Ki-4.dgA) in patients with refractory CD30+ Hodgkin's
and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 8:1779–1786.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Borchmann P, Schnell R, Fuss I, Manzke O,
Davis T, Lewis LD, Behnke D, Wickenhauser C, Schiller P, Diehl V
and Engert A: Phase 1 trial of the novel bispecific molecule
H22xKi-4 in patients with refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood.
100:3101–3107. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schnell R, Dietlein M, Staak JO, Borchmann
P, Schomaecker K, Fischer T, Eschner W, Hansen H, Morschhauser F,
Schicha H, et al: Treatment of refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma
patients with an iodine-131-labeled murine anti-CD30 monoclonal
antibody. J Clin Oncol. 23:4669–4678. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Forero-Torres A, Leonard JP, Younes A,
Rosenblatt JD, Brice P, Bartlett NL, Bosly A, Pinter-Brown L,
Kennedy D, Sievers EL and Gopal AK: A Phase II study of SGN-30
(anti-CD30 mAb) in Hodgkin lymphoma or systemic anaplastic large
cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 146:171–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Okeley NM, Miyamoto JB, Zhang X, Sanderson
RJ, Benjamin DR, Sievers EL, Senter PD and Alley SC: Intracellular
activation of SGN-35, a potent anti-CD30 antibody-drug conjugate.
Clin Cancer Res. 16:888–897. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gordon LI, Hong F, Fisher RI, Bartlett NL,
Connors JM, Gascoyne RD, Wagner H, Stiff PJ, Cheson BD,
Gospodarowicz M, et al: Randomized phase III trial of ABVD versus
Stanford V with or without radiation therapy in locally extensive
and advanced-stage Hodgkin lymphoma: An intergroup study
coordinated by the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (E2496). J
Clin Oncol. 31:684–691. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Federico M, Luminari S, Iannitto E,
Polimeno G, Marcheselli L, Montanini A, La Sala A, Merli F,
Stelitano C, Pozzi S, et al: ABVD compared with BEACOPP compared
with CEC for the initial treatment of patients with advanced
Hodgkin's lymphoma: Results from the HD2000 Gruppo Italiano per lo
Studio dei Linfomi Trial. J Clin Oncol. 27:805–811. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yagoda A, Mukherji B, Young C, Etcubanas
E, Lamonte C, Smith JR, Tan CT and Krakoff IH: Bleomycin, an
antitumor antibiotic. Clinical experience in 274 patients. Ann
Intern Med. 77:861–870. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Duggan DB, Petroni GR, Johnson JL, Glick
JH, Fisher RI, Connors JM, Canellos GP and Peterson BA: Randomized
comparison of ABVD and MOPP/ABV hybrid for the treatment of
advanced Hodgkin's disease: Report of an intergroup trial. J Clin
Oncol. 21:607–614. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hoskin PJ, Lowry L, Horwich A, Jack A,
Mead B, Hancock BW, Smith P, Qian W, Patrick P, Popova B, et al:
Randomized comparison of the stanford V regimen and ABVD in the
treatment of advanced Hodgkin's Lymphoma: United Kingdom National
Cancer Research Institute Lymphoma Group Study ISRCTN 64141244. J
Clin Oncol. 27:5390–5396. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Younes A, Connors JM, Park SI, Fanale M,
O'Meara MM, Hunder NN, Huebner D and Ansell SM: Brentuximab vedotin
combined with ABVD or AVD for patients with newly diagnosed
Hodgkin's lymphoma: A phase 1, open-label, dose-escalation study.
Lancet Oncol. 14:1348–1356. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Connors JM, Ansell SM, Fanale M, Park SI
and Younes A: Five-year follow-up of brentuximab vedotin combined
with ABVD or AVD for advanced-stage classical Hodgkin lymphoma.
Blood. 130:1375–1377. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Connors JM, Jurczak W, Straus DJ, Ansell
SM, Kim WS, Gallamini A, Younes A, Alekseev S, Illés Á, Picardi M,
et al: Brentuximab Vedotin with Chemotherapy for Stage III or IV
Hodgkin's Lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 378:331–344. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Straus DJ, Dlugosz-Danecka M, Alekseev S,
Illes A, Picardi M, Lech-Maranda E, Feldman T, Smolewski P, Savage
KJ, Bartlett NL, et al: Brentuximab vedotin with chemotherapy for
stage III/IV classical Hodgkin lymphoma: 3-year update of the
ECHELON-1 study. Blood. 135:735–742. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Straus DJ, Długosz-Danecka M, Connors JM,
Alekseev S, Illés Á, Picardi M, Lech-Maranda E, Feldman T,
Smolewski P, Savage KJ, et al: Brentuximab vedotin with
chemotherapy for stage III or IV classical Hodgkin lymphoma
(ECHELON-1): 5-year update of an international, open-label,
randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. 8:e410–e421. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Friedberg JW, Forero-Torres A, Bordoni RE,
Cline VJM, Patel Donnelly D, Flynn PJ, Olsen G, Chen R, Fon A, Wang
Y, et al: Frontline brentuximab vedotin in combination with
dacarbazine or bendamustine in patients aged >/=60 years with
HL. Blood. 130:2829–2837. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Moskowitz CH, Nademanee A, Masszi T, Agura
E, Holowiecki J, Abidi MH, Chen AI, Stiff P, Gianni AM, Carella A,
et al: Brentuximab vedotin as consolidation therapy after
autologous stem-cell transplantation in patients with Hodgkin's
lymphoma at risk of relapse or progression (AETHERA): A randomised,
double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet.
385:1853–1862. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Moskowitz CH, Walewski J, Nademanee A,
Masszi T, Agura E, Holowiecki J, Abidi MH, Chen AI, Stiff P,
Viviani S, et al: Five-year PFS from the AETHERA trial of
brentuximab vedotin for Hodgkin lymphoma at high risk of
progression or relapse. Blood. 132:2639–2642. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Younes A, Gopal AK, Smith SE, Ansell SM,
Rosenblatt JD, Savage KJ, Ramchandren R, Bartlett NL, Cheson BD, de
Vos S, et al: Results of a pivotal phase II study of brentuximab
vedotin for patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin's
lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 30:2183–2189. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen R, Gopal AK, Smith SE, Ansell SM,
Rosenblatt JD, Savage KJ, Connors JM, Engert A, Larsen EK, Huebner
D, et al: Five-year survival and durability results of brentuximab
vedotin in patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma.
Blood. 128:1562–1566. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kersten MJ, Driessen J, Zijlstra JM,
Plattel WJ, Morschhauser F, Lugtenburg PJ, Brice P, Hutchings M,
Gastinne T, Liu R, et al: Combining brentuximab vedotin with
dexamethasone, high-dose cytarabine and cisplatin as salvage
treatment in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: The phase II
HOVON/LLPC Transplant BRaVE study. Haematologica. 106:1129–1137.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Moskowitz AJ, Schoder H, Yahalom J, McCall
SJ, Fox SY, Gerecitano J, Grewal R, Hamlin PA, Horwitz S, Kobos R,
et al: PET-adapted sequential salvage therapy with brentuximab
vedotin followed by augmented ifosamide, carboplatin, and etoposide
for patients with relapsed and refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma: A
non-randomised, open-label, single-centre, phase 2 study. Lancet
Oncol. 16:284–292. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Garcia-Sanz R, Sureda A, de la Cruz F,
Canales M, Gonzalez AP, Pinana JL, Rodriguez A, Gutierrez A,
Domingo-Domenech E, Sanchez-Gonzalez B, et al: Brentuximab vedotin
and ESHAP is highly effective as second-line therapy for Hodgkin
lymphoma patients (long-term results of a trial by the Spanish
GELTAMO Group). Ann Oncol. 30:612–620. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
LaCasce AS, Bociek RG, Sawas A, Caimi P,
Agura E, Matous J, Ansell SM, Crosswell HE, Islas-Ohlmayer M,
Behler C, et al: Brentuximab vedotin plus bendamustine: A highly
active first salvage regimen for relapsed or refractory Hodgkin
lymphoma. Blood. 132:40–48. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
LaCasce AS, Bociek RG, Sawas A, Caimi P,
Agura E, Matous J, Ansell SM, Crosswell HE, Islas-Ohlmayer M,
Behler C, et al: Three-year outcomes with brentuximab vedotin plus
bendamustine as first salvage therapy in relapsed or refractory
Hodgkin lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 189:e86–e90. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
O'Connor OA, Lue JK, Sawas A, Amengual JE,
Deng C, Kalac M, Marchi E, Turenne I, Lichtenstein R, Rojas C, et
al: Brentuximab vedotin plus bendamustine in relapsed or refractory
Hodgkin's lymphoma: An international, multicentre, single-arm,
phase 1-2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 19:257–266. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Picardi M, Della Pepa R, Giordano C,
Pugliese N, Mortaruolo C, Trastulli F, Rascato MG, Cappuccio I,
Raimondo M, Memoli M, et al: Brentuximab vedotin followed by
bendamustine supercharge for refractory or relapsed Hodgkin
lymphoma. Blood Adv. 3:1546–1552. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Broccoli A, Argnani L, Botto B, Corradini
P, Pinto A, Re A, Vitolo U, Fanti S, Stefoni V and Zinzani PL;
Fondazione Italiana Linfomi ONLUS: First salvage treatment with
bendamustine and brentuximab vedotin in Hodgkin lymphoma: A phase 2
study of the Fondazione Italiana Linfomi. Blood Cancer J.
9:1002019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Iannitto E, Romano A, Scalzulli PR,
Bonanno V, Scalone R, Chiarenza A, Pirosa MC, Caruso AL, Minoia C,
Mantuano S, et al: Brentuximab vedotin in association with
bendamustine in refractory or multiple relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma. A
retrospective real-world study. Eur J Haematol. 104:581–587. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ and Sharpe
AH: PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev
Immunol. 26:677–704. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yamamoto R, Nishikori M, Kitawaki T, Sakai
T, Hishizawa M, Tashima M, Kondo T, Ohmori K, Kurata M, Hayashi T
and Uchiyama T: PD-1-PD-1 ligand interaction contributes to
immunosuppressive microenvironment of Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood.
111:3220–3224. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Roemer MG, Advani RH, Ligon AH, Natkunam
Y, Redd RA, Homer H, Connelly CF, Sun HH, Daadi SE, Freeman GJ, et
al: PD-L1 and PD-L2 genetic alterations define classical Hodgkin
lymphoma and predict outcome. J Clin Oncol. 34:2690–2697. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Green MR, Monti S, Rodig SJ, Juszczynski
P, Currie T, O'Donnell E, Chapuy B, Takeyama K, Neuberg D, Golub
TR, et al: Integrative analysis reveals selective 9p241
amplification, increased PD-1 ligand expression, and further
induction via JAK2 in nodular sclerosing Hodgkin lymphoma and
primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 116:3268–3277.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Green MR, Rodig S, Juszczynski P, Ouyang
J, Sinha P, O'Donnell E, Neuberg D and Shipp MA: Constitutive AP-1
activity and EBV infection induce PD-L1 in Hodgkin lymphomas and
posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders: Implications for
targeted therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 18:1611–1618. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ansell SM, Lesokhin AM, Borrello I,
Halwani A, Scott EC, Gutierrez M, Schuster SJ, Millenson MM, Cattry
D, Freeman GJ, et al: PD-1 blockade with nivolumab in relapsed or
refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 372:311–319. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
52
|
Armand P, Engert A, Younes A, Fanale M,
Santoro A, Zinzani PL, Timmerman JM, Collins GP, Ramchandren R,
Cohen JB, et al: Nivolumab for Relapsed/Refractory classic Hodgkin
lymphoma after failure of autologous hematopoietic cell
transplantation: Extended follow-up of the multicohort single-arm
phase II CheckMate 205 trial. J Clin Oncol. 36:1428–1439. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ansell S, Bröckelmann P, von Keudell G,
Lee HJ, Santoro A, Zinzani PL, Collins G, Cohen J, De Boer JP,
Kuruvilla J, et al: HL-398: Five-year overall survival from the
CheckMate 205 study of nivolumab for relapsed or refractory (R/R)
classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL). Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk.
21(Suppl 1): S373–S374. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Ramchandren R, Domingo-Domenech E, Rueda
A, Trneny M, Feldman TA, Lee HJ, Provencio M, Sillaber C, Cohen JB,
Savage KJ, et al: Nivolumab for Newly diagnosed Advanced-Stage
classic Hodgkin lymphoma: Safety and efficacy in the phase II
CheckMate 205 Study. J Clin Oncol. 37:1997–12007. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Brockelmann PJ, Goergen H, Keller U,
Meissner J, Ordemann R, Halbsguth TV, Sasse S, Sökler M, Kerkhoff
A, Mathas S, et al: Efficacy of Nivolumab and AVD in early-stage
unfavorable classic Hodgkin lymphoma: The randomized phase 2 german
Hodgkin study group NIVAHL Trial. JAMA Oncol. 6:872–880. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Herrera AF, Moskowitz AJ, Bartlett NL,
Vose JM, Ramchandren R, Feldman TA, LaCasce AS, Ansell SM,
Moskowitz CH, Fenton K, et al: Interim results of brentuximab
vedotin in combination with nivolumab in patients with relapsed or
refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 131:1183–1194. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
57
|
Wang Y, Zhou S, Yang F, Qi X, Wang X, Guan
X, Shen C, Duma N, Vera Aguilera J, Chintakuntlawar A, et al:
Treatment-related adverse events of PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors in
clinical trials: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol.
5:1008–1019. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chen R, Zinzani PL, Fanale MA, Armand P,
Johnson NA, Brice P, Radford J, Ribrag V, Molin D, Vassilakopoulos
TP, et al: Phase II study of the efficacy and safety of
pembrolizumab for relapsed/refractory classic Hodgkin lymphoma. J
Clin Oncol. 35:2125–2132. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zinzani PL, Lee HJ, Armand P, Johnson N,
Brice P, Radford J, Ribrag V, Molin D, Radford J, Ribrag V, et al:
Three-year Follow-up of Keynote-087: Pembrolizumab monotherapy in
relapsed/refractory classic Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 134:2402019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Armand P, Chen YB, Redd RA, Joyce RM, Bsat
J, Jeter E, Merryman RW, Coleman KC, Dahi PB, Nieto Y, et al: PD-1
blockade with pembrolizumab for classical Hodgkin lymphoma after
autologous stem cell transplantation. Blood. 134:22–29. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Moskowitz AJ, Shah G, Schöder H, Ganesan
N, Drill E, Hancock H, Ganesan N, Drill E, Hancock H, Davey T, et
al: Phase II trial of pembrolizumab plus gemcitabine, vinorelbine,
and liposomal doxorubicin as second-line therapy for relapsed or
refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 39:3109–3117.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Shi Y, Su H, Song Y, Jiang W, Sun X, Qian
W, Zhang W, Gao Y, Jin Z, Zhou J, et al: Safety and activity of
sintilimab in patients with relapsed or refractory classical
Hodgkin lymphoma (ORIENT-1): A multicentre, single-arm, phase 2
trial. Lancet Haematol. 6:e12–e9. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Fang W, Yang Y, Ma Y, Hong S, Lin L, He X,
Xiong J, Li P, Zhao H, Huang Y, et al: Camrelizumab (SHR-1210)
alone or in combination with gemcitabine plus cisplatin for
nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Results from two single-arm, phase 1
trials. Lancet Oncol. 19:1338–1350. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Mo H, Huang J, Xu J, Chen X, Wu D, Qu D,
Wang X, Lan B, Wang X, Xu J, et al: Safety, anti-tumour activity,
and pharmacokinetics of fixed-dose SHR-1210, an anti-PD-1 antibody
in advanced solid tumours: A dose-escalation, phase 1 study. Br J
Cancer. 119:538–545. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Huang J, Xu B, Mo H, Zhang W, Chen X, Wu
D, Qu D, Wang X, Lan B, Yang B, et al: Safety, activity, and
biomarkers of SHR-1210, an Anti-PD-1 antibody, for patients with
advanced esophageal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 24:1296–1304. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Song Y, Wu J, Chen X, Lin T, Cao J, Liu Y,
Zhao Y, Jin J, Huang H, Hu J, et al: A Single-arm, multicenter,
phase II study of camrelizumab in relapsed or refractory classical
Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 25:7363–7369. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Nie J, Wang C, Liu Y, Yang Q, Mei Q, Dong
L, Li X, Liu J, Ku W, Zhang Y, et al: Addition of low-dose
decitabine to Anti-PD-1 antibody camrelizumab in
relapsed/refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma. J Clin Oncol.
37:1479–1489. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Dahan R, Sega E, Engelhardt J, Selby M,
Korman AJ and Ravetch JV: FcγRs modulate the anti-tumor activity of
antibodies targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 axis. Cancer Cell. 28:285–295.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Song Y, Gao Q, Zhang H, Fan L, Zhou J, Zou
D, Li W, Yang H, Liu T, Wang Q, et al: Treatment of relapsed or
refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma with the anti-PD-1,
tislelizumab: Results of a phase 2, single-arm, multicenter study.
Leukemia. 34:533–542. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
70
|
Song Y, Gao Q, Zhang H, Fan L, Zhou J, Zou
D, Li W, Yang H, Liu T, Wang Q, et al: Tislelizumab for
relapsed/refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma: 3-year follow-up
and correlative biomarker analysis. Clin Cancer Res. 28:1147–1156.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Boles KS, Vermi W, Facchetti F, Fuchs A,
Wilson TJ, Diacovo TG, Cella M and Colonna M: A novel molecular
interaction for the adhesion of follicular CD4 T cells to
follicular DC. Eur J Immunol. 39:695–703. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Yu X, Harden K, Gonzalez LC, Francesco M,
Chiang E, Irving B, Tom I, Ivelja S, Refino CJ, Clark H, et al: The
surface protein TIGIT suppresses T cell activation by promoting the
generation of mature immunoregulatory dendritic cells. Nat Immunol.
10:48–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Stanietsky N, Simic H, Arapovic J, Toporik
A, Levy O, Novik A, Levine Z, Beiman M, Dassa L, Achdout H, et al:
The interaction of TIGIT with PVR and PVRL2 inhibits human NK cell
cytotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:17858–17863. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Garralda E, Sanborn RE, Minchom AR, Davar
D, Curigliano G, Ribrag V, Mehta A, Foss FM, Zain JM, Forero-Torres
A and Ansell SM: SGNTGT-001: A phase 1 study of SEA-TGT, an
effector-function enhanced monoclonal antibody (mAb), in advanced
malignancies (trial in progress). J Clin Oncol. 39(15_Suppl):
TPS26572021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Navarro A, Diaz T, Martinez A, Gaya A,
Pons A, Gel B, Codony C, Ferrer G, Martinez C, Montserrat E and
Monzo M: Regulation of JAK2 by miR-135a: Prognostic impact in
classic Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 114:2945–2951. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Meier C, Hoeller S, Bourgau C, Hirschmann
P, Schwaller J, Went P, Pileri SA, Reiter A, Dirnhofer S and
Tzankov A: Recurrent numerical aberrations of JAK2 and deregulation
of the JAK2-STAT cascade in lymphomas. Mod Pathol. 22:476–487.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Joos S, Granzow M, Holtgreve-Grez H,
Siebert R, Harder L, Martín-Subero JI, Wolf J, Adamowicz M, Barth
TF, Lichter P and Jauch A: Hodgkin's lymphoma cell lines are
characterized by frequent aberrations on chromosomes 2p and 9p
including REL and JAK2. Int J Cancer. 103:489–495. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Van Den Neste E, André M, Gastinne T,
Stamatoullas A, Haioun C, Belhabri A, Reman O, Casasnovas O,
Ghesquieres H, Verhoef G, et al: A phase II study of the oral
JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor ruxolitinib in advanced relapsed/refractory
Hodgkin lymphoma. Haematologica. 103:840–848. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Kim SJ, Yoon DH, Kang HJ, Hong JY, Lee HS,
Oh SY, Shin HJ, Kong JH, Yi JH, Sakamoto K, et al: Ruxolitinib
shows activity against Hodgkin lymphoma but not primary mediastinal
large B-cell lymphoma. BMC Cancer. 19:10802019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Dutton A, Reynolds GM, Dawson CW, Young LS
and Murray PG: Constitutive activation of phosphatidyl-inositide 3
kinase contributes to the survival of Hodgkin's lymphoma cells
through a mechanism involving Akt kinase and mTOR. J Pathol.
205:498–506. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Jundt F, Raetzel N, Muller C, Calkhoven
CF, Kley K, Mathas S, Lietz A, Leutz A and Dörken B: A rapamycin
derivative (everolimus) controls proliferation through
down-regulation of truncated CCAAT enhancer binding protein {beta}
and NF-{kappa} B activity in Hodgkin and anaplastic large cell
lymphomas. Blood. 106:1801–1807. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Johnston PB, Pinter-Brown LC, Warsi G,
White K and Ramchandren R: Phase 2 study of everolimus for relapsed
or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Exp Hematol Oncol.
7:122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Gillessen S, Hüttmann A, Vucinic V, Müller
H, Plütschow A, Viardot A, Topp MS, Kobe C, Böll B, Eichenauer DA,
et al: Reinduction therapy with everolimus in combination with
dexamethasone, high-dose cytarabin and cisplatinum in patients with
relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma: An experimental
phase I/II multicentre trial of the German Hodgkin Study Group
(GHSG HD-R3i). Br J Haematol. 196:606–616. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Kotla V, Goel S, Nischal S, Heuck C, Vivek
K, Das B and Verma A: Mechanism of action of lenalidomide in
hematological malignancies. J Hematol Oncol. 2:362009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Bartlett JB, Dredge K and Dalgleish AG:
The evolution of thalidomide and its IMiD derivatives as anticancer
agents. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:314–322. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Marriott JB, Muller G, Stirling D and
Dalgleish AG: Immunotherapeutic and antitumour potential of
thalidomide analogues. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 1:675–682. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Fehniger TA, Larson S, Trinkaus K, Siegel
MJ, Cashen AF, Blum KA, Fenske TS, Hurd DD, Goy A, Schneider SE, et
al: A phase 2 multicenter study of lenalidomide in relapsed or
refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 118:5119–5125. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Boll B, Plutschow A, Burkle C, Atta J,
Pfreundschuh M, Feuring-Buske M, Vogelhuber M, Sökler M, Eichenauer
DA, Thielen I, et al: Doxorubicin, vinblastine, dacarbazine and
lenalidomide for older Hodgkin lymphoma patients: Final results of
a German Hodgkin Study Group (GHSG) phase-I trial. Br J Haematol.
185:42–52. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Padrnos L, Ernst B, Dueck AC, Kosiorek HE,
Ginos BF, Toro A, Johnston PB, Habermann TM, Leis JF, Mikhael JR,
et al: A Novel Combination of the mTORC1 inhibitor everolimus and
the immunomodulatory drug lenalidomide produces durable responses
in patients with heavily pretreated relapsed lymphoma. Clin
Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 18:664–672.e2. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Marks PA and Xu WS: Histone deacetylase
inhibitors: Potential in cancer therapy. J Cell Biochem.
107:600–708. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Lane AA and Chabner BA: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol.
27:5459–5468. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Younes A, Oki Y, Bociek RG, Kuruvilla J,
Fanale M, Neelapu S, Copeland A, Buglio D, Galal A, Besterman J, et
al: Mocetinostat for relapsed classical Hodgkin's lymphoma: An
open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 12:1222–1228.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Younes A, Sureda A, Ben-Yehuda D, Zinzani
PL, Ong TC, Prince HM, Harrison SJ, Kirschbaum M, Johnston P,
Gallagher J, et al: Panobinostat in patients with
relapsed/refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma after autologous stem-cell
transplantation: Results of a phase II study. J Clin Oncol.
30:2197–2203. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Kirschbaum MH, Goldman BH, Zain JM, Cook
JR, Rimsza LM, Forman SJ and Fisher RI: A phase 2 study of
vorinostat for treatment of relapsed or refractory Hodgkin
lymphoma: Southwest Oncology Group Study S0517. Leuk Lymphoma.
53:259–262. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Herrera AF, Chen L, Popplewell LL, Budde
LE, Mei M, Armenian SH, Darrah J, Nikolaenko L, Chen RW, Peters L,
et al: Preliminary results from a phase I trial of pembrolizumab
plus vorinostat in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse
large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, and Hodgkin lymphoma.
Blood. 134:7592019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Buglio D, Mamidipudi V, Khaskhely NM,
Brady H, Heise C, Besterman J, Martell RE, MacBeth K and Younes A:
The class-I HDAC inhibitor MGCD0103 induces apoptosis in Hodgkin
lymphoma cell lines and synergizes with proteasome inhibitors by an
HDAC6-independent mechanism. Br J Haematol. 151:387–396. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Lemoine M, Derenzini E, Buglio D, Medeiros
LJ, Davis RE, Zhang J, Ji Y and Younes A: The pan-deacetylase
inhibitor panobinostat induces cell death and synergizes with
everolimus in Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines. Blood. 119:4017–4025.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Georgakis GV, Yazbeck VY, Li Y and Younes
A: The histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat (SAHA) induces
apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) cell lines
by altering several survival signaling pathways and synergizes with
doxorubicin, gemcitabine and bortezomib. Blood. 108:22602006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Hu B, Younes A, Westin JR, Turturro F,
Claret L, Feng L, Fowler N, Neelapu S, Romaguera J, Hagemeister FB,
et al: Phase-I and randomized phase-II trial of panobinostat in
combination with ICE (ifosfamide, carboplatin, etoposide) in
relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma.
59:863–870. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Maly JJ, Christian BA, Zhu X, Wei L,
Sexton JL, Jaglowski SM, Devine SM, Fehniger TA, Wagner-Johnston
ND, Phelps MA, et al: A Phase I/II Trial of panobinostat in
combination with lenalidomide in patients with relapsed or
refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk.
17:347–353. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Hamadani M, Collins GP, Samaniego F, Spira
AI, Davies A, Radford J, Caimi P, Menne T, Boni J, Cruz H, et al:
Phase 1 study of Adct-301 (Camidanlumab Tesirine), a novel
pyrrolobenzodiazepine-based antibody drug conjugate, in
relapsed/refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 132(Suppl
1): S9282018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Rothe A, Sasse S, Topp MS, Eichenauer DA,
Hummel H, Reiners KS, Dietlein M, Kuhnert G, Kessler J, Buerkle C,
et al: A phase 1 study of the bispecific anti-CD30/CD16A antibody
construct AFM13 in patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin
lymphoma. Blood. 125:4024–4031. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Bartlett NL, Chen RW, Domingo-Domenech E,
Forero-Torres A, Garcia-Sanz R, Armand P, Devata S, Rodriguez
Izquierdo A, Lossos IS, Reeder CB, et al: A Phase 1b study
investigating the combination of the tetravalent bispecific NK cell
engager AFM13 and pembrolizumab in patients with
relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma after brentuximab vedotin
failure: Updated safety and efficacy data. Blood. 132:16202018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Kochenderfer JN and Rosenberg SA: Treating
B-cell cancer with T cells expressing anti-CD19 chimeric antigen
receptors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 10:267–2676. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Sadelain M, Brentjens R and Riviere I: The
basic principles of chimeric antigen receptor design. Cancer
Discov. 3:388–3898. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Johnson LA and June CH: Driving
gene-engineered T cell immunotherapy of cancer. Cell Res. 27:38–58.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
107
|
Wang CM, Wu ZQ, Wang Y, Guo YL, Dai HR,
Wang XH, Li X, Zhang YJ, Zhang WY, Chen MX, et al: Autologous T
cells expressing CD30 chimeric antigen receptors for relapsed or
refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: An open-label phase I trial. Clin
Cancer Res. 23:1156–1166. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Zanotti R, Trolese A, Ambrosetti A, Nadali
G, Visco C, Ricetti MM, Benedetti F and Pizzolo G: Serum levels of
soluble CD30 improve International Prognostic Score in predicting
the outcome of advanced Hodgkin's lymphoma. Ann Oncol.
13:1908–1914. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Ramos CA, Ballard B, Zhang H, Dakhova O,
Gee AP, Mei Z, Bilgi M, Wu MF, Liu H, Grilley B, et al: Clinical
and immunological responses after CD30-specific chimeric antigen
receptor-redirected lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 127:3462–3471.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Wang D, Zeng C, Xu B, Xu JH, Wang J, Jiang
LJ, Wang QX, Li CR, Wang N, Huang L, et al: Anti-CD30 chimeric
antigen receptor T cell therapy for relapsed/refractory
CD30+ lymphoma patients. Blood Cancer J. 10:82020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Ramos CA, Grover NS, Beaven AW, Lulla PD,
Wu MF, Ivanova A, Wang T, Shea TC, Rooney CM, Dittus C, et al:
Anti-CD30 CAR-T cell therapy in relapsed and refractory Hodgkin
lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 38:3794–3804. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Jones RJ, Gocke CD, Kasamon YL, Miller CB,
Perkins B, Barber JP, Vala MS, Gerber JM, Gellert LL, Siedner M, et
al: Circulating clonotypic B cells in classic Hodgkin lymphoma.
Blood. 113:5920–5926. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Beatty GL, Haas AR, Maus MV, Torigian DA,
Soulen MC, Plesa G, Chew A, Zhao Y, Levine BL, Albelda SM, et al:
Mesothelin-specific chimeric antigen receptor mRNA-engineered T
cells induce anti-tumor activity in solid malignancies. Cancer
Immunol Res. 2:112–1120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Svoboda J, Rheingold SR, Gill SI, Grupp
SA, Lacey SF, Kulikovskaya I, Suhoski MM, Melenhorst JJ, Loudon B,
Mato AR, et al: Nonviral RNA chimeric antigen receptormodified T
cells in patients with Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 132:1022–1026.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Nademanee A, O'Donnell MR, Snyder DS,
Schmidt GM, Parker PM, Stein AS, Smith EP, Molina A, Stepan DE,
Somlo G, et al: High-dose chemotherapy with or without total body
irradiation followed by autologous bone marrow and/or peripheral
blood stem cell transplantation for patients with relapsed and
refractory Hodgkin's disease: Results in 85 patients with analysis
of prognostic factors. Blood. 85:1381–1390. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Burroughs LM, O'Donnell PV, Sandmaier BM,
Storer BE, Luznik L, Symons HJ, Jones RJ, Ambinder RF, Maris MB,
Blume KG, et al: Comparison of outcomes of HLA-matched related,
unrelated, or HLA-haploidentical related hematopoietic cell
transplantation following nonmyeloablative conditioning for
relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Biol Blood Marrow
Transplant. 14:1279–1287. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|