|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jeon J, Du M, Schoen RE, Hoffmeister M,
Newcomb PA, Berndt SI, Caan B, Campbell PT, Chan AT, Chang-Claude
J, et al: Determining risk of colorectal cancer and starting age of
screening based on lifestyle, environmental, and genetic factors.
Gastroenterology. 154:2152–2164.e2119. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kulaylat MN and Dayton MT: Ulcerative
colitis and cancer. J Surg Oncol. 101:706–712. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jensen AB, Larsen M, Gislum M, Skriver MV,
Jepsen P, Nørgaard B and Sørensen HT: Survival after colorectal
cancer in patients with ulcerative colitis: A nationwide
population-based Danish study. Am J Gastroenterol. 101:1283–1287.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dolin TG, Christensen IJ, Johansen AZ,
Nielsen HJ, Jakobsen HL, Klein MF, Lund CM, Bojesen SE, Nielsen DL,
Jensen BV and Johansen JS: Pre- and perioperative inflammatory
biomarkers in older patients resected for localized colorectal
cancer: Associations with complications and prognosis. Cancers
(Basel). 14:1612022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Giovannucci E: The prevention of
colorectal cancer by aspirin use. Biomed Pharmacother. 53:303–308.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Watson AJ: Chemopreventive effects of
NSAIDs against colorectal cancer: Regulation of apoptosis and
mitosis by COX-1 and COX-2. Histol Histopathol. 13:591–597.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bus PJ, Verspaget HW, Lamers CB and
Griffioen G: Chemoprevention of colorectal cancer by non-steroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 2000:101–104.
2000.
|
|
9
|
Andersen V, Halekoh U, Tjønneland A, Vogel
U and Kopp TI: Intake of red and processed meat, use of non-steroid
anti-inflammatory drugs, genetic variants and risk of colorectal
cancer: A prospective study of the danish 'Diet, Cancer and Health'
cohort. Int J Mol Sci. 20:11212019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Balkwill F and Mantovani A: Inflammation
and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet. 357:539–545. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schmitt M and Greten FR: The inflammatory
pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. 21:653–667.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lichtenstern CR, Ngu RK, Shalapour S and
Karin M: Immunotherapy, inflammation and colorectal cancer. Cells.
9:6182020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Percario R, Panaccio P, di Mola FF,
Grottola T and Di Sebastiano P: The complex network between
inflammation and colorectal cancer: A systematic review of the
literature. Cancers (Basel). 13:62372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Khanapure SP, Garvey DS, Janero DR and
Letts LG: Eicosanoids in inflammation: Biosynthesis, pharmacology,
and therapeutic frontiers. Curr Top Med Chem. 7:311–340. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sonnweber T, Pizzini A, Nairz M, Weiss G
and Tancevski I: Arachidonic acid metabolites in cardiovascular and
metabolic diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 19:32852018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen X, Sood S, Yang CS, Li N and Sun Z:
Five-lipoxygenase pathway of arachidonic acid metabolism in
carcino-genesis and cancer chemoprevention. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 6:613–622. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Y, Wang W, Sanidad KZ, Shih PA, Zhao
X and Zhang G: Eicosanoid signaling in carcinogenesis of colorectal
cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 37:257–267. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Harkins L, Volk AL, Samanta M, Mikolaenko
I, Britt WJ, Bland KI and Cobbs CS: Specific localisation of human
cytomegalovirus nucleic acids and proteins in human colorectal
cancer. Lancet. 360:1557–1563. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kany S, Vollrath JT and Relja B: Cytokines
in inflammatory disease. Int J Mol Sci. 20:60082019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Radmark O and Samuelsson B:
5-Lipoxygenase: Mechanisms of regulation. J Lipid Res. 50(Suppl):
S40–S45. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Uhl J, Klan N, Rose M, Entian KD, Werz O
and Steinhilber D: The 5-lipoxygenase promoter is regulated by DNA
methylation. J Biol Chem. 277:4374–4379. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lee SJ, Seo KW and Kim CD: LPS increases
5-LO expression on monocytes via an activation of Akt-Sp1/NF-kappaB
pathways. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 19:263–268. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zappavigna S, Cossu AM, Grimaldi A,
Bocchetti M, Ferraro GA, Nicoletti GF, Filosa R and Caraglia M:
Anti-inflammatory drugs as anticancer agents. Int J Mol Sci.
21:26052020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Harris RE, Beebe-Donk J and Alshafie GA:
Reduction in the risk of human breast cancer by selective
cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors. BMC Cancer. 6:272006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Harris RE, Beebe-Donk J and Alshafie GA:
Reduced risk of human lung cancer by selective cyclooxygenase 2
(Cox-2) blockade: Results of a case control study. Int J Biol Sci.
3:328–334. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jacobs EJ, Rodriguez C, Mondul AM, Connell
CJ, Henley SJ, Calle EE and Thun MJ: A large cohort study of
aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and prostate
cancer incidence. J Natl Cancer Inst. 97:975–980. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Patel MI, Subbaramaiah K, Du B, Chang M,
Yang P, Newman RA, Cordon-Cardo C, Thaler HT and Dannenberg AJ:
Celecoxib inhibits prostate cancer growth: Evidence of a
cyclooxygenase-2-independent mechanism. Clin Cancer Res.
11:1999–2007. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Maniewska J and Jeżewska D: Non-steroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs in colorectal cancer chemoprevention.
Cancers (Basel). 13:5942021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cole BF, Logan RF, Halabi S, Benamouzig R,
Sandler RS, Grainge MJ, Chaussade S and Baron JA: Aspirin for the
chemoprevention of colorectal adenomas: Meta-analysis of the
randomized trials. J Natl Cancer Inst. 101:256–266. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cook NR, Lee IM, Zhang SM, Moorthy MV and
Buring JE: Alternate-day, low-dose aspirin and cancer risk:
Long-term observational follow-up of a randomized trial. Ann Intern
Med. 159:77–85. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rothwell PM, Fowkes FG, Belch JF, Ogawa H,
Warlow CP and Meade TW: Effect of daily aspirin on long-term risk
of death due to cancer: Analysis of individual patient data from
randomised trials. Lancet. 377:31–41. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Rothwell PM, Wilson M, Elwin CE, Norrving
B, Algra A, Warlow CP and Meade TW: Long-term effect of aspirin on
colorectal cancer incidence and mortality: 20-year follow-up of
five randomised trials. Lancet. 376:1741–1750. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Guo CG, Ma W, Drew DA, Cao Y, Nguyen LH,
Joshi AD, Ng K, Ogino S, Meyerhardt JA, Song M, et al: Aspirin use
and risk of colorectal cancer among older adults. JAMA Oncol.
7:428–435. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Coyle C, Cafferty FH and Langley RE:
Aspirin and colorectal cancer prevention and treatment: Is it for
everyone? Curr Colorectal Cancer Rep. 12:27–34. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Avis I, Hong SH, Martinez A, Moody T, Choi
YH, Trepel J, Das R, Jett M and Mulshine JL: Five-lipoxygenase
inhibitors can mediate apoptosis in human breast cancer cell lines
through complex eicosanoid interactions. FASEB J. 15:2007–2009.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Rao CV, Janakiram NB and Mohammed A:
Lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase pathways and colorectal cancer
prevention. Curr Colorectal Cancer Rep. 8:316–324. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Nauclér CS, Geisler J and Vetvik K: The
emerging role of human cytomegalovirus infection in human
carcinogenesis: A review of current evidence and potential
therapeutic implications. Oncotarget. 10:4333–4347. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Zuhair M, Smit GSA, Wallis G, Jabbar F,
Smith C, Devleesschauwer B and Griffiths P: Estimation of the
worldwide seroprevalence of cytomegalovirus: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Rev Med Virol. 29:e20342019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Stern-Ginossar N, Weisburd B, Michalski A,
Le VT, Hein MY, Huang SX, Ma M, Shen B, Qian SB, Hengel H, et al:
Decoding human cytomegalovirus. Science. 338:1088–1093. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Murphy E, Rigoutsos I, Shibuya T and Shenk
TE: Reevaluation of human cytomegalovirus coding potential. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:13585–13590. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Chen HP, Jiang JK, Chen CY, Chou TY, Chen
YC, Chang YT, Lin SF, Chan CH, Yang CY, Lin CH, et al: Human
cytomegalovirus preferentially infects the neoplastic epithelium of
colorectal cancer: A quantitative and histological analysis. J Clin
Virol. 54:240–244. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Huang ES and Roche JK: Cytomegalovirus
D.N.A. and adenocarcinoma of the colon: Evidence for latent viral
infection. Lancet. 1:957–960. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Harkins LE, Matlaf LA, Soroceanu L, Klemm
K, Britt WJ, Wang W, Bland KI and Cobbs CS: Detection of human
cytomegalovirus in normal and neoplastic breast epithelium.
Herpesviridae. 1:82010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Samanta M, Harkins L, Klemm K, Britt WJ
and Cobbs CS: High prevalence of human cytomegalovirus in prostatic
intraepithelial neoplasia and prostatic carcinoma. J Urol.
170:998–1002. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Baryawno N, Rahbar A, Wolmer-Solberg N,
Taher C, Odeberg J, Darabi A, Khan Z, Sveinbjörnsson B, FuskevÅg
OM, Segerström L, et al: Detection of human cytomegalovirus in
medulloblastomas reveals a potential therapeutic target. J Clin
Invest. 121:4043–4055. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wolmer-Solberg N, Baryawno N, Rahbar A,
Fuchs D, Odeberg J, Taher C, Wilhelmi V, Milosevic J, Mohammad AA,
Martinsson T, et al: Frequent detection of human cytomegalovirus in
neuroblastoma: A novel therapeutic target? Int J Cancer.
133:2351–2361. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cobbs CS, Harkins L, Samanta M, Gillespie
GY, Bharara S, King PH, Nabors LB, Cobbs CG and Britt WJ: Human
cytomegalovirus infection and expression in human malignant glioma.
Cancer Res. 62:3347–3350. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Forte E, Zhang Z, Thorp EB and Hummel M:
Cytomegalovirus latency and reactivation: An intricate interplay
with the host immune response. Front Cell Infect Microbiol.
10:1302020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Diggins NL, Skalsky RL and Hancock MH:
Regulation of latency and reactivation by human cytomegalovirus
miRNAs. Pathogens. 10:2002021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Maussang D, Langemeijer E, Fitzsimons CP,
Stigter-van Walsum M, Dijkman R, Borg MK, Slinger E, Schreiber A,
Michel D, Tensen CP, et al: The human cytomegalovirus-encoded
chemokine receptor US28 promotes angiogenesis and tumor formation
via cyclooxygenase-2. Cancer Res. 69:2861–2869. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Zhu H, Cong JP, Yu D, Bresnahan WA and
Shenk TE: Inhibition of cyclooxygenase 2 blocks human
cytomegalovirus replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:3932–3937.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Benard M, Straat K, Omarsdottir S,
Leghmari K, Bertrand J, Davrinche C, Duga-Neulat I,
Söderberg-Nauclér C, Rahbar A and Casper C: Human cytomegalovirus
infection induces leukotriene B4 and 5-lipoxygenase expression in
human placentae and umbilical vein endothelial cells. Placenta.
35:345–350. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Costa H, Touma J, Davoudi B, Benard M,
Sauer T, Geisler J, Vetvik K, Rahbar A and Söderberg-Naucler C:
Human cytomegalovirus infection is correlated with enhanced
cyclooxygenase-2 and 5-lipoxygenase protein expression in breast
cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 145:2083–2095. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Taher C, Frisk G, Fuentes S, Religa P,
Costa H, Assinger A, Vetvik KK, Bukholm IR, Yaiw KC, Smedby KE, et
al: High prevalence of human cytomegalovirus in brain metastases of
patients with primary breast and colorectal cancers. Transl Oncol.
7:732–740. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Rahbar A, Pantalone MR, Religa P, Rådestad
AF and Söderberg-Naucler C: Evidence of human cytomegalovirus
infection and expression of 5-lipoxygenase in borderline ovarian
tumors. J Med Virol. 93:4023–4027. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bai B, Wang X, Chen E and Zhu H: Human
cytomegalovirus infection and colorectal cancer risk: A
meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 7:76735–76742. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Lv YL, Han FF, An ZL, Jia Y, Xuan LL, Gong
LL, Zhang W, Ren LL, Yang S, Liu H and Liu LH: Cytomegalovirus
infection is a risk factor in gastrointestinal cancer: A
cross-sectional and meta-analysis study. Intervirology. 63:10–16.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Chen HP, Jiang JK, Lai PY, Chen CY, Chou
TY, Chen YC, Chan CH, Lin SF, Yang CY, Chen CY, et al: Tumoral
presence of human cytomegalovirus is associated with shorter
disease-free survival in elderly patients with colorectal cancer
and higher levels of intratumoral interleukin-17. Clin Microbiol
Infect. 20:664–671. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Bongers G, Maussang D, Muniz LR, Noriega
VM, Fraile-Ramos A, Barker N, Marchesi F, Thirunarayanan N, Vischer
HF, Qin L, et al: The cytomegalovirus-encoded chemokine receptor
US28 promotes intestinal neoplasia in transgenic mice. J Clin
Invest. 120:3969–3978. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Mahdavinia M, Bishehsari F, Verginelli F,
Cumashi A, Lattanzio R, Sotoudeh M, Ansari R, Semeraro D, Hormazdi
M, Fakheri H, et al: P53 mutations in colorectal cancer from
northern Iran: Relationships with site of tumor origin,
microsatellite instability and K-ras mutations. J Cell Physiol.
216:543–550. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Bishehsari F, Mahdavinia M, Malekzadeh R,
Verginelli F, Catalano T, Sotoudeh M, Bazan V, Agnese V, Esposito
DL, De Lellis L, et al: Patterns of K-ras mutation in colorectal
carcinomas from Iran and Italy (a Gruppo Oncologico dell'Italia
Meridionale study): Influence of microsatellite instability status
and country of origin. Ann Oncol. 17(Suppl 7): vii91–vii96. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Esposito DL, Aru F, Lattanzio R, Morgano
A, Abbondanza M, Malekzadeh R, Bishehsari F, Valanzano R, Russo A,
Piantelli M, et al: The insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1) in
intestinal epithelial differentiation and in colorectal cancer.
PLoS One. 7:e361902012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Lattanzio R, Marchisio M, La Sorda R,
Tinari N, Falasca M, Alberti S, Miscia S, Ercolani C, Di Benedetto
A, Perracchio L, et al: Overexpression of activated phospholipase
Cγ1 is a risk factor for distant metastases in T1-T2, N0 breast
cancer patients undergoing adjuvant chemotherapy. Int J Cancer.
132:1022–1031. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Rahbar A, Orrego A, Peredo I, Dzabic M,
Wolmer-Solberg N, Strååt K, Stragliotto G and Söderberg-Nauclér C:
Human cytomegalovirus infection levels in glioblastoma multiforme
are of prognostic value for survival. J Clin Virol. 57:36–42. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
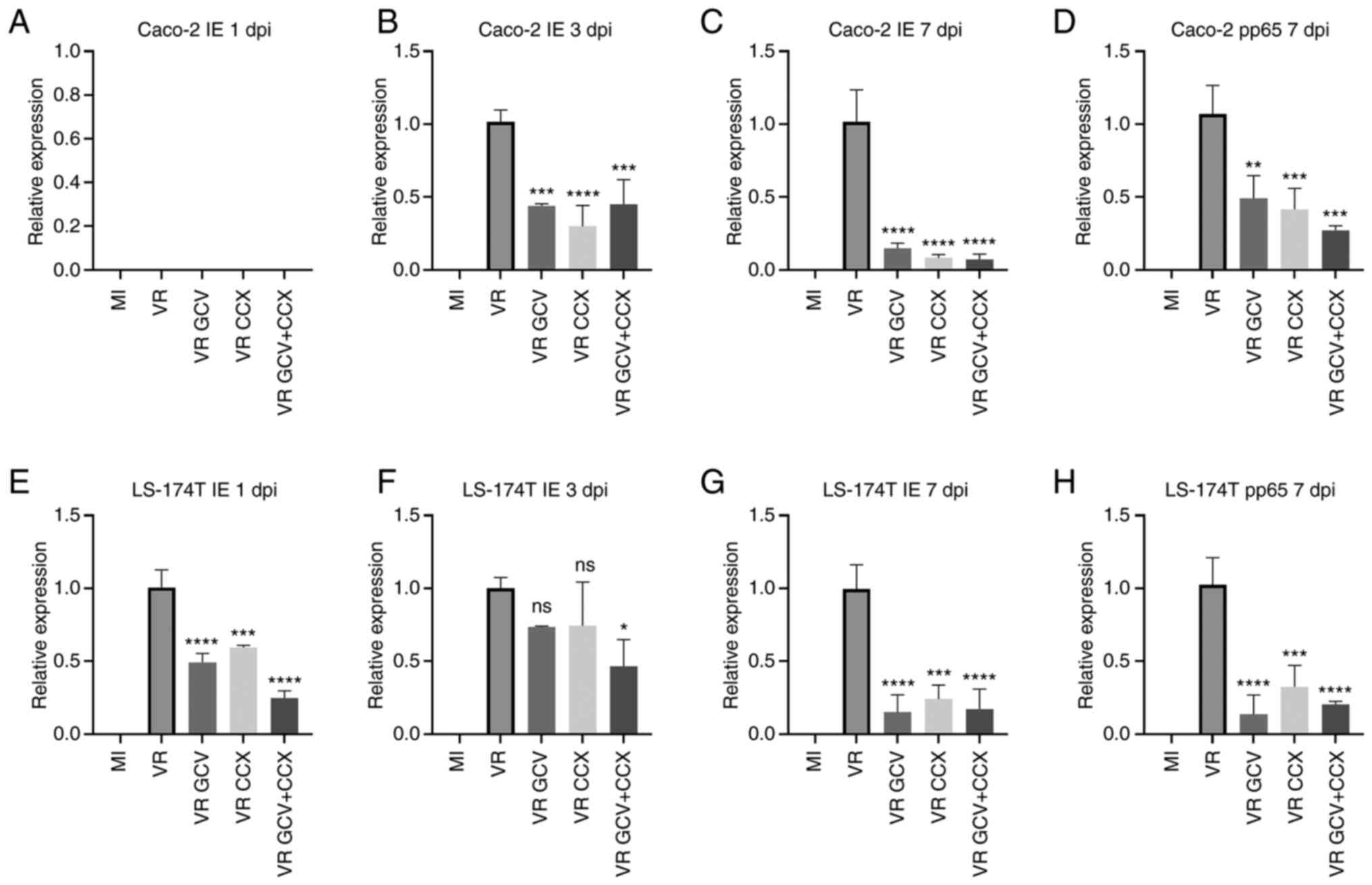
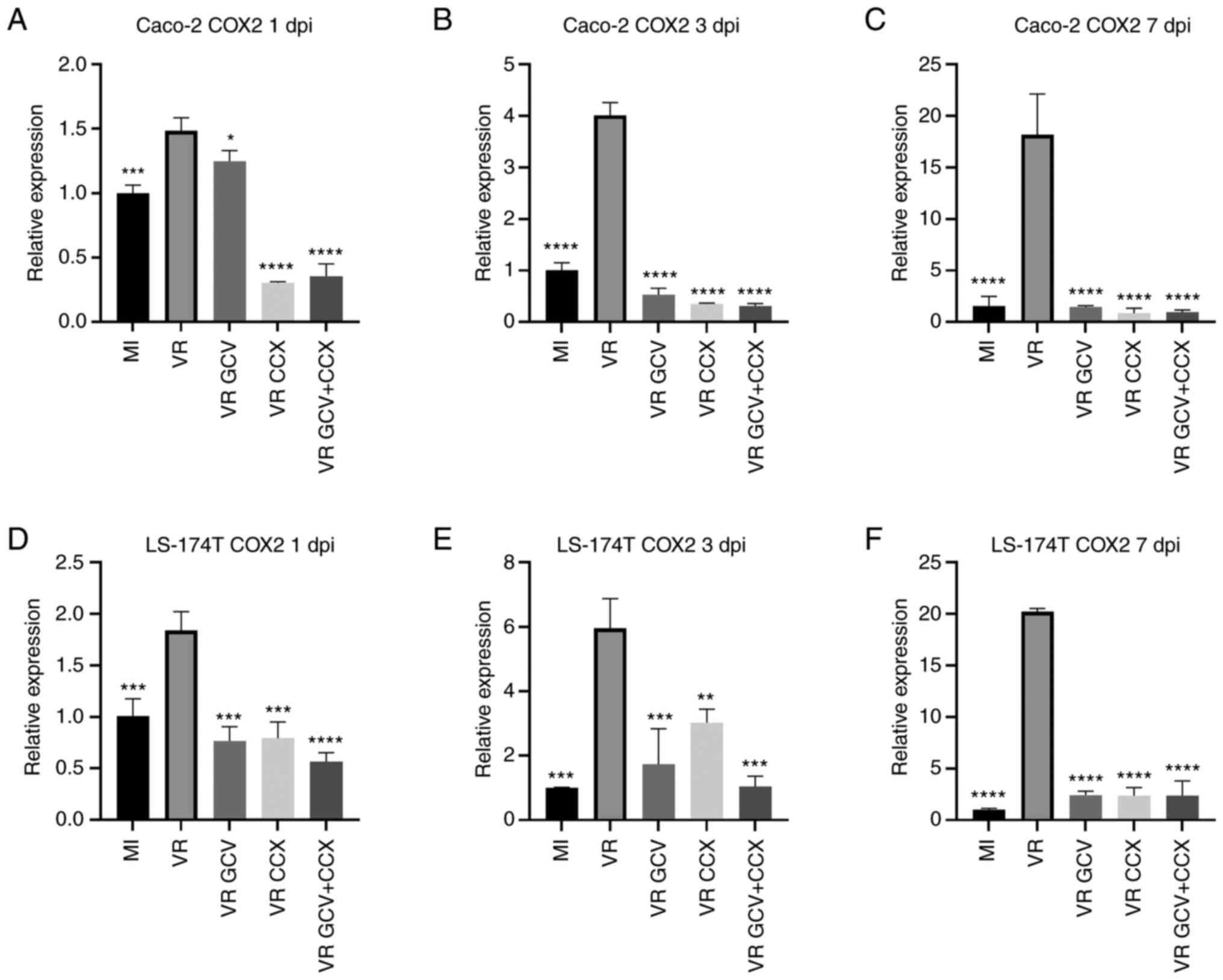
Bu XD, Li N, Tian XQ and Huang PL: Caco-2
and LS174T cell lines provide different models for studying mucin
expression in colon cancer. Tissue Cell. 43:201–206. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Al-Badr AA and Ajarim TDS: Ganciclovir.
Profiles Drug Subst Excip Relat Methodol. 43:1–208. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Cai H, Kapoor A, He R, Venkatadri R,
Forman M, Posner GH and Arav-Boger R: In vitro combination of
anti-cytomegalovirus compounds acting through different targets:
Role of the slope parameter and insights into mechanisms of action.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 58:986–994. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
68
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Sinzger C, Digel M and Jahn G:
Cytomegalovirus cell tropism. Curr Top Mirobiol Immunol. 325:63–83.
2008.
|
|
70
|
Fields BN, Knipe DM and Howley PM: Fields
virology. Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;
Philadelphia: 2007
|
|
71
|
Herbein G: Tumors and cytomegalovirus: An
intimate interplay. Viruses. 14:8122022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Peredo-Harvey I, Rahbar A and
Söderberg-Nauclér C: Presence of the human cytomegalovirus in
glioblastomas-a systematic review. Cancers (Basel). 13:50512021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Cobbs CS, Matlaf L and Harkins LE: Methods
for the detection of cytomegalovirus in glioblastoma cells and
tissues. Methods Mol Biol. 1119:165–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Dziurzynski K, Chang SM, Heimberger AB,
Kalejta RF, Dallas SR, Smit M, Soroceanu L and Cobbs CS; HCMV and
Gliomas Symposium: Consensus on the role of human cytomegalovirus
in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 14:246–255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
75
|
Herbein G: The human cytomegalovirus, from
oncomodulation to oncogenesis. Viruses. 10:4082018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Cobbs C: Cytomegalovirus is a
tumor-associated virus: Armed and dangerous. Curr Opin Virol.
39:49–59. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Qiu H, Straat K, Rahbar A, Wan M,
Soderberg-Naucler C and Haeggstrom JZ: Human CMV infection induces
5-lipoxygenase expression and leukotriene B4 production in vascular
smooth muscle cells. J Exp Med. 205:19–24. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Hooks JJ, Chin MS, Srinivasan K, Momma Y,
Hooper LC, Nagineni CN, Chan CC and Detrick B: Human
cytomegalovirus induced cyclooxygenase-2 in human retinal pigment
epithelial cells augments viral replication through a prostaglandin
pathway. Microbes Infect. 8:2236–2244. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Söderberg-Nauclér C, Fish KN and Nelson
JA: Reactivation of latent human cytomegalovirus by allogeneic
stimulation of blood cells from healthy donors. Cell. 91:119–126.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Reeves M and Sinclair J: Aspects of human
cytomegalovirus latency and reactivation. Curr Top Microbiol
Immunol. 325:297–313. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Söderberg-Nauclér C, Fish KN and Nelson
JA: Interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha specifically
induce formation of cytomegalovirus-permissive monocyte-derived
macrophages that are refractory to the antiviral activity of these
cytokines. J Clin Invest. 100:3154–3163. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Reeves MB and Compton T: Inhibition of
inflammatory interleukin-6 activity via extracellular
signal-regulated kinase-mitogen- activated protein kinase signaling
antagonizes human cytomegalovirus reactivation from dendritic
cells. J Virol. 85:12750–12758. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Griffiths P, Baraniak I and Reeves M: The
pathogenesis of human cytomegalovirus. J Pathol. 235:288–297. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Yi HA, Kim MS, Jang SY, Lee YM, Ahn JH and
Lee CH: Cellular signals involved in cyclooxygenase-2 expression
induced by human cytomegalovirus. Virus Res. 146:89–96. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Huang Y, Ma D, Huang H, Lu Y, Liao Y, Liu
L, Liu X and Fang F: Interaction between HCMV pUL83 and human AIM2
disrupts the activation of the AIM2 inflammasome. Virol J.
14:342017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Söderberg-Nauclér C: Does cytomegalovirus
play a causative role in the development of various inflammatory
diseases and cancer? J Intern Med. 259:219–246. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Teo WH, Chen HP, Huang JC and Chan YJ:
Human cytomegalovirus infection enhances cell proliferation,
migration and upregulation of EMT markers in colorectal
cancer-derived stem cell-like cells. Int J Oncol. 51:1415–1426.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Maussang D, Verzijl D, van Walsum M, Leurs
R, Holl J, Pleskoff O, Michel D, van Dongen GA and Smit MJ: Human
cytomegalovirus-encoded chemokine receptor US28 promotes
tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:13068–13073. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Heukers R, Fan TS, de Wit RH, van Senten
JR, De Groof TWM, Bebelman MP, Lagerweij T, Vieira J, de Munnik SM,
Smits-de Vries L, et al: The constitutive activity of the virally
encoded chemokine receptor US28 accelerates glioblastoma growth.
Oncogene. 37:4110–4121. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Rahbar A, Boström L, Lagerstedt U,
Magnusson I, Söderberg-Naucler C and Sundqvist VA: Evidence of
active cytomegalovirus infection and increased production of IL-6
in tissue specimens obtained from patients with inflammatory bowel
diseases. Inflam Bowel Dis. 9:154–161. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Sääf AM, Halbleib JM, Chen X, Yuen ST,
Leung SY, Nelson WJ and Brown PO: Parallels between global
transcriptional programs of polarizing Caco-2 intestinal epithelial
cells in vitro and gene expression programs in normal colon and
colon cancer. Mol Biol Cell. 18:4245–4260. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Creff J, Malaquin L and Besson A: In vitro
models of intestinal epithelium: Toward bioengineered systems. J
Tissue Eng. 12:20417314209852022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Schröer J and Shenk T: Inhibition of
cyclooxygenase activity blocks cell-to-cell spread of human
cytomegalovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:19468–19473. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Speir E, Yu ZX, Ferrans VJ, Huang ES and
Epstein SE: Aspirin attenuates cytomegalovirus infectivity and gene
expression mediated by cyclooxygenase-2 in coronary artery smooth
muscle cells. Circ Res. 83:210–216. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Merchut-Maya JM, Bartek J Jr, Bartkova J,
Galanos P, Pantalone MR, Lee M, Cui HL, Shilling PJ, Brøchner CB,
Broholm H, et al: Human cytomegalovirus hijacks host stress
response fueling replication stress and genome instability. Cell
Death Differ. 29:1639–1653. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Guirguis-Blake JM, Evans CV, Perdue LA,
Bean SI and Senger CA: Aspirin use to prevent cardiovascular
disease and colorectal cancer: Updated evidence report and
systematic review for the US preventive services task force. JAMA.
327:1585–1597. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Rovati G, Contursi A, Bruno A, Tacconelli
S, Ballerini P and Patrignani P: Antiplatelet agents affecting GPCR
signaling implicated in tumor metastasis. Cells. 11:7252022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Wojtukiewicz MZ, Hempel D, Sierko E,
Tucker SC and Honn KV: Antiplatelet agents for cancer treatment: A
real perspective or just an echo from the past? Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 36:305–329. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Gareau AJ, Brien C, Gebremeskel S, Liwski
RS, Johnston B and Bezuhly M: Ticagrelor inhibits platelet-tumor
cell interactions and metastasis in human and murine breast cancer.
Clin Exp Metastasis. 35:25–35. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Hobson AR, Qureshi Z, Banks P and Curzen
NP: Effects of clopidogrel on 'aspirin specific' pathways of
platelet inhibition. Platelets. 20:386–390. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Landolfi R, Mower RL and Steiner M:
Modification of platelet function and arachidonic acid metabolism
by bioflavonoids. Structure-activity relations. Biochem Pharmacol.
33:1525–1530. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Ribeiro D, Freitas M, Tome SM, Silva AM,
Laufer S, Lima JL and Fernandes E: Flavonoids inhibit COX-1 and
COX-2 enzymes and cytokine/chemokine production in human whole
blood. Inflammation. 38:858–870. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Stragliotto G, Pantalone MR, Rahbar A,
Bartek J and Söderberg-Naucler C: Valganciclovir as add-on to
standard therapy in glioblastoma patients. Clin Cancer Res.
26:4031–4039. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Stragliotto G, Pantalone MR, Rahbar A and
Söderberg-Nauclér C: Valganciclovir as add-on to standard therapy
in secondary glioblastoma. Microorganisms. 8:14712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Pantalone MR, Rahbar A, Söderberg-Naucler
C and Stragliotto G: Valganciclovir as Add-on to second-line
therapy in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Cancers (Basel).
14:19582022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Batich KA, Reap EA, Archer GE,
Sanchez-Perez L, Nair SK, Schmittling RJ, Norberg P, Xie W, Herndon
JE II, Healy P, et al: Long-term survival in glioblastoma with
cytomegalovirus pp65-targeted vaccination. Clin Cancer Res.
23:1898–1909. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Batich KA, Mitchell DA, Healy P, Herndon
JE II and Sampson JH: Once, twice, three times a finding:
Reproducibility of dendritic cell vaccine trials targeting
cytomegalovirus in glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 26:5297–5303.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|