|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zacharakis M, Xynos ID, Lazaris A, Smaro
T, Kosmas C, Dokou A, Felekouras E, Antoniou E, Polyzos A,
Sarantonis J, et al: Predictors of survival in stage IV metastatic
colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 30:653–660. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
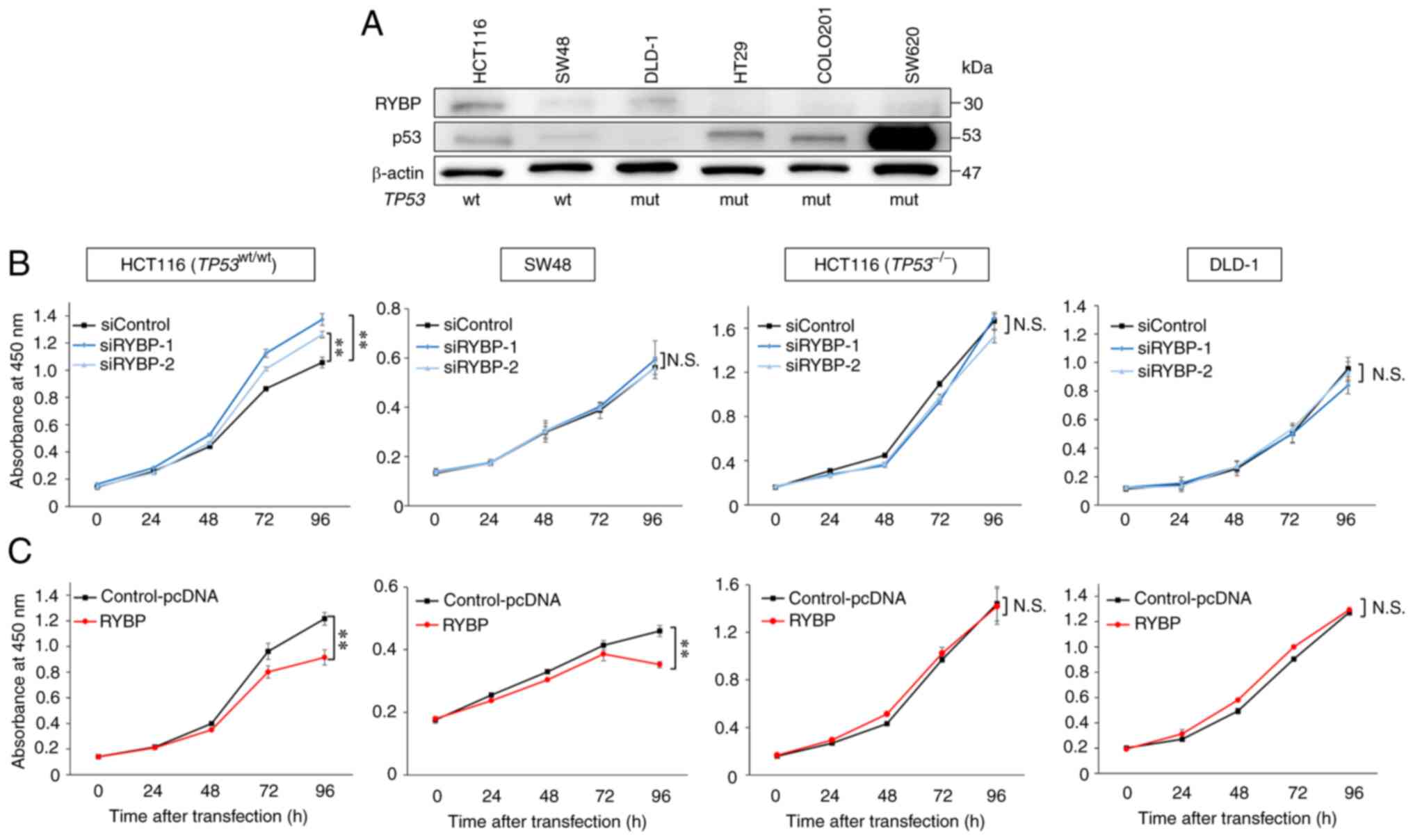
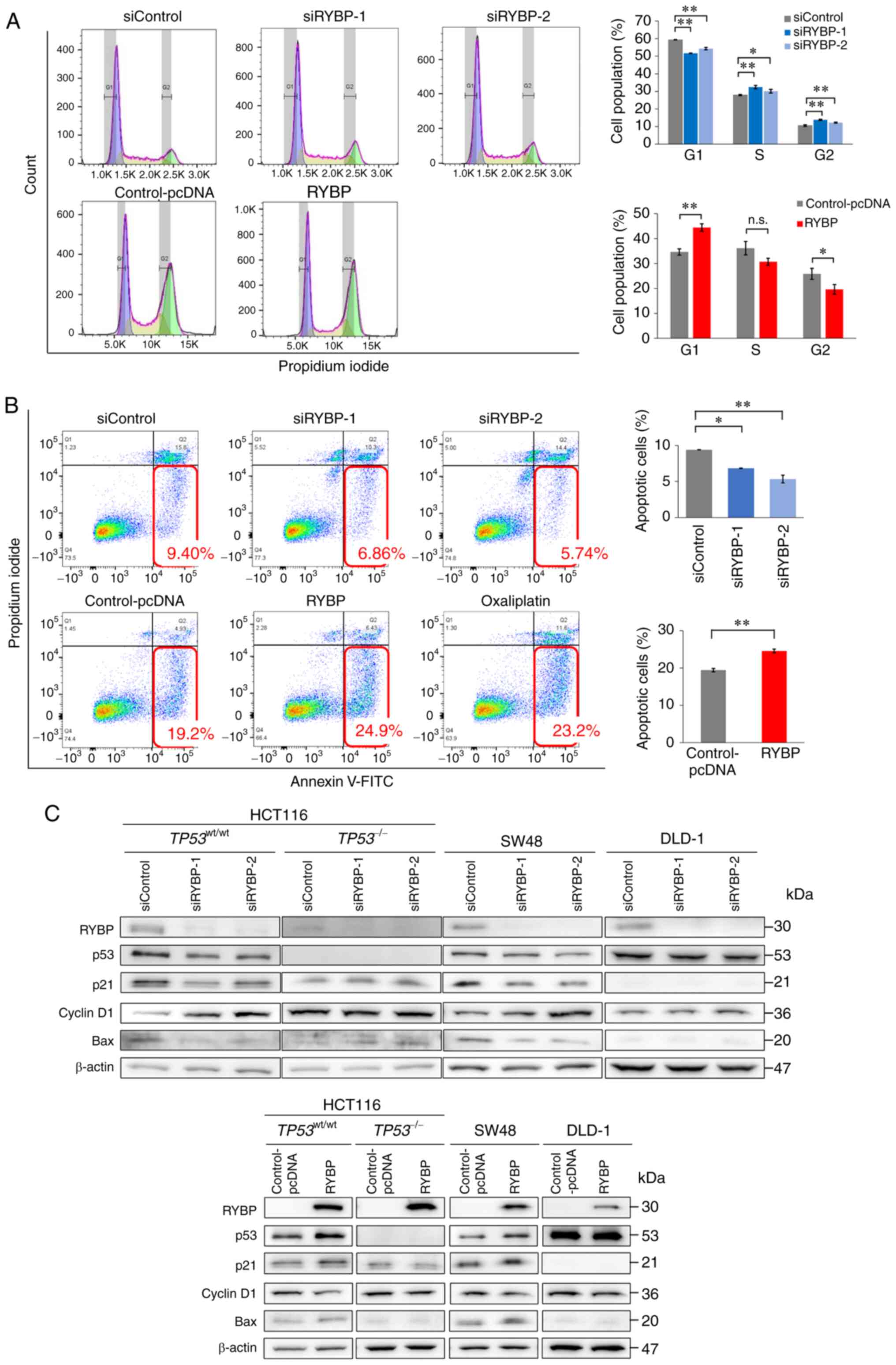
3
|
Manfredi S, Lepage C, Hatem C, Coatmeur O,
Faivre J and Bouvier AM: Epidemiology and management of liver
metastases from colorectal cancer. Ann Surg. 244:254–259. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sato N, Sakai N, Furukawa K, Takayashiki
T, Kuboki S, Takano S, Ohira G, Matsubara H and Ohtsuka M: Yin Yang
1 regulates ITGAV and ITGB1, contributing to improved prognosis of
colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 47:872022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Takagi Y, Sakai N, Yoshitomi H, Furukawa
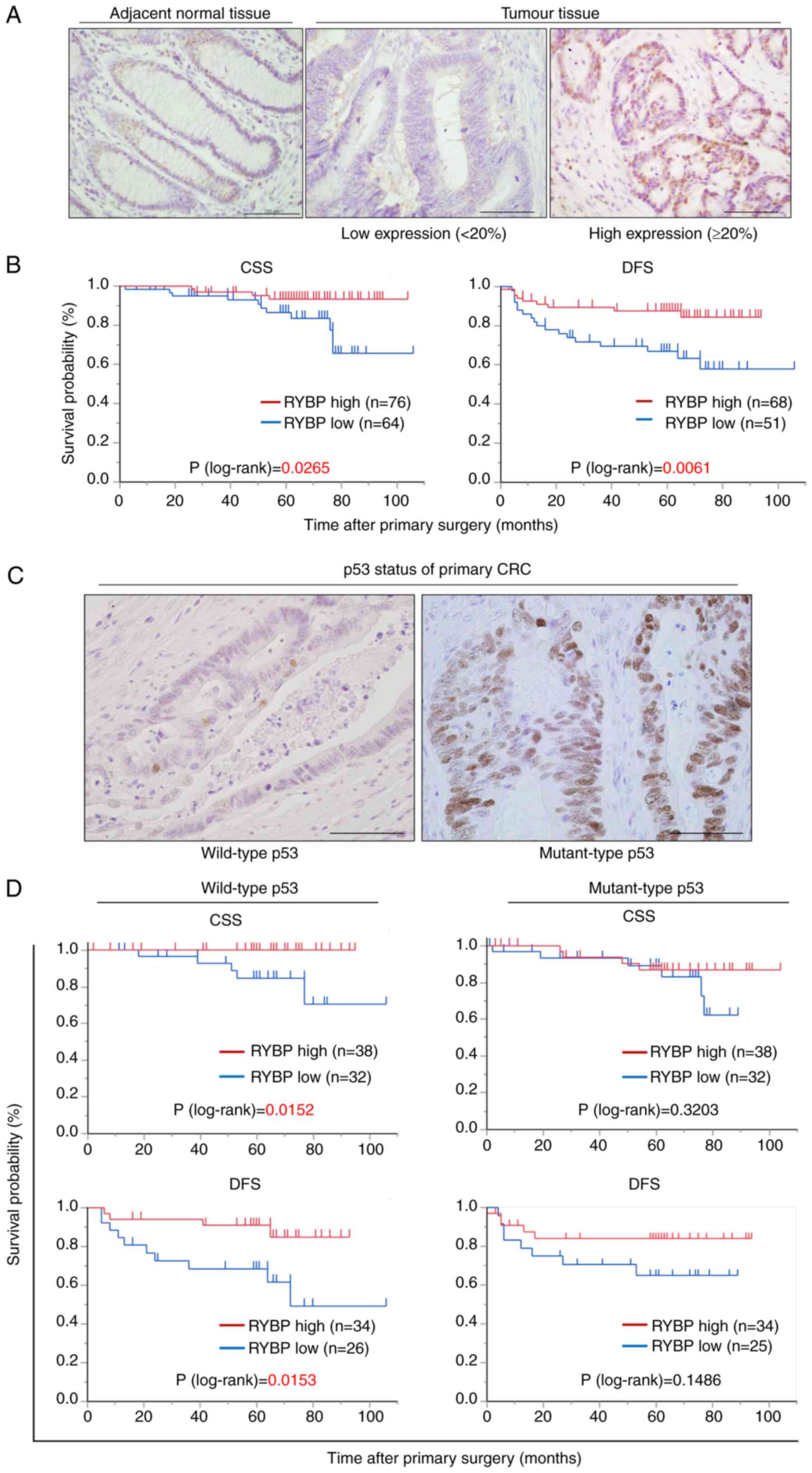
K, Takayashiki T, Kuboki S, Takano S, Suzuki D, Kagawa S, Mishima
T, et al: High expression of Krüppel-like factor 5 is associated
with poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci.
111:2078–2092. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
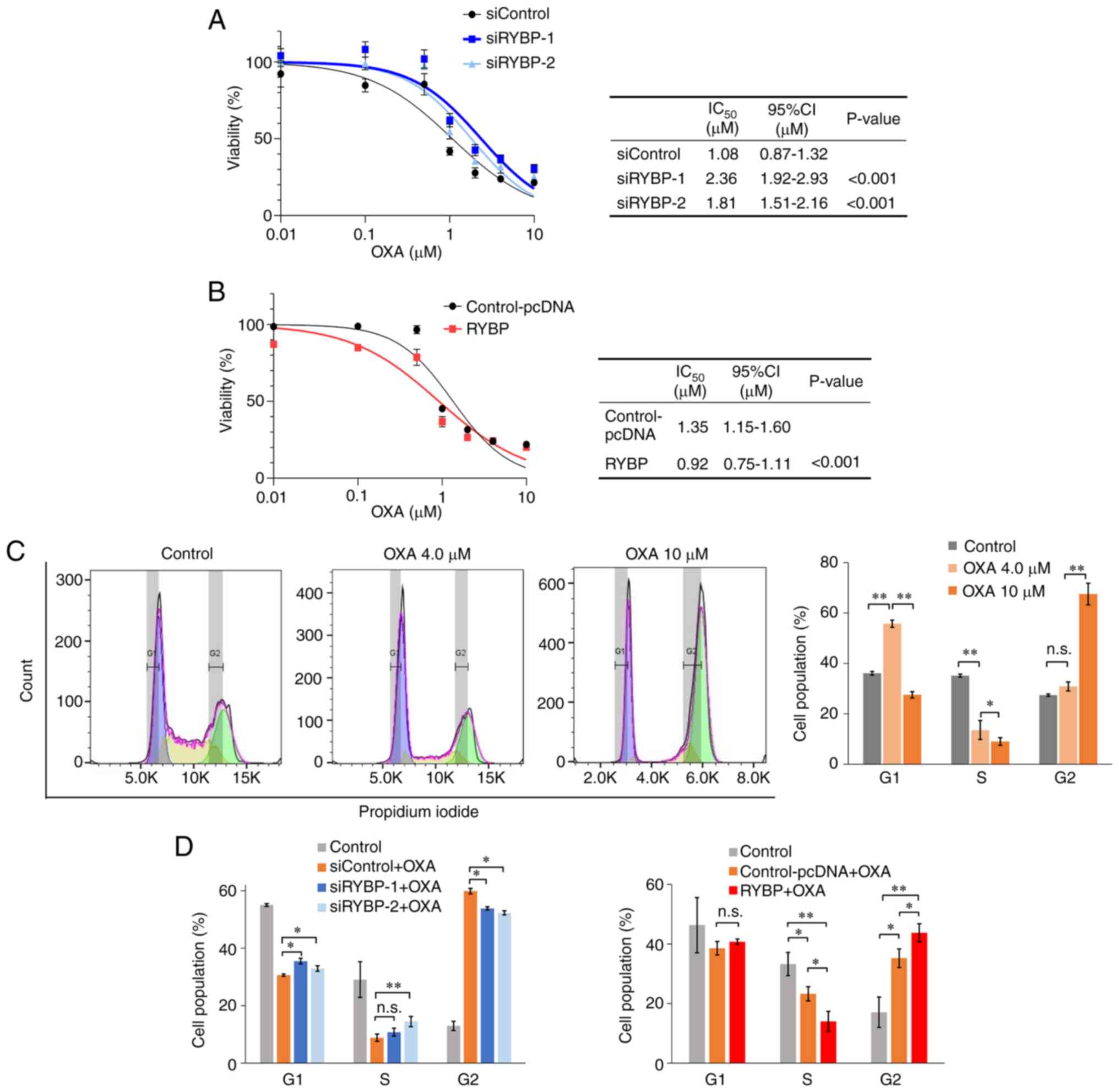
6
|
Sato N, Sakai N, Furukawa K, Takayashiki
T, Kuboki S, Takano S, Ohira G, Miyauchi H, Matsubara H and Ohtsuka
M: Tumor-suppressive role of Smad ubiquitination regulatory factor
2 in patients with colorectal cancer. Sci Rep. 12:54952022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
García E, Marcos-Gutiérrez C, del Mar
Lorente M, Moreno JC and Vidal M: RYBP, a new repressor protein
that interacts with components of the mammalian polycomb complex,
and with the transcription factor YY1. EMBO J. 18:3404–3418. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tavares L, Dimitrova E, Oxley D, Webster
J, Poot R, Demmers J, Bezstarosti K, Taylor S, Ura H, Koide H, et
al: RYBP-PRC1 complexes mediate H2A ubiquitylation at polycomb
target sites independently of PRC2 and H3K27me3. Cell. 148:664–678.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Simoes da Silva CJ, Simón R and Busturia
A: Epigenetic and non-epigenetic functions of the RYBP protein in
development and disease. Mech Ageing Dev. 174:111–120. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sawa C, Yoshikawa T, Matsuda-Suzuki F,
Deléhouzée S, Goto M, Watanabe H, Sawada J, Kataoka K and Handa H:
YEAF1/RYBP and YAF-2 are functionally distinct members of a
cofactor family for the YY1 and E4TF1/hGABP transcription factors.
J Biol Chem. 277:22484–22490. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schlisio S, Halperin T, Vidal M and Nevins
JR: Interaction of YY1 with E2Fs, mediated by RYBP, provides a
mechanism for specificity of E2F function. EMBO J. 21:5775–5786.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang W, Cheng J, Qin JJ, Voruganti S, Nag
S, Fan J, Gao Q and Zhang R: RYBP expression is associated with
better survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and
responsiveness to chemotherapy of HCC cells in vitro and in vivo.
Oncotarget. 5:11604–11619. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou H, Li J, Zhang Z, Ye R, Shao N,
Cheang T and Wang S: RING1 and YY1 binding protein suppresses
breast cancer growth and metastasis. Int J Oncol. 49:2442–2452.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dinglin X, Ding L, Li Q, Liu Y, Zhang J
and Yao H: RYBP inhibits progression and metastasis of lung cancer
by suppressing EGFR signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Transl Oncol. 10:280–287. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ke Y, Guo W, Huang S, Li Y, Guo Y, Liu X,
Jin Y and Ma H: RYBP inhibits esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
proliferation through downregulating CDC6 and CDC45 in G1-S phase
transition process. Life Sci. 250:1175782020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brierley JD, Gospodarowicz MK and
Wittekind C (eds): TNM classification of malignant tumours. 8th
edition. Wiley-Blackwel; 2016
|
|
17
|
He G, Siddik ZH, Huang Z, Wang R, Koomen
J, Kobayashi R, Khokhar AR and Kuang J: Induction of p21 by p53
following DNA damage inhibits both Cdk4 and Cdk2 activities.
Oncogene. 24:2929–2943. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen D, Zhang J, Li M, Rayburn ER, Wang H
and Zhang R: RYBP stabilizes p53 by modulating MDM2. EMBO Rep.
10:166–172. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Meyerhardt JA and Mayer RJ: Systemic
therapy for colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 352:476–487. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang C, Wang H, Deng M, He L, Ping F, He
Y, Fan Z, Cheng B and Xia J: Upregulated miR-411-5p levels promote
lymph node metastasis by targeting RYBP in head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 47:362021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Voruganti S, Xu F, Qin JJ, Guo Y, Sarkar
S, Gao M, Zheng Z, Wang MH, Zhou J, Qian B, et al: RYBP predicts
survival of patients with non-small cell lung cancer and regulates
tumor cell growth and the response to chemotherapy. Cancer Lett.
369:386–395. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tong AH, Tan J, Zhang JH, Xu FJ, Li FY and
Cao CY: Overexpression of RYBP inhibits proliferation, invasion,
and chemoresistance to cisplatin in anaplastic thyroid cancer cells
via the EGFR pathway. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 33:e222412019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhu X, Yan M, Luo W, Liu W, Ren Y, Bei C,
Tang G, Chen R and Tan S: Expression and clinical significance of
PcG-associated protein RYBP in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol
Lett. 13:141–150. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Alt JR, Gladden AB and Diehl JA: p21(Cip1)
promotes cyclin D1 nuclear accumulation via direct inhibition of
nuclear export. J Biol Chem. 277:8517–8523. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Diehl JA, Zindy F and Sherr CJ: Inhibition
of cyclin D1 phosphorylation on threonine-286 prevents its rapid
degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Genes Dev.
11:957–972. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chipuk JE, Kuwana T, Bouchier-Hayes L,
Droin NM, Newmeyer DD, Schuler M and Green DR: Direct activation of
Bax by p53 mediates mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and
apoptosis. Science. 303:1010–1014. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tan K, Zhang X, Cong X, Huang B, Chen H
and Chen D: Tumor suppressor RYBP harbors three nuclear
localization signals and its cytoplasm-located mutant exerts more
potent anti-cancer activities than corresponding wild type. Cell
Signal. 29:127–137. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Danen-van Oorschot AA, Voskamp P, Seelen
MC, van Miltenburg MH, Bolk MW, Tait SW, Boesen-de Cock JG, Rohn
JL, Borst J and Noteborn MH: Human death effector domain-associated
factor interacts with the viral apoptosis agonist apoptin and
exerts tumor-preferential cell killing. Cell Death Differ.
11:564–573. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zheng L, Schickling O, Peter ME and
Lenardo MJ: The death effector domain-associated factor plays
distinct regulatory roles in the nucleus and cytoplasm. J Biol
Chem. 276:31945–31952. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ilie M, Long-Mira E, Bence C, Butori C,
Lassalle S, Bouhlel L, Fazzalari L, Zahaf K, Lalvée S, Washetine K,
et al: Comparative study of the PD-L1 status between surgically
resected specimens and matched biopsies of NSCLC patients reveal
major discordances: A potential issue for anti-PD-L1 therapeutic
strategies. Ann Oncol. 27:147–153. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ganepola GAP, Mazziotta RM, Weeresinghe D,
Corner GA, Parish CJ, Chang DH, Tebbutt NC, Murone C, Ahmed N,
Augenlicht LH and Mariadason JM: Gene expression profiling of
primary and metastatic colon cancers identifies a reduced
proliferative rate in metastatic tumors. Clin Exp Metastasis.
27:1–9. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Swanton C: Intratumor heterogeneity:
Evolution through space and time. Cancer Res. 72:4875–4882. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Burrell RA, McGranahan N, Bartek J and
Swanton C: The causes and consequences of genetic heterogeneity in
cancer evolution. Nature. 501:338–345. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rogel A, Popliker M, Webb CG and Oren M:
p53 cellular tumor antigen: Analysis of mRNA levels in normal adult
tissues, embryos, and tumors. Mol Cell Biol. 5:2851–2855.
1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Finlay CA, Hinds PW, Tan TH, Eliyahu D,
Oren M and Levine AJ: Activating mutations for transformation by
p53 produce a gene product that forms an hsc70-p53 complex with an
altered half-life. Mol Cell Biol. 8:531–539. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Oh HJ, Bae JM, Wen X, Jung S, Kim Y, Kim
KJ, Cho NY, Kim JH, Han SW, Kim TY and Kang GH: p53 expression
status is associated with cancer-specific survival in stage III and
high-risk stage II colorectal cancer patients treated with
oxaliplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy. Br J Cancer. 120:797–805.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rehman SK, Haynes J, Collignon E, Brown
KR, Wang Y, Nixon AML, Bruce JP, Wintersinger JA, Singh Mer A, Lo
EBL, et al: Colorectal cancer cells enter a diapause-like DTP state
to survive chemotherapy. Cell. 184:226–242.e21. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ketkar M and Dutt S: Epigenetic regulation
towards acquired drug resistance in cancer. Subcell Biochem.
100:473–502. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kobayashi T, Makino T, Yamashita K, Saito
T, Tanaka K, Takahashi T, Kurokawa Y, Yamasaki M, Nakajima K, Morii
E, et al: APR-246 induces apoptosis and enhances chemo-sensitivity
via activation of ROS and TAp73-Noxa signal in oesophageal squamous
cell cancer with TP53 missense mutation. Br J Cancer.
125:1523–1532. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Geisler S, Børresen-Dale AL, Johnsen H,
Aas T, Geisler J, Akslen LA, Anker G and Lønning PE: TP53 gene
mutations predict the response to neoadjuvant treatment with
5-fluorouracil and mitomycin in locally advanced breast cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 9:5582–5588. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen X, Zhang T, Su W, Dou Z, Zhao D, Jin
X, Lei H, Wang J, Xie X, Cheng B, et al: Mutant p53 in cancer: from
molecular mechanism to therapeutic modulation. Cell Death Dis.
13:9742022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Longley DB, Harkin DP and Johnston PG:
5-fluorouracil: Mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat
Rev Cancer. 3:330–338. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xu Y and Villalona-Calero MA: Irinotecan:
Mechanisms of tumor resistance and novel strategies for modulating
its activity. Ann Oncol. 13:1841–1851. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Blagih J, Buck MD and Vousden KH: p53,
cancer and the immune response. J Cell Sci. 133:jcs2374532020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Levine AJ: P53 and the immune response: 40
Years of exploration-a plan for the future. Int J Mol Sci.
21:5412020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Oshima H, Nakayama M, Han TS, Naoi K, Ju
X, Maeda Y, Robine S, Tsuchiya K, Sato T, Sato H, et al:
Suppressing TGFβ signaling in regenerating epithelia in an
inflammatory microenvironment is sufficient to cause invasive
intestinal cancer. Cancer Res. 75:766–776. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Goodla L and Xue X: The role of
inflammatory mediators in colorectal cancer hepatic metastasis.
Cells. 11:23132022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|