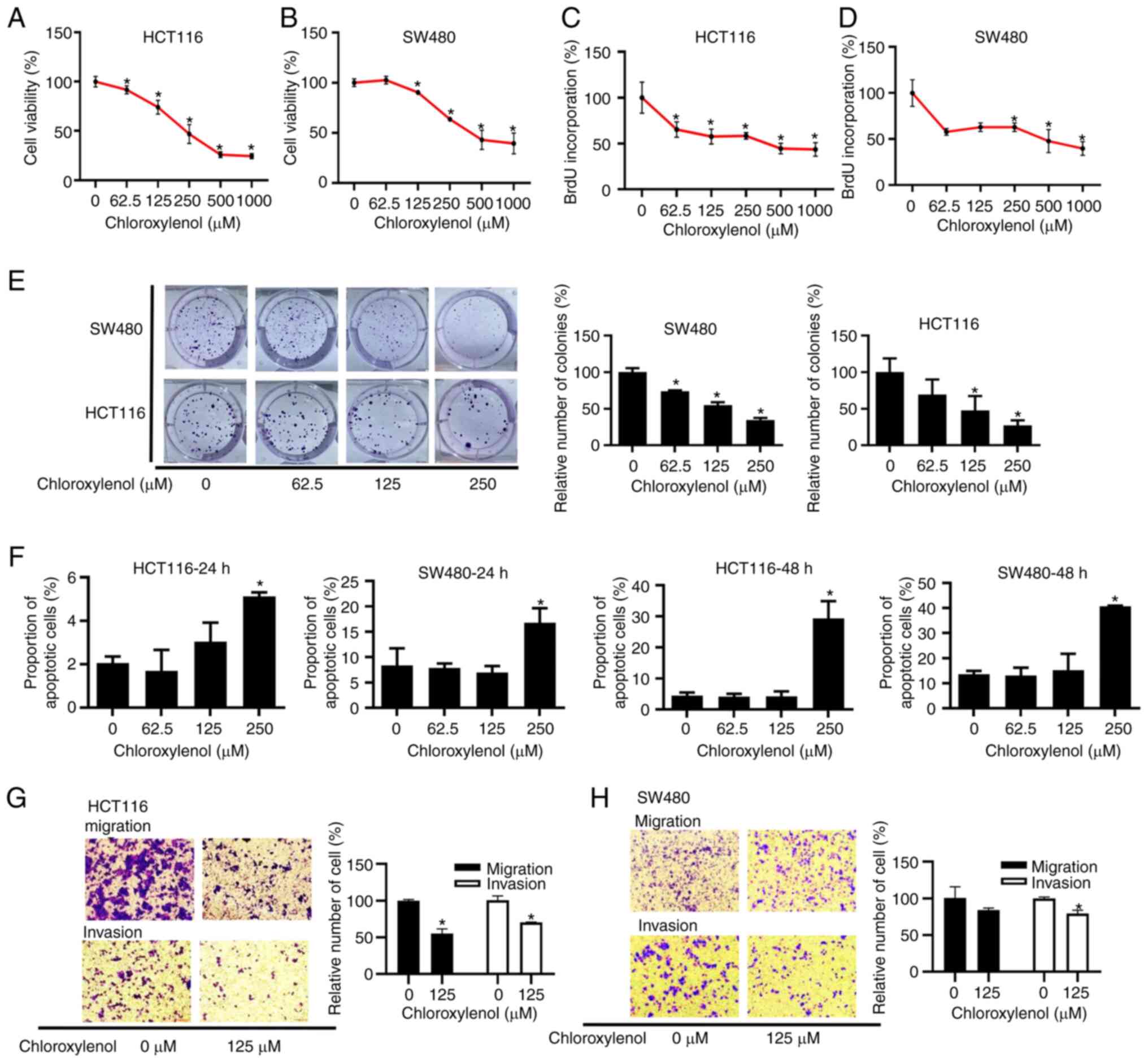
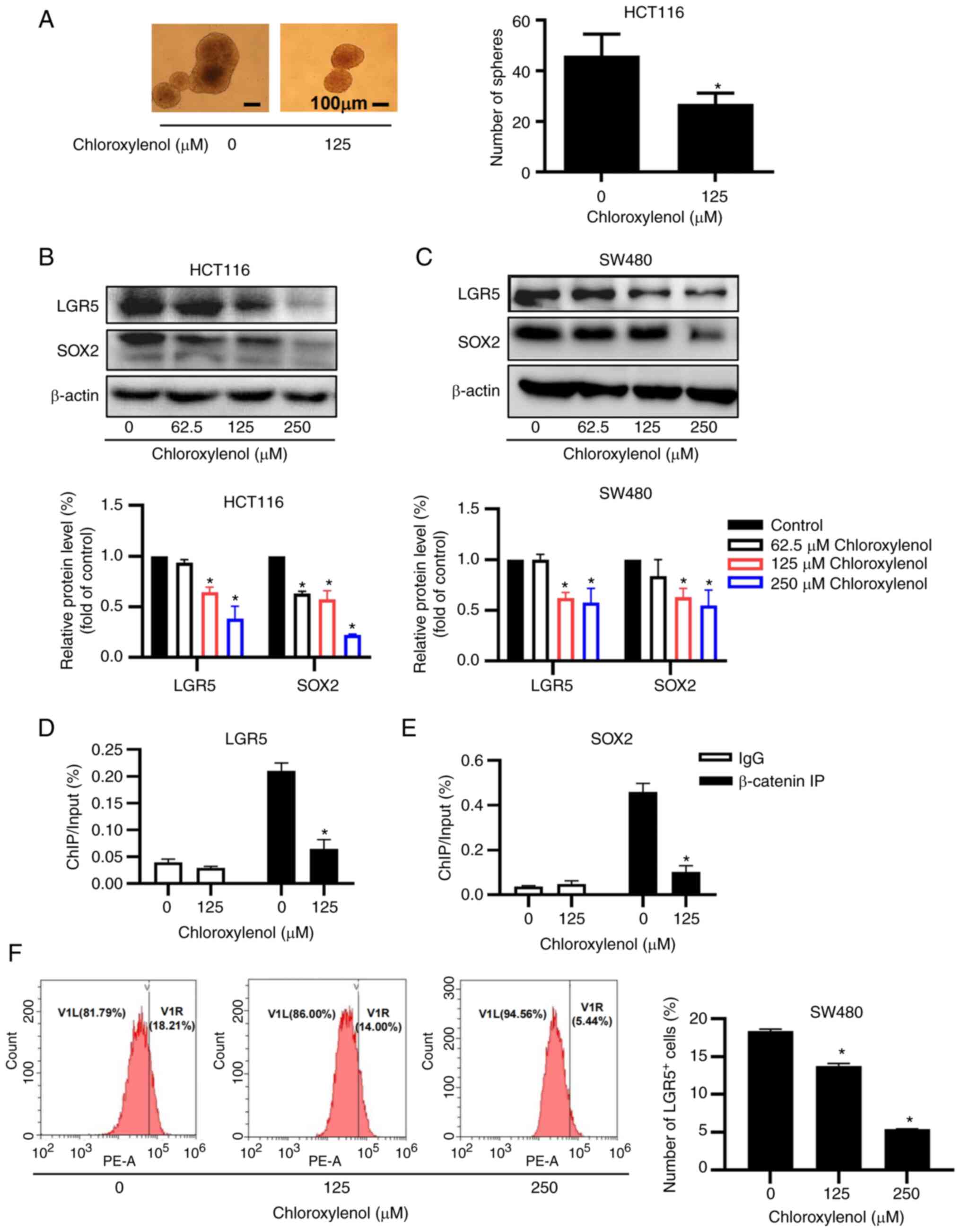
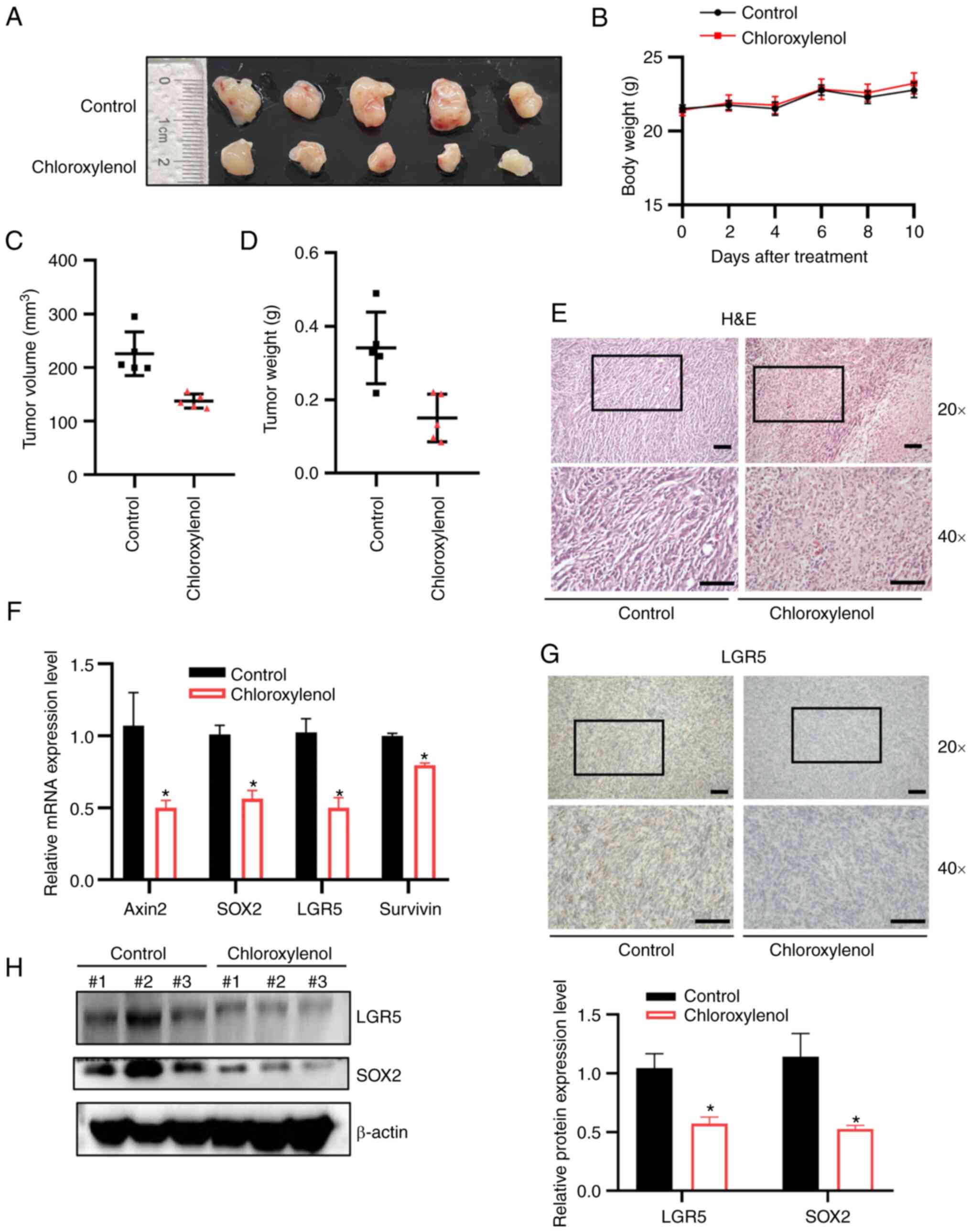
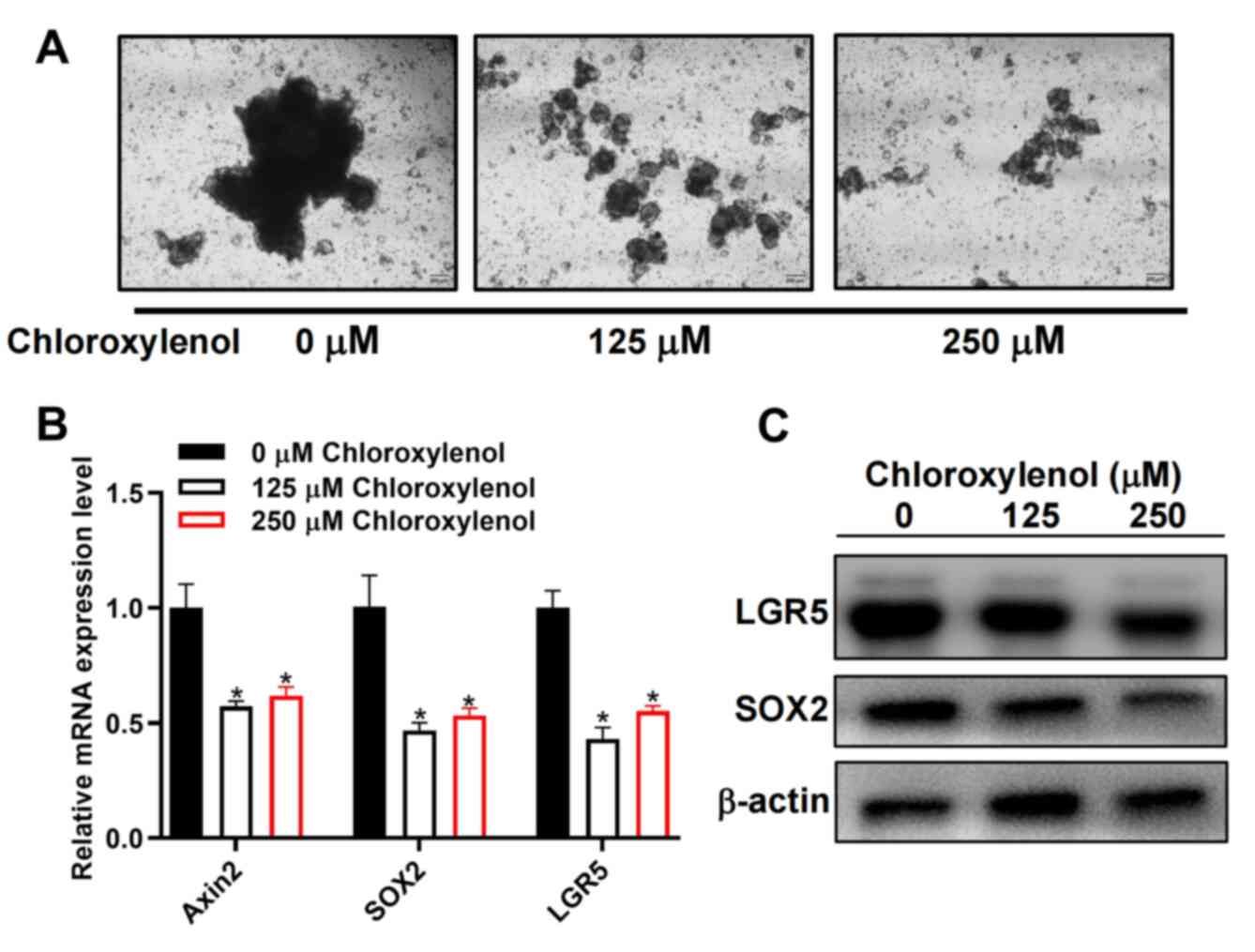
|
1
|
Rundle CW, Hu S, Presley CL and Dunnick
CA: Triclosen and its alternatives in antibacterial soaps.
Dermatitis. 30:352–357. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sreevidya VS, Lenz KA, Svoboda KR and Ma
H: Benzalkonium chloride, benzethonium chloride, and
chloroxylenol-three replacement antimicrobials are more toxic than
triclosan and triclocarban in two model organisms. Environ Pollut.
235:814–824. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Antunes SC, Nunes B, Rodrigues S, Nunes R,
Fernandes J and Correia AT: Effects of chronic exposure to
benzalkonium chloride in Oncorhynchus mykiss: Cholinergic
neurotoxicity, oxidative stress, peroxidative damage and
genotoxicity. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 45:115–122. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Food and Drug Adminnistration, HHS: Safety
and effectiveness of consumer antiseptics; topical antimicrobial
drug products for over-the-counter human use. Final rule. Fed
Regist. 81:61106–61130. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang J, Shan S, Li D, Zhang Z and Ma Q:
Long-term influence of chloroxylenol on anaerobic microbial
community: Performance, microbial interaction, and antibiotic
resistance gene behaviors. Sci Total Environ. 897:1653302023.Epub
ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA
and Jemal A: Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin.
73:233–254. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Biller LH and Schrag D: Diagnosis and
treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: A review. JAMA.
325:669–685. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Doubeni CA, Corley DA, Quinn VP, Jensen
CD, Zauber AG, Goodman M, Johnson JR, Mehta SJ, Becerra TA, Zhao
WK, et al: Effectiveness of screening colonoscopy in reducing the
risk of death from right and left colon cancer: A large
community-based study. Gut. 67:291–298. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Song M, Garrett WS and Chan AT: Nutrients,
foods, and colorectal cancer prevention. Gastroenterology.
148:1244–1260.e16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lytle NK, Barber AG and Reya T: Stem cell
fate in cancer growth, progression and therapy resistance. Nat Rev
Cancer. 18:669–680. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Meacham CE and Morrison SJ: Tumour
heterogeneity and cancer cell plasticity. Nature. 501:328–337.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chaffer CL and Weinberg RA: A perspective
on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 331:1559–1564. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang L, Shi P, Zhao G, Xu J, Peng W, Zhang
J, Zhang G, Wang X, Dong Z, Chen F and Cui H: Targeting cancer stem
cell pathways for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
5:82020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Clevers H: The cancer stem cell: Premises,
promises and challenges. Nat Med. 17:313–319. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Medema JP: Targeting the colorectal cancer
stem cell. N Engl J Med. 377:888–890. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shimokawa M, Ohta Y, Nishikori S, Matano
M, Takano A, Fujii M, Date S, Sugimoto S, Kanai T and Sato T:
Visualization and targeting of LGR5+ human colon cancer
stem cells. Nature. 545:187–192. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Frank MH, Wilson BJ, Gold JS and Frank NY:
Clinical implications of colorectal cancer stem cells in the age of
single-cell omics and targeted therapies. Gastroenterology.
160:1947–1960. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Batlle E and Clevers H: Cancer stem cells
revisited. Nat Med. 23:1124–1134. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nusse R and Clevers H: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell.
169:985–999. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
MacDonald BT, Tamai K and He X:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases.
Dev Cell. 17:9–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network: Comprehensive
molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer.
Nature. 487:330–337. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wood LD, Parsons DW, Jones S, Lin J,
Sjöblom T, Leary RJ, Shen D, Boca SM, Barber T, Ptak J, et al: The
genomic landscapes of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science.
318:1108–1113. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang L and Shay JW: Multiple roles of APC
and its therapeutic implications in colorectal cancer. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 109:djw3322017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Krishnamurthy N and Kurzrock R: Targeting
the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in cancer: Update on effectors and
inhibitors. Cancer Treat Rev. 62:50–60. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Bilic J, Huang YL, Davidson G, Zimmermann
T, Cruciat CM, Bienz M and Niehrs C: Wnt induces LRP6 signalosomes
and promotes dishevelled-dependent LRP6 phosphorylation. Science.
316:1619–1622. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gao C and Chen YG: Dishevelled: The hub of
Wnt signaling. Cell Signal. 22:717–727. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Valenta T, Hausmann G and Basler K: The
many faces and functions of β-catenin. EMBO J. 31:2714–2736. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Behrens J, von Kries JP, Kühl M, Bruhn L,
Wedlich D, Grosschedl R and Birchmeier W: Functional interaction of
beta-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature.
382:638–642. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Doumpas N, Lampart F, Robinson MD, Lentini
A, Nestor CE, Cantù C and Basler K: TCF/LEF dependent and
independent transcriptional regulation of Wnt/β-catenin target
genes. EMBO J. 38:e988732019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Poger D and Mark AE: Effect of triclosan
and chloroxylenol on bacterial membranes. J Phys Chem B.
123:5291–5301. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cutts TA, Ijaz MK, Nims RW, Rubino JR and
Theriault SS: Effectiveness of dettol antiseptic liquid for
inactivation of Ebola virus in suspension. Sci Rep. 9:65902019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nowak M, Zawadzka K, Szemraj J,
Góralczyk-Bińkowska A and Lisowska K: Biodegradation of
chloroxylenol by cunninghamella elegans IM 1785/21GP and trametes
versicolor IM 373: Insight into ecotoxicity and metabolic pathways.
Int J Mol Sci. 22:43602021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang Z, Zhou L, Xiong Y, Yu S, Li H, Fan
J, Li F, Su Z, Song J, Sun Q, et al: Salinomycin exerts
anti-colorectal cancer activity by targeting the β-catenin/T-cell
factor complex. Br J Pharmacol. 176:3390–3406. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wang L, Deng K, Gong L, Zhou L, Sayed S,
Li H, Sun Q, Su Z, Wang Z, Liu S, et al: Chlorquinaldol targets the
β-catenin and T-cell factor 4 complex and exerts anti-colorectal
cancer activity. Pharmacol Res. 159:1049552020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Sun Q, Wang Y, Fu Q, Ouyang A, Liu S, Wang
Z, Su Z, Song J, Zhang Q, Zhang P and Lu D: Sulfur-coordinated
organoiridium(III) complexes exert breast anticancer activity via
inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl.
60:4841–4848. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhao H, Ming T, Tang S, Ren S, Yang H, Liu
M, Tao Q and Xu H: Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer: Pathogenic
role and therapeutic target. Mol Cancer. 21:1442022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hagen T, Di Daniel E, Culbert AA and Reith
AD: Expression and characterization of GSK-3 mutants and their
effect on beta-catenin phosphorylation in intact cells. J Biol
Chem. 277:23330–23335. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xu C, Xu Z, Zhang Y, Evert M, Calvisi DF
and Chen X: β-Catenin signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin
Invest. 132:e1545152022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Su Z, Song J, Wang Z, Zhou L, Xia Y, Yu S,
Sun Q, Liu SS, Zhao L, Li S, et al: Tumor promoter TPA activates
Wnt/β-catenin signaling in a casein kinase 1-dependent manner. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 115:E7522–E7531. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Bazzi H, Fantauzzo KA, Richardson GD,
Jahoda CA and Christiano AM: The Wnt inhibitor, Dickkopf 4, is
induced by canonical Wnt signaling during ectodermal appendage
morphogenesis. Dev Biol. 305:498–507. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lundberg IV, Edin S, Eklöf V, Öberg Å,
Palmqvist R and Wikberg ML: SOX2 expression is associated with a
cancer stem cell state and down-regulation of CDX2 in colorectal
cancer. BMC Cancer. 16:4712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dellanno C, Vega Q and Boesenberg D: The
antiviral action of common household disinfectants and antiseptics
against murine hepatitis virus, a potential surrogate for SARS
coronavirus. Am J Infect Control. 37:649–652. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yost LJ, Rodricks JD, Turnbull D, DeLeo
PC, Nash JF, Quiñones-Rivera A and Carlson PA: Human health risk
assessment of chloroxylenol in liquid hand soap and dishwashing
soap used by consumers and health-care professionals. Regul Toxicol
Pharmacol. 80:116–124. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yang H, Wang W, Romano KA, Gu M, Sanidad
KZ, Kim D, Yang J, Schmidt B, Panigrahy D, Pei R, et al: A common
antimicrobial additive increases colonic inflammation and
colitis-associated colon tumorigenesis in mice. Sci Transl Med.
10:eaan41162018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yang H, Sanidad KZ, Wang W, Xie M, Gu M,
Cao X, Xiao H and Zhang G: Triclocarban exposure exaggerates
colitis and colon tumorigenesis: Roles of gut microbiota involved.
Gut Microbes. 12:16903642020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
48
|
Sanidad KZ, Yang H, Wang W, Ozay EI, Yang
J, Gu M, Karner E, Zhang J, Kim D, Minter LM, et al: Effects of
consumer antimicrobials benzalkonium chloride, benzethonium
chloride, and chloroxylenol on colonic inflammation and
colitis-associated colon tumorigenesis in mice. Toxicol Sci.
163:490–499. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kaplan GG: The global burden of IBD: From
2015 to 2025. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 12:720–727. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Rogler G: Chronic ulcerative colitis and
colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 345:235–241. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Rubin DC, Shaker A and Levin MS: Chronic
intestinal inflammation: Inflammatory bowel disease and
colitis-associated colon cancer. Front Immunol. 3:1072012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tian A, Benchabane H and Ahmed Y:
Wingless/Wnt signaling in intestinal development, homeostasis,
regeneration and tumorigenesis: A drosophila perspective. J Dev
Biol. 6:82018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
You J, Nguyen AV, Albers CG, Lin F and
Holcombe RF: Wnt pathway-related gene expression in inflammatory
bowel disease. Dig Dis Sci. 53:1013–1019. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Swafford D, Shanmugam A, Ranganathan P,
Hussein MS, Koni PA, Prasad PD, Thangaraju M and Manicassamy S:
Canonical Wnt signaling in CD11c+ APCs regulates
microbiota-induced inflammation and immune cell homeostasis in the
colon. J Immunol. 200:3259–3268. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Shlush LI, Mitchell A, Heisler L, Abelson
S, Ng SWK, Trotman-Grant A, Medeiros JJF, Rao-Bhatia A,
Jaciw-Zurakowsky I, Marke R, et al: Tracing the origins of relapse
in acute myeloid leukaemia to stem cells. Nature. 547:104–108.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Phi LTH, Sari IN, Yang YG, Lee SH, Jun N,
Kim KS, Lee YK and Kwon HY: Cancer stem cells (CSCs) in drug
resistance and their therapeutic implications in cancer treatment.
Stem Cells Int. 2018:54169232018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Katoh M and Katoh M: WNT signaling and
cancer stemness. Essays Biochem. 66:319–331. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ring A, Kim YM and Kahn M: Wnt/catenin
signaling in adult stem cell physiology and disease. Stem Cell Rev
Rep. 10:512–525. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|