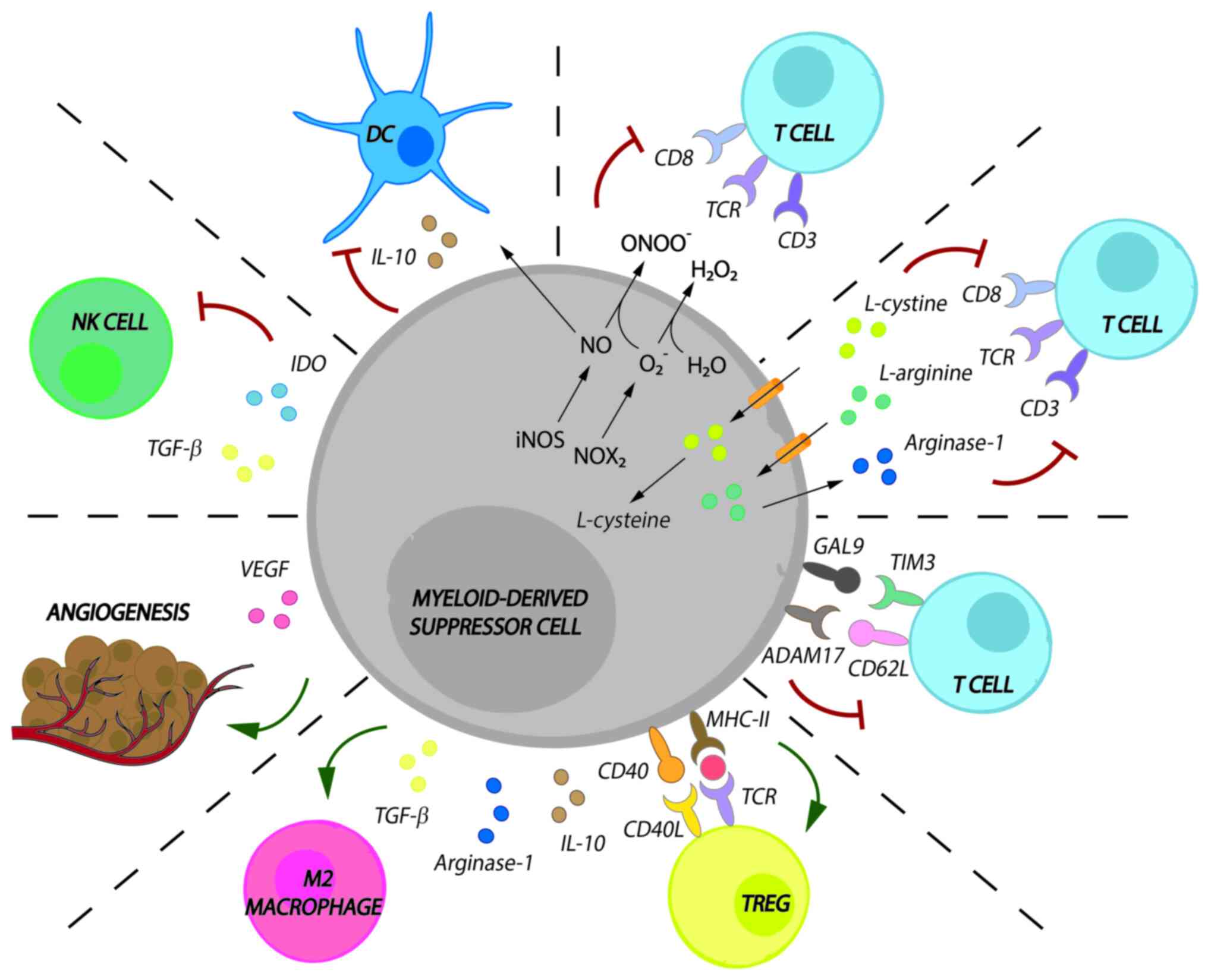
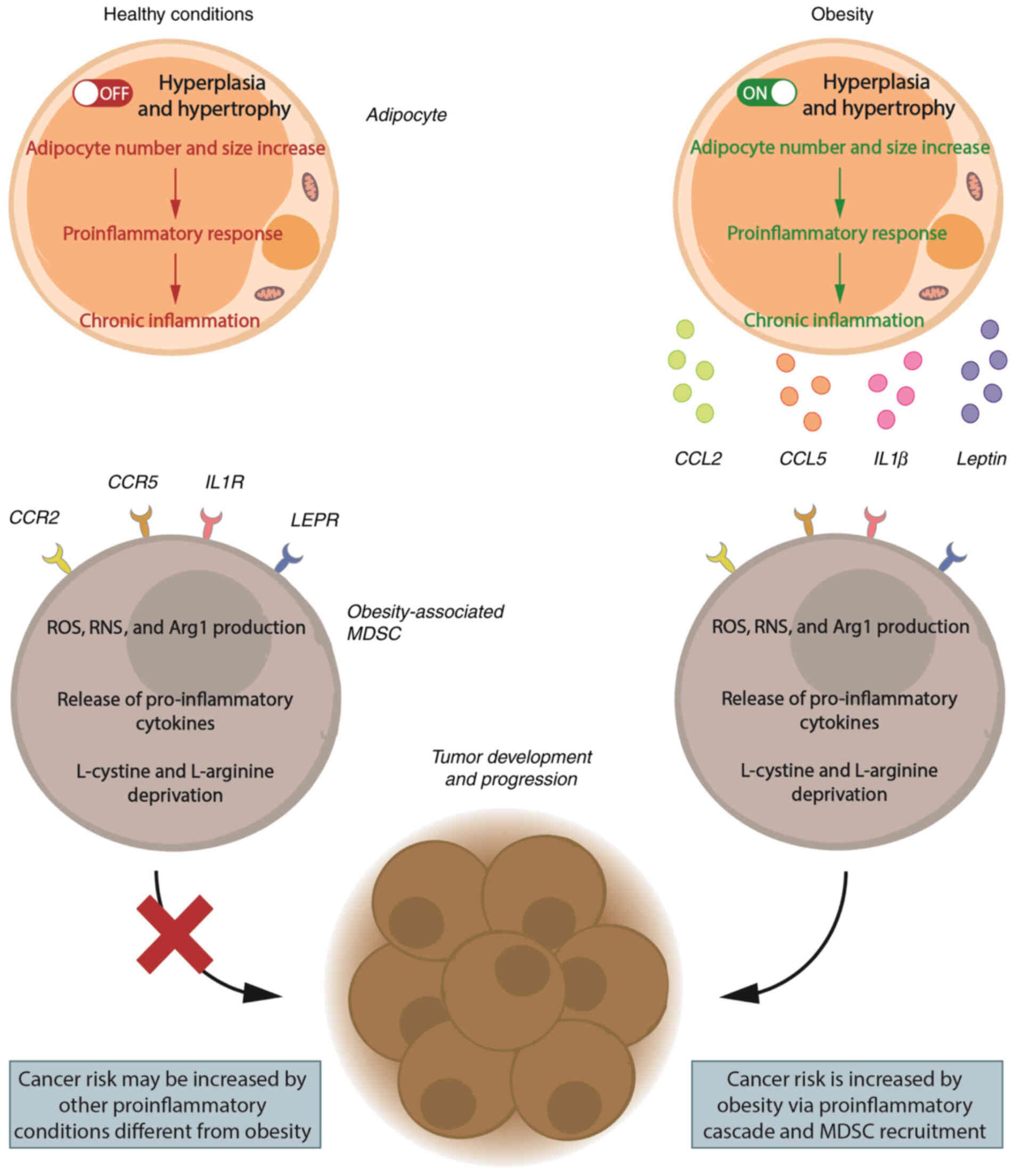
|
1
|
Lee H, Lee IS and Choue R: Obesity,
inflammation and diet. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
16:143–152. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ben-Shmuel S, Rostoker R, Scheinman EJ and
LeRoith D: Metabolic Syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and cancer:
Epidemiology and potential mechanisms. Handb Exp Pharmacol.
233:355–372. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Jiang SZ, Lu W, Zong XF, Ruan HY and Liu
Y: Obesity and hypertension. Exp Ther Med. 12:2395–2399. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Klop B, Elte JW and Cabezas MC:
Dyslipidemia in obesity: Mechanisms and potential targets.
Nutrients. 5:1218–1240. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Broughton DE and Moley KH: Obesity and
female infertility: Potential mediators of obesity's impact. Fertil
Steril. 107:840–847. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sanchez-Pino MD, Gilmore LA, Ochoa AC and
Brown JC: Obesity-Associated myeloid immunosuppressive cells, key
players in cancer risk and response to immunotherapy. Obesity
(Silver Spring). 29:944–953. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Munn LL: Cancer and inflammation. Wiley
Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 9: View Article : Google Scholar : 2017.
|
|
8
|
Greten FR and Grivennikov SI: Inflammation
and Cancer: Triggers, mechanisms, and consequences. Immunity.
51:27–41. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jimenez-Cortegana C, Palazon-Carrion N,
Martin Garcia-Sancho A, Nogales-Fer nandez E, Carnicero-Gonzalez F,
Rios-Herranz E, de la Cruz-Vicente F, Rodríguez-García G,
Fernández-Álvarez R, Rueda Dominguez A, et al: Circulating
myeloid-derived suppressor cells and regulatory T cells as
immunological biomarkers in refractory/relapsed diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma: Translational results from the R2-GDP-GOTEL trial.
J Immunother Cancer. 9:e0023232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Karin N: The development and homing of
myeloid-derived suppressor cells: From a two-stage model to a
multistep narrative. Front Immunol. 11:5575862020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Law AMK, Valdes-Mora F and Gallego-Ortega
D: Myeloid-Derived suppressor cells as a therapeutic target for
cancer. Cells. 9:5612020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Movahedi K, Guilliams M, Van den Bossche
J, Van den Bergh R, Gysemans C, Beschin A, De Baetselier P and Van
Ginderachter JA: Identification of discrete tumor-induced
myeloid-derived suppressor cell subpopulations with distinct T
cell-suppressive activity. Blood. 111:4233–4244. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bronte V, Brandau S, Chen SH, Colombo MP,
Frey AB, Greten TF, Mandruzzato S, Murray PJ, Ochoa A,
Ostrand-Rosenberg S, et al: Recommendations for myeloid-derived
suppressor cell nomenclature and characterization standards. Nat
Commun. 7:121502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jimenez-Cortegana C, Liro J,
Palazon-Carrion N, Salamanca E, Sojo-Dorado J, de la Cruz-Merino L,
Pascual Á, Rodríguez-Baño J and Sánchez-Margalet V: Increased blood
monocytic myeloid derived suppressor cells but low regulatory T
lymphocytes in patients with mild COVID-19. Viral Immunol.
34:639–645. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jimenez-Cortegana C, Sanchez - Martinez P
M, Palazon-Carrion N, Nogales-Fernandez E, Henao-Carrasco F, Martin
Garcia-Sancho A, Rueda A, Provencio M, de la Cruz-Merino L and
Sánchez-Margalet V: Lower survival and increased circulating
suppressor cells in patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large
B-Cell lymphoma with deficit of vitamin D Levels Using R-GDP Plus
Lenalidomide (R2-GDP): Results from the R2-GDP-GOTEL Trial. Cancers
(Basel). 13:46222021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Farshidpour M, Ahmed M, Junna S and
Merchant JL: Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in gastrointestinal
cancers: A systemic review. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 13:1–11.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
O'Connor MA, Rastad JL and Green WR: The
role of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in viral infection. Viral
Immunol. 30:82–97. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yan L, Liang M, Yang T, Ji J, Jose Kumar
Sreena GS, Hou X, Cao M and Feng Z: The immunoregulatory role of
myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the pathogenesis of Rheumatoid
arthritis. Front Immunol. 11:5683622020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang Z, Guo J, Weng L, Tang W, Jin S and
Ma W: Myeloid-derived suppressor cells-new and exciting players in
lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 13:102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Youn JI, Nagaraj S, Collazo M and
Gabrilovich DI: Subsets of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in
tumor-bearing mice. J Immunol. 181:5791–5802. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Talmadge JE and Gabrilovich DI: History of
myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:739–752. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Arner E, Mejhert N, Kulyte A, Balwierz PJ,
Pachkov M, Cormont M, Lorente-Cebrián S, Ehrlund A, Laurencikiene
J, Hedén P, et al: Adipose tissue microRNAs as regulators of CCL2
production in human obesity. Diabetes. 61:1986–1993. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Oo MW, Kawai H, Takabatake K, Tomida S,
Eguchi T, Ono K, Shan Q, Ohara T, Yoshida S, Omori H, et al:
Resident stroma-secreted chemokine CCL2 governs myeloid-derived
suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment. JCI Insight.
7:e1489602022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Martinez-Chacon G, Yatkin E, Polari L,
Deniz Dinc D, Peuhu E, Hartiala P, Saarinen N and Mäkelä S: CC
chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2) stimulates aromatase gene expression in
mammary adipose tissue. FASEB J. 35:e215362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Friesenhengst A, Pribitzer-Winner T, Miedl
H, Prostling K and Schreiber M: Elevated aromatase (CYP19A1)
expression is associated with a poor survival of patients with
estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. Horm Cancer. 9:128–138.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Boi SK, Orlandella RM, Gibson JT, Turbitt
WJ, Wald G, Thomas L, Buchta Rosean C, Norris KE, Bing M, Bertrand
L, et al: Obesity diminishes response to PD-1-based immunotherapies
in renal cancer. J Immunother Cancer. 8:e0007252020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Liu Y, Tiruthani K, Wang M, Zhou X, Qiu N,
Xiong Y, Pecot CV, Liu R and Huang L: Tumor-targeted gene therapy
with lipid nanoparticles inhibits tumor-associated adipocytes and
remodels the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in
triple-negative breast cancer. Nanoscale Horiz. 6:319–329. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
James BR, Anderson KG, Brincks EL, Kucaba
TA, Norian LA, Masopust D and Griffith TS: CpG-mediated modulation
of MDSC contributes to the efficacy of Ad5-TRAIL therapy against
renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 63:1213–1227.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hale M, Itani F, Buchta CM, Wald G, Bing M
and Norian LA: Obesity triggers enhanced MDSC accumulation in
murine renal tumors via elevated local production of CCL2. PLoS
One. 10:e01187842015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiao P, Chen Q, Shah S, Du J, Tao B,
Tzameli I, Yan W and Xu H: Obesity-related upregulation of monocyte
chemotactic factors in adipocytes: Involvement of nuclear
factor-kappaB and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathways. Diabetes.
58:104–115. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Li B, Zhang S, Huang N, Chen H, Wang P,
Yang J and Li Z: CCL9/CCR1 induces myeloidderived suppressor cell
recruitment to the spleen in a murine H22 orthotopic hepatoma
model. Oncol Rep. 41:608–618. 2019.
|
|
32
|
Peng J, Hu Q, Chen X, Wang C, Zhang J, Ren
X, Wang Y, Tao X, Li H, Song M, et al: Diet-induced obesity
accelerates oral carcinogenesis by recruitment and functional
enhancement of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Cell Death Dis.
12:9462021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang Q, Yu B, Kang J, Li A and Sun J:
Obesity promotes tumor immune evasion in ovarian cancer through
increased production of myeloid-derived suppressor cells via IL-6.
Cancer Manag Res. 13:7355–7363. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Turbitt WJ, Collins SD, Meng H and Rogers
CJ: Increased adiposity enhances the accumulation of MDSCs in the
tumor microenvironment and adipose tissue of pancreatic
tumor-bearing mice and in immune organs of tumor-free hosts.
Nutrients. 11:30122019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gibson JT, Orlandella RM, Turbitt WJ,
Behring M, Manne U, Sorge RE and Norian LA: Obesity-Associated
myeloid-derived suppressor cells promote apoptosis of
tumor-infiltrating CD8 T cells and immunotherapy resistance in
breast cancer. Front Immunol. 11:5907942020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Alfaro C, Teijeira A, Onate C, Perez G,
Sanmamed MF, Andueza MP, Alignani D, Labiano S, Azpilikueta A,
Rodriguez-Paulete A, et al: Tumor-Produced interleukin-8 attracts
human myeloid-derived suppressor cells and elicits extrusion of
neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). Clin Cancer Res.
22:3924–3936. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang T, Tseng C, Zhang Y, Sirin O, Corn
PG, Li-Ning-Tapia EM, Troncoso P, Davis J, Pettaway C, Ward J, et
al: CXCL1 mediates obesity-associated adipose stromal cell
trafficking and function in the tumour microenvironment. Nat
Commun. 7:116742016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
De Pergola G and Silvestris F: Obesity as
a major risk factor for cancer. J Obes. 2013:2915462013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ross KH, Gogineni K, Subhedar PD, Lin JY
and McCullough LE: Obesity and cancer treatment efficacy: Existing
challenges and opportunities. Cancer. 125:1588–1592. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bao Y, Mo J, Ruan L and Li G: Increased
monocytic CD14(+) HLADRlow/-myeloid-derived suppressor cells in
obesity. Mol Med Rep. 11:2322–2328. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Rudolph BM, Loquai C, Gerwe A, Bacher N,
Steinbrink K, Grabbe S and Tuettenberg A: Increased frequencies of
CD11b(+) CD33(+) CD14(+) HLA-DR(low) myeloid-derived suppressor
cells are an early event in melanoma patients. Exp Dermatol.
23:202–204. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Verschoor CP, Johnstone J, Millar J,
Dorrington MG, Habibagahi M, Lelic A, Loeb M, Bramson JL and
Bowdish DM: Blood CD33(+)HLA-DR(-) myeloid-derived suppressor cells
are increased with age and a history of cancer. J Leukoc Biol.
93:633–637. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Margaroli C, Cardenas MA, Jansen CS, Moon
Reyes A, Hosseinzadeh F, Hong G, Zhang Y, Kissick H, Tirouvanziam R
and Master VA: The immunosuppressive phenotype of
tumor-infiltrating neutrophils is associated with obesity in kidney
cancer patients. Oncoimmunology. 9:17477312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Noman MZ, Desantis G, Janji B, Hasmim M,
Karray S, Dessen P, Bronte V and Chouaib S: PD-L1 is a novel direct
target of HIF-1α, and its blockade under hypoxia enhanced
MDSC-mediated T cell activation. J Exp Med. 211:781–790. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hafida S, Mirshahi T and Nikolajczyk BS:
The impact of bariatric surgery on inflammation: Quenching the fire
of obesity? Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 23:373–378. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Grzywa TM, Sosnowska A, Matryba P,
Rydzynska Z, Jasinski M, Nowis D and Golab J: Myeloid cell-derived
arginase in cancer immune response. Front Immunol. 11:9382020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Deryugina E, Carre A, Ardi V, Muramatsu T,
Schmidt J, Pham C and Quigley JP: Neutrophil elastase facilitates
tumor cell intravasation and early metastatic events. iScience.
23:1017992020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lerman I, Garcia-Hernandez ML,
Rangel-Moreno J, Chiriboga L, Pan C, Nastiuk KL, Krolewski JJ, Sen
A and Hammes SR: Infiltrating myeloid cells exert protumorigenic
actions via neutrophil elastase. Mol Cancer Res. 15:1138–1152.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Saitta C, Pollicino T and Raimondo G:
Obesity and liver cancer. Ann Hepatol. 18:810–815. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li M, Wang L, Cong L, Wong CC, Zhang X,
Chen H, Zeng T, Li B, Jia X, Huo J, et al: Spatial proteomics of
immune microenvironment in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis-associated
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 79:560–574. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Ponziani FR, Bhoori S, Castelli C,
Putignani L, Rivoltini L, Del Chierico F, Sanguinetti M, Morelli D,
Paroni Sterbini F, Petito V, et al: Hepatocellular carcinoma is
associated with gut microbiota profile and inflammation in
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 69:107–120. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Wang L, Zhu L, Liang C, Huang X, Liu Z,
Huo J, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Chen L, Xu H, et al: Targeting
N6-methyladenosine reader YTHDF1 with siRNA boosts antitumor
immunity in NASH-HCC by inhibiting EZH2-IL-6 axis. J Hepatol.
79:1185–1200. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sun H, Yang W, Tian Y, Zeng X, Zhou J, Mok
MTS, Tang W, Feng Y, Xu L, Chan AWH, et al: An inflammatory-CCRK
circuitry drives mTORC1-dependent metabolic and immunosuppressive
reprogramming in obesity-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat
Commun. 9:52142018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Furman D, Campisi J, Verdin E,
Carrera-Bastos P, Targ S, Franceschi C, Ferrucci L, Gilroy DW,
Fasano A, Miller GW, et al: Chronic inflammation in the etiology of
disease across the life span. Nat Med. 25:1822–1832. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Muller WA: Getting leukocytes to the site
of inflammation. Vet Pathol. 50:7–22. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Klevebro S, Bjorkander S, Ekstrom S, Merid
SK, Gruzieva O, Malarstig A, Johansson Å, Kull I, Bergström A and
Melén E: Inflammation-related plasma protein levels and association
with adiposity measurements in young adults. Sci Rep. 11:113912021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ellulu MS, Patimah I, Khaza'ai H, Rahmat A
and Abed Y: Obesity and inflammation: The linking mechanism and the
complications. Arch Med Sci. 13:851–863. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Sakai Y and Kobayashi M: Lymphocyte
'homing' and chronic inflammation. Pathol Int. 65:344–354. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ingersoll MA, Platt AM, Potteaux S and
Randolph GJ: Monocyte trafficking in acute and chronic
inflammation. Trends Immunol. 32:470–477. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wensveen FM, Valentic S, Sestan M,
Wensveen TT and Polic B: Interactions between adipose tissue and
the immune system in health and malnutrition. Semin Immunol.
27:322–333. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kumar DP, Koka S, Li C and Rajagopal S:
Inflammatory mediators in obesity. Mediators Inflamm.
2019:94818192019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Howe LR, Subbaramaiah K, Hudis CA and
Dannenberg AJ: Molecular pathways: Adipose inflammation as a
mediator of obesity-associated cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
19:6074–6083. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kawanishi S, Ohnishi S, Ma N, Hiraku Y and
Murata M: Crosstalk between DNA damage and inflammation in the
multiple steps of carcinogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 18:18082017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Murata M: Inflammation and cancer. Environ
Health Prev Med. 23:502018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Fan Y, Mao R and Yang J: NF-ĸB and STAT3
signaling pathways collaboratively link inflammation to cancer.
Protein Cell. 4:176–185. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Del Prete A, Allavena P, Santoro G,
Fumarulo R, Corsi MM and Mantovani A: Molecular pathways in
cancer-related inflammation. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 21:264–275.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Yang Y, Li C, Liu T, Dai X and Bazhin AV:
Myeloid-Derived suppressor cells in tumors: From mechanisms to
antigen specificity and microenvironmental regulation. Front
Immunol. 11:13712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ma P, Beatty PL, McKolanis J, Brand R,
Schoen RE and Finn OJ: Circulating myeloid derived suppressor cells
(MDSC) that accumulate in premalignancy share phenotypic and
functional characteristics with MDSC in cancer. Front Immunol.
10:14012019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Veglia F, Sanseviero E and Gabrilovich DI:
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the era of increasing myeloid
cell diversity. Nat Rev Immunol. 21:485–498. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Xia S, Sha H, Yang L, Ji Y,
Ostrand-Rosenberg S and Qi L: Gr-1+ CD11b+ myeloid-derived
suppressor cells suppress inflammation and promote insulin
sensitivity in obesity. J Biol Chem. 286:23591–23599. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Srikrishna G: S100A8 and S100A9: New
insights into their roles in malignancy. J Innate Immun. 4:31–40.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
72
|
Siddiqui S and Glauben R: Fatty acid
metabolism in myeloid-derived suppressor cells and tumor-associated
macrophages: Key factor in cancer immune evasion. Cancers (Basel).
14:2502022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Adeshakin AO, Liu W, Adeshakin FO, Afolabi
LO, Zhang M, Zhang G, Wang L, Li Z, Lin L, Cao Q, et al: Regulation
of ROS in myeloid-derived suppressor cells through targeting fatty
acid transport protein 2 enhanced anti-PD-L1 tumor immunotherapy.
Cell Immunol. 362:1042862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Xin G, Chen Y, Topchyan P, Kasmani MY,
Burns R, Volberding PJ, Wu X, Cohn A, Chen Y, Lin CW, et al:
Targeting PIM1-Mediated metabolism in myeloid suppressor cells to
treat cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. 9:454–469. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Sanchez-Pino MD, Dean MJ and Ochoa AC:
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC): When good intentions go
awry. Cell Immunol. 362:1043022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zhen Y, Shu W, Hou X and Wang Y: Innate
immune system orchestrates metabolic homeostasis and dysfunction in
visceral adipose tissue during obesity. Front Immunol.
12:7028352021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Klein S, Gastaldelli A, Yki-Jarvinen H and
Scherer PE: Why does obesity cause diabetes? Cell Metab. 34:11–20.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Clements VK, Long T, Long R, Figley C,
Smith DMC and Ostrand-Rosenberg S: Frontline Science: High fat diet
and leptin promote tumor progression by inducing myeloid-derived
suppressor cells. J Leukoc Biol. 103:395–407. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Ingalls AM, Dickie MM and Snell GD: Obese,
a new mutation in the house mouse. J Hered. 41:317–318. 1950.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Hummel KP, Dickie MM and Coleman DL:
Diabetes, a new mutation in the mouse. Science. 153:1127–1278.
1966. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M,
Leopold L and Friedman JM: Positional cloning of the mouse obese
gene and its human homologue. Nature. 372:425–432. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Munzberg H and Heymsfield SB: New insights
into the regulation of leptin gene expression. Cell Metab.
29:1013–1014. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Gorska E, Popko K, Stelmaszczyk-Emmel A,
Ciepiela O, Kucharska A and Wasik M: Leptin receptors. Eur J Med
Res. 15(Suppl 2): S50–S54. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Park HK and Ahima RS: Leptin signaling.
F1000Prime Rep. 6:732014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Perez-Perez A, Sanchez-Jimenez F,
Vilarino-Garcia T and Sanchez-Margalet V: Role of leptin in
inflammation and vice versa. Int J Mol Sci. 21:58872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Obradovic M, Sudar-Milovanovic E, Soskic
S, Essack M, Arya S, Stewart AJ, Gojobori T and Isenovic ER: Leptin
and Obesity: Role and Clinical Implication. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 12:5858872021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Vilarino-Garcia T, Perez-Perez A,
Santamaria-Lopez E, Prados N, Fernandez-Sanchez M and
Sanchez-Margalet V: Sam68 mediates leptin signaling and action in
human granulosa cells: Possible role in leptin resistance in PCOS.
Endocr Connect. 9:479–488. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Perez-Perez A, Toro A, Vilarino-Garcia T,
Maymo J, Guadix P, Duenas JL, Fernández-Sánchez M, Varone C and
Sánchez-Margalet V: Leptin action in normal and pathological
pregnancies. J Cell Mol Med. 22:716–727. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
89
|
Fernandez-Riejos P, Najib S,
Santos-Alvarez J, Martin-Romero C, Perez-Perez A, Gonzalez-Yanes C
and Sánchez-Margalet V: Role of leptin in the activation of immune
cells. Mediators Inflamm. 2010:5683432010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Perez-Perez A, Vilarino-Garcia T,
Fernandez-Riejos P, Martin-Gonzalez J, Segura-Egea JJ and
Sanchez-Margalet V: Role of leptin as a link between metabolism and
the immune system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 35:71–84. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Dutta D, Ghosh S, Pandit K, Mukhopadhyay P
and Chowdhury S: Leptin and cancer: Pathogenesis and modulation.
Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 16(Suppl 3): S596–S600. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Ando S and Catalano S: The multifactorial
role of leptin in driving the breast cancer microenvironment. Nat
Rev Endocrinol. 8:263–275. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Feldman DE, Chen C, Punj V, Tsukamoto H
and Machida K: Pluripotency factor-mediated expression of the
leptin receptor (OB-R) links obesity to oncogenesis through
tumor-initiating stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:829–834.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
94
|
Ghasemi A, Saeidi J, Azimi-Nejad M and
Hashemy SI: Leptin-induced signaling pathways in cancer cell
migration and invasion. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 42:243–260. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Ray A and Cleary MP: The potential role of
leptin in tumor invasion and metastasis. Cytokine Growth Factor
Rev. 38:80–97. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Jimenez-Cortegana C, Lopez-Saavedra A,
Sanchez-Jimenez F, Perez-Perez A, Castineiras J, Virizuela-Echaburu
JA, de la Cruz-Merino L and Sánchez-Margalet V: Leptin, both bad
and good actor in cancer. Biomolecules. 11:9132021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Sanchez-Jimenez F, Perez-Perez A, de la
Cruz-Merino L and Sanchez-Margalet V: Obesity and breast cancer:
Role of leptin. Front Oncol. 9:5962019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Greer KB, Falk GW, Bednarchik B, Li L and
Chak A: Associations of serum adiponectin and leptin with barrett's
esophagus. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 13:2265–2272. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Li C, Quan J, Wei R, Zhao Z, Guan X, Liu
Z, Zou S, Wang X and Jiang Z: Leptin overexpression as a poor
prognostic factor for colorectal cancer. Biomed Res Int.
2020:75325142020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Koprivčić I, Marjanovic K, Matic A,
Tolusic Levak M, Lovric I, Pauzar B, Erić I and Wertheimer V: Serum
leptin level in breast cancer. Acta Clin Croat. 61:79–85. 2022.
|
|
101
|
Wu MH, Chou YC, Chou WY, Hsu GC, Chu CH,
Yu CP, Yu JC and Sun CA: Circulating levels of leptin, adiposity
and breast cancer risk. Br J Cancer. 100:578–582. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Singh SK, Grifson JJ, Mavuduru RS, Agarwal
MM, Mandal AK and Jha V: Serum leptin: A marker of prostate cancer
irrespective of obesity. Cancer Biomark. 7:11–15. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Tong X, Ma Y, Zhou Q, He J, Peng B, Liu S,
Yan Z, Yang X and Fan H: Serum and tissue leptin in lung cancer: A
meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 8:19699–19711. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Chludzinska-Kasperuk S, Lewko J,
Sierzantowicz R, Krajewska-Kulak E and Reszec-Gielazyn J: The
effect of serum leptin concentration and leptin receptor expression
on colorectal cancer. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 20:49512023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Inacio Pinto N, Carnier J, Oyama LM, Otoch
JP, Alcantara PS, Tokeshi F and Nascimento CM: Cancer as a
proinflammatory environment: Metastasis and cachexia. Mediators
Inflamm. 2015:7910602015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Ostrand-Rosenberg S: Myeloid
derived-suppressor cells: Their role in cancer and obesity. Curr
Opin Immunol. 51:68–75. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Zhao X, Rong L, Zhao X, Li X, Liu X, Deng
J, Wu H, Xu X, Erben U, Wu P, et al: TNF signaling drives
myeloid-derived suppressor cell accumulation. J Clin Invest.
122:4094–4104. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Weber R, Groth C, Lasser S, Arkhypov I,
Petrova V, Altevogt P, Utikal J and Umansky V: IL-6 as a major
regulator of MDSC activity and possible target for cancer
immunotherapy. Cell Immunol. 359:1042542021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Elkabets M, Ribeiro VS, Dinarello CA,
Ostrand-Rosenberg S, Di Santo P, Apte RN and Vosshenrich CA: IL-1β
regulates a novel myeloid-derived suppressor cell subset that
impairs NK cell development and function. Eur J Immunol.
40:3347–3357. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Avgerinos KI, Spyrou N, Mantzoros CS and
Dalamaga M: Obesity and cancer risk: Emerging biological mechanisms
and perspectives. Metabolism. 92:121–135. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Lauby-Secretan B, Scoccianti C, Loomis D,
Grosse Y, Bianchini F and Straif K; International Agency for
Research on Cancer Handbook Working Group: Body Fatness and
Cancer-Viewpoint of the IARC Working Group. N Engl J Med.
375:794–798. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Griggs JJ, Mangu PB, Anderson H, Balaban
EP, Dignam JJ, Hryniuk WM, Morrison VA, Pini TM, Runowicz CD,
Rosner GL, et al: Appropriate chemotherapy dosing for obese adult
patients with cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology
clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol. 30:1553–1561. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Griggs JJ, Bohlke K, Balaban EP, Dignam
JJ, Hall ET, Harvey RD, Hecht DP, Klute KA, Morrison VA, Pini TM,
et al: Appropriate systemic therapy dosing for obese adult patients
with cancer: ASCO Guideline Update. J Clin Oncol. 39:2037–2048.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
De Cicco P, Ercolano G and Ianaro A: The
new Era of cancer immunotherapy: Targeting myeloid-derived
suppressor cells to overcome immune evasion. Front Immunol.
11:16802020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Wang Y, Jia A, Bi Y, Wang Y, Yang Q, Cao
Y, Li Y and Liu G: Targeting myeloid-derived suppressor cells in
cancer immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel). 12:26262020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Horowitz NS and Wright AA: Impact of
obesity on chemotherapy management and outcomes in women with
gynecologic malignancies. Gynecol Oncol. 138:201–206. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Li X, Zhong J, Deng X, Guo X, Lu Y, Lin J,
Huang X and Wang C: Targeting myeloid-derived suppressor cells to
enhance the antitumor efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade
therapy. Front Immunol. 12:7541962021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Pingili AK, Chaib M, Sipe LM, Miller EJ,
Teng B, Sharma R, Asemota S, Al Abdallah Q, Mims TS, Marion TN, et
al: Immune checkpoint blockade reprograms systemic immune landscape
and tumor microenvironment in obesity-associated breast cancer.
Cell Rep. 35:1092852021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Greene S, Robbins Y, Mydlarz WK, Huynh AP,
Schmitt NC, Friedman J, Horn LA, Palena C, Schlom J, Maeda DY, et
al: Inhibition of MDSC Trafficking with SX-682, a CXCR1/2
Inhibitor, Enhances NK-cell immunotherapy in head and neck cancer
models. Clin Cancer Res. 26:1420–1431. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Zoglmeier C, Bauer H, Noerenberg D,
Wedekind G, Bittner P, Sandholzer N, Rapp M, Anz D, Endres S and
Bourquin C: CpG blocks immunosuppression by myeloid-derived
suppressor cells in tumor-bearing mice. Clin Cancer Res.
17:1765–1775. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
VanOosten RL and Griffith TS: Activation
of tumor-specific CD8+ T Cells after intratumoral Ad5-TRAIL/CpG
oligodeoxynucleotide combination therapy. Cancer Res.
67:11980–11990. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Griffith TS and Broghammer EL: Suppression
of tumor growth following intralesional therapy with TRAIL
recombinant adenovirus. Mol Ther. 4:257–266. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Condamine T, Kumar V, Ramachandran IR,
Youn JI, Celis E, Finnberg N, El-Deiry WS, Winograd R, Vonderheide
RH, English NR, et al: ER stress regulates myeloid-derived
suppressor cell fate through TRAIL-R-mediated apoptosis. J Clin
Invest. 124:2626–2639. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Dominguez GA, Condamine T, Mony S,
Hashimoto A, Wang F, Liu Q, Forero A, Bendell J, Witt R, Hockstein
N, et al: Selective targeting of myeloid-derived suppressor cells
in cancer patients using DS-8273a, an Agonistic TRAIL-R2 Antibody.
Clin Cancer Res. 23:2942–2950. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
125
|
Zou S, Tong Q, Liu B, Huang W, Tian Y and
Fu X: Targeting STAT3 in Cancer Immunotherapy. Mol Cancer.
19:1452020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Nefedova Y, Fishman M, Sherman S, Wang X,
Beg AA and Gabrilovich DI: Mechanism of all-trans retinoic acid
effect on tumor-associated myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Cancer
Res. 67:11021–11028. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Chen PT, Hsieh CC, Wu CT, Yen TC, Lin PY,
Chen WC and Chen MF: 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma progression by Reducing IL6 Signaling. Mol
Cancer Ther. 14:1365–1375. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Chang CC, Wu MJ, Yang JY, Camarillo IG and
Chang CJ: Leptin-STAT3-G9a signaling promotes obesity-mediated
breast cancer progression. Cancer Res. 75:2375–2386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Park JW, Han CR, Zhao L, Willingham MC and
Cheng SY: Inhibition of STAT3 activity delays obesity-induced
thyroid carcinogenesis in a mouse model. Endocr Relat Cancer.
23:53–63. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Berry DC and Noy N: All-trans-retinoic
acid represses obesity and insulin resistance by activating both
peroxisome proliferation-activated receptor beta/delta and retinoic
acid receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 29:3286–3296. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Karampela I, Sakelliou A, Vallianou N,
Christodoulatos GS, Magkos F and Dalamaga M: Vitamin D and Obesity:
Current evidence and controversies. Curr Obes Rep. 10:162–180.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Lennon H, Sperrin M, Badrick E and Renehan
AG: The obesity paradox in cancer: A review. Curr Oncol Rep.
18:562016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Lee DH and Giovannucci EL: The obesity
paradox in cancer: Epidemiologic insights and perspectives. Curr
Nutr Rep. 8:175–181. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Weiss L, Melchardt T, Habringer S,
Boekstegers A, Hufnagl C, Neureiter D, Hopfinger G, Greil R and
Egle A: Increased body mass index is associated with improved
overall survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Ann Oncol.
25:171–176. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Stevenson JKR, Qiao Y, Chan KKW, Beca J,
Isaranuwatchai W, Guo H, Schwartz D, Arias J, Gavura S, Dai WF, et
al: Improved survival in overweight and obese patients with
aggressive B-cell lymphoma treated with rituximab-containing
chemotherapy for curative intent. Leuk Lymphoma. 60:1399–1408.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Brunner AM, Sadrzadeh H, Feng Y, Drapkin
BJ, Ballen KK, Attar EC, Amrein PC, McAfee SL, Chen YB, Neuberg DS
and Fathi AT: Association between baseline body mass index and
overall survival among patients over age 60 with acute myeloid
leukemia. Am J Hematol. 88:642–646. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Tsang NM, Pai PC, Chuang CC, Chuang WC,
Tseng CK, Chang KP, Yen TC, Lin JD and Chang JT: Overweight and
obesity predict better overall survival rates in cancer patients
with distant metastases. Cancer Med. 5:665–675. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Schlesinger S, Siegert S, Koch M, Walter
J, Heits N, Hinz S, Jacobs G, Hampe J, Schafmayer C and Nöthlings
U: Postdiagnosis body mass index and risk of mortality in
colorectal cancer survivors: A prospective study and meta-analysis.
Cancer Causes Control. 25:1407–1418. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Amptoulach S, Gross G and Kalaitzakis E:
Differential impact of obesity and diabetes mellitus on survival
after liver resection for colorectal cancer metastases. J Surg Res.
199:378–385. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Parker AS, Lohse CM, Cheville JC, Thiel
DD, Leibovich BC and Blute ML: Greater body mass index is
associated with better pathologic features and improved outcome
among patients treated surgically for clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Urology. 68:741–746. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Waalkes S, Merseburger AS, Kramer MW,
Herrmann TR, Wegener G, Rustemeier J, Hofmann R, Schrader M, Kuczyk
MA and Schrader AJ: Obesity is associated with improved survival in
patients with organ-confined clear-cell kidney cancer. Cancer
Causes Control. 21:1905–1910. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Hakimi AA, Furberg H, Zabor EC, Jacobsen
A, Schultz N, Ciriello G, Mikklineni N, Fiegoli B, Kim PH, Voss MH,
et al: An epidemiologic and genomic investigation into the obesity
paradox in renal cell carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 105:1862–1870.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Albiges L, Hakimi AA, Xie W, McKay RR,
Simantov R, Lin X, Lee JL, Rini BI, Srinivas S, Bjarnason GA, et
al: Body mass index and metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Clinical
and biological correlations. J Clin Oncol. 34:3655–3663. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Lam VK, Bentzen SM, Mohindra P, Nichols
EM, Bhooshan N, Vyfhuis M, Scilla KA, Feigenberg SJ, Edelman MJ and
Feliciano JL: Obesity is associated with long-term improved
survival in definitively treated locally advanced non-small cell
lung cancer (NSCLC). Lung Cancer. 104:52–57. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Shepshelovich D, Xu W, Lu L, Fares A, Yang
P, Christiani D, Zhang J, Shiraishi K, Ryan BM, Chen C, et al: Body
Mass Index (BMI), BMI change, and overall survival in patients with
SCLC and NSCLC: A pooled analysis of the International lung cancer
consortium. J Thorac Oncol. 14:1594–1607. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Ardesch FH, Ruiter R, Mulder M, Lahousse
L, Stricker BHC and Kiefte-de Jong JC: The obesity paradox in lung
cancer: Associations with body size versus body shape. Front Oncol.
10:5911102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Hayes AJ and Larkin J: BMI and outcomes in
melanoma: More evidence for the obesity paradox. Lancet Oncol.
19:269–270. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
McQuade JL, Daniel CR, Hess KR, Mak C,
Wang DY, Rai RR, Park JJ, Haydu LE, Spencer C, Wongchenko M, et al:
Association of body-mass index and outcomes in patients with
metastatic melanoma treated with targeted therapy, immunotherapy,
or chemotherapy: A retrospective, multicohort analysis. Lancet
Oncol. 19:310–322. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Smith LK, Arabi S, Lelliott EJ, McArthur
GA and Sheppard KE: Obesity and the impact on cutaneous melanoma:
Friend or Foe? Cancers (Basel). 12:15832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Somasundar P, Yu AK, Vona-Davis L and
McFadden DW: Differential effects of leptin on cancer in vitro. J
Surg Res. 113:50–55. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Thompson KJ, Lau KN, Johnson S, Martinie
JB, Iannitti DA, McKillop IH and Sindram D: Leptin inhibits
hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation via p38-MAPK-dependent
signalling. HPB (Oxford). 13:225–233. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Paik SS, Jang SM, Jang KS, Lee KH, Choi D
and Jang SJ: Leptin expression correlates with favorable
clinicopathologic phenotype and better prognosis in colorectal
adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 16:297–303. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
153
|
Murphy WJ and Longo DL: The surprisingly
positive association between obesity and cancer immunotherapy
efficacy. JAMA. 321:1247–1248. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Cespedes Feliciano EM, Kroenke CH and Caan
BJ: The obesity paradox in cancer: How important is muscle? Annu
Rev Nutr. 38:357–379. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Donini LM, Pinto A, Giusti AM, Lenzi A and
Poggiogalle E: Obesity or BMI Paradox? Beneath the Tip of the
Iceberg. Front Nutr. 7:532020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|