|
1
|
Poyet JL, Srinivasula SM, Tnani M, Razmara
M, Fernandes-Alnemri T and Alnemri ES: Identification of Ipaf, a
human caspase-1-activating protein related to Apaf-1. J Biol Chem.
276:28309–28313. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Duncan JA and Canna SW: The NLRC4
inflammasome. Immunol Rev. 281:115–123. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Gutierrez O, Pipaon C and Fernandez-Luna
JL: Ipaf is upregulated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human
leukemia cells. FEBS Lett. 568:79–82. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sadasivam S, Gupta S, Radha V, Batta K,
Kundu TK and Swarup G: Caspase-1 activator Ipaf is a p53-inducible
gene involved in apoptosis. Oncogene. 24:627–636. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Mariathasan S, Newton K, Monack DM, Vucic
D, French DM, Lee WP, Roose-Girma M, Erickson S and Dixit VM:
Differential activation of the inflammasome by caspase-1 adaptors
ASC and Ipaf. Nature. 430:213–218. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hu Z, Yan C, Liu P, Huang Z, Ma R, Zhang
C, Wang R, Zhang Y, Martinon F, Miao D, et al: Crystal structure of
NLRC4 reveals its autoinhibition mechanism. Science. 341:172–175.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang X, Shaw DK, Hammond HL, Sutterwala
FS, Rayamajhi M, Shirey KA, Perkins DJ, Bonventre JV, Velayutham
TS, Evans SM, et al: The prostaglandin E2-EP3 receptor axis
regulates anaplasma phagocytophilum-mediated NLRC4 inflammasome
activation. PLoS Pathog. 12:e10058032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang L, Chen S, Ruan J, Wu J, Tong AB,
Yin Q, Li Y, David L, Lu A, Wang WL, et al: Cryo-EM structure of
the activated NAIP2-NLRC4 inflammasome reveals nucleated
polymerization. Science. 350:404–409. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sellin ME, Müller AA, Felmy B, Dolowschiak
T, Diard M, Tardivel A, Maslowski KM and Hardt WD:
Epithelium-intrinsic NAIP/NLRC4 inflammasome drives infected
enterocyte expulsion to restrict Salmonella replication in the
intestinal mucosa. Cell Host Microbe. 16:237–248. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rauch I, Deets KA, Ji DX, von Moltke J,
Tenthorey JL, Lee AY, Philip NH, Ayres JS, Brodsky IE, Gronert K
and Vance RE: NAIP-NLRC4 inflammasomes coordinate intestinal
epithelial cell expulsion with eicosanoid and IL-18 release via
activation of caspase-1 and -8. Immunity. 46:649–659. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nordlander S, Pott J and Maloy KJ: NLRC4
expression in intestinal epithelial cells mediates protection
against an enteric pathogen. Mucosal Immunol. 7:775–785. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Janowski AM, Kolb R, Zhang W and
Sutterwala FS: Beneficial and detrimental roles of NLRs in
carcinogenesis. Front Immunol. 4:3702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dupaul-Chicoine J, Yeretssian G, Doiron K,
Bergstrom KSB, McIntire CR, LeBlanc PM, Meunier C, Turbide C, Gros
P, Beauchemin N, et al: Control of intestinal homeostasis, colitis,
and colitis-associated colorectal cancer by the inflammatory
caspases. Immunity. 32:367–378. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhiyu W, Wang N, Wang Q, Peng C, Zhang J,
Liu P, Ou A, Zhong S, Cordero MD and Lin Y: The inflammasome: An
emerging therapeutic oncotarget for cancer prevention. Oncotarget.
7:50766–50780. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Steiner A, Reygaerts T, Pontillo A,
Ceccherini I, Moecking J, Moghaddas F, Davidson S, Caroli F, Grossi
A, Castro FFM, et al: Recessive NLRC4-autoinflammatory disease
reveals an ulcerative colitis locus. J Clin Immunol. 42:325–335.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Wang J, Ye Q, Zheng W, Yu X, Luo F, Fang
R, Shangguan Y, Du Z, Lee PY, Jin T and Zhou Q: Low-ratio somatic
NLRC4 mutation causes late-onset autoinflammatory disease. Ann
Rheum Dis. 81:1173–1178. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu C, Zhao J, Wang X, Wang Y, Zhang W and
Zhu G: A novel pyroptosis related genes signature for predicting
prognosis and estimating tumor immune microenvironment in lung
adenocarcinoma. Transl Cancer Res. 11:2647–2659. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sundaram B and Kanneganti TD: Advances in
understanding activation and function of the NLRC4 inflammasome.
Int J Mol Sci. 22:10482021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jin H and Kim HJ: NLRC4, ASC and caspase-1
are inflammasome components that are mediated by P2Y2R
activation in breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 21:33372020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lim J, Kim MJ, Park Y, Ahn JW, Hwang SJ,
Moon JS, Cho KG and Kwack K: Upregulation of the NLRC4 inflammasome
contributes to poor prognosis in glioma patients. Sci Rep.
9:78952019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sonohara F, Inokawa Y, Kanda M, Nishikawa
Y, Yamada S, Fujii T, Sugimoto H, Kodera Y and Nomoto S:
Association of inflammasome components in background liver with
poor prognosis after curatively-resected hepatocellular carcinoma.
Anticancer Res. 37:293–300. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Janowski AM, Colegio OR, Hornick EE,
McNiff JM, Martin MD, Badovinac VP, Norian LA, Zhang W, Cassel SL
and Sutterwala FS: NLRC4 suppresses melanoma tumor progression
independently of inflammasome activation. J Clin Invest.
126:3917–3928. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hu B, Elinav E, Huber S, Booth CJ, Strowig
T, Jin C, Eisenbarth SC and Flavell RA: Inflammation-induced
tumorigenesis in the colon is regulated by caspase-1 and NLRC4.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:21635–21640. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Peng L, Zhu N, Wang D, Zhou Y and Liu Y:
Comprehensive analysis of prognostic value and immune infiltration
of NLRC4 and CASP1 in colorectal cancer. Int J Gen Med.
15:5425–5440. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Abdelaziz DH, Amr K and Amer AO:
Nlrc4/Ipaf/CLAN/CARD12: More than a flagellin sensor. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 42:789–791. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sun Q and Scott MJ: Caspase-1 as a
multifunctional inflammatory mediator: Noncytokine maturation
roles. J Leukoc Biol. 100:961–967. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lamkanfi M, Kanneganti TD, Franchi L and
Núñez G: Caspase-1 inflammasomes in infection and inflammation. J
Leukoc Biol. 82:220–225. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Naseer N, Zhang J, Bauer R, Constant DA,
Nice TJ, Brodsky IE, Rauch I and Shin S: Salmonella enterica
Serovar typhimurium induces NAIP/NLRC4- and NLRP3/ASC-independent,
caspase-4-dependent inflammasome activation in human intestinal
epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 90:e00663212022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Naseer N, Egan MS, Reyes Ruiz VM, Scott
WP, Hunter EN, Demissie T, Rauch I, Brodsky IE and Shin S: Human
NAIP/NLRC4 and NLRP3 inflammasomes detect Salmonella type III
secretion system activities to restrict intracellular bacterial
replication. PLoS Pathog. 18:e10097182022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gram AM, Wright JA, Pickering RJ, Lam NL,
Booty LM, Webster SJ and Bryant CE: Salmonella flagellin activates
NAIP/NLRC4 and canonical NLRP3 inflammasomes in human macrophages.
J Immunol. 206:631–640. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schell U, Simon S and Hilbi H:
Inflammasome recognition and regulation of the Legionella
flagellum. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 397:161–181. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cerqueira DM, Pereira MS, Silva AL, Cunha
LD and Zamboni DS: Caspase-1 but not caspase-11 is required for
NLRC4-mediated pyroptosis and restriction of infection by
flagellated Legionella species in mouse macrophages and in vivo. J
Immunol. 195:2303–2311. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhao Y, Yang J, Shi J, Gong YN, Lu Q, Xu
H, Liu L and Shao F: The NLRC4 inflammasome receptors for bacterial
flagellin and type III secretion apparatus. Nature. 477:596–600.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pereira MSF, Morgantetti GF, Massis LM,
Horta CV, Hori JI and Zamboni DS: Activation of NLRC4 by
flagellated bacteria triggers caspase-1-dependent and -independent
responses to restrict Legionella pneumophila replication in
macrophages and in vivo. J Immunol. 187:6447–6455. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Luchetti G, Roncaioli JL, Chavez RA,
Schubert AF, Kofoed EM, Reja R, Cheung TK, Liang Y, Webster JD,
Lehoux I, et al: Shigella ubiquitin ligase IpaH7.8 targets
gasdermin D for degradation to prevent pyroptosis and enable
infection. Cell Host Microbe. 29:1521–1530.e10. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mitchell PS, Roncaioli JL, Turcotte EA,
Goers L, Chavez RA, Lee AY, Lesser CF, Rauch I and Vance RE:
NAIP-NLRC4-deficient mice are susceptible to shigellosis. Elife.
9:e590222020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hermansson AK, Paciello I and Bernardini
ML: The orchestra and its maestro: Shigella's fine-tuning of the
inflammasome platforms. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 397:91–115.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Suzuki S, Mimuro H, Kim M, Ogawa M, Ashida
H, Toyotome T, Franchi L, Suzuki M, Sanada T, Suzuki T, et al:
Shigella IpaH7.8 E3 ubiquitin ligase targets glomulin and activates
inflammasomes to demolish macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:E4254–E4263. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Santoni K, Pericat D, Gorse L, Buyck J,
Pinilla M, Prouvensier L, Bagayoko S, Hessel A, Leon-Icaza SA,
Bellard E, et al: Caspase-1-driven neutrophil pyroptosis and its
role in host susceptibility to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS Pathog.
18:e10103052022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mohamed MF, Gupta K, Goldufsky JW, Roy R,
Callaghan LT, Wetzel DM, Kuzel TM, Reiser J and Shafikhani SH:
CrkII/Abl phosphorylation cascade is critical for NLRC4
inflammasome activity and is blocked by Pseudomonas aeruginosa
ExoT. Nat Commun. 13:12952022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Graustein AD, Berrington WR, Buckingham
KJ, Nguyen FK, Joudeh LL, Rosenfeld M, Bamshad MJ, Gibson RL, Hawn
TR and Emond MJ: Inflammasome genetic variants, macrophage
function, and clinical outcomes in cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 65:157–166. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Karki R, Lee E, Place D, Samir P, Mavuluri
J, Sharma BR, Balakrishnan A, Malireddi RKS, Geiger R, Zhu Q, et
al: IRF8 regulates transcription of Naips for NLRC4 inflammasome
activation. Cell. 173:920–933.e13. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mascarenhas DPA, Cerqueira DM, Pereira
MSF, Castanheira FVS, Fernandes TD, Manin GZ, Cunha LD and Zamboni
DS: Inhibition of caspase-1 or gasdermin-D enable caspase-8
activation in the Naip5/NLRC4/ASC inflammasome. PLoS Pathog.
13:e10065022017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Furuoka M, Ozaki K, Sadatomi D, Mamiya S,
Yonezawa T, Tanimura S and Takeda K: TNF-α induces caspase-1
activation independently of simultaneously induced NLRP3 in 3T3-L1
cells. J Cell Physiol. 231:2761–2767. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hua L, Liang S, Zhou Y, Wu X, Cai H, Liu
Z, Ou Y, Chen Y, Chen X, Yan Y, et al: Artemisinin-derived
artemisitene blocks ROS-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome and alleviates
ulcerative colitis. Int Immunopharmacol. 113:1094312022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Taman H, Fenton CG, Anderssen E,
Florholmen J and Paulssen RH: DNA hypo-methylation facilitates
anti-inflammatory responses in severe ulcerative colitis. PLoS One.
16:e02489052021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Miao EA, Mao DP, Yudkovsky N, Bonneau R,
Lorang CG, Warren SE, Leaf IA and Aderem A: Innate immune detection
of the type III secretion apparatus through the NLRC4 inflammasome.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:3076–3080. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Miao EA, Alpuche-Aranda CM, Dors M, Clark
AE, Bader MW, Miller SI and Aderem A: Cytoplasmic flagellin
activates caspase-1 and secretion of interleukin 1beta via Ipaf.
Nat Immunol. 7:569–575. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Endrizzi MG, Hadinoto V, Growney JD,
Miller W and Dietrich WF: Genomic sequence analysis of the mouse
Naip gene array. Genome Res. 10:1095–1102. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kofoed EM and Vance RE: Innate immune
recognition of bacterial ligands by NAIPs determines inflammasome
specificity. Nature. 477:592–595. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Rayamajhi M, Zak DE, Chavarria-Smith J,
Vance RE and Miao EA: Cutting edge: Mouse NAIP1 detects the type
III secretion system needle protein. J Immunol. 191:3986–3989.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yang J, Zhao Y, Shi J and Shao F: Human
NAIP and mouse NAIP1 recognize bacterial type III secretion needle
protein for inflammasome activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:14408–14413. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kortmann J, Brubaker SW and Monack DM:
Cutting edge: Inflammasome activation in primary human macrophages
is dependent on flagellin. J Immunol. 195:815–819. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Broz P, Newton K, Lamkanfi M, Mariathasan
S, Dixit VM and Monack DM: Redundant roles for inflammasome
receptors NLRP3 and NLRC4 in host defense against Salmonella. J Exp
Med. 207:1745–1755. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Liu Z, Zaki MH, Vogel P, Gurung P, Finlay
BB, Deng W, Lamkanfi M and Kanneganti TD: Role of inflammasomes in
host defense against Citrobacter rodentium infection. J Biol Chem.
287:16955–16964. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Man SM, Karki R, Briard B, Burton A,
Gingras S, Pelletier S and Kanneganti TD: Differential roles of
caspase-1 and caspase-11 in infection and inflammation. Sci Rep.
7:451262017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Gonçalves AV, Margolis SR, Quirino GFS,
Mascarenhas DPA, Rauch I, Nichols RD, Ansaldo E, Fontana MF, Vance
RE and Zamboni DS: Gasdermin-D and caspase-7 are the key
caspase-1/8 substrates downstream of the NAIP5/NLRC4 inflammasome
required for restriction of Legionella pneumophila. PLoS Pathog.
15:e10078862019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Canna SW, de Jesus AA, Gouni S, Brooks SR,
Marrero B, Liu Y, DiMattia MA, Zaal KJ, Sanchez GA, Kim H, et al:
An activating NLRC4 inflammasome mutation causes autoinflammation
with recurrent macrophage activation syndrome. Nat Genet.
46:1140–1146. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Romberg N, Al Moussawi K, Nelson-Williams
C, Stiegler AL, Loring E, Choi M, Overton J, Meffre E, Khokha MK,
Huttner AJ, et al: Mutation of NLRC4 causes a syndrome of
enterocolitis and autoinflammation. Nat Genet. 46:1135–1139. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kitamura A, Sasaki Y, Abe T, Kano H and
Yasutomo K: An inherited mutation in NLRC4 causes autoinflammation
in human and mice. J Exp Med. 211:2385–2396. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Chear CT, Nallusamy R, Canna SW, Chan KC,
Baharin MF, Hishamshah M, Ghani H, Ripen AM and Mohamad SB: A novel
de novo NLRC4 mutation reinforces the likely pathogenicity of
specific LRR domain mutation. Clin Immunol. 211:1083282020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Barsalou J, Blincoe A, Fernandez I,
Dal-Soglio D, Marchitto L, Selleri S, Haddad E, Benyoucef A and
Touzot F: Rapamycin as an adjunctive therapy for NLRC4 associated
macrophage activation syndrome. Front Immunol. 9:21622018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wang Y, Gao W, Shi X, Ding J, Liu W, He H,
Wang K and Shao F: Chemotherapy drugs induce pyroptosis through
caspase-3 cleavage of a gasdermin. Nature. 547:99–103. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Christgen S, Zheng M, Kesavardhana S,
Karki R, Malireddi RKS, Banoth B, Place DE, Briard B, Sharma BR,
Tuladhar S, et al: Identification of the PANoptosome: A molecular
platform triggering pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis
(PANoptosis). Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 10:2372020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Pandian N and Kanneganti TD: PANoptosis: A
unique innate immune inflammatory cell death modality. J Immunol.
209:1625–1633. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Pan H, Pan J, Li P and Gao J:
Characterization of PANoptosis patterns predicts survival and
immunotherapy response in gastric cancer. Clin Immunol.
238:1090192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Lin JF, Hu PS, Wang YY, Tan YT, Yu K, Liao
K, Wu QN, Li T, Meng Q, Lin JZ, et al: Phosphorylated NFS1 weakens
oxaliplatin-based chemosensitivity of colorectal cancer by
preventing PANoptosis. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7:542022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wang Y and Kanneganti TD: From pyroptosis,
apoptosis and necroptosis to PANoptosis: A mechanistic compendium
of programmed cell death pathways. Comput Struct Biotechnol J.
19:4641–4657. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Place DE, Lee S and Kanneganti TD:
PANoptosis in microbial infection. Curr Opin Microbiol. 59:42–49.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Lee S, Karki R, Wang Y, Nguyen LN,
Kalathur RC and Kanneganti TD: AIM2 forms a complex with pyrin and
ZBP1 to drive PANoptosis and host defence. Nature. 597:415–419.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Karki R, Sundaram B, Sharma BR, Lee S,
Malireddi RKS, Nguyen LN, Christgen S, Zheng M, Wang Y, Samir P, et
al: ADAR1 restricts ZBP1-mediated immune response and PANoptosis to
promote tumorigenesis. Cell Rep. 37:1098582021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Jiang W, Deng Z, Dai X and Zhao W:
PANoptosis: A new insight into oral infectious diseases. Front
Immunol. 12:7896102021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
73
|
Zheng M and Kanneganti TD: The regulation
of the ZBP1-NLRP3 inflammasome and its implications in pyroptosis,
apoptosis, and necroptosis (PANoptosis). Immunol Rev. 297:26–38.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Samir P, Malireddi RKS and Kanneganti TD:
The PANoptosome: A deadly protein complex driving pyroptosis,
apoptosis, and necroptosis (PANoptosis). Front Cell Infect
Microbiol. 10:2382020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Chen H, Deng Y, Gan X, Li Y, Huang W, Lu
L, Wei L, Su L, Luo J, Zou B, et al: NLRP12 collaborates with NLRP3
and NLRC4 to promote pyroptosis inducing ganglion cell death of
acute glaucoma. Mol Neurodegener. 15:262020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Pistritto G, Trisciuoglio D, Ceci C,
Garufi A and D'Orazi G: Apoptosis as anticancer mechanism: Function
and dysfunction of its modulators and targeted therapeutic
strategies. Aging (Albany NY). 8:603–619. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Yan J, Wan P, Choksi S and Liu ZG:
Necroptosis and tumor progression. Trends Cancer. 8:21–27. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Karki R and Kanneganti TD: Diverging
inflammasome signals in tumorigenesis and potential targeting. Nat
Rev Cancer. 19:197–214. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Allen IC, TeKippe EM, Woodford RM, Uronis
JM, Holl EK, Rogers AB, Herfarth HH, Jobin C and Ting JP: The NLRP3
inflammasome functions as a negative regulator of tumorigenesis
during colitis-associated cancer. J Exp Med. 207:1045–1056. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Zaki MH, Boyd KL, Vogel P, Kastan MB,
Lamkanfi M and Kanneganti TD: The NLRP3 inflammasome protects
against loss of epithelial integrity and mortality during
experimental colitis. Immunity. 32:379–391. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zaki MH, Vogel P, Body-Malapel M, Lamkanfi
M and Kanneganti TD: IL-18 production downstream of the Nlrp3
inflammasome confers protection against colorectal tumor formation.
J Immunol. 185:4912–4920. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Carvalho FA, Nalbantoglu I, Aitken JD,
Uchiyama R, Su Y, Doho GH, Vijay-Kumar M and Gewirtz AT: Cytosolic
flagellin receptor NLRC4 protects mice against mucosal and systemic
challenges. Mucosal Immunol. 5:288–298. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Karki R, Man SM and Kanneganti TD:
Inflammasomes and cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. 5:94–99. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Tenthorey JL, Chavez RA, Thompson TW,
Deets KA, Vance RE and Rauch I: NLRC4 inflammasome activation is
NLRP3- and phosphorylation-independent during infection and does
not protect from melanoma. J Exp Med. 217:e201917362020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Ohashi K, Wang Z, Yang YM, Billet S, Tu W,
Pimienta M, Cassel SL, Pandol SJ, Lu SC, Sutterwala FS, et al:
NOD-like receptor C4 inflammasome regulates the growth of colon
cancer liver metastasis in NAFLD. Hepatology. 70:1582–1599. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Chen GY and Núñez G: Inflammasomes in
intestinal inflammation and cancer. Gastroenterology.
141:1986–1999. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Peng L, Youwei R and Yanghong Z: Research
progress of NLRC4 and colorectal cancer. J Hubei Univ Sci Technol
(Med Sci). 36:176–179. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Bast A, Krause K, Schmidt IHE, Pudla M,
Brakopp S, Hopf V, Breitbach K and Steinmetz I: Caspase-1-dependent
and -independent cell death pathways in Burkholderia pseudomallei
infection of macrophages. PLoS Pathog. 10:e10039862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Freeman L, Guo H, David CN, Brickey WJ,
Jha S and Ting JPY: NLR members NLRC4 and NLRP3 mediate sterile
inflammasome activation in microglia and astrocytes. J Exp Med.
214:1351–1370. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Guo Q, Wu Y, Hou Y, Liu Y, Liu T, Zhang H,
Fan C, Guan H, Li Y, Shan Z and Teng W: Cytokine secretion and
pyroptosis of thyroid follicular cells mediated by enhanced NLRP3,
NLRP1, NLRC4, and AIM2 inflammasomes are associated with autoimmune
thyroiditis. Front Immunol. 9:11972018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Chiarini A, Armato U, Gui L and Dal Prà I:
'Other than NLRP3' inflammasomes: Multiple roles in brain disease.
Neuroscientist. 30:23–48. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Salcedo R, Worschech A, Cardone M, Jones
Y, Gyulai Z, Dai RM, Wang E, Ma W, Haines D, O'HUigin C, et al:
MyD88-mediated signaling prevents development of adenocarcinomas of
the colon: Role of interleukin 18. J Exp Med. 207:1625–1636. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Takagi H, Kanai T, Okazawa A, Kishi Y,
Sato T, Takaishi H, Inoue N, Ogata H, Iwao Y, Hoshino K, et al:
Contrasting action of IL-12 and IL-18 in the development of dextran
sodium sulphate colitis in mice. Scand J Gastroenterol. 38:837–844.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Chen GY, Liu M, Wang F, Bertin J and Núñez
G: A functional role for Nlrp6 in intestinal inflammation and
tumorigenesis. J Immunol. 186:7187–7194. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Wilson JE, Petrucelli AS, Chen L,
Koblansky AA, Truax AD, Oyama Y, Rogers AB, Brickey WJ, Wang Y,
Schneider M, et al: Inflammasome-independent role of AIM2 in
suppressing colon tumorigenesis via DNA-PK and Akt. Nat Med.
21:906–913. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Bakhshi S and Shamsi S: MCC950 in the
treatment of NLRP3-mediated inflammatory diseases: Latest evidence
and therapeutic outcomes. Int Immunopharmacol. 106:1085952022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Cai Y, Chen J, Liu J, Zhu K, Xu Z, Shen J,
Wang D and Chu L: Identification of six hub genes and two key
pathways in two rat renal fibrosis models based on bioinformatics
and RNA-seq transcriptome analyses. Front Mol Biosci.
9:10357722022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Di Q, Zhao X, Tang H, Li X, Xiao Y, Wu H,
Wu Z, Quan J and Chen W: USP22 suppresses the NLRP3 inflammasome by
degrading NLRP3 via ATG5-dependent autophagy. Autophagy.
19:873–885. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
99
|
Kolb R, Phan L, Borcherding N, Liu Y, Yuan
F, Janowski AM, Xie Q, Markan KR, Li W, Potthoff MJ, et al:
Obesity-associated NLRC4 inflammasome activation drives breast
cancer progression. Nat Commun. 7:130072016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Ghiringhelli F, Apetoh L, Tesniere A,
Aymeric L, Ma Y, Ortiz C, Vermaelen K, Panaretakis T, Mignot G,
Ullrich E, et al: Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in dendritic
cells induces IL-1beta-dependent adaptive immunity against tumors.
Nat Med. 15:1170–1178. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Allam R, Maillard MH, Tardivel A,
Chennupati V, Bega H, Yu CW, Velin D, Schneider P and Maslowski KM:
Epithelial NAIPs protect against colonic tumorigenesis. J Exp Med.
212:369–383. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Güllülü Ö, Hehlgans S, Rödel C, Fokas E
and Rödel F: Tumor suppressor protein p53 and inhibitor of
apoptosis proteins in colorectal cancer-A promising signaling
network for therapeutic interventions. Cancers (Basel). 13:6242021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Lee C, Do HTT, Her J, Kim Y, Seo D and
Rhee I: Inflammasome as a promising therapeutic target for cancer.
Life Sci. 231:1165932019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Naqishbandi AM: Cytotoxic and apoptotic
potential of gemini-chrysophanol nanoparticles against human
colorectal cancer HCT-116 cell lines. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol.
23:562022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Moazzendizaji S, Sevbitov A, Ezzatifar F,
Jalili HR, Aalii M, Hemmatzadeh M, Aslani S, Gholizadeh Navashenaq
J, Safari R, Hosseinzadeh R, et al: microRNAs: Small molecules with
a large impact on colorectal cancer. Biotechnol Appl Biochem.
69:1893–1908. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Elrebehy MA, Al-Saeed S, Gamal S, El-Sayed
A, Ahmed AA, Waheed O, Ismail A, El-Mahdy HAM, Sallam AM and
Doghish AS: miRNAs as cornerstones in colorectal cancer
pathogenesis and resistance to therapy: A spotlight on signaling
pathways interplay-a review. Int J Biol Macromol. 214:583–600.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Dai F, Guo M, Shao Y and Li C: Vibrio
splendidus flagellin C binds tropomodulin to induce p38
MAPK-mediated p53-dependent coelomocyte apoptosis in Echinodermata.
J Biol Chem. 298:1020912022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Mello SS and Attardi LD: Deciphering p53
signaling in tumor suppression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 51:65–72.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
109
|
Raghu D and Karunagaran D: Plumbagin
downregulates Wnt signaling independent of p53 in human colorectal
cancer cells. J Nat Prod. 77:1130–1134. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Golubovskaya VM and Cance WG: Targeting
the p53 pathway. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 22:747–764. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Stegh AH: Targeting the p53 signaling
pathway in cancer therapy-the promises, challenges and perils.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 16:67–83. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Morandell S and Yaffe MB: Exploiting
synthetic lethal interactions between DNA damage signaling,
checkpoint control, and p53 for targeted cancer therapy. Prog Mol
Biol Transl Sci. 110:289–314. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Golubovskaya VM and Cance WG: Focal
adhesion kinase and p53 signaling in cancer cells. Int Rev Cytol.
263:103–153. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
El-Deiry WS: Insights into cancer
therapeutic design based on p53 and TRAIL receptor signaling. Cell
Death Differ. 8:1066–1075. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Bates S and Vousden KH: p53 in signaling
checkpoint arrest or apoptosis. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 6:12–18. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Khan M, Ai M, Du K, Song J, Wang B, Lin J,
Ren A, Chen C, Huang Z, Qiu W, et al: Pyroptosis relates to tumor
microenvironment remodeling and prognosis: A pan-cancer
perspective. Front Immunol. 13:10622252022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Ding J, Wang K, Liu W, She Y, Sun Q, Shi
J, Sun H, Wang DC and Shao F: Pore-forming activity and structural
autoinhibition of the gasdermin family. Nature. 535:111–116. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Liu X, Zhang Z, Ruan J, Pan Y, Magupalli
VG, Wu H and Lieberman J: Inflammasome-activated gasdermin D causes
pyroptosis by forming membrane pores. Nature. 535:153–158. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Broz P and Dixit VM: Inflammasomes:
Mechanism of assembly, regulation and signalling. Nat Rev Immunol.
16:407–420. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Kay C, Wang R, Kirkby M and Man SM:
Molecular mechanisms activating the NAIP-NLRC4 inflammasome:
Implications in infectious disease, autoinflammation, and cancer.
Immunol Rev. 297:67–82. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Man SM: Inflammasomes in the
gastrointestinal tract: Infection, cancer and gut microbiota
homeostasis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 15:721–737. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Irak K, Bayram M, Cifci S and Sener G:
Serum levels of NLRC4 and MCP-2/CCL8 in patients with active
Crohn's disease. PLoS One. 16:e02600342021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Fattinger SA, Geiser P, Samperio Ventayol
P, Di Martino ML, Furter M, Felmy B, Bakkeren E, Hausmann A,
Barthel-Scherrer M, Gül E, et al: Epithelium-autonomous NAIP/NLRC4
prevents TNF-driven inflammatory destruction of the gut epithelial
barrier in Salmonella-infected mice. Mucosal Immunol. 14:615–629.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Mizoguchi A: Animal models of inflammatory
bowel disease. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 105:263–320. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Saleh M and Trinchieri G: Innate immune
mechanisms of colitis and colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Nat
Rev Immunol. 11:9–20. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Kiesler P, Fuss IJ and Strober W:
Experimental models of inflammatory bowel diseases. Cell Mol
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1:154–170. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Henderson LA and Cron RQ: Macrophage
activation syndrome and secondary hemophagocytic
lymphohistiocytosis in childhood inflammatory disorders: Diagnosis
and management. Paediatric drugs. 22:29–44. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
128
|
Bardet J, Laverdure N, Fusaro M, Picard C,
Garnier L, Viel S, Collardeau-Frachon S, De Guillebon JM, Durieu I,
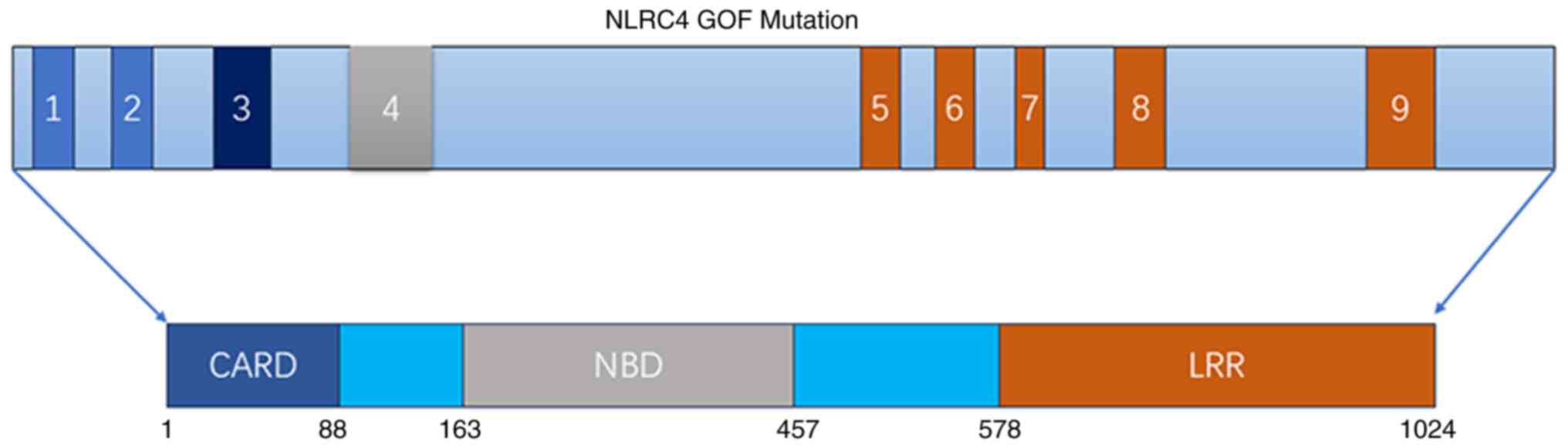
Casari-Thery C, et al: NLRC4 GOF mutations, a challenging diagnosis
from neonatal age to adulthood. J Clin Med. 10:43692021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Volker-Touw CM, de Koning HD, Giltay JC,
de Kovel CGF, van Kempen TS, Oberndorff KMEJ, Boes ML, van Steensel
MAM, van Well GTJ, Blokx WAM, et al: Erythematous nodes, urticarial
rash and arthralgias in a large pedigree with NLRC4-related
autoinflammatory disease, expansion of the phenotype. Br J
Dermatol. 176:244–248. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Moghaddas F, Zeng P, Zhang Y, Schützle H,
Brenner S, Hofmann SR, Berner R, Zhao Y, Lu B, Chen X, et al:
Autoinflammatory mutation in NLRC4 reveals a leucine-rich repeat
(LRR)-LRR oligomerization interface. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
142:1956–1967.e6. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Trifiletti R, Lachman HM, Manusama O,
Zheng D, Spalice A, Chiurazzi P, Schornagel A, Serban AM, van Wijck
R, Cunningham JL, et al: Identification of ultra-rare genetic
variants in pediatric acute onset neuropsychiatric syndrome (PANS)
by exome and whole genome sequencing. Sci Rep. 12:111062022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Eeckhout E, Asaoka T, Van Gorp H, Demon D,
Girard-Guyonvarc'h C, Andries V, Vereecke L, Gabay C, Lamkanfi M,
van Loo G and Wullaert A: The autoinflammation-associated
NLRC4V341A mutation increases microbiota-independent
IL-18 production but does not recapitulate human autoinflammatory
symptoms in mice. Front Immunol. 14:12726392023. View Article : Google Scholar
|