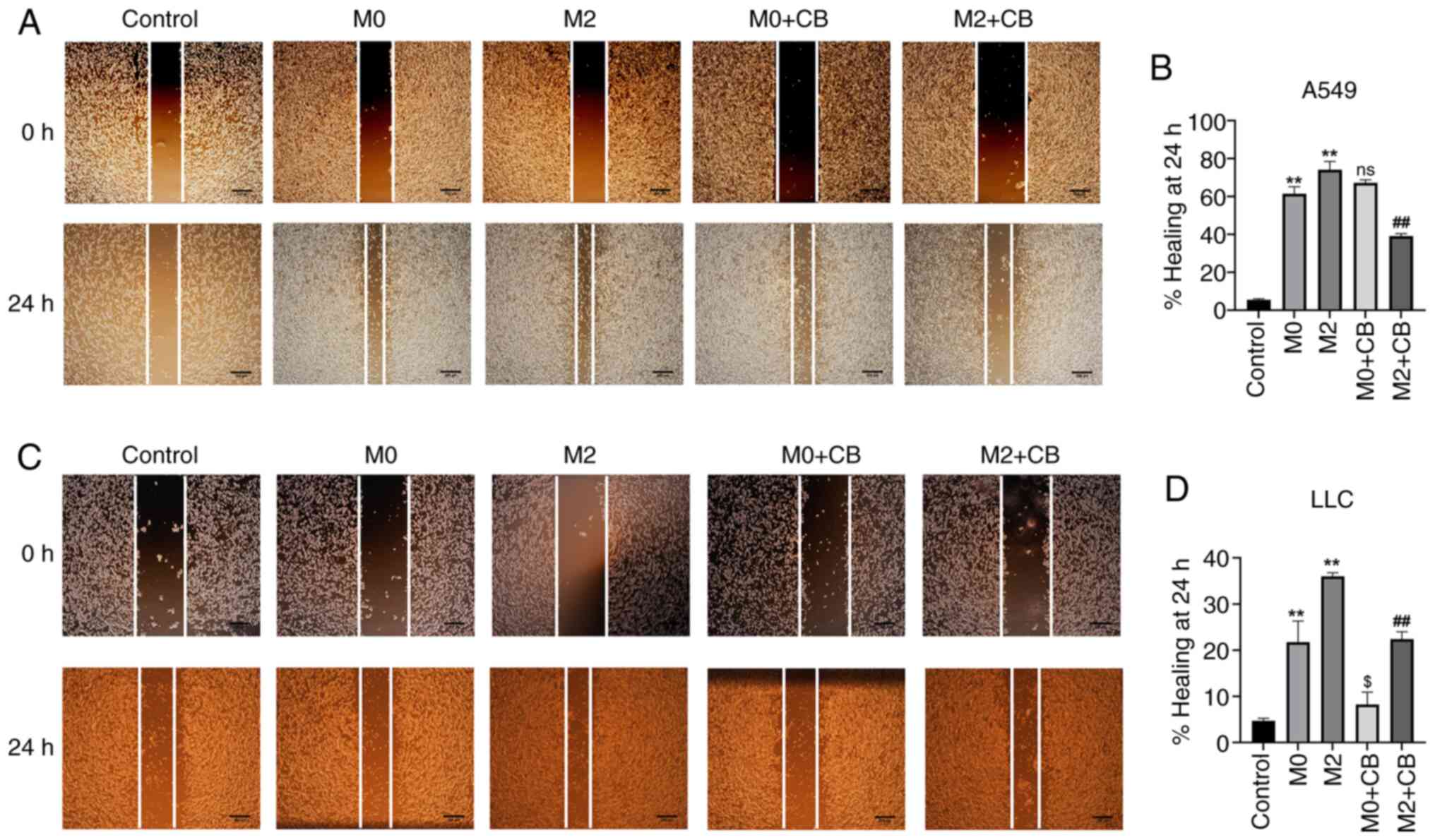
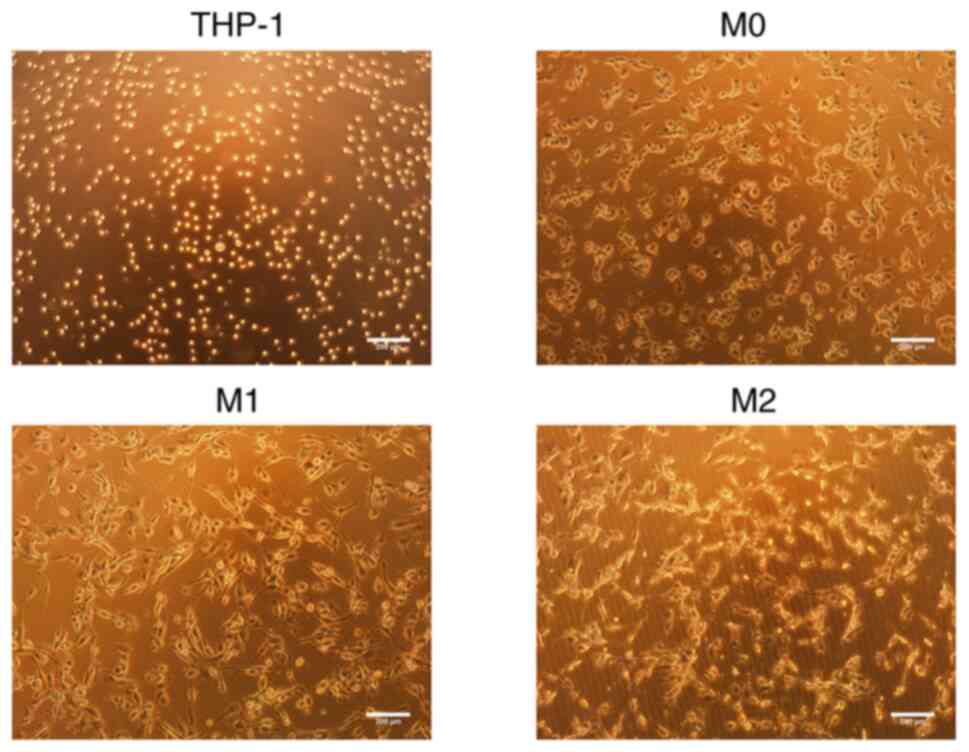
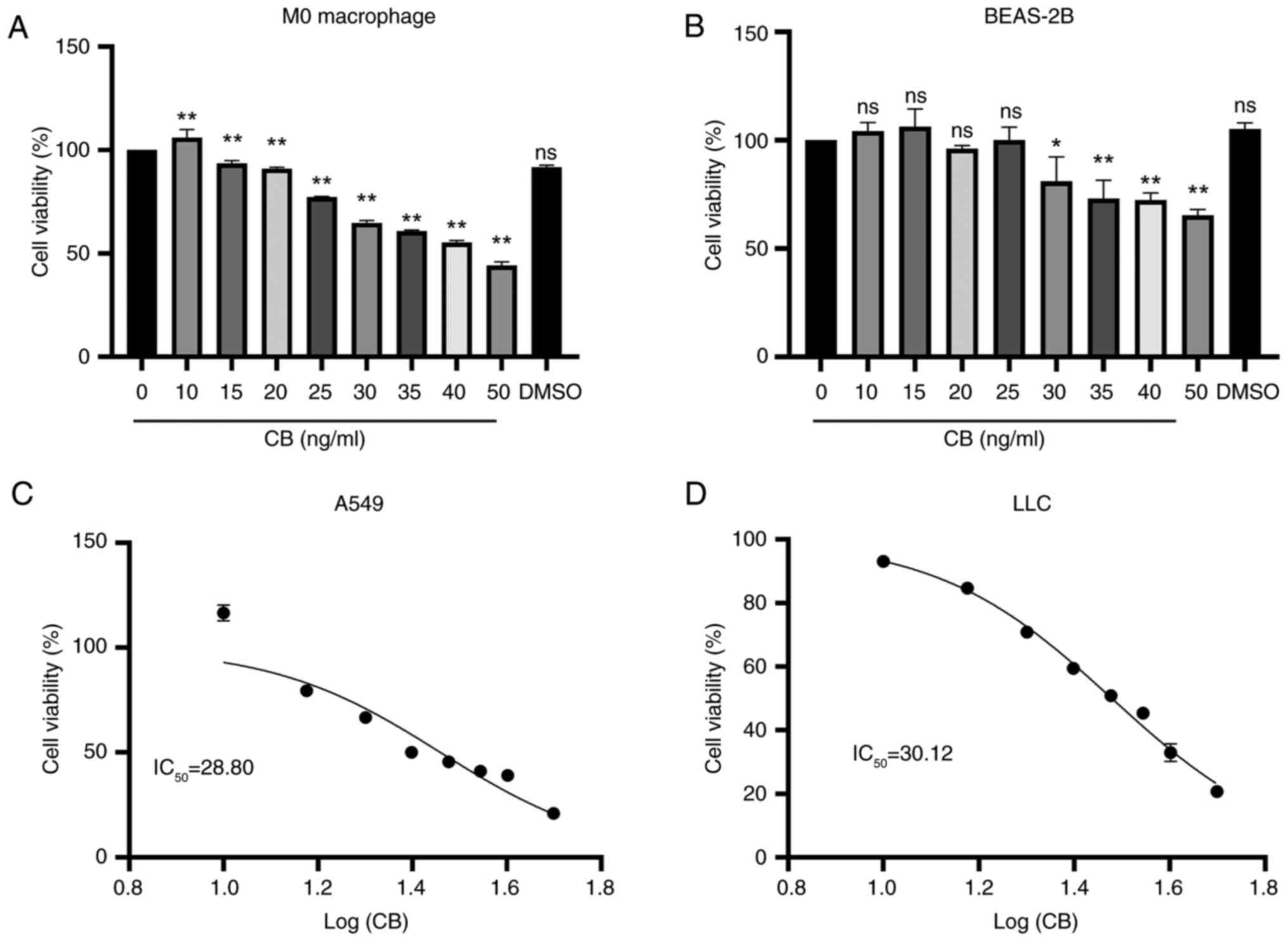
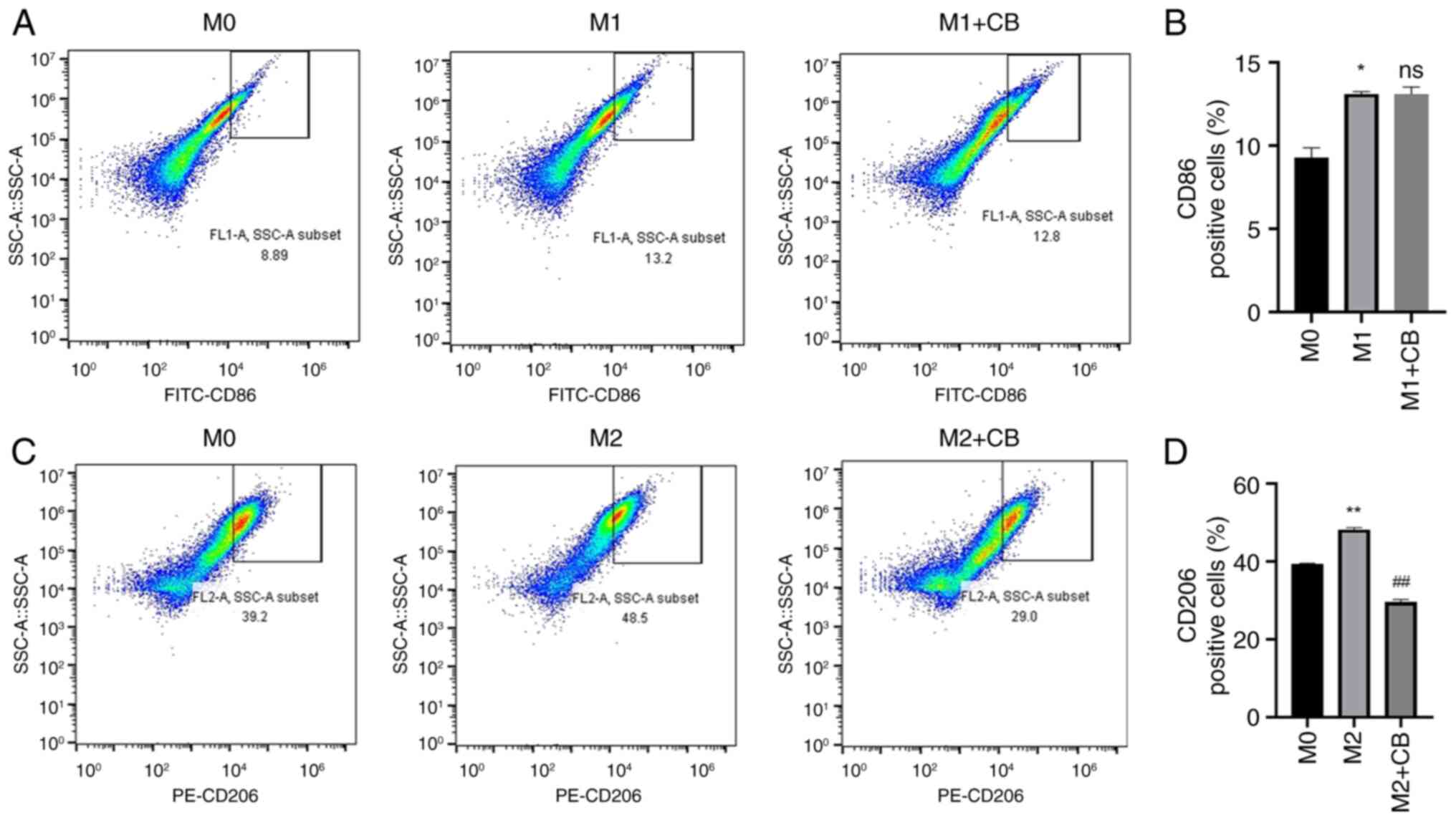
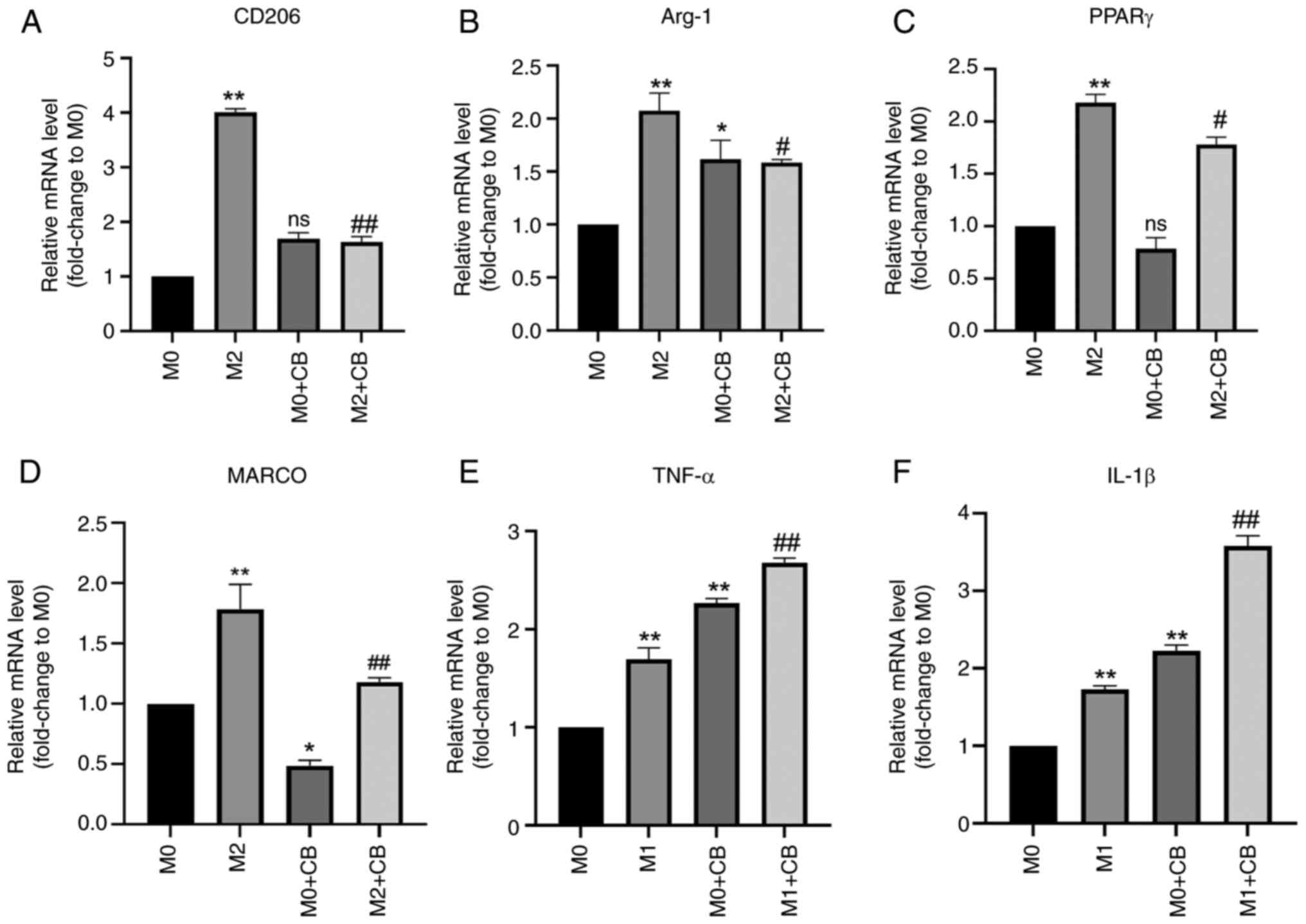
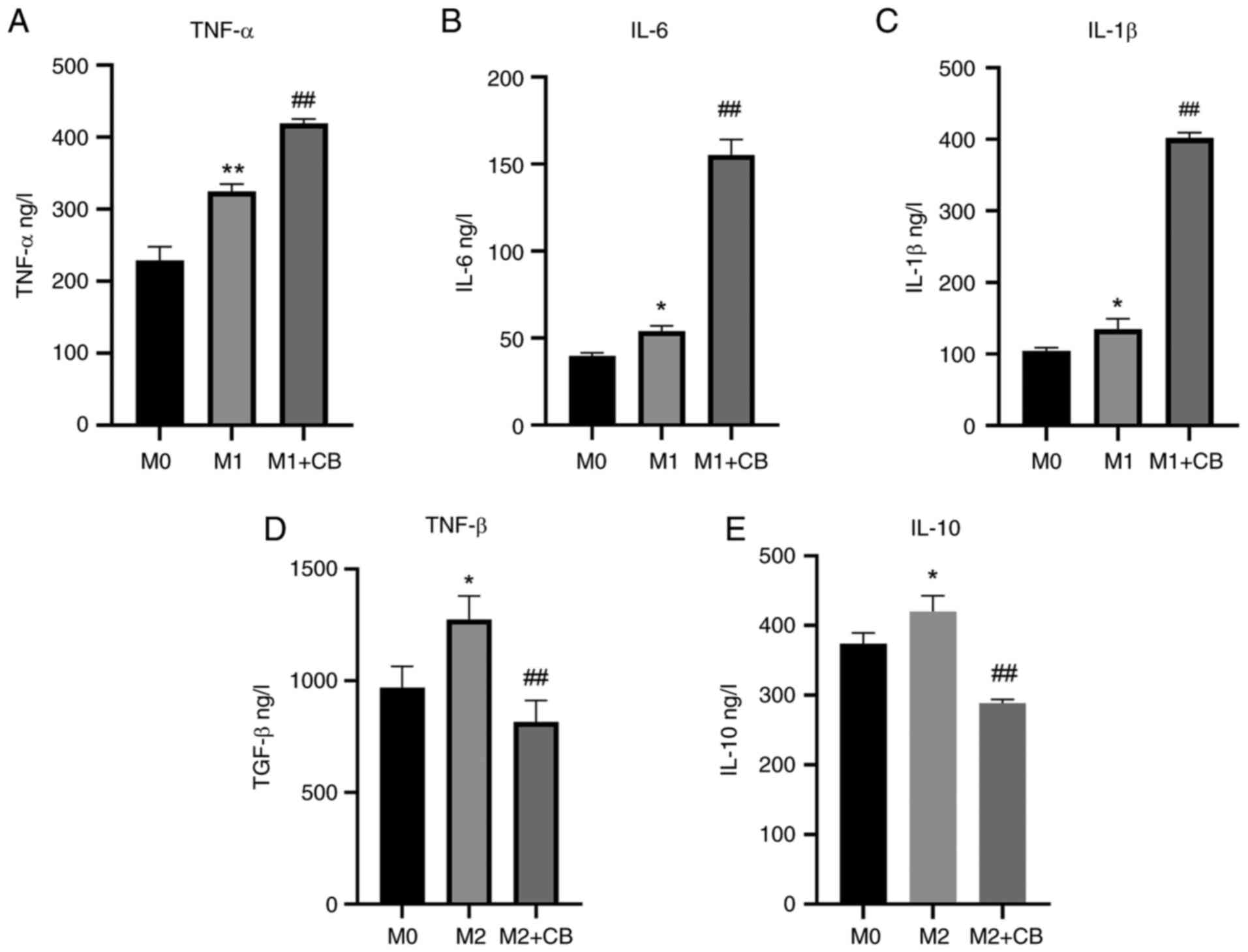
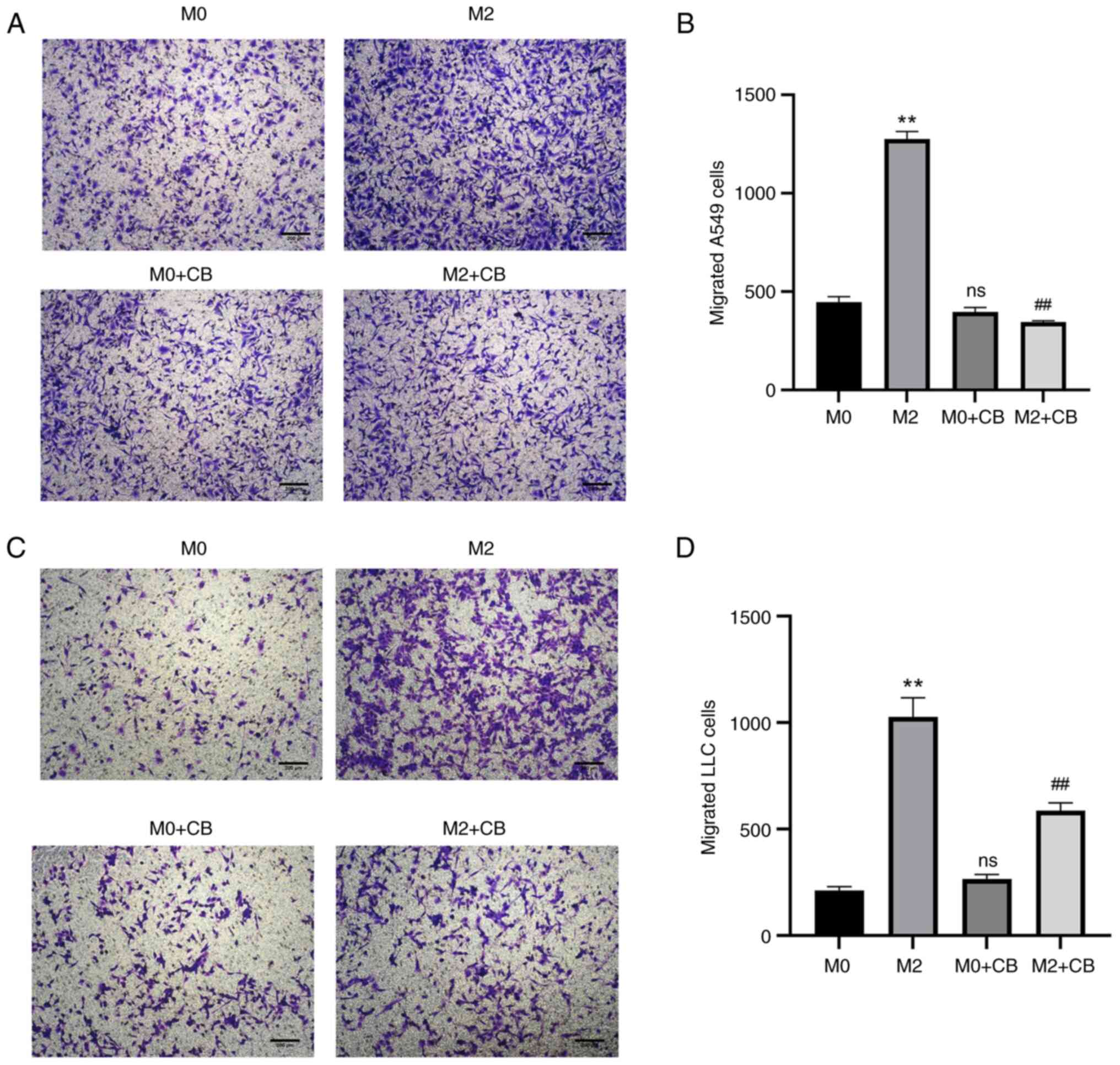
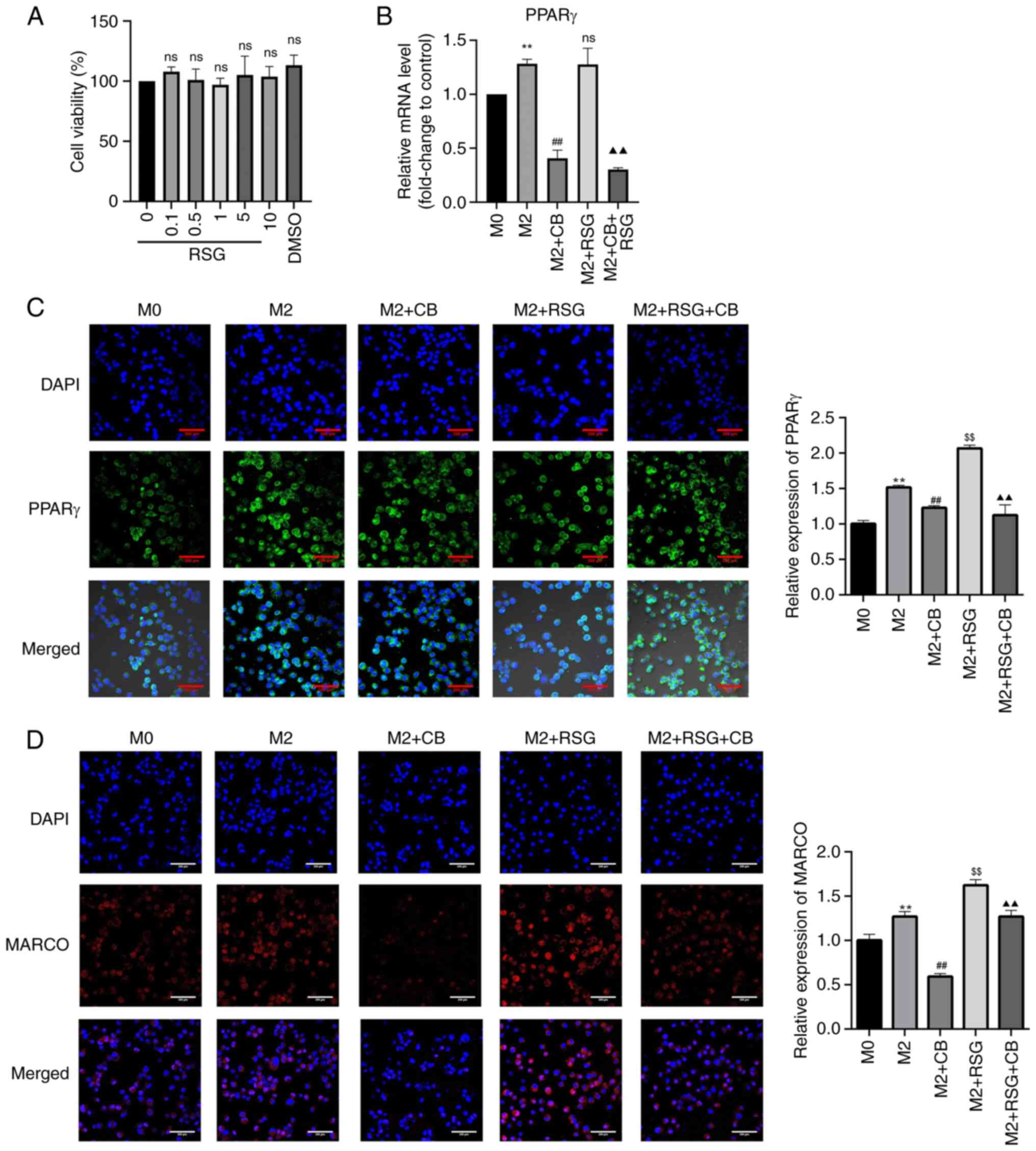
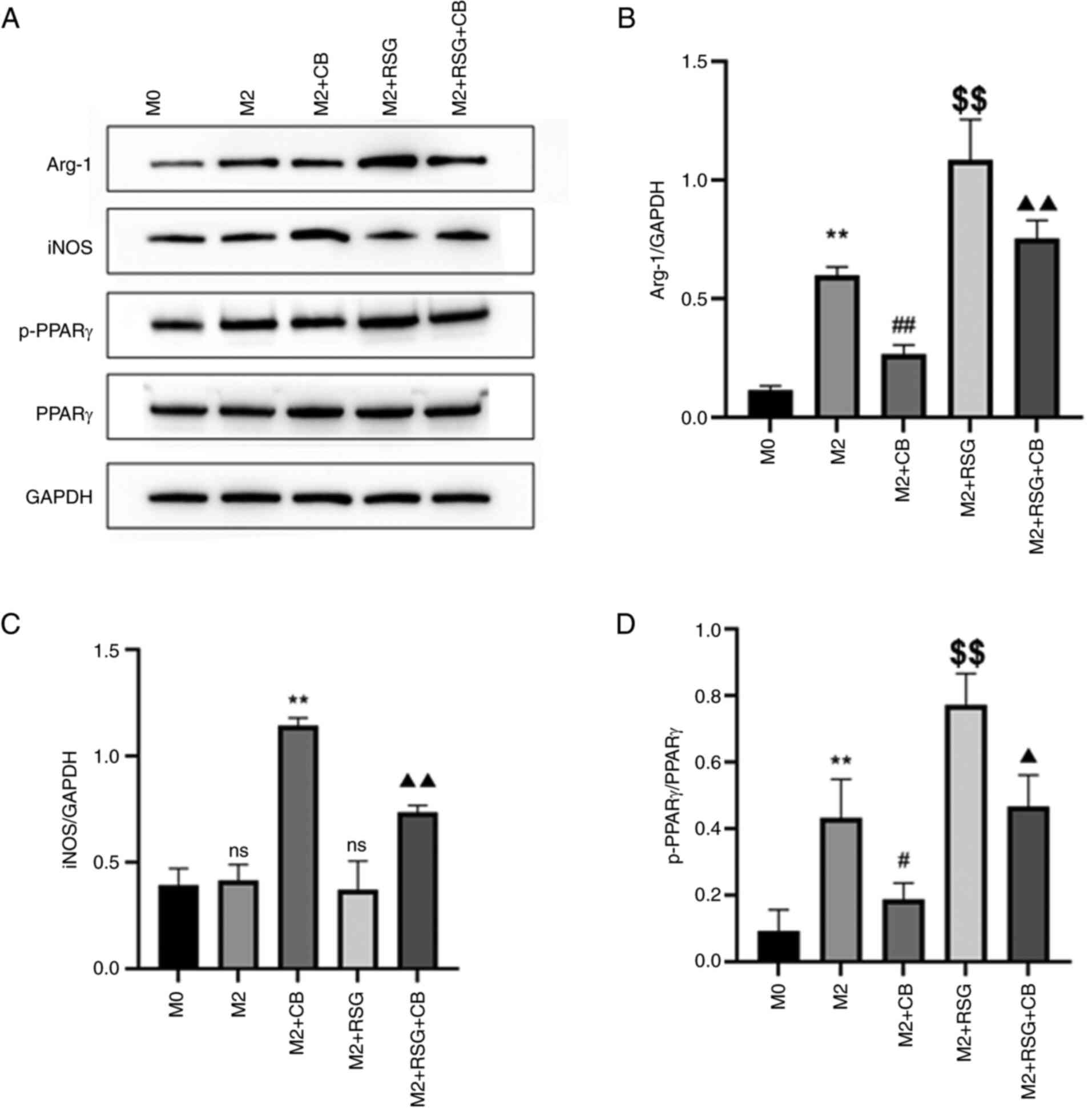
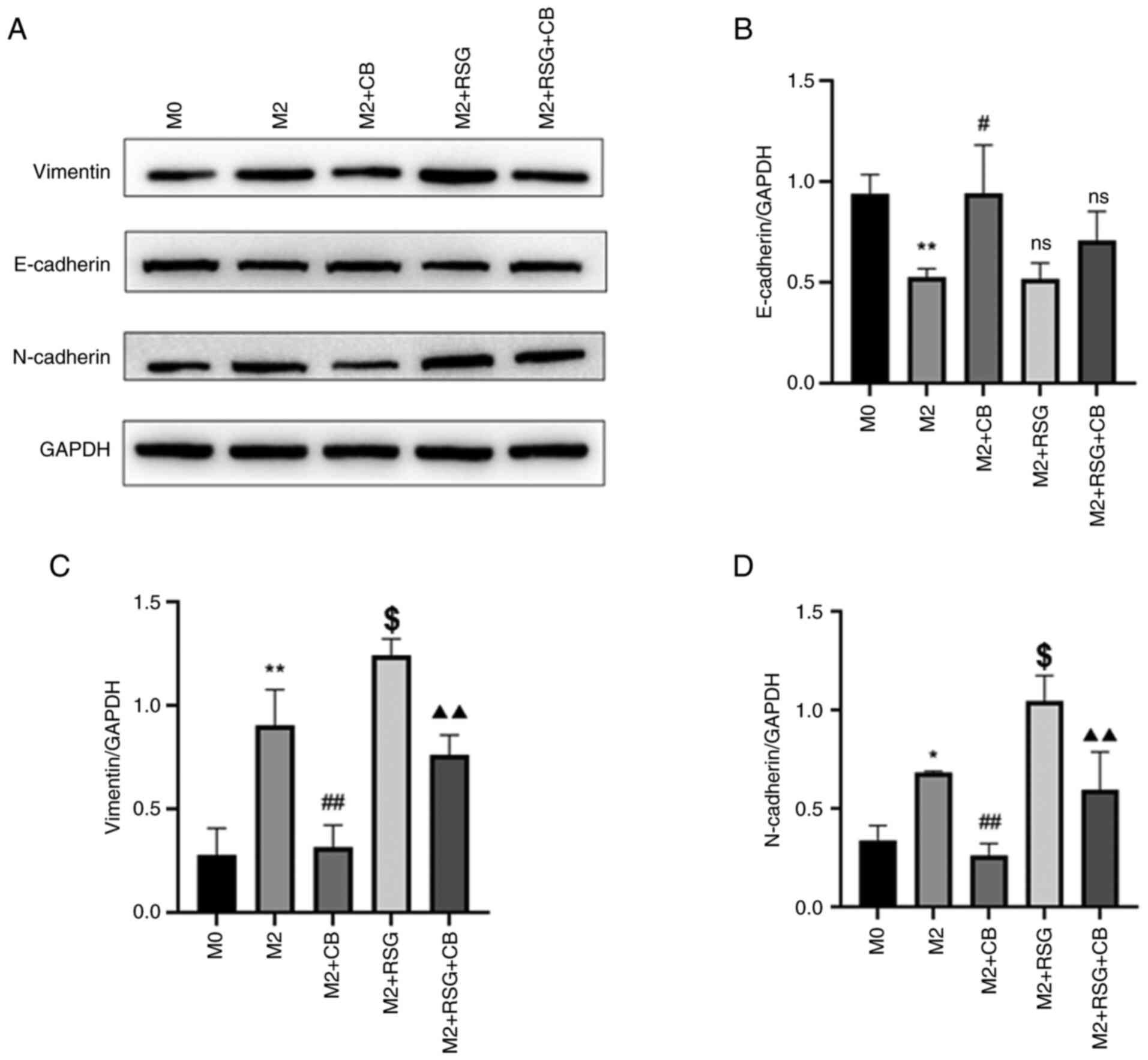
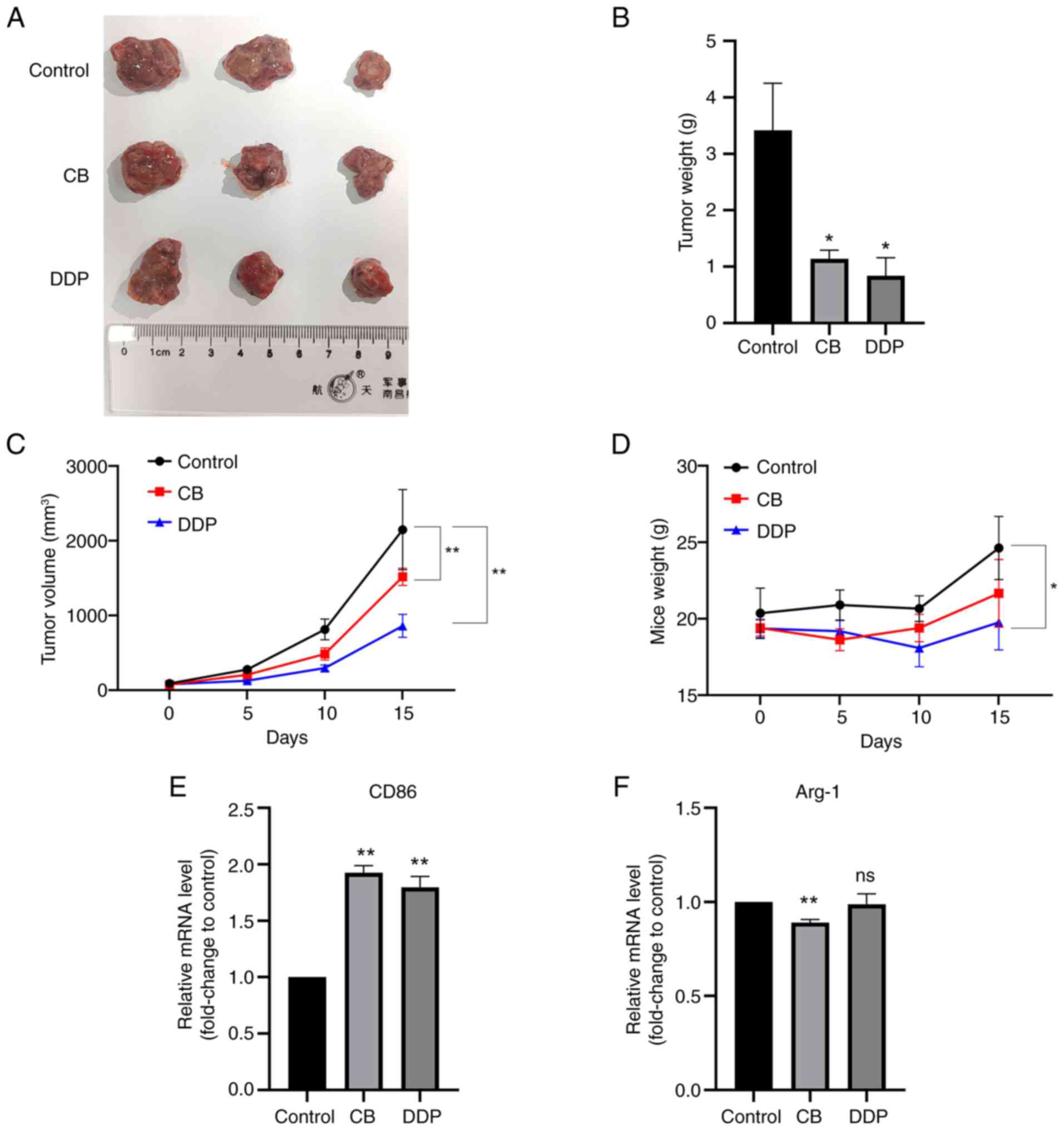
|
1
|
Kratzer TB, Bandi P, Freedman ND, Smith
RA, Travis WD, Jemal A and Siegel RL: Lung cancer statistics, 2023.
Cancer. 130:1330–1348. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lee E and Kazerooni EA: Lung cancer
screening. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 43:839–850. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schabath MB and Cote ML: Cancer progress
and priorities: Lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
28:1563–1579. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zheng M: Classification and pathology of
lung cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 25:447–468. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rodriguez-Canales J, Parra-Cuentas E and
Wistuba II: Diagnosis and molecular classification of lung cancer.
Cancer Treat Res. 170:25–46. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Srivastava S, Mohanty A, Nam A, Singhal S
and Salgia R: Chemokines and NSCLC: Emerging role in prognosis,
heterogeneity, and therapeutics. Semin Cancer Biol. 86:233–246.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Duma N, Santana-Davila R and Molina JR:
Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, screening, diagnosis, and
treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 94:1623–1640. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Miller M and Hanna N: Advances in systemic
therapy for non-small cell lung cancer. BMJ. 375:n23632021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Osmani L, Askin F, Gabrielson E and Li QK:
Current WHO guidelines and the critical role of immunohistochemical
markers in the subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinoma
(NSCLC): Moving from targeted therapy to immunotherapy. Semin
Cancer Biol. 52:103–109. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wang Y, Chen R, Wa Y, Ding S, Yang Y, Liao
J, Tong L and Xiao G: Tumor immune microenvironment and
immunotherapy in brain metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer.
Front Immunol. 13:8294512022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cascone T, Fradette J, Pradhan M and
Gibbons DL: Tumor immunology and immunotherapy of non-small-cell
lung cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 12:a0378952022.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Sivori S, Pende D, Quatrini L, Pietra G,
Della Chiesa M, Vacca P, Tumino N, Moretta F, Mingari MC, Locatelli
F and Moretta L: NK cells and ILCs in tumor immunotherapy. Mol
Aspects Med. 80:1008702021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Herbst RS, Morgensztern D and Boshoff C:
The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature.
553:446–454. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cheng D, Ge K, Yao X, Wang B, Chen R, Zhao
W, Fang C and Ji M: Tumor-associated macrophages mediate resistance
of EGFR-TKIs in non-small cell lung cancer: Mechanisms and
prospects. Front Immunol. 14:12099472023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sedighzadeh SS, Khoshbin AP, Razi S,
Keshavarz-Fathi M and Rezaei N: A narrative review of
tumor-associated macrophages in lung cancer: Regulation of
macrophage polarization and therapeutic implications. Transl Lung
Cancer Res. 10:1889–1916. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Genova C, Dellepiane C, Carrega P,
Sommariva S, Ferlazzo G, Pronzato P, Gangemi R, Filaci G, Coco S
and Croce M: Therapeutic implications of tumor microenvironment in
lung cancer: Focus on immune checkpoint blockade. Front Immunol.
12:7994552022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yuan A, Hsiao YJ, Chen HY, Chen HW, Ho CC,
Chen YY, Liu YC, Hong TH, Yu SL, Chen JJ and Yang PC: Opposite
effects of M1 and M2 macrophage subtypes on lung cancer
progression. Sci Rep. 5:142732015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sumitomo R, Hirai T, Fujita M, Murakami H,
Otake Y and Huang CL: M2 tumor-associated macrophages promote tumor
progression in non-small-cell lung cancer. Exp Ther Med.
18:4490–4498. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hu JM, Liu K, Liu JH, Jiang XL, Wang XL,
Yang L, Chen YZ, Liu CX, Li SG, Cui XB, et al: The increased number
of tumor-associated macrophage is associated with overexpression of
VEGF-C, plays an important role in Kazakh ESCC invasion and
metastasis. Exp Mol Pathol. 102:15–21. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Frezzetti D, Gallo M, Maiello MR,
D'Alessio A, Esposito C, Chicchinelli N, Normanno N and De Luca A:
VEGF as a potential target in lung cancer. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 21:959–966. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zeni E, Mazzetti L, Miotto D, Lo Cascio N,
Maestrelli P, Querzoli P, Pedriali M, De Rosa E, Fabbri LM, Mapp CE
and Boschetto P: Macrophage expression of interleukin-10 is a
prognostic factor in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Eur Respir J.
30:627–632. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vahl JM, Friedrich J, Mittler S, Trump S,
Heim L, Kachler K, Balabko L, Fuhrich N, Geppert CI, Trufa DI, et
al: Interleukin-10-regulated tumour tolerance in non-small cell
lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 117:1644–1655. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Maltarollo VG, Kronenberger T, Windshugel
B, Wrenger C, Trossini GHG and Honorio KM: Advances and challenges
in drug design of PPARδ ligands. Curr Drug Targets. 19:144–154.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Tontonoz P and Spiegelman BM: Fat and
beyond: The diverse biology of PPARgamma. Annu Rev Biochem.
77:289–312. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gallardo-Soler A, Gómez-Nieto C, Campo ML,
Marathe C, Tontonoz P, Castrillo A and Corraliza I: Arginase I
induction by modified lipoproteins in macrophages: A peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma/delta-mediated effect that
links lipid metabolism and immunity. Mol Endocrinol. 22:1394–1402.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang JT, Welch JS, Ricote M, Binder CJ,
Willson TM, Kelly C, Witztum JL, Funk CD, Conrad D and Glass CK:
Interleukin-4-dependent production of PPAR-gamma ligands in
macrophages by 12/15-lipoxygenase. Nature. 400:378–382. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bu ZJ, Wan SR, Steinmann P, Yin ZT, Tan
JP, Li WX, Tang ZY, Jiang S, Ye MM and Xu JY: Effectiveness and
safety of Chinese herbal injections combined with SOX chemotherapy
regimens for advanced gastric cancer: A Bayesian network
meta-analysis. J Cancer. 15:889–907. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tarasiuk A, Mirocha G and Fichna J:
Current status of complementary and alternative medicine
interventions in the management of pancreatic cancer-an overview.
Curr Treat Options Oncol. 24:1852–1869. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xu YF, Chen YR, Bu FL, Huang YB, Sun YX,
Li CY, Sellick J, Liu JP, Qin DM and Liu ZL: Chinese herbal
injections versus intrapleural cisplatin for lung cancer patients
with malignant pleural effusion: A Bayesian network meta-analysis
of randomized controlled trials. Front Oncol. 12:9429412022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tan X, Liang X, Xi J, Guo S, Meng M, Chen
X and Li Y: Clinical efficacy and safety of Huachansu injection
combination with platinum-based chemotherapy for advanced non-small
cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of
randomized controlled trials. Medicine (Baltimore). 100:e271612021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
He K, Wang GX, Zhao LN, Cui XF, Su XB, Shi
Y, Xie TP, Hou SW and Han ZG: Cinobufagin is a selective
anti-cancer agent against tumors with EGFR amplification and PTEN
deletion. Front Pharmacol. 12:7756022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bai Y, Wang X, Cai M, Ma C, Xiang Y, Hu W,
Zhou B, Zhao C, Dai X, Li X and Zhao H: Cinobufagin suppresses
colorectal cancer growth via STAT3 pathway inhibition. Am J Cancer
Res. 11:200–214. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ma X, Suo Z, Ma X, Zhan C, Luo G and Song
J: Cinobufagin inhibits tumor progression and reduces doxorubicin
resistance by enhancing FOXO1-mediated transcription of FCGBP in
osteosarcoma. J Ethnopharmacol. 296:1154332022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang L, Liang B, Xu H, Gong Y, Hu W, Jin
Z, Wu X, Chen X, Li M, Shi L, et al: Cinobufagin induces
FOXO1-regulated apoptosis, proliferation, migration, and invasion
by inhibiting G9a in non-small-cell lung cancer A549 cells. J
Ethnopharmacol. 291:1150952022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Locati M, Allavena
P and Sica A: Macrophage polarization: Tumor-associated macrophages
as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends
Immunol. 23:549–555. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xu F, Cui WQ, Wei Y, Cui J, Qiu J, Hu LL,
Gong WY, Dong JC and Liu BJ: Astragaloside IV inhibits lung cancer
progression and metastasis by modulating macrophage polarization
through AMPK signaling. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:2072018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Niu J, Wang J, Zhang Q, Zou Z and Ding Y:
Cinobufagin-induced DNA damage response activates G2/M checkpoint
and apoptosis to cause selective cytotoxicity in cancer cells.
Cancer Cell Int. 21:4462021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Lu XS, Qiao YB, Li Y, Yang B, Chen MB and
Xing CG: Preclinical study of cinobufagin as a promising
anti-colorectal cancer agent. Oncotarget. 8:988–998. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Murray PJ, Allen JE, Biswas SK, Fisher EA,
Gilroy DW, Goerdt S, Gordon S, Hamilton JA, Ivashkiv LB, Lawrence
T, et al: Macrophage activation and polarization: Nomenclature and
experimental guidelines. Immunity. 41:14–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mittal V: Epithelial mesenchymal
transition in tumor metastasis. Annu Rev Pathol. 13:395–412. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Qi F, Inagaki Y, Gao B, Cui X, Xu H,
Kokudo N, Li A and Tang W: Bufalin and cinobufagin induce apoptosis
of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells via Fas- and
mitochondria-mediated pathways. Cancer Sci. 102:951–958. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Netea-Maier RT, Smit JWA and Netea MG:
Metabolic changes in tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages:
A mutual relationship. Cancer Lett. 413:102–109. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Redente EF, Dwyer-Nield LD, Merrick DT,
Raina K, Agarwal R, Pao W, Rice PL, Shroyer KR and Malkinson AM:
Tumor progression stage and anatomical site regulate
tumor-associated macrophage and bone marrow-derived monocyte
polarization. Am J Pathol. 176:2972–2985. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xue J, Fu C, Cong Z, Peng L, Peng Z, Chen
T, Wang W, Jiang H, Wei Q and Qin C: Galectin-3 promotes
caspase-independent cell death of HIV-1-infected macrophages. FEBS
J. 284:97–113. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Genin M, Clement F, Fattaccioli A, Raes M
and Michiels C: M1 and M2 macrophages derived from THP-1 cells
differentially modulate the response of cancer cells to etoposide.
BMC Cancer. 15:5772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen R, Lu X, Li Z, Sun Y, He Z and Li X:
Dihydroartemisinin prevents progression and metastasis of head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting polarization of
macrophages in tumor microenvironment. Onco Targets Ther.
13:3375–3387. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Huang J, Chen F, Zhong Z, Tan HY, Wang N,
Liu Y, Fang X, Yang T and Feng Y: Interpreting the pharmacological
mechanisms of huachansu capsules on hepatocellular carcinoma
through combining network pharmacology and experimental evaluation.
Front Pharmacol. 11:4142020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Dai CL, Zhang RJ, An P, Deng YQ, Rahman K
and Zhang H: Cinobufagin: A promising therapeutic agent for cancer.
J Pharm Pharmacol. 75:1141–1153. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Asrorov AM, Kayumov M, Mukhamedov N,
Yashinov A, Mirakhmetova Z, Huang Y, Yili A, Aisa HA,
Tashmukhamedov M, Salikhov S and Mirzaakhmedov S: Toad venom
bufadienolides and bufotoxins: An updated review. Drug Dev Res.
84:815–838. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li X, Bu W, Meng L, Liu X, Wang S, Jiang
L, Ren M, Fan Y and Sun H: CXCL12/CXCR4 pathway orchestrates
CSC-like properties by CAF recruited tumor associated macrophage in
OSCC. Exp Cell Res. 378:131–138. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Schmall A, Al-Tamari HM, Herold S,
Kampschulte M, Weigert A, Wietelmann A, Vipotnik N, Grimminger F,
Seeger W, Pullamsetti SS and Savai R: Macrophage and cancer cell
cross-talk via CCR2 and CX3CR1 is a fundamental mechanism driving
lung cancer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 191:437–447. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Nakatsumi H, Matsumoto M and Nakayama KI:
Noncanonical pathway for regulation of CCL2 expression by an
mTORC1-FOXK1 axis promotes recruitment of tumor-associated
macrophages. Cell Rep. 21:2471–2486. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wu CY, Cherng JY, Yang YH, Lin CL, Kuan
FC, Lin YY, Lin YS, Shu LH, Cheng YC, Liu HT, et al: Danshen
improves survival of patients with advanced lung cancer and
targeting the relationship between macrophages and lung cancer
cells. Oncotarget. 8:90925–90947. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Fu XH, Li JP, Li XY, Tan Y, Zhao M, Zhang
SF, Wu XD and Xu JG: M2-macrophage-derived exosomes promote
meningioma progression through TGF-β signaling pathway. J Immunol
Res. 2022:83265912022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Sa JK, Chang N, Lee HW, Cho HJ, Ceccarelli
M, Cerulo L, Yin J, Kim SS, Caruso FP, Lee M, et al:
Transcriptional regulatory networks of tumor-associated macrophages
that drive malignancy in mesenchymal glioblastoma. Genome Biol.
21:2162020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yu J, Deng H and Xu Z: Targeting
macrophage priming by polyphyllin VII triggers anti-tumor immunity
via STING-governed cytotoxic T-cell infiltration in lung cancer.
Sci Rep. 10:213602020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|