|
1
|
Zhang X, Wang Z, Tang W, Wang X, Liu R,
Bao H, Chen X, Wei Y, Wu S, Bao H, et al: Ultrasensitive and
affordable assay for early detection of primary liver cancer using
plasma cell-free DNA fragmentomics. Hepatology. 76:317–329. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Rumgay H, Ferlay J, de Martel C, Georges
D, Ibrahim AS, Zheng R, Wei W, Lemmens VEPP and Soerjomataram I:
Global, regional and national burden of primary liver cancer by
subtype. Eur J Cancer. 161:108–118. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
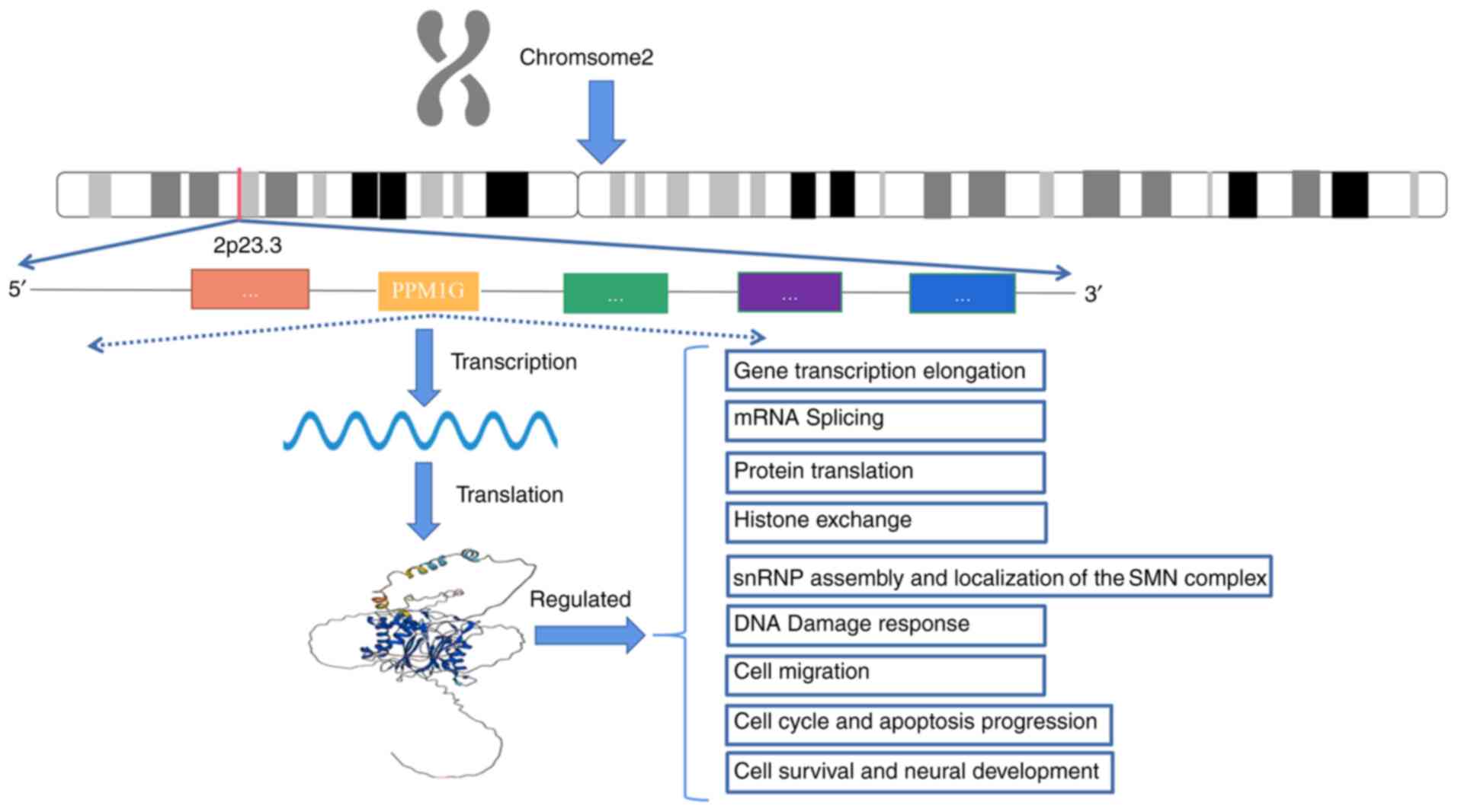
Feng M, Pan Y, Kong R and Shu S: Therapy
of primary liver cancer. Innovation (Camb). 1:1000322020.
|
|
4
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rumgay H, Arnold M, Ferlay J, Lesi O,
Cabasag CJ, Vignat J, Laversanne M, McGlynn KA and Soerjomataram I:
Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to
2040. J Hepatol. 77:1598–1606. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stroffolini T and Stroffolini G: A
historical overview on the role of hepatitis B and C viruses as
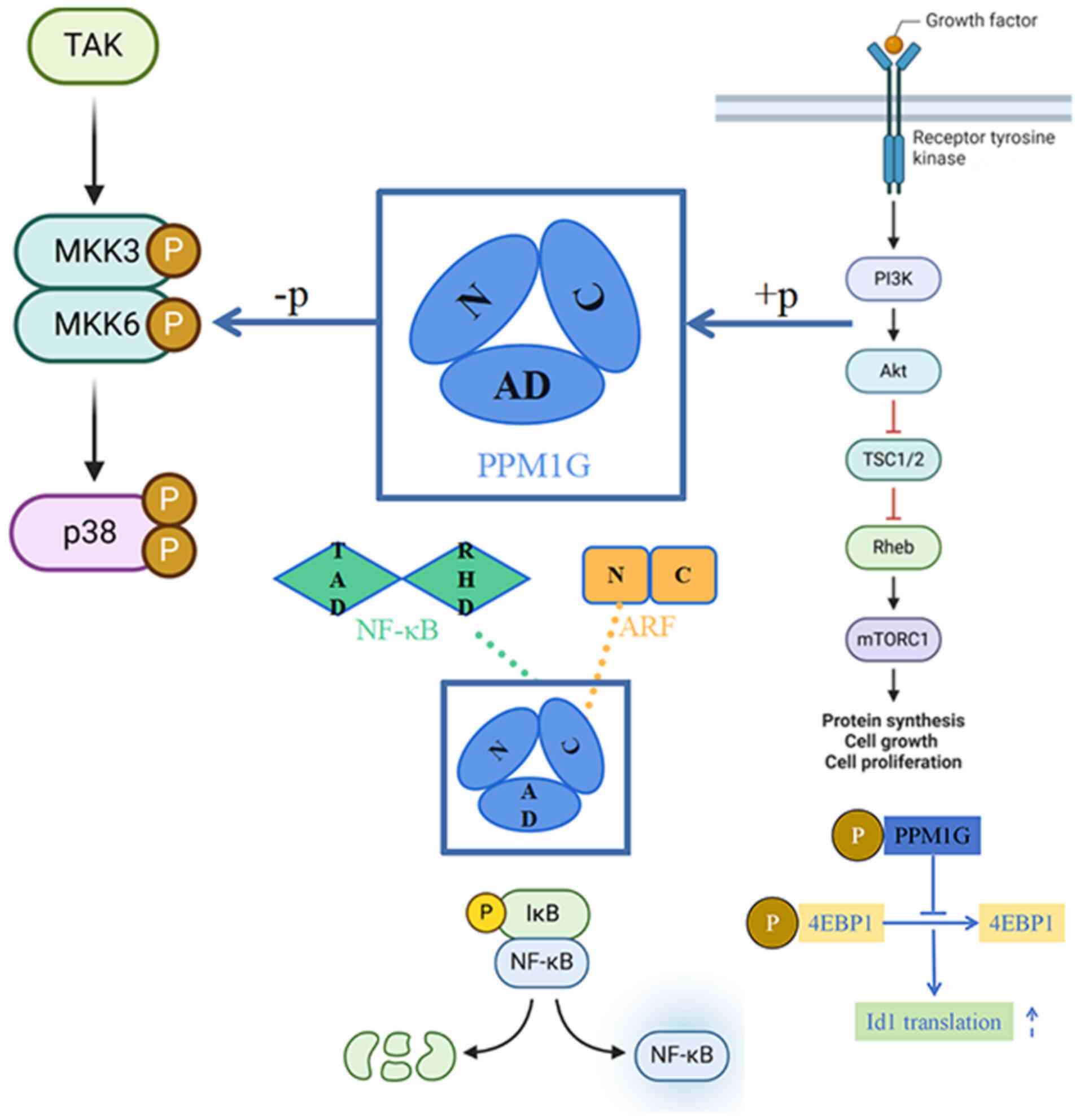
aetiological factors for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel).
15:23882023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Foerster F, Gairing SJ, Müller L and Galle
PR: NAFLD-driven HCC: Safety and efficacy of current and emerging
treatment options. J Hepatol. 76:446–457. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Huang KY, Su MG, Kao HJ, Hsieh YC, Jhong
JH, Cheng KH, Huang HD and Lee TY: dbPTM 2016: 10-Year anniversary
of a resource for post-translational modification of proteins.
Nucleic Acids Res. 44(D1): D435–D446. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
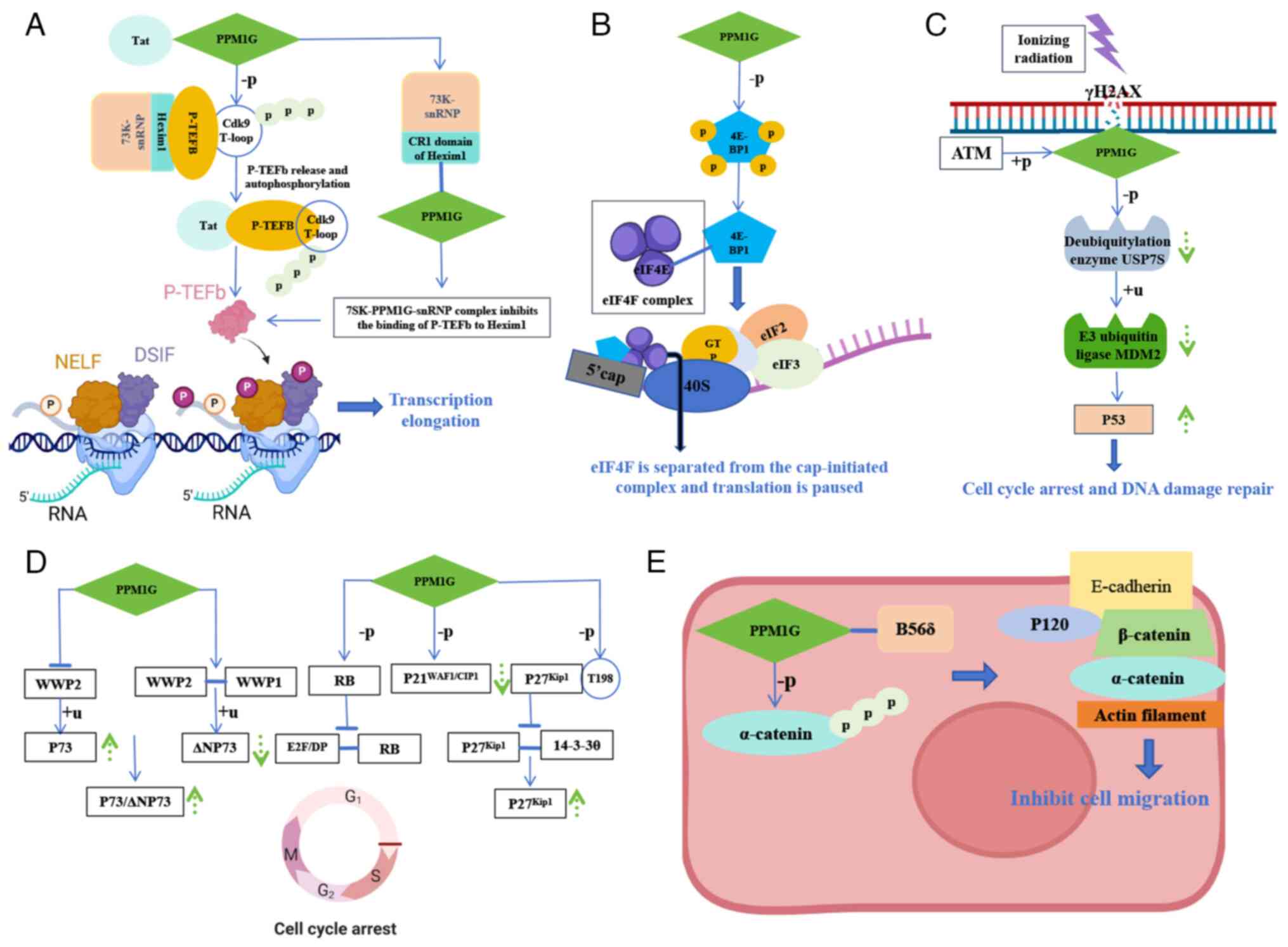
|
Ebert T, Tran N, Schurgers L, Stenvinkel P
and Shiels PG: Ageing-oxidative stress, PTMs and disease. Mol
Aspects Med. 86:1010992022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zafar S, Fatima SI, Schmitz M and Zerr I:
Current technologies unraveling the significance of
post-translational modifications (PTMs) as crucial players in
neurodegeneration. Biomolecules. 14:1182024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Y, Liu Z, Bian X, Zhao C, Zhang X,
Liu X and Wang N: Function and regulation of ubiquitin-like SUMO
system in heart. Front Cell Dev Biol. 11:12947172023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen L, Huang L, Gu Y, Cang W, Sun P and
Xiang Y: lactate-lactylation hands between metabolic reprogramming
and immunosuppression. Int J Mol Sci. 23:119432022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Safabakhsh S, Panwar P, Barichello S,
Sangha SS, Hanson PJ, Petegem FV and Laksman Z: The role of
phosphorylation in atrial fibrillation: A focus on mass
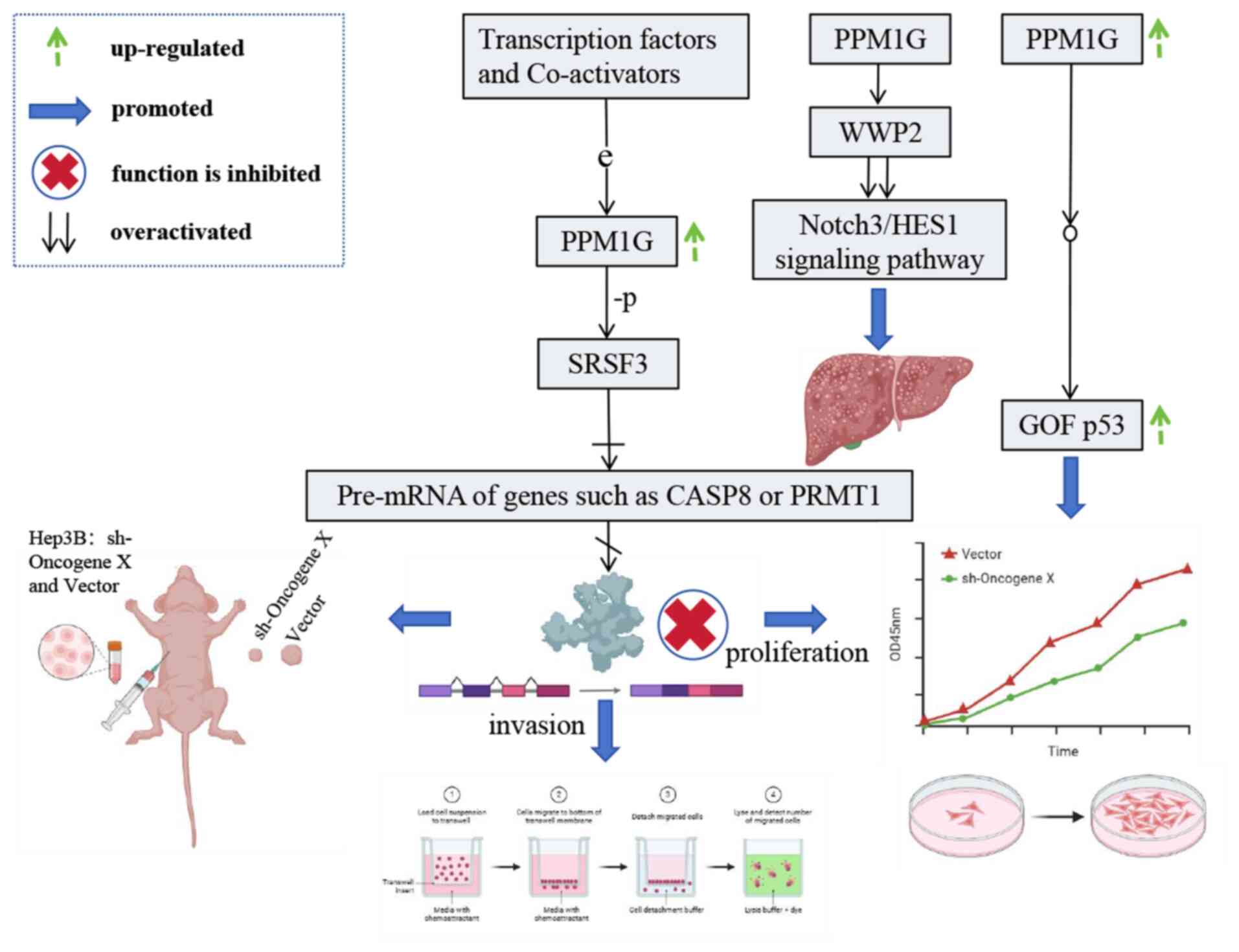
spectrometry approaches. Cardiovasc Res. 118:1205–1217. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Song W, Hu L, Ma Z, Yang L and Li J:
Importance of tyrosine phosphorylation in hormone-regulated plant
growth and development. Int J Mol Sci. 23:66032022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stanford SM and Bottini N: Targeting
protein phosphatases in cancer immunotherapy and autoimmune
disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 22:273–294. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gao C, Cao N and Wang Y: Metal dependent
protein phosphatase PPM family in cardiac health and diseases. Cell
Signal. 85:1100612021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kamada R, Kudoh F, Ito S, Tani I, Janairo
JIB, Omichinski JG and Sakaguchi K: Metal-dependent Ser/Thr protein
phosphatase PPM family: Evolution, structures, diseases and
inhibitors. Pharmacol Ther. 215:1076222020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Das AK, Helps NR, Cohen PT and Barford D:
Crystal structure of the protein serine/threonine phosphatase 2C at
2.0 A resolution. EMBO J. 15:6798–6809. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pan C, Tang JY, Xu YF, Xiao P, Liu HD,
Wang HA, Wang WB, Meng FG, Yu X and Su JP: The catalytic role of
the M2 metal ion in PP2Cα. Sci Rep. 5:85602015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
The GeneCards human gene database:
Weizmann Institute of Science; [updated 30-5-2024]. Available from:
www.genecards.org/Search/Keyword?queryString=PPM1G.
|
|
21
|
Travis SM and Welsh MJ: PP2C gamma: A
human protein phosphatase with a unique acidic domain. FEBS Lett.
412:415–419. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen D, Zhao Z, Chen L, Li Q, Zou J and
Liu S: PPM1G promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
via phosphorylation regulation of alternative splicing protein
SRSF3. Cell Death Dis. 12:7222021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mandal R, Becker S and Strebhardt K:
Targeting CDK9 for anti-cancer therapeutics. Cancers (Basel).
13:31812021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Whelan M and Pelchat M: Role of RNA
polymerase II promoter-proximal pausing in viral transcription.
Viruses. 14:20292022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tellier M, Zaborowska J, Neve J, Nojima T,
Hester S, Fournier M, Furger A and Murphy S: CDK9 and PP2A regulate
RNA polymerase II transcription termination and coupled RNA
maturation. EMBO Rep. 23:e545202022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fujinaga K, Huang F and Peterlin BM:
P-TEFb: The master regulator of transcription elongation. Mol Cell.
83:393–403. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yamayoshi A, Fukumoto H, Hayashi R,
Kishimoto K, Kobori A, Koyanagi Y, Komano JA and Murakami A:
Development of 7SK snRNA mimics that inhibit HIV transcription.
ChemMedChem. 16:3181–3184. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
McNamara RP, McCann JL, Gudipaty SA and
D'Orso I: Transcription factors mediate the enzymatic disassembly
of promoter-bound 7SK snRNP to locally recruit P-TEFb for
transcription elongation. Cell Rep. 5:1256–1268. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gudipaty SA, McNamara RP, Morton EL and
D'Orso I: PPM1G binds 7SK RNA and Hexim1 to block P-TEFb assembly
into the 7SK snRNP and sustain transcription elongation. Mol Cell
Biol. 35:3810–3828. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gudipaty SA and D'Orso I: Functional
interplay between PPM1G and the transcription elongation machinery.
RNA Dis. 3:e12152016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bagashev A and Sawaya BE: Roles and
functions of HIV-1 Tat protein in the CNS: an overview. Virol J.
10:3582013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mbonye U, Wang B, Gokulrangan G, Shi W,
Yang S and Karn J: Cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7)-mediated
phosphorylation of the CDK9 activation loop promotes P-TEFb
assembly with Tat and proviral HIV reactivation. J Biol Chem.
293:10009–10025. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Schulze-Gahmen U and Hurley JH: Structural
mechanism for HIV-1 TAR loop recognition by Tat and the super
elongation complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 115:12973–12978. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hluchý M, Gajdušková P, Ruiz de Los Mozos
I, Rájecký M, Kluge M, Berger BT, Slabá Z, Potěšil D, Weiß E, Ule
J, et al: CDK11 regulates pre-mRNA splicing by phosphorylation of
SF3B1. Nature. 609:829–834. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Borišek J, Casalino L, Saltalamacchia A,
Mays SG, Malcovati L and Magistrato A: Atomic-level mechanism of
pre-mRNA splicing in health and disease. Acc Chem Res. 54:144–154.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ule J and Blencowe BJ: Alternative
splicing regulatory networks: Functions, mechanisms, and evolution.
Mol Cell. 76:329–345. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Murray MV, Kobayashi R and Krainer AR: The
type 2C Ser/Thr phosphatase PP2Cgamma is a pre-mRNA splicing
factor. Genes Dev. 13:87–97. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Allemand E, Hastings ML, Murray MV, Myers
MP and Krainer AR: Alternative splicing regulation by interaction
of phosphatase PP2Cgamma with nucleic acid-binding protein YB-1.
Nat Struct Mol Biol. 14:630–638. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wu S and Wagner G: Computational inference
of eIF4F complex function and structure in human cancers. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 121:e23135891212024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jia X, He X, Huang C, Li J, Dong Z and Liu
K: Protein translation: Biological processes and therapeutic
strategies for human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
9:442024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Thompson L, Depledge DP, Burgess HM and
Mohr I: An eIF3d-dependent switch regulates HCMV replication by
remodeling the infected cell translation landscape to mimic chronic
ER stress. Cell Rep. 39:1107672022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu J, Stevens PD, Eshleman NE and Gao T:
Protein phosphatase PPM1G regulates protein translation and cell
growth by dephosphorylating 4E binding protein 1 (4E-BP1). J Biol
Chem. 288:23225–23233. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gingras AC, Raught B, Gygi SP, Niedzwiecka
A, Miron M, Burley SK, Polakiewicz RD, Wyslouch-Cieszynska A,
Aebersold R and Sonenberg N: Hierarchical phosphorylation of the
translation inhibitor 4E-BP1. Genes Dev. 15:2852–2864. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Takahashi S, Shibutani S and Iwata H:
Nuclear-targeted 4E-BP1 is dephosphorylated, induces nuclear
translocation of eIF4E, and alters mRNA translation. Exp Cell Res.
418:1132462022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xu K, Wang L, Feng W, Feng Y and Shu HK:
Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase-dependent translational regulation of
Id1 involves the PPM1G phosphatase. Oncogene. 35:5807–5816. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sultana S, Zarreen F and Chakraborty S:
Insights into the roles of histone chaperones in nucleosome
assembly and disassembly in virus infection. Virus Res.
297:1983952021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li S, Edwards G, Radebaugh CA, Luger K and
Stargell LA: Spn1 and its dynamic interactions with Spt6, histones
and nucleosomes. J Mol Biol. 434:1676302022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lian Y, Hao H, Xu J, Bo T, Liang A and
Wang W: The histone chaperone Nrp1 is required for chromatin
stability and nuclear division in Tetrahymena thermophila.
Epigenetics Chromatin. 14:342021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kimura H, Takizawa N, Allemand E, Hori T,
Iborra FJ, Nozaki N, Muraki M, Hagiwara M, Krainer AR, Fukagawa T
and Okawa K: A novel histone exchange factor, protein phosphatase
2Cgamma, mediates the exchange and dephosphorylation of H2A-H2B. J
Cell Biol. 175:389–400. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Luo Q, Wang B, Wu Z, Jiang W, Wang Y, Du
K, Zhou N, Zheng L, Gan J, Shen WH, et al: NAP1-Related Protein 1
(NRP1) has multiple interaction modes for chaperoning histones
H2A-H2B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 117:30391–30399. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Farrugia M, Vassallo N and Cauchi RJ:
Disruption of survival motor neuron in glia impacts survival but
has no effect on neuromuscular function in Drosophila.
Neuroscience. 491:32–42. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Riboldi GM, Faravelli I, Kuwajima T,
Delestrée N, Dermentzaki G, De Planell-Saguer M, Rinchetti P, Hao
LT, Beattie CC, Corti S, et al: Sumoylation regulates the assembly
and activity of the SMN complex. Nat Commun. 12:50402021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Musawi S, Donnio LM, Zhao Z, Magnani C,
Rassinoux P, Binda O, Huang J, Jacquier A, Coudert L, Lomonte P, et
al: Nucleolar reorganization after cellular stress is orchestrated
by SMN shuttling between nuclear compartments. Nat Commun.
14:73842023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Franco-Espin J, Gatius A, Armengol JÁ,
Arumugam S, Moradi M, Sendtner M, Calderó J and Tabares L: SMN is
physiologically downregulated at wild-type motor nerve terminals
but aggregates together with neurofilaments in SMA mouse models.
Biomolecules. 12:15242022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Petri S, Grimmler M, Over S, Fischer U and
Gruss OJ: Dephosphorylation of survival motor neurons (SMN) by
PPM1G/PP2Cgamma governs Cajal body localization and stability of
the SMN complex. J Cell Biol. 179:451–465. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Detering NT, Schüning T, Hensel N and
Claus P: The phospho-landscape of the survival of motoneuron
protein (SMN) protein: Relevance for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA).
Cell Mol Life Sci. 79:4972022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Husedzinovic A, Neumann B, Reymann J,
Draeger-Meurer S, Chari A, Erfle H, Fischer U and Gruss OJ: The
catalytically inactive tyrosine phosphatase HD-PTP/PTPN23 is a
novel regulator of SMN complex localization. Mol Biol Cell.
26:161–171. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
58
|
Martinez-Salas E, Embarc-Buh A and
Francisco-Velilla R: Emerging roles of Gemin5: From snRNPs assembly
to translation control. Int J Mol Sci. 21:38682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hu Y, Hou Y, Zhou S, Wang Y, Shen C, Mu L,
Su D and Zhang R: Mechanism of assembly of snRNP cores assisted by
ICln and the SMN complex in fission yeast. iScience. 26:1076042023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Oksenych V and Kainov DE: DNA damage
response. Biomolecules. 11:1232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Santivasi WL and Xia F: Ionizing
radiation-induced DNA damage, response, and repair. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 21:251–259. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Ciccia A and Elledge SJ: The DNA damage
response: Making it safe to play with knives. Mol Cell. 40:179–204.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Georgoulis A, Vorgias CE, Chrousos GP and
Rogakou EP: Genome instability and γH2AX. Int J Mol Sci.
18:19792017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Beli P, Lukashchuk N, Wagner SA, Weinert
BT, Olsen JV, Baskcomb L, Mann M, Jackson SP and Choudhary C:
Proteomic investigations reveal a role for RNA processing factor
THRAP3 in the DNA damage response. Mol Cell. 46:212–225. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Khoronenkova SV, Dianova II, Ternette N,
Kessler BM, Parsons JL and Dianov GL: ATM-dependent downregulation
of USP7/HAUSP by PPM1G activates p53 response to DNA damage. Mol
Cell. 45:801–813. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Koo N, Sharma AK and Narayan S:
Therapeutics targeting p53-MDM2 interaction to induce cancer cell
death. Int J Mol Sci. 23:50052022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Williams AB and Schumacher B: p53 in the
DNA-damage-repair process. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med.
6:a0260702016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Matsuoka S, Ballif BA, Smogorzewska A,
McDonald ER III, Hurov KE, Luo J, Bakalarski CE, Zhao Z, Solimini
N, Lerenthal Y, et al: ATM and ATR substrate analysis reveals
extensive protein networks responsive to DNA damage. Science.
316:1160–1166. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Khoronenkova SV and Dianov GL: Regulation
of USP7/HAUSP in response to DNA damage: Yet another role for ATM.
Cell Cycle. 11:2409–2410. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Chaudhary N and Maddika S: WWP2-WWP1
ubiquitin ligase complex coordinated by PPM1G maintains the balance
between cellular p73 and ΔNp73 levels. Mol Cell Biol. 34:3754–3764.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Chen X, Ma J, Wang ZW and Wang Z: The E3
ubiquitin ligases regulate inflammation in cardiovascular diseases.
Semin Cell Dev Biol. 154:167–174. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Wang Y, Wu Z, Wang C, Wu N, Wang C, Hu S
and Shi J: The role of WWP1 and WWP2 in bone/cartilage development
and diseases. Mol Cell Biochem. Jan 22–2024.Epub ahead of
print.
|
|
73
|
Yoon MK, Ha JH, Lee MS and Chi SW:
Structure and apoptotic function of p73. BMB Rep. 48:81–90. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
74
|
Osterburg C and Dötsch V: Structural
diversity of p63 and p73 isoforms. Cell Death Differ. 29:921–937.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Engeland K: Cell cycle regulation:
p53-p21-RB signaling. Cell Death Differ. 29:946–960. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Kuganesan N, Dlamini S, Tillekeratne LMV
and Taylor WR: Tumor suppressor p53 promotes ferroptosis in
oxidative stress conditions independent of modulation of
ferroptosis by p21, CDKs, RB, and E2F. J Biol Chem. 297:1013652021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Suh EJ, Kim TY and Kim SH:
PP2Cgamma-mediated S-phase accumulation induced by the
proteasome-dependent degradation of p21(WAF1/CIP1). FEBS Lett.
580:6100–6104. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Desvoyes B and Gutierrez C: Roles of plant
retinoblastoma protein: Cell cycle and beyond. EMBO J.
39:e1058022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Sanidas I, Morris R, Fella KA, Rumde PH,
Boukhali M, Tai EC, Ting DT, Lawrence MS, Haas W and Dyson NJ: A
code of mono-phosphorylation modulates the function of RB. Mol
Cell. 73:985–1000.e6. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Sharma SS and Pledger WJ: The
non-canonical functions of p27(Kip1) in normal and tumor biology.
Cell Cycle. 15:1189–1201. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Deshmukh D, Xu J, Yang X, Shimelis H, Fang
S and Qiu Y: Regulation of p27 (Kip1) by ubiquitin E3 ligase RNF6.
Pharmaceutics. 14:8022022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Cassimere EK, Mauvais C and Denicourt C:
p27Kip1 is required to mediate a G1 cell cycle arrest downstream of
ATM following genotoxic stress. PLoS One. 11:e01628062016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Fujita N, Sato S, Katayama K and Tsuruo T:
Akt-dependent phosphorylation of p27Kip1 promotes binding to 14-3-3
and cytoplasmic localization. J Biol Chem. 277:28706–28713. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Sun C, Wang G, Wrighton KH, Lin H,
Songyang Z, Feng XH and Lin X: Regulation of p27Kip1
phosphorylation and G1 cell cycle progression by protein
phosphatase PPM1G. Am J Cancer Res. 6:2207–2220. 2016.
|
|
85
|
Sousa B, Pereira J and Paredes J: The
crosstalk between cell adhesion and cancer metabolism. Int J Mol
Sci. 20:19332019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Sun Y, Zhang J and Ma L: α-Catenin. A
tumor suppressor beyond adherens junctions. Cell Cycle.
13:2334–2339. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
87
|
Lessey LR, Robinson SC, Chaudhary R and
Daniel JM: Adherens junction proteins on the move-from the membrane
to the nucleus in intestinal diseases. Front Cell Dev Biol.
10:9983732022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Duong CN, Brückner R, Schmitt M, Nottebaum
AF, Braun LJ, Meyer Zu Brickwedde M, Ipe U, Vom Bruch H, Schöler
HR, Trapani G, et al: Force-induced changes of α-catenin
conformation stabilize vascular junctions independently of
vinculin. J Cell Sci. 134:jcs2590122021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Kumar P, Tathe P, Chaudhary N and Maddika
S: PPM1G forms a PPP-type phosphatase holoenzyme with B56δ that
maintains adherens junction integrity. EMBO Rep. 20:e469652019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Foster WH, Langenbacher A, Gao C, Chen J
and Wang Y: Nuclear phosphatase PPM1G in cellular survival and
neural development. Dev Dyn. 242:1101–1109. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Chen J, Li J, Sun H, Hu T, Wang Y, Kang G,
Cao M and Li X: PPM1G promotes the progression of lung
adenocarcinoma by inhibiting p38 activation via dephosphorylation
of MEK6. Carcinogenesis. 44:93–104. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Kim EK and Choi EJ: Compromised MAPK
signaling in human diseases: An update. Arch Toxicol. 89:867–882.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Di Rocco A, Camero S, Benedetti A,
Lozanoska-Ochser B, Megiorni F, Marchese C, Stramucci L, Ciccarelli
C, Bouché M, Bossi G, et al: Anti-oncogenic and pro-myogenic action
of the MKK6/p38/AKT axis induced by targeting MEK/ERK in embryonal
rhabdomyosarcoma. Oncol Rep. 48:1512022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
94
|
Martínez-Limón A, Joaquin M, Caballero M,
Posas F and de Nadal E: The p38 pathway: From biology to cancer
therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 21:19132020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
95
|
Ming Z, Lim SY and Rizos H: Genetic
alterations in the INK4a/ARF locus: Effects on melanoma development
and progression. Biomolecules. 10:14472020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Hyder U, McCann JL, Wang J, Fung V, Bayo J
and D'Orso I: The ARF tumor suppressor targets PPM1G/PP2Cγ to
counteract NF-κB transcription tuning cell survival and the
inflammatory response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 117:32594–32605.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Roschger C and Cabrele C: The Id-protein
family in developmental and cancer-associated pathways. Cell Commun
Signal. 15:72017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Xiong DL, Li Q, Wang H, Jin WL, Fan XM and
Ma YY: High expression of PPM1G is associated with the progression
and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biomark.
34:13–22. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Hu W, Ma SL, Qiong L, Du Y, Gong LP, Pan
YH, Sun LP, Wen JY, Chen JN, Guan XY and Shao CK: PPM1G promotes
cell proliferation via modulating mutant GOF p53 protein expression
in hepatocellular carcinoma. iScience. 27:1091162024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Liu X, Zeng J, Li H, Li F, Jiang B, Zhao
M, Liu Z, Li R and Ma T: A risk model based on sorafenib-response
target genes predicts the prognosis of patients with HCC. J Oncol.
2022:72577382022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Li W, Liu J, Zhang D, Gu L and Zhao H: The
prognostic significance and potential mechanism of
ferroptosis-related genes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Genet.
13:8446242022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Yang H, Huo J and Li X: Identification and
validation of a five-gene prognostic signature for hepatocellular
carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol. 19:902021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Li W, Lu J, Ma Z, Zhao J and Liu J: An
integrated model based on a six-gene signature predicts overall
survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Genet.
10:13232020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Zhang BH, Yang J, Jiang L, Lyu T, Kong LX,
Tan YF, Li B, Zhu YF, Xi AY, Xu X, et al: Development and
validation of a 14-gene signature for prognosis prediction in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Genomics. 112:2763–2771. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Jia R and Zheng ZM: Oncogenic SRSF3 in
health and diseases. Int J Biol Sci. 19:3057–3076. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
106
|
Sen S, Langiewicz M, Jumaa H and Webster
NJG: Deletion of serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 3 in
hepatocytes predisposes to hepatocellular carcinoma in mice.
Hepatology. 61:171–183. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Wen C, Tian Z, Li L, Chen T, Chen H, Dai
J, Liang Z, Ma S and Liu X: SRSF3 and HNRNPH1 regulate
radiation-induced alternative splicing of protein arginine
methyltransferase 5 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci.
23:148322022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Hong B, van den Heuvel AP, Prabhu VV,
Zhang S and El-Deiry WS: Targeting tumor suppressor p53 for cancer
therapy: Strategies, challenges and opportunities. Curr Drug
Targets. 15:80–89. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Zhang C, Liu J, Xu D, Zhang T, Hu W and
Feng Z: Gain-of-function mutant p53 in cancer progression and
therapy. J Mol Cell Biol. 12:674–687. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Zhao M, Wang T, Gleber-Netto FO, Chen Z,
McGrail DJ, Gomez JA, Ju W, Gadhikar MA, Ma W, Shen L, et al:
Mutant p53 gains oncogenic functions through a chromosomal
instability-induced cytosolic DNA response. Nat Commun. 15:1802024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Roehlen N, Crouchet E and Baumert TF:
Liver fibrosis: Mechanistic concepts and therapeutic perspectives.
Cells. 9:8752020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Ge MX, Liu HT, Zhang N, Niu WX, Lu ZN, Bao
YY, Huang R, Yu DK, Shao RG and He HW: Costunolide represses
hepatic fibrosis through WW domain-containing protein 2-mediated
Notch3 degradation. Br J Pharmacol. 177:372–387. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Reig M, Forner A, Rimola J, Ferrer-Fàbrega
J, Burrel M, Garcia-Criado Á, Kelley RK, Galle PR, Mazzaferro V,
Salem R, et al: BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and
treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J Hepatol. 76:681–693.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
114
|
Guan Y, Yao W, Yi K, Zheng C, Lv S, Tao Y,
Hei Z and Li M: Nanotheranostics for the management of hepatic
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Small. 17:e20077272021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Peng D, Huang Z, Yang H, Luo Y and Wu Z:
PPM1G regulates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury through
STING-mediated inflammatory pathways in macrophages. Immun Inflamm
Dis. 12:e11892024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Yu K, Tian H and Deng H: PPM1G restricts
innate immune signaling mediated by STING and MAVS and is hijacked
by KSHV for immune evasion. Sci Adv. 6:eabd02762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Ho SY, Chang CM, Liao HN, Chou WH, Guo CL,
Yen Y, Nakamura Y and Chang WC: Current trends in neoantigen-based
cancer vaccines. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 16:3922023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Fu J, Chen F, Lin Y, Gao J, Chen A and
Yang J: Discovery and characterization of tumor antigens in
hepatocellular carcinoma for mRNA vaccine development. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 149:4047–4061. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Wang B, Pei J, Xu S, Liu J and Yu J:
Recent advances in mRNA cancer vaccines: Meeting challenges and
embracing opportunities. Front Immunol. 14:12466822023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Lu TL, Li CL, Gong YQ, Hou FT and Chen CW:
Identification of tumor antigens and immune subtypes of
hepatocellular carcinoma for mRNA vaccine development. World J
Gastrointest Oncol. 15:1717–1738. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|