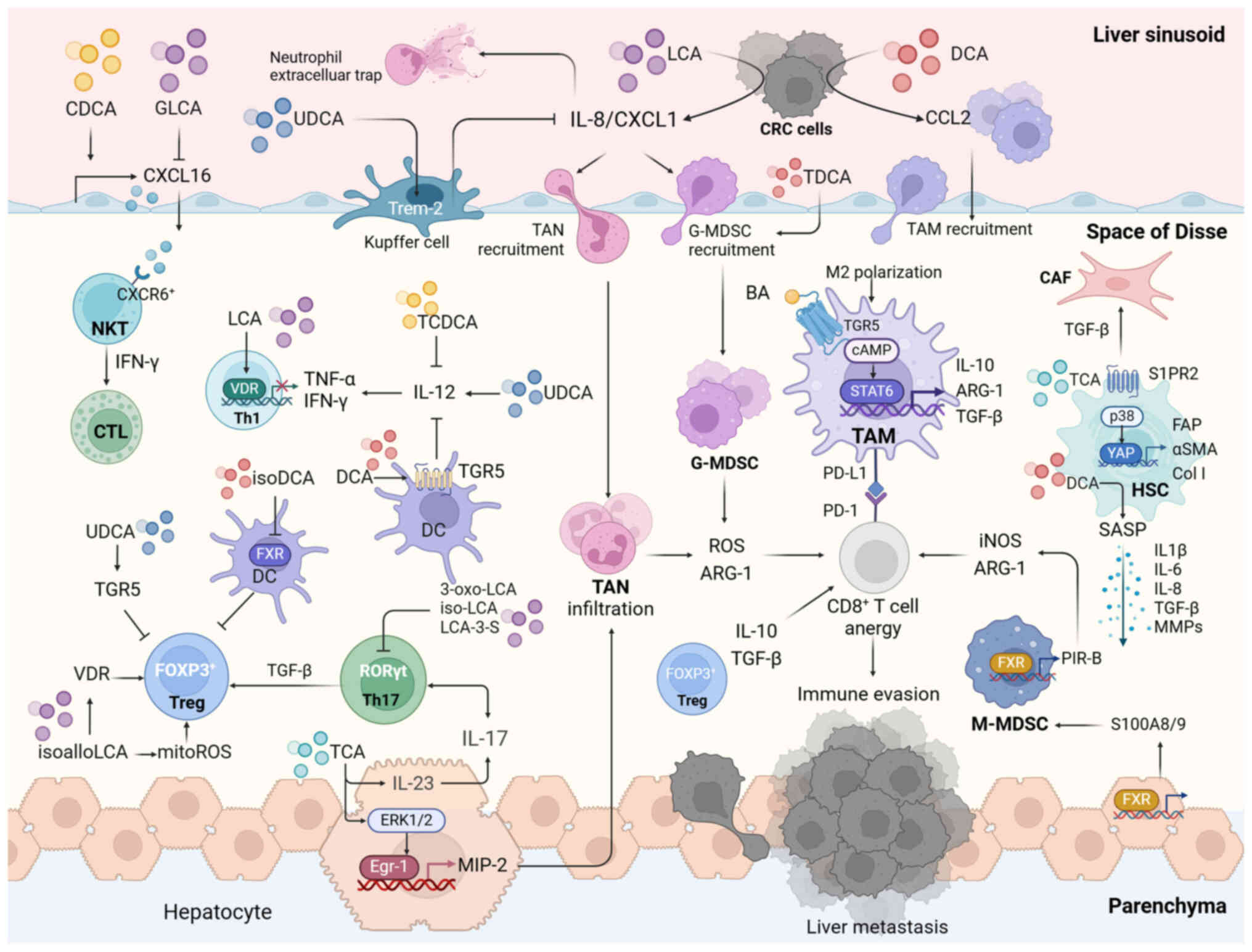
|
1
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Biller LH and Schrag D: Diagnosis and
treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: A review. JAMA.
325:669–685. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yu J, Green MD, Li S, Sun Y, Journey SN,
Choi JE, Rizvi SM, Qin A, Waninger JJ, Lang X, et al: Liver
metastasis restrains immunotherapy efficacy via macrophage-mediated
T cell elimination. Nat Med. 27:152–164. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee JC, Mehdizadeh S, Smith J, Young A,
Mufazalov IA, Mowery CT, Daud A and Bluestone JA: Regulatory T cell
control of systemic immunity and immunotherapy response in liver
metastasis. Sci Immunol. 5:eaba07592020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jones BV, Begley M, Hill C, Gahan CG and
Marchesi JR: Functional and comparative metagenomic analysis of
bile salt hydrolase activity in the human gut microbiome. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 105:13580–13585. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ridlon JM and Gaskins HR: Another
renaissance for bile acid gastrointestinal microbiology. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 21:348–364. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Russell DW: The enzymes, regulation, and
genetics of bile acid synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 72:137–174.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Thibaut MM and Bindels LB: Crosstalk
between bile acid-activated receptors and microbiome in
entero-hepatic inflammation. Trends Mol Med. 28:223–236. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wahlstrom A, Sayin SI, Marschall HU and
Backhed F: Intestinal crosstalk between bile acids and microbiota
and its impact on host metabolism. Cell Metab. 24:41–50. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hao Z, Liu X, He H, Wei Z, Shu X, Wang J,
Sun B, Zhou H, Wang J, Niu Y, et al: CYP2E1 deficit mediates cholic
acid-induced malignant growth in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Mol Med. 30:792024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen W, Ding M, Ji L, Yao J, Guo Y, Yan W,
Yu S, Shen Q, Huang M, Zheng Y, et al: Bile acids promote the
development of HCC by activating inflammasome. Hepatol Commun.
7:e02172023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yao Y, Li X, Xu B, Luo L, Guo Q, Wang X,
Sun L, Zhang Z and Li P: Cholecystectomy promotes colon
carcinogenesis by activating the Wnt signaling pathway by
increasing the deoxycholic acid level. Cell Commun Signal.
20:712022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sánchez B: Bile acid-microbiota crosstalk
in gastrointestinal inflammation and carcinogenesis: A role for
bifidobacteria and lactobacilli? Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
15:2052018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Režen T, Rozman D, Kovács T, Kovács P,
Sipos A, Bai P and Mikó E: The role of bile acids in
carcinogenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 79:2432022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Liu Y, Zhang S, Zhou W, Hu D, Xu H and Ji
G: secondary bile acids and tumorigenesis in colorectal cancer.
Front Oncol. 12:8137452022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Caliceti C, Punzo A, Silla A, Simoni P,
Roda G and Hrelia S: New insights into bile acids related signaling
pathways in the onset of colorectal cancer. Nutrients. 14:29642022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cai J, Sun L and Gonzalez FJ: Gut
microbiota-derived bile acids in intestinal immunity, inflammation,
and tumorigenesis. Cell Host Microbe. 30:289–300. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sipe LM, Chaib M, Pingili AK, Pierre JF
and Makowski L: Microbiome, bile acids, and obesity: How
microbially modified metabolites shape anti-tumor immunity. Immunol
Rev. 295:220–239. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang J, Zhu N, Su X and Yang R: Gut
microbiota: A double-edged sword in immune checkpoint blockade
immunotherapy against tumors. Cancer Lett. 582:2165822024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Imray CH, Radley S, Davis A, Barker G,
Hendrickse CW, Donovan IA, Lawson AM, Baker PR and Neoptolemos JP:
Faecal unconjugated bile acids in patients with colorectal cancer
or polyps. Gut. 33:1239–1245. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bayerdörffer E, Mannes GA, Ochsenkühn T,
Dirschedl P, Wiebecke B and Paumgartner G: Unconjugated secondary
bile acids in the serum of patients with colorectal adenomas. Gut.
36:268–273. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dermadi D, Valo S, Ollila S, Soliymani R,
Sipari N, Pussila M, Sarantaus L, Linden J, Baumann M and Nyström
M: Western diet deregulates bile acid homeostasis, cell
proliferation, and tumorigenesis in colon. Cancer Res.
77:3352–3363. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ocvirk S and O'Keefe SJD: Dietary fat,
bile acid metabolism and colorectal cancer. Semin Cancer Biol.
73:347–355. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
O'Keefe SJ, Li JV, Lahti L, Ou J,
Carbonero F, Mohammed K, Posma JM, Kinross J, Wahl E, Ruder E, et
al: Fat, fibre and cancer risk in African Americans and rural
Africans. Nat Commun. 6:63422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ma Y, Zhang Y, Qu R, Zhou X, Sun L, Wang
K, Jiang C, Zhang Z and Fu W: Promotion of deoxycholic acid effect
on colonic cancer cell lines in vitro by altering the mucosal
microbiota. Microorganisms. 10:24862022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wirbel J, Pyl PT, Kartal E, Zych K,
Kashani A, Milanese A, Fleck JS, Voigt AY, Palleja A, Ponnudurai R,
et al: Meta-analysis of fecal metagenomes reveals global microbial
signatures that are specific for colorectal cancer. Nat Med.
25:679–689. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ridlon JM, Harris SC, Bhowmik S, Kang DJ
and Hylemon PB: Consequences of bile salt biotransformations by
intestinal bacteria. Gut Microbes. 7:22–39. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xie YH, Gao QY, Cai GX, Sun XM, Sun XM,
Zou TH, Chen HM, Yu SY, Qiu YW, Gu WQ, et al: Fecal clostridium
symbiosum for noninvasive detection of early and advanced
colorectal cancer: Test and validation studies. EBioMedicine.
25:32–40. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sun L, Zhang Y, Cai J, Rimal B, Rocha ER,
Coleman JP, Zhang C, Nichols RG, Luo Y, Kim B, et al: Bile salt
hydrolase in non-enterotoxigenic Bacteroides potentiates colorectal
cancer. Nat Commun. 14:7552023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Inagaki T, Choi M, Moschetta A, Peng L,
Cummins CL, McDonald JG, Luo G, Jones SA, Goodwi n B, Richardson
JA, et al: Fibroblast growth factor 15 functions as an
enterohepatic signal to regulate bile acid homeostasis. Cell Metab.
2:217–225. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim I, Ahn SH, Inagaki T, Choi M, Ito S,
Guo GL, Kliewer SA and Gonzalez FJ: Differential regulation of bile
acid homeostasis by the farnesoid X receptor in liver and
intestine. J Lipid Res. 48:2664–2672. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lax S, Schauer G, Prein K, Kapitan M,
Silbert D, Berghold A, Berger A and Trauner M: Expression of the
nuclear bile acid receptor/farnesoid X receptor is reduced in human
colon carcinoma compared to nonneoplastic mucosa independent from
site and may be associated with adverse prognosis. Int J Cancer.
130:2232–2239. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Fu T, Coulter S, Yoshihara E, Oh TG, Fang
S, Cayabyab F, Zhu Q, Zhang T, Leblanc M, Liu S, et al: FXR
regulates intestinal cancer stem cell proliferation. Cell.
176:1098–1112 e18. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Selmin OI, Fang C, Lyon AM, Doetschman TC,
Thompson PA, Martinez JD, Smith JW, Lance PM and Romagnolo DF:
Inactivation of adenomatous polyposis coli reduces bile
acid/farnesoid X receptor expression through Fxr gene CpG
methylation in mouse colon tumors and human colon cancer cells. J
Nutr. 146:236–242. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kim DH and Lee JW: Tumor suppressor p53
regulates bile acid homeostasis via small heterodimer partner. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:12266–12270. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kühn T, Stepien M, López-Nogueroles M,
Damms-Machado A, Sookthai D, Johnson T, Roca M, Hüsing A, Maldonado
SG, Cross AJ, et al: Prediagnostic plasma bile acid levels and
colon cancer risk: A prospective study. J Natl Cancer Inst.
112:516–524. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Ajouz H, Mukherji D and Shamseddine A:
Secondary bile acids: An underrecognized cause of colon cancer.
World J Surg Oncol. 12:1642014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zeng H, Claycombe KJ and Reindl KM:
Butyrate and deoxycholic acid play common and distinct roles in
HCT116 human colon cell proliferation. J Nutr Biochem.
26:1022–1028. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu L, Yang M, Dong W, Liu T, Song X, Gu
Y, Wang S, Liu Y, Abla Z, Qiao X, et al: Gut dysbiosis and abnormal
bile acid metabolism in colitis-associated cancer. Gastroenterol
Res Pract. 2021:66459702021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cao Y, Deng S, Yan L, Gu J, Yang J, Yang
M, Liu L and Cai K: A nomogram based on pretreatment levels of
serum bilirubin and total bile acid levels predicts survival in
colorectal cancer patients. BMC Cancer. 21:852021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tang S, Chen Y, Tian S and Wang Y:
Predictive nomogram for the prediction of early recurrence of
colorectal cancer. Int J Gen Med. 14:4857–4866. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cai Y, Shen X, Lu L, Yan H, Huang H, Gaule
P, Muca E, Theriot CM, Rattray Z, Rattray NJW, et al: Bile acid
distributions, sex-specificity, and prognosis in colorectal cancer.
Biol Sex Differ. 13:612022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jia W, Xie G and Jia W: Bile
acid-microbiota crosstalk in gastrointestinal inflammation and
carcinogenesis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 15:111–128. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Morris MT, Jain A, Sun B, Kurbatov V, Muca
E, Zeng Z, Jin Y, Roper J, Lu J, Paty PB, et al: Multi-omic
analysis reveals metabolic pathways that characterize right-sided
colon cancer liver metastasis. Cancer Lett. 574:2163842023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Engstrand J, Nilsson H, Strömberg C, Jonas
E and Freedman J: Colorectal cancer liver metastases-a
population-based study on incidence, management and survival. BMC
Cancer. 18:782018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Liu W, Wang HW, Wang K and Xing BC: The
primary tumor location impacts survival outcome of colorectal liver
metastases after hepatic resection: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol. 45:1349–1356. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lee CK, Jeong SH, Jang C, Bae H, Kim YH,
Park I, Kim SK and Koh GY: Tumor metastasis to lymph nodes requires
YAP-dependent metabolic adaptation. Science. 363:644–649. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kawarabayashi N, Seki S, Hatsuse K,
Kinoshita M, Takigawa T, Tsujimoto H, Kawabata T, Nakashima H,
Shono S and Mochizuki H: Immunosuppression in the livers of mice
with obstructive jaundice participates in their susceptibility to
bacterial infection and tumor metastasis. Shock. 33:500–506. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Zheng Z, Wei J, Hou X, Jia F, Zhang Z, Guo
H, Yuan F, He F, Ke Z, Wang Y and Zhao L: A high hepatic uptake of
conjugated bile acids promotes colorectal cancer-associated liver
metastasis. Cells. 11:38102022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lambert AW, Pattabiraman DR and Weinberg
RA: Emerging biological principles of metastasis. Cell.
168:670–691. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Debruyne PR, Bruyneel EA, Karaguni IM, Li
X, Flatau G, Müller O, Zimber A, Gespach C and Mareel MM: Bile
acids stimulate invasion and haptotaxis in human colorectal cancer
cells through activation of multiple oncogenic signaling pathways.
Oncogene. 21:6740–6750. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Dongre A and Weinberg RA: New insights
into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
implications for cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:69–84. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Song X, An Y, Chen D, Zhang W, Wu X, Li C,
Wang S, Dong W, Wang B, Liu T, et al: Microbial metabolite
deoxycholic acid promotes vasculogenic mimicry formation in
intestinal carcinogenesis. Cancer Sci. 113:459–477. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
54
|
Stefani C, Miricescu D, Stanescu-Spinu II,
Nica RI, Greabu M, Totan AR and Jinga M: Growth factors,
PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways in colorectal cancer
pathogenesis: Where are we now? Int J Mol Sci. 22:102602021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Centuori SM, Gomes CJ, Trujillo J, Borg J,
Brownlee J, Putnam CW and Martinez JD: Deoxycholic acid mediates
non-canonical EGFR-MAPK activation through the induction of calcium
signaling in colon cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1861:663–670. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Centuori SM and Martinez JD: Differential
regulation of EGFR-MAPK signaling by deoxycholic acid (DCA) and
ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) in colon cancer. Dig Dis Sci.
59:2367–2380. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Lee J, Hong EM, Kim JH, Kim JH, Jung JH,
Park SW and Koh DH: Ursodeoxycholic acid inhibits
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, suppressing invasiveness of bile
duct cancer cells: An in vitro study. Oncol Lett. 24:4482022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yu J, Li S, Guo J, Xu Z, Zheng J and Sun
X: Farnesoid X receptor antagonizes Wnt/β-catenin signaling in
colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell Death Dis. 11:6402020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Zhang D, Weng S, Cui C, Dong L and Shen X:
Decreased expression of farnesoid X receptor may indicate poor
prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Transl Cancer Res.
9:4290–4296. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Li S, Xu Z, Guo J, Zheng J, Sun X and Yu
J: Farnesoid X receptor activation induces antitumour activity in
colorectal cancer by suppressing JAK2/STAT3 signalling via
transactivation of SOCS3 gene. J Cell Mol Med. 24:14549–14560.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Farhana L, Nangia-Makker P, Arbit E,
Shango K, Sarkar S, Mahmud H, Hadden T, Yu Y and Majumdar AP: Bile
acid: A potential inducer of colon cancer stem cells. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 7:1812016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Pezeshkian Z, Nobili S, Peyravian N,
Shojaee B, Nazari H, Soleimani H, Asadzadeh-Aghdaei H, Ashrafian
Bonab M, Nazemalhosseini-Mojarad E and Mini E: Insights into the
role of matrix metalloproteinases in precancerous conditions and in
colorectal cancer. Cancers (Basel). 13:62262021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Li S, Ung TT, Nguyen TT, Sah DK, Park SY
and Jung YD: Cholic acid stimulates MMP-9 in human colon cancer
cells via activation of MAPK, AP-1, and NF-κB activity. Int J Mol
Sci. 21:34202020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Peng Z, Chen J, Drachenberg CB, Raufman JP
and Xie G: Farnesoid X receptor represses matrix metalloproteinase
7 expression, revealing this regulatory axis as a promising
therapeutic target in colon cancer. J Biol Chem. 294:8529–8542.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Halvorsen B, Staff AC, Ligaarden S, Prydz
K and Kolset SO: Lithocholic acid and sulphated lithocholic acid
differ in the ability to promote matrix metalloproteinase secretion
in the human colon cancer cell line CaCo-2. Biochem J. 349(Pt 1):
189–193. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Dass K, Ahmad A, Azmi AS, Sarkar SH and
Sarkar FH: Evolving role of uPA/uPAR system in human cancers.
Cancer Treat Rev. 34:122–136. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Pai R, Tarnawski AS and Tran T:
Deoxycholic acid activates beta-catenin signaling pathway and
increases colon cell cancer growth and invasiveness. Mol Biol Cell.
15:2156–2163. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Baek MK, Park JS, Park JH, Kim MH, Kim HD,
Bae WK, Chung IJ, Shin BA and Jung YD: Lithocholic acid upregulates
uPAR and cell invasiveness via MAPK and AP-1 signaling in colon
cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 290:123–128. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Takeda A, Stoeltzing O, Ahmad SA, Reinmuth
N, Liu W, Parikh A, Fan F, Akagi M and Ellis LM: Role of
angiogenesis in the development and growth of liver metastasis. Ann
Surg Oncol. 9:610–616. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Li S, Nguyen TT, Ung TT, Sah DK, Park SY,
Lakshmanan VK and Jung YD: Piperine attenuates lithocholic
acid-stimulated interleukin-8 by suppressing Src/EGFR and reactive
oxygen species in human colorectal cancer cells. Antioxidants
(Basel). 11:5302022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Nguyen TT, Lian S, Ung TT, Xia Y, Han JY
and Jung YD: Lithocholic acid stimulates IL-8 expression in human
colorectal cancer cells via activation of Erk1/2 MAPK and
suppression of STAT3 activity. J Cell Biochem. 118:2958–2967. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Sun J, Mustafi R, Cerda S, Chumsangsri A,
Xia YR, Li YC and Bissonnette M: Lithocholic acid down-regulation
of NF-kappaB activity through vitamin D receptor in colonic cancer
cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 111:37–40. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Cianchi F, Cortesini C, Bechi P, Fantappiè
O, Messerini L, Vannacci A, Sardi I, Baroni G, Boddi V, Mazzanti R
and Masini E: Up-regulation of cyclooxygenase 2 gene expression
correlates with tumor angiogenesis in human colorectal cancer.
Gastroenterology. 121:1339–1347. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Oshio H, Abe T, Onogawa T, Ohtsuka H, Sato
T, Ii T, Fukase K, Muto M, Katayose Y, Oikawa M, et al: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor alpha activates cyclooxygenase-2
gene transcription through bile acid transport in human colorectal
cancer cell lines. J Gastroenterol. 43:538–549. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Khare S, Mustafi R, Cerda S, Yuan W,
Jagadeeswaran S, Dougherty U, Tretiakova M, Samarel A, Cohen G,
Wang J, et al: Ursodeoxycholic acid suppresses Cox-2 expression in
colon cancer: Roles of Ras, p38, and CCAAT/enhancer-binding
protein. Nutr Cancer. 60:389–400. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Buchheit CL, Weigel KJ and Schafer ZT:
Cancer cell survival during detachment from the ECM: Multiple
barriers to tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:632–641. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Hawk MA and Schafer ZT: Mechanisms of
redox metabolism and cancer cell survival during extracellular
matrix detachment. J Biol Chem. 293:7531–7537. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Elia I, Doglioni G and Fendt SM: Metabolic
hallmarks of metastasis formation. Trends Cell Biol. 28:673–684.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Wang YN, Zeng ZL, Lu J, Wang Y, Liu ZX, He
MM, Zhao Q, Wang ZX, Li T, Lu YX, et al: CPT1A-mediated fatty acid
oxidation promotes colorectal cancer cell metastasis by inhibiting
anoikis. Oncogene. 37:6025–6040. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Zhong X, He X, Wang Y, Hu Z, Huang H, Zhao
S, Wei P and Li D: Warburg effect in colorectal cancer: The
emerging roles in tumor microenvironment and therapeutic
implications. J Hematol Oncol. 15:1602022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Wang Z, Pang J, Wang L, Dong Q and Jin D:
CEBPB regulates the bile acid receptor FXR to accelerate colon
cancer progression by modulating aerobic glycolysis. J Clin Lab
Anal. 36:e247032022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Schafer ZT, Grassian AR, Song L, Jiang Z,
Gerhart-Hines Z, Irie HY, Gao S, Puigserver P and Brugge JS:
Antioxidant and oncogene rescue of metabolic defects caused by loss
of matrix attachment. Nature. 461:109–113. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Carino A, Marchianò S, Biagioli M,
Scarpelli P, Bordoni M, Di Giorgio C, Roselli R, Fiorucci C, Monti
MC, Distrutti E, et al: The bile acid activated receptors GPBAR1
and FXR exert antagonistic effects on autophagy. FASEB J.
35:e212712021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Seok S, Fu T, Choi SE, Li Y, Zhu R, Kumar
S, Sun X, Yoon G, Kang Y, Zhong W, et al: Transcriptional
regulation of autophagy by an FXR-CREB axis. Nature. 516:108–111.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Shasha T, Gruijs M and van Egmond M:
Mechanisms of colorectal liver metastasis development. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 79:6072022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Ma C, Han M, Heinrich B, Fu Q, Zhang Q,
Sandhu M, Agdashian D, Terabe M, Berzofsky JA, Fako V, et al: Gut
microbiome-mediated bile acid metabolism regulates liver cancer via
NKT cells. Science. 360:eaan59312018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Shen Y, Lu C, Song Z, Qiao C, Wang J, Chen
J, Zhang C, Zeng X, Ma Z, Chen T, et al: Ursodeoxycholic acid
reduces antitumor immunosuppression by inducing CHIP-mediated TGF-β
degradation. Nat Commun. 13:34192022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Cong J, Liu P, Han Z, Ying W, Li C, Yang
Y, Wang S, Yang J, Cao F, Shen J, et al: Bile acids modified by the
intestinal microbiota promote colorectal cancer growth by
suppressing CD8(+) T cell effector functions. Immunity.
57:876–889.e811. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Sun L, Yang N, Liu Z, Ye X, Cheng M, Deng
L, Zhang J, Wu J, Shi M and Liao W: Cholestasis-induced phenotypic
transformation of neutrophils contributes to immune escape of
colorectal cancer liver metastasis. J Biomed Sci. 31:662024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Liu QL, Zhou H, Zhou ZG and Chen HN:
Colorectal cancer liver metastasis: genomic evolution and crosstalk
with the liver microenvironment. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 42:575–587.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Plundrich D, Chikhladze S, Fichtner-Feigl
S, Feuerstein R and Briquez PS: Molecular mechanisms of tumor
immunomodulation in the microenvironment of colorectal cancer. Int
J Mol Sci. 23:27822022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Pan Y, Yu Y, Wang X and Zhang T:
Tumor-associated macrophages in tumor immunity. Front Immunol.
11:5830842020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhao S, Mi Y, Guan B, Zheng B, Wei P, Gu
Y, Zhang Z, Cai S, Xu Y, Li X, et al: Tumor-derived exosomal
miR-934 induces macrophage M2 polarization to promote liver
metastasis of colorectal cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 13:1562020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Sun R, Zhang Z, Bao R, Guo X, Gu Y, Yang
W, Wei J, Chen X, Tong L, Meng J, et al: Loss of SIRT5 promotes
bile acid-induced immunosuppressive microenvironment and
hepatocarcinogenesis. J Hepatol. 77:453–466. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Kawamata Y, Fujii R, Hosoya M, Harada M,
Yoshida H, Miwa M, Fukusumi S, Habata Y, Itoh T, Shintani Y, et al:
A G protein-coupled receptor responsive to bile acids. J Biol Chem.
278:9435–9440. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Zhao L, Zhang H, Liu X, Xue S, Chen D, Zou
J and Jiang H: TGR5 deficiency activates antitumor immunity in
non-small cell lung cancer via restraining M2 macrophage
polarization. Acta Pharm Sin B. 12:787–800. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Rao J, Yang C, Yang S, Lu H, Hu Y, Lu L
and Cheng Fand Wang X: Deficiency of TGR5 exacerbates
immune-mediated cholestatic hepatic injury by stabilizing the
beta-catenin destruction complex. Int Immunol. 32:321–334. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Shao J, Ge T, Tang C, Wang G, Pang L and
Chen Z: Synergistic anti-inflammatory effect of gut microbiota and
lithocholic acid on liver fibrosis. Inflamm Res. 71:1389–1401.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Cao H, Xu M, Dong W, Deng B, Wang S, Zhang
Y, Wang S, Luo S, Wang W, Qi Y, et al: Secondary bile acid-induced
dysbiosis promotes intestinal carcinogenesis. Int J Cancer.
140:2545–2556. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Hedrick CC and Malanchi I: Neutrophils in
cancer: Heterogeneous and multifaceted. Nat Rev Immunol.
22:173–187. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Zheng W, Wu J, Peng Y, Sun J, Cheng P and
Huang Q: Tumor-associated neutrophils in colorectal cancer
development, progression and immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel).
14:47552022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Lin N, Li J, Yao X, Zhang X, Liu G, Zhang
Z and Weng S: Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in
colorectal cancer liver metastasis: A meta-analysis of results from
multivariate analysis. Int J Surg. 107:1069592022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
O'Brien KM, Allen KM, Rockwell CE, Towery
K, Luyendyk JP and Copple BL: IL-17A synergistically enhances bile
acid-induced inflammation during obstructive cholestasis. Am J
Pathol. 183:1498–1507. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Labiano I, Agirre-Lizaso A, Olaizola P,
Echebarria A, Huici-Izagirre M, Olaizola I, Esparza-Baquer A,
Sharif O, Hijona E, Milkiewicz P, et al: TREM-2 plays a protective
role in cholestasis by acting as a negative regulator of
inflammation. J Hepatol. 77:991–1004. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Thibaut MM, Sboarina M, Roumain M, Pötgens
SA, Neyrinck AM, Destrée F, Gillard J, Leclercq IA, Dachy G,
Demoulin JB, et al: Inflammation-induced cholestasis in cancer
cachexia. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 12:70–90. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Cui C, Lan P and Fu L: The role of
myeloid-derived suppressor cells in gastrointestinal cancer. Cancer
Commun (Lond). 41:442–471. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Zeng X, Zhou J, Xiong Z, Sun H, Yang W,
Mok MTS, Wang J, Li J, Liu M, Tang W, et al: Cell cycle-related
kinase reprograms the liver immune microenvironment to promote
cancer metastasis. Cell Mol Immunol. 18:1005–1015. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
108
|
Zhang H, Liu Y, Bian Z, Huang S, Han X,
You Z, Wang Q, Qiu D, Miao Q, Peng Y, et al: The critical role of
myeloid-derived suppressor cells and FXR activation in
immune-mediated liver injury. J Autoimmun. 53:55–66. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Chang S, Kim YH, Kim YJ, Kim YW, Moon S,
Lee YY, Jung JS, Kim Y, Jung HE, Kim TJ, et al: Taurodeoxycholate
increases the number of myeloid-derived suppressor cells that
ameliorate sepsis in mice. Front Immunol. 9:19842018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Alfaro C, Teijeira A, Onate C, Pérez G,
Sanmamed MF, Andueza MP, Alignani D, Labiano S, Azpilikueta A,
Rodriguez-Paulete A, et al: Tumor-Produced interleukin-8 attracts
human myeloid-derived suppressor cells and elicits extrusion of
neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). Clin Cancer Res.
22:3924–3936. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Schalper KA, Carleton M, Zhou M, Chen T,
Feng Y, Huang SP, Walsh AM, Baxi V, Pandya D, Baradet T, et al:
Elevated serum interleukin-8 is associated with enhanced intratumor
neutrophils and reduced clinical benefit of immune-checkpoint
inhibitors. Nat Med. 26:688–692. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Gardner A and Ruffell B: Dendritic cells
and cancer immunity. Trends Immunol. 37:855–865. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Campbell C, McKenney PT, Konstantinovsky
D, Isaeva OI, Schizas M, Verter J, Mai C, Jin WB, Guo CJ, Violante
S, et al: Bacterial metabolism of bile acids promotes generation of
peripheral regulatory T cells. Nature. 581:475–479. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Hu J, Wang C, Huang X, Yi S, Pan S, Zhang
Y, Yuan G, Cao Q, Ye X and Li H: Gut microbiota-mediated secondary
bile acids regulate dendritic cells to attenuate autoimmune uveitis
through TGR5 signaling. Cell Rep. 36:1097262021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Hu J, Zhang Y, Yi S, Wang C, Huang X, Pan
S, Yang J, Yuan G, Tan S and Li H: Lithocholic acid inhibits
dendritic cell activation by reducing intracellular glutathione via
TGR5 signaling. Int J Biol Sci. 18:4545–4559. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Tugues S, Burkhard SH, Ohs I, Vrohlings M,
Nussbaum K, Vom Berg J, Kulig P and Becher B: New insights into
IL-12-mediated tumor suppression. Cell Death Differ. 22:237–246.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
117
|
Ichikawa R, Takayama T, Yoneno K, Kamada
N, Kitazume MT, Higuchi H, Matsuoka K, Watanabe M, Itoh H, Kanai T,
et al: Bile acids induce monocyte differentiation toward
interleukin-12 hypo-producing dendritic cells via a TGR5-dependent
pathway. Immunology. 136:153–162. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Willart MA, van Nimwegen M, Grefhorst A,
Hammad H, Moons L, Hoogsteden HC, Lambrecht BN and Kleinjan A:
Ursodeoxycholic acid suppresses eosinophilic airway inflammation by
inhibiting the function of dendritic cells through the nuclear
farnesoid X receptor. Allergy. 67:1501–1510. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Kennedy R and Celis E: Multiple roles for
CD4+ T cells in anti-tumor immune responses. Immunol Rev.
222:129–144. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Laheurte C, Dosset M, Vernerey D,
Boullerot L, Gaugler B, Gravelin E, Kaulek V, Jacquin M, Cuche L,
Eberst G, et al: Distinct prognostic value of circulating
anti-telomerase CD4(+) Th1 immunity and exhausted PD-1(+)/TIM-3(+)
T cells in lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 121:405–416. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Ho TTB, Nasti A, Seki A, Komura T, Inui H,
Kozaka T, Kitamura Y, Shiba K, Yamashita T, Yamashita T, et al:
Combination of gemcitabine and anti-PD-1 antibody enhances the
anticancer effect of M1 macrophages and the Th1 response in a
murine model of pancreatic cancer liver metastasis. J Immunother
Cancer. 8:e0013672020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
De M, Ghosh S, Asad M, Banerjee I and Ali
N: Combining doxorubicin with stearylamine-bearing liposomes
elicits Th1 cytokine responses and cures metastasis in a mouse
model. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 69:1725–1735. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Pols TWH, Puchner T, Korkmaz HI, Vos M,
Soeters MR and de Vries CJM: Lithocholic acid controls adaptive
immune responses by inhibition of Th1 activation through the
vitamin D receptor. PLoS One. 12:e01767152017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B,
Fredriksen T, Mauger S, Bindea G, Berger A, Bruneval P, Fridman WH,
Pagès F and Galon J: Clinical impact of different classes of
infiltrating T cytotoxic and helper cells (Th1, th2, treg, th17) in
patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 71:1263–1271. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Liu X, Wang X, Yang Q, Luo L, Liu Z, Ren
X, Lei K, Li S, Xie Z, Zheng G, et al: Th17 cells secrete TWEAK to
trigger epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promote colorectal
cancer liver metastasis. Cancer Res. 84:1352–1371. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Hang S, Paik D, Yao L, Kim E, Trinath J,
Lu J, Ha S, Nelson BN, Kelly SP, Wu L, et al: Bile acid metabolites
control T(H)17 and T(reg) cell differentiation. Nature.
576:143–148. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Paik D, Yao L, Zhang Y, Bae S, D'Agostino
GD, Zhang M, Kim E, Franzosa EA, Avila-Pacheco J, Bisanz JE, et al:
Human gut bacteria produce Τ(Η)17-modulating bile acid metabolites.
Nature. 603:907–912. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Xiao R, Lei K, Kuok H, Deng W, Zhuang Y,
Tang Y, Guo Z, Qin H, Bai LP and Li T: Synthesis and identification
of lithocholic acid 3-sulfate as RORγt ligand to inhibit Th17 cell
differentiation. J Leukoc Biol. 112:835–843. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Chung AS, Wu X, Zhuang G, Ngu H, Kasman I,
Zhang J, Vernes JM, Jiang Z, Meng YG, Peale FV, et al: An
interleukin-17-mediated paracrine network promotes tumor resistance
to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat Med. 19:1114–1123. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Downs-Canner S, Berkey S, Delgoffe GM,
Edwards RP, Curiel T, Odunsi K, Bartlett DL and Obermajer N:
Suppressive IL-17A(+)Foxp3(+) and ex-Th17 IL-17A(neg)Foxp3(+)
T(reg) cells are a source of tumour-associated T(reg) cells. Nat
Commun. 8:146492017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Gopalakrishnan V, Spencer CN, Nezi L,
Reuben A, Andrews MC, Karpinets TV, Prieto PA, Vicente D, Hoffman
K, Wei SC, et al: Gut microbiome modulates response to anti-PD-1
immunotherapy in melanoma patients. Science. 359:97–103. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Hurtado CG, Wan F, Housseau F and Sears
CL: Roles for interleukin 17 and adaptive immunity in pathogenesis
of colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 155:1706–1715. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Shiri AM, Zhang T, Bedke T, Zazara DE,
Zhao L, Lücke J, Sabihi M, Fazio A, Zhang S, Tauriello DVF, et al:
IL-10 dampens antitumor immunity and promotes liver metastasis via
PD-L1 induction. J Hepatol. 80:634–644. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Ward-Hartstonge KA, McCall JL, McCulloch
TR, Kamps AK, Girardin A, Cretney E, Munro FM and Kemp RA:
Inclusion of BLIMP-1(+) effector regulatory T cells improves the
Immunoscore in a cohort of New Zealand colorectal cancer patients:
A pilot study. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 66:515–522. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Ladoire S, Martin F and Ghiringhelli F:
Prognostic role of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells infiltrating human
carcinomas: the paradox of colorectal cancer. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 60:909–918. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Song X, Sun X, Oh SF, Wu M, Zhang Y, Zheng
W, Geva-Zatorsky N, Jupp R, Mathis D, Benoist C and Kasper DL:
Microbial bile acid metabolites modulate gut RORγ(+) regulatory T
cell homeostasis. Nature. 577:410–415. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Pagès F, Berger A, Camus M, Sanchez-Cabo
F, Costes A, Molidor R, Mlecnik B, Kirilovsky A, Nilsson M, Damotte
D, et al: Effector memory T cells, early metastasis, and survival
in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 353:2654–2666. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Licata LA, Nguyen CT, Burga RA, Falanga V,
Espat NJ, Ayala A, Thorn M, Junghans RP and Katz SC: Biliary
obstruction results in PD-1-dependent liver T cell dysfunction and
acute inflammation mediated by Th17 cells and neutrophils. J Leukoc
Biol. 94:813–823. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Burks J, Olkhanud PB and Berzofsky JA: The
role of NKT cells in gastrointestinal cancers. Oncoimmunology.
11:20096662021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Ji G, Ma L, Yao H, Ma S, Si X, Wang Y, Bao
X, Ma L, Chen F, Ma C, et al: Precise delivery of obeticholic acid
via nanoapproach for triggering natural killer T cell-mediated
liver cancer immunotherapy. Acta Pharm Sin B. 10:2171–2182. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Cheng P, Wu J, Zong G, Wang F, Deng R, Tao
R, Qian C, Shan Y, Wang A, Zhao Y, et al: Capsaicin shapes gut
microbiota and pre-metastatic niche to facilitate cancer metastasis
to liver. Pharmacol Res. 188:1066432023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Huang WH, Zhou MW, Zhu YF, Xiang JB, Li
ZY, Wang ZH, Zhou YM, Yang Y, Chen ZY and Gu XD: The role of
hepatic stellate cells in promoting liver metastasis of colorectal
carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 12:7573–7580. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Eveno C, Hainaud P, Rampanou A, Bonnin P,
Bakhouche S, Dupuy E, Contreres JO and Pocard M: Proof of
prometastatic niche induction by hepatic stellate cells. J Surg
Res. 194:496–504. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Liu B, Wu T, Lin B, Liu X, Liu Y, Song G,
Fan C and Ouyang G: Periostin-TGF-β feedforward loop contributes to
tumour-stroma crosstalk in liver metastatic outgrowth of colorectal
cancer. Br J Cancer. 130:358–368. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Qi M, Fan S, Huang M, Pan J, Li Y, Miao Q,
Lyu W, Li X, Deng L, Qiu S, et al: Targeting FAPalpha-expressing
hepatic stellate cells overcomes resistance to antiangiogenics in
colorectal cancer liver metastasis models. J Clin Invest.
132:e1573992022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Meadows V, Kennedy L, Ekser B, Kyritsi K,
Kundu D, Zhou T, Chen L, Pham L, Wu N, Demieville J, et al: Mast
cells regulate ductular reaction and intestinal inflammation in
cholestasis through farnesoid X receptor signaling. Hepatology.
74:2684–2698. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Yang J, Tang X, Liang Z, Chen M and Sun L:
Taurocholic acid promotes hepatic stellate cell activation via
S1PR2/p38 MAPK/YAP signaling under cholestatic conditions. Clin Mol
Hepatol. 29:465–481. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Saga K, Iwashita Y, Hidano S, Aso Y, Isaka
K, Kido Y, Tada K, Takayama H, Masuda T, Hirashita T, et al:
Secondary unconjugated bile acids induce hepatic stellate cell
activation. Int J Mol Sci. 19:30432018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Nguyen PT, Kanno K, Pham QT, Kikuchi Y,
Kakimoto M, Kobayashi T, Otani Y, Kishikawa N, Miyauchi M, Arihiro
K, et al: Senescent hepatic stellate cells caused by deoxycholic
acid modulates malignant behavior of hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 146:3255–3268. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Theivanthiran B, Yarla N, Haykal T, Nguyen
YV, Cao L, Ferreira M, Holtzhausen A, Al-Rohil R, Salama AKS,
Beasley GM, et al: Tumor-intrinsic NLRP3-HSP70-TLR4 axis drives
premetastatic niche development and hyperprogression during
anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Sci Transl Med. 14:eabq70192022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Gong Z, Zhou J, Zhao S, Tian C, Wang P, Xu
C, Chen Y, Cai W and Wu J: Chenodeoxycholic acid activates NLRP3
inflammasome and contributes to cholestatic liver fibrosis.
Oncotarget. 7:83951–83963. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Hao H, Cao L, Jiang C, Che Y, Zhang S,
Takahashi S, Wang G and Gonzalez FJ: Farnesoid X receptor
regulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome underlies
cholestasis-associated sepsis. Cell Metab. 25:856–867.e5. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Zhao S, Gong Z, Zhou J, Tian C, Gao Y, Xu
C, Chen Y, Cai W and Wu J: Deoxycholic acid triggers NLRP3
inflammasome activation and aggravates DSS-Induced colitis in mice.
Front Immunol. 7:5362016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Holtmann TM, Inzaugarat ME, Knorr J,
Geisler L, Schulz M, Bieghs V, Frissen M, Feldstein AE, Tacke F,
Trautwein C and Wree A: Bile acids activate NLRP3 inflammasome,
promoting murine liver inflammation or fibrosis in a cell
type-specific manner. Cells. 10:26182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Guo C, Xie S, Chi Z, Zhang J, Liu Y, Zhang
L, Zheng M, Zhang X, Xia D, Ke Y, et al: Bile acids control
inflammation and metabolic disorder through inhibition of NLRP3
inflammasome. Immunity. 45:9442016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Sun L, Cai J and Gonzalez FJ: The role of
farnesoid X receptor in metabolic diseases, and gastrointestinal
and liver cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 18:335–347. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Chapman RW and Lynch KD: Obeticholic
acid-a new therapy in PBC and NASH. Br Med Bull. 133:95–104. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Zhang Y, Jackson JP, StClaire RL III,
Freeman K, Brouwer KR and Edwards JE: Obeticholic acid, a selective
farnesoid X receptor agonist, regulates bile acid homeostasis in
sandwich-cultured human hepatocytes. Pharmacol Res Perspect.
5:e003292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Lu L, Jiang YX, Liu XX, Jin JM, Gu WJ,
Luan X, Guan YY and Zhang LJ: FXR agonist GW4064 enhances
anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in colorectal cancer. Oncoimmunology.
12:22170242023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Zhang T, Feng S, Li J, Wu Z, Deng Q, Yang
W, Li J and Pan G: Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonists induce
hepatocellular apoptosis and impair hepatic functions via FXR/SHP
pathway. Arch Toxicol. 96:1829–1843. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Yin Y, Wang M, Gu W and Chen L:
Intestine-specific FXR agonists as potential therapeutic agents for
colorectal cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 186:1144302021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Ji G, Si X, Dong S, Xu Y, Li M, Yang B,
Tang Z, Fang X, Huang L, Song W and Chen X: Manipulating liver bile
acid signaling by nanodelivery of bile acid receptor modulators for
liver cancer immunotherapy. Nano Lett. 21:6781–6791. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Zhang Y, Jiang R, Zheng X, Lei S, Huang F,
Xie G, Kwee S, Yu H, Farrar C, Sun B, et al: Ursodeoxycholic acid
accelerates bile acid enterohepatic circulation. Br J Pharmacol.
176:2848–2863. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Pearson T, Caporaso JG, Yellowhair M,
Bokulich NA, Padi M, Roe DJ, Wertheim BC, Linhart M, Martinez JA,
Bilagody C, et al: Effects of ursodeoxycholic acid on the gut
microbiome and colorectal adenoma development. Cancer Med.
8:617–628. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
He Q, Wu J, Ke J, Zhang Q, Zeng W, Luo Z,
Gong J, Chen Y, He Z and Lan P: Therapeutic role of ursodeoxycholic
acid in colitis-associated cancer via gut microbiota modulation.
Mol Ther. 31:585–598. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Zhang H, Xu H, Zhang C, Tang Q and Bi F:
Ursodeoxycholic acid suppresses the malignant progression of
colorectal cancer through TGR5-YAP axis. Cell Death Discov.
7:2072021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Shah SA, Volkov Y, Arfin Q, Abdel-Latif MM
and Kelleher D: Ursodeoxycholic acid inhibits interleukin 1 beta
[corrected] and deoxycholic acid-induced activation of NF-kappaB
and AP-1 in human colon cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 118:532–539.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
168
|
Zheng Z, Hou X, Bian Z, Jia W and Zhao L:
Gut microbiota and colorectal cancer metastasis. Cancer Lett.
555:2160392023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
169
|
Wang X, Zhu B, Hua Y, Sun R, Tan X, Chang
X, Tang D and Gu J: Astragalus mongholicus Bunge and Curcuma
aromatica Salisb. modulate gut microbiome and bile acid metabolism
to inhibit colon cancer progression. Front Microbiol.
15:13956342024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Liu T, Song X, Khan S, Li Y, Guo Z, Li C,
Wang S, Dong W, Liu W, Wang B and Cao H: The gut microbiota at the
intersection of bile acids and intestinal carcinogenesis: An old
story, yet mesmerizing. Int J Cancer. 146:1780–1790. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
171
|
Deng J, Yuan W, Tan Q, Wei X and Ma J:
Non-absorbable antibiotic treatment inhibits colorectal cancer
liver metastasis by modulating deoxycholic acid metabolism by
intestinal microbes. J Cancer. 13:764–774. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Fidelle M, Rauber C, Alves Costa Silva C,
Tian AL, Lahmar I, de La Varende AM, Zhao L, Thelemaque C, Lebhar
I, Messaoudene M, et al: A microbiota-modulated checkpoint directs
immunosuppressive intestinal T cells into cancers. Science.
380:eabo22962023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Kaźmierczak-Siedlecka K, Daca A, Fic M,
van de Wetering T, Folwarski M and Makarewicz W: Therapeutic
methods of gut microbiota modification in colorectal cancer
management-fecal microbiota transplantation, prebiotics,
probiotics, and synbiotics. Gut Microbes. 11:1518–1530. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
174
|
Routy B, Le Chatelier E, Derosa L, Duong
CPM, Alou MT, Daillère R, Fluckiger A, Messaoudene M, Rauber C,
Roberti MP, et al: Gut microbiome influences efficacy of PD-1-based
immunotherapy against epithelial tumors. Science. 359:91–97. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
175
|
Lan X, Ma J, Huang Z, Xu Y and Hu Y:
Akkermansia muciniphila might improve anti-PD-1 therapy against HCC
by changing host bile acid metabolism. J Gene Med. 26:e36392024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
176
|
Chen D, Wu J, Jin D, Wang B and Cao H:
Fecal microbiota transplantation in cancer management: Current
status and perspectives. Int J Cancer. 145:2021–2031. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
177
|
Fuchs CD and Trauner M: Role of bile acids
and their receptors in gastrointestinal and hepatic
pathophysiology. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 19:432–450. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Kastelijn JB, van der Loos MA, Welsing PM,
Dhondt E, Koopman M, Moons LM and Vleggaar FP: Clinical outcomes of
biliary drainage of malignant biliary obstruction due to colorectal
cancer metastases: A systematic review. Eur J Intern Med. 88:81–88.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Sinha SR, Haileselassie Y, Nguyen LP,
Tropini C, Wang M, Becker LS, Sim D, Jarr K, Spear ET, Singh G, et
al: Dysbiosis-induced secondary bile acid deficiency promotes
intestinal inflammation. Cell Host Microbe. 27:659–670 e5. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Gadaleta RM, Garcia-Irigoyen O and
Moschetta A: Bile acids and colon cancer: Is FXR the solution of
the conundrum? Mol Aspects Med. 56:66–74. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|