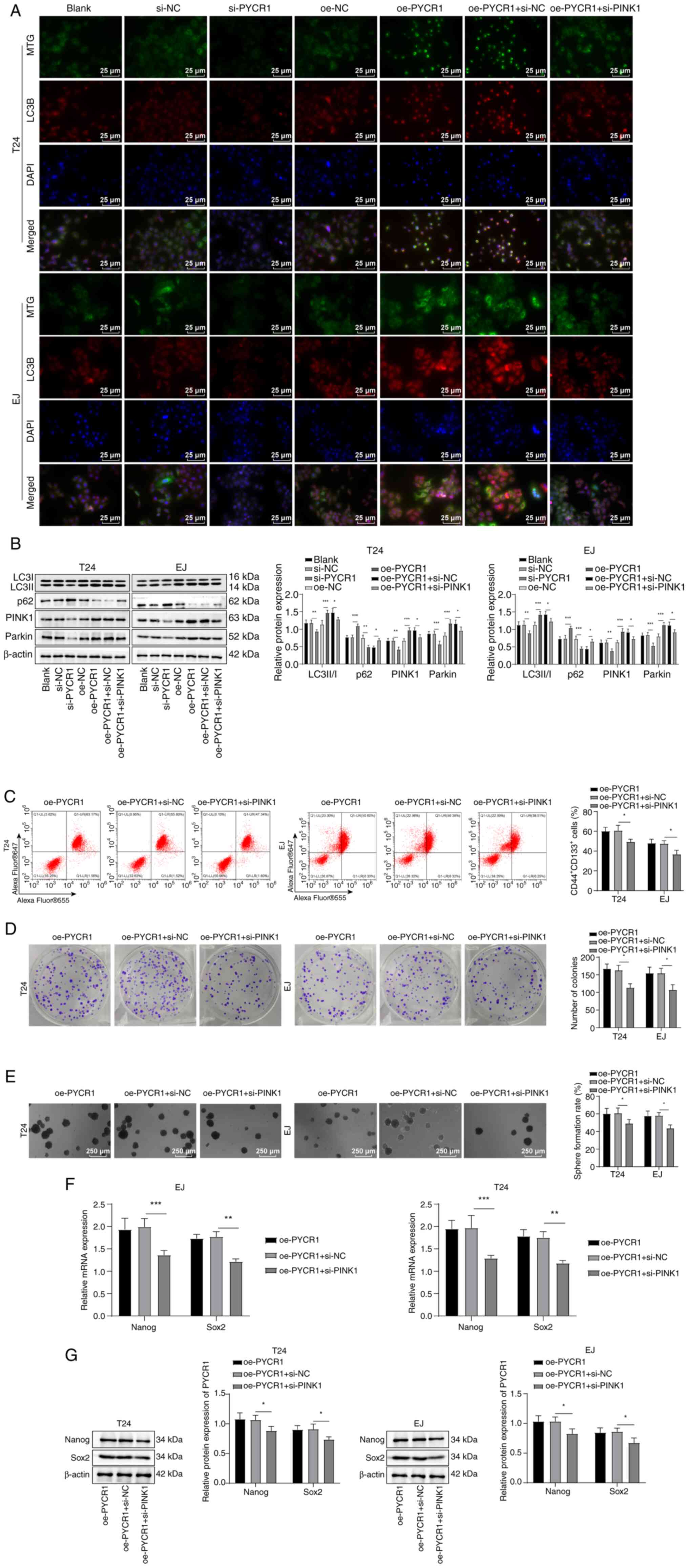
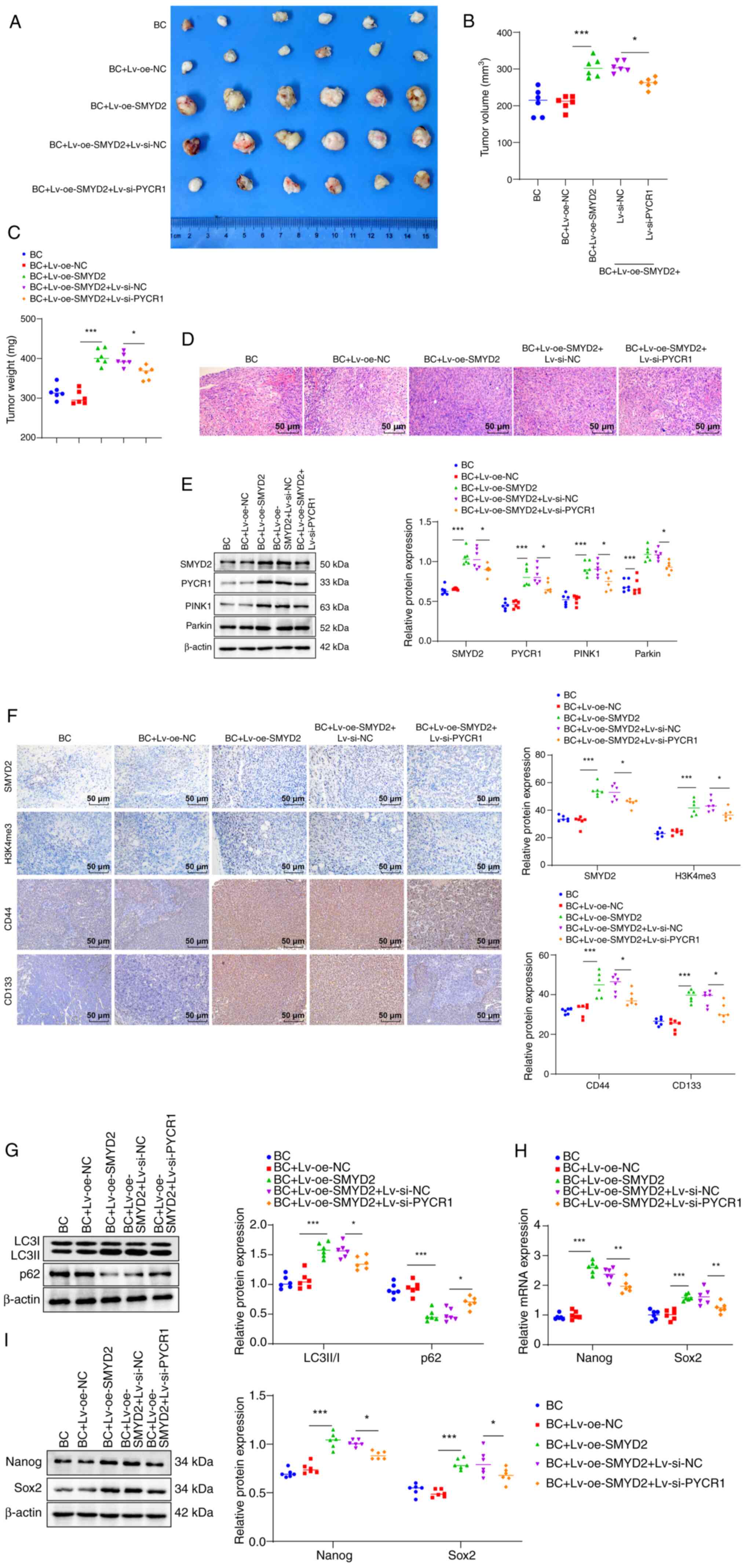
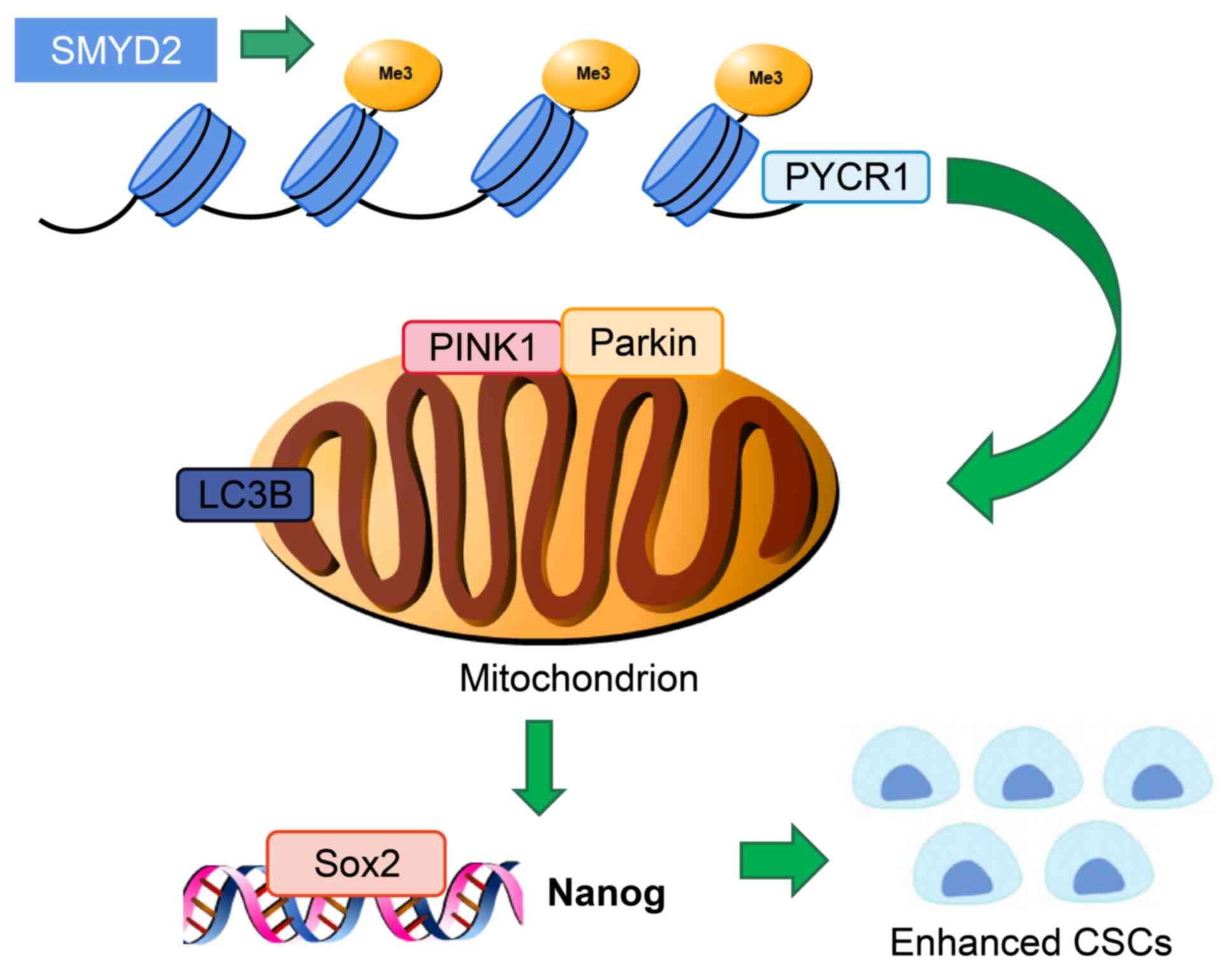
|
1
|
Chen S, Zhu J, Wang F, Guan Z, Ge Y, Yang
X and Cai J: LncRNAs and their role in cancer stem cells.
Oncotarget. 8:110685–110692. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Eid RA, Alaa Edeen M, Shedid EM, Kamal AS,
Warda MM, Mamdouh F, Khedr SA, Soltan MA, Jeon HW, Zaki MS and Kim
B: Targeting Cancer Stem Cells as the Key Driver of Carcinogenesis
and Therapeutic Resistance. Int J Mol Sci. 24:2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Aghaalikhani N, Rashtchizadeh N, Shadpour
P, Allameh A and Mahmoodi M: Cancer stem cells as a therapeutic
target in bladder cancer. J Cell Physiol. 234:3197–3206. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Li Z, Liu J, Fu H, Li Y, Liu Q, Song W and
Zeng M: SENP3 affects the expression of PYCR1 to promote bladder
cancer proliferation and EMT transformation by deSUMOylation of
STAT3. Aging (Albany NY). 14:8032–8045. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Song W, Li Z, Yang K, Gao Z, Zhou Q and Li
P: Antisense lncRNA-RP11-498C9.13 promotes bladder cancer
progression by enhancing reactive oxygen species-induced mitophagy.
J Gene Med. 25:e35272023. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Song W, Yang K, Luo J, Gao Z and Gao Y:
Dysregulation of USP18/FTO/PYCR1 signaling network promotes bladder
cancer development and progression. Aging (Albany NY).
13:3909–3925. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang Y, Zhang X, Huang X, Tang X, Zhang
M, Li Z, Hu X, Zhang M, Wang X and Yan Y: Tumor stemness score to
estimate epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and cancer stem
cells (CSCs) characterization and to predict the prognosis and
immunotherapy response in bladder urothelial carcinoma. Stem Cell
Res Ther. 14:152023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ye Y, Li L, Dai Q, Liu Y and Shen L:
Comprehensive analysis of histone methylation modification
regulators for predicting prognosis and drug sensitivity in lung
adenocarcinoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 10:9919802022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
McCabe MT, Mohammad HP, Barbash O and
Kruger RG: Targeting Histone Methylation in Cancer. Cancer J.
23:292–301. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tan Z, Fu S, Feng R, Huang Y, Li N, Wang H
and Wang J: Identification of potential biomarkers for progression
and prognosis of bladder cancer by comprehensive bioinformatics
analysis. J Oncol. 2022:18027062022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu W, Chen F, Fei X, Yang X and Lu X:
Overexpression of SET and MYND domain-containing protein 2 (SMYD2)
is associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis in patients
with papillary thyroid carcinoma. Med Sci Monit. 24:7357–7365.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu H, Ba Z, Liu C and Yu X: Long noncoding
RNA DLEU1 promotes proliferation and glycolysis of gastric cancer
cells via APOC1 upregulation by recruiting SMYD2 to induce
trimethylation of H3K4 modification. Transl Oncol. 36:1017312023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Whelan KA, Chandramouleeswaran PM, Tanaka
K, Natsuizaka M, Guha M, Srinivasan S, Darling DS, Kita Y, Natsugoe
S, Winkler JD, et al: Autophagy supports generation of cells with
high CD44 expression via modulation of oxidative stress and
Parkin-mediated mitochondrial clearance. Oncogene. 36:4843–4858.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu K, Lee J, Kim JY, Wang L, Tian Y, Chan
ST, Cho C, Machida K, Chen D and Ou JJ: Mitophagy controls the
activities of tumor suppressor p53 to regulate hepatic cancer stem
cells. Mol Cell. 68:281–292. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Panigrahi DP, Praharaj PP, Bhol CS,
Mahapatra KK, Patra S, Behera BP, Mishra SR and Bhutia SK: The
emerging, multifaceted role of mitophagy in cancer and cancer
therapeutics. Semin Cancer Biol. 66:45–58. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lou Y, Ma C, Liu Z, Shi J, Zheng G, Zhang
C and Zhang Z: Antimony exposure promotes bladder tumor cell growth
by inhibiting PINK1-Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Ecotoxicol Environ
Saf. 221:1124202021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nguyen TN, Padman BS and Lazarou M:
Deciphering the molecular signals of PINK1/Parkin mitophagy. Trends
Cell Biol. 26:733–744. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee J, Liu K, Stiles B and Ou JJ:
Mitophagy and hepatic cancer stem cells. Autophagy. 14:715–716.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Choudhury D, Rong N, Senthil Kumar HV,
Swedick S, Samuel RZ, Mehrotra P, Toftegaard J, Rajabian N,
Thiyagarajan R, Podder AK, et al: Proline restores mitochondrial
function and reverses aging hallmarks in senescent cells. Cell Rep.
43:1137382024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cui B, He B, Huang Y, Wang C, Luo H, Lu J,
Su K, Zhang X, Luo Y, Zhao Z, et al: Pyrroline-5-carboxylate
reductase 1 reprograms proline metabolism to drive breast cancer
stemness under psychological stress. Cell Death Dis. 14:6822023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zietzer A, Hosen MR, Wang H, Goody PR,
Sylvester M, Latz E, Nickenig G, Werner N and Jansen F: The
RNA-binding protein hnRNPU regulates the sorting of microRNA-30c-5p
into large extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles.
9:17869672020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Han Y, Liu C, Zhang D, Men H, Huo L, Geng
Q, Wang S, Gao Y, Zhang W, Zhang Y and Jia Z: Mechanosensitive ion
channel Piezo1 promotes prostate cancer development through the
activation of the Akt/mTOR pathway and acceleration of cell cycle.
Int J Oncol. 55:629–644. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dai X, Ren T, Zhang Y and Nan N:
Methylation multiplicity and its clinical values in cancer. Expert
Rev Mol Med. 23:e22021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Hirajima S, Nagata
H, Nishimura Y, Kawaguchi T, Miyamae M, Okajima W, Ohashi T,
Konishi H, et al: Overexpression of SMYD2 contributes to malignant
outcome in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 112:357–364. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Zhang Y, Zhou L, Xu Y, Zhou J, Jiang T,
Wang J, Li C, Sun X, Song H and Song J: Targeting SMYD2 inhibits
angiogenesis and increases the efficiency of apatinib by
suppressing EGFL7 in colorectal cancer. Angiogenesis. 26:1–18.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kim K, Ryu TY, Jung E, Han TS, Lee J, Kim
SK, Roh YN, Lee MS, Jung CR, Lim JH, et al: Epigenetic regulation
of SMAD3 by histone methyltransferase SMYD2 promotes lung cancer
metastasis. Exp Mol Med. 55:952–964. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sakamoto LH, Andrade RV, Felipe MS,
Motoyama AB and Pittella Silva F: SMYD2 is highly expressed in
pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia and constitutes a bad
prognostic factor. Leuk Res. 38:496–502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yi X, Jiang XJ and Fang ZM: Histone
methyltransferase SMYD2: Ubiquitous regulator of disease. Clin
Epigenetics. 11:1122019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Migita T, Ueda A, Ohishi T, Hatano M,
Seimiya H, Horiguchi SI, Koga F and Shibasaki F:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition promotes SOX2 and NANOG
expression in bladder cancer. Lab Invest. 97:567–576. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cho HS, Hayami S, Toyokawa G, Maejima K,
Yamane Y, Suzuki T, Dohmae N, Kogure M and Kang D: RB1 methylation
by SMYD2 enhances cell cycle progression through an increase of RB1
phosphorylation. Neoplasia. 14:476–486. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gao RL, Chen XR, Li YN, Yan XY, Sun JG, He
QL and Cai FZ: Upregulation of miR-543-3p promotes growth and stem
cell-like phenotype in bladder cancer by activating the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
10:9418–9426. 2017.
|
|
33
|
Hu Y, Zhang Y, Gao J, Lian X and Wang Y:
The clinicopathological and prognostic value of CD44 expression in
bladder cancer: A study based on meta-analysis and TCGA data.
Bioengineered. 11:572–581. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xia P, Liu DH, Xu ZJ and Ren F: Cancer
stem cell markers for urinary carcinoma. Stem Cells Int.
2022:36116772022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cai F, Miao Y, Liu C, Wu T, Shen S, Su X
and Shi Y: Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase 1 promotes
proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer.
Oncol Lett. 15:731–740. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shang L and Wei M: Inhibition of SMYD2
sensitized cisplatin to resistant cells in NSCLC through activating
p53 pathway. Front Oncol. 9:3062019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lin X, Chen JD, Wang CY, Cai Z, Zhan R,
Yang C, Zhang LY, Li LY, Xiao Y, Chen MK and Wu M: Cooperation of
MLL1 and Jun in controlling H3K4me3 on enhancers in colorectal
cancer. Genome Biol. 24:2682023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Phoyen S, Sanpavat A, Ma-On C, Stein U,
Hirankarn N, Tangkijvanich P, Jindatip D, Whongsiri P and Boonla C:
H4K20me3 upregulated by reactive oxygen species is associated with
tumor progression and poor prognosis in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. Heliyon. 9:e225892023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhou Z, Zhang B, Deng Y, Deng S, Li J, Wei
W, Wang Y, Wang J, Feng Z, Che M, et al: FBW7/GSK3 β mediated
degradation of IGF2BP2 inhibits IGF2BP2-SLC7A5 positive feedback
loop and radioresistance in lung cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
43:342024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Abu-Farha M, Lambert JP, Al-Madhoun AS,
Elisma F, Skerjanc IS and Figeys D: The tale of two domains:
proteomics and genomics analysis of SMYD2, a new histone
methyltransferase. Mol Cell Proteomics. 7:560–572. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wang S, Long H, Hou L, Feng B, Ma Z, Wu Y,
Zeng Y, Cai J, Zhang DW and Zhao G: The mitophagy pathway and its
implications in human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
8:3042023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Silvian LF: PINK1/parkin pathway
activation for mitochondrial quality control-which is the best
molecular target for therapy? Front Aging Neurosci. 14:8908232022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Yuan X, Chen K, Zheng F, Xu S, Li Y, Wang
Y, Ni H, Wang F, Cui Z, Qin Y, et al: Low-dose BPA and its
substitute BPS promote ovarian cancer cell stemness via a
non-canonical PINK1/p53 mitophagic signaling. J Hazard Mater.
452:1312882023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Feng X, Yin W, Wang J, Feng L and Kang YJ:
Mitophagy promotes the stemness of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal
stem cells. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 246:97–105. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Liu D, Sun Z, Ye T, Li J, Zeng B, Zhao Q,
Wang J and Xing HR: The mitochondrial fission factor FIS1 promotes
stemness of human lung cancer stem cells via mitophagy. FEBS Open
Bio. 11:1997–2007. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Vazquez-Martin A, Van den Haute C, Cufi S,
Corominas-Faja B, Cuyàs E, Lopez-Bonet E, Rodr iguez-Gallego E,
Fernández-Arroyo S, Joven J, Baekelandt V and Menendez JA:
Mitophagy-driven mitochondrial rejuvenation regulates stem cell
fate. Aging (Albany NY). 8:1330–1352. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|