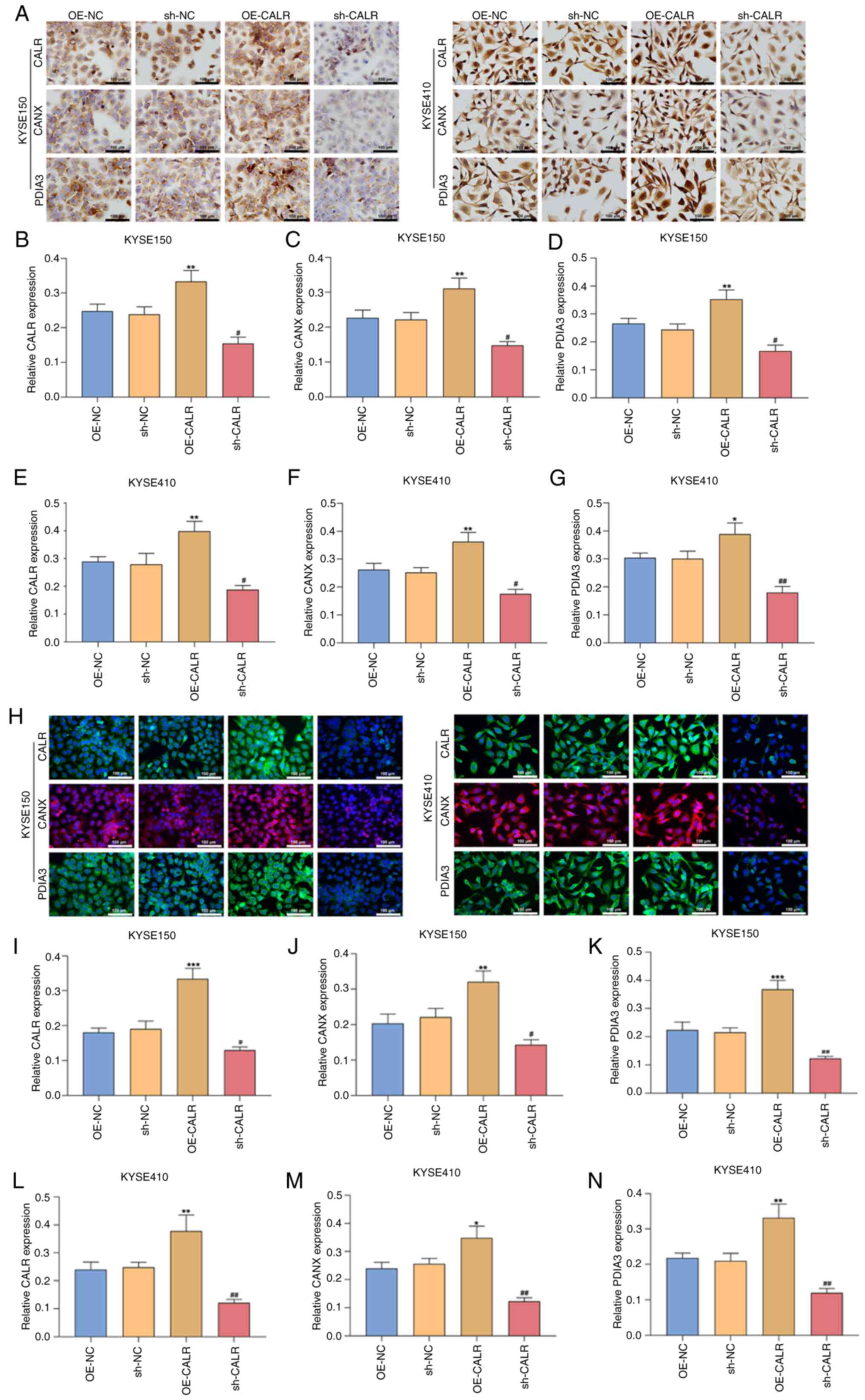
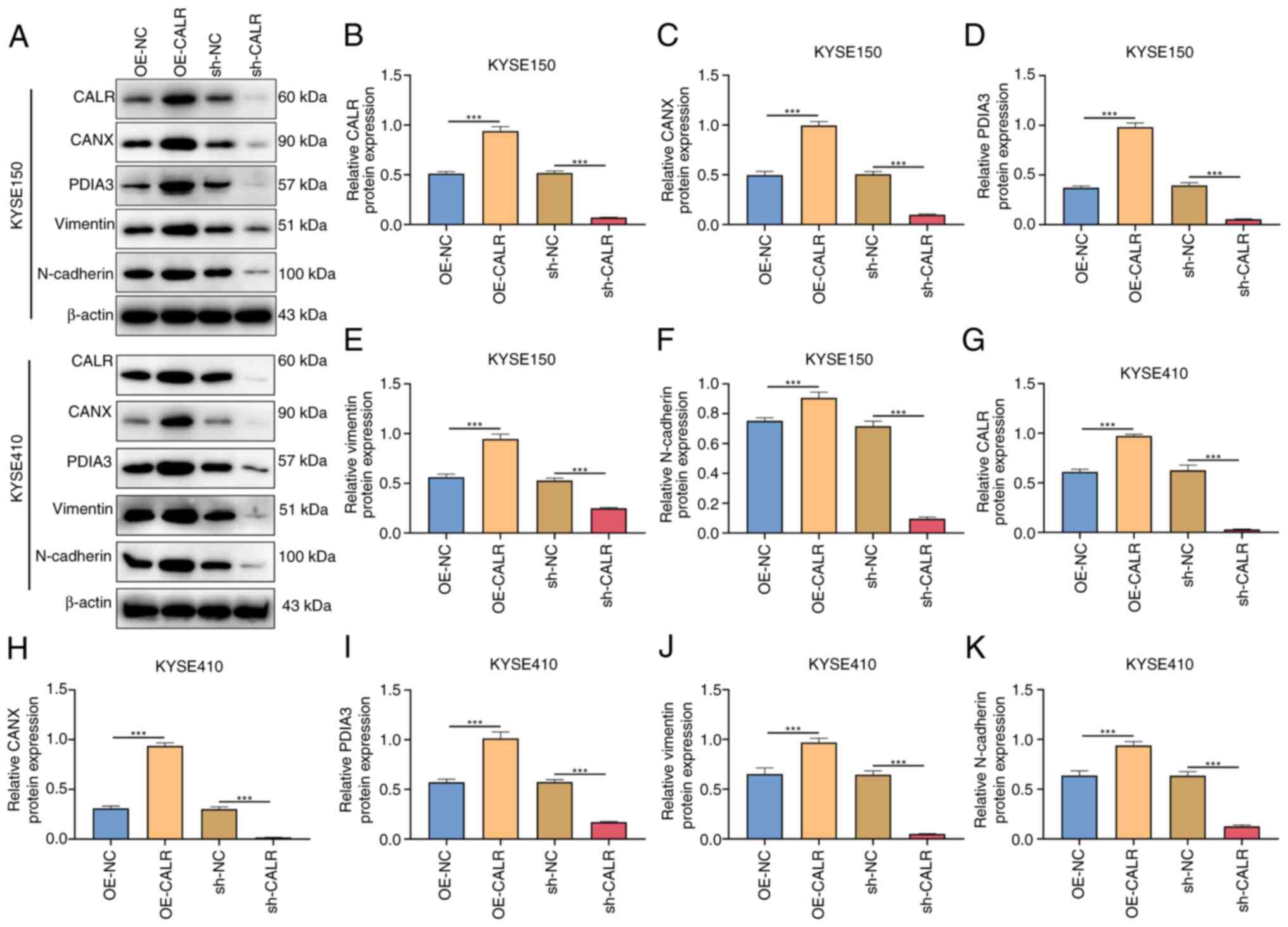
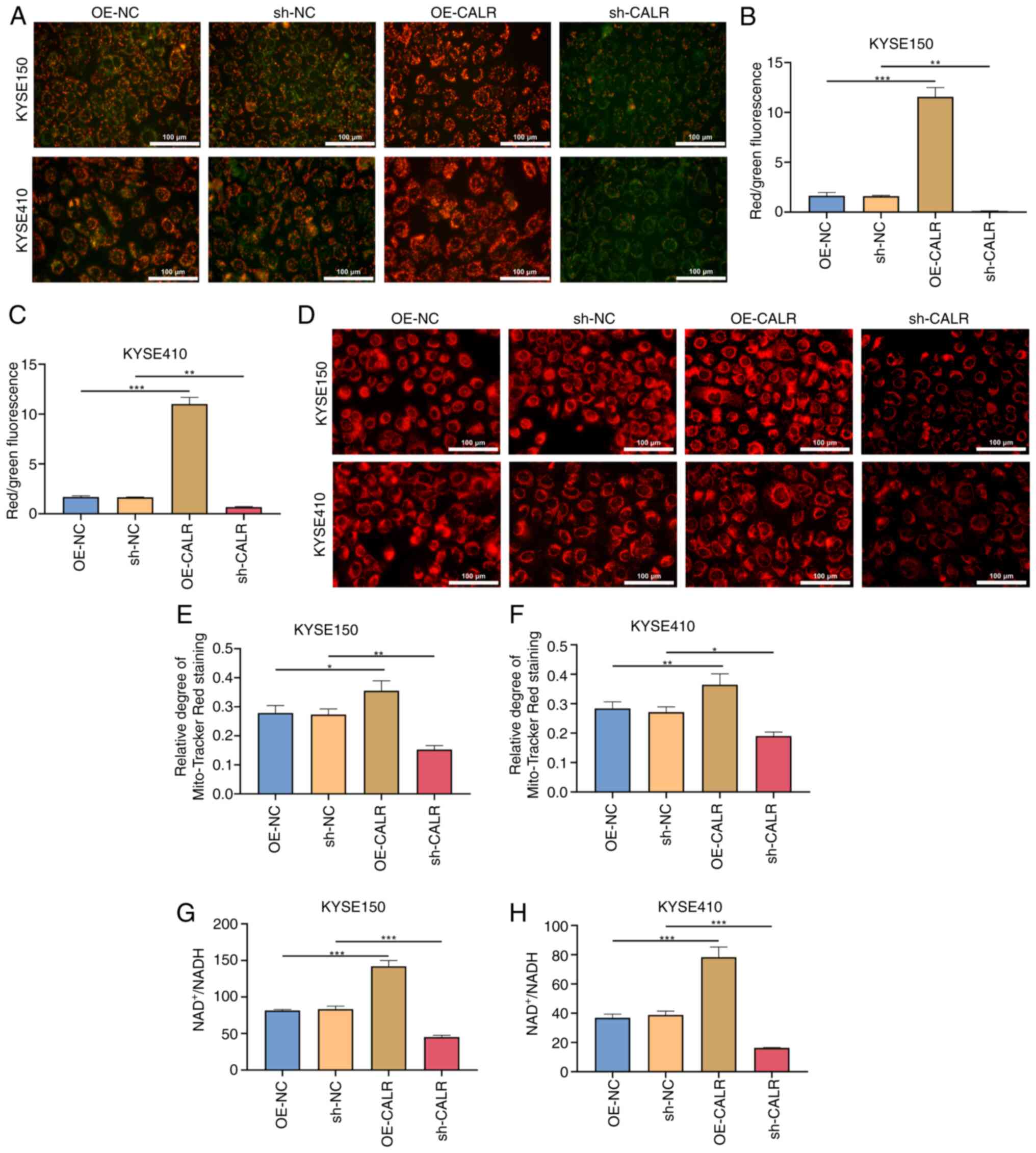
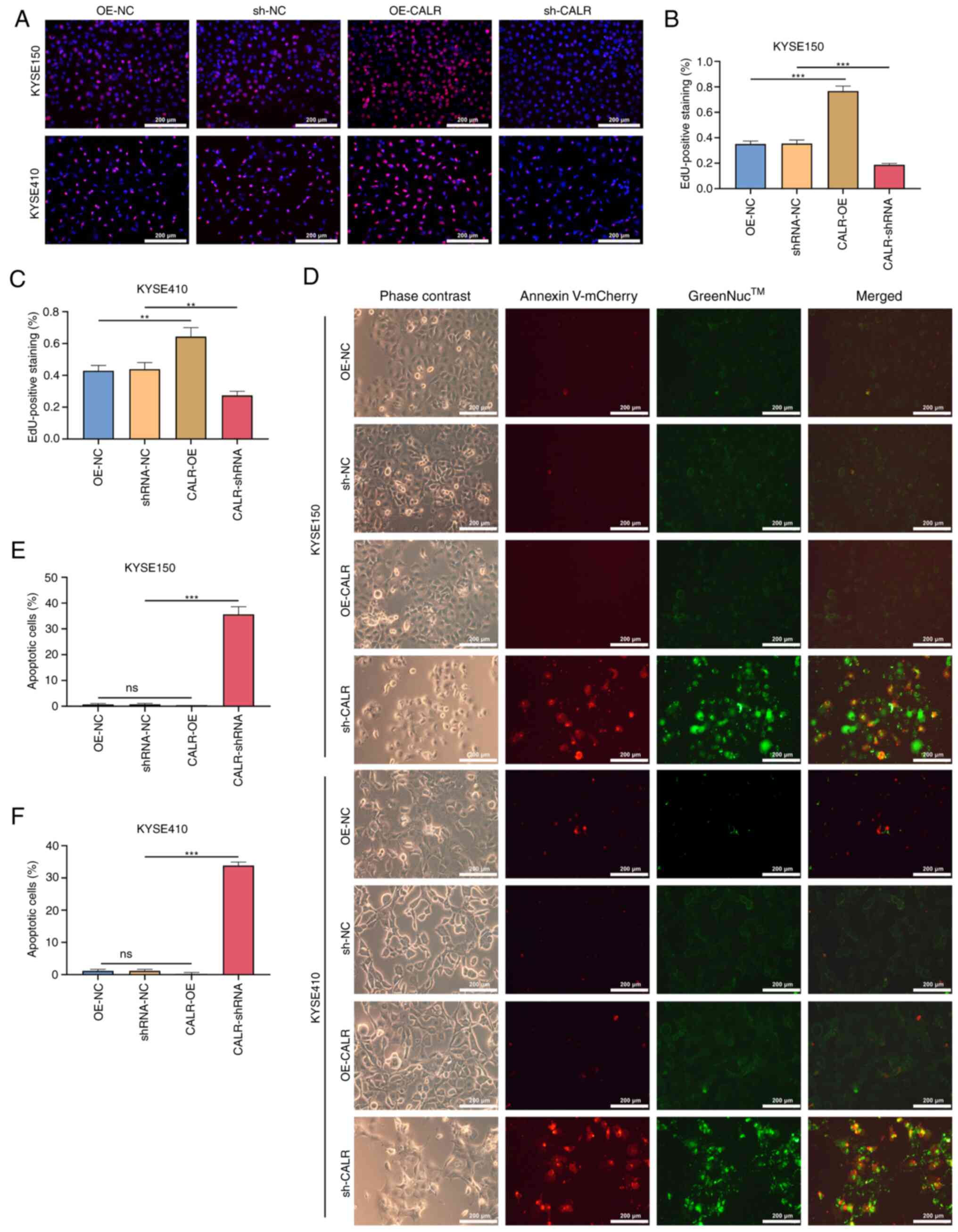
|
1
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu Z, Gu S, Lu T, Wu K, Li L, Dong C and
Zhou Y: IFI6 depletion inhibits esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
progression through reactive oxygen species accumulation via
mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 39:1442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huang J, Xu J, Chen Y, Zhuang W, Zhang Y,
Chen Z, Chen J, Zhang H, Niu Z, Fan Q, et al: Camrelizumab versus
investigator's choice of chemotherapy as second-line therapy for
advanced or metastatic oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma
(ESCORT): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 study.
Lancet Oncol. 21:832–842. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang H, Tang H, Fang Y, Tan L, Yin J, Shen
Y, Zeng Z, Zhu J, Hou Y, Du M, et al: Morbidity and mortality of
patients who underwent minimally invasive esophagectomy after
neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy vs. neoadjuvant chemotherapy for
locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A randomized
clinical trial. JAMA Surg. 156:444–451. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Doki Y, Ajani JA, Kato K, Xu J, Wyrwicz L,
Motoyama S, Ogata T, Kawakami H, Hsu CH, Adenis A, et al: Nivolumab
combination therapy in advanced esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma.
N Engl J Med. 386:449–462. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang ZX, Cui C, Yao J, Zhang Y, Li M, Feng
J, Yang S, Fan Y, Shi J, Zhang X, et al: Toripalimab plus
chemotherapy in treatment-naïve, advanced esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma (JUPITER-06): A multi-center phase 3 trial. Cancer Cell.
40:277–288.e3. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yamamoto S and Kato K: JUPITER-06
establishes immune checkpoint inhibitors as essential first-line
drugs for the treatment of advanced esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 40:238–240. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ma F, Li Y, Xiang C, Wang B, Lv J, Wei J,
Qin Z, Pu Y, Li K, Teng H, et al: Proteomic characterization of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma response to immunotherapy
reveals potential therapeutic strategy and predictive biomarkers. J
Hematol Oncol. 17:112024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Miao Z, Li J, Zeng S, Lv Y, Jia S, Ding D,
Li W and Liu Q: Endoplasmic reticulum-targeting AIE
photosensitizers to boost immunogenic cell death for immunotherapy
of bladder carcinoma. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 16:245–260. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Fucikova J, Spisek R, Kroemer G and
Galluzzi L: Calreticulin and cancer. Cell Res. 31:5–16. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Fabarius A, Samra V, Drews O, Mörz H,
Bierbaum M, Darwich A, Weiss C, Brendel S, Kleiner H, Seifarth W,
et al: Evidence for recombinant GRP78, CALR, PDIA3 and GPI as
mediators of genetic instability in human CD34+ cells. Cancers
(Basel). 14:28832022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang LT, Lin MH, Liu KY, Chiou SS, Wang
SN, Chai CY, Tseng LW, Chiou HC, Wang HC, Yokoyama KK, et al:
WLS/wntless is essential in controlling dendritic cell homeostasis
via a WNT signaling-independent mechanism. Autophagy. 17:4202–4217.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
da Silva DC, Valentão P, Andrade PB and
Pereira DM: Endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling in cancer and
neurodegenerative disorders: Tools and strategies to understand its
complexity. Pharmacol Res. 155:1047022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Antoniotti V, Bellone S, Correia FP, Peri
C, Tini S, Ricotti R, Mancioppi V, Gagliardi M, Spadaccini D,
Caputo M, et al: Calreticulin and PDIA3, two markers of endoplasmic
reticulum stress, are associated with metabolic alterations and
insulin resistance in pediatric obesity: A pilot study. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:10039192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Khan AA, Allemailem KS, Almatroudi A,
Almatroodi SA, Mahzari A, Alsahli MA and Rahmani AH: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress provocation by different nanoparticles: An
innovative approach to manage the cancer and other common diseases.
Molecules. 25:53362020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li J, Qi F, Su H, Zhang C, Zhang Q, Chen
Y, Chen P, Su L, Chen Y, Yang Y, et al: GRP75-faciliated
mitochondria-associated ER membrane (MAM) integrity controls
cisplatin-resistance in ovarian cancer patients. Int J Biol Sci.
18:2914–2931. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li X, Zhao X, Qin Z, Li J, Sun B and Liu
L: Regulation of calcium homeostasis in endoplasmic
reticulum-mitochondria crosstalk: Implications for skeletal muscle
atrophy. Cell Commun Signal. 23:172025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee SY, Oh JY, Kang TH, Shin HS, Cheng MA,
Farmer E, Wu TC and Hung CF: Endoplasmic reticulum stress enhances
the antigen-specific T cell immune responses and therapeutic
antitumor effects generated by therapeutic HPV vaccines. J Biomed
Sci. 26:412019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen R, Huang M, Yang X, Chen XH, Shi MY,
Li ZF, Chen ZN and Wang K: CALR-TLR4 complex inhibits non-small
cell lung cancer progression by regulating the migration and
maturation of dendritic cells. Front Oncol. 11:7430502021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fucikova J, Kepp O, Kasikova L, Petroni G,
Yamazaki T, Liu P, Zhao L, Spisek R, Kroemer G and Galluzzi L:
Detection of immunogenic cell death and its relevance for cancer
therapy. Cell Death Dis. 11:10132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Niu X, Chen L, Li Y, Hu Z and He F:
Ferroptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis in the tumor
microenvironment: Perspectives for immunotherapy of SCLC. Semin
Cancer Biol. 86:273–285. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu X, Song N, Liu Y, Liu Y, Li J, Ding J
and Tong Z: Efficient induction of anti-tumor immune response in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via dendritic cells expressing
MAGE-A3 and CALR antigens. Cell Immunol. 295:77–82. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang X, Song X, Cheng G, Zhang J, Dong L,
Bai J, Luo D, Xiong Y, Li S, Liu F, et al: The regulatory mechanism
and biological significance of mitochondrial calcium uniporter in
the migration, invasion, angiogenesis and growth of gastric cancer.
Onco Targets Ther. 13:11781–11794. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tang Z, Kang B, Li C, Chen T and Zhang Z:
GEPIA2: An enhanced web server for large-scale expression profiling
and interactive analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:W556–W560. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pelosof L, Saung MT, Donoghue M, Casak S,
Mushti S, Cheng J, Jiang X, Liu J, Zhao H, Khazraee M, et al:
Benefit-Risk summary of nivolumab for the treatment of patients
with unresectable advanced, recurrent, or metastatic esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma after prior fluoropyrimidine- and
platinum-based chemotherapy. Oncologist. 26:318–324. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Sugimura K, Miyata H, Tanaka K, Makino T,
Takeno A, Shiraishi O, Motoori M, Yamasaki M, Kimura Y, Hirao M, et
al: Multicenter randomized phase 2 trial comparing
chemoradiotherapy and docetaxel plus 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin
chemotherapy as initial induction therapy for subsequent conversion
surgery in patients with clinical T4b esophageal cancer: Short-term
results. Ann Surg. 274:e465–e472. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yamamoto S, Kawakami H, Kii T, Hara H,
Kawabata R, Kawada J, Takeno A, Matsuyama J, Ueda S, Okita Y, et
al: Randomized phase II study of docetaxel versus paclitaxel in
patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma refractory to
fluoropyrimidine- and platinum-based chemotherapy: OGSG1201. Eur J
Cancer. 154:307–315. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen H, Xu N, Xu J, Zhang C, Li X, Xu H,
Zhu W, Li J, Liang D and Zhou W: A risk signature based on
endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated genes predicts prognosis
and immunity in pancreatic cancer. Front Mol Biosci.
10:12980772023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ciftciler R and Balasar O: A rare CALR
variant mutation and efficient peginterferon alfa-2a response in a
patient with essential thrombocythemia. Cancer Genet.
274-275:51–53. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ye J, Qi L, Du Z, Yu L, Chen K, Li R, Feng
R and Zhai W: Calreticulin: A potential diagnostic and therapeutic
biomarker in gallbladder cancer. Aging (Albany NY). 13:5607–5620.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Han Y, Liao Q, Wang H, Rao S, Yi P, Tang
L, Tian Y, Oyang L, Wang H, Shi Y and Zhou Y: High expression of
calreticulin indicates poor prognosis and modulates cell migration
and invasion via activating Stat3 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J
Cancer. 10:5460–5468. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sheng W, Wang G, Tang J, Shi X, Cao R, Sun
J, Lin YH, Jia C, Chen C, Zhou J and Dong M: Calreticulin promotes
EMT in pancreatic cancer via mediating Ca(2+) dependent acute and
chronic endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
39:2092020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang L, Chen J, Zuo Q, Wu C, Yu T, Zheng
P, Huang H, Deng J, Fang L, Liu H, et al: Calreticulin enhances
gastric cancer metastasis by dimethylating H3K9 in the E-cadherin
promoter region mediating by G9a. Oncogenesis. 11:292022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu X, Xie P, Hao N, Zhang M, Liu Y, Liu
P, Semenza GL, He J and Zhang H: HIF-1-regulated expression of
calreticulin promotes breast tumorigenesis and progression through
Wnt/β-catenin pathway activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
118:e21091441182021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lam STT and Lim CJ: Cancer biology of the
endoplasmic reticulum lectin chaperones calreticulin, calnexin and
PDIA3/ERp57. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 59:181–196. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Liu Y, Liu Z and Wang K: The
Ca(2+)-activated chloride channel ANO1/TMEM16A: An emerging
therapeutic target for epithelium-originated diseases? Acta Pharm
Sin B. 11:1412–1433. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Song LL, Qu YQ, Tang YP, Chen X, Lo HH, Qu
LQ, Yun YX, Wong VKW, Zhang RL, Wang HM, et al: Hyperoside
alleviates toxicity of β-amyloid via endoplasmic
reticulum-mitochondrial calcium signal transduction cascade in
APP/PS1 double transgenic Alzheimer's disease mice. Redox Biol.
61:1026372023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Chang Y, Funk M, Roy S, Stephenson E, Choi
S, Kojouharov HV, Chen B and Pan Z: Developing a mathematical model
of intracellular calcium dynamics for evaluating combined
anticancer effects of afatinib and RP4010 in esophageal cancer. Int
J Mol Sci. 23:17632022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Andrews C, Conneally E and Langabeer SE:
Molecular diagnostic criteria of myeloproliferative neoplasms.
Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 23:1077–1090. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mondesir J, Ghisi M, Poillet L, Bossong
RA, Kepp O, Kroemer G, Sarry JE, Tamburini J and Lane AA: AMPK
activation induces immunogenic cell death in AML. Blood Adv.
7:7585–7596. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Calvillo-Rodríguez KM, Mendoza-Reveles R,
Gómez-Morales L, Uscanga-Palomeque AC, Karoyan P, Martínez-Torres
AC and Rodríguez-Padilla C: PKHB1, a thrombospondin-1 peptide
mimic, induces anti-tumor effect through immunogenic cell death
induction in breast cancer cells. Oncoimmunology. 11:20543052022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xu T, Zhu C, Song F, Zhang W, Yuan M, Pan
Z and Huang P: Immunological characteristics of immunogenic cell
death genes and malignant progression driving roles of TLR4 in
anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 23:11312023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yamashita K, Miyata H, Makino T, Masuike
Y, Furukawa H, Tanaka K, Miyazaki Y, Takahashi T, Kurokawa Y,
Yamasaki M, et al: High expression of the mitophagy-related protein
pink1 is associated with a poor response to chemotherapy and a poor
prognosis for patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy for
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 24:4025–4032.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen X, Zhuo S, Xu W, Chen X, Huang D, Sun
X and Cheng Y: Isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 contributes to radiation
resistance of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma via regulating
mitochondrial function and ROS/pAKT signalling. Br J Cancer.
123:126–136. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lan L, Wei W, Zheng Y, Niu L, Chen X,
Huang D, Gao Y, Mo S, Lu J, Guo M, et al: Deferoxamine suppresses
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell growth via ERK1/2 mediated
mitochondrial dysfunction. Cancer Lett. 432:132–143. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Han A, Li C, Zahed T, Wong M, Smith I,
Hoedel K, Green D and Boiko AD: Calreticulin is a critical cell
survival factor in malignant neoplasms. PLoS Biol. 17:e30004022019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Stoll G, Iribarren K, Michels J, Leary A,
Zitvogel L, Cremer I and Kroemer G: Calreticulin expression:
Interaction with the immune infiltrate and impact on survival in
patients with ovarian and non-small cell lung cancer.
Oncoimmunology. 5:e11776922016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Méndez-Ferrer S, Bonnet D, Steensma DP,
Hasserjian RP, Ghobrial IM, Gribben JG, Andreeff M and Krause DS:
Bone marrow niches in haematological malignancies. Nat Rev Cancer.
20:285–298. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Luo H, Sun Y, Wang L, Liu H, Zhao R, Song
M and Ge H: Targeting endoplasmic reticulum associated degradation
pathway combined with radiotherapy enhances the immunogenicity of
esophageal cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 24:21667632023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|