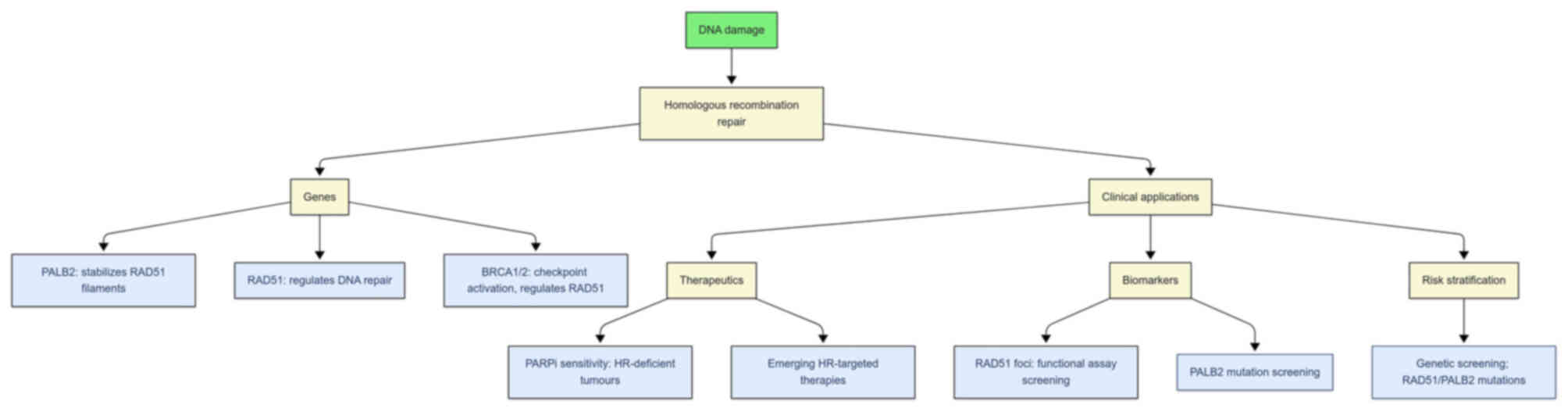
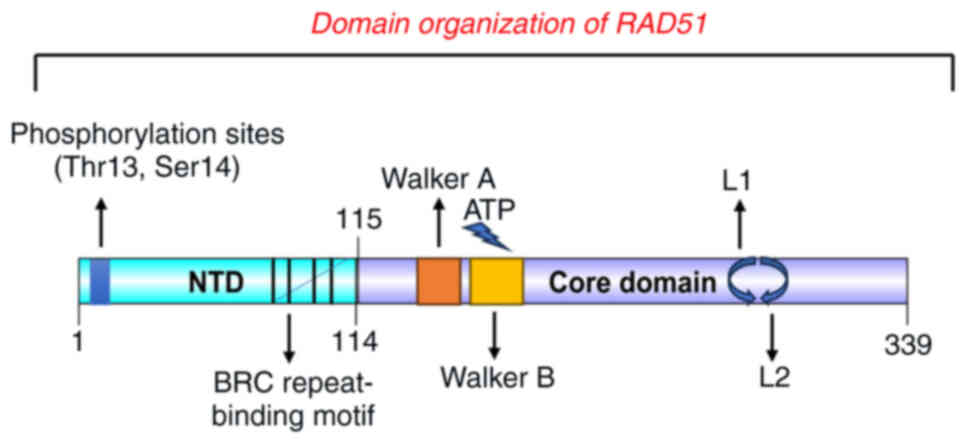
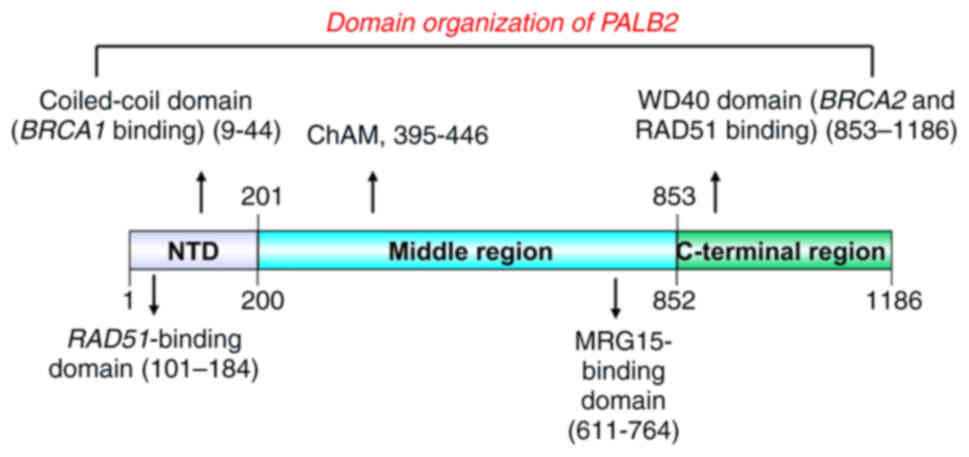
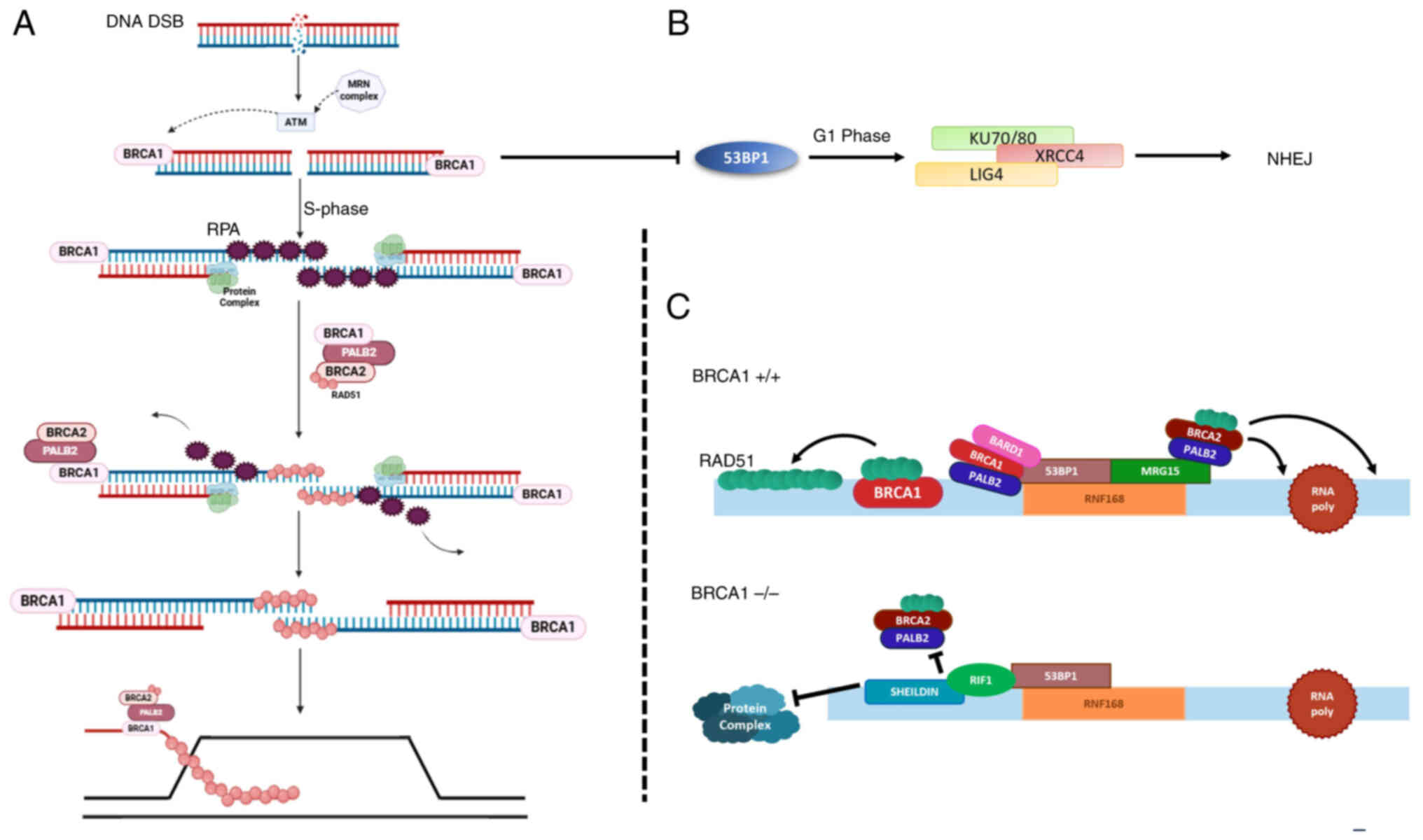
|
1
|
Weinberg RA: How cancer arises. Sci Am.
275:62–70. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wooster R and Weber BL: Breast and ovarian
cancer. N Engl J Med. 348:2339–2347. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
International Agency for Research on
Cancer: Cancer Tomorrow. Dataviz. https://gco.iarc.fr/tomorrow/en/dataviz.
|
|
4
|
Petrucelli N, Daly MB and Pal T: BRCA1-
and BRCA2-Associated Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer.
GeneReviews® [Internet]. Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, et al:
University of Washington; Seattle, WA: 1993-2025, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1247/.
|
|
5
|
Menendez JA, Folguera-Blasco N, Cuyàs E,
Fernández-Arroyo S, Joven J and Alarcón T: Accelerated
geroncogenesis in hereditary breast-ovarian cancer syndrome.
Oncotarget. 7:11959–11971. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fantone S, Marzioni D and Tossetta G:
NRF2/KEAP1 signaling inhibitors in gynecologic cancers. Expert Rev
Anticancer Ther. 24:1191–1194. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Pokhriyal R, Hariprasad R, Kumar L and
Hariprasad G: Chemotherapy resistance in advanced ovarian cancer
patients. Biomark Cancer. 11:1179299X198608152019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Akter S, Rahman MA, Hasan MN, Akhter H,
Noor P, Islam R, Shin Y, Rahman MDH, Gazi MS, Huda MN, et al:
Recent advances in ovarian cancer: Therapeutic strategies,
potential biomarkers and technological improvements. Cells.
11:6502022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Xiong N, Wu H and Yu Z: Advancements and
challenges in triple-negative breast cancer: A comprehensive review
of therapeutic and diagnostic strategies. Front Oncol.
14:14054912024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yin L, Duan JJ, Bian XW and Yu SC:
Triple-negative breast cancer molecular subtyping and treatment
progress. Breast Cancer Res. 22:612020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Campagna R, Pozzi V, Giorgini S,
Morichetti D, Goteri G, Sartini D, Serritelli EN and Emanuelli M:
Paraoxonase-2 is upregulated in triple negative breast cancer and
contributes to tumor progression and chemoresistance. Hum Cell.
36:1108–1119. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Le HP, Heyer WD and Liu J: Guardians of
the Genome: BRCA2 and its partners. Genes (Basel). 12:12292021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Angeli D, Salvi S and Tedaldi G: Genetic
predisposition to breast and ovarian cancers: How many and which
genes to test? Int J Mol Sci. 21:11282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lux MP, Fasching PA and Beckmann MW:
Hereditary breast and ovarian cancer: Review and future
perspectives. J Mol Med (Berl). 84:16–28. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Mekonnen N, Yang H and Shin YK: Homologous
recombination deficiency in ovarian, breast, colorectal,
pancreatic, non-small cell lung and prostate cancers and the
mechanisms of resistance to PARP inhibitors. Front Oncol.
12:8806432022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Krejci L, Altmannova V, Spirek M and Zhao
X: Homologous recombination and its regulation. Nucleic Acids Res.
40:5795–5818. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Grundy MK, Buckanovich RJ and Bernstein
KA: Regulation and pharmacological targeting of RAD51 in cancer.
NAR Cancer. 2:zcaa0242020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nowacka-Zawisza M, Wiśnik E, Wasilewski A,
Skowrońska M, Forma E, Bryś M, Różański W and Krajewska WM:
Polymorphisms of homologous recombination RAD51, RAD51B, XRCC2 and
XRCC3 genes and the risk of prostate cancer. Anal Cell Pathol
(Amst). 2015:8286462015.
|
|
19
|
Wu S, Zhou J, Zhang K, Chen H, Luo M, Lu
Y, Sun Y and Chen Y: Molecular mechanisms of PALB2 function and its
role in breast cancer management. Front Oncol. 10:3012020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Nepomuceno TC, De Gregoriis G, de Oliveira
FMB, Suarez-Kurtz G, Monteiro AN and Carvalho MA: The role of PALB2
in the DNA damage response and cancer predisposition. Int J Mol
Sci. 18:18862017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu X, Jacobs SA, West SC, Ogawa T and
Egelman EH: Domain structure and dynamics in the helical filaments
formed by RecA and RAD51 on DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:8419–8424. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Subramanyam S, Ismail M, Bhattacharya I
and Spies M: Tyrosine phosphorylation stimulates activity of human
RAD51 recombinase through altered nucleoprotein filament dynamics.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:E6045–E6054. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Aihara H, Ito Y, Kurumizaka H, Yokoyama S
and Shibata T: The N-terminal domain of the human RAD51 protein
binds DNA: Structure and a DNA binding surface as revealed by NMR.
J Mol Biol. 290:495–504. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Thomas M, Dubacq C, Rabut E, Lopez BS and
Guirouilh-Barbat J: Noncanonical roles of RAD51. Cells.
12:11692022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wiese C, Hinz JM, Tebbs RS, Nham PB, Urbin
SS, Collins DW, Thompson LH and Schild D: Disparate requirements
for the Walker A and B ATPase motifs of human RAD51D in homologous
recombination. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:2833–2843. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Elbakry A and Löbrich M: Homologous
recombination subpathways: A tangle to resolve. Front Genet.
12:7238472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Conway AB, Lynch TW, Zhang Y, Fortin GS,
Fung CW, Symington LS and Rice PA: Crystal structure of a RAD51
filament. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 11:791–796. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kyriukha Y, Watkins MB, Redington JM,
Dastvan R, Uversky VN, Hopkins J, Pozzi N and Korolev S: The PALB2
DNA-binding domain is an intrinsically disordered recombinase. Res
Sq [Preprint]. rs.3.rs-3235465. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Park Y, Zhang F and Andreassen PR: PALB2:
The hub of a network of tumor suppressors involved in DNA damage
responses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1846:263–275. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun Y, McCorvie TJ, Yates LA and Zhang X:
Structural basis of homologous recombination. Cell Mol Life Sci.
77:3–18. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Bleuyard JY, Buisson R, Masson JY and
Esashi F: ChAM, a novel motif that mediates PALB2 intrinsic
chromatin binding and facilitates DNA repair. EMBO Rep. 13:135–141.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Park JY, Singh TR, Nassar N, Zhang F,
Freund M, Hanenberg H, Meetei AR and Andreassen PR: Breast
cancer-associated missense mutants of the PALB2 WD40 domain, which
directly binds RAD51C, RAD51 and BRCA2, disrupt DNA repair.
Oncogene. 33:4803–4812. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Dray E, Etchin J, Wiese C, Saro D,
Williams GJ, Hammel M, Yu X, Galkin VE, Liu D, Tsai MS, et al:
Enhancement of the RAD51 recombinase activity by the tumor
suppressor PALB2. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 17:1255–1259. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Matos-Rodrigues G, Guirouilh-Barbat J,
Martini E and Lopez BS: Homologous recombination, cancer and the
'RAD51 paradox'. NAR Cancer. 3:zcab0162021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Oliver AW, Swift S, Lord CJ, Ashworth A
and Pearl LH: Structural basis for recruitment of BRCA2 by PALB2.
EMBO Rep. 10:990–996. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Modesti M, Budzowska M, Baldeyron C,
Demmers JA, Ghirlando R and Kanaar R: RAD51AP1 is a
structure-specific DNA binding protein that stimulates joint
molecule formation during RAD51-mediated homologous recombination.
Mol Cell. 28:468–481. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lang SH, Swift SL, White H, Misso K,
Kleijnen J and Quek RG: A systematic review of the prevalence of
DNA damage response gene mutations in prostate cancer. Int J Oncol.
55:597–616. 2019.
|
|
38
|
Foo TK and Xia B: BRCA1-dependent and
independent recruitment of PALB2-BRCA2-RAD51 in the DNA damage
response and cancer. Cancer Res. 82:3191–3197. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Bonilla B, Hengel SR, Grundy MK and
Bernstein KA: RAD51 gene family structure and function. Annu Rev
Genet. 54:25–46. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Wang Z, Jia R, Wang L, Yang Q, Hu X, Fu Q,
Zhang X, Li W and Ren Y: The emerging roles of RAD51 in cancer and
its potential as a therapeutic target. Front Oncol. 12:9355932022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Fantone S, Tossetta G, Cianfruglia L,
Frontini A, Armeni T, Procopio AD, Pugnaloni A, Gualtieri AF and
Marzioni D: Mechanisms of action of mineral fibres in a placental
syncytiotrophoblast model: An in vitro toxicology study. Chem Biol
Interact. 390:1108952024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Smolarz B, Michalska MM, Samulak D,
Romanowicz H and Wójcik L: Polymorphism of DNA repair genes in
breast cancer. Oncotarget. 10:527–535. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Ma É, Maloisel L, Le Falher L, Guérois R
and Coïc É: Rad52 oligomeric N-terminal domain stabilizes RAD51
nucleoprotein filaments and contributes to their protection against
Srs2. Cells. 10:14672021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Carver A and Zhang X: RAD51 filament
dynamics and its antagonistic modulators. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
113:3–13. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Andriuskevicius T, Dubenko A and Makovets
S: The inability to disassemble RAD51 nucleoprotein filaments leads
to aberrant mitosis and cell death. Biomedicines. 11:14502023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Wang X, Zhao X, Yu Z, Fan T, Guo Y, Liang
J, Wang Y, Zhan J, Chen G, Zhou C, et al: Rtt105 stimulates
RAD51-ssDNA assembly and orchestrates RAD51 and RPA actions to
promote homologous recombination repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
121:e24022621212024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ma CJ, Gibb B, Kwon Y, Sung P and Greene
EC: Protein dynamics of human RPA and RAD51 on ssDNA during
assembly and disassembly of the RAD51 filament. Nucleic Acids Res.
45:749–761. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
48
|
Taylor MRG, Špírek M, Chaurasiya KR,
Ward JD, Carzaniga R, Yu X, Egelman EH, Collinson LM, Rueda D,
Krejci L and Boulton SJ: RAD51 paralogs remodel pre-synaptic RAD51
filaments to stimulate homologous recombination. Cell. 162:271–286.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
49
|
Bugreev DV and Mazin AV: Ca2+ activates
human homologous recombination protein RAD51 by modulating its
ATPase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:9988–9993. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Danilowicz C, Peacock-Villada A, Vlassakis
J, Facon A, Feinstein E, Kleckner N and Prentiss M: The
differential extension in dsDNA bound to RAD51 filaments may play
important roles in homology recognition and strand exchange.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42:526–533. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Mazin AV, Bornarth CJ, Solinger JA, Heyer
WD and Kowalczykowski SC: Rad54 protein is targeted to pairing loci
by the RAD51 nucleoprotein filament. Mol Cell. 6:583–592. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Akita M, Girvan P, Špírek M, Novacek J,
Rueda D, Prokop Z and Krejci L: Mechanism of BCDX2-mediated RAD51
nucleation on short ssDNA stretches and fork DNA. Nucleic Acids
Res. 52:11738–11752. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yang H, Li Q, Fan J, Holloman W and
Pavletich N: The BRCA2 homologue Brh2 nucleates RAD51 filament
formation at a dsDNA-ssDNA junction. Nature. 433:653–657. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Richardson C: RAD51, genomic stability and
tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett. 218:127–139. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Liao C, Talluri S, Zhao J, Mu S, Kumar S,
Shi J, Buon L, Munshi NC and Shammas MA: RAD51 is implicated in DNA
damage, chemoresistance and immune dysregulation in solid tumors.
Cancers (Basel). 14:56972022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
So A, Dardillac E, Muhammad A, Chailleux
C, Sesma-Sanz L, Ragu S, Le Cam E, Canitrot Y, Masson JY, Dupaigne
P, et al: RAD51 protects against nonconservative DNA double-strand
break repair through a nonenzymatic function. Nucleic Acids Res.
50:2651–2666. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
So A, Muhammad A, Chailleux C, Sanz L,
Ragu S, Cam L, Canitrot Y, Masson J, Dupaigne P, Lopez B and
Guirouilh-Barbat J: Mammalian RAD51 prevents non-conservative
alternative end-joining and single strand annealing through
non-catalytic mechanisms. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/768887.
|
|
58
|
Mladenov E, Staudt C, Soni A,
Murmann-Konda T, Siemann-Loekes M and Iliakis G: Strong suppression
of gene conversion with increasing DNA double-strand break load
delimited by 53BP1 and RAD52. Nucleic Acids Res. 48:1905–1924.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Willis NA, Panday A, Duffey EE and Scully
R: RAD51 recruitment and exclusion of non-homologous end joining
during homologous recombination at a Tus/Ter mammalian replication
fork barrier. PLoS Genet. 14:e10074862018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
60
|
Gallagher DN, Pham N, Tsai AM, Janto AV,
Choi J, Ira G and Haber JE: A RAD51-independent pathway promotes
single-strand template repair in gene editing. PLoS Genet.
16:e10086892020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
61
|
Zhu Z, Kitano T, Morimatsu M, Tanaka A,
Morioka R, Lin X, Orino K and Yoshikawa Y: BRCA2 C-Terminal
RAD51-binding domain confers resistance to DNA-damaging agents. Int
J Mol Sci. 23:40602022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
62
|
Carreira A and Kowalczykowski SC: Two
classes of BRC repeats in BRCA2 promote RAD51 nucleoprotein
filament function by distinct mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:10448–10453. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Andreassen PR, Seo J, Wiek C and Hanenberg
H: Understanding BRCA2 function as a tumor suppressor based on
domain-specific activities in DNA damage responses. Genes (Basel).
12:10342021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sadeghi F, Asgari M, Matloubi M, Ranjbar
M, Karkhaneh Yousefi N, Azari T and Zaki-Dizaji M: Molecular
contribution of BRCA1 and BRCA2 to genome instability in breast
cancer patients: Review of radiosensitivity assays. Biol Proced
Online. 22:232020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Zhang F, Ma J, Wu J, Ye L, Cai H, Xia B
and Yu X: PALB2 links BRCA1 and BRCA2 in the DNA-damage response.
Curr Biol. 19:524–529. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Simhadri S, Vincelli G, Huo Y, Misenko S,
Foo T, Ahlskog J, Sørensen C, Oakley G, Ganesan S, Bunting S and
Xia B: PALB2 connects BRCA1 and BRCA2 in the G2/M checkpoint
response. Oncogene. 38:1585–1596. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Sy S, Huen M, Zhu Y and Chen J: PALB2
regulates recombinational repair through chromatin association and
oligomerization. J Biol Chem. 284:18302–18310. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Song F, Li M, Liu G, Swapna GVT, Daigham
NS, Xia B, Montelione GT and Bunting SF: Antiparallel coiled-coil
interactions mediate the homodimerization of the DNA damage-repair
protein PALB2. Biochemistry. 57:6581–6591. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Buisson R and Masson JY: PALB2
self-interaction controls homologous recombination. Nucleic Acids
Res. 40:10312–10323. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Buisson R, Niraj J, Pauty J, Maity R, Zhao
W, Coulombe Y, Sung P and Masson J: Breast cancer proteins PALB2
and BRCA2 stimulate polymerase η in recombination-associated DNA
synthesis at blocked replication forks. Cell Rep. 6:553–564. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Luijsterburg MS, Typas D, Caron MC,
Wiegant WW, Van Den Heuvel D, Boonen RA, Couturier AM, Mullenders
LH, Masson JY and Van Attikum H: A PALB2-interacting domain in
RNF168 couples homologous recombination to DNA break-induced
chromatin ubiquitylation. ELife. 6:e209222017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
72
|
Krais JJ, Wang Y, Patel P, Basu J,
Bernhardy AJ and Johnson N: RNF168-mediated localization of BARD1
recruits the BRCA1-PALB2 complex to DNA damage. Nat Commun.
12:50162021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Pauty J, Rodrigue A, Couturier A, Buisson
R and Masson JY: Exploring the roles of PALB2 at the crossroads of
DNA repair and cancer. Biochem J. 460:331–342. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Ducy M, Sesma-Sanz L, Guitton-Sert L,
Lashgari A, Gao Y, Brahiti N, Rodrigue A, Margaillan G, Caron MC,
Côté J, et al: The tumor suppressor PALB2: Inside out. Trends
Biochem Sci. 44:226–240. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Uemura M, Ochiai K, Morimatsu M,
Michishita M, Onozawa E, Azakami D, Uno Y, Yoshikawa Y, Sasaki T,
Watanabe M and Omi T: The canine RAD51 mutation leads to the
attenuation of interaction with PALB2. Vet Comp Oncol. 18:247–255.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Prakash R, Zhang Y, Feng W and Jasin M:
Homologous recombination and human health: The roles of BRCA1,
BRCA2 and associated proteins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
7:a0166002015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Zhao W, Steinfeld JB, Liang F, Chen X,
Maranon DG, Jian Ma C, Kwon Y, Rao T, Wang W, Sheng C, et al:
BRCA1-BARD1 promotes RAD51-mediated homologous DNA pairing. Nature.
550:360–365. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Saxena S, Dixit S, Somyajit K and Nagaraju
G: ATR signaling uncouples the role of RAD51 paralogs in homologous
recombination and replication stress response. Cell Rep.
29:551–559.e4. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Berti M, Teloni F, Mijic S, Ursich S,
Fuchs J, Palumbieri MD, Krietsch J, Schmid JA, Garcin EB, Gon S, et
al: Sequential role of RAD51 paralog complexes in replication fork
remodeling and restart. Nat Commun. 11:35312020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Hanenberg H and Andreassen PR: PALB2
(partner and localizer of BRCA2). Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol
Haematol. 22:484–490. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Michl J, Zimmer J and Tarsounas M:
Interplay between Fanconi anemia and homologous recombination
pathways in genome integrity. EMBO J. 35:909–923. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
82
|
Park D, Bergin SM, Jones D, Ru P, Koivisto
CS, Jeon YJ, Sizemore GM, Kladney RD, Hadjis A, Shakya R and Ludwig
T: Ablation of the BRCA1-PALB2 interaction phenocopies fanconi
anemia in mice. Cancer Res. 80:4172–4184. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Schwarz B, Friedl AA, Girst S, Dollinger G
and Reindl J: Nanoscopic analysis of 53BP1, BRCA1 and RAD51 reveals
new insights in temporal progression of DNA-repair and pathway
choice. Mutat Res. 816-818:1116752019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Isono M, Niimi A, Oike T, Hagiwara Y, Sato
H, Sekine R, Yoshida Y, Isobe SY, Obuse C, Nishi R, et al: BRCA1
directs the repair pathway to homologous recombination by promoting
53BP1 dephosphorylation. Cell Rep. 18:520–532. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Malewicz M: The role of 53BP1 protein in
homology-directed DNA repair: Things get a bit complicated. Cell
Death Differ. 23:1902–1903. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Ochs F, Somyajit K, Altmeyer M, Rask MB,
Lukas J and Lukas C: 53BP1 fosters fidelity of homology-directed
DNA repair. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 23:714–721. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Swift ML, Beishline K, Flashner S and
Azizkhan-Clifford J: DSB repair pathway choice is regulated by
recruitment of 53BP1 through cell cycle-dependent regulation of
Sp1. Cell Rep. 34:1088402021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Mohseni-Salehi FS, Zare-Mirakabad F,
Sadeghi M and Ghafouri-Fard S: A stochastic model of DNA
double-strand breaks repair throughout the cell cycle. Bull Math
Biol. 82:112020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Roy U and Greene EC: The role of the
Rad55-Rad57 complex in DNA repair. Genes (Basel). 12:13902021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Morati F and Modesti M: Insights into the
control of RAD51 nucleoprotein filament dynamics from
single-molecule studies. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 71:182–187. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Wang SSY, Jie YE, Cheng SW, Ling GL and
Ming HVY: PARP inhibitors in breast and ovarian cancer. Cancers
(Basel). 15:23572023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Konecny GE and Kristeleit RS: PARP
inhibitors for BRCA1/2-mutated and sporadic ovarian cancer: Current
practice and future directions. Br J Cancer. 115:1157–1173. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Dilmac S and Ozpolat B: Mechanisms of
PARP-inhibitor-resistance in BRCA-mutated breast cancer and new
therapeutic approaches. Cancers (Basel). 15:36422023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Ghandali M, Huntington K, Srinivasan P,
Dizon DS, Graff SL, Carneiro BA and El-Deiry WS: Abstract 1066:
PARP inhibitor rucaparib in combination with imipridones ONC201 or
ONC212 demonstrates preclinical synergy against BRCA1/2-deficient
breast, ovarian and prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 83(7_Suppl):
S10662023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Vidula N, Damodaran S, Bhave M, Rugo H,
Shah AN, Blouch E, Ruffle-Deignan NR, Ogbenna O, Flaum LE,
Cristofanilli M, et al: Abstract PO4-19-06: Phase II study of a
PARP inhibitor, talazoparib, in HER2-metastatic breast cancer with
a somatic BRCA1/2 mutation present in cell-free DNA or tumor tissue
genotyping. Cancer Res. 84(9_Suppl): PO4-19-062024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Vidula N, Blouch E, Basile E,
Ruffle-Deignan NR, Horick N, Damodaran S, Aspitia AM, Bhave M, Shah
A, Liu MC, et al: Abstract OT2-24-03: Phase II study of a PARP
inhibitor in metastatic breast cancer with somatic BRCA1/2
mutations identified by cell-free DNA: Genotyping based clinical
trial. Cancer Res. 82(4_Suppl): OT2-24-032024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Baldock RA, Pressimone CA, Baird JM,
Khodakov A, Luong TT, Grundy MK, Smith CM, Karpenshif Y,
Bratton-Palmer DS, Prakash R, et al: RAD51D splice variants and
cancer-associated mutations reveal XRCC2 interaction to be critical
for homologous recombination. DNA Repair (Amst). 76:99–107. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Castroviejo-Bermejo M, Cruz C,
Llop-Guevara A, Gutiérrez-Enríquez S, Ducy M, Ibrahim YH,
Gris-Oliver A, Pellegrino B, Bruna A, Guzman M, et al: A RAD51
assay feasible in routine tumor samples calls PARP inhibitor
response beyond BRCA mutation. EMBO Mol Med. 10:e91722018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Pelttari LM, Khan S, Vuorela M, Kiiski JI,
Vilske S, Nevanlinna V, Ranta S, Schleutker J, Winqvist R,
Kallioniemi A, et al: RAD51B in familial breast cancer. PLoS One.
11:e01537882016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Setton J, Selenica P, Mukherjee S, Shah R,
Pecorari I, McMillan B, Pei IX, Kemel Y, Ceyhan-Birsoy O, Sheehan
M, et al: Germline RAD51B variants confer susceptibility to breast
and ovarian cancers deficient in homologous recombination. NPJ
Breast Cancer. 7:1352021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
101
|
Boni J, Idani A, Roca C, Feliubadaló L,
Tomiak E, Weber E, Foulkes WD, Orthwein A, El Haffaf Z, Lázaro C
and Rivera B: A decade of RAD51C and RAD51D germline variants in
cancer. Hum Mutat. 43:285–298. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Kolinjivadi AM, Chong ST, Choudhary R,
Sankar H, Chew EL, Yeo C, Chan SH and Ngeow J: Functional analysis
of germline RAD51C missense variants highlight the role of RAD51C
in replication fork protection. Hum Mol Genet. 32:1401–1409. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Yang X, Song H, Leslie G, Engel C, Hahnen
E, Auber B, Horváth J, Kast K, Niederacher D, Turnbull C, et al:
Ovarian and breast cancer risks associated with pathogenic variants
in RAD51C and RAD51D. J Natl Cancer Inst. 112:1242–1250. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Suszyńska M, Ratajska M and Kozlowski P:
BRIP1, RAD51C and RAD51D mutations are associated with high
susceptibility to ovarian cancer: Mutation prevalence and precise
risk estimates based on a pooled analysis of ~30,000 cases. J
Ovarian Res. 13:502020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Wesoła M and Jeleń M: The risk of breast
cancer due to PALB2 gene mutations. Adv Clin Exp Med. 26:339–342.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Ruberu TLM, Braun D, Parmigiani G and
Biswas S: Meta-analysis of breast cancer risk for individuals with
PALB2 pathogenic variants. Genet Epidemiol. 48:448–454. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Sato K, Koyasu M, Nomura S, Sato Y, Kita
M, Ashihara Y, Adachi Y, Ohno S, Iwase T, Kitagawa D, et al:
Mutation status of RAD 51C, PALB 2 and BRIP 1 in 100 Japanese
familial breast cancer cases without BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 mutations.
Cancer Sci. 108:2287–2294. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Feng Y, Wang D, Xiong L, Zhen G and Tan J:
Predictive value of RAD51 on the survival and drug responsiveness
of ovarian cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 21:2492021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Alizzi Z, Saravi S, Khalique S, McDonald
T, Karteris E and Hall M: Identification of RAD51 foci in
cancer-associated circulating cells of patients with high-grade
serous ovarian cancer: Association with treatment outcomes. Int J
Gynecol Cancer. 33:1427–1433. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
110
|
Compadre AJ, Van Biljon L, Valentine MC,
Llop-Guevara A, Graham E, Fashemi B, Herencia-Ropero A, Kotnik EN,
Cooper I, Harrington SP, et al: RAD51 Foci as a biomarker
predictive of platinum chemotherapy response in ovarian cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 29:2466–2479. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Goel N, Foxall ME, Scalise CB, Wall JA and
Arend RC: Strategies in overcoming homologous recombination
proficiency and PARP inhibitor resistance. Mol Cancer Ther.
20:1542–1549. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
McMullen M, Karakasis K, Madariaga A and
Oza AM: Overcoming platinum and PARP-inhibitor resistance in
ovarian cancer. Cancers (Basel). 12:16072020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Song H, Dicks E, Ramus SJ, Tyrer JP,
Intermaggio MP, Hayward J, Edlund CK, Conti D, Harrington P, Fraser
L, et al: Contribution of germline mutations in the RAD51B, RAD51C
and RAD51D genes to ovarian cancer in the population. J Clin Oncol.
33:2901–2907. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
114
|
Nguyen L, WM Martens J, Van Hoeck A and
Cuppen E: Pan-cancer landscape of homologous recombination
deficiency. Nat Commun. 11:55842020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
115
|
Nickols NG, Maxwell KN, Lee KM, Hausler R,
Anglin-Foote T, Garraway I and Lynch JA: Frequencies of actionable
alterations found by somatic tumor sequencing in veterans with
metastatic prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 40(6_suppl): S1782022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Rajput M, Singh R, Singh N and Singh RP:
EGFR-mediated RAD51 expression potentiates intrinsic resistance in
prostate cancer via EMT and DNA repair pathways. Life Sci.
286:1200312021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Maranto C, Udhane V, Hoang DT, Gu L,
Alexeev V, Malas K, Cardenas K, Brody JR, Rodeck U, Bergom C, et
al: STAT5A/B blockade sensitizes prostate cancer to radiation
through inhibition of RAD51 and DNA repair. Clin Cancer Res.
24:1917–1931. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Arce-Gallego S, Llop-Guevara A, Carreira
S, Porta N, Fasani R, Bianchini D, Seed G, Rescigno P, Paschalis A,
Bertan C, et al: Abstract CT161: A homologous recombination repair
(HRR) functional assay to stratify patients with metastatic
prostate cancer for PARP inhibitor treatment in the TOPARP-B
clinical trial. Cancer Res. 81(Suppl 13): CT1612021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Mason JM, Logan HL, Budke B, Wu M,
Pawłowski M, Weichselbaum RR, Kozikowski AP, Bishop DK and Connell
PP: The RAD51-stimulatory compound RS-1 can exploit the RAD51
overexpression that exists in cancer cells and tumors. Cancer Res.
74:3546–3555. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Zhang Y, Park JY, Zhang F, Olson SH, Orlow
I, Li Y, Kurtz RC, Ladanyi M, Chen J, Toland AE, et al: The p.
Ser64Leu and p.Pro104Leu missense variants of PALB2 identified in
familial pancreatic cancer patients compromise the DNA damage
response. Hum Mutat. 42:150–163. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Nagathihalli NS and Nagaraju G: RAD51 as a
potential biomarker and therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1816:209–218. 2011.
|
|
122
|
Zhang X, Ma N, Yao W, Li S and Ren Z:
RAD51 is a potential marker for prognosis and regulates
proliferation in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 19:3562019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
COSMIC (Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In
Cancer). Sanger Institute. https://cancer.sanger.ac.uk/cosmic/gene/analysis.
Note: Access to the specific data referenced requires logging into
the COSMIC database. Credentials can be provided upon reasonable
request to the corresponding author.
|
|
124
|
Yang X, Leslie G, Doroszuk A, Schneider S,
Allen J, Decker B, Dunning AM, Redman J, Scarth J, Plaskocinska I,
et al: Cancer risks associated with germline PALB2 pathogenic
variants: an international study of 524 families. J Clin Oncol.
38:674–685. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Tischkowitz M, Balmaña J, Foulkes WD,
James P, Ngeow J, Schmutzler R, Voian N, Wick MJ, Stewart DR and
Pal T; ACMG Professional Practice and Guidelines Committee:
Management of individuals with germline variants in PALB2: A
clinical practice resource of the American College of Medical
Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). Genet Med. 23:1416–1423. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Kwong A, Ho CYS, Au CH, Tey SK and Ma ESK:
Germline RAD51C and RAD51D mutations in high-risk Chinese breast
and/ or ovarian cancer patients and families. J Pers Med.
14:8662024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Lee A, Mavaddat N, Wilcox AN, Cunningham
AP, Carver T, Hartley S, Babb de Villiers C, Izquierdo A, Simard J,
Schmidt MK, et al: BOADICEA: A comprehensive breast cancer risk
prediction model incorporating genetic and nongenetic risk factors.
Genet Med. 21:1708–1718. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Natiaonal Cancer Institute: Genetic:
Testing for Inherited Cancer Risk. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/genetics/genetic-testing-fact-sheet.
Accessed April 18, 2024
|
|
129
|
Faucett WA, Peay H and Coghlin CR II:
Genetic testing: Consent and result disclosure for the primary care
provider. Med Clin North Am. 103:967–976. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
130
|
Al-Shamsi HO, Alwbari A, Azribi F, Calaud
F, Thuruthel S, Tirmazy SHH, Kullab S, Ostomane S and Abulkhair O:
BRCA testing and management of BRCA-mutated early-stage breast
cancer: A comprehensive statement by expert group from GCC region.
Front Oncol. 14:13589822024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Natiaonal Cancer Institute: Surgery to
Reduce the Risk of Breast Cancer. https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/risk-reducing-surgery-fact-sheet#:~:text=Risk%2Dreducing%20salpingo%2Doophorectomy%20greatly,gene%20(23%E2%80%9325).
Accessed June 26, 2024
|
|
132
|
Mai PL, Miller A, Gail MH, Skates S, Lu K,
Sherman ME, Ioffe OB, Rodriguez G, Cohn DE, Boggess J, et al:
Risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy and breast cancer risk
reduction in the Gynecologic Oncology Group Protocol-0199
(GOG-0199). JNCI Cancer Spectr. 4:pkz0752019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Wang Y, Song Z, Zhang S, Wang X and Li P:
Risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy and breast cancer risk in BRCA1
or BRCA2 mutation carriers: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Eur J Surg Oncol. 48:1209–1216. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Oceguera-Basurto P, Topete A,
Oceguera-Villanueva A, Rivas-Carrillo J, Paz-Davalos M,
Quintero-Ramos A and Daneri-Navarro A: Selective estrogen receptor
modulators in the prevention of breast cancer in premenopausal
women: A review. Transl Cancer Res. 9:4444–4456. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Peters A and Tadi P: Aromatase inhibitors.
StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL:
2023
|
|
136
|
American Cancer Society (ACS): Aromatase
Inhibitors for Lowering Breast Cancer Risk. ACS; Atlanta, GA: 2021,
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/breast-cancer/risk-and-preven-tion/aromatase-inhibitors-for-lowering-breast-cancer-risk.html.
|
|
137
|
Lord CJ and Ashworth A: PARP inhibitors:
Synthetic lethality in the clinic. Science. 355:1152–1158. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Galland L, Ballot E, Mananet H, Boidot R,
Lecuelle J, Albuisson J, Arnould L, Desmoulins I, Mayeur D,
Kaderbhai C, et al: Efficacy of platinum-based chemotherapy in
metastatic breast cancer and HRD biomarkers: Utility of exome
sequencing. NPJ Breast Cancer. 8:282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Qiu Z, Oleinick NL and Zhang J: ATR/CHK1
inhibitors and cancer therapy. Radiother Oncol. 126:450–464. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Biegała Ł, Gajek A, Szymczak-Pajor I,
Marczak A, Śliwińska A and Rogalska A: Targeted inhibition of the
ATR/CHK1 pathway overcomes resistance to olaparib and dysregulates
DNA damage response protein expression in BRCA2 MUT ovarian cancer
cells. Sci Rep. 13:226592023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Ha DH, Min A, Kim S, Jang H, Kim SH, Kim
HJ, Ryu HS, Ku JL, Lee KH and Im SA: Antitumor effect of a WEE1
inhibitor and potentiation of olaparib sensitivity by DNA damage
response modulation in triple-negative breast cancer. Sci Rep.
10:99302020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
142
|
Jiang X, Bai H, Li X, Li W and Zhang Z:
Current status and future prospects of PARP inhibitor clinical
trials in ovarian cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 11:4371–4390. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Liposits G, Loh KP, Soto-Perez-de-Celis E,
Dumas L, Battisti NML, Kadambi S, Baldini C, Banerjee S and
Lichtman SM: PARP inhibitors in older patients with ovarian and
breast cancer: Young International Society of Geriatric Oncology
review paper. J Geriatr Oncol. 10:337–345. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Boussios S, Moschetta M, Karihtala P,
Samartzis EP, Sheriff M, Pappas-Gogos G, Ozturk MA, Uccello M,
Karathanasi A, Tringos M, et al: Development of new
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors in ovarian cancer:
Quo Vadis? Ann Transl Med. 8:17062020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Boussios S, Karihtala P, Moschetta M,
Karathanasi A, Rassy E, Sadauskaite A and Pavlidis N: Combined
strategies with poly (ADP-Ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors for
the treatment of ovarian cancer: A literature review. Diagnostics
(Basel). 9:872019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Plummer R: Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase
inhibition: A new direction for BRCA and triple-negative breast
cancer? Breast Cancer Res. 13:2182011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Boussios S, Abson C, Moschetta M, Rassy E,
Karathanasi A, Bhat T, Ghumman F, Sheriff M and Pavlidis N: Poly
(ADP-Ribose) polymerase inhibitors: Talazoparib in ovarian cancer
and beyond. Drugs R D. 20:55–73. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
O'Sullivan Coyne G, Chen A and Kummar S:
Delivering on the promise: Poly ADP ribose polymerase inhibition as
targeted anticancer therapy. Curr Opin Oncol. 27:475–481. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Mittica G, Ghisoni E, Giannone G, Genta S,
Aglietta M, Sapino A and Valabrega G: PARP inhibitors in ovarian
cancer. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 13:392–410. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Zimmer AS, Gillard M, Lipkowitz S and Lee
JM: Update on PARP inhibitors in breast cancer. Curr Treat Options
Oncol. 19:212018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Alva AS, Mangat PK, Garrett-Mayer E,
Halabi S, Hansra D, Calfa CJ, Khalil MF, Ahn ER, Cannon TL, Crilley
P, et al: Pembrolizumab in patients with metastatic breast cancer
with high tumor mutational burden: Results from the targeted agent
and profiling utilization registry (TAPUR) study. J Clin Oncol.
39:2443–2451. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Cortesi L, Rugo HS and Jackisch C: An
Overview of PARP inhibitors for the treatment of breast cancer.
Target Oncol. 16:255–282. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
153
|
Jenner ZB, Sood AK and Coleman RL:
Evaluation of rucaparib and companion diagnostics in the PARP
inhibitor landscape for recurrent ovarian cancer therapy. Future
Oncol. 12:1439–1456. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Slootbeek PHJ, Overbeek JK, Ligtenberg
MJL, Van Erp NP and Mehra N: PARPing up the right tree; an overview
of PARP inhibitors for metastatic castration-resistant prostate
cancer. Cancer Lett. 577:2163672023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Cruz C, Castroviejo-Bermejo M,
Gutiérrez-Enríquez S, Llop-Guevara A, Ibrahim YH, Gris-Oliver A,
Bonache S, Morancho B, Bruna A, Rueda OM, et al: RAD51 foci as a
functional biomarker of homologous recombination repair and PARP
inhibitor resistance in germline BRCA-mutated breast cancer. Ann
Oncol. 29:1203–1210. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
156
|
Orhan E, Velázquez C, Tabet I, Sardet C
and Theillet C: Regulation of RAD51 at the transcriptional and
functional levels: What prospects for cancer therapy? Cancers
(Basel). 13:29302021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Zhao L, Si CS, Yu Y, Lu JW and Zhuang Y:
Depletion of DNA damage binding protein 2 sensitizes
triple-negative breast cancer cells to poly ADP-ribose polymerase
inhibition by destabilizing RAD51. Cancer Sci. 110:3543–3552. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Jia Y, Song Y, Dong G, Hao C, Zhao W, Li S
and Tong Z: Aberrant regulation of RAD51 promotes resistance of
neoadjuvant endocrine therapy in ER-positive breast cancer. Sci
Rep. 9:129392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Goričar K, Dugar F, Dolžan V and Marinko
T: NBN, RAD51 and XRCC3 polymorphisms as potential predictive
biomarkers of adjuvant radiotherapy toxicity in early HER2-positive
breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). 14:43652022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
160
|
Yu J and Wang CG: Relationship between
polymorphisms in homologous recombination repair genes RAD51 G172T,
XRCC2 & XRCC3 and risk of breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Front
Oncol. 13:10473362023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
161
|
Day M, Lapierre J, O'Shea T and Mills K:
Abstract C14: A novel RAD51 inhibitor, CYT-0851, shows anticancer
activity in preclinical models of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res.
79(24_Suppl): C142019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
162
|
Tsai YF, Chan LP, Chen YK, Su CW, Hsu CW,
Wang YY and Yuan SF: RAD51 is a poor prognostic marker and a
potential therapeutic target for oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Cancer Cell Int. 23:2312023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Korsholm LM, Kjeldsen M, Perino L, Mariani
L, Nyvang GB, Kristensen E, Bagger FO, Mirza MR and Rossing M:
Combining homologous recombination-deficient testing and functional
RAD51 analysis enhances the prediction of poly(ADP-Ribose)
polymerase inhibitor sensitivity. JCO Precis Oncol. 8:e23004832024.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
164
|
QI AGEN: Browse the manual. Calculate HRD
Score (beta). https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/biomedicalgenomicsanalysis/current/index.php?manual=Calculate_HRD_Score_beta.html.
|
|
165
|
van Wijk LM, Nilas AB, Vrieling H and
Vreeswijk MPG: RAD51 as a functional biomarker for homologous
recombination deficiency in cancer: A promising addition to the HRD
toolbox? Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 22:185–199. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
166
|
Vogel A, Haupts A, Kloth M, Roth W and
Hartmann N: A novel targeted NGS panel identifies numerous
homologous recombination deficiency (HRD)-associated gene mutations
in addition to known BRCA mutations. Diagn Pathol. 19:92024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Witz A, Dardare J, Betz M, Michel C,
Husson M, Gilson P, Merlin JL and Harlé A: Homologous recombination
deficiency (HRD) testing landscape: Clinical applications and
technical validation for routine diagnostics. Biomark Res.
13:312025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Xu Y, Chen YA, Wu Y, Saverimuthu A, Jadhav
A, Bhuiyan R, Sandler J, Yio J and Kumar V: The prognostic and
predictive value of homologous recombination deficiency status in
patients with advanced stage epithelial ovarian carcinoma after
first-line platinum-based chemotherapy. Front Oncol.
14:13724822024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
169
|
Pellegrino B, Herencia-Ropero A,
Llop-Guevara A, Pedretti F, Moles-Fernández A, Viaplana C,
Villacampa G, Guzmán M, Rodríguez O, Grueso J, et al: Preclinical
in vivo validation of the RAD51 test for identification of
homologous recombination-deficient tumors and patient
stratification. Cancer Res. 82:16462022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
170
|
Guffanti F, Mengoli I and Damia G: Current
HRD assays in ovarian cancer: Differences, pitfalls, limitations
and novel approaches. Front Oncol. 14:14053612024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
171
|
Zhou J, Wang H, Fu F, Li Z, Feng Q, Wu W,
Liu Y, Wang C and Chen Y: Spectrum of PALB2 germline mutations and
characteristics of PALB2-related breast cancer: Screening of 16,501
unselected patients with breast cancer and 5890 controls by
next-generation sequencing. Cancer. 126:3202–3208. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
172
|
Woods NT, Baskin R, Golubeva V, Jhuraney
A, De-Gregoriis G, Vaclova T, Goldgar DE, Couch FJ, Carvalho MA,
Iversen ES and Monteiro AN: Functional assays provide a robust tool
for the clinical annotation of genetic variants of uncertain
significance. NPJ Genom Med. 1:160012016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Rein HL and Bernstein KA: Finding
significance: New perspectives in variant classification of the
RAD51 regulators, BRCA2 and beyond. DNA Repair (Amst).
130:1035632023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Zielli T, Labidi-Galy I, Del Grande M,
Sessa C and Colombo I: The clinical challenges of homologous
recombination proficiency in ovarian cancer: From intrinsic
resistance to new treatment opportunities. Cancer Drug Resist.
6:499–516. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
175
|
Li A, Geyer FC, Blecua P, Lee JY, Selenica
P, Brown DN, Pareja F, Lee SSK, Kumar R, Rivera B, et al:
Homologous recombination DNA repair defects in PALB2-associated
breast cancers. NPJ Breast Cancer. 5:232019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|