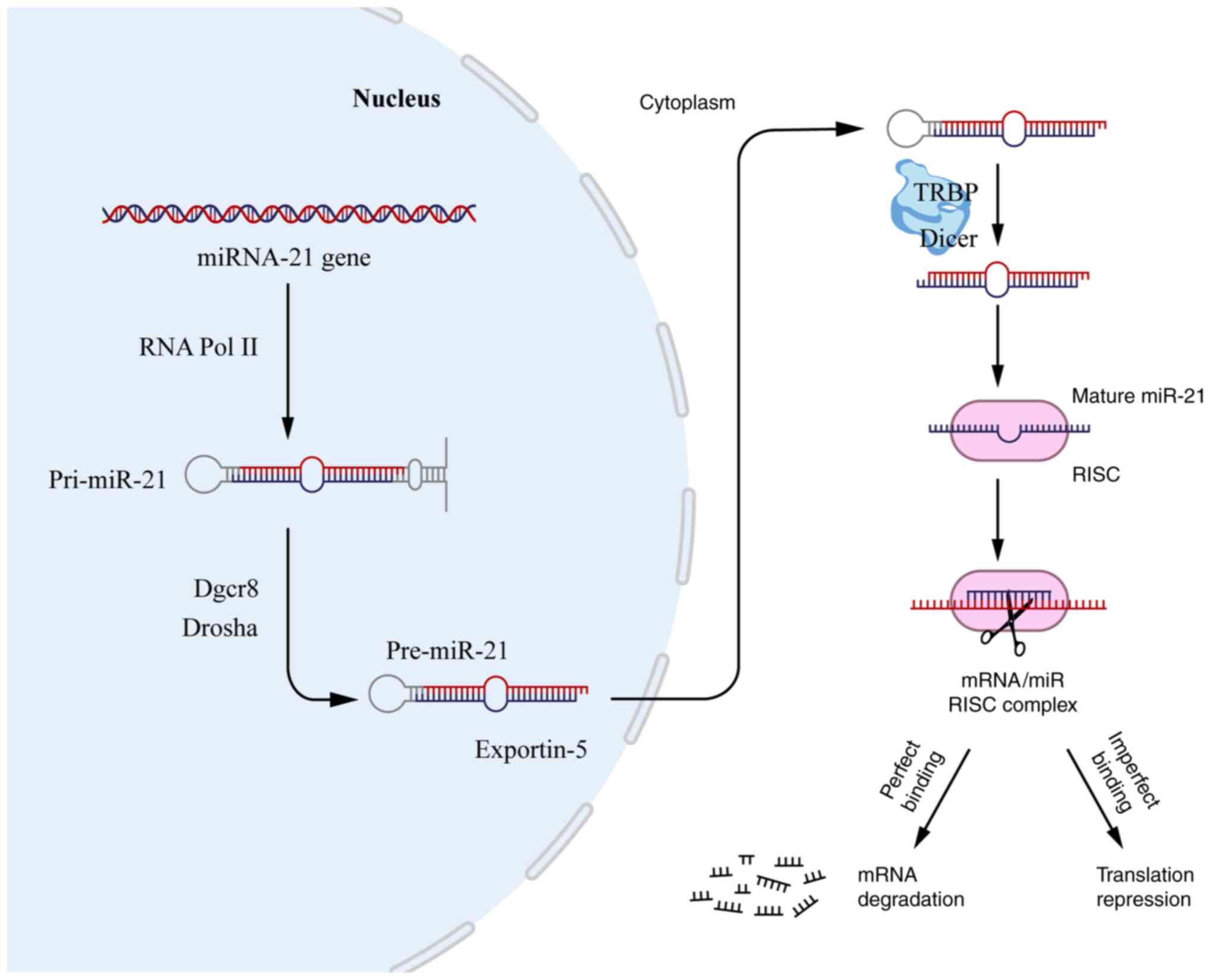
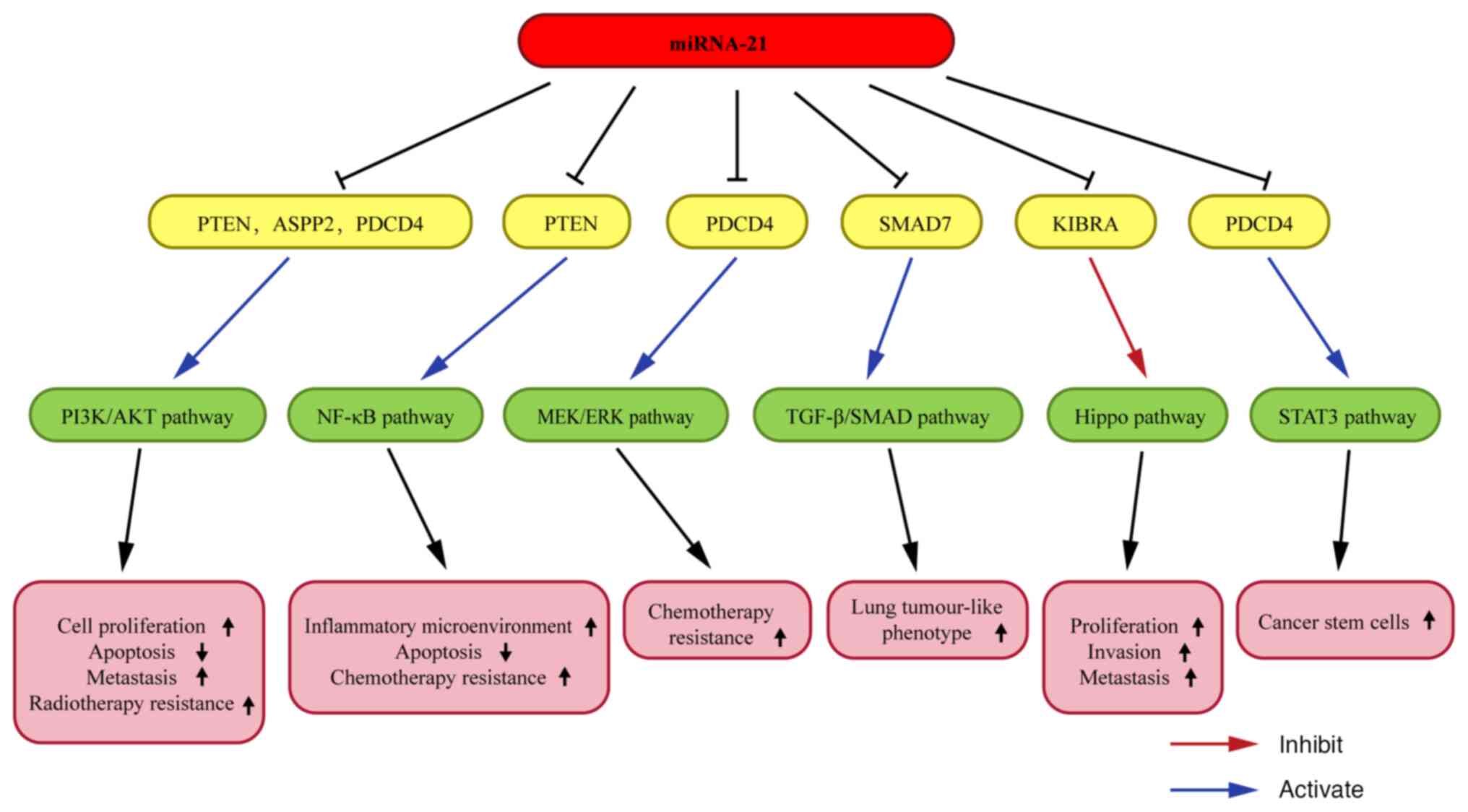
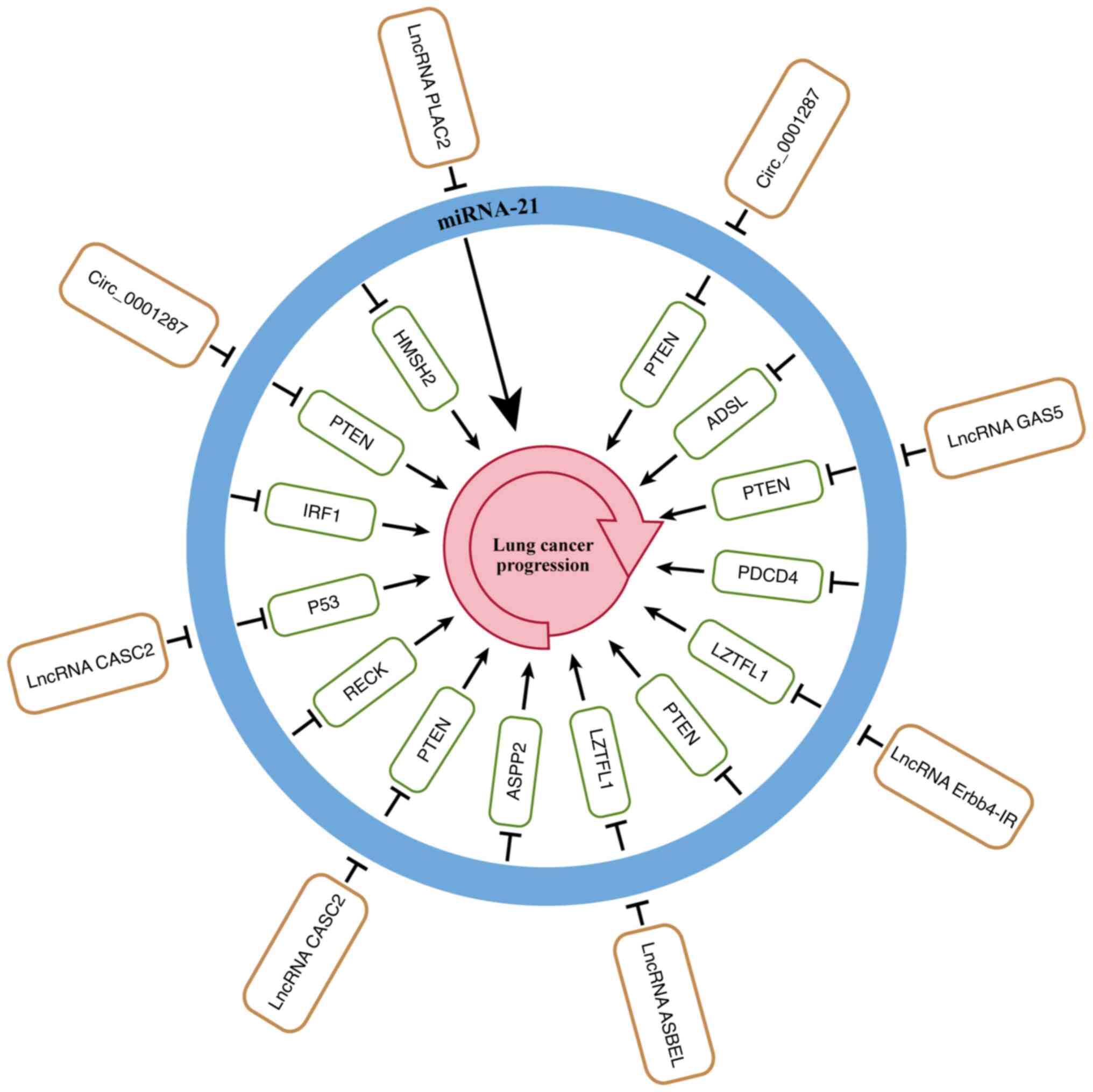
|
1
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Reck M, Remon J and Hellmann MD:
First-line immunotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 40:586–597. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
He S, Li H, Cao M, Sun D, Yang F, Yan X,
Zhang S, He Y, Du L, Sun X, et al: Survival of 7,311 lung cancer
patients by pathological stage and histological classification: A
multicenter hospital-based study in China. Transl Lung Cancer Res.
11:1591–1605. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Goulart BHL and Ramsey SD: Moving beyond
the national lung screening trial: Discussing strategies for
implementation of lung cancer screening programs. Oncologist.
18:941–946. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Barlesi F, Dixmier A, Debieuvre D, Raspaud
C, Auliac JB, Benoit N, Bombaron P, Moro-Sibilot D, Asselain B,
Audigier-Valette C, et al: Final 3-year results from the EVIDENS
study, an observational study of nivolumab in non-small cell lung
cancer. Oncoimmunology. 14:24929322025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sheikh MSA and Salma U: Impact of
microRNAs on cardiovascular diseases and aging. J Int Med Res.
52:30006052412791902024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Martino MTD, Tagliaferri P and Tassone P:
MicroRNA in cancer therapy: Breakthroughs and challenges in early
clinical applications. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 44:1262025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Y, Huang D, Li M and Yang M:
MicroRNA-99 family in cancer: molecular mechanisms for clinical
applications. PeerJ. 13:e191882025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen Z and Qin Y: Role of miRNA-145-5p in
cancer (review). Oncol Rep. 53:392025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Liu L, Liu X, Gao C, Liu M, Peng M and
Wang L: Hsa-miR-21 promoted the progression of lung adenocarcinoma
by regulating LRIG1 expression. BMC Pulm Med. 25:1892025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wan J, Niu C, Wang B, Han Q, Chen Y, Feng
S and Yang L: Human esophageal fibroblast-derived exosomal miR-21
reduced the cisplatin sensitivity to esophageal carcinoma EC9706
cells. Braz J Med Biol Res. 54:e111562021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mharrach I, Tadlaoui KA, Aqerrout M,
Laraqui A, Ameur A, El Ghazzaly A, Ennibi K and Ennaji MM:
Diagnostic value of miR-21 and miR-221 as potential biomarkers for
early diagnosis of prostate cancer. Mol Clin Oncol. 22:402025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Prasad M, Hamsa D, Fareed M and Karobari
MI: An update on the molecular mechanisms underlying the
progression of miR-21 in oral cancer. World J Surg Oncol.
23:732025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim K, Jung KO, Oh S, Kim YH, Lee SY, Hong
S, Cho SH, Kim H, Rhee S, Cheon GJ, et al: Radiation-induced
exosomal miR-21 enhances tumor proliferation and invasiveness in
breast cancer: Implications for poor prognosis in radiotherapy
patients. Exp Hematol Oncol. 13:1202024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gong Z, Han S, Zhang C, Zhao H, Xu J and
Sun X: Value of serum miR-21, HE4 and CA125 in surveillance for
postoperative recurrent or metastatic ovarian cancer. Pak J Med
Sci. 38:939–945. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen Y, Su C, Cai Y, Ke L and Huang Y:
miR-21 promotes cervical cancer by regulating NTF3. Sci Rep.
15:24422025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tohidast M, Amini M, Doustvandi MA,
Hosseini SS, Bilan F, Mozammel N, Sameti P, Mokhtarzadeh AA and
Baradaran B: Simultaneous effect of miR-21 suppression and miR-143
restoration on inhibition of proliferation and migration in SW-480
colorectal cancer cells. Bioimpacts. 15:302552024.
|
|
18
|
Correia de Sousa M, Calo N, Sobolewski C,
Gjorgjieva M, Clément S, Maeder C, Dolicka D, Fournier M, Vinet L,
Montet X, et al: Mir-21 suppression promotes mouse
hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancers (Basel). 13:49832021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dos Santos PRM, da Silva Gomes PR, Romão
P, Maluf FC, Guimarães VR, Candido P, Gonçalves GL, de Camargo JA,
Dos Santos GA, Silva I, et al: Enhancing RECK expression through
miR-21 inhibition: A promising strategy for bladder carcinoma
control. Biochem Genet. 63:817–831. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Pesta M, Travnicek I, Kulda V, Ostasov P,
Windrichova J, Houfkova K, Knizkova T, Bendova B, Hes O, Hora M, et
al: Prognostic value of tumor tissue up-regulated microRNAs in
clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). In Vivo. 38:1799–1805.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Y, Ren X, Yuan Y and Yuan BS:
Downregulated lncRNA GAS5 and upregulated miR-21 lead to
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and lung metastasis of
osteosarcomas. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:7076932021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shaikh MAJ, Altamimi ASA, Afzal M, Gupta
G, Singla N, Gilhotra R, Almalki WH, Kazmi I, Alzarea SI, Prasher
P, et al: Unraveling the impact of miR-21 on apoptosis regulation
in glioblastoma. Pathol Res Pract. 254:1551212024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ritter A, Han J, Bianconi S, Henrich D,
Marzi I, Leppik L and Weber B: The ambivalent role of miRNA-21 in
trauma and acute organ injury. Int J Mol Sci. 25:112822024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hill M and Tran N: miRNA interplay:
Mechanisms and consequences in cancer. Dis Model Mech.
14:dmm0476622021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ortiz IMDP, Barros-Filho MC, Dos Reis MB,
Beltrami CM, Marchi FA, Kuasne H, do Canto LM, de Mello JBH,
Abildgaard C, Pinto CAL, et al: Loss of DNA methylation is related
to increased expression of miR-21 and miR-146b in papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Clin Epigenetics. 10:1442018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lu J, Tan T, Zhu L, Dong H and Xian R:
Hypomethylation causes MIR21 overexpression in tumors. Mol Ther
Oncolytics. 18:47–57. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Weng PW, Yadav VK, Pikatan NW, Fong IH,
Lin IH, Yeh CT and Lee WH: Novel NFκB inhibitor SC75741 mitigates
chondrocyte degradation and prevents activated fibroblast
transformation by modulating miR-21/GDF-5/SOX5 signaling. Int J Mol
Sci. 22:110822021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Liu L, Pan Y, Zhai C, Zhu Y, Ke R, Shi W,
Wang J, Yan X, Su X, Song Y, et al: Activation of peroxisome
proliferation-activated receptor-γ inhibits transforming growth
factor-β1-induced airway smooth muscle cell proliferation by
suppressing Smad-miR-21 signaling. J Cell Physiol. 234:669–681.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu ZH, Zhou J, Hu GH, Liu J, Li WC, Lai XH
and Liu M: LncRNA CASC2 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma progression
through forming feedback loop with miR-21/p53 axis. Kaohsiung J Med
Sci. 37:675–685. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang Y, Zheng F, Wang Z, Lu J and Zhang H:
Circular RNA circ-SLC7A6 acts as a tumor suppressor in non-small
cell lung cancer through abundantly sponging miR-21. Cell Cycle.
19:2235–2246. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rama AR, Quiñonero F, Mesas C, Melguizo C
and Prados J: Synthetic circular miR-21 sponge as tool for lung
cancer treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 23:29632022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Angel CZ, Stafford MYC, McNally CJ,
Nesbitt H and McKenna DJ: MiR-21 is induced by hypoxia and
down-regulates RHOB in prostate cancer. Cancers (Basel).
15:12912023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Garg P, Ramisetty S, Nair M, Kulkarni P,
Horne D, Salgia R and Singhal SS: Strategic advancements in
targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway for Breast cancer therapy.
Biochem Pharmacol. 236:1168502025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ma SY, Liu YM and Wang J: Potential
bidirectional regulatory effects of botanical drug metabolites on
tumors and cardiovascular diseases based on the PI3K/Akt/mTOR
pathway. Front Pharmacol. 16:14678942025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chawra HS, Agarwal M, Mishra A, Chandel
SS, Singh RP, Dubey G, Kukreti N and Singh M: MicroRNA-21's role in
PTEN suppression and PI3K/AKT activation: Implications for cancer
biology. Pathol Res Pract. 254:1550912024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhou B, Wang D, Sun G, Mei F, Cui Y and Xu
H: Effect of miR-21 on apoptosis in lung cancer cell through
inhibiting the PI3K/ Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway in vitro and in
vivo. Cell Physiol Biochem. 46:999–1008. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Jiang LP, He CY and Zhu ZT: Role of
microRNA-21 in radiosensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer cells
by targeting PDCD4 gene. Oncotarget. 8:23675–23689. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li L, Zhang H, Wang X, Wang J and Wei H:
Long non-coding RNA CASC2 enhanced cisplatin-induced viability
inhibition of non-small cell lung cancer cells by regulating the
PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway through down-regulation of miR-18a and
miR-21. RSC Adv. 8:15923–15932. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yakubov R, Kaloti R, Persaud P, McCracken
A, Zadeh G and Bunda S: It's all downstream from here:
RTK/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway resistance mechanisms in glioblastoma. J
Neurooncol. 172:327–345. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Suryavanshi A, Vandana, Shukla YK, Kumar
V, Gupta P, Asati V, Mahapatra DK, Keservani RK, Jain SK and Bharti
SK: MEK inhibitors in oncology: A patent review and update
(2016-present). Expert Opin Ther Pat. 34:963–1007. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hofmann MH, Gmachl M, Ramharter J,
Savarese F, Gerlach D, Marszalek JR, Sanderson MP, Kessler D,
Trapani F, Arnhof H, et al: BI-3406, a potent and selective
SOS1-KRAS interaction inhibitor, is effective in KRAS-driven
cancers through combined MEK inhibition. Cancer Discov. 11:142–157.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Odogwu L, Mathieu L, Blumenthal G, Larkins
E, Goldberg KB, Griffin N, Bijwaard K, Lee EY, Philip R, Jiang X,
et al: FDA approval summary: Dabrafenib and treatment of metastatic
non-small cell lung cancers harboring BRAF V600E mutations.
Oncologist. 23:740–745. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Huang WC, Yadav VK, Cheng WH, Wang CH,
Hsieh MS, Huang TY, Lin SF, Yeh CT and Kuo KT: The MEK/ERK/miR-21
signaling is critical in osimertinib resistance in EGFR-mutant
non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancers (Basel). 13:60052021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Runa F, Ortiz-Soto G, de Barros NR and
Kelber JA: Targeting SMAD-dependent signaling: Considerations in
epithelial and mesenchymal solid tumors. Pharmaceuticals (Basel).
17:3262024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Antognelli C, Gambelunghe A, Muzi G and
Talesa VN: Glyoxalase I drives epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
via argpyrimidine-modified Hsp70, miR-21 and SMAD signalling in
human bronchial cells BEAS-2B chronically exposed to crystalline
silica Min-U-Sil 5: Transformation into a neoplastic-like
phenotype. Free Radic Biol Med. 92:110–125. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Xin X, Cheng X, Zeng F, Xu Q and Hou L:
The role of TGF-β/SMAD signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma: From
mechanism to therapy and prognosis. Int J Biol Sci. 20:1436–1451.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
47
|
Xu K, Wei G, Qi W, Ye C, Liu Y, Wang S,
Yang F and Tang J: CircPOLA2 sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer
cells to ferroptosis and suppresses tumorigenesis via the
Merlin-YAP signaling pathway. iScience. 27:1108322024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
An Y, Zhang Q, Li X, Wang Z, Li Y and Tang
X: Upregulated microRNA miR-21 promotes the progression of lung
adenocarcinoma through inhibition of KIBRA and the Hippo signaling
pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 108:1845–1855. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhang L, Li J, Feng M, Xu X, Tang W, Jiang
Y, Xia Z, Liu H, Shen F, Li X and Jiang L: Tigecycline modulates
LPS-induced inflammatory response in sepsis via NF-κB signalling
pathways: Experimental insights into immune regulation. Int J
Antimicrob Agents. 66:1074962025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Shi S, Ou X, Liu C, Li R, Zheng Q and Hu
L: NF-κB signaling and the tumor microenvironment in osteosarcoma:
Implications for immune evasion and therapeutic resistance. Front
Immunol. 16:15186642025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Bahrami A, Khalaji A, Bahri Najafi M,
Sadati S, Raisi A, Abolhassani A, Eshraghi R, Khaksary Mahabady M,
Rahimian N and Mirzaei H: NF-κB pathway and angiogenesis: Insights
into colorectal cancer development and therapeutic targets. Eur J
Med Res. 29:6102024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Sai X, Qin C, Zhang Z, Yu H and Bian T: A
miRNA-21-Mediated PTEN/Akt/NF-κB axis promotes chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease pathogenesis. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis.
19:1141–1151. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
53
|
Yang Z, Fang S, Di Y, Ying W, Tan Y and Gu
W: Modulation of NF-κB/miR-21/PTEN pathway sensitizes non-small
cell lung cancer to cisplatin. PLoS One. 10:e01215472015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Samad MA, Ahmad I, Hasan A, Alhashmi MH,
Ayub A, Al-Abbasi FA, Kumer A and Tabrez S: STAT3 signaling pathway
in health and disease. MedComm (2020). 6:e701522025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Perner F, Pahl HL, Zeiser R and Heidel FH:
Malignant JAK-signaling: At the interface of inflammation and
malignant transformation. Leukemia. 39:1011–1030. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Jang JY, Jeon YK, Lee CE and Kim CW: ANT2
suppression by shRNA may be able to exert anticancer effects in HCC
further by restoring SOCS1 expression. Int J Oncol. 42:574–582.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Almutairy B, Fu Y, Bi Z, Zhang W,
Wadgaonkar P, Qiu Y, Thakur C and Chen F: Arsenic activates STAT3
signaling during the transformation of the human bronchial
epithelial cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 436:1158842022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wang L, Gao L, Ding F, Gao K, Liu Q and
Yin X: Prognostic value and molecular mechanisms of OAS1 in lung
adenocarcinoma. BMC Pulm Med. 24:4732024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lara P, Aguilar-González A, Martín F,
Mesas C, Moreno J and Rama AR: Exploring miR-21 knock-out using
CRISPR/Cas as a treatment for lung cancer. Genes (Basel).
16:1332025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Jin J and Yu G: Hypoxic lung cancer
cell-derived exosomal miR-21 mediates macrophage M2 polarization
and promotes cancer cell proliferation through targeting IRF1.
World J Surg Oncol. 20:2412022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Li H, Zhao J, Jia X, Zhang Y, Du Y, Li H,
Ma L and Huang J: miR-21 promotes growth, invasion and migration of
lung cancer cells by AKT/P-AKT/cleaved-caspase 3/MMP-2/MMP-9
signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 13:692–700.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Meng G, Wei J, Wang Y, Qu D and Zhang J:
miR-21 regulates immunosuppression mediated by myeloid-derived
suppressor cells by impairing RUNX1-YAP interaction in lung cancer.
Cancer Cell Int. 20:4952020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Liang ZY, Zhang ZM, Sun GR, Zhao BS, Xin
GH and Zhang L: lncRNA ASBEL and lncRNA Erbb4-IR reduce
chemoresistance against gemcitabine and cisplatin in stage IV lung
squamous cell carcinoma via the microRNA-21/LZTFL1 axis. Am J
Cancer Res. 13:2732–2750. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhang CC, Li Y, Feng XZ and Li DB:
Circular RNA circ_0001287 inhibits the proliferation, metastasis,
and radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells by
sponging microRNA miR-21 and up-regulating phosphatase and tensin
homolog expression. Bioengineered. 12:414–425. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Liang M, Wang L, Cao C, Song S and Wu F:
LncRNA SNHG10 is downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer and
predicts poor survival. BMC Pulm Med. 20:2732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Xia H, Xiu M, Gao J and Jing H: LncRNA
PLAC 2 downregulated miR-21 in non-small cell lung cancer and
predicted survival. BMC Pulm Med. 19:1722019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Su C, Cheng X, Li Y, Han Y, Song X, Yu D,
Cao X and Liu Z: MiR-21 improves invasion and migration of
drug-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cancer cell and transformation
of EMT through targeting HBP1. Cancer Med. 7:2485–2503. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Dai Q, Li N and Zhou X: Increased miR-21a
provides metabolic advantages through suppression of FBP1
expression in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Am J Cancer Res.
7:2121–2130. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zhang Z, Huang Y, Li J, Su F, Kuo JC, Hu
Y, Zhao X and Lee RJ: Antitumor activity of anti-miR-21 delivered
through lipid nanoparticles. Adv Healthc Mater. 12:e22024122023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Folahan JT and Barabutis N: NEK kinases in
cell cycle regulation, DNA damage response, and cancer progression.
Tissue Cell. 94:1028112025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zabihi M, Lotfi R, Yousefi AM and Bashash
D: Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases: From biology to
tumorigenesis and therapeutic opportunities. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 149:1585–1606. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Dai L, Chen F, Zheng Y, Zhang D, Qian B,
Ji H, Long F and Cretoiu D: miR-21 regulates growth and EMT in lung
cancer cells via PTEN/Akt/GSK3β signaling. Front Biosci (Landmark
Ed). 24:1426–1439. 2019. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Xia H, Zhang W, Zhang B, Zhao Y, Zhao Y,
Li S and Liu Y: miR-21 modulates the effect of EZH2 on the
biological behavior of human lung cancer stem cells in vitro.
Oncotarget. 8:85442–85451. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhong Z, Dong Z, Yang L and Gong Z: miR-21
induces cell cycle at S phase and modulates cell proliferation by
down-regulating hMSH2 in lung cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
138:1781–1788. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhang D, Zhang W, Liu H, Liu P, Li C, Liu
Y, Han J and Zhu G: Recent advances in the treatment of non-small
cell lung cancer with MET inhibitors. Front Chem. 12:15018442024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Aftabi S, Barzegar Behrooz A, Cordani M,
Rahiman N, Sadeghdoust M, Aligolighasemabadi F, Pistorius S,
Alavizadeh SH, Taefehshokr N and Ghavami S: Therapeutic targeting
of TGF-β in lung cancer. FEBS J. 292:1520–1557. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Reddy RA, Varshini MS and Kumar RS: Matrix
metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2): As an essential factor in cancer
progression. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 20:26–44. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Shen KH, Hung JH, Liao YC, Tsai ST, Wu MJ
and Chen PS: Sinomenine inhibits migration and invasion of human
lung cancer cell through downregulating expression of miR-21 and
MMPs. Int J Mol Sci. 21:30802020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Masuda T, Fukuda A, Yamakawa G, Omatsu M,
Namikawa M, Sono M, Fukunaga Y, Nagao M, Araki O, Yoshikawa T, et
al: Pancreatic RECK inactivation promotes cancer formation,
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and metastasis. J Clin Invest.
133:e1618472023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Tiong TY, Chan ML, Wang CH, Yadav VK,
Pikatan NW, Fong IH, Yeh CT, Kuo KT and Huang WC: Exosomal miR-21
determines lung-to-brain metastasis specificity through the
DGKB/ERK axis within the tumor microenvironment. Life Sci.
329:1219452023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Bai J, Shi Z, Wang S, Pan H and Zhang T:
MiR-21 and let-7 cooperation in the regulation of lung cancer.
Front Oncol. 12:9500432022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Chaudhary B, Arya P, Sharma V, Kumar P,
Singla D and Grewal AS: Targeting anti-apoptotic mechanisms in
tumour cells: Strategies for enhancing cancer therapy. Bioorg Chem.
159:1083882025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Mustafa M, Ahmad R, Tantry IQ, Ahmad W,
Siddiqui S, Alam M, Abbas K, Moinuddin, Hassan MI, Habib S and
Islam S: Apoptosis: A comprehensive overview of signaling pathways,
morphological changes, and physiological significance and
therapeutic implications. Cells. 13:18382024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Ge JH, Zhu JW, Fu HY, Shi WB and Zhang CL:
An antisense oligonucleotide drug targeting miR-21 induces H1650
apoptosis and caspase activation. Technol Cancer Res Treat.
18:15330338198922632019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Liu X, Zhang J, Yi T, Li H, Tang X, Liu D,
Wu D and Li Y: Decoding tumor angiogenesis: Pathways, mechanisms,
and future directions in anti-cancer strategies. Biomark Res.
13:622025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Liu Y, Luo F, Wang B, Li H, Xu Y, Liu X,
Shi L, Lu X, Xu W, Lu L, et al: STAT3-regulated exosomal miR-21
promotes angiogenesis and is involved in neoplastic processes of
transformed human bronchial epithelial cells. Cancer Lett.
370:125–135. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Zhao Y, Xu Y, Luo F, Xu W, Wang B, Pang Y,
Zhou J, Wang X and Liu Q: Angiogenesis, mediated by miR-21, is
involved arsenite-induced carcinogenesis. Toxicol Lett. 223:35–41.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Dong J, Zhang Z, Gu T, Xu SF, Dong LX, Li
X, Fu BH and Fu ZZ: The role of microRNA-21 in predicting brain
metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. Onco Targets Ther.
10:185–194. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Yang JC, Lee DH, Lee JS, Fan Y, de Marinis
F, Iwama E, Inoue T, Rodríguez-Cid J, Zhang L, Yang CT, et al:
Phase III KEYNOTE-789 study of pemetrexed and platinum with or
without pembrolizumab for tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant,
EGFR-mutant, metastatic nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer. J
Clin Oncol. 42:4029–4039. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Im JH, Lee KY, Seo Y, Rhim J, Dho YS, Yoo
BC, Park JB, Shin SH, Yoo H, Kim JH and Gwak HS: Extracellular
vesicles from cerebrospinal fluid of leptomeningeal metastasis
patients deliver MiR-21 and induce methotrexate resistance in lung
cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 25:31242024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Chen L, Ren P, Zhang Y, Gong B, Yu D and
Sun X: Long non-coding RNA GAS5 increases the radiosensitivity of
A549 cells through interaction with the miR-21/PTEN/Akt axis. Oncol
Rep. 43:897–907. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Zhang Y, Zhu J, Qiu L, Lv Z, Zhao Z, Ren
X, Guo Y, Chen Y, Li M, Fan Y, et al: Stimulus-activated
ribonuclease targeting chimeras for tumor microenvironment
activated cancer therapy. Nat Commun. 16:12882025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhang WC, Skiados N, Aftab F, Moreno C,
Silva L, Corbilla PJA, Asara JM, Hata AN and Slack FJ: MicroRNA-21
guide and passenger strand regulation of adenylosuccinate
lyase-mediated purine metabolism promotes transition to an
EGFR-TKI-tolerant persister state. Cancer Gene Ther. 29:1878–1894.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Gamal-Eldeen AM, Alrehaili AA, Alharthi A
and Raafat BM: Perftoran ® inhibits hypoxia-associated
resistance in lung cancer cells to carboplatin. Front Pharmacol.
13:8608982022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Jiang S, Wang R, Yan H, Jin L, Dou X and
Chen D: MicroRNA-21 modulates radiation resistance through
upregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α-promoted glycolysis in
non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 13:4101–4107. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Chen Z, Gong J, Chen J, Yang L, Hu S, Chen
L and Lu H: Clinical outcomes of EGFR-TKI in advanced lung squamous
cell carcinoma and EGFR-TKI remodel tumor immune microenvironment.
Ann Med. 57:24881092025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Jing C, Cao H, Qin X, Yu S, Wu J, Wang Z,
Ma R and Feng J: Exosome-mediated gefitinib resistance in lung
cancer HCC827 cells via delivery of miR-21. Oncol Lett.
15:9811–9817. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Song S, Guo Y, Mao D, Gao H, Gao YP and
Kang W: An ultrasensitive electrochemical/colorimetric dual-mode
self-powered biosensing platform for lung cancer marker detection
by multiple-signal amplification strategy. Anal Chim Acta.
1316:3428272024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Chen J, Zhang J, Xie Q, Chu Z, Lu Y, Zhang
F and Wang Q: Isothermal strand displacement polymerase reaction
(ISDPR)-assisted microchip electrophoresis for highly sensitive
detection of cancer associated microRNAs. Anal Chim Acta.
1300:3424692024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Pang H, Gong Y, Wang Y and Zhang L: The
expression of miR-21, HSP90a and gGASP-1 in serum of patients with
lung cancer and their correlation with pathological subtypes. J Med
Biochem. 43:460–468. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Wang Z, Liu J, Liu Q, Ren Y, Wang Q, Tian
Q, Li Z and Liu H: Clinical value of peripheral blood miR-21 and
miR-486 combined with CT forearly cancer diagnosis in pulmonary
nodulessmoking. J Cardiothorac Surg. 19:5392024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Liu Q, Liu J, He N, Zhang M, Wu L, Chen X,
Zhu J, Ran F, Chen Q and Zhang H: CRISPR/Cas12a coupling with
magnetic nanoparticles and cascaded strand displacement reaction
for ultrasensitive fluorescence determination of exosomal miR-21.
Molecules. 27:53382022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Hetta HF, Zahran AM, Shafik EA, El-Mahdy
RI, Mohamed NA, Nabil EE, Esmaeel HM, Alkady OA, Elkady A, Mohareb
DA, et al: Circulating miRNA-21 and miRNA-23a expression signature
as potential biomarkers for early detection of non-small-cell lung
cancer. Microrna. 8:206–215. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Watabe S, Kikuchi Y, Morita S, Komura D,
Numakura S, Kumagai-Togashi A, Watanabe M, Matsutani N, Kawamura M,
Yasuda M and Uozaki H: Clinicopathological significance of
microRNA-21 in extracellular vesicles of pleural lavage fluid of
lung adenocarcinoma and its functions inducing the mesothelial to
mesenchymal transition. Cancer Med. 9:2879–2890. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Xu S and Shi L: High expression of miR-155
and miR-21 in the recurrence or metastasis of non-small cell lung
cancer. Oncol Lett. 18:758–763. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Zhu Z, Li Q, Xu M and Qi Z: Effect of
whole-brain and intensity-modulated radiotherapy on serum levels of
miR-21 and prognosis for lung cancer metastatic to the brain. Med
Sci Monit. 26:e9246402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
D'Antonio L, Fieni C, Ciummo SL, Vespa S,
Lotti L, Sorrentino C and Di Carlo E: Inactivation of
interleukin-30 in colon cancer stem cells via CRISPR/Cas9 genome
editing inhibits their oncogenicity and improves host survival. J
Immunother Cancer. 11:e0060562023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Zhu G, Li D, Wang X, Guo Q, Zhao Y, Hou W,
Li J and Zheng Q: Drug monomers from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge.
Promoting tight junction protein expression for therapeutic effects
on lung cancer. Sci Rep. 13:229282023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Shortridge MD, Chaubey B, Zhang HJ,
Pavelitz T, Vidadala V, Tang C, Olsen GL, Calin GA and Varani G:
Drug-like small molecules that inhibit expression of the oncogenic
MicroRNA-21. ACS Chem Biol. 18:237–250. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Giordo R, Ahmadi FAM, Husaini NA,
Al-Nuaimi NRAM, Ahmad SMS, Pintus G and Zayed H: microRNA 21 and
long non-coding RNAs interplays underlie cancer pathophysiology: A
narrative review. Noncoding RNA Res. 9:831–852. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Sriram V and Lee JY: Calcium
phosphate-polymeric nanoparticle system for co-delivery of
microRNA-21 inhibitor and doxorubicin. Colloids Surf B
Biointerfaces. 208:1120612021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Zhang J, Zhang C, Hu L, He Y, Shi Z, Tang
S and Chen Y: Abnormal expression of miR-21 and miR-95 in cancer
stem-like cells is associated with radioresistance of lung cancer.
Cancer Invest. 33:165–171. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Beg MS, Brenner AJ, Sachdev J, Borad M,
Kang YK, Stoudemire J, Smith S, Bader AG, Kim S and Hong DS: Phase
I study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, administered twice
weekly in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest New Drugs.
35:180–188. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Hong DS, Kang YK, Borad M, Sachdev J,
Ejadi S, Lim HY, Brenner AJ, Park K, Lee JL, Kim TY, et al: Phase 1
study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, in patients with
advanced solid tumours. Br J Cancer. 122:1630–1637. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
van Zandwijk N, Pavlakis N, Kao SC, Linton
A, Boyer MJ, Clarke S, Huynh Y, Chrzanowska A, Fulham MJ, Bailey
DL, et al: Safety and activity of microRNA-loaded minicells in
patients with recurrent malignant pleural mesothelioma: A
first-in-man, phase 1, open-label, dose-escalation study. Lancet
Oncol. 18:1386–1396. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Reid G, Kao SC, Pavlakis N, Brahmbhatt H,
MacDiarmid J, Clarke S, Boyer M and van Zandwijk N: Clinical
development of TargomiRs, a miRNA mimic-based treatment for
patients with recurrent thoracic cancer. Epigenomics. 8:1079–1085.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
van der Ree MH, de Vree JM, Stelma F,
Willemse S, van der Valk M, Rietdijk S, Molenkamp R, Schinkel J,
van Nuenen AC, Beuers U, et al: Safety, tolerability, and antiviral
effect of RG-101 in patients with chronic hepatitis C: A phase 1B,
double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 389:709–717.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Stelma F, van der Ree MH, Sinnige MJ,
Brown A, Swadling L, de Vree JML, Willemse SB, van der Valk M,
Grint P, Neben S, et al: Immune phenotype and function of natural
killer and T cells in chronic hepatitis C patients who received a
single dose of anti-MicroRNA-122, RG-101. Hepatology. 66:57–68.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Deng Y, Campbell F, Han K, Theodore D,
Deeg M, Huang M, Hamatake R, Lahiri S, Chen S, Horvath G, et al:
Randomized clinical trials towards a single-visit cure for chronic
hepatitis C: Oral GSK2878175 and injectable RG-101 in chronic
hepatitis C patients and long-acting injectable GSK2878175 in
healthy participants. J Viral Hepat. 27:699–708. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Diener C, Keller A and Meese E: Emerging
concepts of miRNA therapeutics: From cells to clinic. Trends Genet.
38:613–626. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Ottosen S, Parsley TB, Yang L, Zeh K, van
Doorn LJ, van der Veer E, Raney AK, Hodges MR and Patick AK: In
vitro antiviral activity and preclinical and clinical resistance
profile of miravirsen, a novel anti-hepatitis C virus therapeutic
targeting the human factor miR-122. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
59:599–608. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
122
|
Elmén J, Lindow M, Schütz S, Lawrence M,
Petri A, Obad S, Lindholm M, Hedtjärn M, Hansen HF, Berger U, et
al: LNA-mediated microRNA silencing in non-human primates. Nature.
452:896–899. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Gebert LFR, Rebhan MAE, Crivelli SEM,
Denzler R, Stoffel M and Hall J: Miravirsen (SPC3649) can inhibit
the biogenesis of miR-122. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:609–621. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Janssen HL, Reesink HW, Lawitz EJ, Zeuzem
S, Rodriguez-Torres M, Patel K, van der Meer AJ, Patick AK, Chen A,
Zhou Y, et al: Treatment of HCV infection by targeting microRNA. N
Engl J Med. 368:1685–1694. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Keskin S, Brouwers CC, Sogorb-Gonzalez M,
Martier R, Depla JA, Vallès A, van Deventer SJ, Konstantinova P and
Evers MM: AAV5-miHTT lowers huntingtin mRNA and protein without
off-target effects in patient-derived neuronal cultures and
astrocytes. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 15:275–284. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Miniarikova J, Zanella I, Huseinovic A,
van der Zon T, Hanemaaijer E, Martier R, Koornneef A, Southwell AL,
Hayden MR, van Deventer SJ, et al: Design, characterization, and
lead selection of therapeutic miRNAs targeting huntingtin for
development of gene therapy for Huntington's disease. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 5:e2972016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Ho PTB, Clark IM and Le LTT:
MicroRNA-based diagnosis and therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 23:71672022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Seto AG, Beatty X, Lynch JM, Hermreck M,
Tetzlaff M, Duvic M and Jackson AL: Cobomarsen, an oligonucleotide
inhibitor of miR-155, co-ordinately regulates multiple survival
pathways to reduce cellular proliferation and survival in cutaneous
T-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 183:428–444. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Cheng M, Zain J, Rosen ST and Querfeld C:
Emerging drugs for the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 27:45–54. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Gallant-Behm CL, Piper J, Dickinson BA,
Dalby CM, Pestano LA and Jackson AL: A synthetic microRNA-92a
inhibitor (MRG-110) accelerates angiogenesis and wound healing in
diabetic and nondiabetic wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 26:311–323.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Abplanalp WT, Fischer A, John D, Zeiher
AM, Gosgnach W, Darville H, Montgomery R, Pestano L, Allée G, Paty
I, et al: Efficiency and target derepression of anti-miR-92a:
Results of a first in human study. Nucleic Acid Ther. 30:335–345.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Täubel J, Hauke W, Rump S, Viereck J,
Batkai S, Poetzsch J, Rode L, Weigt H, Genschel C, Lorch U, et al:
Novel antisense therapy targeting microRNA-132 in patients with
heart failure: Results of a first-in-human phase 1b randomized,
double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur Heart J. 42:178–188.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
133
|
Lee EC, Valencia T, Allerson C, Schairer
A, Flaten A, Yheskel M, Kersjes K, Li J, Gatto S, Takhar M, et al:
Discovery and preclinical evaluation of anti-miR-17 oligonucleotide
RGLS4326 for the treatment of polycystic kidney disease. Nat
Commun. 10:41482019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Gale DP, Gross O, Wang F, Esteban de la
Rosa RJ, Hall M, Sayer JA, Appel G, Hariri A, Liu S, Maski M, et
al: A randomized controlled clinical trial testing effects of
lademirsen on kidney function decline in adults with alport
syndrome. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 19:995–1004. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Chen YY, Chen XG and Zhang S: Druggability
of lipid metabolism modulation against renal fibrosis. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 43:505–519. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|