|
1
|
Dennis EA, Cao J, Hsu YH, Magrioti V and
Kokotos G: Phospholipase A2 enzymes: Physical structure, biological
function, disease implication, chemical inhibition, and therapeutic
intervention. Chem Rev. 111:6130–6185. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Farr RS, Cox CP, Wardlow ML and Jorgensen
R: Preliminary studies of an acid-labile factor (ALF) in human sera
that inactivates platelet-activating factor (PAF). Clin Immunol
Immunopathol. 15:318–330. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Batsika CS, Gerogiannopoulou ADD,
Mantzourani C, Vasilakaki S and Kokotos G: The design and discovery
of phospholipase A2 inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory
diseases. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 16:1287–1305. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jin L, Jiang M, Qian J, Ge Z, Xu F and
Liao W: The role of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 in
inflammatory response and macrophage infiltration in sepsis and the
regulatory mechanisms. Funct Integr Genomics. 24:1782024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Khan SA and Ilies MA: The phospholipase A2
superfamily: Structure, isozymes, catalysis, physiologic and
pathologic roles. Int J Mol Sci. 24:13532023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lordan R, Tsoupras A, Zabetakis I and
Demopoulos CA: Forty years since the structural elucidation of
platelet-activating factor (PAF): Historical, current, and future
research perspectives. Molecules. 24:44142019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tselepis AD: Oxidized phospholipids and
lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 as important determinants
of Lp(a) functionality and pathophysiological role. J Biomed Res.
31:13–22. 2018.
|
|
8
|
Bonnefont-Rousselot D: Lp-PLA2, a
biomarker of vascular inflammation and vulnerability of
atherosclerosis plaques. Ann Pharm Fr. 74:190–197. 2016.In French.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
von Eckardstein A, Nordestgaard BG,
Remaley AT and Catapano AL: High-density lipoprotein revisited:
Biological functions and clinical relevance. Eur Heart J.
44:1394–1407. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Zhang S, Huang S, Hu D, Jiang F, Lv Y and
Liu G: Biological properties and clinical significance of
lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 in ischemic stroke.
Cardiovasc Ther. 2022:33285742022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Maiolino G, Bisogni V, Rossitto G and
Rossi GP: Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 prognostic role
in atherosclerotic complications. World J Cardiol. 7:609–620. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fras Z, Tršan J and Banach M: On the
present and future role of Lp-PLA2 in atherosclerosis-related
cardiovascular risk prediction and management. Arch Med Sci.
17:954–964. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pavlova NN and Thompson CB: The emerging
hallmarks of cancer metabolism. Cell Metab. 23:27–47. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jin HR, Wang J, Wang ZJ, Xi MJ, Xia BH,
Deng K and Yang JL: Lipid metabolic reprogramming in tumor
microenvironment: From mechanisms to therapeutics. J Hematol Oncol.
16:1032023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zheng H, Cui D, Quan X, Yang W, Li Y,
Zhang L and Liu E: Lp-PLA2 silencing protects against
ox-LDL-induced oxidative stress and cell apoptosis via Akt/mTOR
signaling pathway in human THP1 macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 477:1017–1023. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lehtinen L, Vainio P, Wikman H, Huhtala H,
Mueller V, Kallioniemi A, Pantel K, Kronqvist P, Kallioniemi O,
Carpèn O and Iljin K: PLA2G7 associates with hormone receptor
negativity in clinical breast cancer samples and regulates
epithelialmesenchymal transition in cultured breast cancer cells. J
Pathol Clin Res. 3:123–138. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Peng Z, Chang Y, Fan J, Ji W and Su C:
Phospholipase A2 superfamily in cancer. Cancer Lett. 497:165–177.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Huang F, Wang K and Shen J:
Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2: The story continues. Med
Res Rev. 40:79–134. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang J, Jin M, Chen Y, Yuan Y, Ruan Y and
Lu G: Lp-PLA2, a potential protector of lung cancer patients
complicated with pleural effusion from lung diseases, proves
effective for the diagnosis and pathological classification of lung
cancer. Transl Oncol. 14:1010302021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Laface C, Ricci AD, Vallarelli S, Ostuni
C, Rizzo A, Ambrogio F, Centonze M, Schirizzi A, Leonardis GD and
D'Alessandro R: Autotaxin-lysophosphatidate axis: Promoter of
cancer development and possible therapeutic implications. Int J Mol
Sci. 25:77372024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tannock LR, De Beer MC, Ji A, Shridas P,
Noffsinger VP, den Hartigh L, Chait A, De Beer FC and Webb NR:
Serum amyloid A3 is a high density lipoprotein-associated
acute-phase protein. J Lipid Res. 59:339–347. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Xu C, Reichert EC, Nakano T, Lohse M,
Gardner AA, Revelo MP, Topham MK and Stafforini DM: Deficiency of
phospholipase A2 group 7 decreases intestinal polyposis and colon
tumorigenesis in Apc(Min/+) mice. Cancer Res. 73:2806–2816. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Liu K, Li Y, Shen M, Xu W, Wu S, Yang X,
Zhang B and Lin N: Epigenetic regulation of stromal and immune
cells and therapeutic targets in the tumor microenvironment.
Biomolecules. 15:712025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li Z, Zhao J and Tang Y: Advances in the
role of SWI/SNF complexes in tumours. J Cell Mol Med. 27:1023–1031.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Flavahan WA, Gaskell E and Bernstein BE:
Epigenetic plasticity and the hallmarks of cancer. Science.
357:eaal23802017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ito A and Suganami T: Lipid metabolism in
myeloid cell function and chronic inflammatory diseases. Front
Immunol. 15:14958532025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Shu YJ, Lao B and Qiu YY: Research
progress of ferroptosis regulating lipid peroxidation and
metabolism in occurrence and development of primary liver cancer.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. 16:2335–2349. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Babar MU, Nassar AF, Nie X, Zhang T, He J,
Yeung J, Norris P, Ogura H, Muldoon A, Chen L and Libreros S: Is
lipid metabolism of value in cancer research and treatment? Part
II: Role of specialized pro-resolving mediators in inflammation,
infections, and cancer. Metabolites. 14:3142024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oh M, Jang SY, Lee JY, Kim JW, Jung Y, Kim
J, Seo J, Han TS, Jang E, Son HY, et al: The lipoprotein-associated
phospholipase A2 inhibitor Darapladib sensitises cancer cells to
ferroptosis by remodelling lipid metabolism. Nat Commun.
14:57282023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bi Y, Ying X, Chen W, Wu J, Kong C, Hu W,
Fang S, Yu J, Zhai M, Jiang C, et al: Glycerophospholipid-driven
lipid metabolic reprogramming as a common key mechanism in the
progression of human primary hepatocellular carcinoma and
cholangiocarcinoma. Lipids Health Dis. 23:3262024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xie J, Zhu L, Yang X, Yu F, Fan B, Wu Y,
Zhou Z, Lin W and Yang Y: Combination of theoretical analysis and
experiments: Exploring the role of PLA2G7 in human cancers,
including renal cancer. Heliyon. 10:e279062024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Srivastava R and Lodhi N: DNA methylation
malleability and dysregulation in cancer progression: understanding
the role of PARP1. Biomolecules. 12:4172022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yu X, Zhao H, Wang R, Chen Y, Ouyang X, Li
W, Sun Y and Peng A: Cancer epigenetics: From laboratory studies
and clinical trials to precision medicine. Cell Death Discov.
10:282024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Jiang D, Wang Y, Shen Y, Xu Y, Zhu H, Wang
J, Wang H and Duan S: Estrogen and promoter methylation in the
regulation of PLA2G7 transcription. Gene. 591:262–267. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu D, Wang H, Li X, Liu J, Zhang Y and Hu
J: Small molecule inhibitors for cancer metabolism: Promising
prospects to be explored. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 149:8051–8076.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Maan M, Peters JM, Dutta M and Patterson
AD: Lipid metabolism and lipophagy in cancer. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 504:582–589. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Vainio P, Lehtinen L, Mirtti T, Hilvo M,
Seppänen-Laakso T, Virtanen J, Sankila A, Nordling S, Lundin J,
Rannikko A, et al: Phospholipase PLA2G7, associated with aggressive
prostate cancer, promotes prostate cancer cell migration and
invasion and is inhibited by statins. Oncotarget. 2:1176–1190.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Candels LS, Becker S and Trautwein C:
PLA2G7: A new player in shaping energy metabolism and lifespan.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7:1952022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Blomme A, Ford CA, Mui E, Patel R, Ntala
C, Jamieson LE, Planque M, McGregor GH, Peixoto P, Hervouet E, et
al: 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase regulates lipid homeostasis in
treatment-resistant prostate cancer. Nat Commun. 11:25082020.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Han C, Yu G, Mao Y, Song S, Li L, Zhou L,
Wang Z, Liu Y, Li M and Xu B: LPCAT1 enhances castration resistant
prostate cancer progression via increased mRNA synthesis and PAF
production. PLoS One. 15:e02408012020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xu Z, Xu X, Hu J, Tan J, Wan Y and Cui F:
Characteristics, clinical significance, and cancer immune
interactions of lipid metabolism in prostate cancer. Transl Cancer
Res. 13:3575–3588. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Khan F, Elsori D, Verma M, Pandey S, Rab
SO, Siddiqui S, Alabdallah NM, Saeed M and Pandey P: Unraveling the
intricate relationship between lipid metabolism and oncogenic
signaling pathways. Front Cell Dev Biol. 12:13990652024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Winkelkotte AM, Al-Shami K, Chaves-Filho
AB, Vogel FCE and Schulze A: Interactions of fatty acid and
cholesterol metabolism with cellular stress response pathways in
cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 15:a0415482024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Park H, Lee S, Lee J, Moon H and Ro SW:
Exploring the JAK/STAT signaling pathway in hepatocellular
carcinoma: Unraveling signaling complexity and therapeutic
implications. Int J Mol Sci. 24:137642023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
46
|
Guo S and Yang Q: Bioinformatics analysis
identifies PLA2G7 as a key antigen-presenting prognostic related
gene promoting hepatocellular carcinoma through the STAT1/PD-L1
axis. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 29:392024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Fernando W, Cruickshank BM, Arun RP,
MacLean MR, Cahill HF, Morales-Quintanilla F, Dean CA, Wasson MD,
Dahn ML, Coyle KM, et al: ALDH1A3 is the switch that determines the
balance of ALDH+ and CD24-CD44+ cancer stem cells, EMT-MET, and
glucose metabolism in breast cancer. Oncogene. 43:3151–3169. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gavert N and Ben-Ze'ev A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the invasive potential of
tumors. Trends Mol Med. 14:199–209. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Mallini P, Lennard T, Kirby J and Meeson
A: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition: What is the impact on
breast cancer stem cells and drug resistance. Cancer Treat Rev.
40:341–348. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Suman S, Das TP and Damodaran C: Silencing
NOTCH signaling causes growth arrest in both breast cancer stem
cells and breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 109:2587–2596. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yang CK, Wang XK, Liao XW, Han CY, Yu TD,
Qin W, Zhu GZ, Su H, Yu L, Liu XG, et al: Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1
(ALDH1) isoform expression and potential clinical implications in
hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 12:e01822082017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lavudi K, Nuguri SM, Olverson Z,
Dhanabalan AK, Patnaik S and Kokkanti RR: Targeting the retinoic
acid signaling pathway as a modern precision therapy against
cancers. Front Cell Dev Biol. 11:12546122023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
53
|
Liu C, Qiang J, Deng Q, Xia J, Deng L,
Zhou L, Wang D, He X, Liu Y, Zhao B, et al: ALDH1A1 activity in
tumor-initiating cells remodels myeloid-derived suppressor cells to
promote breast cancer progression. Cancer Res. 81:5919–5934. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Stafforini DM: Diverse functions of plasma
PAF-AH in tumorigenesis. Enzymes. 38:157–179. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Vermonden P, Martin M, Glowacka K, Neefs
I, Ecker J, Höring M, Liebisch G, Debier C, Feron O and Larondell
Y: Phospholipase PLA2G7 is complementary to GPX4 in mitigating
punicic-acid-induced ferroptosis in prostate cancer cells.
iScience. 27:1097742024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liao Y, Badmann S, Kraus F, Topalov NE,
Mayr D, Kolben T, Hester A, Beyer S, Mahner S, Jeschke U, et al:
PLA2G7/PAF-AH as potential negative regulator of the Wnt signaling
pathway mediates protective effects in BRCA1 mutant breast cancer.
Int J Mol Sci. 24:8822023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
57
|
Youssef KK and Nieto MA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in tissue repair and
degeneration. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 25:720–739. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Fontana R, Mestre-Farrera A and Yang J:
Update on epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in cancer progression.
Annu Rev Pathol. 19:133–156. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
59
|
Aban CE, Lombardi A, Neiman G, Biani MC,
La Greca A, Waisman A, Moro LN, Sevlever G, Miriuka S and Luzzani
C: Downregulation of E-cadherin in pluripotent stem cells triggers
partial EMT. Sci Rep. 11:20482021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Taube JH, Herschkowitz JI, Komurov K, Zhou
AY, Gupta S, Yang J, Hartwell K, Onder TT, Gupta PB, Evans KW, et
al: Core epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition interactome
gene-expression signature is associated with claudin-low and
metaplastic breast cancer subtypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:15449–15454. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Al-Maghrabi J: Vimentin immunoexpression
is associated with higher tumor grade, metastasis, and shorter
survival in colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 13:493–500.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Hjelmeland ME, Lien HE, Berg HF, Woie K,
Werner HMJ, Amant F, Haldorsen IS, Trovik J and Krakstad C: Loss of
vimentin expression in preoperative biopsies independently predicts
poor prognosis, lymph node metastasis and recurrence in endometrial
cancer. BJC Rep. 2:812024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Shao W, Li J, Piao Q, Yao X, Li M, Wang S,
Song Z, Sun Y, Zheng L, Wang G, et al: FRMD3 inhibits the growth
and metastasis of breast cancer through the ubiquitination-mediated
degradation of vimentin and subsequent impairment of focal
adhesion. Cell Death Dis. 14:132023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Brabletz S, Bajdak K, Meidhof S, Burk U,
Niedermann G, Firat E, Wellner U, Dimmler A, Faller G, Schubert J
and Brabletz T: The ZEB1/miR-200 feedback loop controls Notch
signalling in cancer cells. EMBO J. 30:770–782. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Du JW, Xu KY, Fang LY and Qi XL:
Interleukin-17, produced by lymphocytes, promotes tumor growth and
angiogenesis in a mouse model of breast cancer. Mol Med Rep.
6:1099–1102. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Benevides L, Cardoso CRB, Tiezzi DG,
Marana HRC, Andrade JM and Silva JS: Enrichment of regulatory T
cells in invasive breast tumor correlates with the upregulation of
IL-17A expression and invasiveness of the tumor. Eur J Immunol.
43:1518–1528. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Cochaud S, Giustiniani J, Thomas C,
Laprevotte E, Garbar C, Savoye AM, Curé H, Mascaux C, Alberici G,
Bonnefoy N, et al: IL-17A is produced by breast cancer TILs and
promotes chemoresistance and proliferation through ERK1/2. Sci Rep.
3:34562013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhang N, Ji J, Zhou D, Liu X, Zhang X, Liu
Y, Xiang W, Wang M, Zhang L, Wang G, et al: The interaction of the
senescent and adjacent breast cancer cells promotes the metastasis
of heterogeneous breast cancer cells through Notch signaling. Int J
Mol Sci. 22:8492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
He Y, Lin Y, Song J, Song M, Nie X, Sun H,
Xu C, Han Z and Cai J: From mechanisms to medicine: Ferroptosis as
a therapeutic target in liver disorders. Cell Commun Signal.
23:1252025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
70
|
Liu C, Liu Z, Dong Z, Liu S, Kan H and
Zhang S: Multifaceted interplays between the essential players and
lipid peroxidation in ferroptosis. J Genet Genomics.
23:S1673-S8527(25)00024-4. 2025.
|
|
71
|
Bipasha M, Deepali V, Prabal D, Supriya K
and Megha B: Ferroptosis: A mechanism of cell death with potential
scope in cancer therapy. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 16: View Article : Google Scholar : 2025.
|
|
72
|
Fujii J and Imai H: Oxidative metabolism
as a cause of lipid peroxidation in the execution of ferroptosis.
Int J Mol Sci. 25:75442024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Li K, Fan C, Chen J, Xu X, Lu C, Shao H
and Xi Y: Role of oxidative stress-induced ferroptosis in cancer
therapy. J Cell Mol Med. 28:e183992024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Forcina GC and Dixon SJ: GPX4 at the
crossroads of lipid homeostasis and ferroptosis. Proteomics.
19:e18003112019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Liu Q, Chen X, Chen W, Yuan X, Su H, Shen
J and Xu Y: Structural and thermodynamic characterization of
protein-ligand interactions formed between lipoprotein-associated
phospholipase A2 and inhibitors. J Med Chem. 59:5115–5120. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Liu JP, Cen SY, Xue Z, Wang TX, Gao Y,
Zheng J, Zhang C, Hu J, Nie S, Xiong Y, et al: A class of disulfide
compounds suppresses ferroptosis by stabilizing GPX4. ACS Chem
Biol. 17:3389–3406. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Ubellacker JM, Tasdogan A, Ramesh V, Shen
B, Mitchell EC, Martin-Sandoval MS, Gu Z, McCormick ML, Durham AB,
Spitz DR, et al: Lymph protects metastasizing melanoma cells from
ferroptosis. Nature. 585:113–118. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Fan Y, Wang Y, Dan W, Zhang Y, Nie L, Ma
Z, Zhuang Y, Liu B, Li M, Liu T, et al: PRMT5-mediated arginine
methylation stabilizes GPX4 to suppress ferroptosis in cancer. Nat
Cell Biol. 27:641–653. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Lane DJR, Metselaar B, Greenough M, Bush
AI and Ayton SJ: Ferroptosis and NRF2: an emerging battlefield in
the neurodegeneration of Alzheimer's disease. Essays Biochem.
65:925–940. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G and Tang D:
Ferroptosis in infection, inflammation, and immunity. J Exp Med.
218:e202105182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Mabeta P and Steenkamp V: The VEGF/VEGFR
axis revisited: Implications for cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci.
23:155852022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Malekan M, Haass NK, Rokni GR, Gholizadeh
N, Ebrahimzadeh MA and Kazeminejad A: VEGF/VEGFR axis and its
signaling in melanoma: Current knowledge toward therapeutic
targeting agents and future perspectives. Life Sci. 345:1225632024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zhang Y and Brekken RA: Direct and
indirect regulation of the tumor immune microenvironment by VEGF. J
Leukoc Biol. 111:1269–1286. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Hoeres T, Wilhelm M, Smetak M, Holzmann E,
Schulze-Tanzil G and Birkmann J: Immune cells regulate VEGF
signalling via release of VEGF and antagonistic soluble VEGF
receptor-1. Clin Exp Immunol. 192:54–67. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
85
|
Vecchi L, Araújo TG, Azevedo FVPDV, Mota
STS, Ávila VDMR, Ribeiro MA and Goulart LR: Phospholipase A2 drives
tumorigenesis and cancer aggressiveness through its interaction
with annexin A1. Cells. 10:14722021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
86
|
Musumeci F and Schenone S: Unlocking
potential and limits of kinase inhibitors: The highway to enhanced
cancer targeted therapy. Pharmaceutics. 16:6252024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Alinezhad S, Väänänen RM, Mattsson J, Li
Y, Tallgrén T, Ochoa N, Bjartell A, Åkerfelt M, Taimen P, Boström
PJ, et al: Validation of novel biomarkers for prostate cancer
progression by the combination of bioinformatics, clinical and
functional studies. PLoS One. 11:e01582552016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
He Y, He Z, Zhang X and Liu S:
Platelet-activating factor acetyl hydrolase IB2 dysregulated cell
proliferation in ovarian cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 21:6972021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Carneiro BA and El-Deiry WS: Targeting
apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 17:395–417. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Cetraro P, Plaza-Diaz J, MacKenzie A and
Abadía-Molina F: A review of the current impact of inhibitors of
apoptosis proteins and their repression in cancer. Cancers (Basel).
14:16712022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Vainio P, Gupta S, Ketola K, Mirtti T,
Mpindi JP, Kohonen P, Fey V, Perälä M, Smit F, Verhaegh G, et al:
Arachidonic acid pathway members PLA2G7, HPGD, EPHX2, and CYP4F8
identified as putative novel therapeutic targets in prostate
cancer. Am J Pathol. 178:525–536. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
92
|
Zheng W, Lin Q, Issah MA, Liao Z and Shen
J: Identification of PLA2G7 as a novel biomarker of diffuse large B
cell lymphoma. BMC Cancer. 21:9272021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
93
|
Qaderi K, Shahmoradi A, Thyagarajan A and
Sahu RP: Impact of targeting the platelet-activating factor and its
receptor in cancer treatment. Mil Med Res. 12:102025.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Liao Y, Badmann S, Kaltofen T, Mayr D,
Schmoeckel E, Deuster E, Mannewitz M, Landgrebe S, Kolben T, Hester
A, et al: Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase expression in
BRCA1 mutant ovarian cancer as a protective factor and potential
negative regulator of the Wnt signaling pathway. Biomedicines.
9:7062021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
95
|
Wang X, Luo G, Zhang K, Cao J, Huang C,
Jiang T, Liu B, Su L and Qiu Z: Correction: hypoxic tumor-derived
exosomal miR-301a mediates M2 macrophage polarization via
PTEN/PI3Kγ to promote pancreatic cancer metastasis. Cancer Res.
80:9222020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Zhang L, Li Z, Skrzypczynska KM, Fang Q,
Zhang W, O'Brien SA, He Y, Wang L, Zhang Q, Kim A, et al:
Single-cell analyses inform mechanisms of myeloid-targeted
therapies in colon cancer. Cell. 181:442–459.e29. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Bonnefont-Rousselot D:
Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2): Relevant
biomarker and therapeutic target? Ann Pharm Fr. 83:45–57. 2025.In
French. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Bharadwaj D and Mandal M: Tumor
microenvironment: A playground for cells from multiple diverse
origins. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1879:1891582024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Zhang F, Liu W, Meng F, Jiang Q, Tang W,
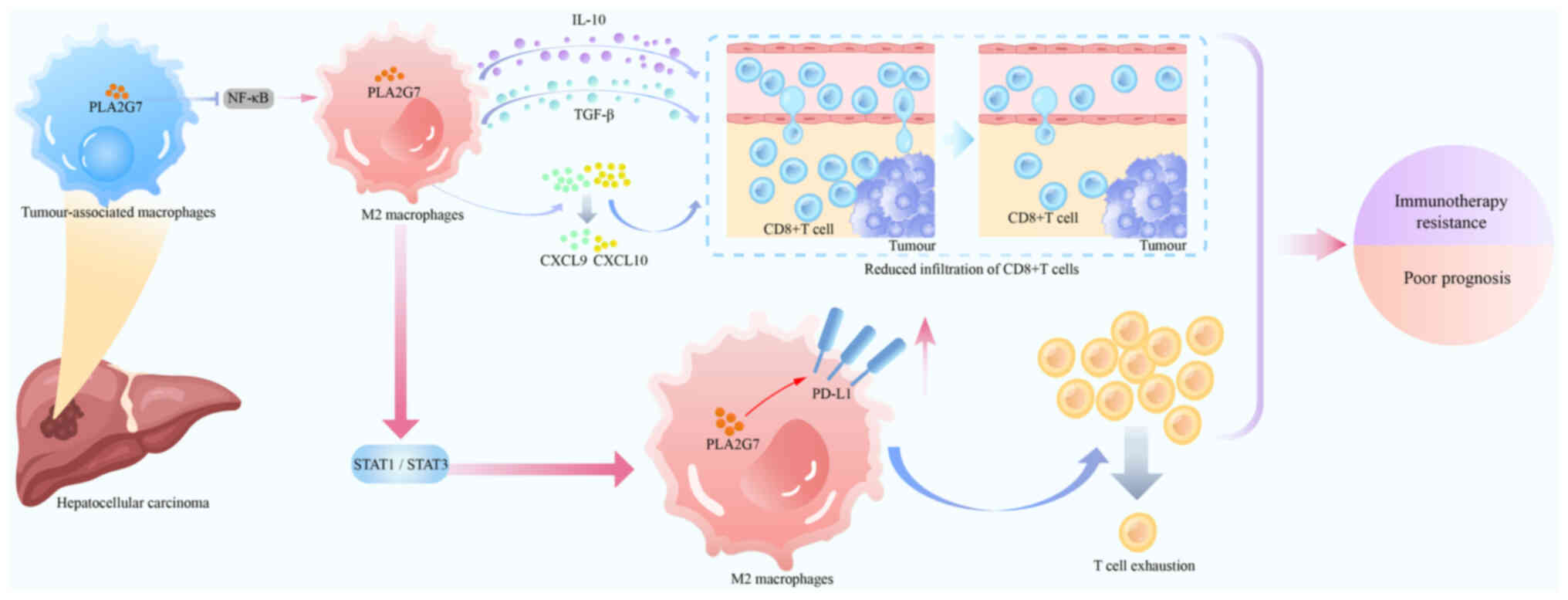
Liu Z, Lin X, Xue R, Zhang S and Dong L: Inhibiting PLA2G7 reverses
the immunosuppressive function of intratumoral macrophages and
augments immunotherapy response in hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Immunother Cancer. 12:e0080942024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Pantazi D, Tellis C and Tselepis AD:
Oxidized phospholipids and lipoprotein-associated phospholipase
A2 (Lp-PLA2) in atherosclerotic
cardiovascular disease: An update. Biofactors. 48:1257–1270. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Assunção LS, Magalhães KG, Carneiro AB,
Molinaro R, Almeida PE, Atella GC, Castro-Faria-Neto HC and Bozza
PT: Schistosomal-derived lysophosphatidylcholine triggers M2
polarization of macrophages through PPARγ dependent mechanisms.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 1862:246–254. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Chu M, Ji H, Li K, Liu H, Peng M, Wang Z
and Zhu X: Investigating the potential mechanism of quercetin
against cervical cancer. Discov Oncol. 14:1702023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Zhao H, Wu L, Yan G, Chen Y, Zhou M, Wu Y
and Li Y: Inflammation and tumor progression: Signaling pathways
and targeted intervention. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:2632021.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
104
|
Habanjar O, Bingula R, Decombat C,
Diab-Assaf M, Caldefie-Chezet F and Delort L: Crosstalk of
inflammatory cytokines within the breast tumor microenvironment.
Int J Mol Sci. 24:40022023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Nezos A, Skarlis C, Psarrou A, Markakis K,
Garantziotis P, Papanikolaou A, Gravani F, Voulgarelis M, Tzioufas
AG, Koutsilieris M, et al: Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2:
A novel contributor in Sjögren's syndrome-related lymphoma? Front
Immunol. 12:6836232021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Benli E, Bayrak A, Cirakoglu A, Bayrak T
and Noyan T: Comparison of serum acetyl hydrolase (PAF-AH) and
paraoxonase 1 (PON1) values between prostate cancer patients and a
control group. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 33:572–577. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Wu B, Zhang B, Li B, Wu H and Jiang M:
Cold and hot tumors: From molecular mechanisms to targeted therapy.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 9:2742024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
de Oliveira JB, Silva SB, Fernandes IL,
Batah SS, Herrera AJR, Cetlin ADCVA and Fabro AT: Dendritic
cell-based immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer: A
comprehensive critical review. Front Immunol. 15:13767042024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Cha YJ and Koo JS: Role of
tumor-associated myeloid cells in breast cancer. Cells. 9:17852020.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
110
|
Yang J, Li X, Liu X and Liu Y: The role of
tumor-associated macrophages in breast carcinoma invasion and
metastasis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:6656–6664. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Oliveira G, Stromhaug K, Klaeger S, Kula
T, Frederick DT, Le PM, Forman J, Huang T, Li S, Zhang W, et al:
Phenotype, specificity and avidity of antitumour CD8+ T cells in
melanoma. Nature. 596:119–125. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Schol P, van Elsas MJ, Middelburg J,
Twilhaar MKN, van Hall T, van der Sluis TC and van der Burg SH:
Myeloid effector cells in cancer. Cancer Cell. 42:1997–2014. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Song J, Li Y, Wu K, Hu Y and Fang L: MyD88
and its inhibitors in cancer: Prospects and challenges.
Biomolecules. 14:5622024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Wang Y, He M, Zhang G, Cao K, Yang M,
Zhang H and Liu H: The immune landscape during the tumorigenesis of
cervical cancer. Cancer Med. 10:2380–2095. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
115
|
Pang G, Li Y, Shi Q, Tian J, Lou H and
Feng Y: Omics sciences for cervical cancer precision medicine from
the perspective of the tumor immune microenvironment. Oncol Res.
33:821–836. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
116
|
Morigny P, Kaltenecker D, Zuber J, Machado
J, Mehr L, Tsokanos FF, Kuzi H, Hermann CD, Voelkl M, Monogarov G,
et al: Association of circulating PLA2G7 levels with cancer
cachexia and assessment of darapladib as a therapy. J Cachexia
Sarcopenia Muscle. 12:1333–1351. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
117
|
Noyori O, Komohara Y, Nasser H, Hiyoshi M,
Ma C, Pan C, Carreras J, Nakamura N, Sato A, Ando K, et al:
Expression of IL-34 correlates with macrophage infiltration and
prognosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin Transl Immunology.
8:e10742019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Saenger Y, Magidson J, Liaw B, de Moll E,
Harcharik S, Fu Y, Wassmann K, Fisher D, Kirkwood J, Oh WK and
Friedlander P: Blood mRNA expression profiling predicts survival in
patients treated with tremelimumab. Clin Cancer Res. 20:3310–3318.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Zhu H, Shi H, Lu J, Zhu K, Yang L, Guo L,
Tang L, Shi Y and Hu X: Proteomic profiling reveals the
significance of lipid metabolism in small cell lung cancer
recurrence and metastasis. J Transl Med. 22:11172024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Li J, Cao F, Yin HL, Huang ZJ, Lin ZT, Mao
N, Sun B and Wang G: Ferroptosis: Past, present and future. Cell
Death Dis. 11:882020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
121
|
Avci CB, Bagca BG, Nikanfar M, Takanlou
LS, Takanlou MS and Nourazarian A: Tumor microenvironment and
cancer metastasis: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic
implications. Front Pharmacol. 15:14428882024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Chu X, Tian W, Ning J, Xiao G, Zhou Y,
Wang Z, Zhai Z, Tanzhu G, Yang J and Zhou R: Cancer stem cells:
Advances in knowledge and implications for cancer therapy. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 9:1702024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Chen Y, Chen K, Zhu H, Qin H, Liu J and
Cao X: Methyltransferase Setd2 prevents T cell-mediated autoimmune
diseases via phospholipid remodeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
121:e23145611212024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Jiang X, Stockwell BR and Conrad M:
Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 22:266–282. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Zou Y, Henry WS, Ricq EL, Graham ET,
Phadnis VV, Maretich P, Paradkar S, Boehnke N, Deik AA, Reinhardt
F, et al: Plasticity of ether lipids promotes ferroptosis
susceptibility and evasion. Nature. 585:603–608. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Ko CJ, Gao SL, Lin TK, Chu PY and Lin HY:
Ferroptosis as a major factor and therapeutic target for
neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease. Biomedicines. 9:16792021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Zhang X, Li LX, Ding H, Torres VE, Yu C
and Li X: Ferroptosis promotes cyst growth in autosomal dominant
polycystic kidney disease mouse models. J Am Soc Nephrol.
32:2759–2776. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Lee JY, Nam M, Son HY, Hyun K, Jang SY,
Kim JW, Kim MW, Jung Y, Jang E, Yoon S, et al: Polyunsaturated
fatty acid biosynthesis pathway determines ferroptosis sensitivity
in gastric cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 117:32433–32442. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Rodriguez R, Schreiber SL and Conrad M:
Persister cancer cells: Iron addiction and vulnerability to
ferroptosis. Mol Cell. 82:728–740. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
130
|
Viswanathan VS, Ryan MJ, Dhruv HD, Gill S,
Eichhoff OM, Seashore-Ludlow B, Kaffenberger SD, Eaton JK, Shimada
K, Aguirre AJ, et al: Dependency of a therapy-resistant state of
cancer cells on a lipid peroxidase pathway. Nature. 547:453–457.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Shin S, Baek DS, Mellors JW, Dimitrov DS
and Li W: Development of fully human antibodies targeting SIRPα and
PLA2G7 for cancer therapy. Antibodies (Basel). 14:212025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|