|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nolan E, Lindeman GJ and Visvader JE:
Deciphering breast cancer: From biology to the clinic. Cell.
186:1708–1728. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lehmann BD, Jovanović B, Chen X, Estrada
MV, Johnson KN, Shyr Y, Moses HL, Sanders ME and Pietenpol JA:
Refinement of triple-negative breast cancer molecular subtypes:
Implications for neoadjuvant chemotherapy selection. PLoS One.
11:e01573682016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Bianchini G, De Angelis C, Licata L and
Gianni L: Treatment landscape of triple-negative breast
cancer-expanded options, evolving needs. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
19:91–113. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
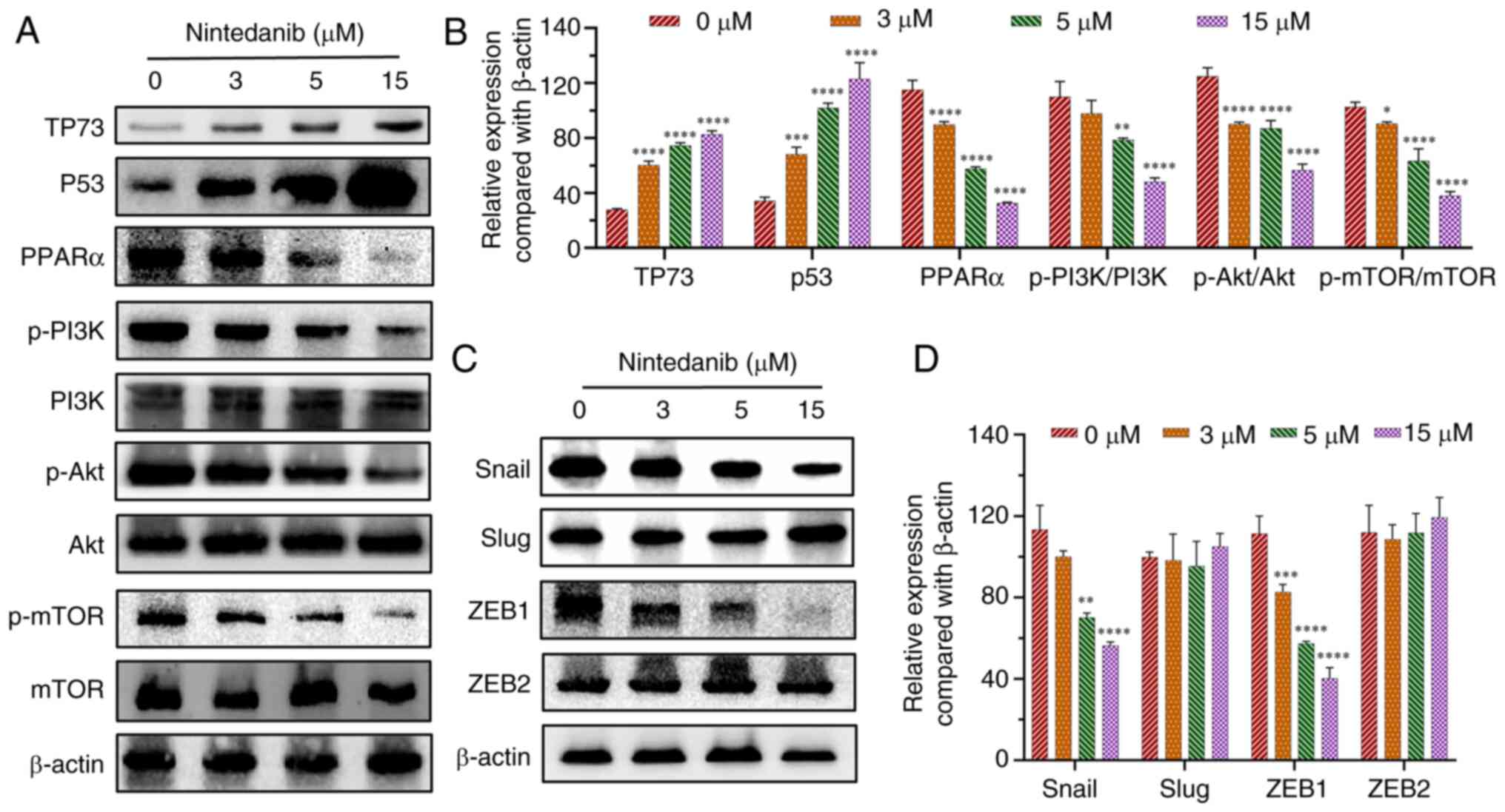
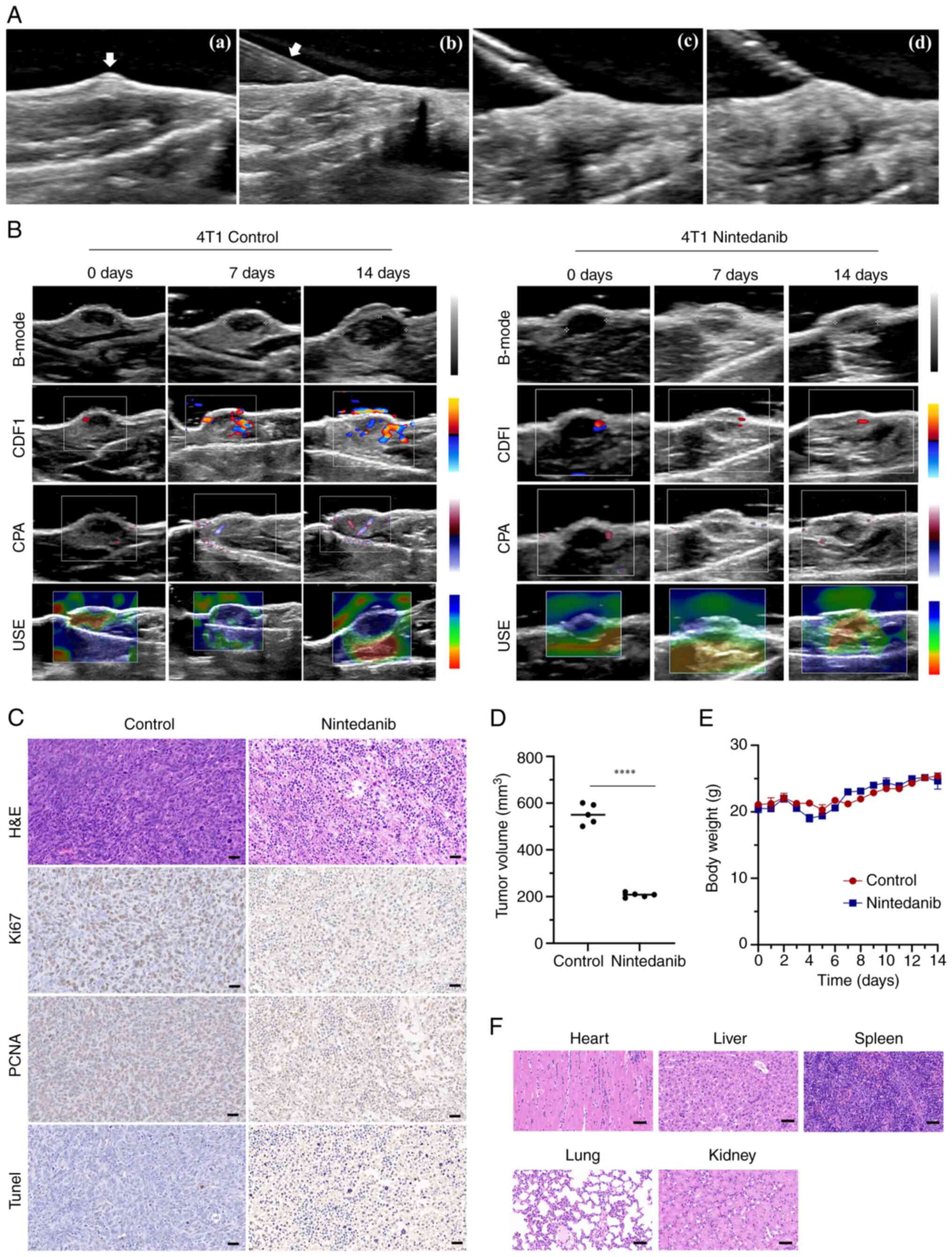
|
5
|
Waks AG and Winer EP: Breast cancer
treatment: A review. JAMA. 321:288–300. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Loibl S, Poortmans P, Morrow M, Denkert C
and Curigliano G: Breast cancer. Lancet. 397:1750–1769. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cruwys S, Hein P, Humphries B and Black D:
Drug discovery and development in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis:
The changing landscape. Drug Discov Today. 29:1042072024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wollin L, Distler JHW, Redente EF, Riches
DWH, Stowasser S, Schlenker-Herceg R, Maher TM and Kolb M:
Potential of nintedanib in treatment of progressive fibrosing
interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir J. 54:19001612019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Peng M, Deng J and Li X: Clinical advances
and challenges in targeting FGF/FGFR signaling in lung cancer. Mol
Cancer. 23:2562024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yao H, Ren Y, Wu F, Cao L, Liu J, Yan M
and Li X: The discovery of a novel AXL/triple angiokinase inhibitor
based on 6-chloro-substituted indolinone and side chain methyl
substitution inhibiting pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis. J
Med Chem. 68:465–490. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Dong X, Wang L, Wang D, Yu M, Yang XJ and
Cai H: Proteomic study on nintedanib in gastric cancer cells.
PeerJ. 12:e167712024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Quintela-Fandino M, Urruticoechea A,
Guerra J, Gil M, Gonzalez-Martin A, Marquez R, Hernandez-Agudo E,
Rodriguez-Martin C, Gil-Martin M, Bratos R, et al: Phase I clinical
trial of nintedanib plus paclitaxel in early HER-2-negative breast
cancer (CNIO-BR-01-2010/GEICAM-2010-10 study). British Br J Cancer.
111:1060–1064. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Adams CM, Mitra R, Xiao Y, Michener P,
Palazzo J, Chao A, Gour J, Cassel J, Salvino JM and Eischen CM:
Targeted MDM2 degradation reveals a new vulnerability for
p53-inactivated triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Discov.
13:1210–1229. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu Z, Dong X, Song M, Xu A, He Q, Li H,
Ouyang W, Chouchane L and Ma X: Targeting UBR5 inhibits
postsurgical breast cancer lung metastases by inducing CDC73 and
p53 mediated apoptosis. Int J Cancer. 154:723–737. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Li G, Lin SS, Yu Zl, Wu XH, Liu JW, Tu GH,
Liu QY, Tang YL, Jiang QN, Xu JH, et al: A PARP1 PROTAC as a novel
strategy against PARP inhibitor resistance via promotion of
ferroptosis in p53-positive breast cancer. Biochem Pharmacol.
206:1153292022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Musa S, Amara N, Selawi A, Wang J,
Marchini C, Agbarya A and Mahajna J: Overcoming chemoresistance in
cancer: The promise of crizotinib. Cancers (Basel). 16:24792024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ramos H, Raimundo L and Saraiva L: p73:
From the p53 shadow to a major pharmacological target in anticancer
therapy. Pharmacol Res. 162:1052452020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Bisso A, Collavin L and Del Sal G: p73 as
a pharmaceutical target for cancer therapy. Curr Pharm Des.
17:578–590. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rozenberg JM, Zvereva S, Dalina A, Blatov
I, Zubarev I, Luppov D, Bessmertnyi A, Romanishin A, Alsoulaiman L,
Kumeiko V, et al: Dual role of p73 in cancer microenvironment and
DNA damage response. Cells. 10:35162021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang X, Shen Y, Wang S, Li S, Zhang W, Liu
X, Lai L, Pei J and Li H: PharmMapper 2017 update: A web server for
potential drug target identification with a comprehensive target
pharmacophore database. Nucleic Acids Res. 45(W1): W356–W60. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang Z, Wang HY, Chung CR, Horng JT, Lu JJ
and Lee TY: Large-scale mass spectrometry data combined with
demographics analysis rapidly predicts methicillin resistance in
Staphylococcus aureus. Brief Bioinform. 22:bbaa2932021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sui X, Kong N, Ye L, Han W, Zhou J, Zhang
Q, He C and Pan H: p38 and JNK MAPK pathways control the balance of
apoptosis and autophagy in response to chemotherapeutic agents.
Cancer Lett. 344:174–179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kiri S and Ryba T: Cancer, metastasis, and
the epigenome. Mol Cancer. 23:1542024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Teufelsbauer M, Stickler S, Eggerstorfer
MT, Hammond DC and Hamilton G: BET-directed PROTACs in triple
negative breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-436. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 208:89–101. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Pham TH, Park HM, Kim J, Hong JT and Yoon
DY: Interleukin-32θ triggers cellular senescence and reduces
sensitivity to doxorubicin-mediated cytotoxicity in MDA-MB-231
Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 22:49752021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hwang SY, Park S and Kwon Y: Recent
therapeutic trends and promising targets in triple negative breast
cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 199:30–57. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
van Dorst DCH, Dobbin SJH, Neves KB,
Herrmann J, Herrmann SM, Versmissen J, Mathijssen RHJ, Danser AHJ
and Lang NN: Hypertension and prohypertensive antineoplastic
therapies in cancer patients. Circ Res. 128:1040–1061. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li Y, Zhang H, Merkher Y, Chen L, Liu N,
Leonov S and Chen Y: Recent advances in therapeutic strategies for
triple-negative breast cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 15:1212022.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Pushpakom S, Iorio F, Eyers PA, Escott KJ,
Hopper S, Wells A, Doig A, Guilliams T, Latimer J, McNamee C, et
al: Drug repurposing: Progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 18:41–58. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Pan L, Cheng Y, Yang W, Wu X, Zhu H, Hu M,
Zhang Y and Zhang M: Nintedanib ameliorates bleomycin-induced
pulmonary fibrosis, inflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress
by modulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in mice. Inflammation.
46:1531–1542. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ferrara N, Gerber HP and LeCouter J: The
biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 9:669–676. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tomuleasa C, Tigu AB, Munteanu R, Moldovan
CS, Kegyes D, Onaciu A, Gulei D, Ghiaur G, Einsele H and Croce CM:
Therapeutic advances of targeting receptor tyrosine kinases in
cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 9:2012024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Peuget S, Zhou X and Selivanova G:
Translating p53-based therapies for cancer into the clinic. Nat Rev
Cancer. 24:192–215. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tuval A, Strandgren C, Heldin A,
Palomar-Siles M and Wiman KG: Pharmacological reactivation of p53
in the era of precision anticancer medicine. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
21:106–120. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Rodriguez Calleja L, Lavaud M, Tesfaye R,
Brounais-Le-Royer B, Baud'huin M, Georges S, Lamoureux F,
Verrecchia F and Ory B: The p53 family members p63 and p73 roles in
the metastatic dissemination: Interactions with microRNAs and TGFβ
pathway. Cancers (Basel). 14:59482022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Sampath D, Calin GA, Puduvalli VK,
Gopisetty G, Taccioli C, Liu CG, Ewald B, Liu C, Keating MJ and
Plunkett W: Specific activation of microRNA106b enables the p73
apoptotic response in chronic lymphocytic leukemia by targeting the
ubiquitin ligase Itch for degradation. Blood. 113:3744–3753. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Humbert M, Federzoni EA and Tschan MP:
Distinct TP73-DAPK2-ATG5 pathway involvement in ATO-mediated cell
death versus ATRA-mediated autophagy responses in APL. J Leukoc
Biol. 102:1357–1370. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Browne IM, André F, Chandarlapaty S, Carey
LA and Turner NC: Optimal targeting of PI3K-AKT and mTOR in
advanced oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Lancet Oncol.
25:e139–e151. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhu L, Li XX, Shi L, Wu J, Qian JY, Xia
TS, Zhou WB, Sun X, Zhou XJ, Wei JF and Ding Q: Rapamycin enhances
the sensitivity of ER-positive breast cancer cells to tamoxifen by
upregulating p73 expression. Oncol Rep. 41:455–464. 2019.
|
|
40
|
Lu Z, Jiao D, Qiao J, Yang S, Yan M, Cui S
and Liu Z: Restin suppressed epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
tumor metastasis in breast cancer cells through upregulating
mir-200a/b expression via association with p73. Mol Cancer.
14:1022015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Goossens S, Vandamme N, Van Vlierberghe P
and Berx G: EMT transcription factors in cancer development
re-evaluated: Beyond EMT and MET. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer.
1868:584–591. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Garinet S, Didelot A, Denize T, Perrier A,
Beinse G, Leclere JB, Oudart JB, Gibault L, Badoual C, Le
Pimpec-Barthes F, et al: Clinical assessment of the miR-34,
miR-200, ZEB1 and SNAIL EMT regulation hub underlines the
differential prognostic value of EMT miRs to drive mesenchymal
transition and prognosis in resected NSCLC. Br J Cancer.
125:1544–1551. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Capdevila J, Carrato A, Tabernero J and
Grande E: What could Nintedanib (BIBF 1120), a triple inhibitor of
VEGFR, PDGFR, and FGFR, add to the current treatment options for
patients with metastatic colorectal cancer? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
92:83–106. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Khalique S and Banerjee S: Nintedanib in
ovarian cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 26:1073–1081. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Roth GJ, Binder R, Colbatzky F, Dallinger
C, Schlenker-Herceg R, Hilberg F, Wollin SL and Kaiser R:
Nintedanib: From discovery to the clinic. J Med Chem. 58:1053–1063.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Tu J, Xu H, Ma L, Li C, Qin W, Chen X, Yi
M, Sun L, Liu B and Yuan X: Nintedanib enhances the efficacy of
PD-L1 blockade by upregulating MHC-I and PD-L1 expression in tumor
cells. Theranostics. 12:747–766. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mukhopadhyay B, Singh S and Singh A:
Utilizing nanomaterials for cancer treatment and diagnosis: An
overview. Discov Nano. 19:2152024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|