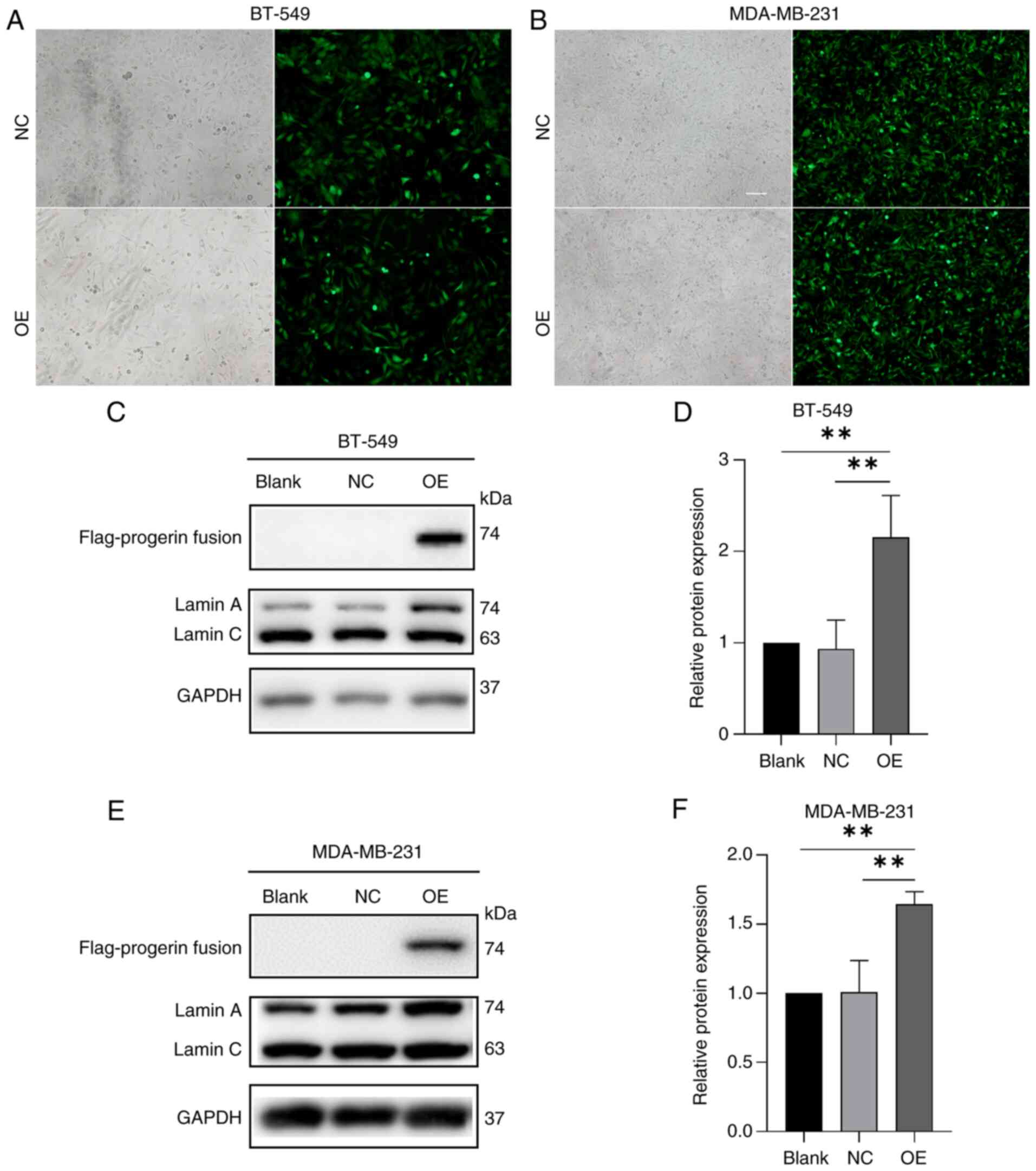
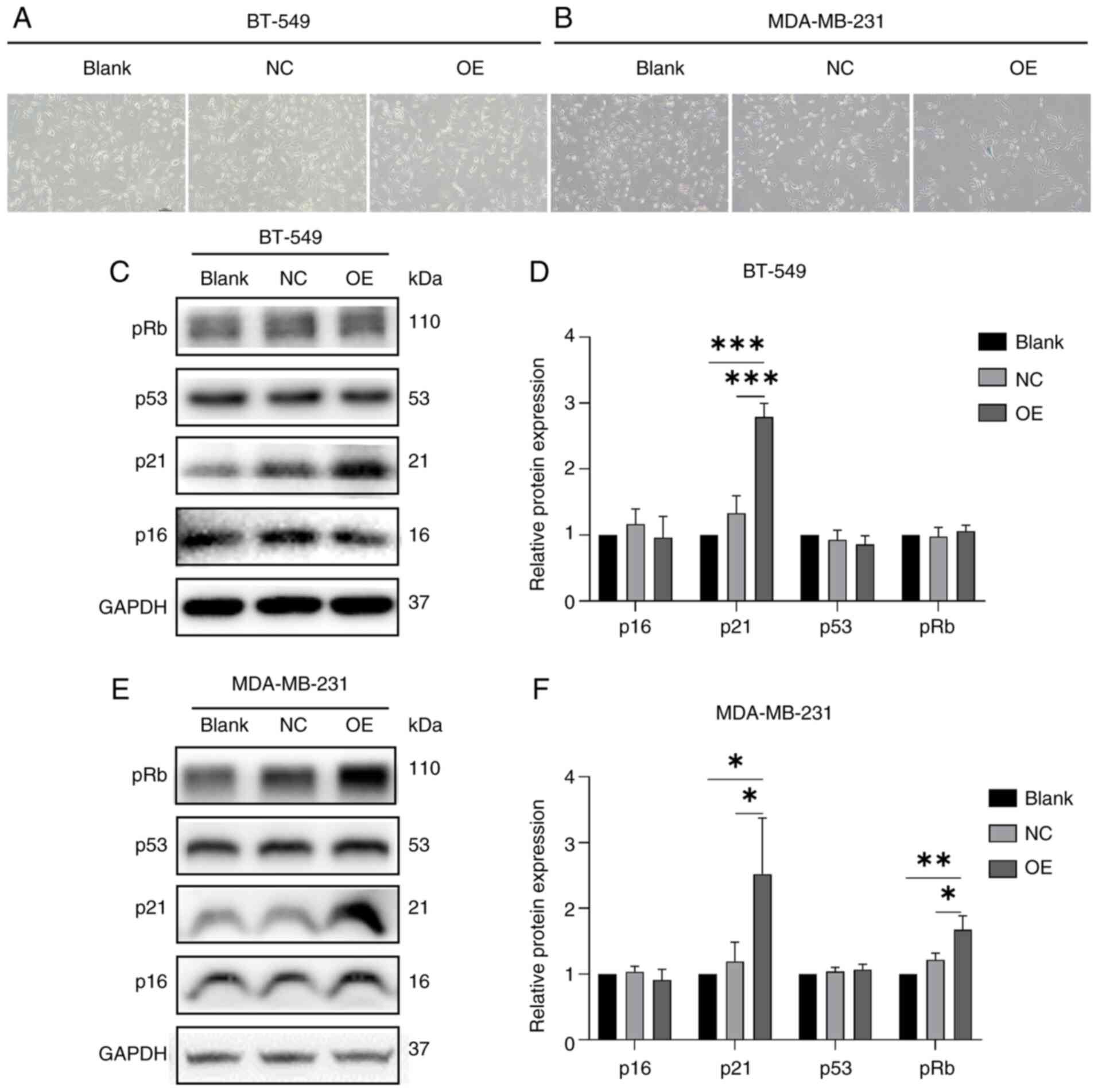
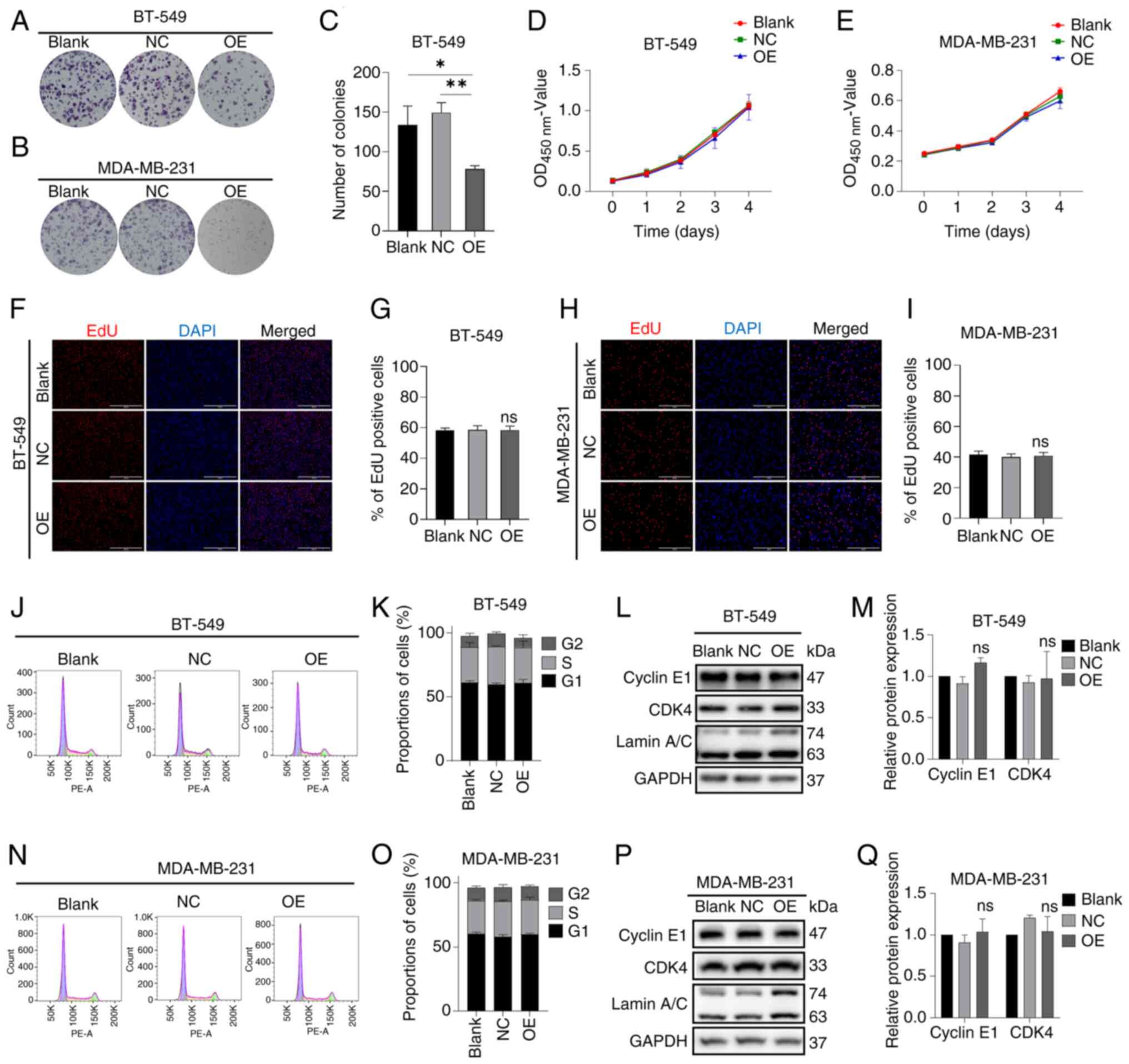
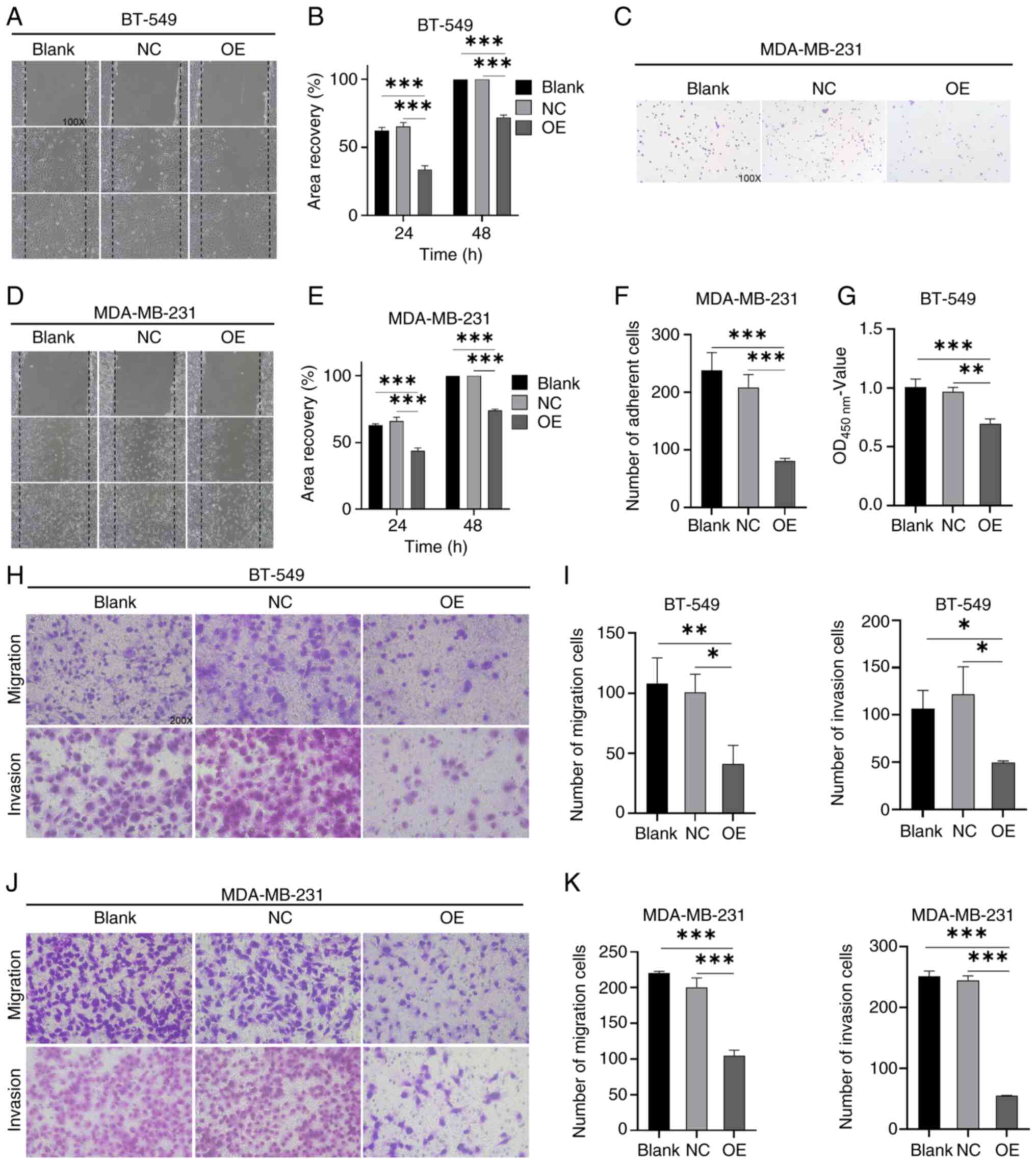
|
1
|
López-Otín C, Pietrocola F, Roiz-Valle D,
Galluzzi L and Kroemer G: Meta-hallmarks of aging and cancer. Cell
Metab. 35:12–35. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kerstens C, Wildiers H, Schroyen G, Almela
M, Mark RE, Lambrecht M, Deprez S and Sleurs C: A systematic review
on the potential acceleration of neurocognitive aging in older
cancer survivors. Cancers (Basel). 15:12152023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim BH, Chung YH, Woo TG, Kang SM, Park S
and Park BJ: Progerin, an aberrant spliced form of lamin A, is a
potential therapeutic target for HGPS. Cells. 12:22992023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lamis A, Siddiqui SW, Ashok T, Patni N,
Fatima M and Aneef AN: Hutchinson-gilford progeria syndrome: A
literature review. Cureus. 14:e286292022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gonzalo S, Kreienkamp R and Askjaer P:
Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome: A premature aging disease
caused by LMNA gene mutations. Ageing Res Rev. 33:18–29. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bar DZ, Arlt MF, Brazier JF, Norris WE,
Campbell SE, Chines P, Larrieu D, Jackson SP, Collins FS, Glover TW
and Gordon LB: A novel somatic mutation achieves partial rescue in
a child with Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. J Med Genet.
54:212–216. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wang F, Zhang W, Yang Q, Kang Y, Fan Y,
Wei J, Liu Z, Dai S, Li H, Li Z, et al: Generation of a
Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome monkey model by base editing.
Protein Cell. 11:809–824. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Danielsson BE, Tieu KV, Bathula K, Armiger
TJ, Vellala PS, Taylor RE, Dahl KN and Conway DE: Lamin
microaggregates lead to altered mechanotransmission in
progerin-expressing cells. Nucleus. 11:194–204. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bidault G, Garcia M, Capeau J, Morichon R,
Vigouroux C and Béréziat V: Progerin expression induces
inflammation, oxidative stress and senescence in human coronary
endothelial cells. Cells. 9:12012020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Matrone G, Thandavarayan RA, Walther BK,
Meng S, Mojiri A and Cooke JP: Dysfunction of iPSC-derived
endothelial cells in human Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome.
Cell Cycle. 18:2495–2508. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Miller KN, Victorelli SG, Salmonowicz H,
Dasgupta N, Liu T, Passos JF and Adams PD: Cytoplasmic DNA:
Sources, sensing, and role in aging and disease. Cell.
184:5506–5526. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zagami P and Carey LA: Triple negative
breast cancer: Pitfalls and progress. NPJ Breast Cancer. 8:952022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yin L, Duan JJ, Bian XW and Yu SC:
Triple-negative breast cancer molecular subtyping and treatment
progress. Breast Cancer Res. 22:612020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin NU, Vanderplas A, Hughes ME, Theriault
RL, Edge SB, Wong YN, Blayney DW, Niland JC, Winer EP and Weeks JC:
Clinicopathologic features, patterns of recurrence, and survival
among women with triple-negative breast cancer in the national
comprehensive cancer network. Cancer. 118:5463–5472. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li Y, Zhang H, Merkher Y, Chen L, Liu N,
Leonov S and Chen Y: Recent advances in therapeutic strategies for
triple-negative breast cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 15:1212022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu W, Huang X, Luo W, Liu X and Chen W:
Progerin inhibits the proliferation and migration of melanoma cells
by regulating the expression of paxillin. Onco Targets Ther.
17:227–242. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu XT, Song HC, Yu H, Wu ZC, Liu XG and
Chen WC: Overexpression of progerin results in impaired
proliferation and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells.
Onco Targets Ther. 13:2629–2642. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tang Y, Chen Y, Jiang H and Nie D:
Promotion of tumor development in prostate cancer by progerin.
Cancer Cell Int. 10:472010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Grasset EM, Dunworth M, Sharma G, Loth M,
Tandurella J, Cimino-Mathews A, Gentz M, Bracht S, Haynes M, Fertig
EJ and Ewald AJ: Triple-negative breast cancer metastasis involves
complex epithelial-mesenchymal transition dynamics and requires
vimentin. Sci Transl Med. 14:eabn75712022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Morel AP, Lièvre M, Thomas C, Hinkal G,
Ansieau S and Puisieux A: Generation of breast cancer stem cells
through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS One. 3:e28882008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
De Cock JM, Shibue T, Dongre A, Keckesova
Z, Reinhardt F and Weinberg RA: Inflammation triggers
Zeb1-dependent escape from tumor latency. Cancer Res. 76:6778–6784.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chaffer CL, Juan BP, Lim E and Weinberg
RA: EMT, cell plasticity and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
35:645–654. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fischer KR, Durrans A, Lee S, Sheng J, Li
F, Wong ST, Choi H, El Rayes T, Ryu S, Troeger J, et al:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is not required for lung
metastasis but contributes to chemoresistance. Nature. 527:472–476.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Smith BN and Bhowmick NA: Role of EMT in
metastasis and therapy resistance. J Clin Med. 5:172016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen J, Li Y, Yu TS, McKay RM, Burns DK,
Kernie SG and Parada LF: A restricted cell population propagates
glioblastoma growth after chemotherapy. Nature. 488:522–526. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Terry S and Chouaib S: EMT in
immuno-resistance. Oncoscience. 2:841–842. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kudo-Saito C, Shirako H, Takeuchi T and
Kawakami Y: Cancer metastasis is accelerated through
immunosuppression during snail-induced EMT of cancer cells. Cancer
Cell. 15:195–206. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Voon DC, Wang H, Koo JK, Chai JH, Hor YT,
Tan TZ, Chu YS, Mori S and Ito Y: EMT-induced stemness and
tumorigenicity are fueled by the EGFR/Ras pathway. PLoS One.
8:e704272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yilmaz M and Christofori G: EMT, the
cytoskeleton, and cancer cell invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
28:15–33. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lionetti MC, Bonfanti S, Fumagalli MR,
Budrikis Z, Font-Clos F, Costantini G, Chepizhko O, Zapperi S and
La Porta CAM: Chromatin and cytoskeletal tethering determine
nuclear morphology in progerin-expressing cells. Biophys J.
118:2319–2332. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
de la Rosa J, Freije JM, Cabanillas R,
Osorio FG, Fraga MF, Fernández-García MS, Rad R, Fanjul V, Ugalde
AP, Liang Q, et al: Prelamin A causes progeria through
cell-extrinsic mechanisms and prevents cancer invasion. Nat Commun.
4:22682013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang D, Naydenov NG, Dozmorov MG,
Koblinski JE and Ivanov AI: Anillin regulates breast cancer cell
migration, growth, and metastasis by non-canonical mechanisms
involving control of cell stemness and differentiation. Breast
Cancer Res. 22:32020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Takeichi M: Multiple functions of
α-catenin beyond cell adhesion regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
54:24–29. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dasgupta A, Sawant MA, Kavishwar G,
Lavhale M and Sitasawad S: AECHL-1 targets breast cancer
progression via inhibition of metastasis, prevention of EMT and
suppression of cancer stem cell characteristics. Sci Rep.
6:380452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|